Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand Curves 20
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Federal Funds Rate
Interest rate banks charge each other for loans.
Real Interest Rate
Nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation.
Monetary Policy Curve
Shows relationship between real interest rates and inflation.
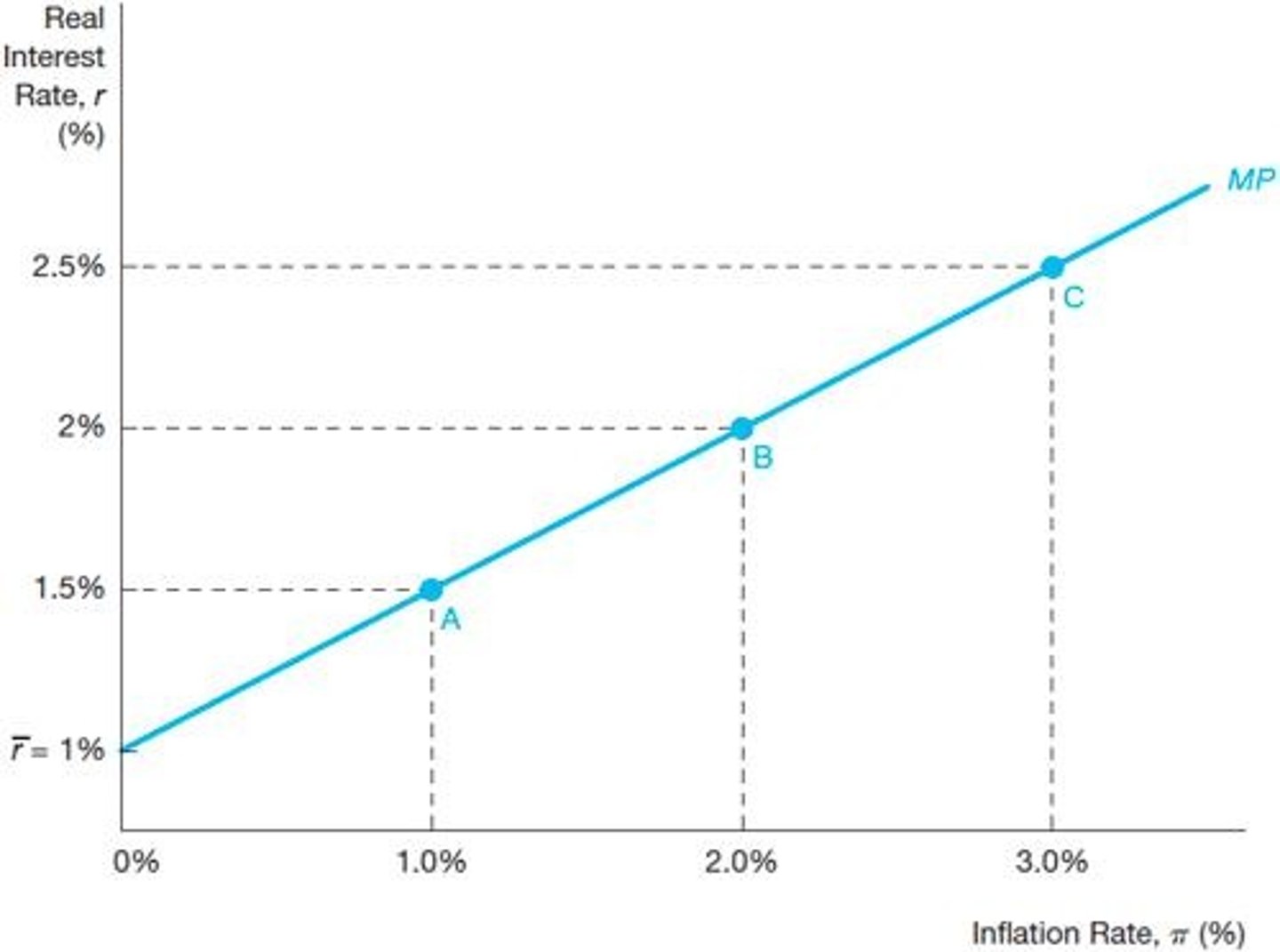
Upward Sloping MP Curve
Real interest rates rise with increasing inflation rates.
