TV4101 - Bovine - Semen Eval
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Macroscopic evaluation inc?
• Volume
• Colour
• Consistency
• Smell
• pH
Microscopic evaluation inc?
• Mass activity
• Individual motility
• Morphology
• Foreign cells (eg. neutrophils)* (This test isn’t recognised in the BULLCHECK system)
Macro eval - Consistency
Scale, volume and approx conc?
0 Clear 0
1 Cloudy <200
2 Milky 200-500
3 Thick milky 500-1000
4 Creamy 1000 – 1500
5 Thick creamy 1500+
Macro eval - pH?
normal pH of bull semen 6.2 – 7.4, falls over time due to build-up of lactic acid
Micro eval - Mass activity?
How to observe?
• Small drop of semen on a prewarmed slide (no coverslip)
• Usually reserved for ruminant semen (highly concentrated)
Micro eval - Mass activity
Mass activity is a function of?
Describe this?
concentration AND motility
Good mass activity may be seen with highly concentrated semen moderate motility.
Similarly, mass activity may be poor due to low concentration despite excellent motility.
Micro eval - Mass activity scores (BULLCHECKTM)
Scale and description?
0 No swirl; generalised oscillation of individual sperm only
1 Very slow swirl
2 Slow swirl
3 Moderate swirl
4 Fast swirl
5 Very fast swirl. Fast distinct swirl with continuous dark waves
(score infrequent in bull semen but common in ram semen)
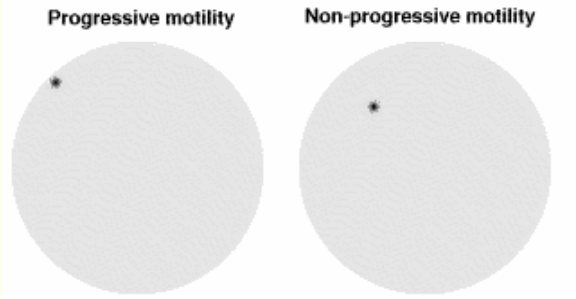
Micro eval - Individual Motility
Measurement of?
• Movement of individual sperm
• Total motility: % of sperm cells moving in any direction
• Progressive motility: % of sperm cells moving progressively across the field of view (moving actively forward)
• Speed of movement: some assessors assess speed of individual sperm movement
Micro eval - Individual Motility
Sample prep
Steps?
Dilution required esp for rums (use any sterile isotonic solution like Phosphate buffered saline, sodium citrate, triladyl
Avoid cold and osmotic shock when diluting
Dilute to extent that you can visualise individual sperm
Place a drop of diluted semen on a pre-warmed microscope slide, use coverslip
Small drop + large cover slip may help to visualise individual sperm
Alternative method: Dip wooden applicator in semen, shake and dip in dilutent
Micro eval - Individual Motility
Estimating individual (progressive) motility
How?
If low?
Subjective (but we should be within around 10 to 20% of each other)
Assess different parts of the slide (dead sperm tend to float
outwards toward the edge)
If low – check handling technique, media, insufficient fluid under cover slip, repeat collection either immediately or in a few weeks time
Micro eval - Morphology
Measures what?
Semen prep?
% of normal vs abnormal appearing spermatozoa within an ejaculate
Semen must be immotile for this assessment
• Preserve in glutaraldehyde (instantly kills sperm) or mix with stain (e.g. eosin-nigrosin)
Micro eval - Morphology
Methods of exam?
