molecules
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
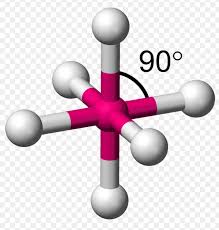
shape of SF6 molecule (6 bonding pairs)
-octahedral
-90 degree bond angles
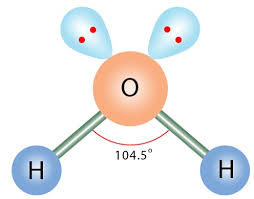
shape of H2O molecule
-non linear
-109.5 - (2x2.5)= 104.5
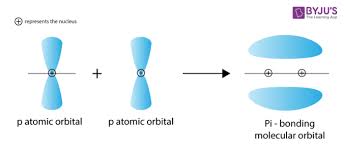
pi bond
-formed by sideways overlap of 2 p-orbitals
-weaker than sigma bonds because electron density is spread out above and below nuclei
dative covalent bond
-a covalent bond where both electrons being shared originate from the same atom
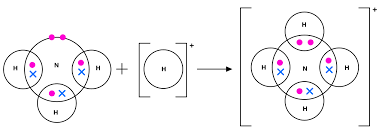
covalent bond
-the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of bonded atoms
average bond enthalpy
-a measurement of the strength of a covalent bond
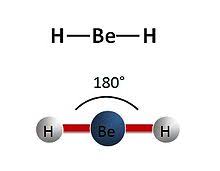
BeCL2 molecule? (2 electrons bonding pairs)
-linear
-180 degree bond angle
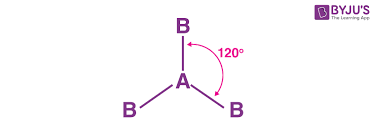
BF3 molecule
-trigonal planar
-120 degree bond angle
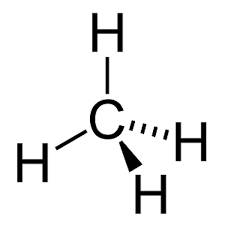
CH4 molecule (4 electron bonding pairs)
-tetrahedral
-109.5 degree bond angles
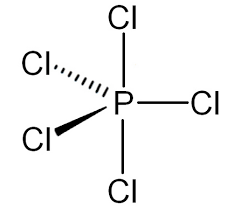
PCl5 molecule(5 electron bonding pairs)
trigonal bipyramidal
120 and 90 degree bond angle
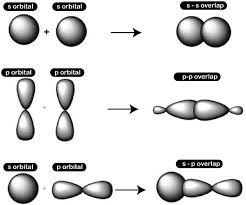
sigma bond
-formed when 2 s-orbitals overlap
-overlap in a straight line, giving highest electron density between 2 nuclei
-thus there are strong electrostatic forces between nuclei and electron pair
-e.g. C-H
What are some anomalous properties of water resulting from hydrogen bonding?
-ice is less dense than water bacause in ice, water molecules are held in a LATTICE by hydrogen bonds, which break when ice melts
-so ice has more hydrogen bonds than water and hydrogen bonds are relatively long, holding molecules further apart
-water has relatively high melting and boiling points because hydrogen bonds have to be broken
What are the requirements of induced dipole-dipole forces (London dispersion forces)
-only needs electrons, more electrons=stronger forces
-they're the weakest intermolecular force
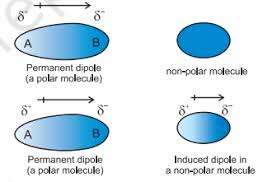
What are the requirements for permanent dipole-dipole forces and how do they form?
-electronegativity difference between atoms (polar bond)
-asymmetric molecule (polar molecules have permanent dipoles)
-strength is intermediate, stronger when electronegativity difference is bigger
-negative end of molecule will attract postiive end of another
-e.g. HCl
What are the requirements for hydrogen bonds and how are they formed?
-hydrogen
-attached to a lone pair
-an electronegaative atom (fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen)
-fromed by attraction between delta + and delta -
-they're the strongest, if number of lone pair matches number of H atoms, maximum number of hydrogen bonds form per molecule
What's the definition of electronegativity and what are polar bonds?
-the ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons within a covalent bond
-fluorine, oxygen, chlorine and nitrogen are the most electronegative elements (top right of the periodic table)
-this makes polar bonds
lone pairs
-2 electrons in same orbital that aren't involved in forming covalent bonds
-for every lone pair around central atom, minus 2.5 from original bond angles without lone pairs
electron pair repulsion theory
-used to explain the shape and bond angles of molecules
-electrons pairs repel each other to get as far apart as possible
-lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs, pushing bonding pairs closer together
WHt's the shape of a molecule woth 6e- pairs? (4 bonding, 2 lone)
-square planar
-90 degree bond angle
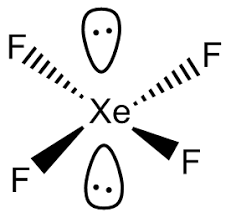
What's the shape of a molecules with 3e- pairs, 1 lone and 2 bonding?
-non-linear
-120 - 2.5 = 117.5 degree bond angle
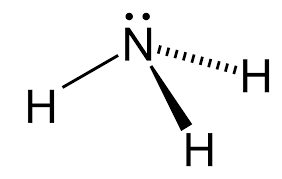
WHat's the shape of an NH3 molecule? (4 e- pairs, 3 bonding, one lone)
-trigonal pyramidal
-109.5-2.5 = 107 degree bond angle
requirements for polar molecule
-polar bond
-asymmetric molecules (so dipoles don't cancel out when they act in opposing directions
how are induced-dipole forces formed
-due to electrons moving quickly/randomly, giving molecule a temporary dipole
-instantaneous dipole on one atom/molecule induces a dipole on neighbouring atom/molecule