Taylor Principle
Nominal rates must rise more than expected inflation.
Aggregate Demand Curve
Relationship between inflation rate and aggregate demand.
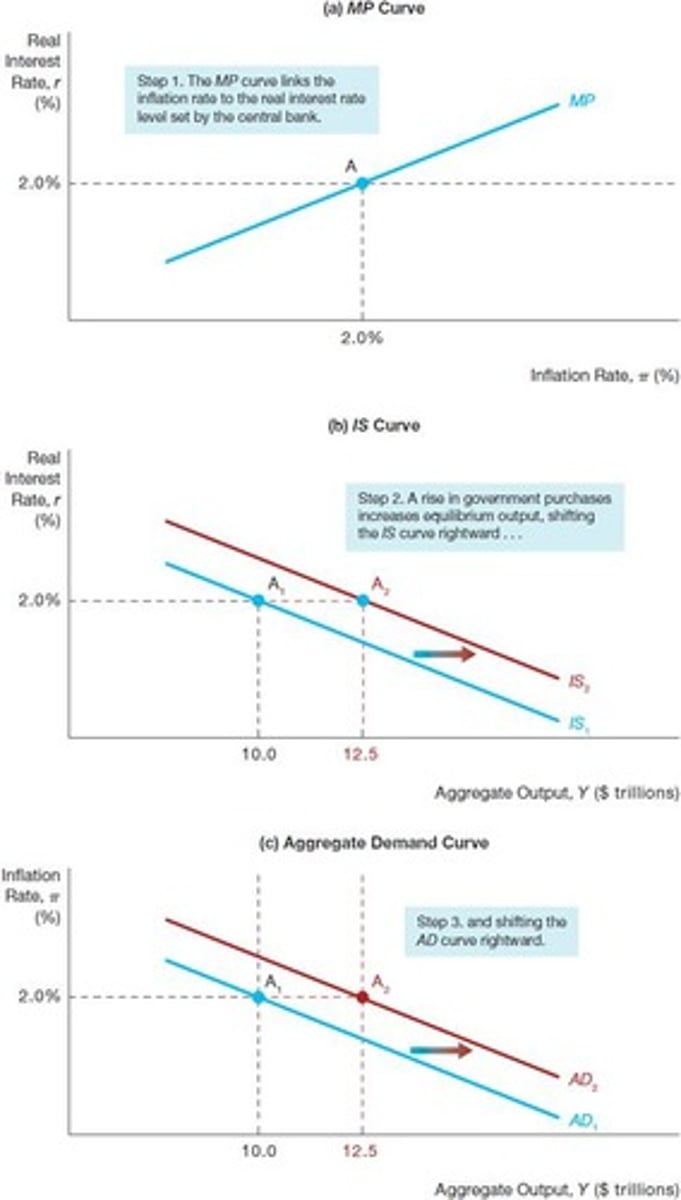
Downward Sloping AD Curve
Higher inflation leads to lower aggregate output.
IS Curve
Represents equilibrium in the goods market.
