9/8 Signal Transmission and Osmolarity
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Hydrophilic signaling molecule
- Binds to extracellular receptors
- Initiate second messenger cascades
- Alter ion channel conformations (open/close)
- Typically have a FAST effect and are metabolized/excreted quickly
Example of hydrophilic signaling molecule
Norepinephrine
Hydrophobic signaling molecule
- Binds to intracellular receptors
- Alters gene transcription and protein synthesis
- Typically have a SLOW effect and are metabolized/excreted slowly
Example of hydrophobic signaling molecule
Steroid hormones
Autocrine signaling
The target cell is also the secreting cell
Paracrine signaling
Secreting cell releases signals that act on nearby cells
Endocrine signaling
Secreting cell releases signals (hormones) that travel through the bloodstream to act on distant cells
Neurotransmission
Communication between neurons involving release of signals (neurotransmitters) across synapses that bind to nearby cells
Neurohormonal signaling
Hormones released into bloodstream by neurosecretory cells
Signal transduction
A series of molecular changes that converts a signal on a target cell's surface to a specific response inside the cell.
Why are second messengers important?
They can significantly amplify the first signal
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Aquaporins
Protein channels that allow water to diffuse across cell membranes
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration per liter of solution (includes both penetrating and non-penetrating solutes)
Milliosmole
mOsm, unit of osmolarity
Normal osmolarity of ECF and ICF
300 mOsm
How to calculate osmolarity?
Molarity * n (# of particles in solution)
Penetrating solute
A solute that freely crosses the cell membrane (e.g. urea, glucose, EtOH)
Non-penetrating solutes
Solutes that cannot cross the cell membrane (e.g. Na+, K+, Cl-)
Penetrating solute effects on osmolarity vs tonicity
Osmolarity: affected
Tonicity: unaffected (they can move freely to reach equilibrium)
