Unit 4 Political Patterns and Processes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Last updated 4:37 PM on 5/7/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
African Union (AU)
An organization of African nations pursuing greater political and economic integration across the continent.
2
New cards
antecedent boundary
a boundary that existed before the cultural landscape emerged and stayed in place while people moved in to occupy the surrounding area.
3
New cards
Arctic Council
1996 Members include countries with territory in the Arctic Promotes sustainable development
Dedicated to protecting the regions environment.
Dedicated to protecting the regions environment.
4
New cards
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
a trade alliance that promotes trade and economic integration among member nations in Southeast Asia
5
New cards
autonomous region
a defined area within a state(country) that has a high degree of self-government and freedom from its parent state
6
New cards
Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules and the division/colonization of Africa during the time period of imperialism. These colonies were strictly controlled politically and economically for the benefit of industrializing European countries
7
New cards
choke point
a strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water OR a strategic land route that can be easily controlled or cut off
8
New cards
Colonialism
Attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory from 1500-1800s.
9
New cards
consequent boundary
A type of subsequent boundary that is drawn to accommodate existing linguistic, cultural, or religious boundaries
10
New cards
Cultural cohesion
The capacity of different national and ethnic groups to make a mutual commitment to live together as citizens of the same state.
11
New cards
Defined Boundary
boundary is created in agreement between two parties in a treaty or other legal document
12
New cards
Delimited Boundary
A boundary, DRAWN on a map, and agreed upon.
13
New cards
Demarcated Boundary
actual placing of a political boundary on the physical landscape by means of fences, barriers, signs, etc.
14
New cards
demilitarized zone
A region where no military forces or weapons are permitted.
15
New cards
Democratization
the spread of representative government to more countries and the process of making governments more representative
16
New cards
Devolution
when a central government authority grants more political power to a subnational region within their territory
17
New cards
Ethnic cleansing (genocide)
the systematic killing, torturing, or removal of persons with the intention of eliminating a specific racial or ethnic group
18
New cards
ethnic nationalist movement
Ethnic, racial, and nationalist movements seek to advance group‐based politics in relation to their distinct identities. At different times movements can switch interchangeably between being ethnic, racial, or nationalist in character.
19
New cards
ethnic separatism
The advocacy of a state of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, or racial separation from the larger group usually expressed by the promotion of regional autonomy.
20
New cards
Ethnonationalism
the tendency for an ethnic group to see itself as a distinct nation with a right to autonomy or independence (positive in a nation-state, negative in multi-nation state).
21
New cards
European Union (EU)
an economic association established in 1957 by a number of Western European countries to promote free trade among its members.
22
New cards
failed state
a state whose political or economic system has become so weak that the government is no longer in control.
23
New cards
Federal State
An internal organization of a state in which the national government shares power with subnational units of local government. Examples: the United States, Mexico
24
New cards
geometric boundary
Political boundaries that are formed by arcs or straight lines(usually latitude or longitude lines) irrespective of the physical and cultural features of the land it passes through.
25
New cards
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
26
New cards
Imperialism
domination by one country of the political, economic, or cultural life of another country or region, a policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or economic policy or military force.( 1800s to the present)
27
New cards
Independence Movements
The process of gaining self-rule; for example, After WWII, Europe was greatly weakened. African nations such as Ghana, Algeria, and Kenya and other former colonies took advantage of this and gained independence through peaceful and violent means.
28
New cards
infrastructure development
Creating or strengthening fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, such as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools (loans by LDCs are usually focused on this).
29
New cards
Irredentism
a policy of cultural extension and potential political expansion by a country aimed at a group of its nationals living in a neighboring country, many times to regain former territory
30
New cards
maritime boundary
An international boundary that lies in the ocean. Like all boundaries, it is a vertical plane, extending from the seafloor to the upper limit of the air space in the atmosphere above the water.
