Practice Exam
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Any molecule that serves as the genetic material must have the following characteristics except...*
the ability to be replicated
the ability to store information
the ability to directly influence the development of traits
the ability to express stored infomation
the potential to be changed via mutation
the ability to directly influence the development of traits
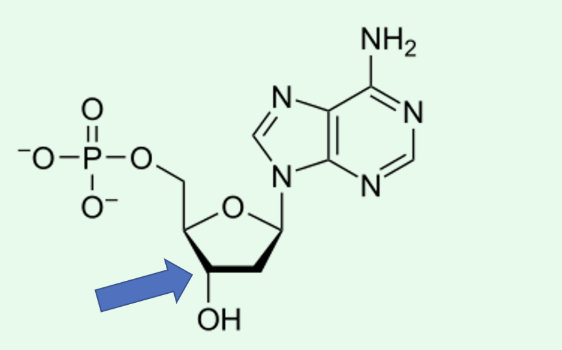
The arrow is pointing to the 3' carbon.
The base of this nucleotide is adenine.
This nucleotide belongs in RNA.
It is a deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate.
This nucleotide belongs in RNA.
Which of the following is an example of a genomics study?*
Using CRISPR-Cas9 to make a transgenic mouse with a DNA mutation of interest and analyzing the resulting phenotype.
GWAS revealed that the circadian disorder, familial advanced sleep phase syndrome (FASPS), is associated with mutations in the clock genes PERIOD2 (PER2) and CASEIN KINASE 1 DELTA (CK1δ).
A gene that controls stomata opening in soybeans was added to tomato plants to see if the tomato plants become drought resistant.
Modifying viral genomes to alter their pathogenicity in the development of live attenuated vaccines
GWAS revealed that the circadian disorder, familial advanced sleep phase syndrome (FASPS), is associated with mutations in the clock genes PERIOD2 (PER2) and CASEIN KINASE 1 DELTA (CK1δ).
Which of the following clusters of terms accurately describes DNA as it is generally viewed to exist in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?*
double-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C + T) = variable
double-stranded, parallel, (A + T)/C + G) = 1.0, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
single-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = 1.0, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
double-stranded, parallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
double-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C+ T) = 1.0
double-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C+ T) = 1.0
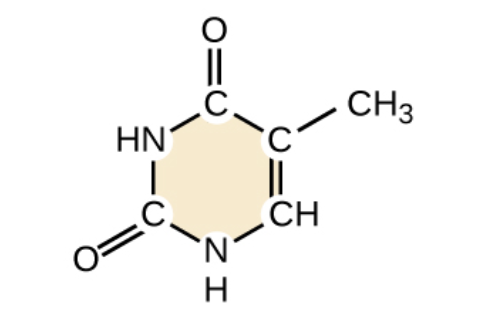
What base is shown below?
thymine
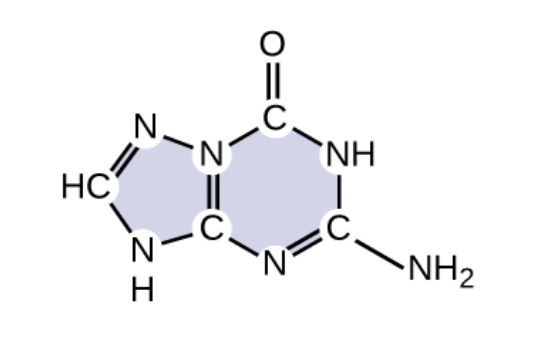
What base is shown below?
guanine
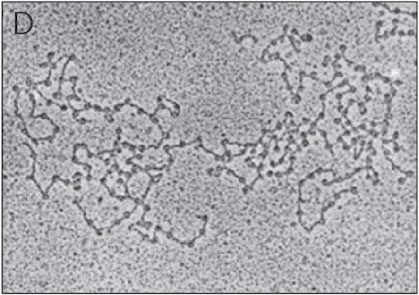
Identify the fiber below
2 nm fiber
30 nm fiber
10 nm fiber
3 nm fiber
10 nm fiber
What is the chromosomal theory of inheritance?*
Genes are located on chromosomes, which are passed down from parent to offspring
Traits are inherited independently of chromosomes
Inheritance is determined by proteins, not DNA
Chromosomes are not involved in inheritance
Correct answer
Traits are inherited independently of chromosomes
Traits are inherited independently of chromosomes
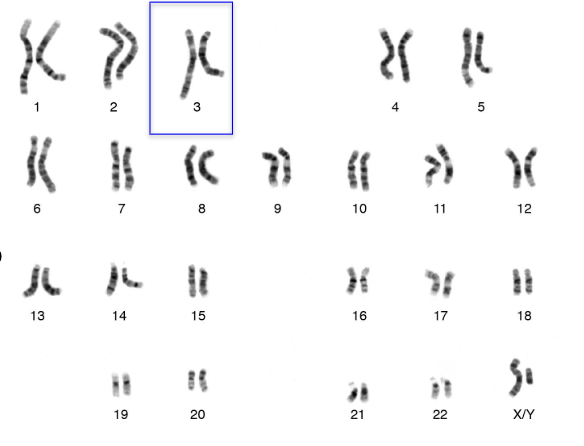
How many chromosomes and DNA molecules are in the blue box?
