Disorders of Digestion and Absorption
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
nausea and vomiting
unpleasant sensation usually preceding vomiting, may have abdominal pain, pallor, sweating, clammy skin
vomiting
forceful expulsions of stomach contents throught the mouth
projectile vomiting
is forceful ejection of stomach contents
regurgitation
gentle ejection of stomach contents without nausea or retching
antiemetics
IV Fluids
NG tube
TPN
treatments for nausea and vomiting
dehydration
metabolic alkalosis
aspiration
complications of nausea and vomiting:
hiatal hernia
opening in the diaphragm thru w/c the esophagis passes becoms enlarged and part of the upper stomach moves up into the lower portion of the thorax
occurs more often in women than in women
hiatal hernia
it is caused by the lower esophageal sphincter related to increased abdominal pressure, long term bed rest, trauma
type 1: sliding
occurs when the upper stomach and the gastroesophageal junction are dislplaced upward and slide in and out of the thorax
type 2: rolling / PARAESOPHAGEAL
occurs when all or part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm beside the esophagus
further classified as types II, III, IV
2 types of hiatal hernia
type 1: sliding
what type of hiatal hernia: occurs when the upper stomach and the gastroesophageal junction are dislplaced upward and slide in and out of the thorax
type 2: rolling / PARAESOPHAGEAL
what type of hiatal hernia:
occurs when all or part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm beside the esophagus
further classified as types II, III, IV
type 1: sliding type
what type of hiatal hernia:
dysphagia
regurgitation
heartburn (pyrosis)
intermittent epigasruc pain or fullness after eating
hemorrhage, obsyruction and strangulation can occur with any type of hernia
type 2: rolling / paraesophageal
what type of hiatal hernia:
sense of fullness or chest pain after eating

disgnostics of hiatal hernia:
esophagogastroduodonescopy
what is EGD (it is for hiatal hernia)
small freq feedins
not to recline for q hour after eating
elevate head of bed on 4 to 8 inch blocks
what should be considered for hiatal hernia:
h2 receptor antagonists: to reduce stomach secretion
tagamet
zantac
pepsid
antacids: neutralize stomach acids
reglan, propulsid: increase stomach emptying
drug theraoy for hiatal hernia:
decrease caffeine, fatty foods, alcohol, acidic and spicy foods, avoiding bedtime snack
diet therapy for hiatal hernia:
fundoplication
stomach fundus is wrapped around the lower part of the esphagus
gastritis
inflammation of the gastric or lining of the stomach (mucosa)
acute
what type of gastritis: lasting several hours to a few days; may develop in acute illnesses
chronic
a type of gastritis that is from repeated exposure to irritating agents or recurring episodes of acute gastritis
erosive, non-erosive
acute gastritis can be classified as:
erosive
what type of acute gastritis: caused by local irritants such as aspirin and other NSAIDS, alcohol abuse and recent exposure o radiation therapy
this type of acute gastritis is most often caused by infection with helicobacter pylori
more severe form
caused by indigestion of strong acid or alkali
may also develop in acute illlnesses (burns, severe infetion, hepatic, kidney or respi failure)
type a (autoimmune disorders)
type b (underlying causative mechanism)
chronic gastritis is classified to:
hashimoto thyroiditis
addison’s disease
grave’s disease
type a chronic gastritis disorders:
h. pylori
long term drug therapy
reflux of duodenal contents into the stomach
type b chrnoic gastritis disorders:
acute
acute or chronic gastritis:
epigastric pain or discomfort
dyspepsia
ausea and vomiting
anorexia
hiccups
bleeding (hematemesis, melena, hematochezia)
chronic
acute or chronic gastritis:
anorexia
heartbirn after eating
belching
sour taste in the mouth
nausea and vomiting
early satiety
vit. b12 deficiency (pernicious anemia)
poor absorption of certain vitamin in chronic gastritis can lead to:
endoscopy
definitive diagnosis of gastritis

medical management of gastritis:
dumping syndrome
this is common after gastric surgery:

dumping syndrome
dumping syndrome
rapid emptying of gastric contents into the small intestine