Non-penetrating solute effects on osmolarity vs tonicity
Osmolarity: affected
Tonicity: affected (water must move to achieve equilibrium)
Hypoosmotic
< 300 mOsm
Isosmotic
= 300 mOsm
Hyperosmotic
> 300 mOsm
Tonicity
A solution's effect on cell volume by influencing water movement through a cell membrane. It is directly influenced by non-penetrating solutes.
Hypotonic solution
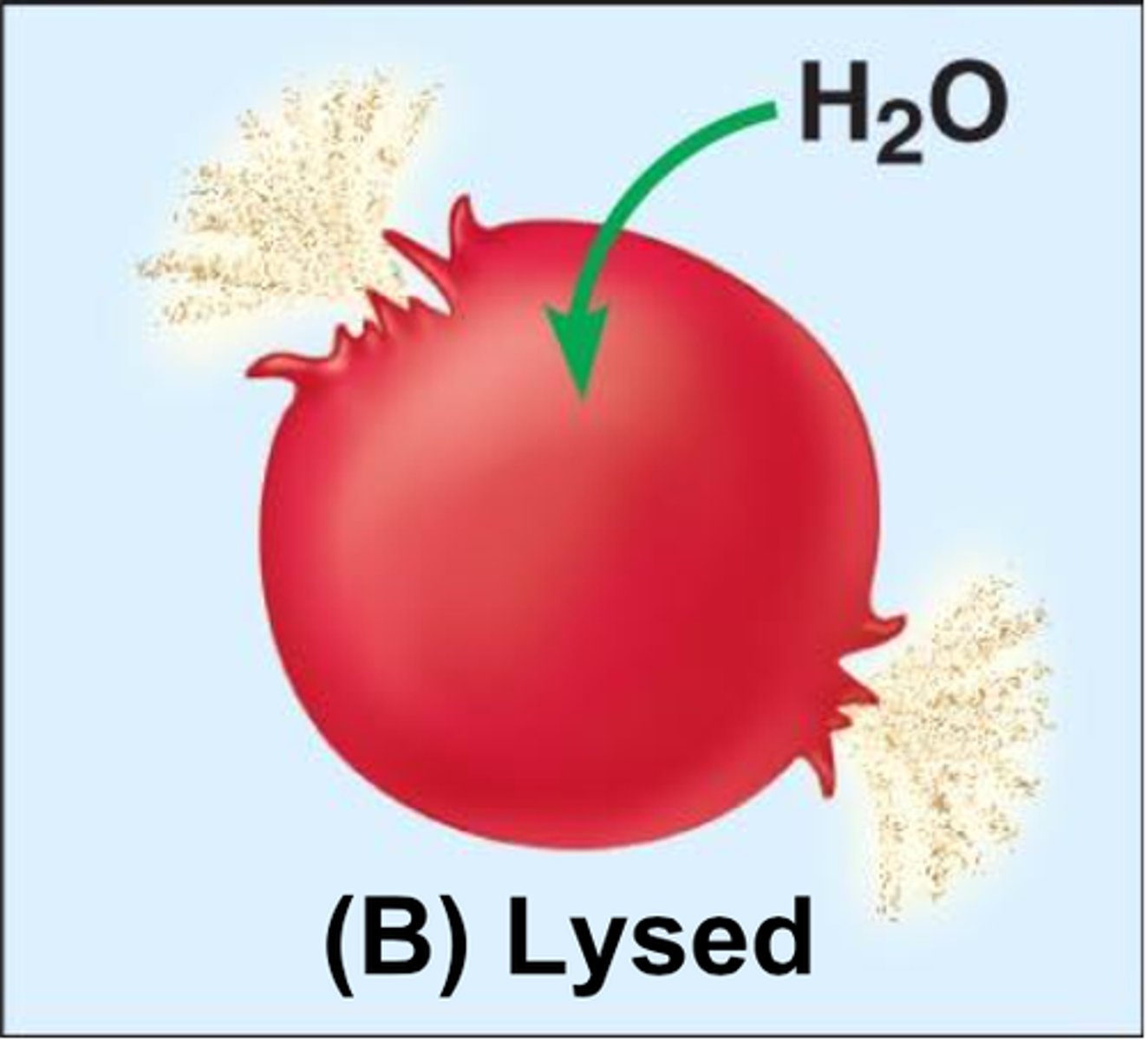
Solute concentration outside the cell is less than that inside the cell; water rushes into the cell and lyses the cell
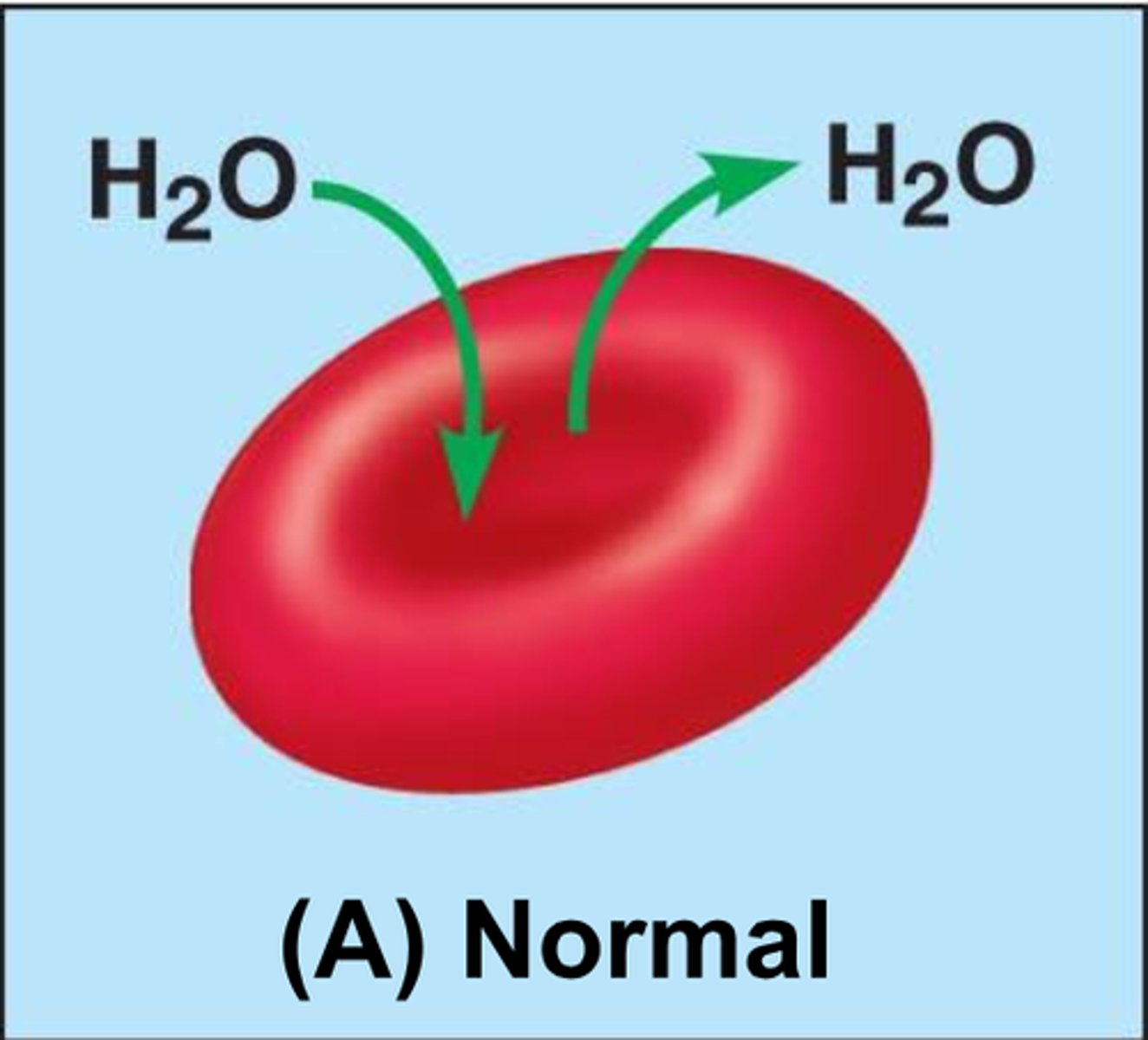
Isotonic solution
Solute concentration outside the cell is equal to that inside the cell; no net water movement
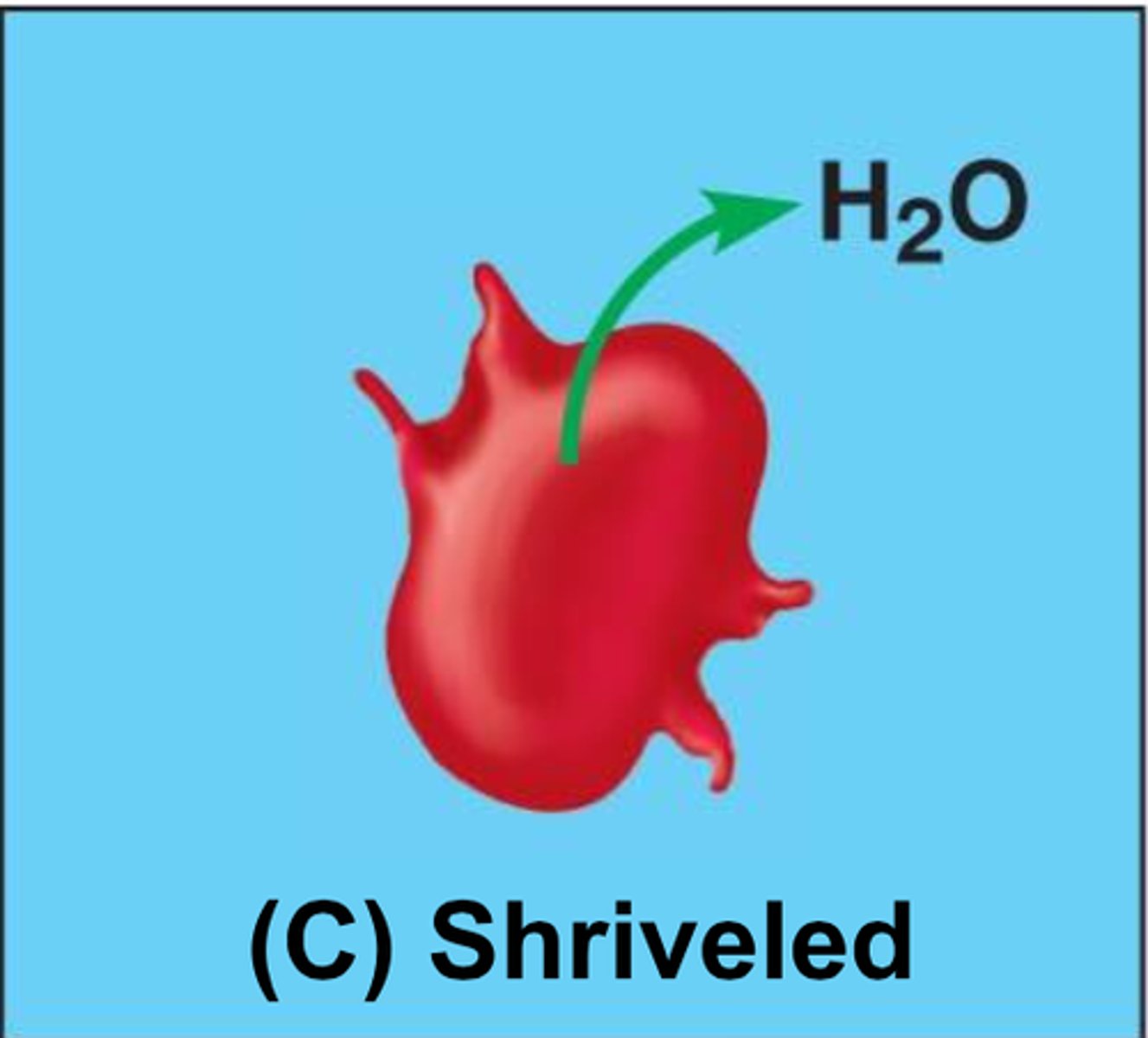
Hypertonic solution
Solute concentration outside the cell is greater than that inside the cell; water rushes out of the cell and causes shrinkage
Can osmolarity be less than tonicity?
No, because tonicity is the part of a solution's total osmolarity that can cause water movement across a membrane.
Hemolysis
Rupture of red blood cells