NU 125 Mental Health Nursing: Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Anxiety
feeling of apprehension or dread in anticipation of danger, often with an unknown source
What should be considered before diagnosing anxiety?
Rule out medical causes (thyroid, substance use)
Anxiety is the most _____ psychiatric disorder.
common
Stress Response Pathway (Mind-Stress Feedback Loop)
Body senses a threat, triggers brain response which triggers body to respond
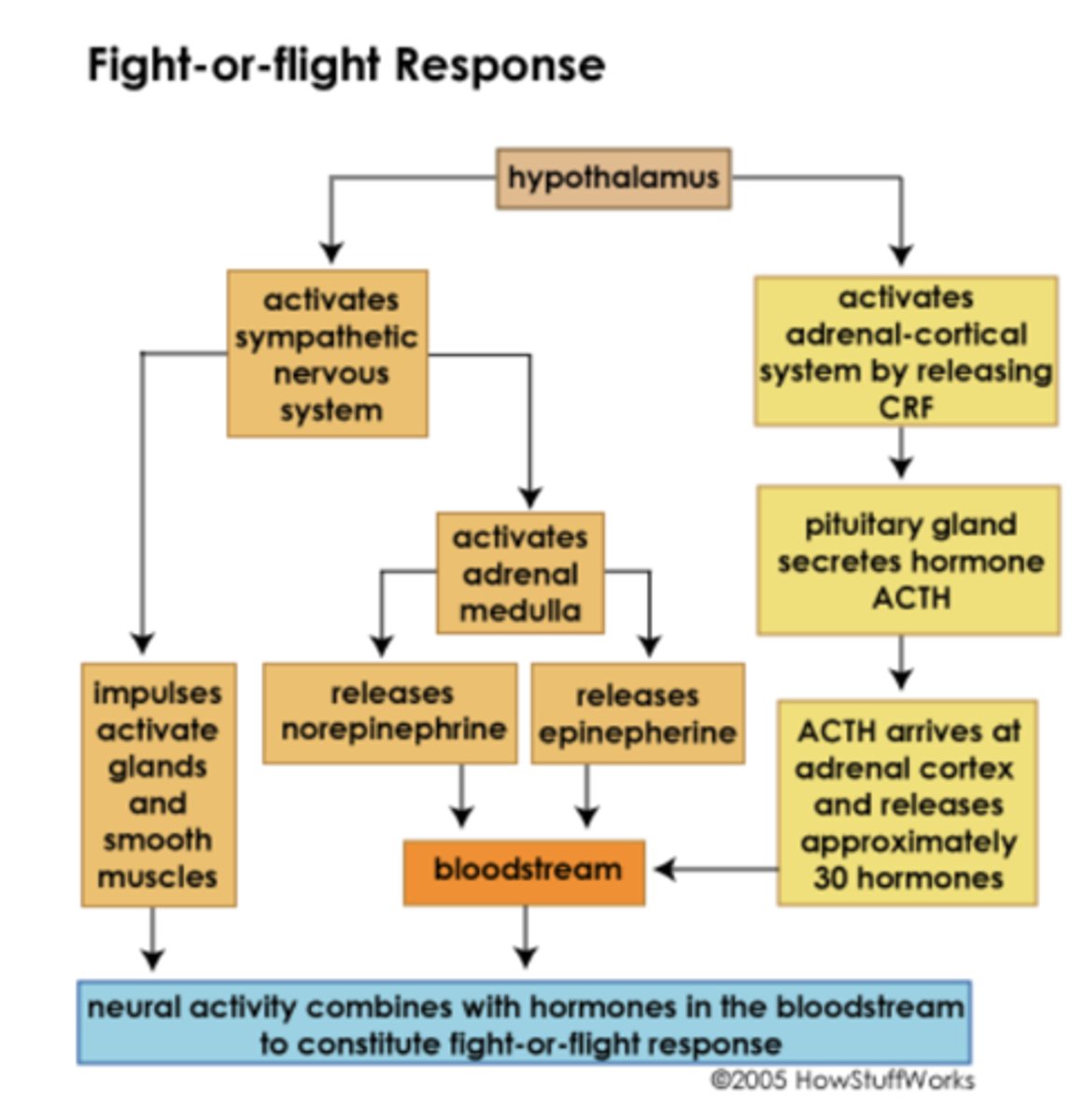
What is the goal in treating anxiety?
Targetting the feedback loop
Neurotransmitter involved in anxiety
GABA
Anxiety vs. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress triggered by a specific stressor and can be helpful while anxiety disorders interfere with day to day life and is impossible to manage
What is evaluated when recognizing anxiety?
Cognitive
Affective
Behavioral
Physiologic
Cognitive symptoms of anxiety
fear, worry, poor focus
Affective symptoms of anxiety
irritability, tension
Behavioral symptoms of anxiety
pacing, restlessness
Physiologic symptoms of anxiety
tachycardia, shortness of breath, dizziness
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
excessive worry lasting over 6 months
Criteria for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
1. Excessive worry and anxiety occuring more days than not for at least 6 months about a number of events or activities
2. Difficult to control worry
3. Associated with three or more of the 6 symptoms, with at least some present for more days than not for the past 6 months.
