APMacro Unit 2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Gross Domestic Product
The dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders in one year.
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the population. Used to measure if standard of living is improving.
GDP expenditures approach
Adds up all the spending (C + I + G + Xn) on final goods and services that were produced in a given year
GDP income approach
Alternative method of calculating GDP that adds up all the income that resulted from selling all final goods and services produced in a given year
Value added approach
An alternative method of calculating GDP by adding up the increases in product value as it makes its way through the production process. This approach would look at the increase in value of intermediate goods throughout the production process.
Nominal GDP
GDP measured in current prices.
Real GDP
GDP adjusted for inflation, necessary to understand whether a change in GDP is due to a change in productivity or simply a change in price level.
Business Cycle
The natural rise and fall of economic growth that occurs over time.
C + I + G + Xn
The formula for calculating GDP using the expenditure approach.
Unemployed
Workers that are out of work, actively looking for a job, but unable to find a job.
Frictional Unemployment
When a worker is between jobs, or a student has graduated and is looking for her/his first job. Individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills
Seasonal Unemployment
A type of frictional unemployment which is due to time of year and the nature of the job
Structural Unemployment
Workers do not have transferable skills and these jobs won't come back. This category includes technological unemployment.
Technological Unemployment
A type of structural unemployment where automation and machinery replace workers
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment caused by a reduction in the output of a country, when a country is operating inside it's PPC.
Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
Estimated in the US at 4-6%, it is determined by adding frictional + structural unemployment which are expected (while excluding cyclical unemployment which is undesirable). An economy at this level would be on the PPC and be considered healthy. Also known as full employment.
Labor Force Participation Rate
A measure of the percentage of the population, age 16+, that is able and willing to work. Includes both employed and unemployed workers.
Excludes anyone who is under 16 or is not wanting to work or is incapable of working due to hospitalization / incarceration.
(labor force/total population) x 100
The formula for calculating the labor force participation rate of a country.
Inflation
The rising in the general level of prices which reduces the purchasing power of money
Deflation
A decrease in the general level of prices.
Disinflation
Prices are increasing at a slower rate (a reduction in the rate of inflation but NOT a reduction in the general level of prices)
Nominal Wage
The wage an employee is paid
Real Wage
The wage an employee is paid, adjusted for inflation, in order to determine the purchasing power of those wages.
Inflation Rate
The percent change in prices from year to year
(change/old) x 100
Formula for inflation rate
Price Indices
Index numbers assigned to each year that show how prices have changed relative to a specific base year (base year is given an index number of 100)
Substitution Bias
A criticism of price indices caused by consumers buying less of a product in a price index and instead shifting demand to a competitive good which is not in the market basket used to calculate the price index.
Real Interest Rate
The portion of the nominal interest rate after the inflation rate is removed. It is calculated as follows: Nominal interest - Inflation
Nominal Interest Rate
The advertised rate of interest
Hidden unemployment
The unemployment of potential workers that is not taken into account in official unemployment statistics because of how the data is collected. For example, workers are only considered unemployed if they are looking for work so those without jobs who have stopped looking are no longer considered "unemployed" but in all reality may truly be.
Discouraged worker
A person of legal employment age who desires to be employed but is not actively seeking employment, often because they couldn't find a job and thus gave up.
Underemployed workers
Workers who are highly skilled but working in low skill jobs OR part-time workers who would prefer to be full time but are unable to locate full-time work. These workers are not counted in the unemployment rate.
Economic growth
An increase in real GDP, often measured on a per capita basis.
Intermediate goods
Goods used in the production of other goods, including final goods. Not counted in GDP.
Non-production transactions
Financial transactions and re-sale (second-hand) transactions. Not counted in GDP.
Non-market transactions
This category includes goods or services supplied to others for free (household production) as well as illegal transactions. Not counted in GDP.
Household production
Goods and services produced by households for their own use/consumption. It is a non-market transaction and thus not counted in GDP.