interventions on dumping syndrome:
PEPTIC ULCER
Excavation (hollowed out area) that forms in the mucosal wall of stomach, pylorus, duodenum, esophagus
Loss of tissue from the lining of the digestive tract. May be acute or chronic.
location
peptic ulcer is classified depending on?
gastric
duodenal
esophageal
what are the classifications of peptic ulcer?
infection ( gram (-)H .pylori bacteria)
what bacteria causes of peptic ulcer
drugs -Ibuprofen, Aspirin (NSAIDS), Steroids
stress
smoking, chewing tobacco
heavy alcohol
conditions that cause high gastric acid concentration
familial tendency
with blood type”O”(more susceptible)
what are the risk factors of peptic ulcer?
heartburn
pyrosis is also known as what?
Dull, gnawing pain or burning sensation
Pyrosis ( heartburn )
burning sensation in the stomach and esophagus that moves up to the mouth
accompanied by sour eructation(burping)Vomiting
Constipation or Diarrhea
Bleeding
peptic ulcer s/sx
(burping)
eructation
Gastric Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Burning/gnawing pain which occur immediately or 1-2 hrs after meals, more pain w/ food; upper left abd/back
Duodenal Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: burning/ cramping pain 2-4 hrs. after meals, beneath xiphoid and back, relieved by antacids/food
Gastric Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: N/V, anorexia, wt loss
Duodenal Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Secrete more acid than normal
Gastric Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Secrete normal or decreased levels of acid
Duodenal Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Young men, all social classes, bld type O, chronic illnesses
Gastric Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Older men, working class, bld type A, under stress
Duodenal Ulcers
peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer: Awake with pain during the night
gnawing, burning, cramping
what are the type of pain?
Gnawing
what type of pain:
Dull, aching, like hunger
Epigastric area
Peptic ulcer
Burning
what type of pain:
Sharp, hot, fiery
Epigastric or chest
GERD, peptic ulcer
Cramping
what type of pain:
Squeezing, wave-like, tight
Lower or whole abdomen
IBS, stomach flu, gas, periods
Physical Exam
reveal pain, epigastric tenderness or abdominal distention
Upper endoscopy
Biopsy
Histologic exam of tissue specimen
Urea breath test
IgG antibody detection test for H. pylori
Culture
Upper GI series (Barium swallow)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Assessment/Diagnostic findings: PEPTIC ULCER
esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
This diagnostic procedure examines the esophagus, stomach, and upper duodenum with a small camera (flexible endoscope) which is inserted down the throat
STRESS ULCER
Occurs after physiologically stressful events ( burns, shock, severe sepsis, multiple organ trauma )
Curling’s ulcer
Cushing’s ulcer
classifications of stress ulcer:
Curling’s ulcer
this classification of stress ulcer occurs 72 hrsafter extensive burns
Cushing’s ulcer
this classification of stress ulcer includes head injury, stroke and brain trauma
hemorrhage
perforation
pyloric obstruction
peptic ulcer complications:
Antibiotics (Metronidazole,Clarithromycin, Tetracycline, Amoxicillin)
Proton pump inhibitor (Omeprazole)
Bismuth salts that suppress/eradicate
H. pylori
Triple therapy( 2 Antibiotics + 1 PPI)
Quadruple therapy (2 Antibiotics + PPI +
Bismuth)
Antacids
H2 RECEPTOR BLOCKERS
ANTICHOLINERGICS-Pro-Banthine, Robinul, Bentyl
Octreotide –suppresses gastrin levels
Smoking cessation
Dietary modification
drug therapy for peptic ulcer:
intractable ulcers
those failing to heal after 12-16 weeks of medical treatment ), life threatening hemorrhage, perforation, obstruction, with ZES( ZollingerEllison Syndrome)
surgery
what is recommended for those with intractable ulcers
vit. B12
folic acid
iron
calcium
vit. D
gastric surgeries (vagotomy, pyloroplasty, antrectomy) can have serious effects on absorption of what?
GASTRIC (STOMACH) CANCER
Rare(25,000/yr.), common in males, African American, over 70 and low socioeconomic status. 60% decrease in past 40 yrs.
No S/Sx in early stages
Late stages S/Sx: N/V, ascites, liver enlargement, abd. mass
Mets to bone and lung
10% survival rate after 5 yrs.
n/v
ascites
liver enlargement
abdominal mass
what are the late stages s/sx of gastric (stomach) cancer:
H. pylori infection, pernicious anemia, chronic gastritis/inflammation, cigarette smoking, obesity, diet high in smoked, salted, pickled foods, low in fruits & veg.,achlorhydria – No HCl, gastric ulcers, previous partial gastrectomy, genetics
