Electricity in the home - AQA GCSE Physics P5
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Van der Graaf generator
an electric field is formed when electrons move from the dome so a force is applied -> the insulating belt turns to charge the dome -> sparks are formed when an object is within the electric field
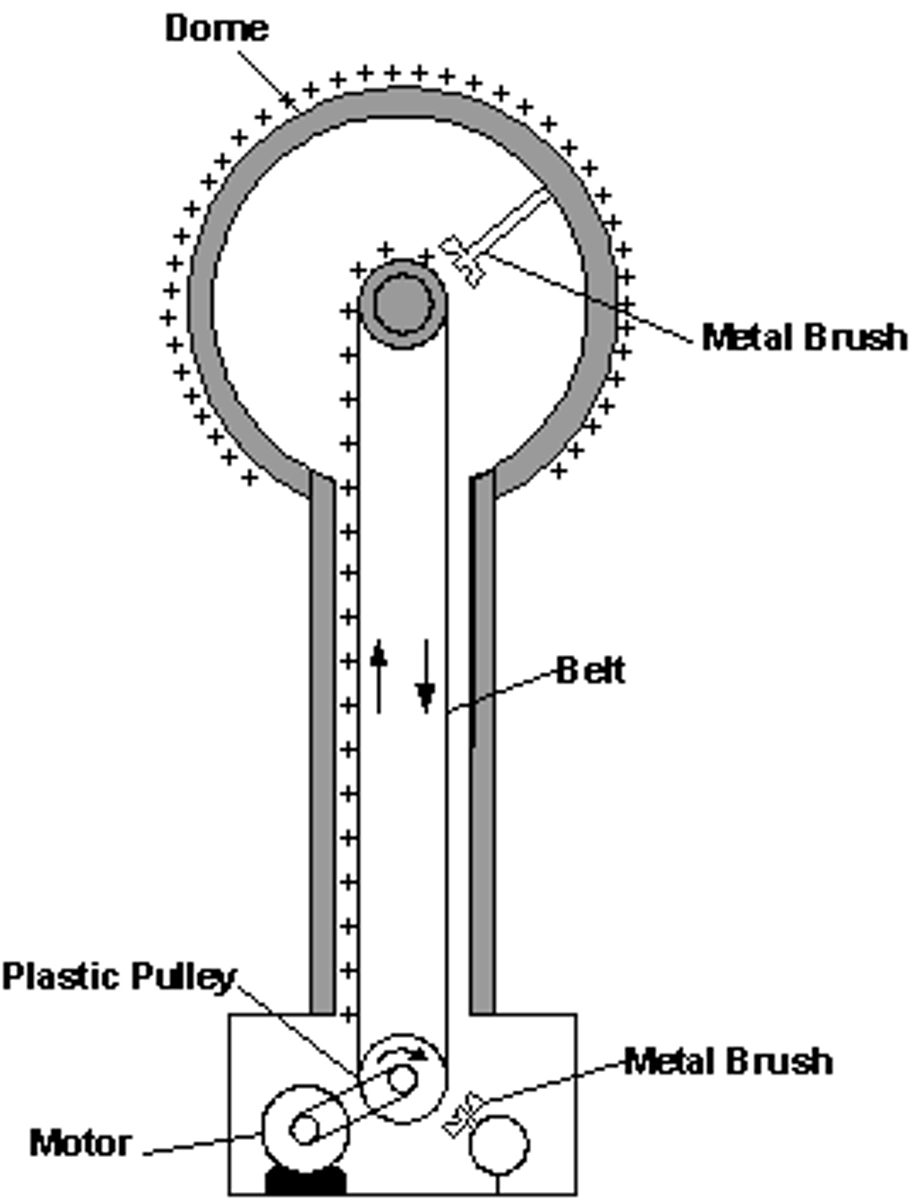
thermistor
resistor whose resistance reduces with heat
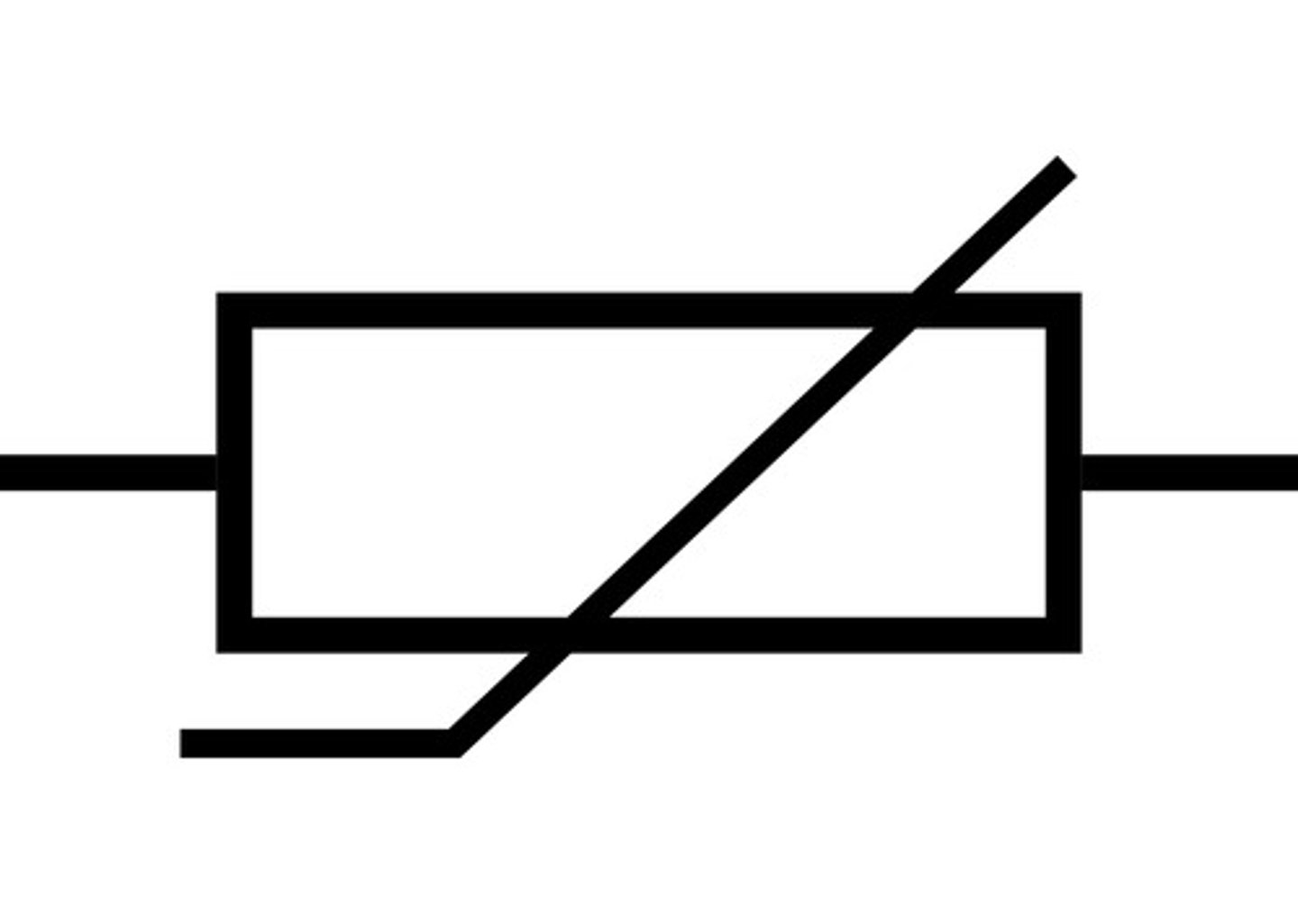
LDR
light dependent resistor, resistance decreases with light
electrons are
negatively charged particles
protons are
positively charged particles
when an atom has more electrons than protons, it is
negatively charged
electric fields
an area around an object where it can experience a force
ways to prevent electric shocks (4)
- wear protective clothing made from insulating materials
- avoid friction
- no water
- don't touch conductors if they are in contact with a running power source
cell
pushes electrons
