Hair, Skin, and Nails
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
General Survey: Purpose
-It establishes a baseline by assessing factors such as physical appearance, body structure, mobility, and demeanor, which guide and support the more detailed examination.
-to provide an overall impression of the patient's health, appearance, and behavior.
When should you begin a general survey?
at the moment you first encounter the person; this is your first impression of a person's wellbeing.
4 areas to consider in a general survey
•Physical appearance
•Body Structure
•Mobility
•Behavior
AAOx4
Neuro Status Assessment: Awake, alert, and oriented to person, place, time, and situation
Physical Appearence
•Age
•Level of consciousness (neuro/mental status)
•Are they Awake Alert and Oriented x4
•Skin color (color tone is even; note tattoos and piercing and stages of healing)
•Facial features
•Overall appearance
Body Structure
-Stature-
Height appears normal range for age, heritage
-Nutrition-
weight appears within normal range for height and body build, normal fat distribution
-Symmetry-
Body parts equal bilaterally & relative proportion
-Posture-
Stands erect with straight posture
-Position-
Standing with arms comfortable at side
-Body build or contour-
Normal in proportion arm span and body length
-Obvious deformities-
no noted deformities or defects
Mobility
•Gait
•Range of motion
•Presence of involuntary movement
Behavior
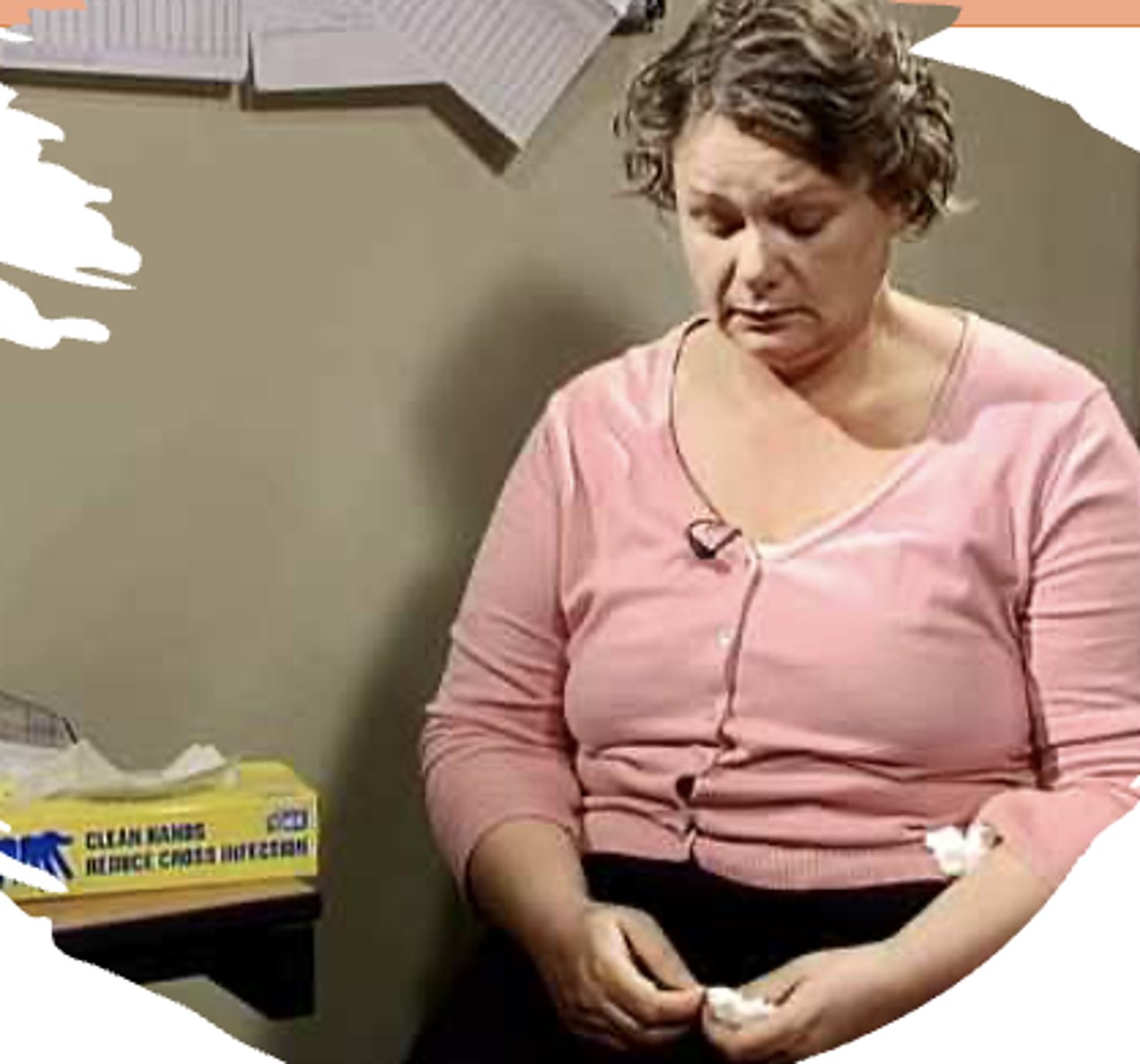
Facial expression- the patient does not maintain eye contact; she is looking down at her hands; her expression of sadness may or may not be appropriate for the situation.
Mood and affect- The patient seems to be crying as noted by the box of tissues on the table, in her hand, and up her sleeve.
Speech and speech pattern- The patient is talking fluently at even pace. She is conveying ideas clearly and her word choice is appropriate.
Dress- Clothing is appropriate, the patient looks clean.
Personal hygiene- The patient appears clean and well groomed for her age.

Anthropometric Measurements
Measures of height, weight, and BMI
Subjective data
Previous history of skin disease
Change in pigmentation
Change in a mole (size, color, shape)
Itching
Rash or lesions
Cancers
Pressure injuries
Objective data
color, temp, moisture, texture, thickness, edema, mobility and turgor
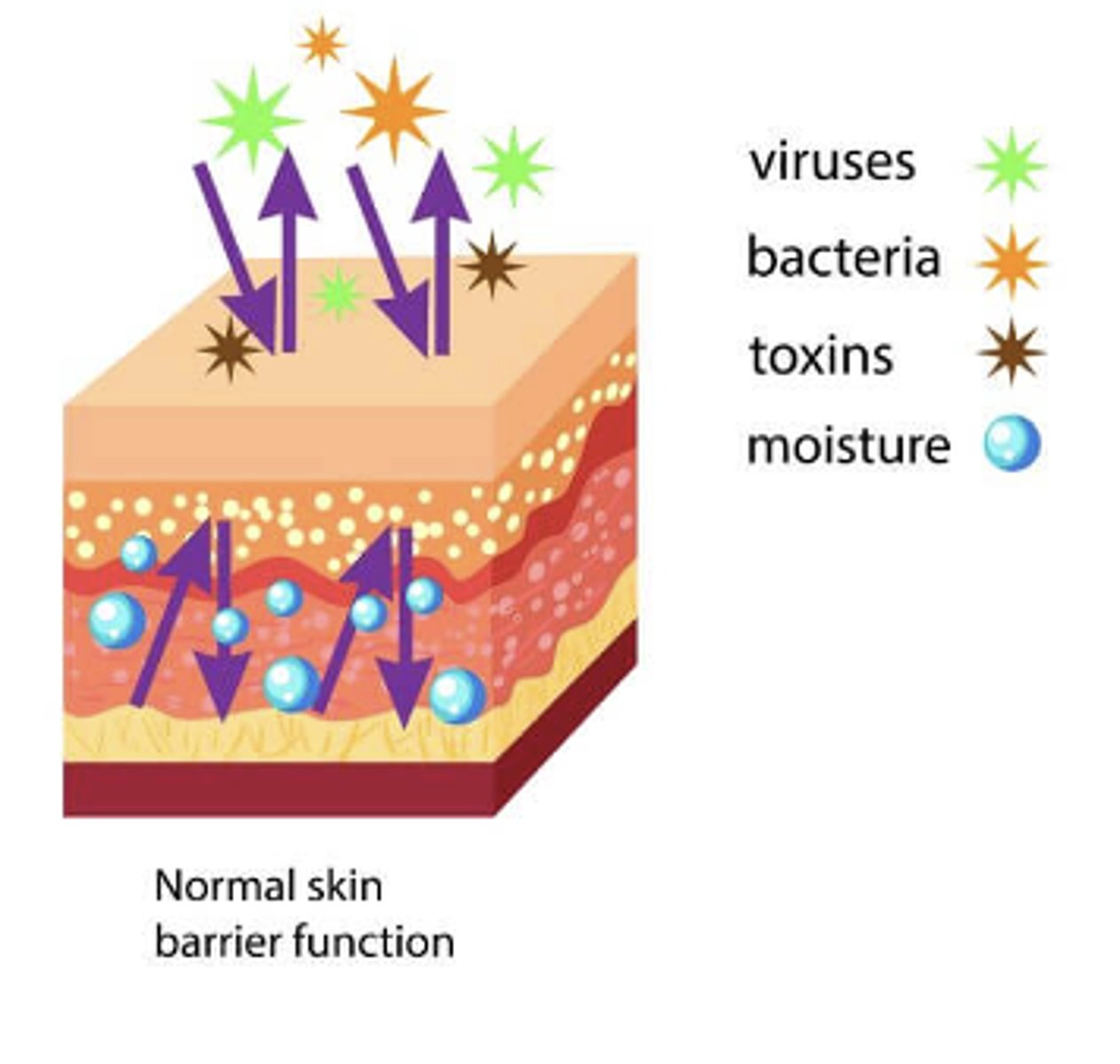
Epidermis-
outermost skin layer; serves as the first line of defense against pathogens; has no blood supply and is nourished by oxygen
Dermis-
the second layer; contains blood vessels, nerves, sebaceous glands, hair follicles.
Subcutaneous layer-
provides insulation, storage of caloric reserve, and cushioning. Composed of fat and loose connective tissue.
Skin facts!
The skin is the largest organ system in the body—it covers 20 square feet of surface area in the average adult.
The skin guards the body from environmental stresses (e.g., trauma, pathogens, dirt) and adapts it to other environmental influences (e.g., heat, cold).
The skin has two layers: the outer, highly differentiated epidermis and the inner, supportive dermis. Beneath these is the subcutaneous layer of adipose tissue.
Functions of the skin
protection, prevents penetration, perception, temperature regulation, identification, communication, wound repair, absorption and excretion, production of vitamin D
Hair
-An appendage of skin that protects various body areas from debris and invasion, provides insulation, enables sensory stimulation
-composed of keratin
-produced by hair follicles located deep in the dermis.
-present in all body areas except the palms and soles
Keratin
hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails
Nails
epidermal appendages that arise from a matrix in the epidermal layer.