risk factors of gastric/stomach cancer:
antacids
early stage s/sx of gastric cancer can be relived by:
abdominal pain above umbilicus,dyspepsia(indigestion), decrease or loss of appetite, weight loss, bloating after meals, nausea and vomiting, early satiety, fatigue
Sister Mary Joseph’s nodules
palpable nodules around umbilicus
sign of GI malignancy
adavance stage s/sx of gastric/stomach cancer:
Sister Mary Joseph’s nodules
peri-umbilical nodules (small lumps or bumps) that are often indicative of advanced abdominal malignancy, particularly gastrointestinal cancer
named after Sister Mary Joseph, a surgical nurse who first observed and described this clinical sign in the early 20th century.
OBESITY
Chronic relapsing disease characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat & weight gain, 20% over ideal
Results from a metabolic imbalance, characterized by an excess of caloric consumption relative to caloric expenditures
heredity
body build
metabolism,
psychosocial factors
Calorie intake exceeds demands
causes of obesity:
Vagal blocking therapy
Intragastric balloon therapy
Non-Surgical Management of obesity
Bariatric surgery
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB)
Gastric banding
Sleeve gastrectomy
Biliopancreatic diversion w/ duodenal switch
Surgical Management of obesity
Bariatric surgery
work by restricting patient’s ability to eat, interfering w/ ingested nutrient absorption or both
gastroesophageal reflux disease
acid reflux
a condition in which the liquid content of the stomach regurgitates into the esophagus
acid
pepsin
what components are found in the regurgitated liquid in GERD?
pepsin
an enzyme that is present in the regurgitated liquid in GERD that begins the digestion of proteins in the stomach
Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter
Pyloric stenosis
Hiatal hernia
Motility disorder
Associated with: tobacco use, coffee drinking, alcohol consumption, gastric infection w/ H.pylori
Causes of excessive reflux:
pyrosis
odynophagia
esophagitis
dysphagia
regurgitation
s/sx of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Dental erosion
Ulcerations in the pharynx & esophagus
Laryngeal damage
Laryngeal damage
Adenocarcinoma
pulmonary complications
GERD can result in:
bilirubin monitorin (bilitec)
used to measure bile reflux patterns, exposure to bile can cause mucosal damage
Fluoroscopy
real-time imaging technique that uses X-rays to create continuous live images of the inside of the body
nissen fundoplication
wrapping of a portion of the gastric fundus aroudn the pshincter area of the esophagus
can be performed by the open method or by laparoscopy
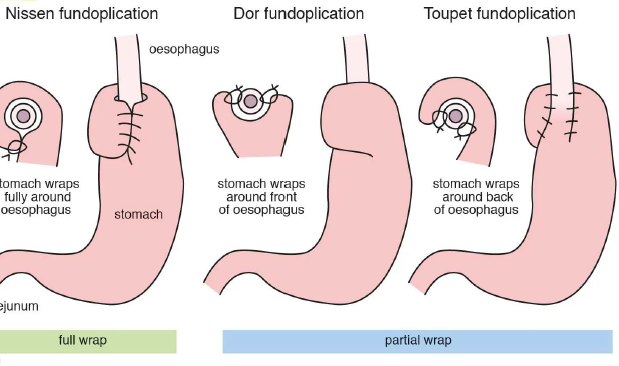
types of fundoplication:
6 to 8 inches blocks
with GERD patients, how would you elevate their head?
Esophagitis
Barrett’s esophagus
precancerous lesion that puts the patient at risk of developing esophageal cancer
Respiratory complications
bronchospasm, laryngospasm, aspiration pneumonia
complications of GERD:
Barrett’s esophagus
precancerous lesion that puts the patient at risk of developing esophageal cancer
Barrett’s esophagus
Columnar epithelium with goblet cells (like in the intestines)
Adapts to chronic acid exposure, but not protective
Chronic acid reflux (GERD) causes the change
Increased risk of esophageal cancer (adenocarcinoma)
ACHALASIA
It is also known as CARDIOSPASM
muscular activity of the esophagus (gullet) is disturbed, which delays the passage of swallowed material
Absent or ineffective peristalsis of the distal esophagus accompanied by failure of the esophageal sphincter to relax in response to swallowing
progressive dysphagia
regurgitation of undigested food
chest pain or epigastric pain & pyrosis
Coughing and choking
if the food enters the wind pipe it can cause aspiration pneumonia
Weight loss
s/sx of achalasia:
X-ray studies/video-esophagram
the video x-ray of the esophagus are taken after barium is swallowed
Manometry
measures the pressure and movement of muscles in the esophagus

Oral medication
Including nitrates, calcium channel blockers
It provide short term relief of the symptoms and many patients experience side effect of the drug
Dilation of the LES(Lower Esophageal Sphincter)
It is done by having patient swallow a tube with a balloon on the end
The balloon is placed across the lower sphincter with the help of x-ray and the balloon is blown up suddenly
Pneumatic dilation
stretch the narrowed area of the esophagus
treatment of achalasia