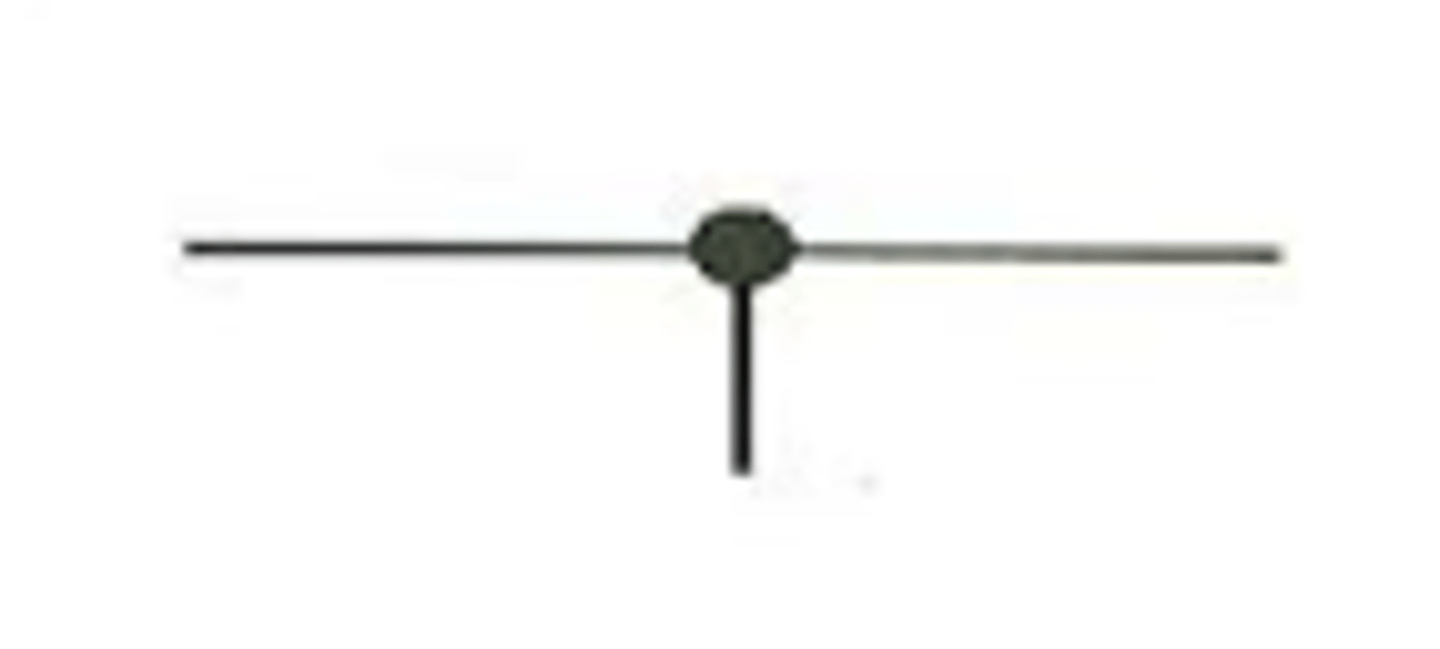
wire junction
connects wires at splits in a circuit

heater
converts electric energy to heat
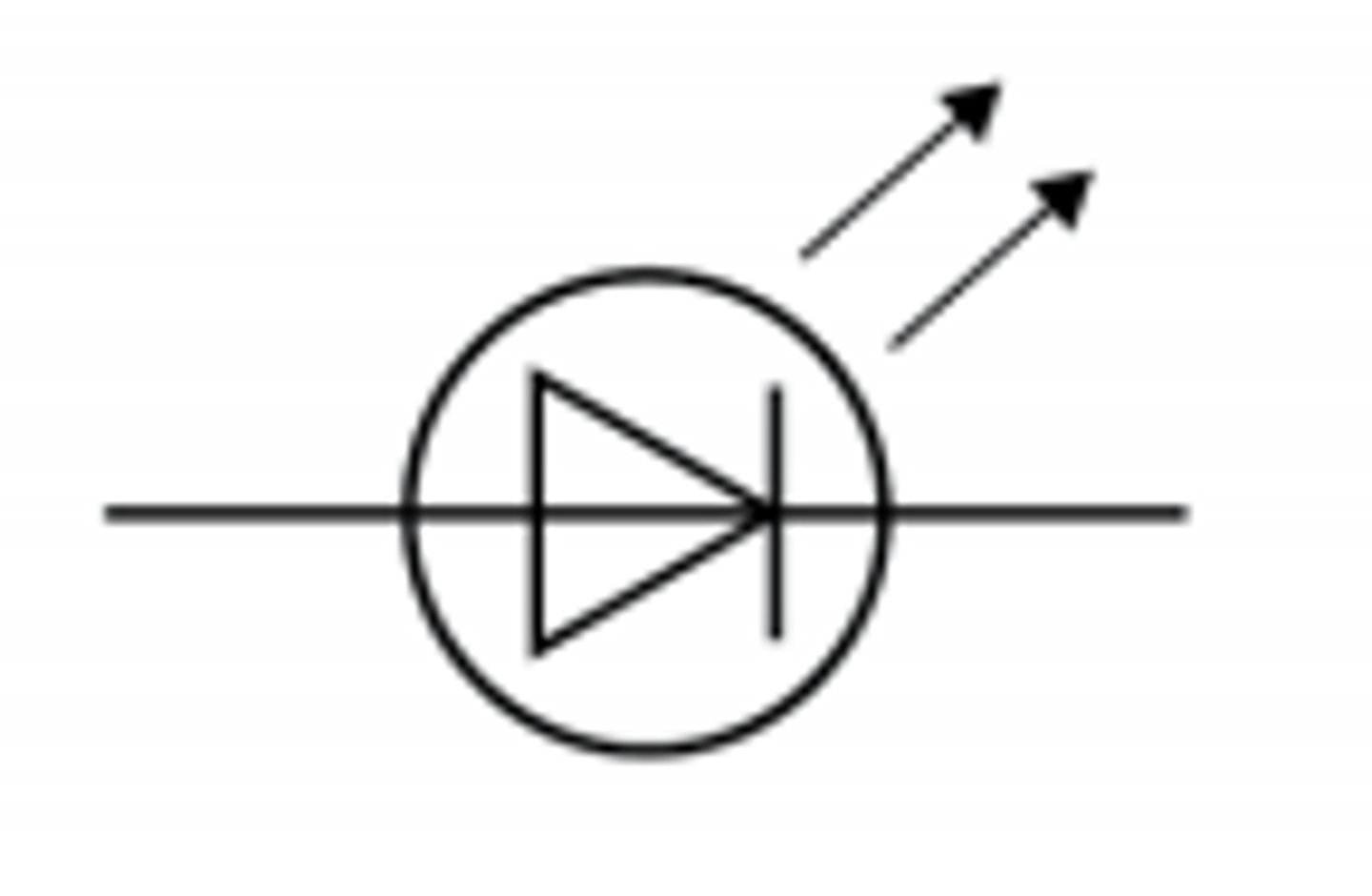
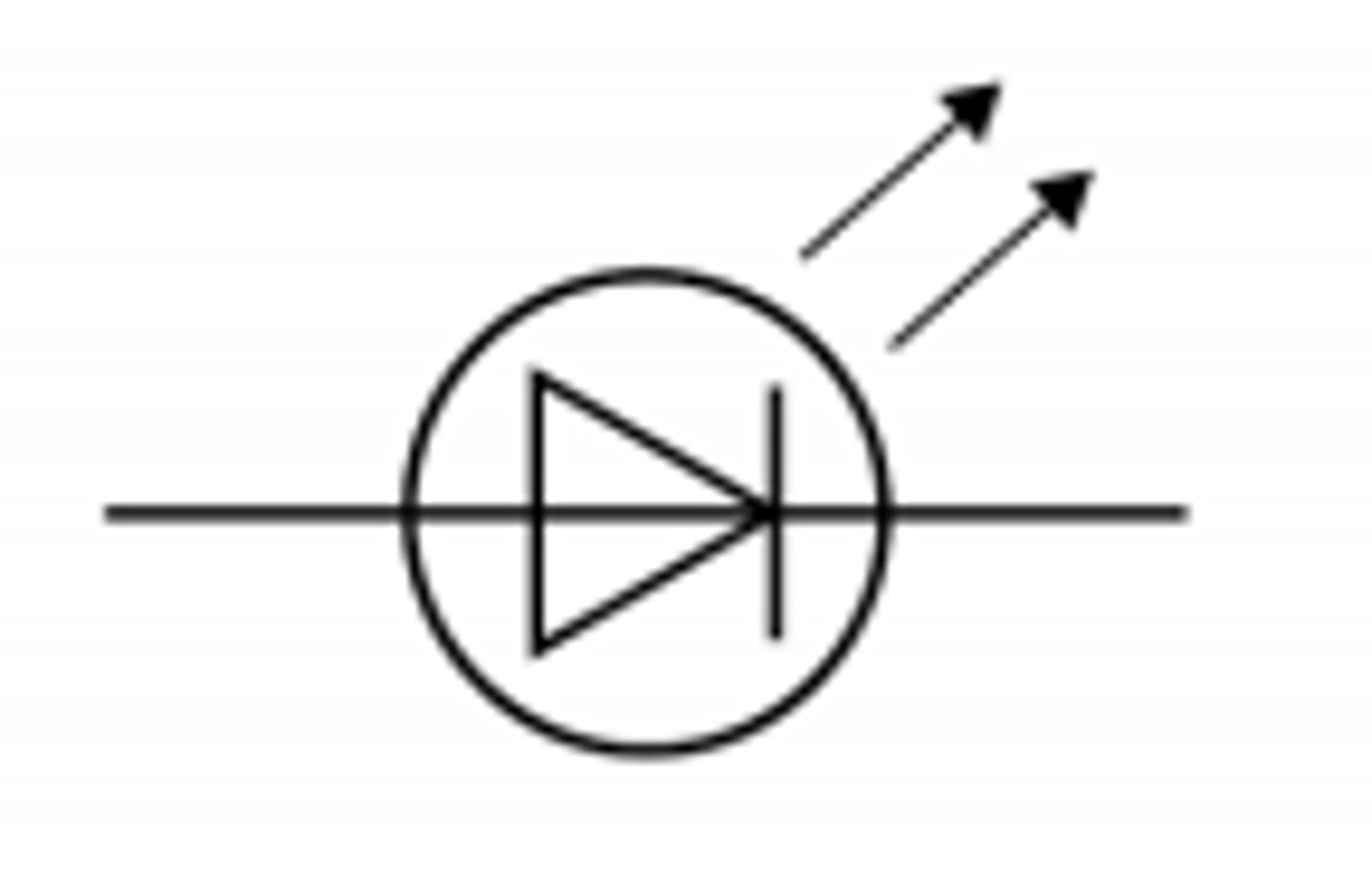
LED
Light emitting diode, emits light when current flows
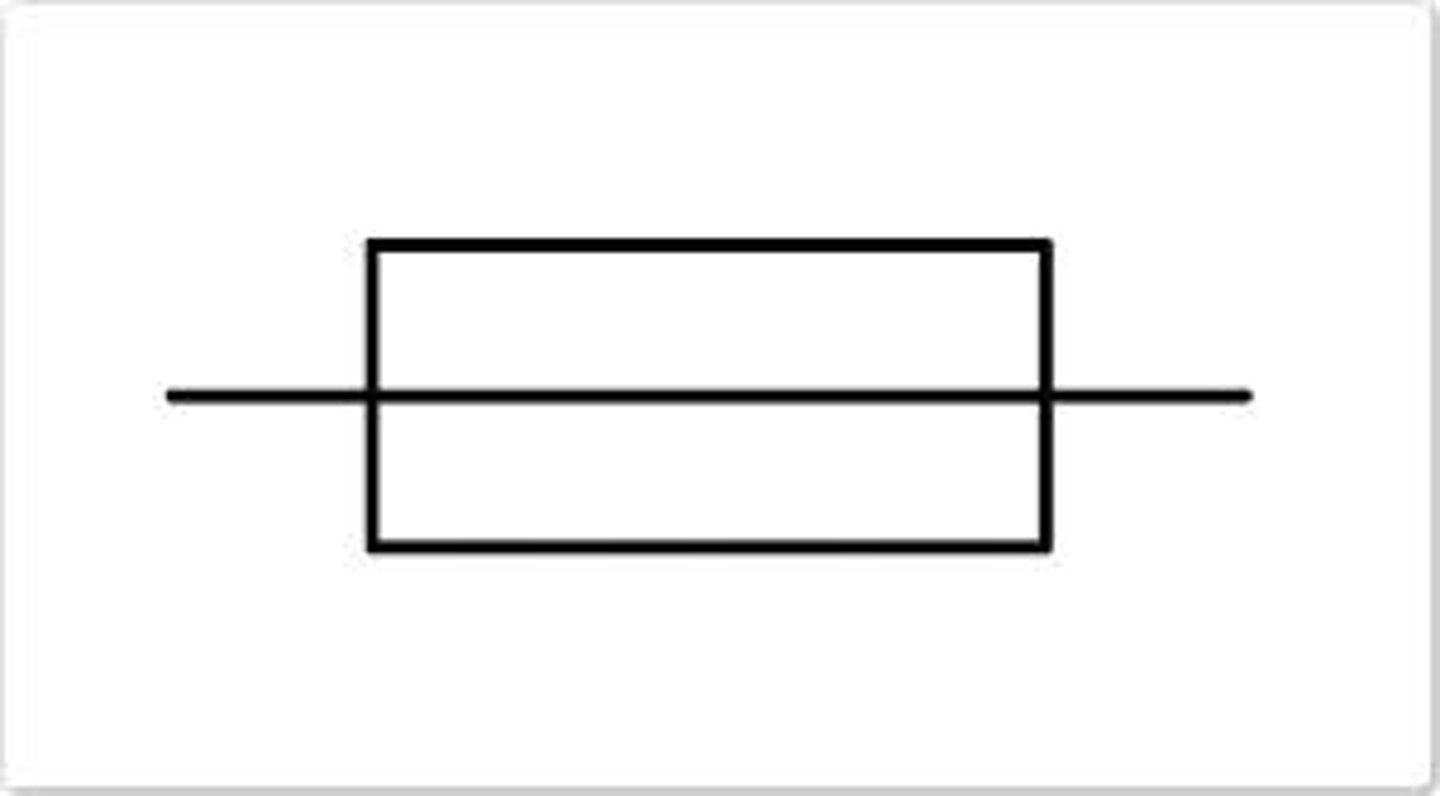
fuse
melts to break circuit if there is too much current flowing
how does the amount of cells affect current?
more cells = higher current
how does the amount of bulbs affect current?
more bulbs = lower current
more components increases resistance to it's harder for electrons to flow around the circuit
Ohm's law symbol equation
R = V/I
2 types of electricity
static and current electricity
charge
- causes objects to experience a force when in an electric field
- represented by Q
- measured in Coulombs (c)
when an atom has more protons than electrons, it is
positively charged
electrostatic forces
forces of repulsion or attraction between particles