2 homologous chromosomes, 4 molecules of DNA
4 homologous chromosomes, 2 molecules of DNA
1 homologous chromosome, 2 molecules of DNA
1 homologous chromosome, 4 molecules of DNA
2 homologous chromosomes, 4 molecules of DNA
What qualities make something genetic material?*
Provides information about cell structure, function, development and reproduction
The ability to be expressed
The ability to be replicated accurately through generations
The ability to be changed in order to provide variety in a population
Provides information about cell structure, function, development and reproduction
The ability to be expressed
The ability to be replicated accurately through generations
The ability to be changed in order to provide variety in a population
What is the glycosidic bond?*
Bond between sugar and base
Bond between two sugars
Bond between phosphate groups
Bond between sugar and phosphate
Bond between sugar and base
You are given the following mRNA sequence:
5′–GCU AAG UCC GAU–3′
Which DNA template strand sequence produced this mRNA?
5′–GCT AAG TCC GAT–3′
5′–TAG GAC TTC AGC–3′
5′–ATC GGA CTT AGC–3′
5′–CGA TTC AGG CTA–3
5′–ATC GGA CTT AGC–3′
What is the phosphodiester bond?*
Bond between phosphate and base
Bond between phosphate and sugar
Bond between two phosphates
Bond between two sugars
Bond between phosphate and sugar
What are the three major steps of PCR?
Denature
Anneal
Extend
True or False: Increased C value means increased complexity *
True
False
False
DNA polymerase I adds nucleotides...*
to the 5' end of the primer
in place of RNA primer after it degrades the primer using its exonuclease activity
to the 3' end of the primer
in a 5' to 5' direction
in place of RNA primer after it degrades the primer using its exonuclease activity
Which statement below is correct?*
Only positively supercoiled DNA can exhibit writhe
Positive twist is not found in cells
Only negatively supercoiled DNA can exhibit writhe
Eukaryotic DNA is supercoiled around histones
Eukaryotic DNA is supercoiled around histones
After S phase how many copies of each gene would u have in a diploid organism?
4
What does fidelity mean?*
efficiency
accuracy
stability
proccesitvity
accuracy
How many base pairs are found in a full turn of the helix?*
10 base pairs
20 base pairs
5 base pairs
8 base pairs
10 base pairs
How is DNA stored in prokaryotes like E.coli?*
In linear chromosomes inside a membrane-bound nucleus
In multiple circular chromosomes inside the cytoplasm
In a single circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region
In histone-bound chromatin inside the nuclear envelope
In a single circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region
True or False: Prokaryotes have multiple origins of replication*
True
False
False
All known DNA polymerases....*
can initiate DNA chain synthesis
have 5' to 3' polymerization activity
have 5' exonuclease activity
have 3' to 5' polymerization actvity
all of the above
have 5' to 3' polymerization activity
How is the end replication problem solved?*
By using RNA primers that extend indefinitely past the ends of chromosomes
By telomerase, which removes DNA at the 3′ overhangs
By telomerase, which adds repetitive sequences to chromosome ends
By topoisomerase, which prevents supercoiling at chromosome termini
By telomerase, which adds repetitive sequences to chromosome ends
A DNA sample is analyzed and found to contain 28% adenine (A). Based on Chargaff’s rule, what is the percentage of guanine (G) in the sample?
22%
You are given the DNA sequence below:
5′–ATGCGTATCGGCATTAACG–3′
What is the approximate melting temperature (Tm) of this fragment?
48 °C
56 °C
64 °C
72 °C
56%
Which cluster of terms accurately reflects the nature of DNA replication in E. coli?*
many origins per chromosome, bidirectional, semiconservative
many origins per chromosome, unidirectional, conservative
one origin per chromosome, bidirectional, semiconservative
one origin per chromosome, bidirectional, conservative
many origins per chromosome, unidirectional, semiconservative
one origin per chromosome, bidirectional, semiconservative
A mutation at the first base of the 5′ splice site of an intron changes a G-C base pair to a T-A base pair. Mutant mice with this mutation produce longer transcripts compared to wild type. Why?*
The mutation prevents correct splicing, so the intron is retained.
The mutation enhances splicing efficiency.
The mutation leads to premature transcription termination.
The mutation causes loss of the poly(A) tail.
The mutation prevents correct splicing, so the intron is retained.
What is the role of eukaryotic general transcription factors (GTFs)?