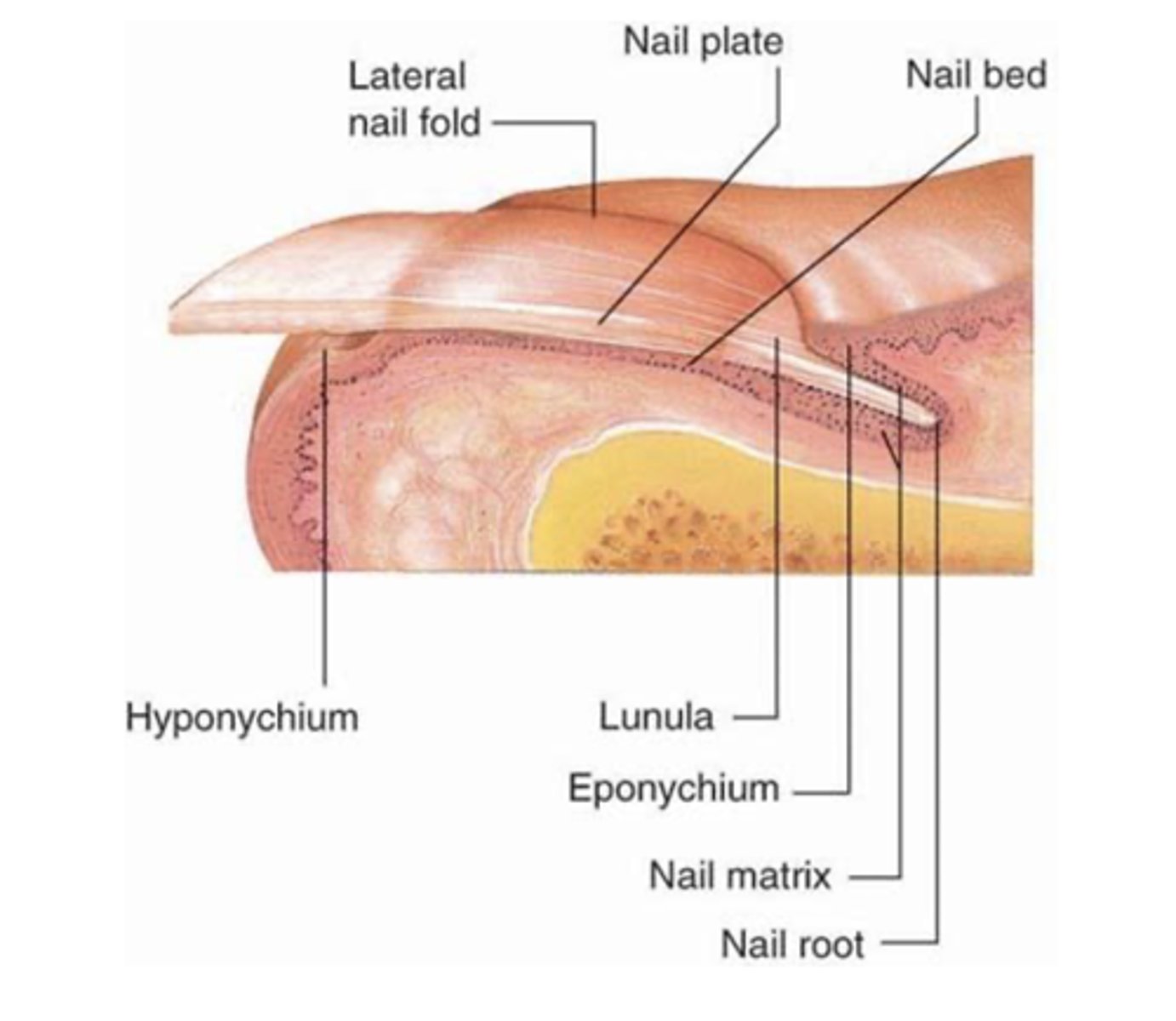
Nail plate
hardened keratin
grows at varying rates (fingernails grow faster than toenails)
transparent
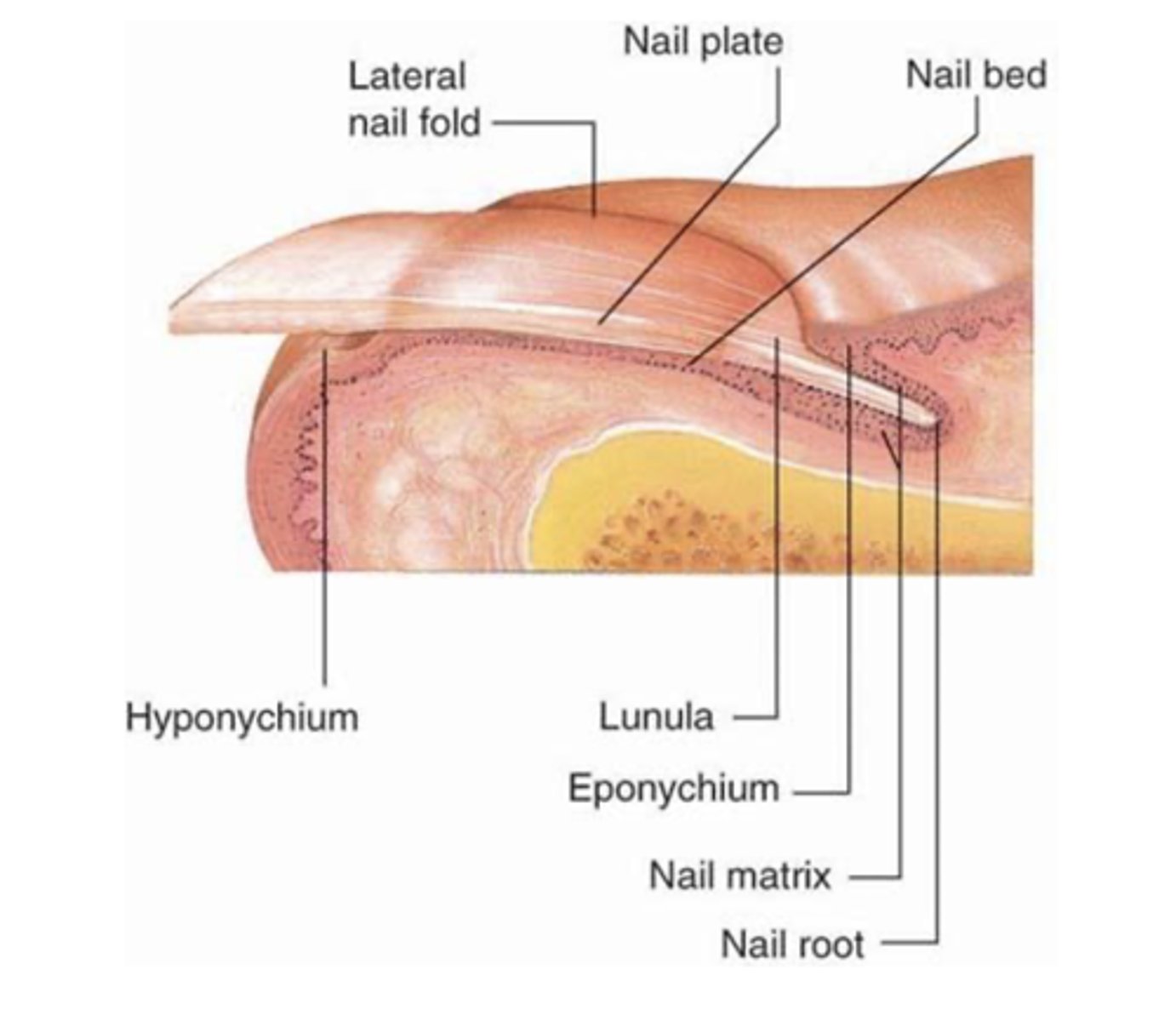
nail bed
highly vascular tissue under the nail
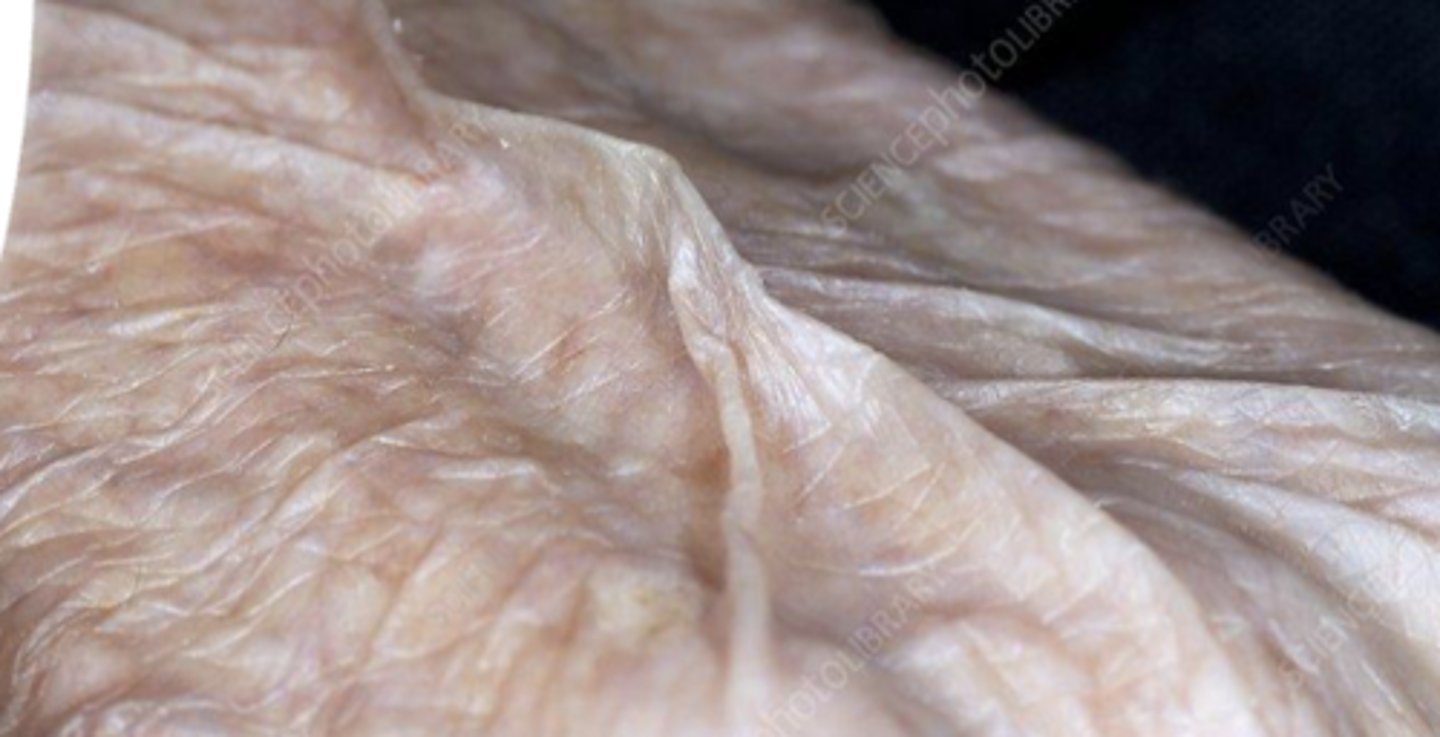
Effects of old age on skin
-gets thinner
-loses elastin, collagen, fat
-more fragile (risk for skin breakdown, sun damage, burising, injury, etc...)
-Turgor decreases
-Decreased melanin production
Cultural Considerations
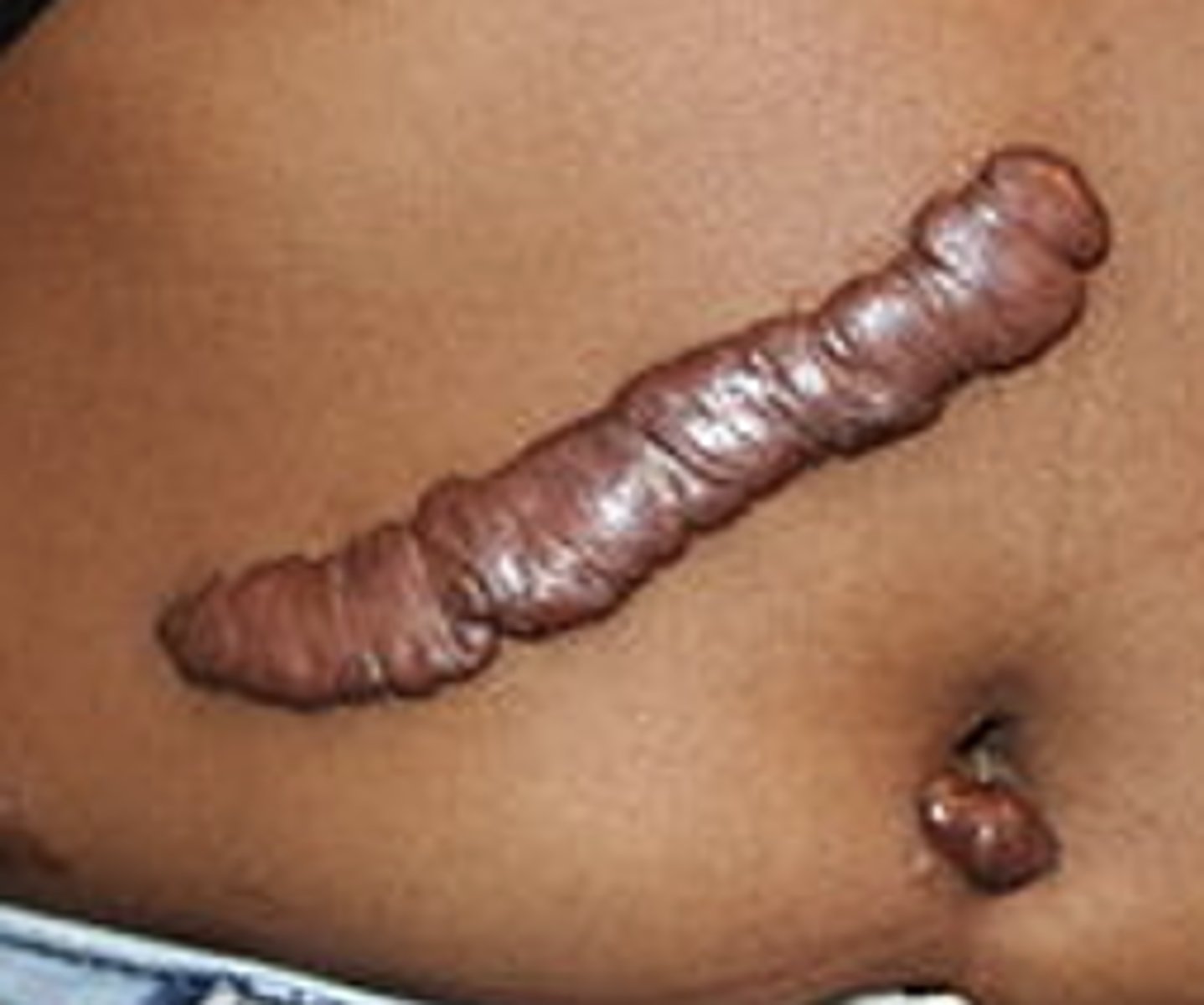
Keloids-scarring formed at site of wounds and grow beyond boundaries; more common in darker-skinned patients
psuedo-folliculists "razor bumps" more common in black males
pityriasis rosea as macular hyperpigmented viral dermatitis is common in caucasians
Melanin protects the skin against UV rays; resulting in low incidence of skin cancer in darkly pigmented people
Priority Urgent Assessment
•acute lacerations, burns, tissue injury
•These injuries may require interventions with fluids, oxygen, skin protection. Patients with burns can lose large amounts of fluid through their wounds, so rapid fluid replacement is a necessity.
•Acute trauma and burns may require immediate attention; they are potentially life-threatening requiring advanced and sometimes complex treatment plans and interventions
Questions to inquire about skin
•Past medical history of skin disease
-Do you have pigmented skin lesions?
How many? What size? Have they changed?
Have you ever had severe sunburn?
•Family history of skin disease
•Changes to skin
•Medications/Allergies
-Certain medications can cause phototoxicity and photoallergic reactions (tetracycline, doxycycline, hydrochlorothiazide, etc.)
•Hair loss
•Change in fingernails
•Environmental or occupational hazards
•Self care behaviors
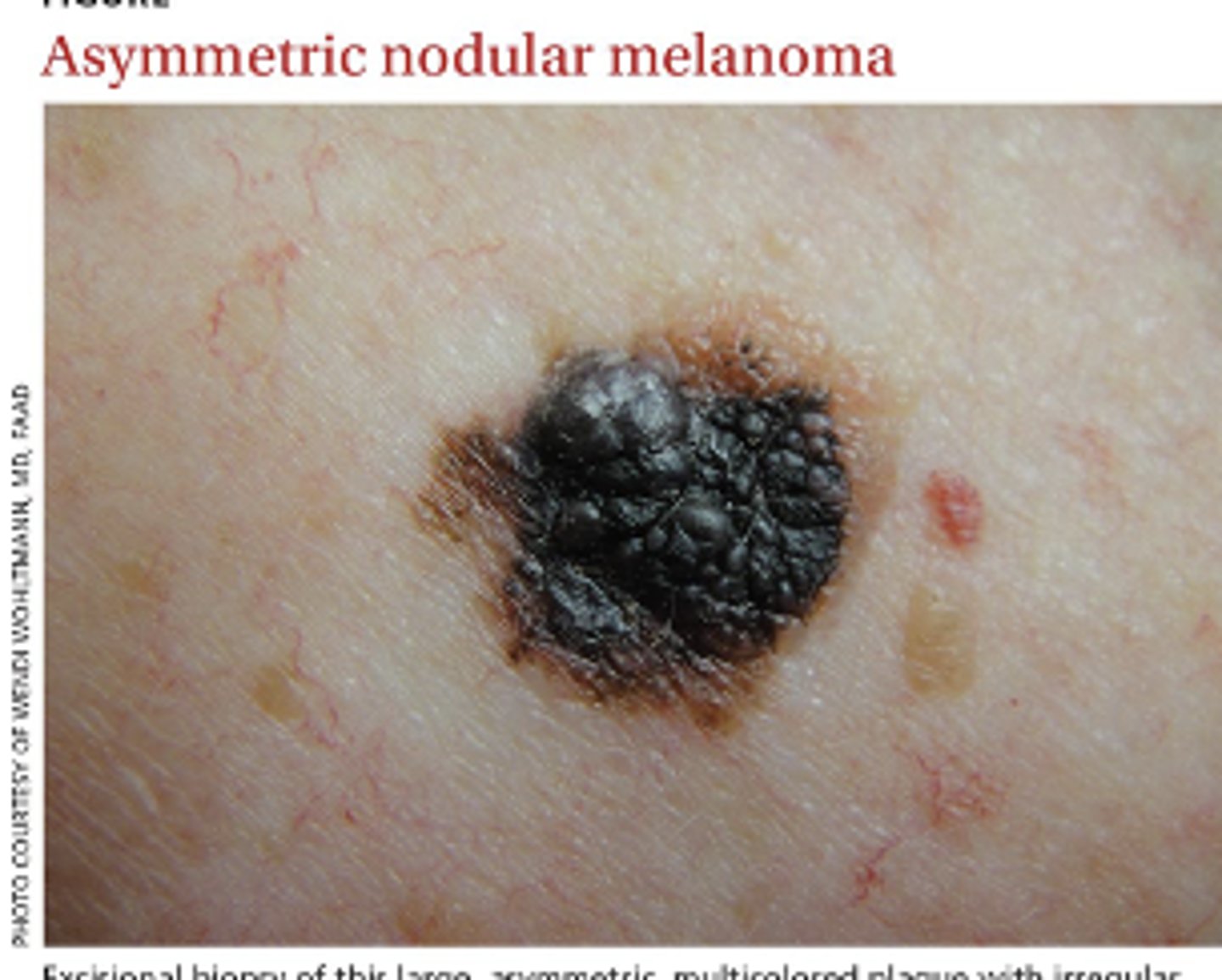
ABCDE's of Skin Assessment
•Asymmetry
•Borders
•Color variation
•Diameter
•Is the diameter >6 mm (pencil eraser)?