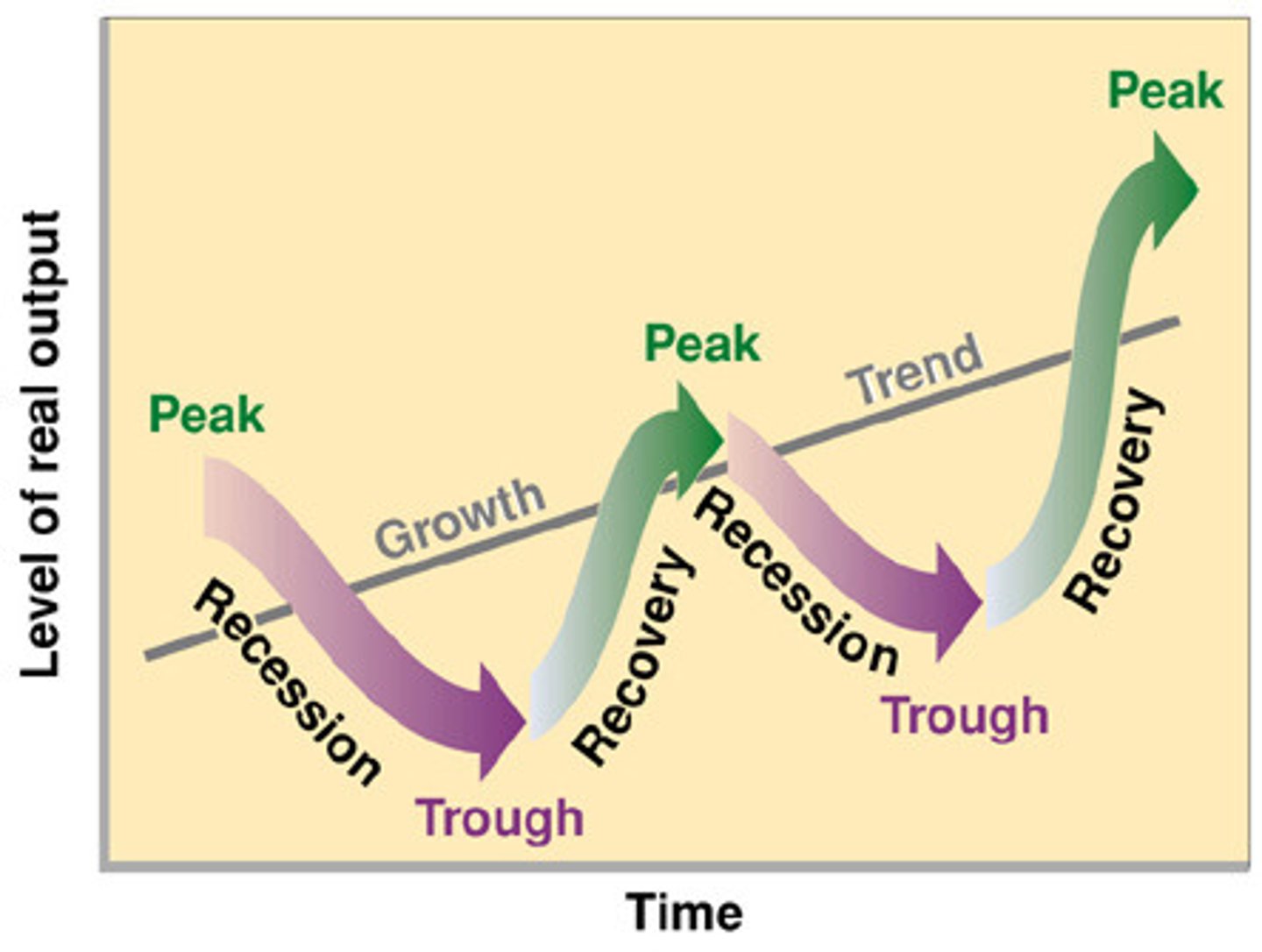
Peak
The highest point between the end of an economic expansion and the start of a contraction in a business cycle
Trough
The lowest point between the end of a contraction and the start of an economic expansion in the business cycle.
Expansion
Phase of the business cycle in which the economy as a whole is growing. Also known as a recovery.
Contraction
Phase of the business cycle in which the economy as a whole is in decline. Multiple periods of this lead to a recession.
Full Employment
Typically around 4-6% unemployed, at this level there is no cyclical unemployment but rather just structural and frictional unemployment.. Also known as NRU.
Inflationary gap
A situation where actual GDP exceeds full-employment/NRU GDP. At this level even some structural/frictional workers are finding jobs, and businesses face severe competition for workers compete by offering higher wages. This drives up the price level.
Hyperinflation
A situation where prices rise more than 50% in a period of a month.
Stagflation
A situation where there is high inflation with high unemployment along with limited economic growth.
Consumer Price Index
A measure calculated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services. May include domestic and international consumer goods.
(Price of Basket / Price of Basket in Base Year) x 100
Formula for CPI
GDP Deflator
Calculated by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) in the US, it is an index value that allows for the removal of inflation from a nominal GDP value in order to calculate the real GDP.
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP) x 100
Formula for the GDP deflator
Cost of Living Adjustments (COLA)
An adjustment made to Social Security and Supplemental Security Income to counteract the effects of inflation.
Trend line
Indicates the general pattern or direction of the economy in the business cycle. In the US, this is upward sloping indicating growth in real GDP over time.
Fluctuation
A change (rising or falling)
Boom
An economic expansion period when GDP is above the long-run trend.
Bust
An economic contraction period when GDP is below the long-run trend.
Recessionary Gap
The amount by which actual GDP is less than full-employment GDP.
Recession
Two quarters of consecutive negative GDP growth.
(# of unemployed / # in labor force) x 100
Formula for unemployment rate
Unemployment rate
The percent of people in the labor force who want a job but are not working
Labor force
The sum of employed + unemployed people (unemployed = actively searching, able to work, 16+, not retired or underemployed, not in jail or hospital or military or school full time).
Standard of Living
The degree of wealth and material comfort available to a person or community.
Output growth
Also known as GDP growth, this measures the change in real GDP from one year to the next.
((Year 2 real GDP - Year 1 real GDP)/Year 1 real GDP) x 100
Formula for calculating percent change in GDP (output growth)