same charges...
repel/experience forces of repulsion
opposite charges...
attract/experience forces of attraction
what is the relationship between charge and electrostatic forces?
greater charge = greater electrostatic forces
what is static electricity?
stationary charge that builds up on an object
how are sparks formed?
when an electric field is too strong, electrons are pulled out of it and collide with other air molecules to balance charges, making sparks
which direction to field lines go in?
direction of the force depending on the charge (away from centre if positive, towards if negative)
what does the space between field lines represent?
the strength of the force (lines closer = force stronger)
what is the relationship between forces and an object's distance from an electric field?
the further an object is from a field, the weaker the forces are
discharging
the movement of charge to balances charges where there is a potential difference
current electricity
continuous flow of electricity in a complete circuit with a power supply
current
- rate of charge flow
- repesented by I
- measured in Amps (A) or Coulombs per second (C/s)
current equation word equation
current (A) = charge (C)/time (s)
current symbol equation
I = Q/t
battery
2+ cells

wire
connects circuit components

switch
stops/starts flow of current by breaking circuit
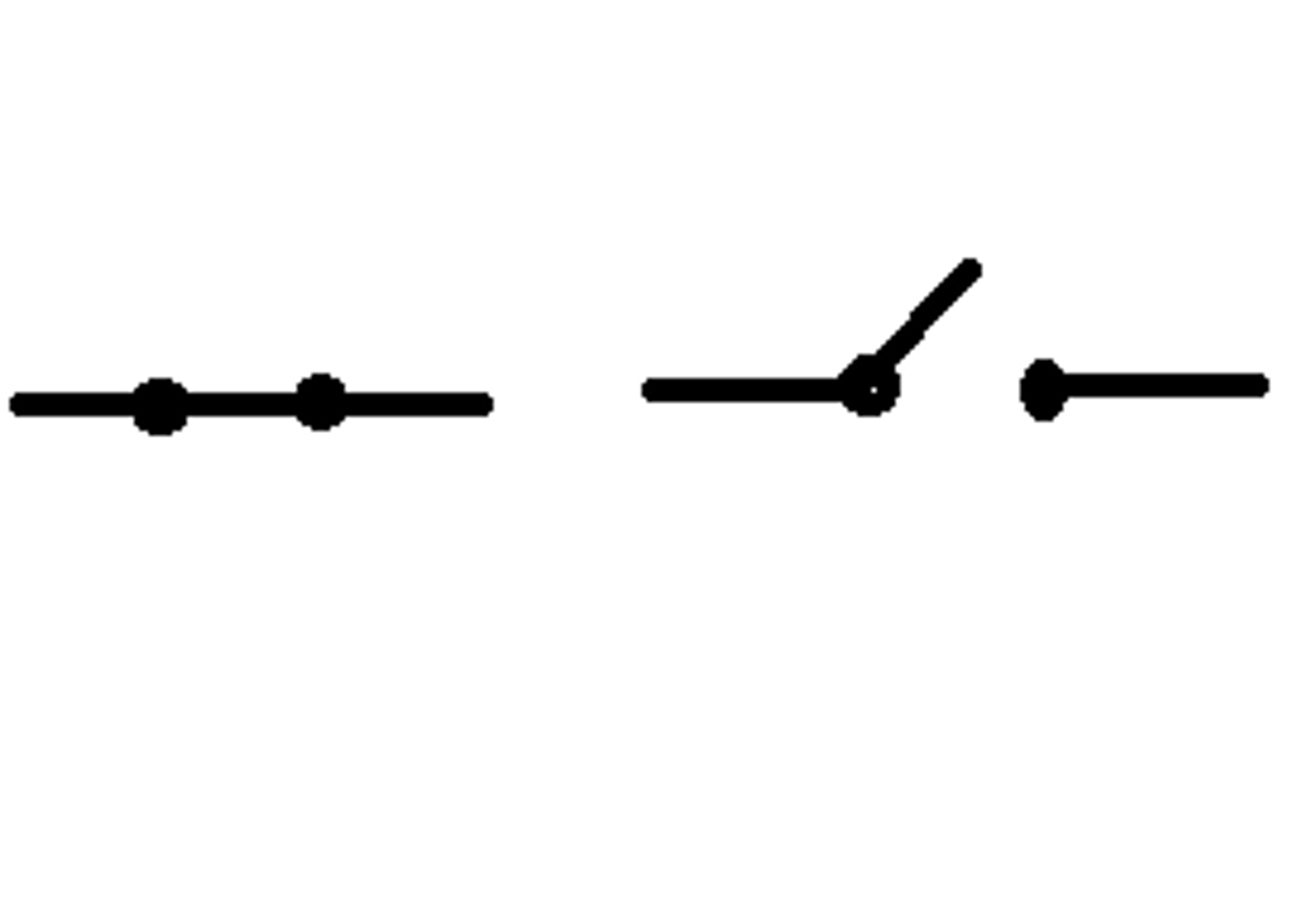
bulb/indicator
emits light when current flows through it
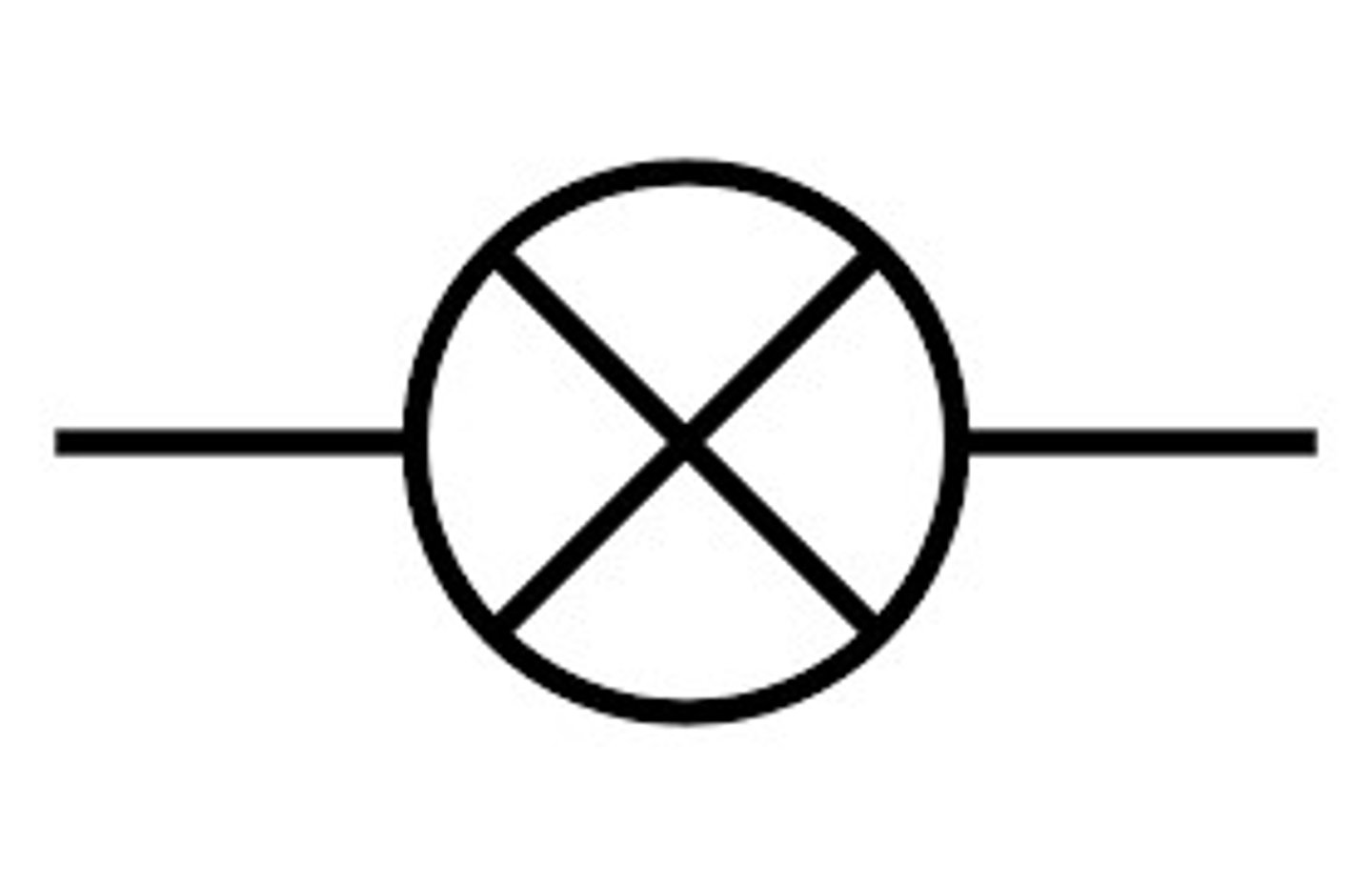
ammeter
measures current
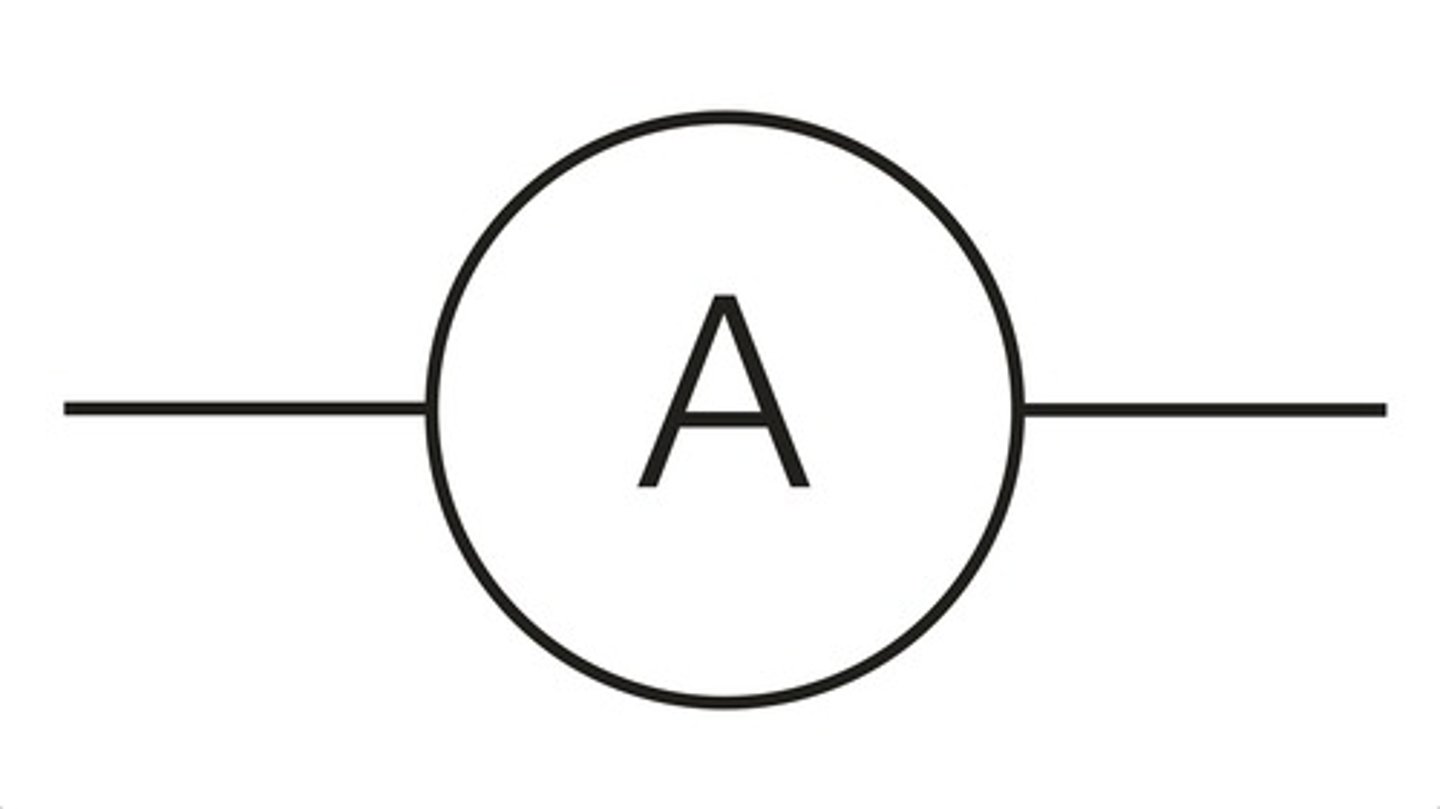
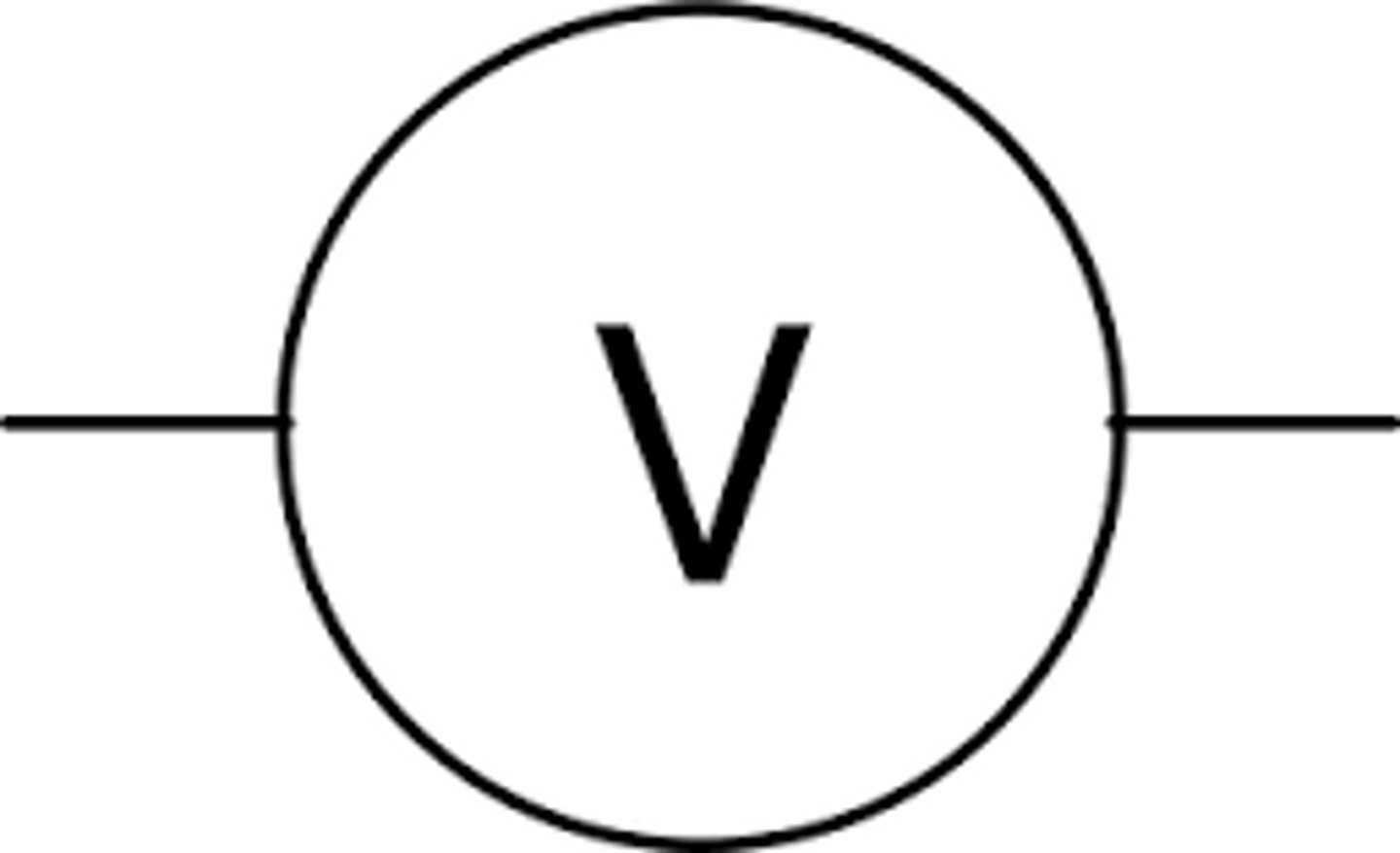
voltmeter
measures potential difference
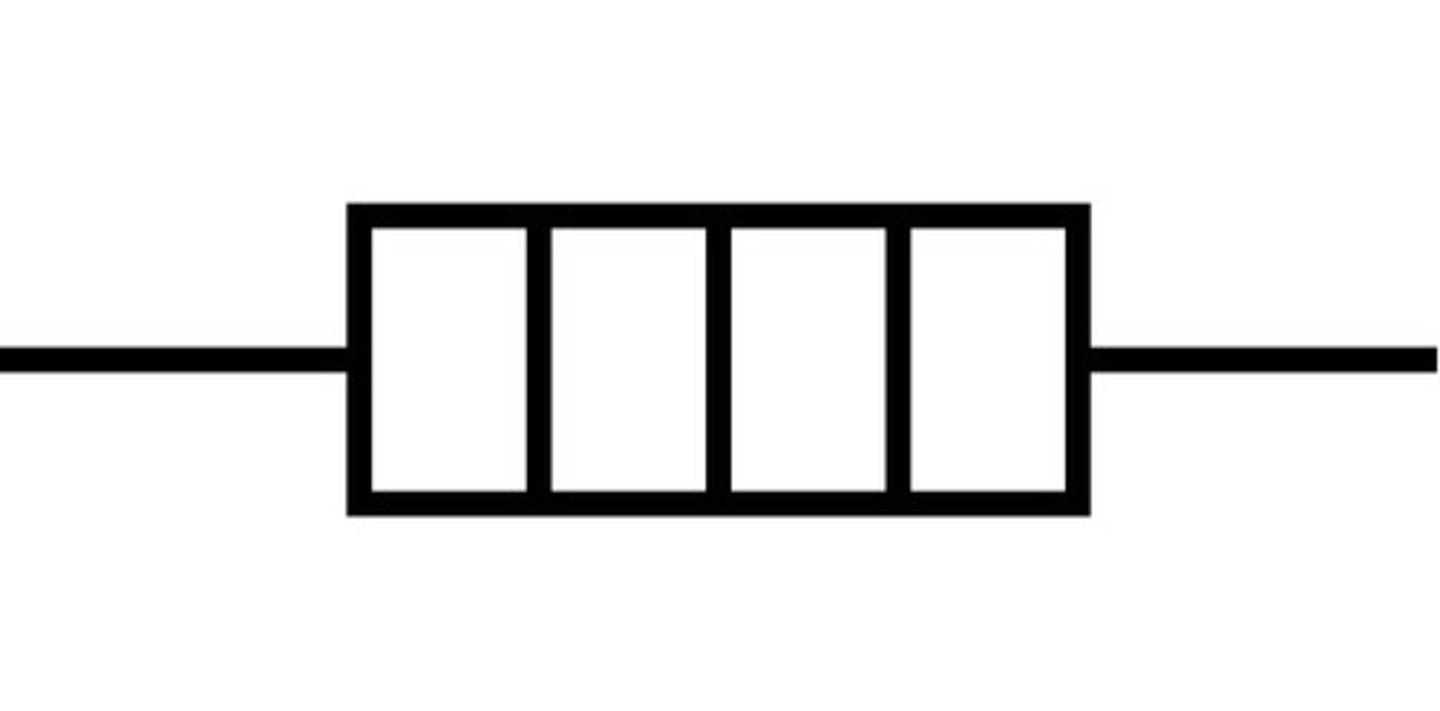
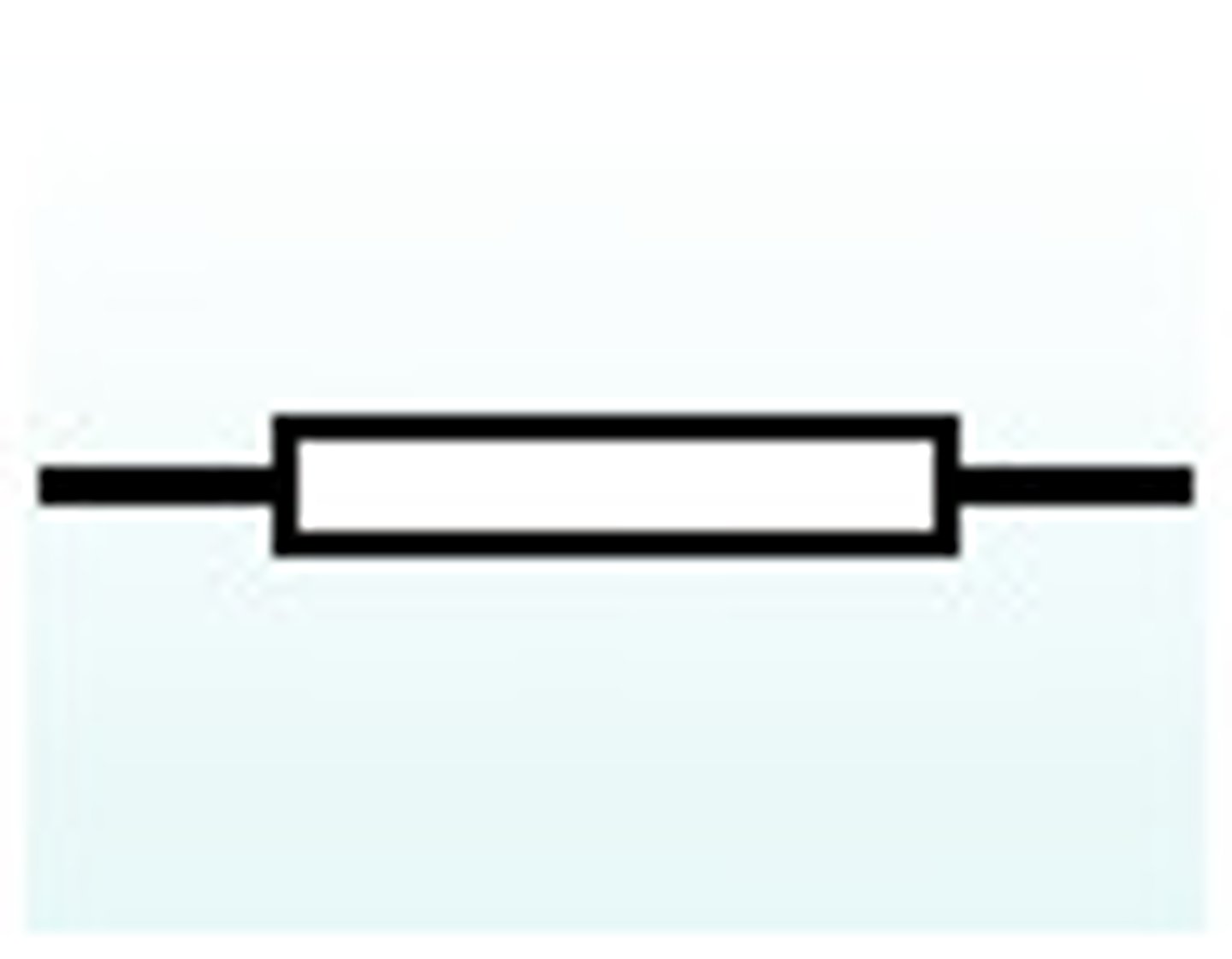
fixed resistor
limits current
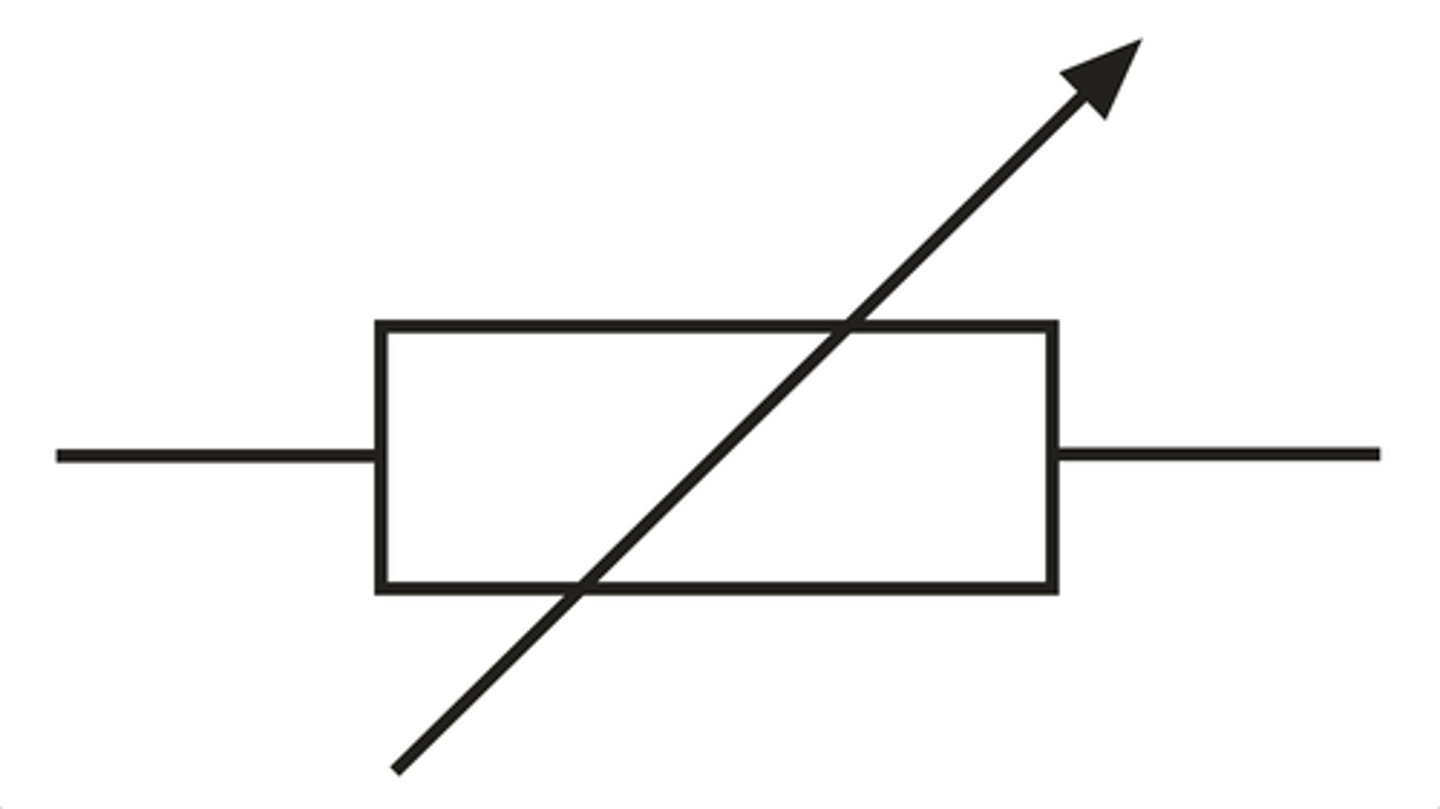
variable resistor
limits current but resistance can be changed
diode
only allows current to flow in one direction
*symbol has no arrows going out! (no other pic option)