• Wet preparations – drop of semen (preserved in glutaraldehyde) on a slide with cover slip
• Use phase contrast or DIC microscope
Eosin-nigrosin stain – mix small drop semen with large drop
stain, place small drop on new slide close to frosted edge, draw stain along slide as for a blood smear
• Examine under bright field
• Alternative stains are available

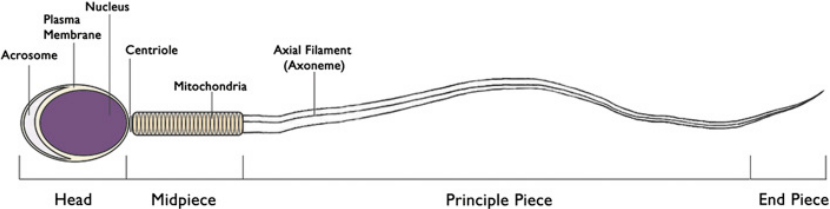
Normal structure of a spermatozoan
IDK if we need all these
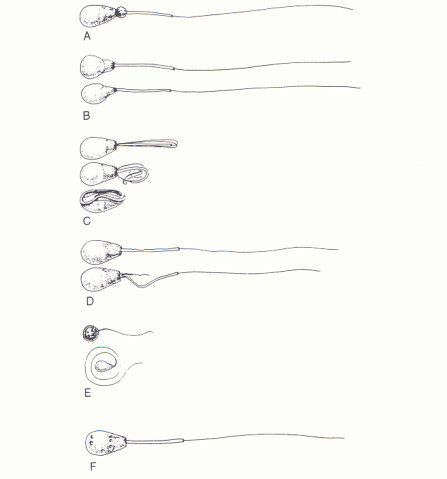
Examples of abnormal morphology: major defects
Which is which?
A - Proximal cytoplasmic droplets
B - Pyriform heads
C- Strongly folded or coiled tails, tails coiled around head
D - Middle-piece defects
E - Maldeveloped
F - Craters
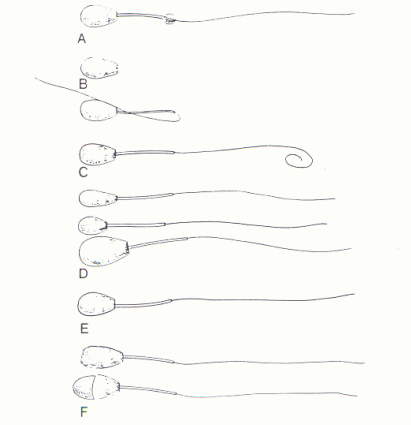
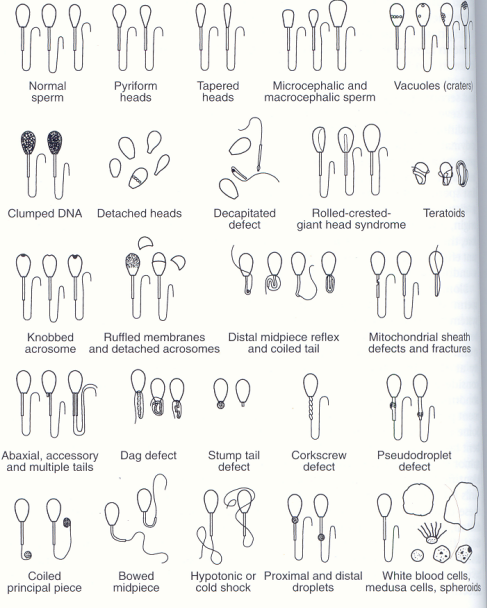
Examples of abnormal morphology: minor defects
Which is which?
A - Distal cytoplasmic droplets
B - Tailess normal heads
C - Simple bend or terminally coiled tails
D - Narrow, small or giant heads
E - Abaxial implantation
F - Abnormal acrosomes (Ruffled, detached)
What this?
Detached heads
What this?
Pyriform head Abnormal if obvious pear shape

What this?
Nuclear craters
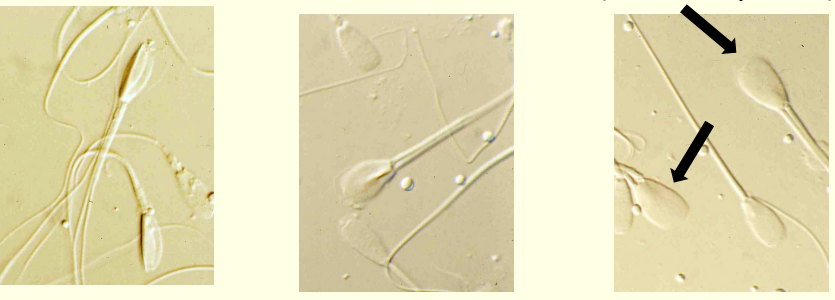
What is each?