•Elevation or Evolution
Teaching integumentary health
•Self-skin examination
•Educate patients who are immune suppressed, history of skin cancer, or a family history of skin cancer to perform a skin self-examination
•Utilize sunscreen
Pruritis
•Itchy skin- uncomfortable, irritating sensation, sensation to scratch
•Many possible causes (underlying condition, hair regrowth, sunburns, insect bites, dry skin, or healing wounds)
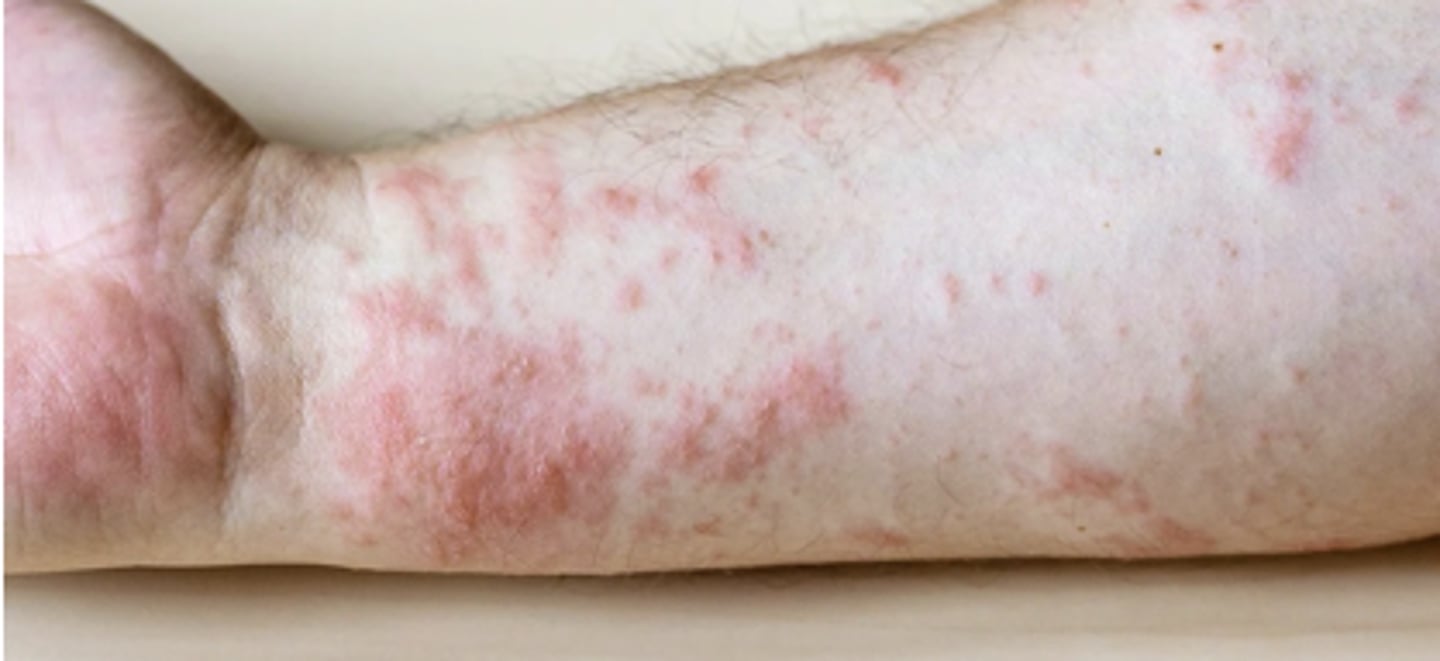
Rash (multiple lesions)
•Appear as blotches, welts, or blisters; they can be red, itchy, scaly, or dry
•Many possible causes that aren't due to an underlying disease (chemicals, animals, scratchy clothes, sun exposure, medications, etc.)
single lesion or wound
•May appear as bumps or patches, or they may be smooth
Many causes (acne, cellulitis, chickenpox, infection, cancer)
Braden or Norton Scale
used to identify risk of skin breakdown.
a scale of 14-18 or less than 14 respectively-indicates high risk of pressure ulcer development
Inspection of the Skin
•General color/pigmentation
•Uniformity of color or widespread color change
•Surface temperature and moisture
•Texture, thickness, edema
(Edema is fluid accumulating in the interstitial spaces. To check for edema, imprint your thumbs firmly for 3 to 4 seconds against the ankle malleolus or the tibia. If it leaves a dent in the skin, edema is present.)
•Mobility and turgor
(Pinch up a large fold of skin on the anterior chest under the clavicle. Mobility is the ease of skin to rise, and turgor is its ability to return to place promptly when released. This reflects the elasticity of the skin.)
•Vascularity or Bruising
•Presence of masses, lesions, trauma
•Hygiene
•If any lesions are present, note the following:
-Color
-Elevation
(flat, raised, or pedunculated)
-Pattern or shape
-Size in cm
(use a ruler to measure)
-Location and Distribution on body
(generalized or localized to the area of irritant)
-Note any exudate (discharge/drainage)
Macule
A flat, distinct, discolored area of the skin that is not elevated; usually less than 1 cm in size. Examples: Freckles and certain birthmarks.
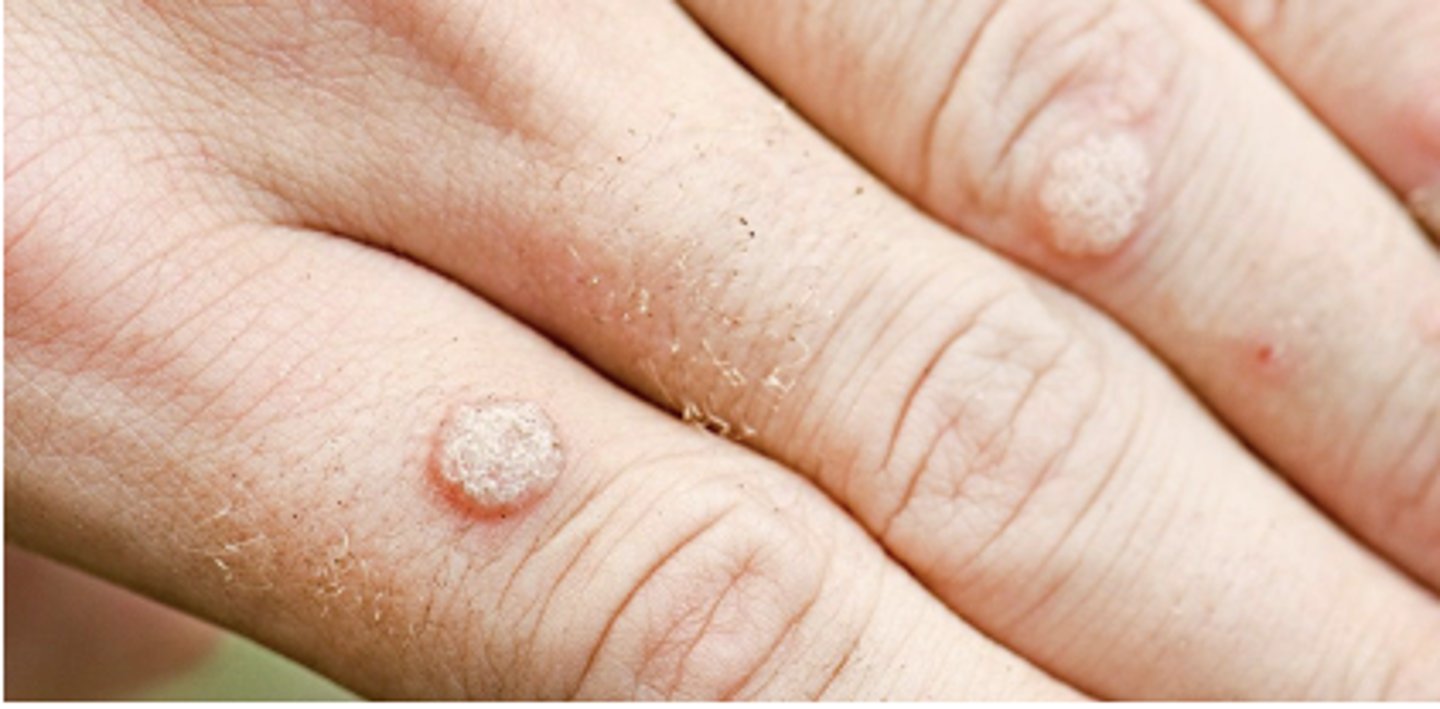
Papule
Something you can feel (i.e., solid, elevated, circumscribed, less than 1 cm diameter) caused by superficial thickening in epidermis. Examples: mole and wart.
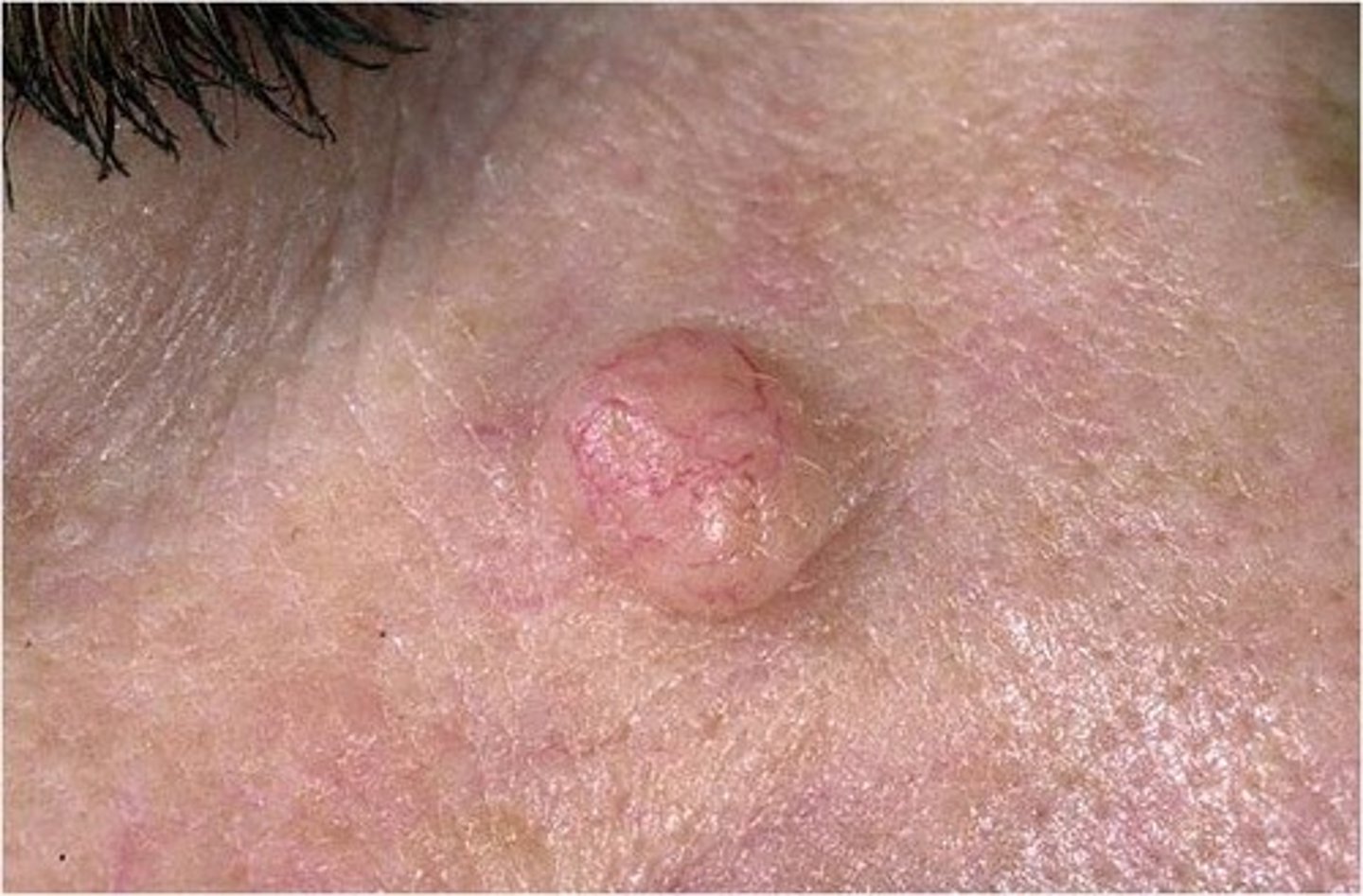
Nodule:
Solid, elevated, hard or soft, larger than 1 cm. May extend deeper into dermis than papule. Examples: xanthoma, fibroma, intradermal nevi.