where should an ammeter be placed in a curcuit?
anywhere because current is the same everywhere in a series circuit
Ohm's law word equation
resistance (Ohms) = potential difference (V)/current (A)
potential difference equation
potential difference (V) = energy or work done (J)/charge (C)
V = E/Q or V = W/Q
how does the number of cells affect potential diffference across a bulb?
more cells increases potential difference as they provide more electrical potential energy
factors that affect resistance (5)
- material's thermal conductivity
- potential difference
- current
- thickness of material
- length of material
method for resistance required practical
1. create circuit with D.C. power supply, switch, ammeter, ruler with resistance wire and voltmeter connected to it in parallel
2. connect clip to resistance wire
3. record ammeter and voltmeter readings
4. move crocodile clip 10cm
5. take readings again
6. repeat steps 2-5, increasing wire length by 10cm each time
7. calculate resistance from results
8. create graph for resistance against wire length
what is the independent variable for the resistance required practical?
length of wire
what is the dependent variable for the resistance required practical?
resistance
what are some controlled variables for the resistance required practical?
wire (temperature, thickness), voltage
what are some potential safety concerns for the resistance required practical and how can they be avoided?
- burns or electric shocks from hot wire, so don't touch it
- fire if wire is too far
what are the 2 types of circuits?
series and parallel
series circuit
a circuit with only one path for current to flow through
current in a series circuit is...
the same everywhere/through each component
potential difference in a series circuit is...
shared between components
resistance in a series circuit is...
the sum of all resistances
Rt = R1 + R2
parallel circuit