They bind enhancers to fine-tune transcription
They bind the core promoter to recruit RNA polymerase
They are DNA sequences called cis-regulatory elements
They regulate the length of mRNA
They bind the core promoter to recruit RNA polymerase
True or False: In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose, which lacks a hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 2′ carbon.
True
Complementary strands are held together by ______________ bonds.
Ionic
Hydrogen
Covalent
Phosphate
Hydrogen
A mutant E. coli strain has a defective ε subunit of DNA polymerase III, which normally provides proofreading. The cells replicate DNA but accumulate mutations at a very high rate.
Question: Which activity is most likely lost in this mutant?
5′ → 3′ polymerase activity
3′ → 5′ exonuclease activity
5′ exonuclease activity
RNA primer synthesis
3′ → 5′ exonuclease activity
Which of the following correctly describes the three main processing steps required to produce mature mRNA in eukaryotes?*
Addition of a 3′ poly-A tail, removal of exons, and phosphorylation of the 5′ end
Addition of a 5′ cap, splicing out of introns, and addition of a 3′ poly-A tail
Splicing out of introns, addition of a 5′ cap, and methylation of all cytosines
Addition of a 5′ cap, duplication of exons, and addition of a 3′ hydroxyl group
Addition of a 5′ cap, splicing out of introns, and addition of a 3′ poly-A tail
A researcher is studying two different DNA fragments to design primers for PCR.
Fragment 1 is 20 base pairs long and has 60% GC content.
Fragment 2 is 20 base pairs long and has 35% GC content.
When she runs a melting analysis, she observes that Fragment 1 denatures at a significantly higher temperature than Fragment 2.
Which of the following best explains this observation?
Fragment 1 has more hydrogen bonds due to its higher GC content, increasing stability.
Fragment 2 has more hydrogen bonds due to higher AT content, increasing stability.
Both fragments should melt at the same temperature because they are the same length.
Fragment 1 is more unstable because GC pairs are harder to replicate than AT pairs.
Fragment 1 has more hydrogen bonds due to its higher GC content, increasing stability.
What does “processivity” of DNA polymerase mean?*
Completion of holoenzyme assembly
Replicating bidirectionally from the origin
The ability to replicate a long stretch of DNA before detaching
Ability to move backward for proofreading
The ability to replicate a long stretch of DNA before detaching
What subunits compose a histone core?*
4 subunits: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
2 subunits: H1 and H5
6 subunits: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4, and H5
3 subunits: H2A, H2B, and H1
4 subunits: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
You are given the following mRNA sequence:
5′–AUG CCA UGA CUA–3′
Which DNA coding strand sequence corresponds to this mRNA?
5′–ATG CCA TGA CTA–3′
5′–TAG GGT AGT CAT–3′
5′–TAC GGT ACT GAT–3′
5′–UAC GGU ACU GAU–3′
5′–ATG CCA TGA CTA–3′
During lagging strand DNA synthesis, what role does flap endonuclease play?*
It seals nicks between Okazaki fragments after RNA primers are removed.
It removes RNA primers by cleaving the displaced flap structures during Okazaki fragment processing.
It unwinds the DNA duplex ahead of the replication fork to prevent supercoiling.
It synthesizes short RNA primers needed to initiate Okazaki fragment synthesis.
It removes RNA primers by cleaving the displaced flap structures during Okazaki fragment processing
Which of the following functions are performed by topoisomerases? (select all that apply)*
Relieving supercoils ahead of replication forks
Decatenation of plasmids after replication
Adding repetitive sequences to the ends of chromosomes
Synthesizing RNA primers
Relieving supercoils ahead of replication forks
Decatenation of plasmids after replication
Satellite DNA is best described as:*
A term for small chromosomes
A form of repetitive DNA
DNA outside the nucleus
Telomere-only DNA
A form of repetitive DNA
Which enzyme synthesizes RNA? (select all possible answers)
Primase, RNA Pol.
Which enzyme prevents reassociation of DNA strands?
SSBs
Which enzyme has 5' exonuclease?
DNA Pol 1
Which enzyme synthesizes DNA in 5'-->3'
DNA pol 1 and 3
Which enzyme unwinds the DNA helix?
Helicase
Which enzyme has 3' exonuclease?
DNA Pol 1 and 3
Which enzyme joins Okazaki fragments?
Ligase
A 12-year-old patient presents with developmental delays and distinctive facial features. Genetic testing reveals that the child carries a heterozygous deletion in the TBX1 gene (involved in 22q11 deletion syndrome). The remaining allele is intact and functional. Which of the following best explains the child’s symptoms?
The remaining allele produces enough protein to maintain normal function.
Both alleles must be mutated for the phenotype to appear.
One functional allele does not produce sufficient protein for normal function, leading to disease.
The deletion causes gain-of-function of the TBX1 protein.
One functional allele does not produce sufficient protein for normal function, leading to disease.