Lecture 12 - Standing Waves
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are standing waves
waves formed due to superposition of two waves of same A-amplitude, f-frequency and wavelength travelling in opposite directions in the same medium
why are standing waves called standing waves
doesn’t appear to be travelling, the cord appears to have segments that oscillate up and down in a fixed position
stand waves can occur in….
strings = transverse waves
air columns = longitudinal waves
frequency of harmonics: string fixed at both ends
fn = n(v/2L) where n = 1, 2, 3…
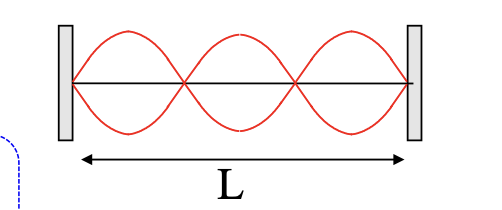
speed of wave on string
v = root(F/(m/L))
standing waves in air columns: types
open pipes = flute
closed pipes = clarinet
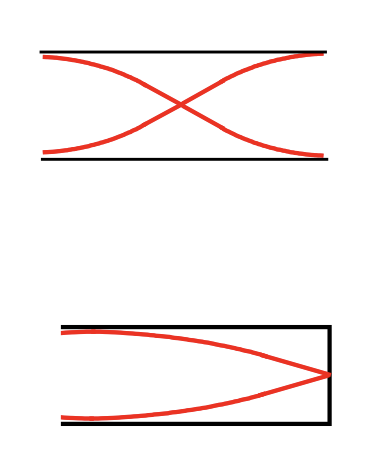
harmonics for flutes
fn = nf1 where n = 1, 2, 3…
closed pipes (clarinets) only produce … harmonics
odd
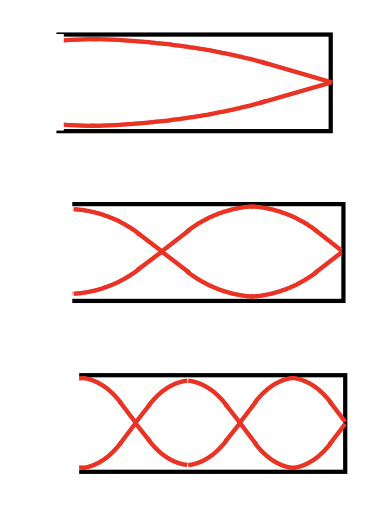
the shorter the length of a clarinet the … the frequency
higher
interference of waves: what are they and types
superposition of two travelling waves in the same medium
constructive = waves are in phase
restructure = when waves are out of phase
beats - interference in time
when two sound waves of slightly different frequencies f1 and f2 superimpose the loudness of the resulting sound rises and falls periodically = beats
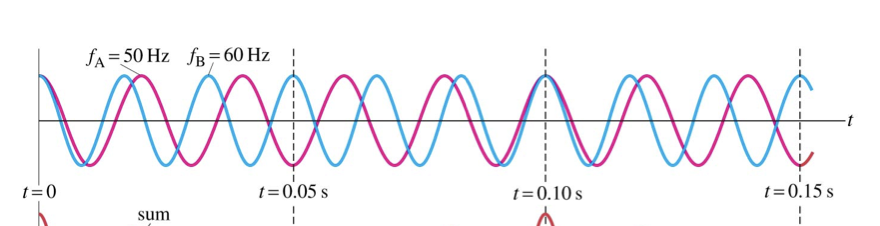
2 successive overtones of vibrating string are 280 Hz and 350 Hz, frequency of fundamental?
f2 - f1 = 350 - 280 = 70 Hz