a circuit with multiple paths in parallel to eachother for current to flow through
current in a parallel circuit is...
the sum of currents through each component
what happens to current in a parallel circuit at a wire junction?
current splits
potential difference in a parallel circuit is...
the same everywhere/across all components
resistance in a parallel circuit is...
lower than the resistance of the smallest resistor
what happens to resistance in a parallel circuit as more branches are added and why?
resistance decreases as there are more paths for current to flow through
D.C.
direct current, current only flows in one direction and is usually low
A.C.
alternatiing current, current constantly switches direction as electrons collide and bounce back
mains electricity
- energy supply to buildings from the national grid
- A.C.
- 50Hz frequency and changes direction 50 times a second
- average 230V, maximum of 325V
oscilloscope
instrument that shows how voltage varies over time on a graph
peak voltage
voltage between 0V and the top of a wave
frequency
number of waves past a fixed point per second
period
time taken for 1 full cycle of the waveform
what are the 3 cables within plugs in the UK?
live, neutral and earth
live wire
brown, carries A.C. potential difference from the mains supply, dangerous
neutral wire
blue, completes circuit to the live wire, at or near 0V
earth wire
green and yellow striped, safety wire which directs current into the ground if there is a fault with the live wire, should have no voltage
dangers of mains electricity
if the live wire came loose and touched metal casing, it would become electrified and pose a risk of electrocution
the earth wire is a low resistance path into the ground to direct current away, causing a surge of current to melt the fuse and break the circuit so the connected appliance is safe to touch
the live wire can cause shocks even if the device is switched off