31
New cards
multinational state
a state with more than one nation inside its borders
32
New cards
Nation
a large group of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language
33
New cards
nation-state
A state whose territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality
34
New cards
Neocolonialism
Also called economic imperialism, this is the domination of newly independent countries by foreign business interests that causes colonial-style economies to continue, which often caused monoculture (a country only producing one main export like sugar, oil, etc).
35
New cards
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
1949 alliance of democratic nations that agreed to band together in the event of war and to support and protect each nation involved from the threat of communist forces. Since the end of the Cold War, these democratic countries in North America and Europe have continued this military alliance
36
New cards
Redistricting
The drawing of new electoral district boundary lines in response to population changes, usually every 10 years after the census
37
New cards
relic boundary
A boundary no longer observed but that still affects the present-day area (e.g. border between West and East Germany in Berlin)
38
New cards
Self-determination
Concept that ethnic groups have the right to govern themselves
39
New cards
semi-autonomous region
area where a group has some type of political autonomy. Semi-autonomous regions, like Kurdistan, has a degree of power and self-determination, but not fully like autonomous regions
40
New cards
Shatterbelt
a region caught between stronger colliding external cultural-political forces, under persistent stress, and often fragmented by aggressive rivals (e.g., Israel or Kashmir today; Eastern Europe during the Cold War,...).
41
New cards
Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnic groups, named for the break-up of the former Yugoslavia into 8 ethnic majority countries on the Balkan peninsula
42
New cards
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.
43
New cards
State
A body of people living in a defined territory who have a government with the power to make and enforce law without the consent of any higher authority, and is recognized as such by the international community a.k.a a country
44
New cards
stateless nation
a group of people with a common culture and political identity who do not have sovereign territory
45
New cards
subsequent boundary
a boundary line that is established after the area in question has been settled and that considers the cultural characteristics of the bounded area
46
New cards
superimposed boundary
a boundary that is placed by an outside power on the cultural landscape which ignores pre-existing cultural patterns (typically a colonial boundary)
47
New cards
Supranationalism
term applied to associations created by three or more states for their mutual benefit and achievement of shared objectives (usually economic or for common defense)
48
New cards
Territoriality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended.
49
New cards
Terrorism
Acts of violence designed to promote a specific ideology or agenda by creating panic among an enemy population
50
New cards
Unitary State
An internal organization of a state that places most power in the hands of central government officials. Example: Japan, China
51
New cards
United Nations (UN)
an organization of independent states formed in 1945 to promote international peace and security. Some of the UN Developmental Goals: Goal 1: End poverty in all its forms.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger.
Goal 3: Health.
Goal 4: Education.
Goal 5: Gender equality and women's empowerment.
Goal 6: Water and Sanitation.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger.
Goal 3: Health.
Goal 4: Education.
Goal 5: Gender equality and women's empowerment.
Goal 6: Water and Sanitation.
52
New cards
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea: a code of maritime law approved by the UN in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200 nautical mile wide exclusive economic zones.
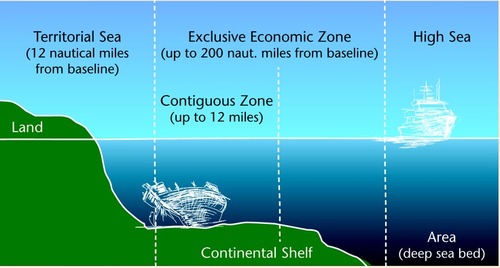
53
New cards
voting districts
generic term adopted by the Bureau of the Census to include the wide variety of small polling areas, such as election districts, precincts, or wards, that State and local governments create for the purpose of administering elections
54
New cards
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
as established in the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, a zone of exploitation extending 200 nautical miles seaward from the a coastal state that has exclusive mineral and fishing rights over it
55
New cards
multi-state nation
a nation or cultural group that is divided across two or more state borders
56
New cards
centripetal force
An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state, can be political, economic, or cultural
57
New cards
centrifugal force
a force that divides people and countries, can be political, cultural, or economic