Left -rolled head
Middle - nuclear crest
Right - Giant head (macrocephalic)
What this?
Stump tail defect
What this? Descibe it
Dag defect
The tail and midpiece are tightly coiled
What this?
Teratoid spermatozoa (Severely deformed sperm cell)
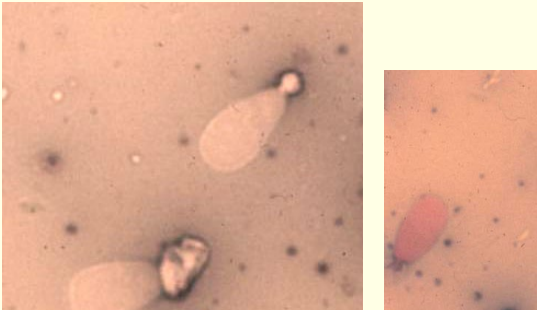
This?
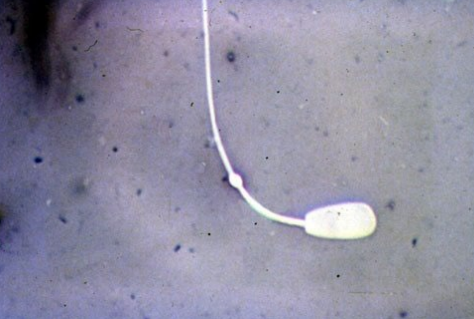
Proximal cytoplasmic droplet
This?
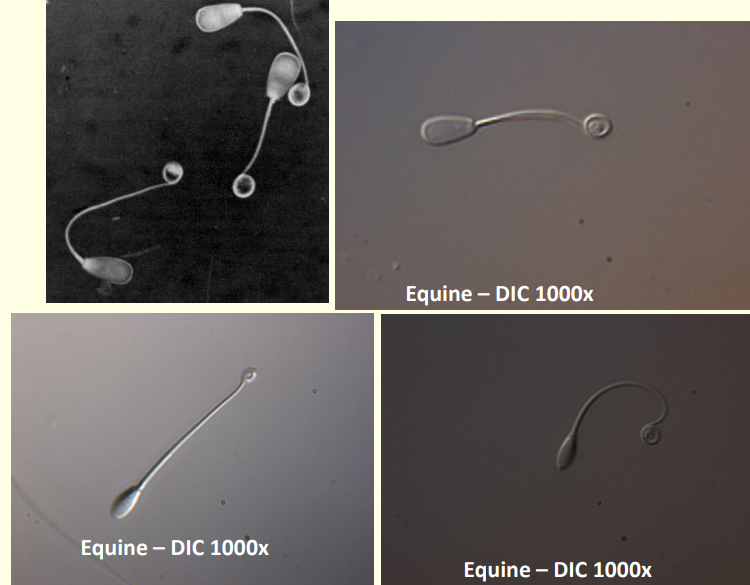
Distal cytoplasmic droplet
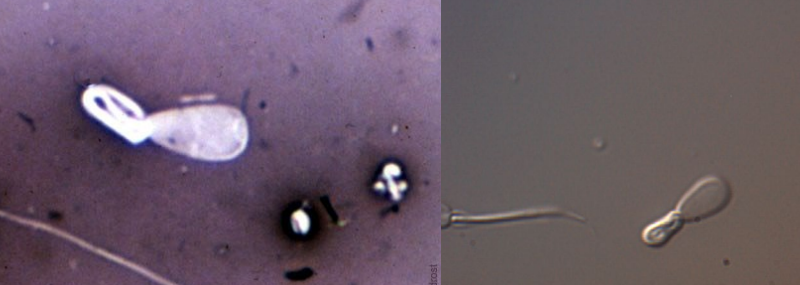
This?