How many items are required in children?
one
6 Symptoms according to DSM-5
Restlessness, feeling tense or on edge
Easily fatigued
Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
Irritability
Muscle tension
Sleep disturbances
What should be ruled out before diagnosing anxiety?
Medical causes
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
recurrent obsessions or compulsions that are severe enough to be time-consuming or cause marked distress or significant impairment
Obsessions
unwanted intrusive thoughts, impulses, or images
Compulsions
repetitive actions, or ritualistic behaviors
Example of compulsion
excessive handwashing
What is the reason for this time-consuming behavior in OCD?
to decrease anxiety
With OCD, the thoughts or actions..
IMPACT social or occupational function, as behavior is excessive or unreasonable
OCD occurs in..
across the lifespan
Other OCD related disorders
Hoarding
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Trichotillomania
Hoarding
collecting and putting things away in a guarded manner
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
a disorder characterized by the unrealistic perception of physical flaws
Trichotillomania
a disorder characterized by the repeated pulling out of one's own hair
Phobias
irrational persistent fear of an object or situation
Fear
involves intellectual appraisal of threatening situation
If anxiety is severe enough, the ___ or ___ is avoided.
situation, object, or activity
Types of Phobias
Agoraphobia
Social
Specific
Agoraphobia
fear of being in a place or situation from which escape is difficult or impossible, feeling unsafe or trapped
Social phobia
fear of social situations or performance
Specific phobia
fear of something specific, like snakes or spiders
Panic Disorder
onset occurs in early adulthood or menopause and is characterized by recurrent episodes of panic attacks
At least one of the attacks has been followed by one month of..
1. Persistent concern (of another attack)
2. Worry about consequences
3. Significant change in behavior
Panic Attack Symptoms (must have 4/5)
Sweating
Shaking
Choking
Chest pain
Nausea
Dizziness
Fear of dying or going crazy
Paresthesia
Chills
Hot flashes
Derealization
Depersonalization
Derealization
detached from reality or the situation
Depersonalization
detached from themselves
Interventions for Panic Attacks
Stay with person
Convey calm
Minimize stimuli
Encourage breathing
Offer fluids
Provide distraction
What should the nurse tell someone experiencing a panic attack?
"This will not last"
"You have experienced this before"
"You are safe"
"I will stay with you"
Goal of intervention for panic attacks
relieve immediate symptoms
Acute Stress Disorder
short-term disorder that develops after a traumatic event and stress related symptoms occur within a month of this event
How long do symptoms persist with ASD?
at least two days and cause much distress
If symptoms persist for a month of longer, diagnosis changes to..
PTSD
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
exposure or experience of a traumatic event and severity/duration of the stressor can impact degree of distress along with timely support
Symptoms of PTSD
Recurrent nightmares
Flashbacks
Intense fear
Detached
Sleep disturbance
Hypervigilant
What can cause a re-experience of symptoms?
triggers such as images, sounds, words, etc.
Who is PTSD common in?
military personnel
Nursing interventions for PTSD
Stay calm & stay present
Encourage breathing & grounding
Reassure: 'You are safe. This will pass.
Minimize stimuli; use soft voice
Teach relaxation, mindfulness, CBT
Empower recovery through trauma-informed care
Pharmacologic Treatments for Anxiety
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines
drugs that lower anxiety and reduce stress
Lorazepam (Ativan)
Benzodiazepine
Diazepam (Valium)
Benzodiazepine
Clonazepam (Klonopin)
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines provide..
fast relief, short-term only
Risks of Benzodiazepines
dependence and sedation
What is the action of benzodiazepines?
increase GABA to increase relaxation and neuronal slowing
Non-benzodiazepines
Buspirone
SSRIs
Buspirone (Buspar)
slow onset, no dependence, must be scheduled not PRN
SSRIs
long-term maintenence, do not stop abruptly
Black Box Warnings for Benzodiazepines
avoid use with opiods, risk of addiction, abuse, misuse, and do not drink alcohol
Nonpharmacologic Treatments
CBT
Behavioral therapy
Breathing, mindfulness, exercise
Support groups and journaling
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
refines maladaptive thought patterns and motivates towards adaptive actions through examining thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
Unhelpful Thinking Styles: Cognitive Distortions
Dichotomous
Personalization
Overgeneralization
Catastrophizing
Jumping to conclusions
Disqualifying the positives
Dichotomous thinking
black and white thinking (e.g. "if I don't score 100% I have no future")
Personalization thinking
"When I walk through the hospital hallway, I know everyone is looking at me."
Overgeneralization thinking
after car accident, says "I should not be on the road"
Catastrophizing
"If I fail this test, I will be a total failure"
Jumping to conclusions
Friend does not return phone, you assume he is avoiding you
Disqualifying the positives
"They are just congratulating me to be nice"
Anxiety Evaluation
Can the patient..
Recognize anxiety signs
Use coping
Maintain function and safety
Verbalize long-term plan