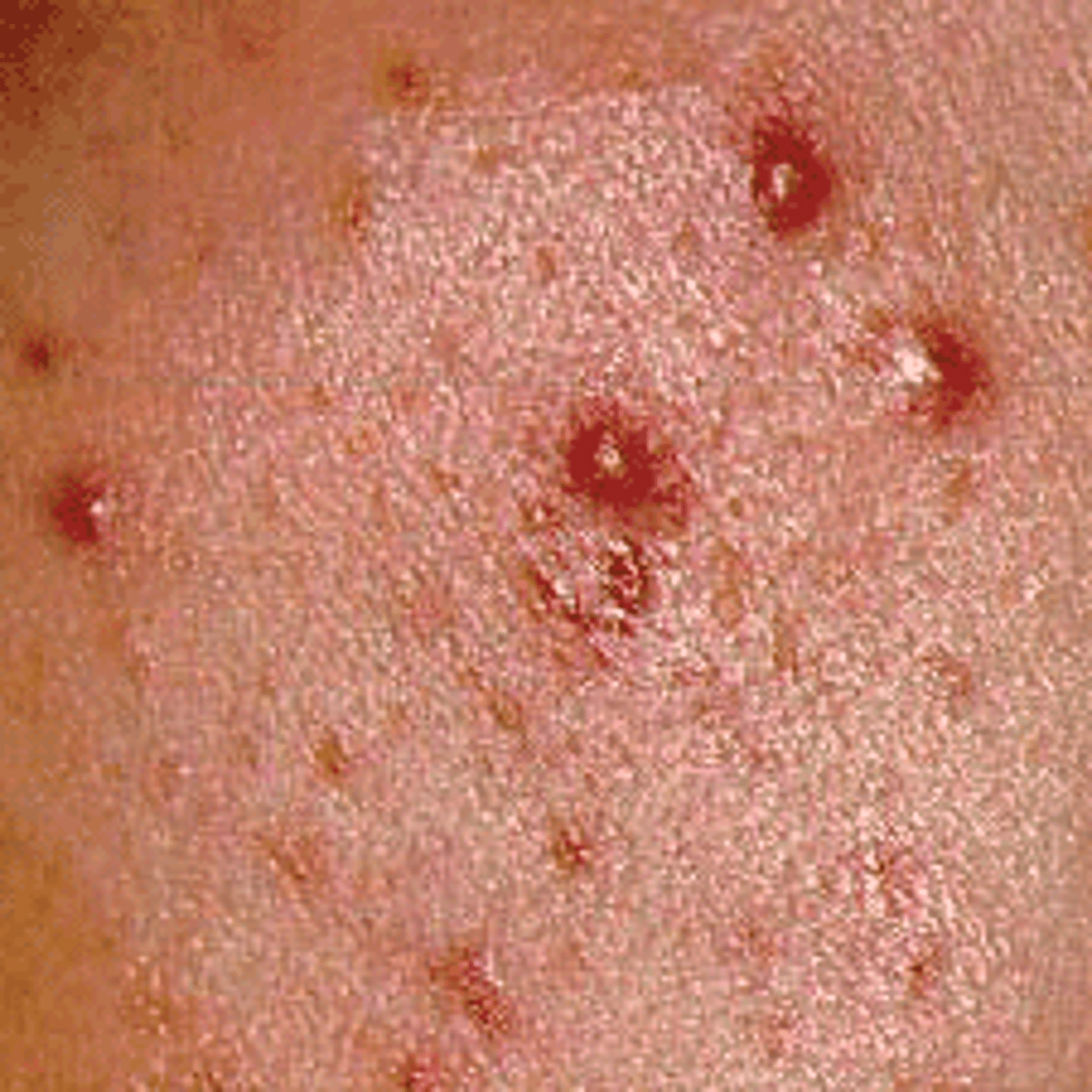
Vesicles
Elevated cavity containing free fluid, up to 1 cm; a "blister." Clear serum flows if wall is ruptured. Examples: herpes simplex, early chickenpox, herpes zoster
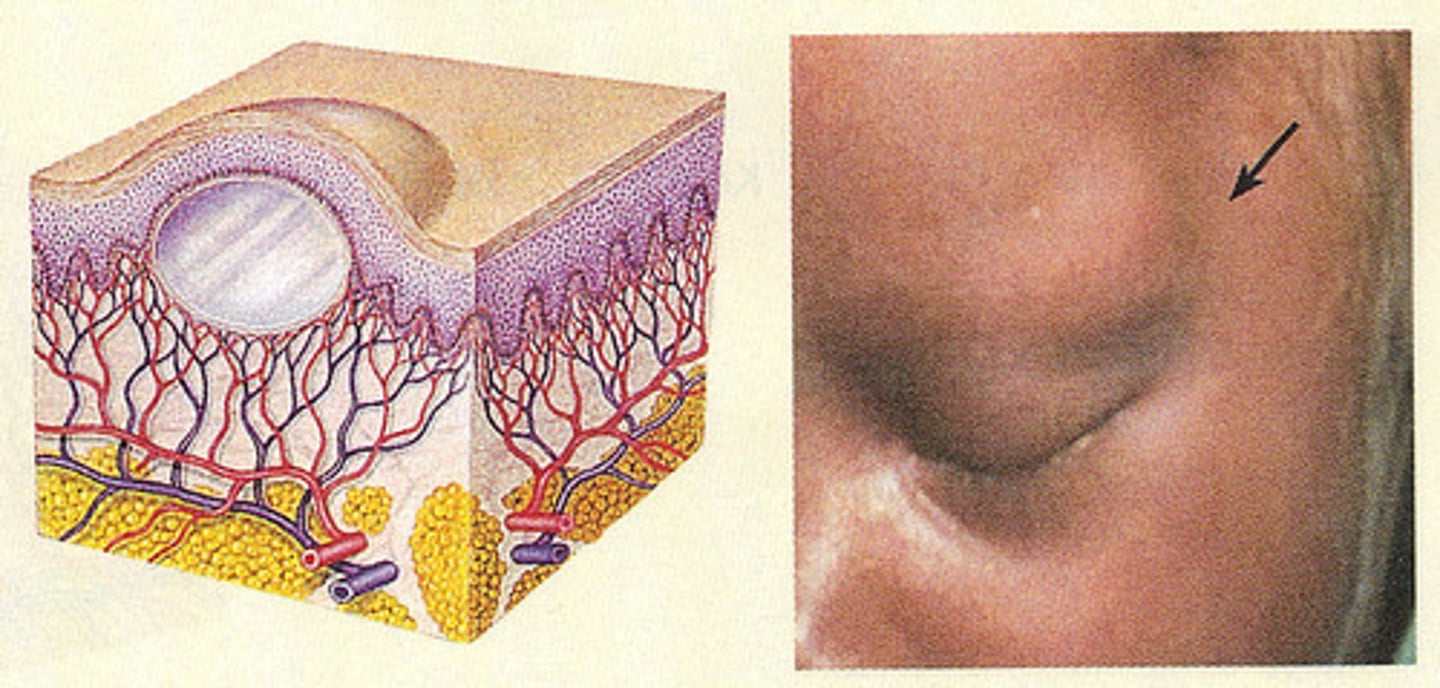
Cysts:
Encapsulated fluid-filled cavity in dermis or subcutaneous layer, tensely elevating skin. Examples: sebaceous cyst, wen.
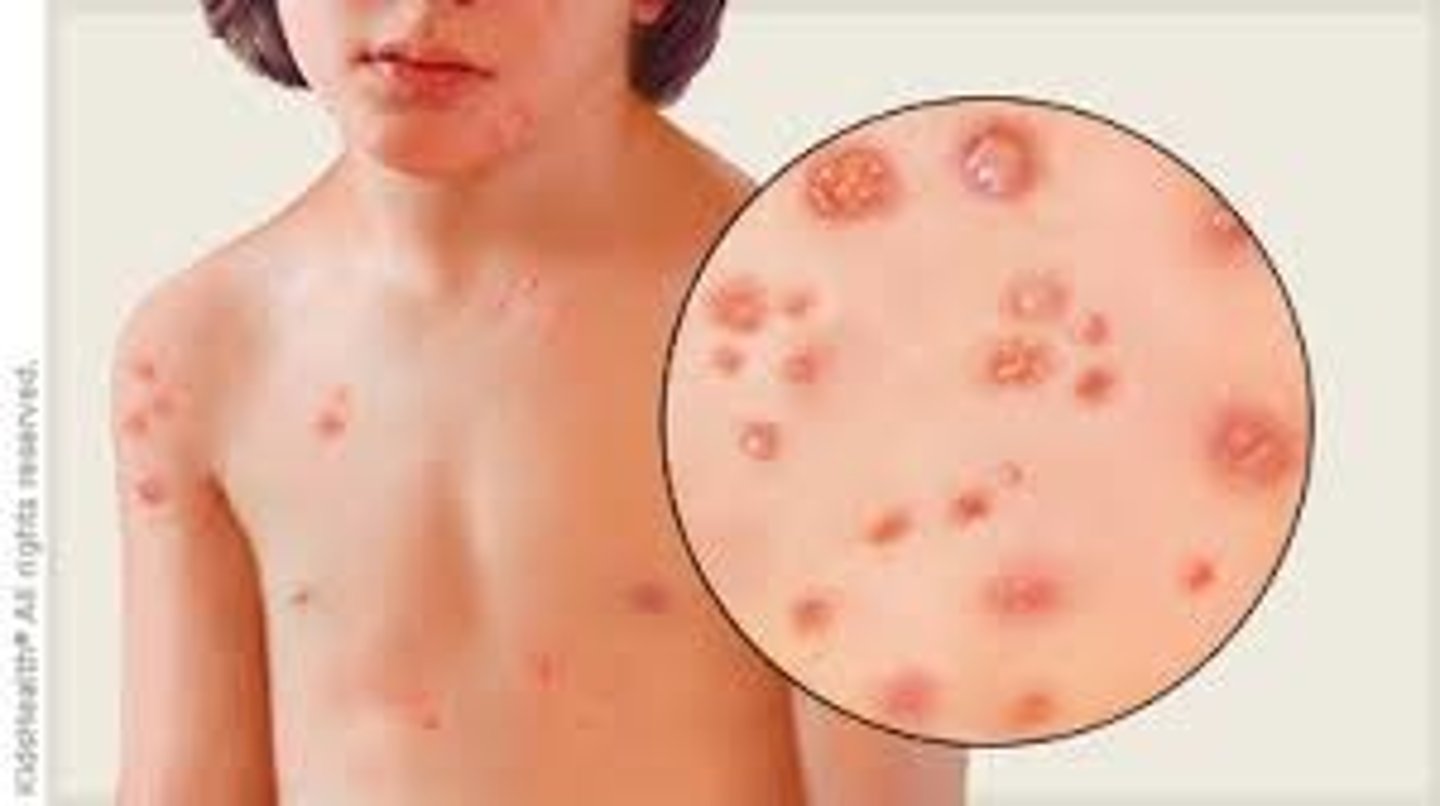
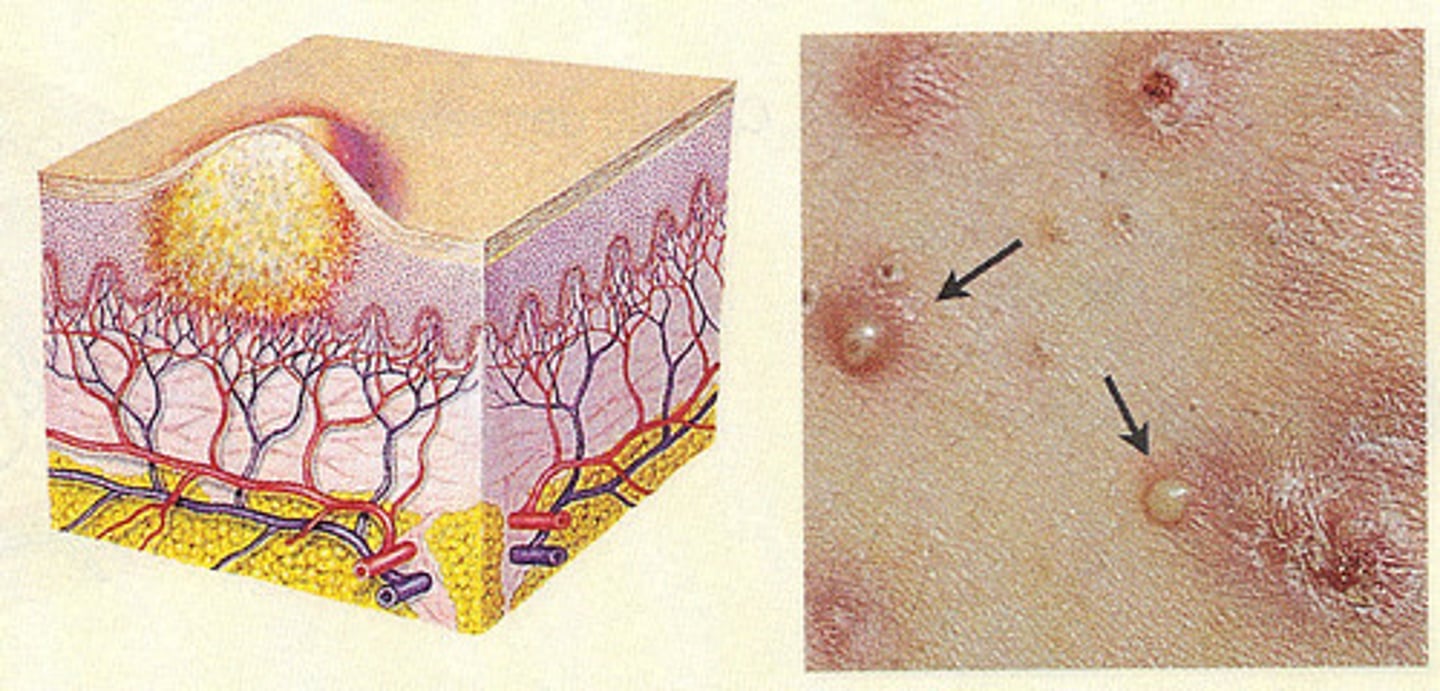
Pustule:
Turbid fluid (pus) in the cavity. Circumscribed and elevated. Examples: impetigo, acne.
Tumors:
Larger than a few centimeters in diameter, firm or soft, deeper into dermis; may be benign or malignant
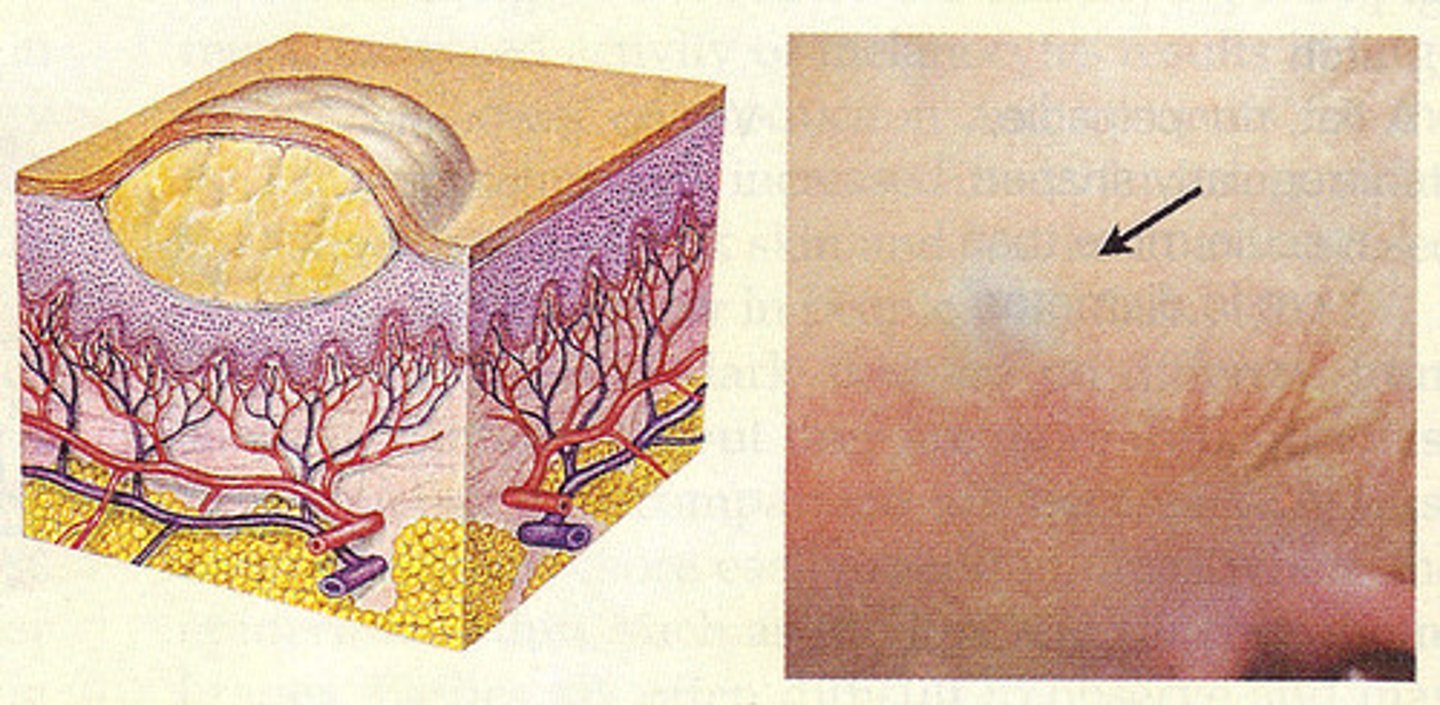
Scales:
Compact, desiccated (dried out) flakes of skin. Examples: drug reaction, psoriasis, eczema, and dry skin.