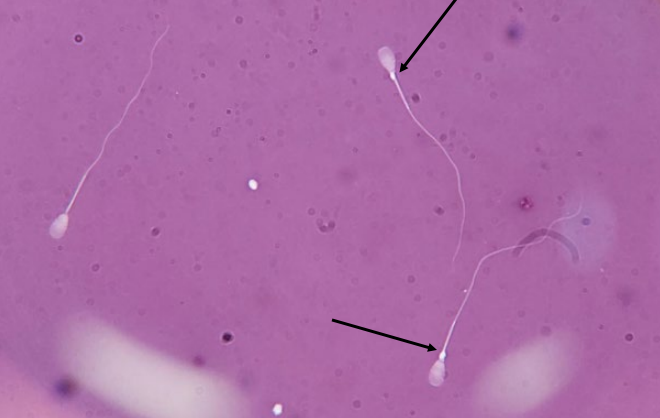
Coiled tails
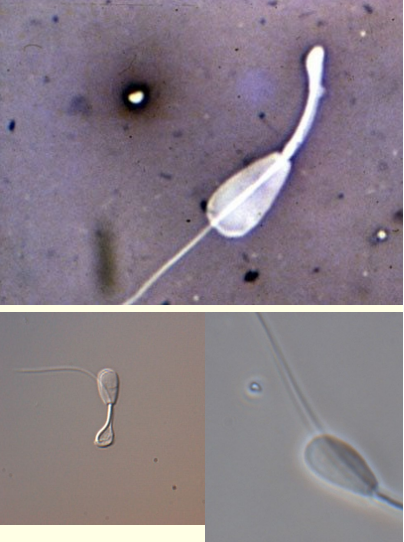
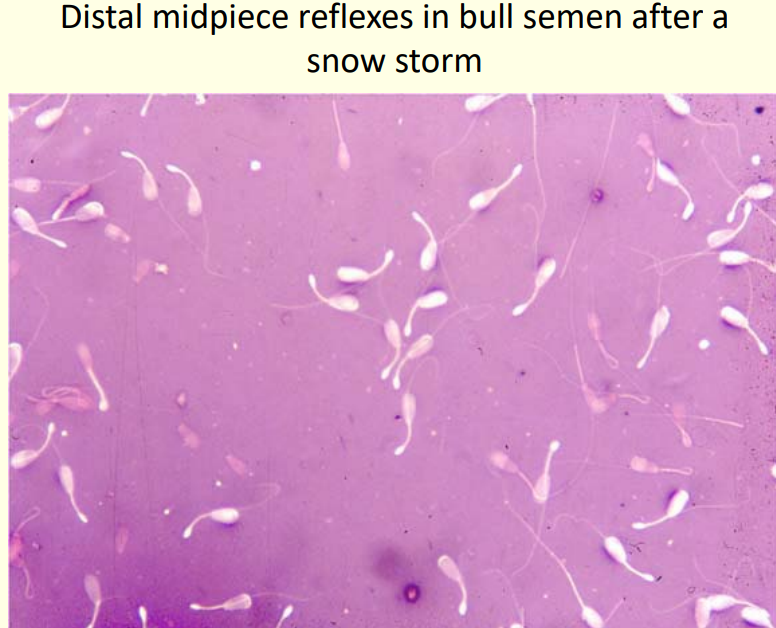
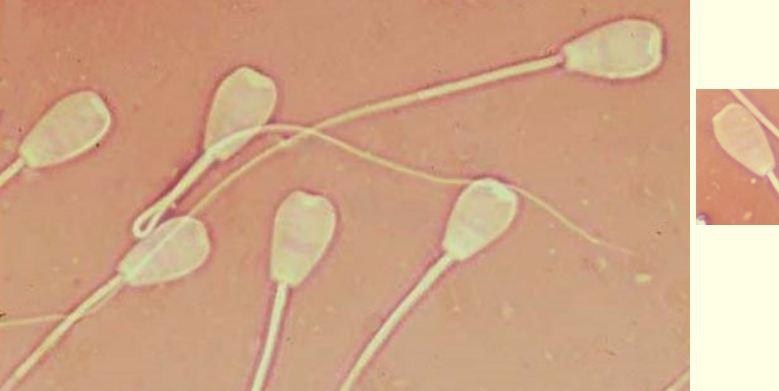
This?