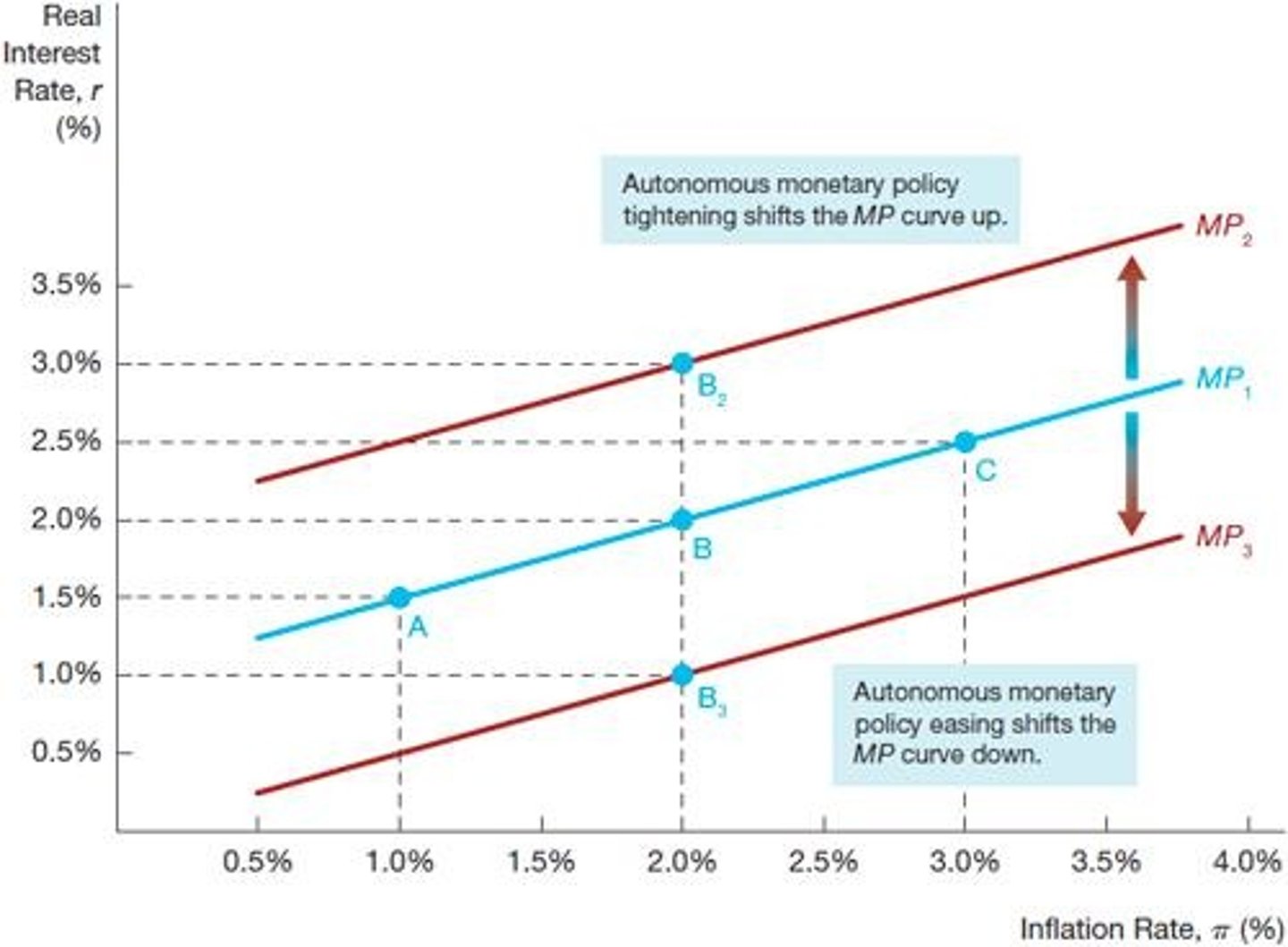
Autonomous Changes
Policy shifts that directly affect the MP curve.
Automatic Changes
Changes along the MP curve due to the Taylor principle.
Monetary Policy Tightening
Raising interest rates to reduce inflation.
Monetary Policy Easing
Lowering interest rates to stimulate the economy.
Shifts in the AD Curve
Changes in aggregate demand due to various factors.
Factors Shifting AD Curve
Include consumption, investment, government spending, and taxes.
Equilibrium Aggregate Output
Level of output where aggregate demand equals supply.
Inflation Rate (π)
Rate at which general price levels rise.
Nominal Interest Rates
Interest rates not adjusted for inflation.
Short-term Real Interest Rates
Real interest rates over a short period.
Aggregate Demand and Supply Analysis
Explains short-run fluctuations in output and inflation.
Equilibrium in Goods Market
Condition where supply equals demand in the market.
Autonomous Net Exports
Exports minus imports that shift the AD curve.
Government Purchases
Spending by government that affects aggregate demand.