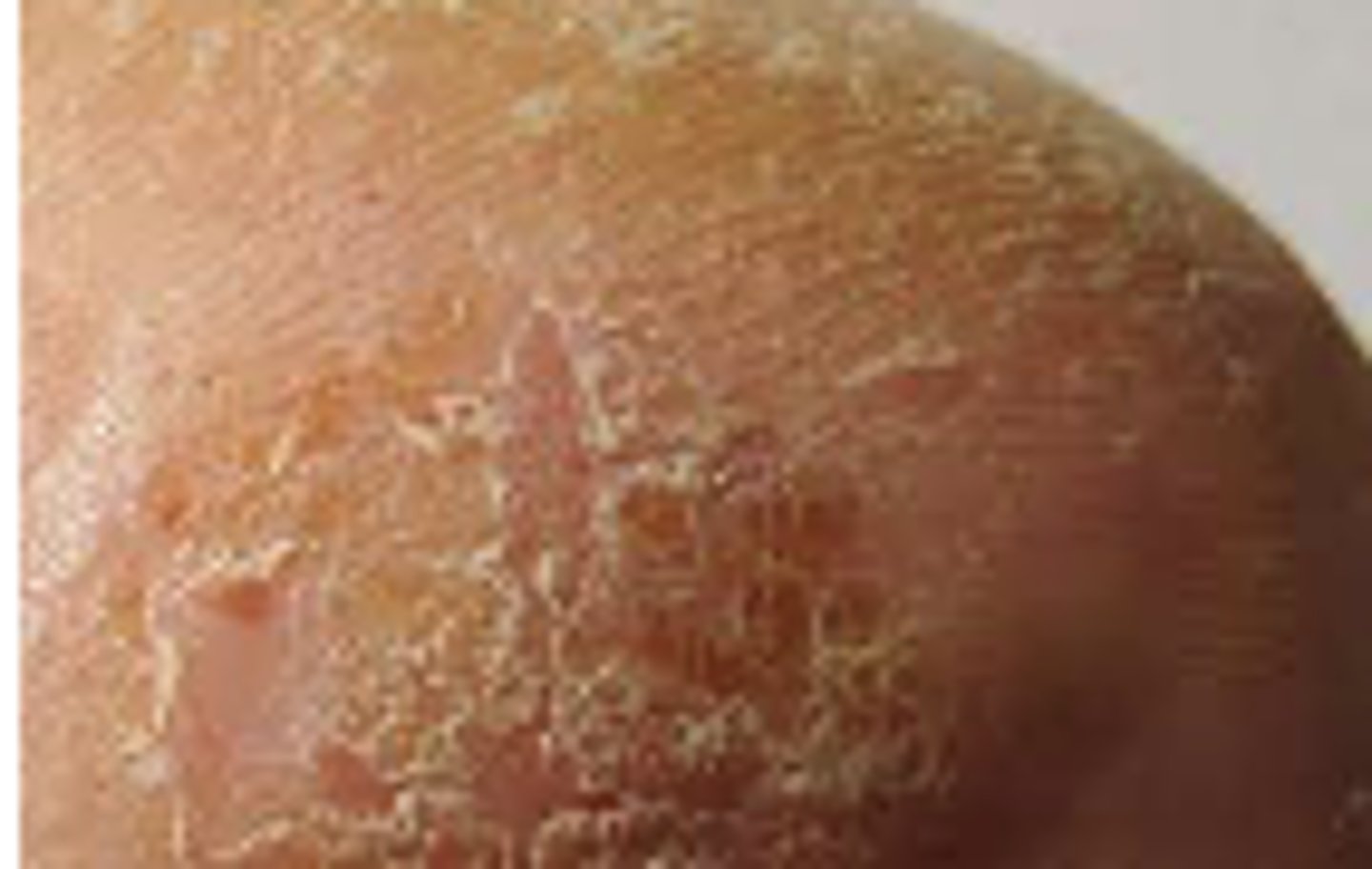
Crusts
The thickened, dried-out exudate left when vesicles/pustules burst or dry up. Examples: impetigo or scab after abrasion.
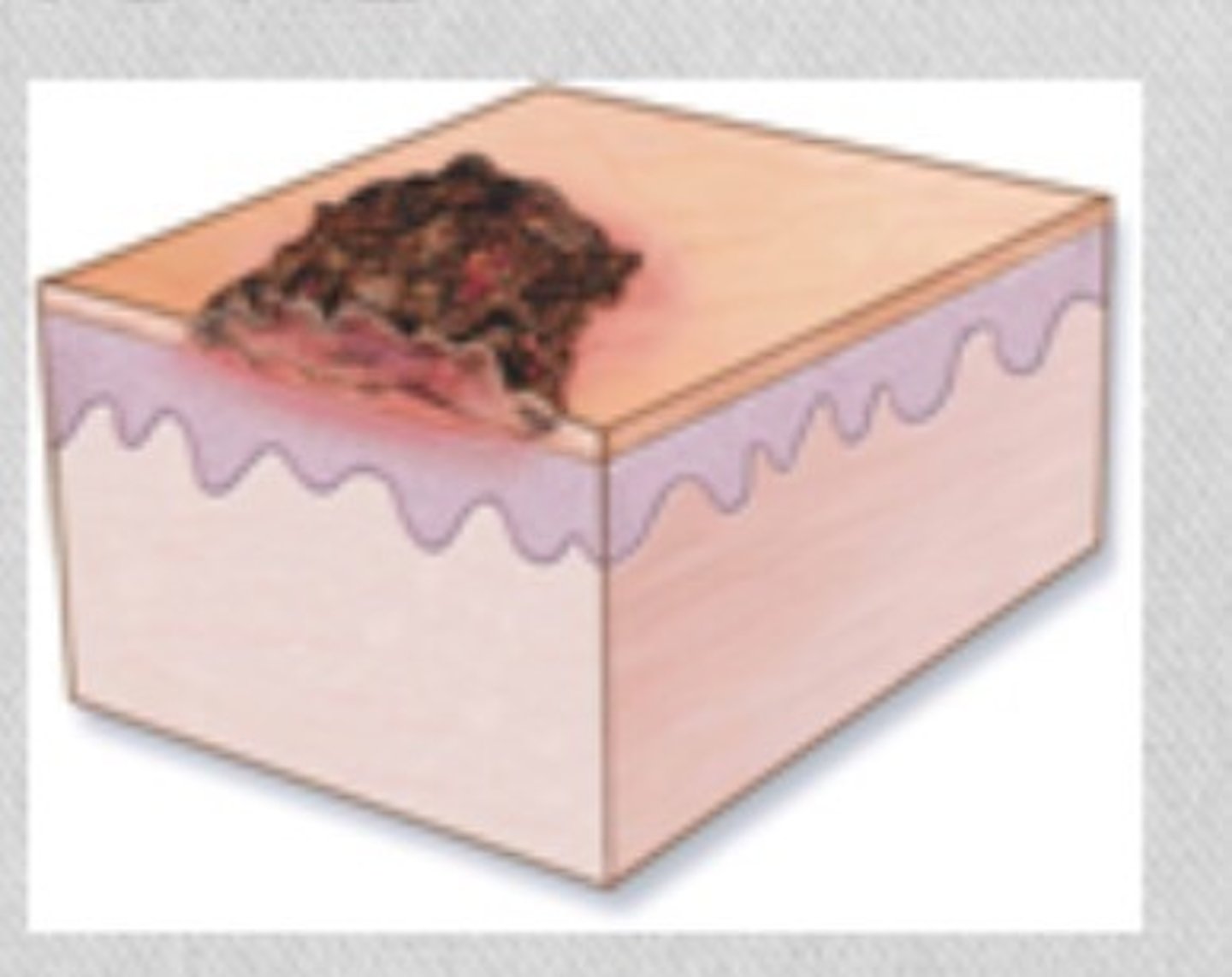
Fissure
Linear crack with abrupt edges; dry or moist. Examples: athlete's foot.
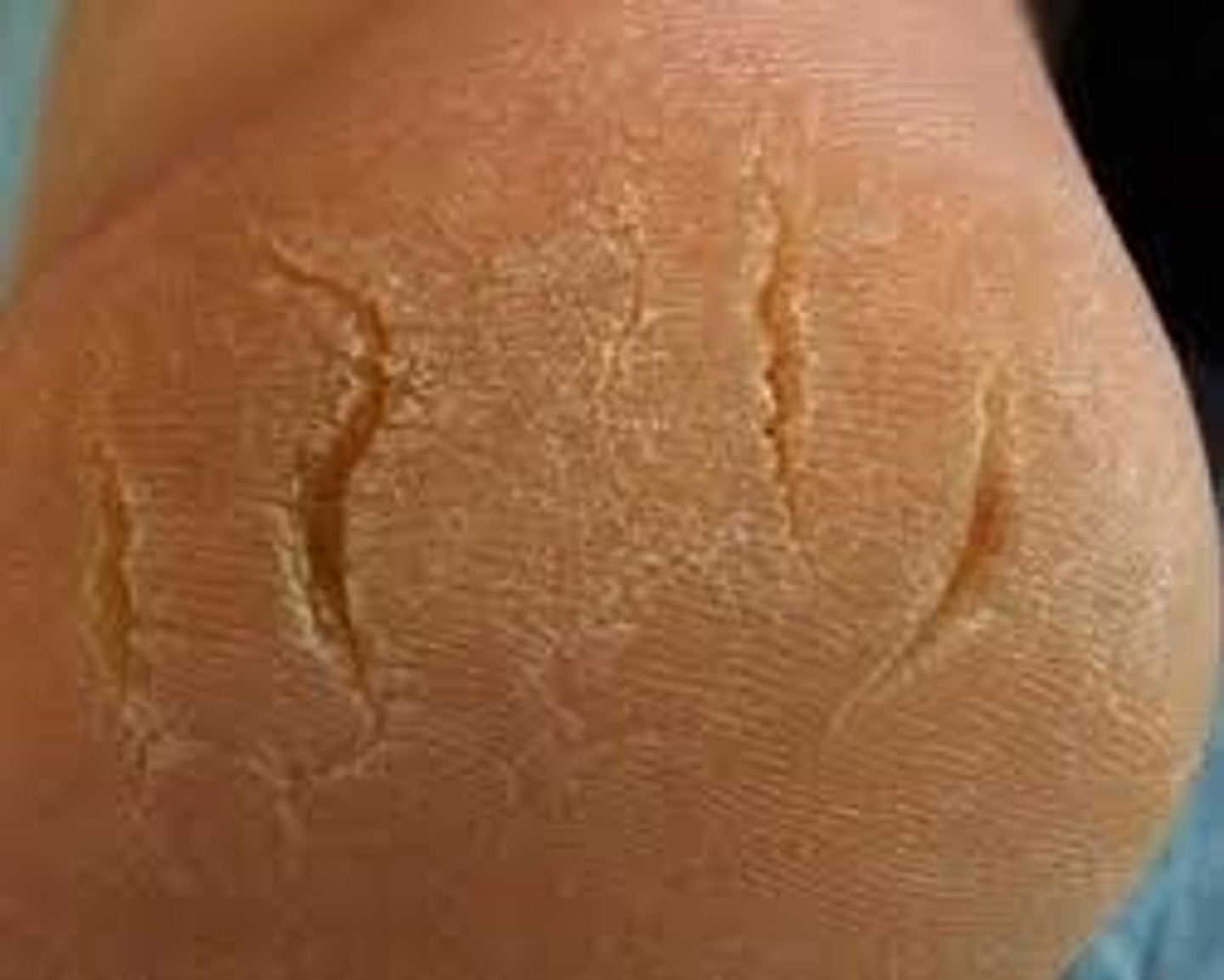
Excoriation
Lesion from scratching or excessive rubbing. Examples: insect bites, scabies, dermatitis, varicella.

Ulcer
Loss of skin surface, extending into dermis, irregular shape; may bleed; leaves scar when heals. Examples: stasis ulcer, pressure injury, chancre.
Scar:
After a skin lesion is repaired, normal tissue is lost and replaced with connective tissue (collagen). Examples: healed area of surgery or injury, acne.