Prevalence?
Appearance?
Caused by?
Midpiece reflex
• Common
• Often a cytoplasmic droplet is visible in the bend
• Prolonged contact with hypotonic solution can induce
• Ass. with abnormal epididymal environment
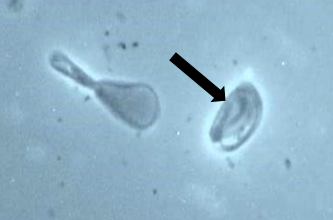
This?
Indented or knobbed acrosome

Foreign cell smear
Smear made from?
Stain?
Cells that can be seen include?
Raw semen directly or from a pellet of semen after
centrifuging
Stained with Diff-quick
sperm (obviously!), neutrophils,
lymphocytes, epithelial cells, spermatogenic cells and others
Foreign cell smear
Some white blood cells normally seen, why?
Smegma contamination
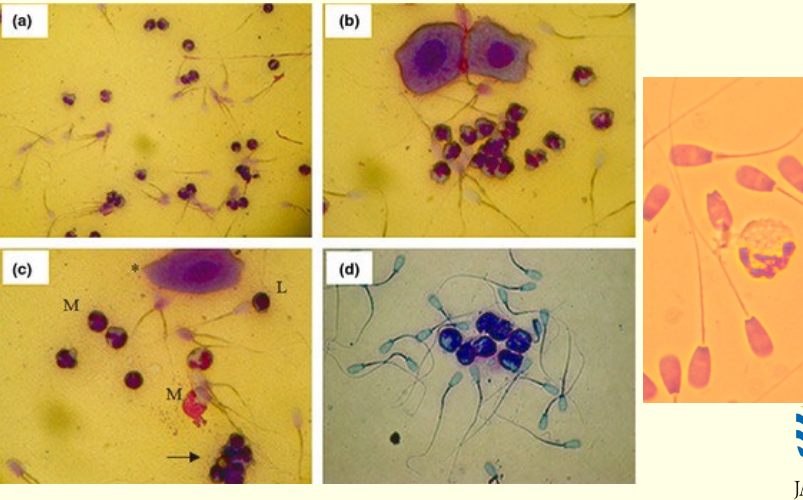
These?
White blood cells Note WBC larger than sperm heads
Semen concentration Manual Method
How do?
Manual method: Using a haemocytometer (slide) to count the number of sperm within a specific volume of semen
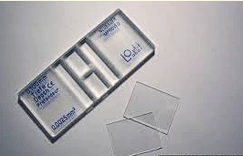
Semen concentration Manual Method - Haematocytometer Counting Area image
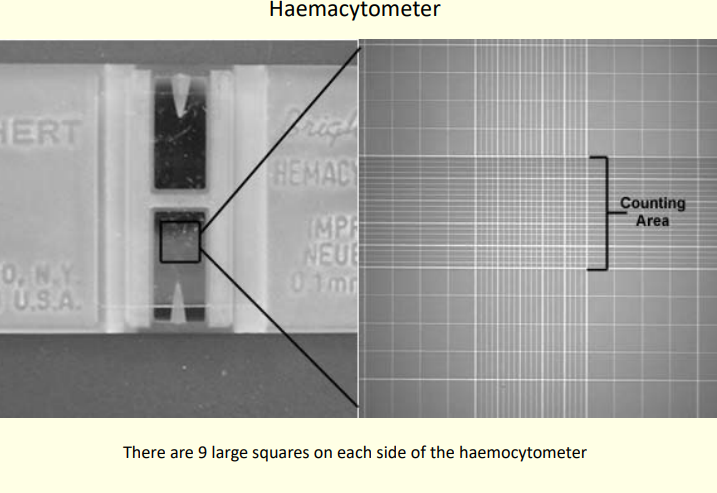
Using a haemocytometer
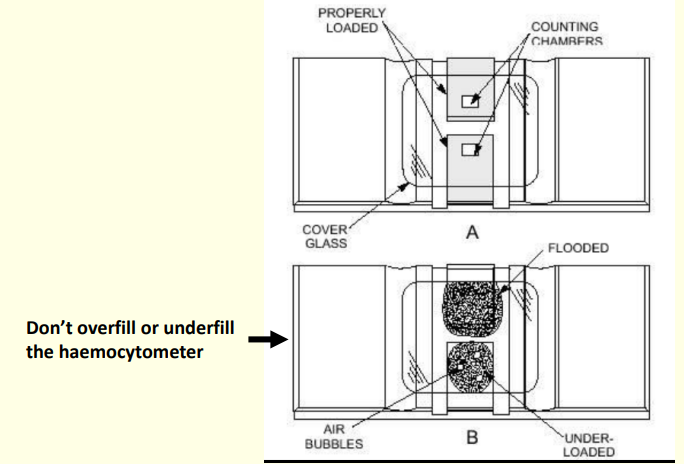