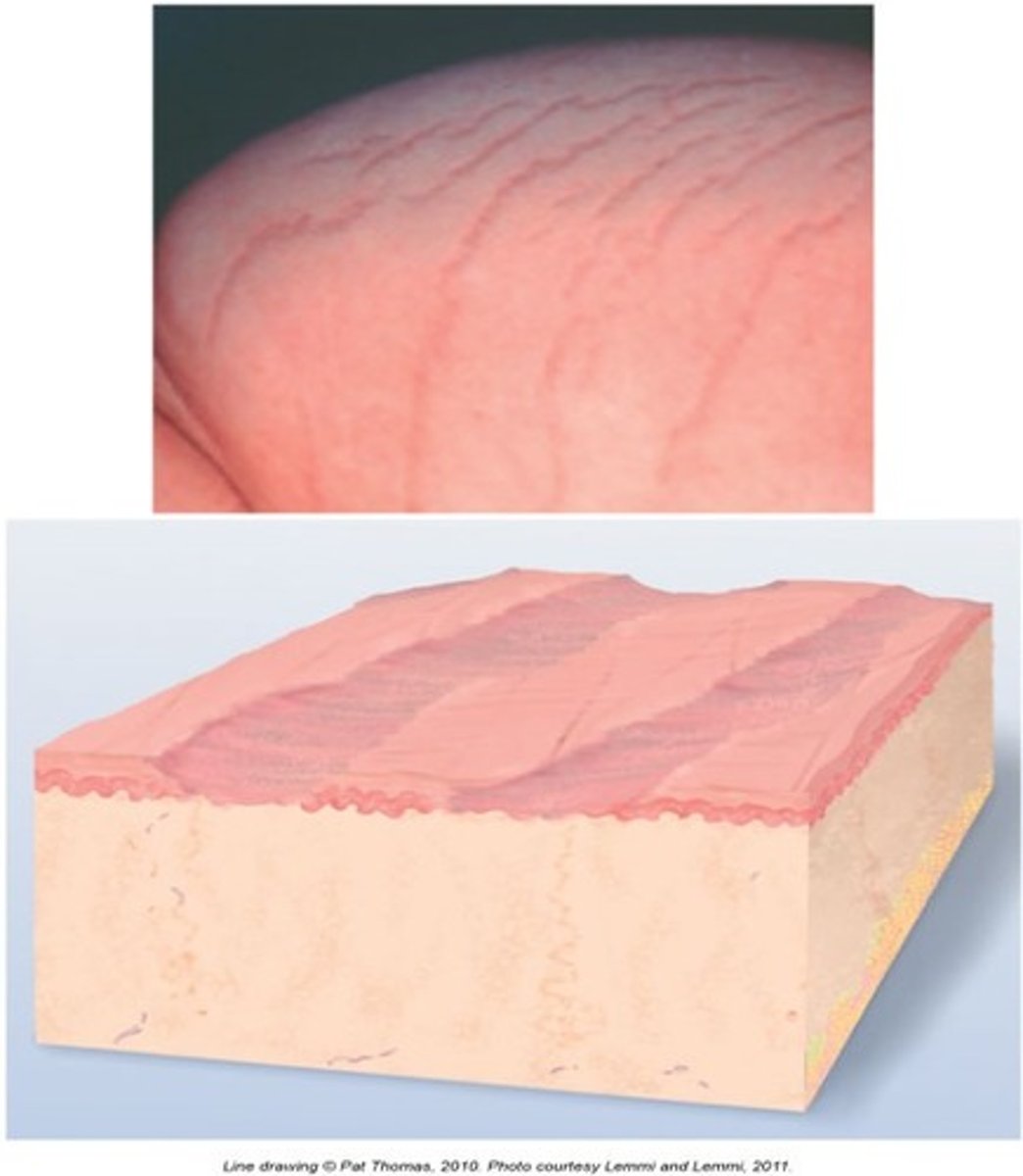
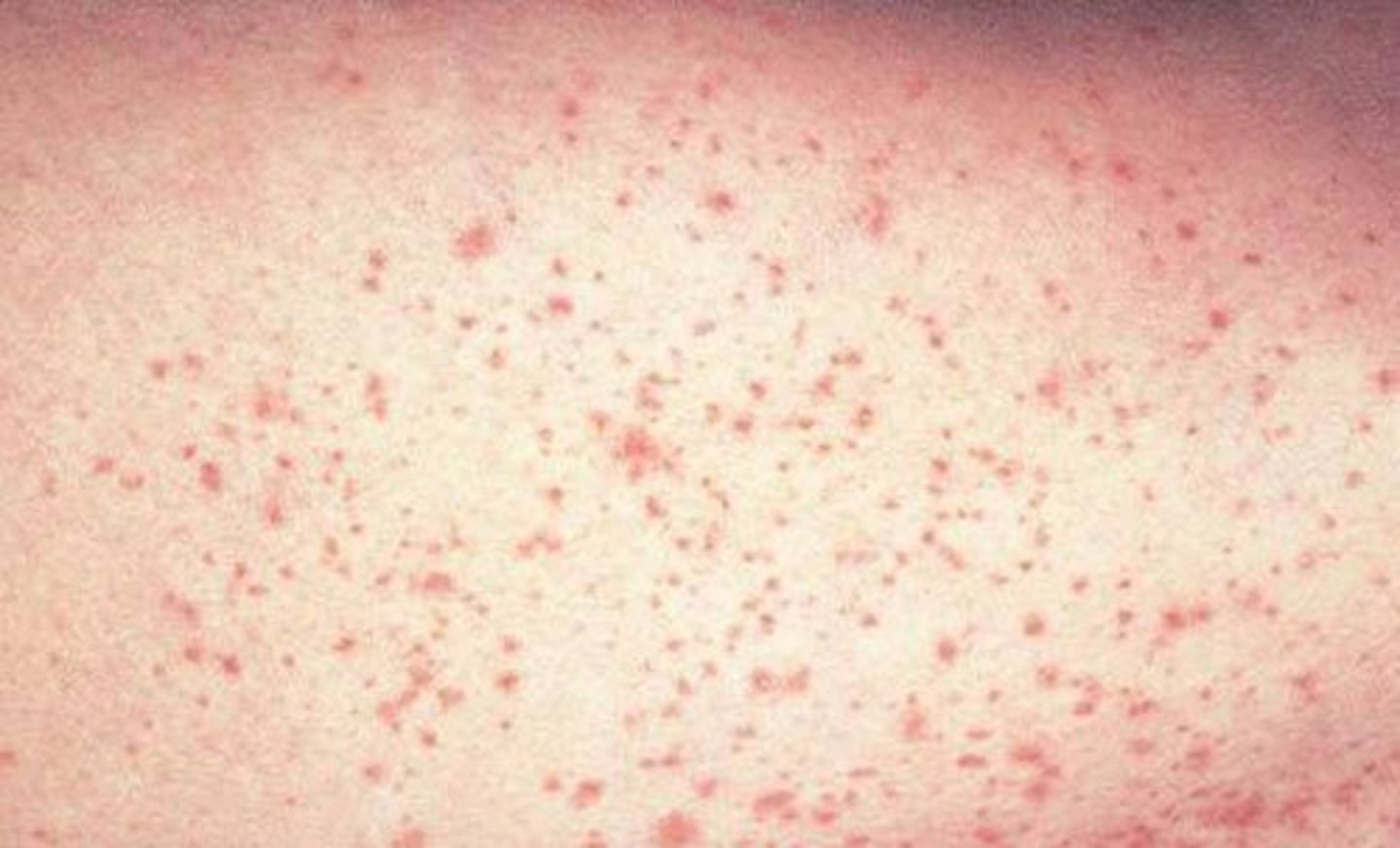
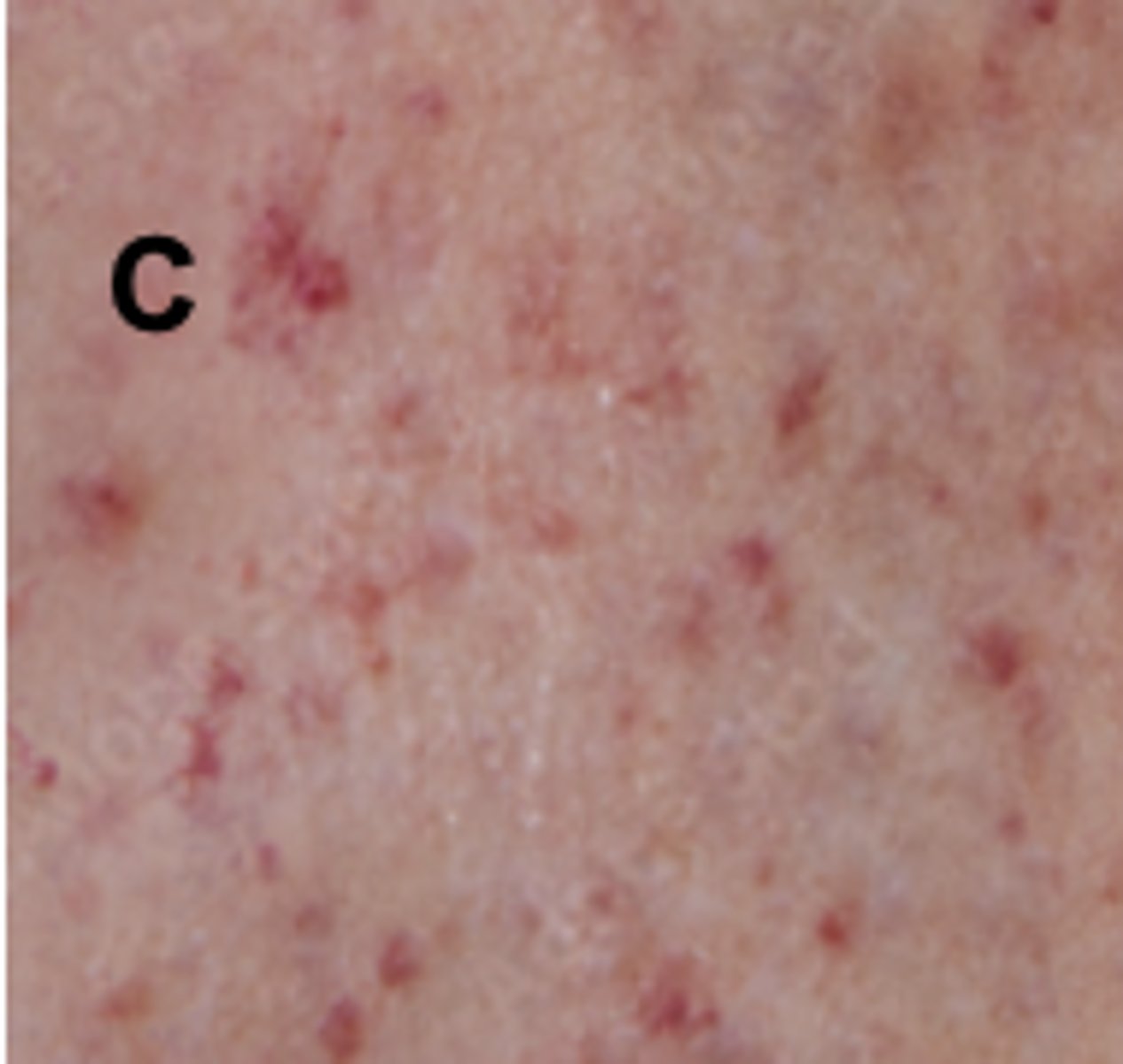
petechiae
Tiny punctate hemorrhages, 1 to 3 mm, round and discrete; dark red, purple, or brown in color. Caused by bleeding from superficial capillaries; will not blanch. Assault injury.
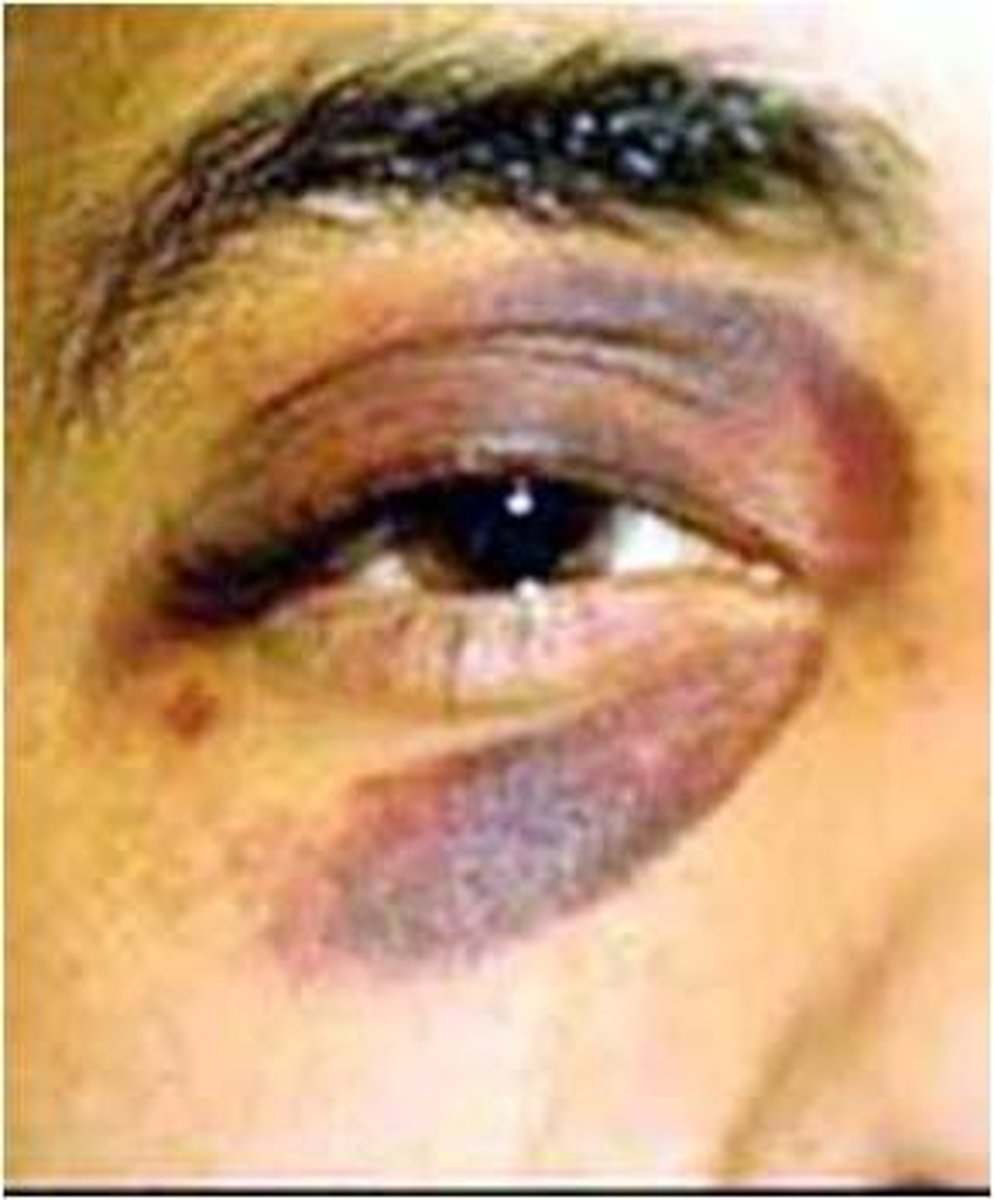
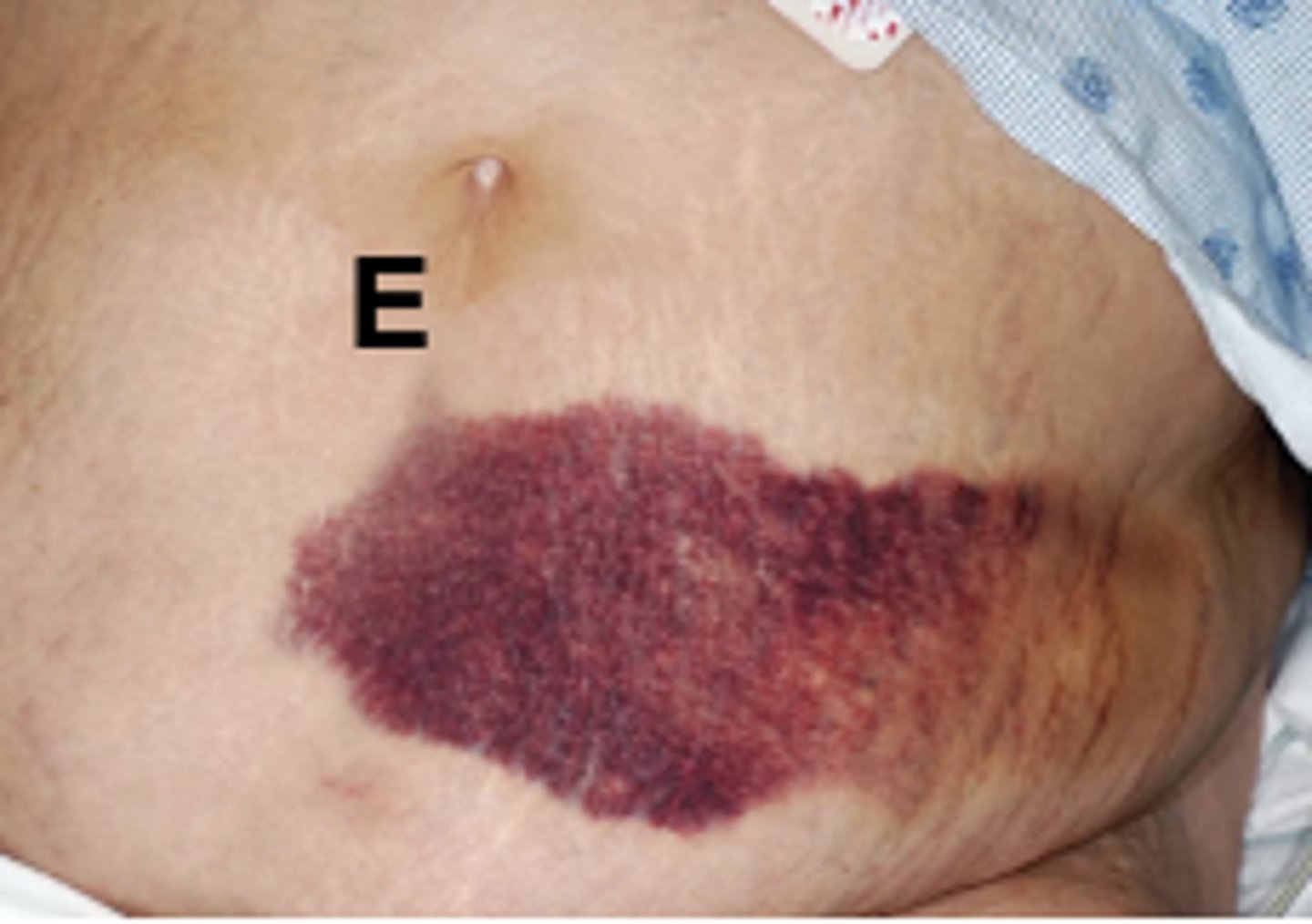
Ecchymosis
A purplish patch resulting from extravasation (blood leaks from vessel) of blood into the skin (ex. black eye), >3 mm in diameter.
-large region on the skin that looks purple because of blood that has leaked out of damaged vessels. the injured blood vessels have moved into the layers of the skin. The causes include injury from bumping yourself or medical conditions like leukemia or hemophilia.
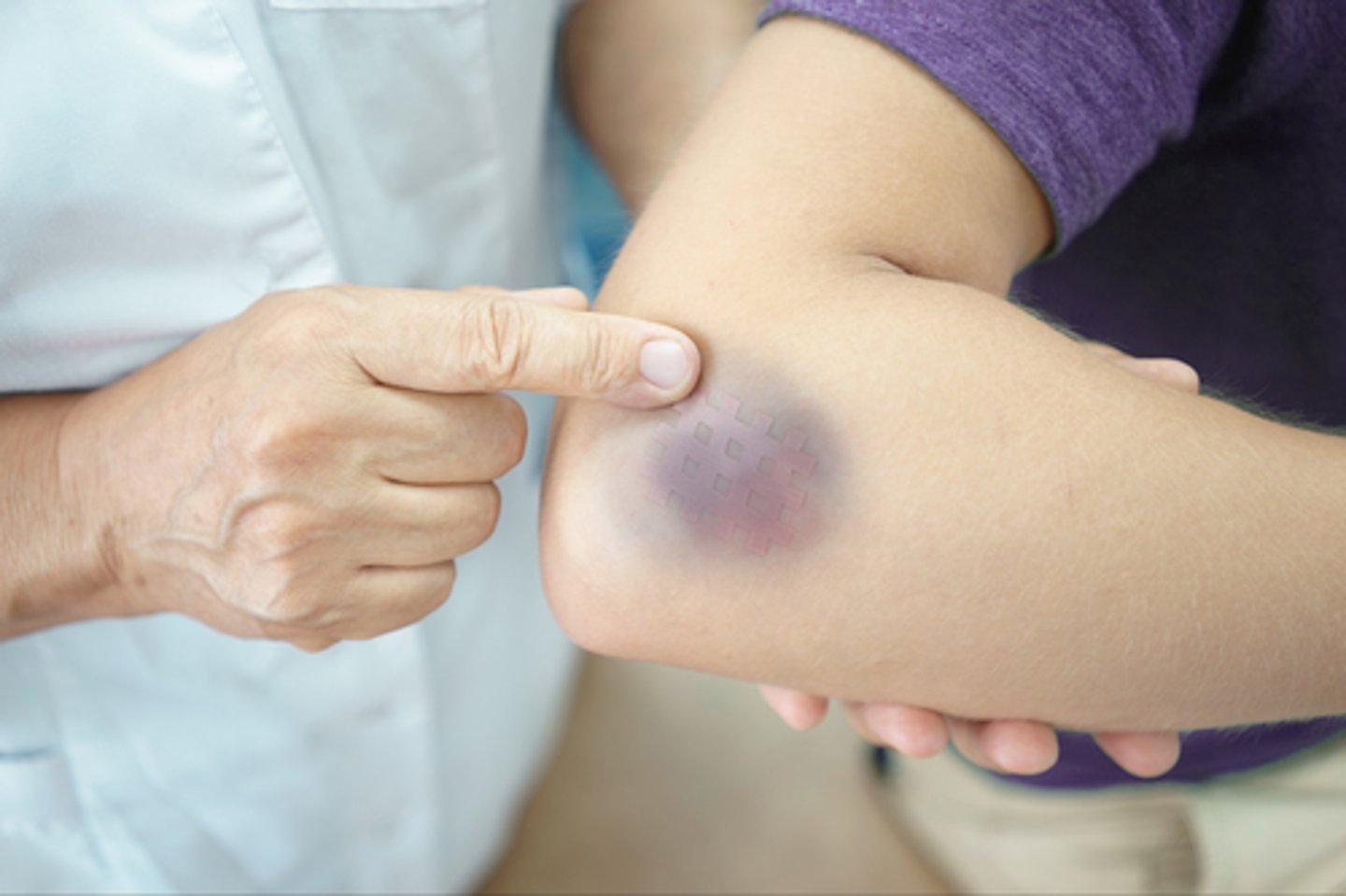
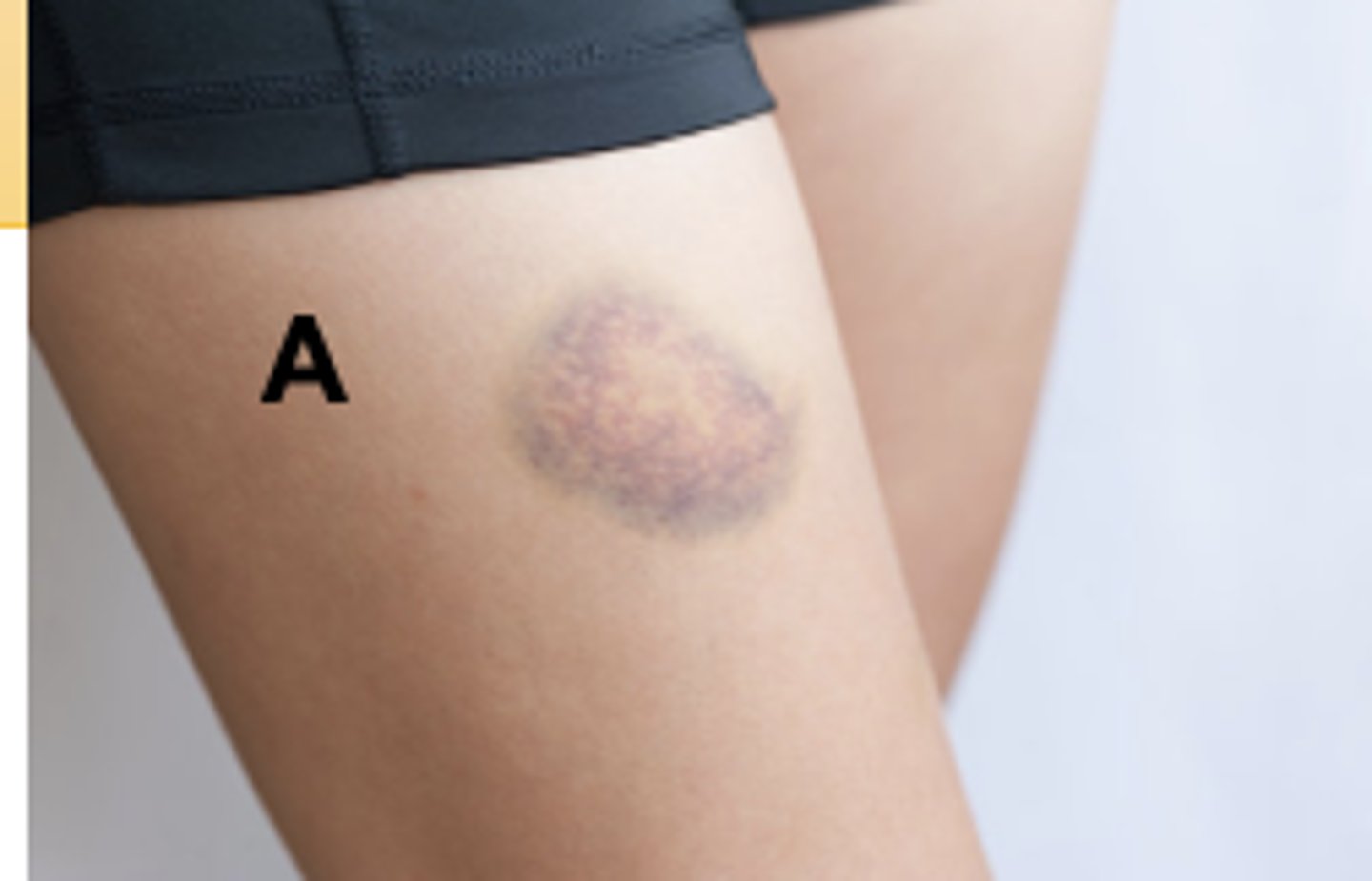
Contusion (Bruise):
A mechanical injury (e.g., a blow) results in hemorrhage into tissues. Skin is intact. Color in a light-skinned person is usually (1) red-blue or purple immediately after or within 24 hours of trauma and generally progresses to (2) blue to purple, (3) blue-green, (4) yellow, and (5) brown to disappearing.
-This is due to blood capillaries being damaged. Some causes include injury due to an accident or playing sports. It is usually the result of some type of blunt impact on the body.
Name the vascular lesion!
Contusion
Name the vascular lesion!
petechiae
Name the vascular lesion!
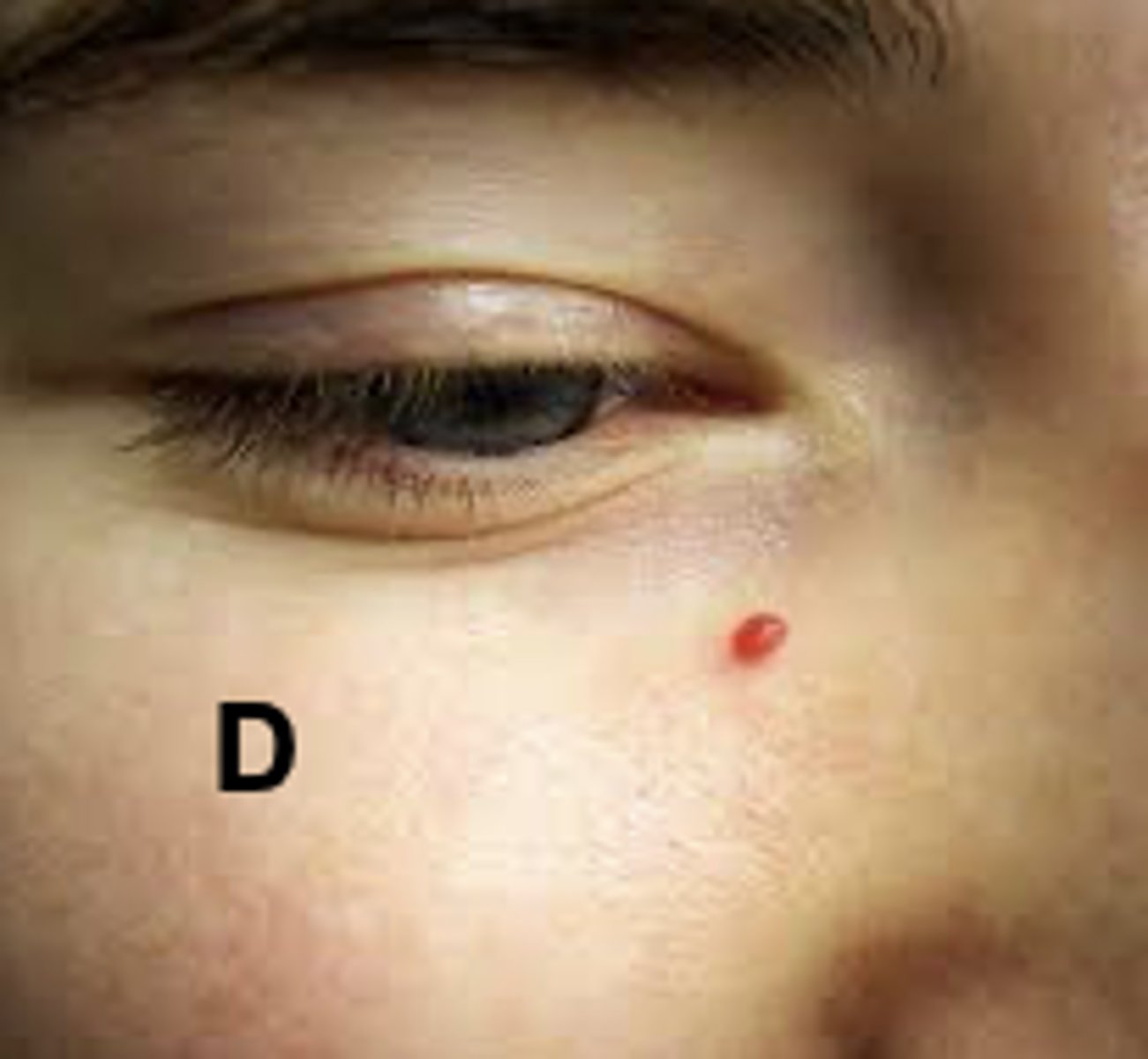
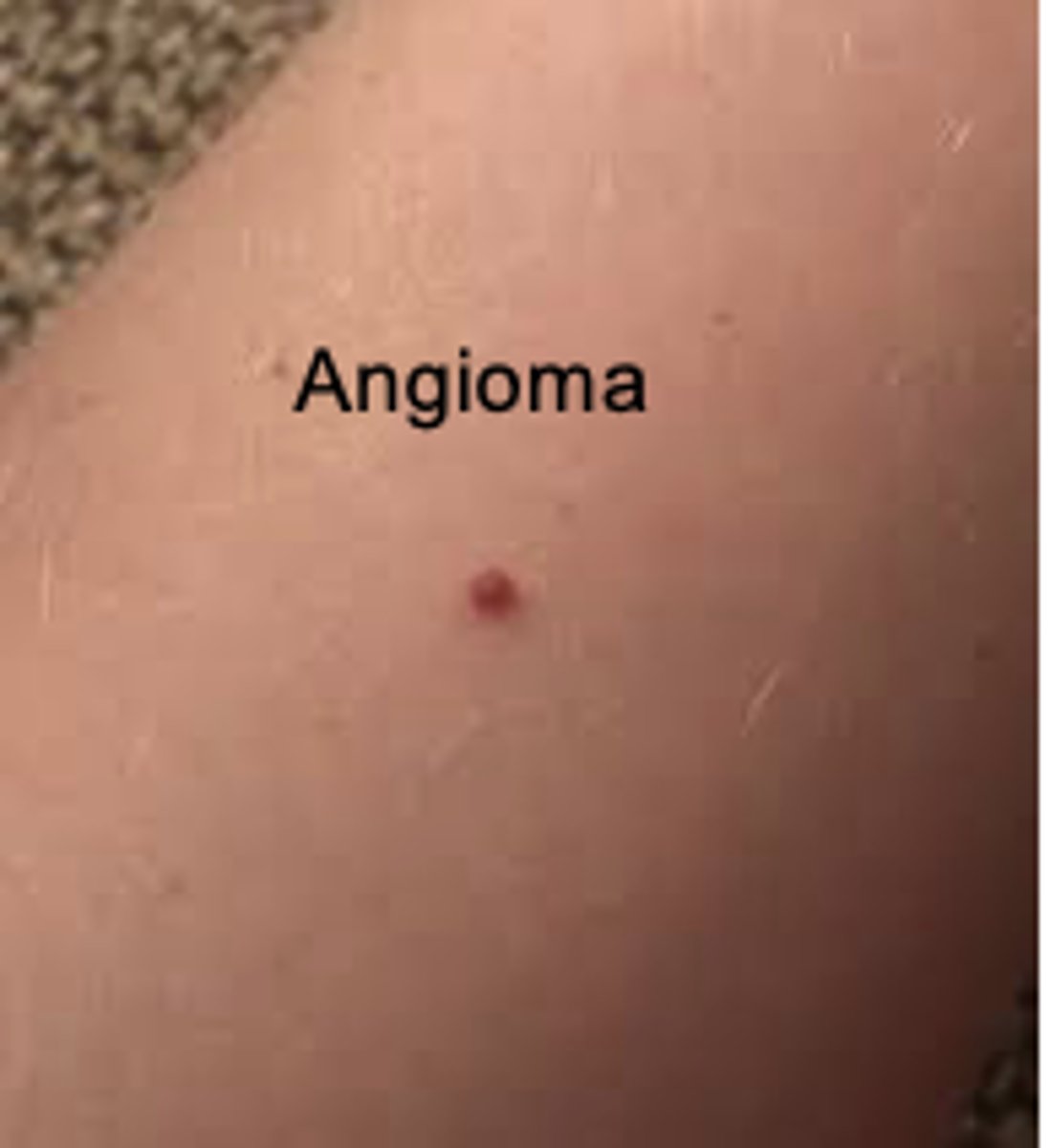
Angioma
Name the vascular lesion!