Sample prep? Result
Dilute a sample of semen in formal saline or phosphate buffered glutaraldehyde solution. Sperm now dead but preserved
Using a haemocytometer - After sample is prepped and mixed, what next?
Couting?
Load an aliquot into each side of a haemocytometer
Count the number of sperm heads within the counting area
boarded by triple lines
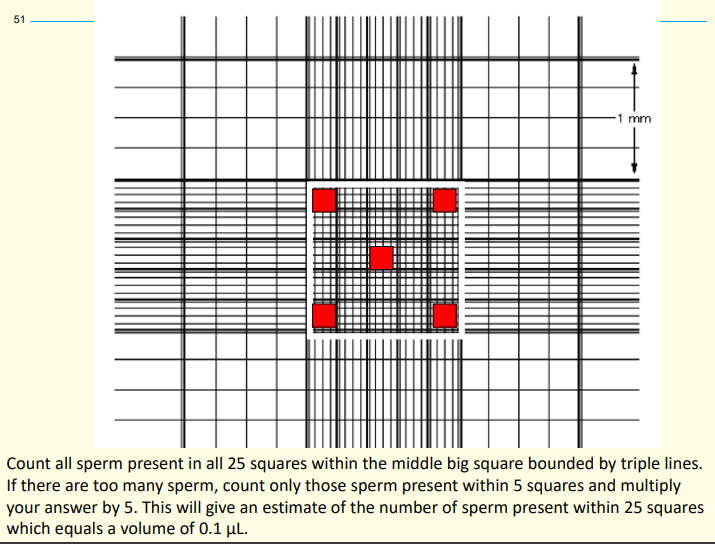
Using a haemocytometer - Counting area squares we use?
There are 25 squares but 5 squares is easier if too many sperm
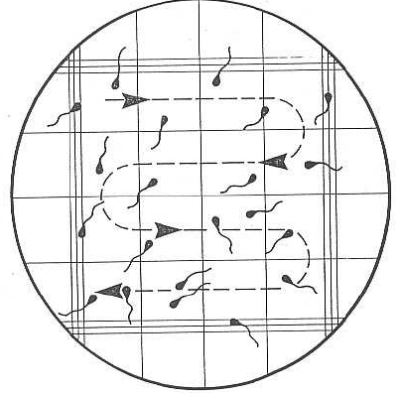
Using a haemocytometer - Direction to avoid double counting?
Formula for calculating concentrations from haemocytometer counts
For 5 squares?
If you count only 5 squares
Conc. (/ml) = Count in 5 squares x 5 x 10,000 x Dilution Factor
Formula for calculating concentrations from haemocytometer counts
If you make up a 1 in 100 dilution (Dilution Factor = 100), then the formula simplifies to?
How to make the solution?
Concentration of raw semen (x106/mL) = Count in 25 squares
Dilute 0.1 mL of raw semen in 9.9 mL of diluent
Other ways of measuring sperm concentration