ECCHYMOSIS
Name the vascular lesion!
VENOUS STAR
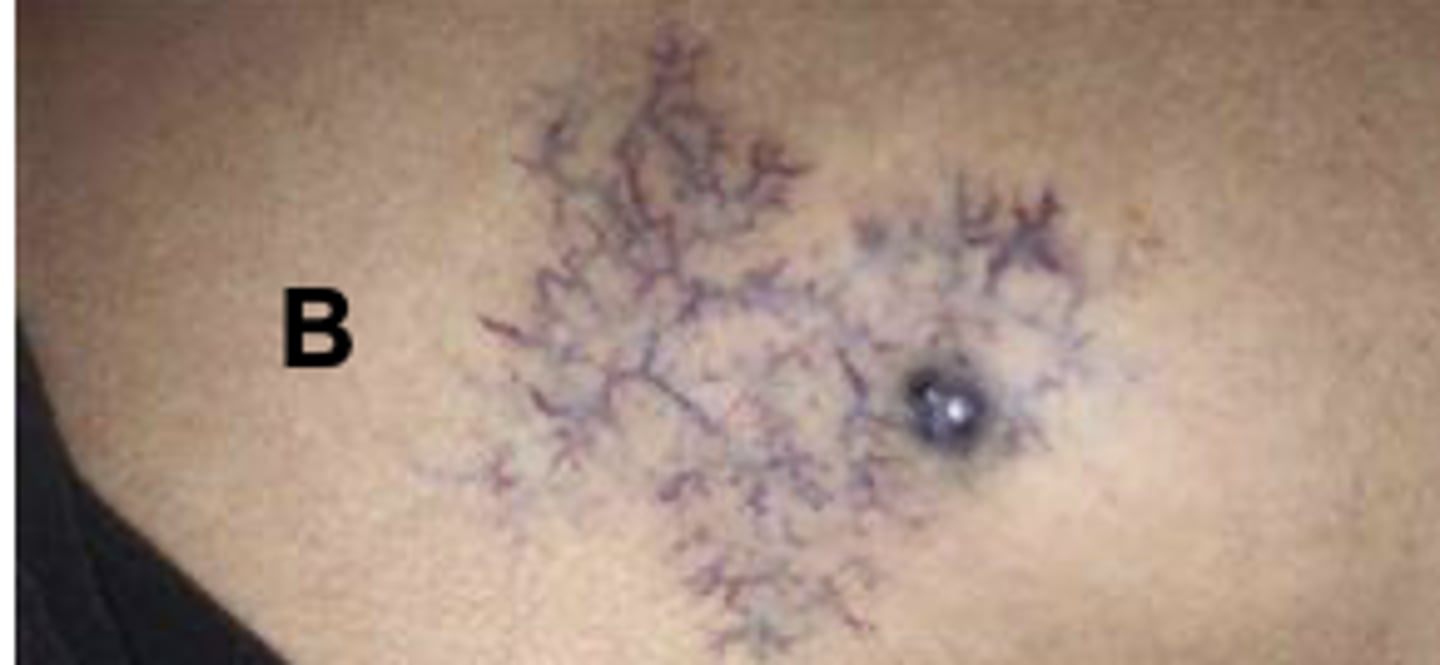
Angiomas
A fiery red, marking with a solid circular center. With pressure, note blanching. Develops on face, neck, or chest.
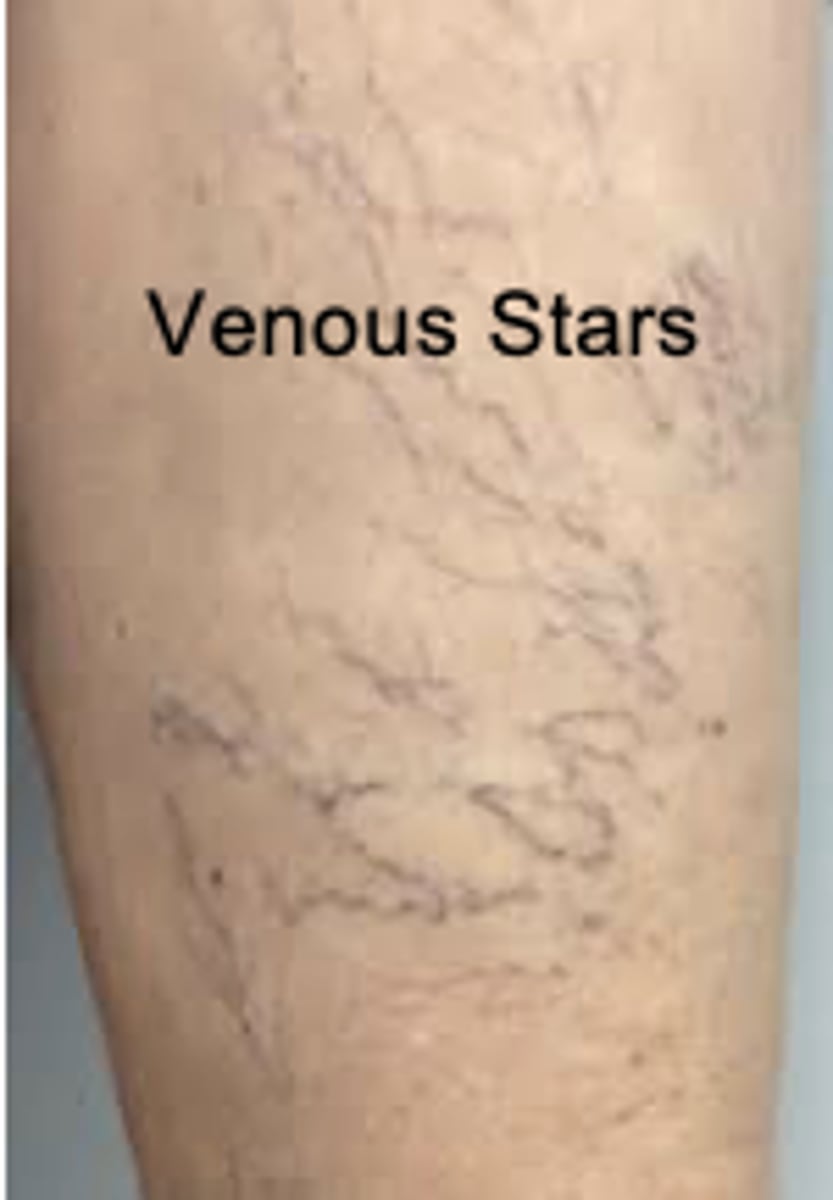
Venous Stars
blue-purple dilation of venules and capillaries in a star-shaped, linear, or flaring pattern. Pressure causes them to empty or disappear. Located on the legs near varicose veins and also on the face, lips, ears, and chest.
Hair color
comes from melanin production and vary
Hair Texture
Scalp hair may be fine or thick and may look straight, curly, or kinky
Hair Distribution
•Fine vellus hair coats the body, whereas coarser terminal hairs grow at the eyebrows, lashes, and scalp
Normal finding for hair assessment
Hair is equally and symmetrically distributed across the scalp. Shafts are smooth, shiny, of even consistency, and without evidence of breakage, lesions, or pest inhabitants.
Normal finding for nail assessment
-Nails smooth, translucent, and consistent in coloration and thickness.
-The nail surface is slightly curved or flat; nail edges are smooth and rounded
-Consistency is smooth and regular, not brittle or splitting
Nail color
•The translucent nail plate is a window to the pink nail bed underneath
Dark-skinned people may have brown-black pigmented areas or linear bands or streaks along the nail edge. All people normally may have white hairline linear markings from trauma or picking at the cuticle called leukonychia.
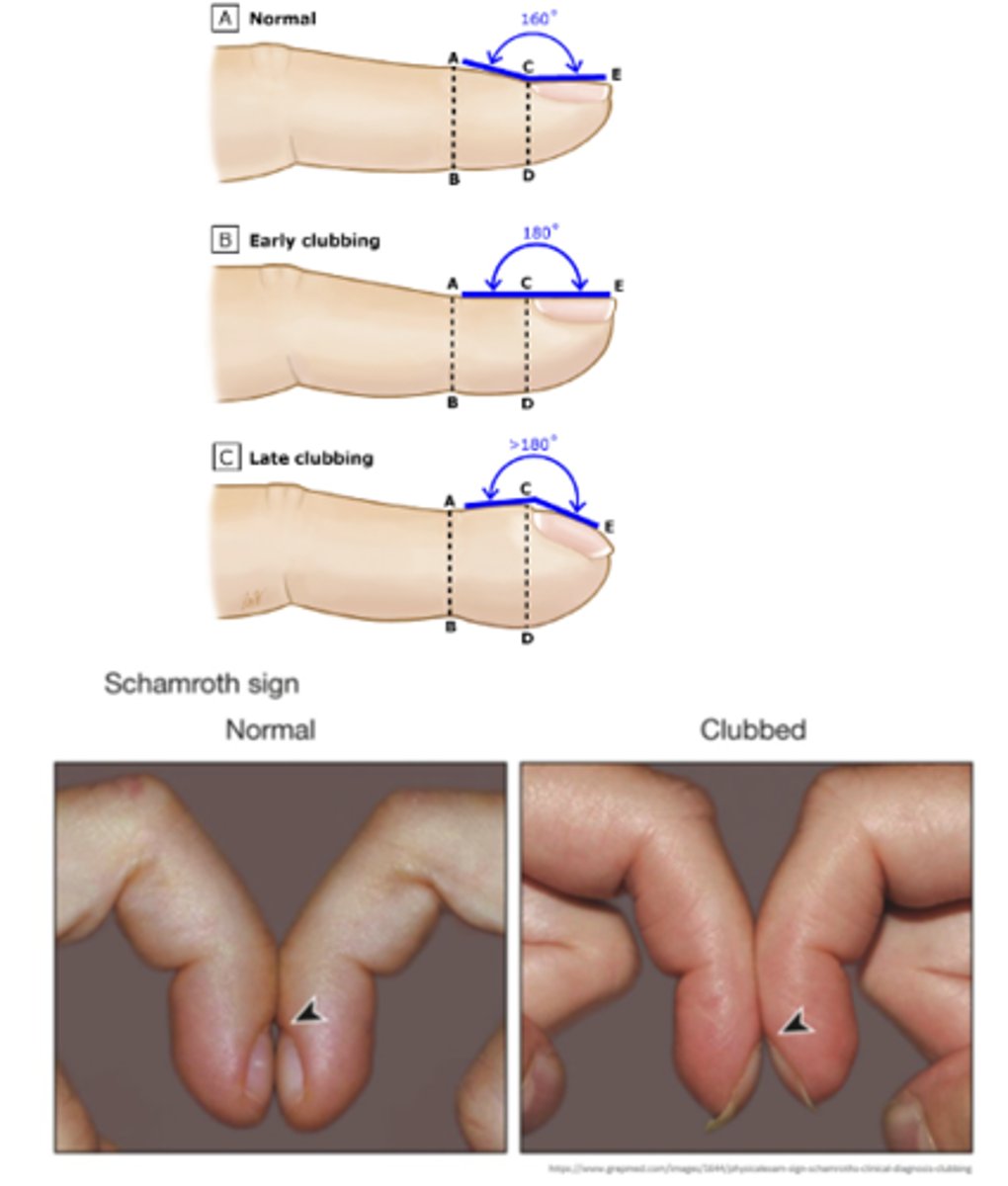
Clubbing
-abnormal curving of the nails that is often accompanied by enlargement of the fingertips
-occurs with congenital cyanotic heart disease, lung cancer, and pulmonary diseases (abnormal finding).
angle straightens out to 180 degrees, and the nail base feels spongy to palpation (abnormal finding).
hair skin and nails
hair skin and nails
hair skin and nails
hair skin and