GCD 3022 chapter 9- Molecular structure of DNA and RNA
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Molecular Genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
Information, Transmission, Replication, Variation
The genetic material must meet four criteria
Information
DNA must provide the blueprint for determining the inherited traits of an organism
Transmission
during replicationmthe genetic material must be passed from parent to offspring
Replication
DNA must be copied
variation
within any species, a significant amount of phenotypic differences occur
Griffiths experiment
S. pneumoniae was able to transfer its DNA to non lethal streptococcus strand which demonstrated Variation, transmission, replication, and information
transformation
process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria
DNase
breaks down DNA
RNase
degrades RNA
protease
enzyme that digests protein
bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
- acidic molecules that release hydrogen ions in solution and have a negative charge at neutral PH
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
strand
nucleotides that are covalently linked to one another
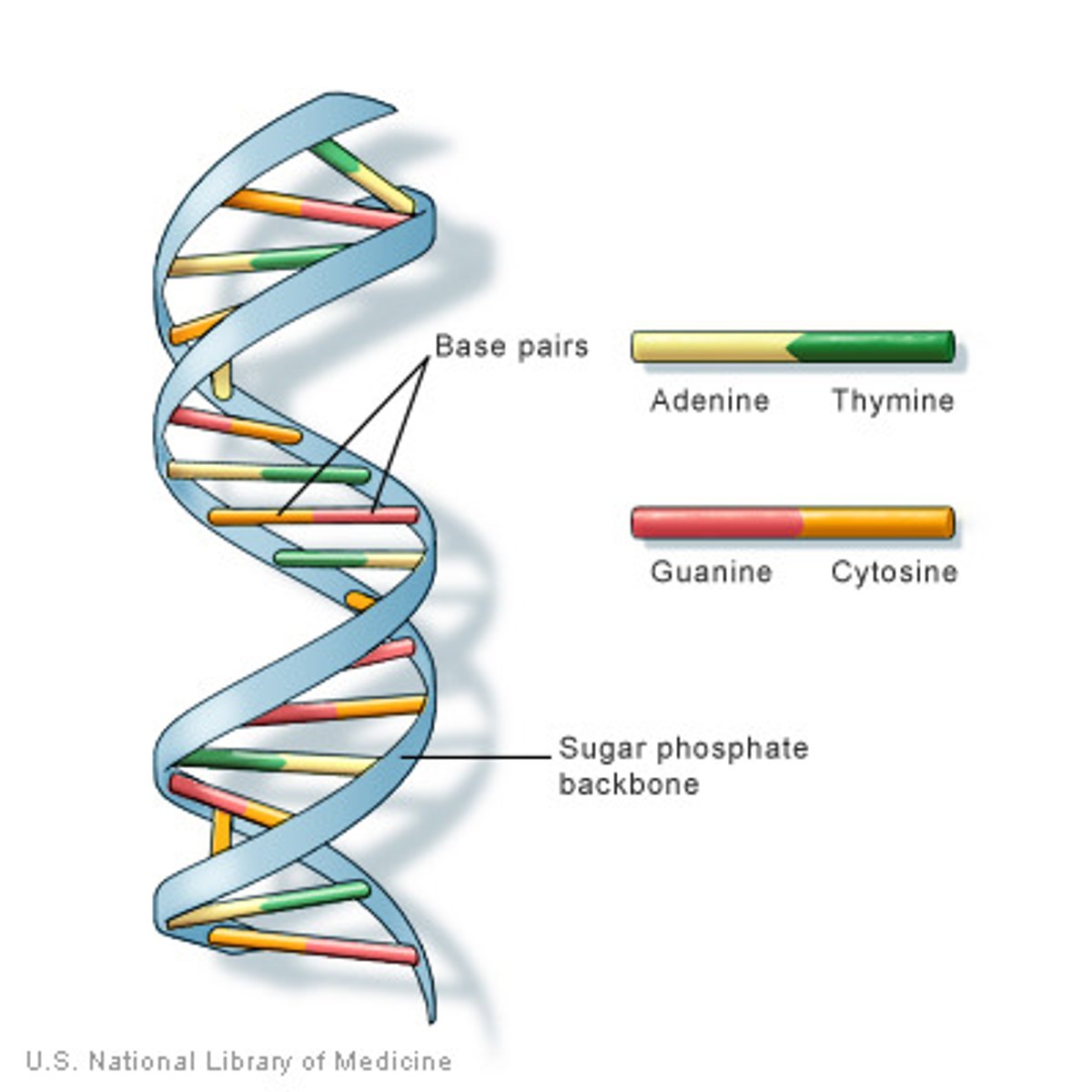
double helix
two strands of dna interact with each other through hydrogen bonds to form this structure
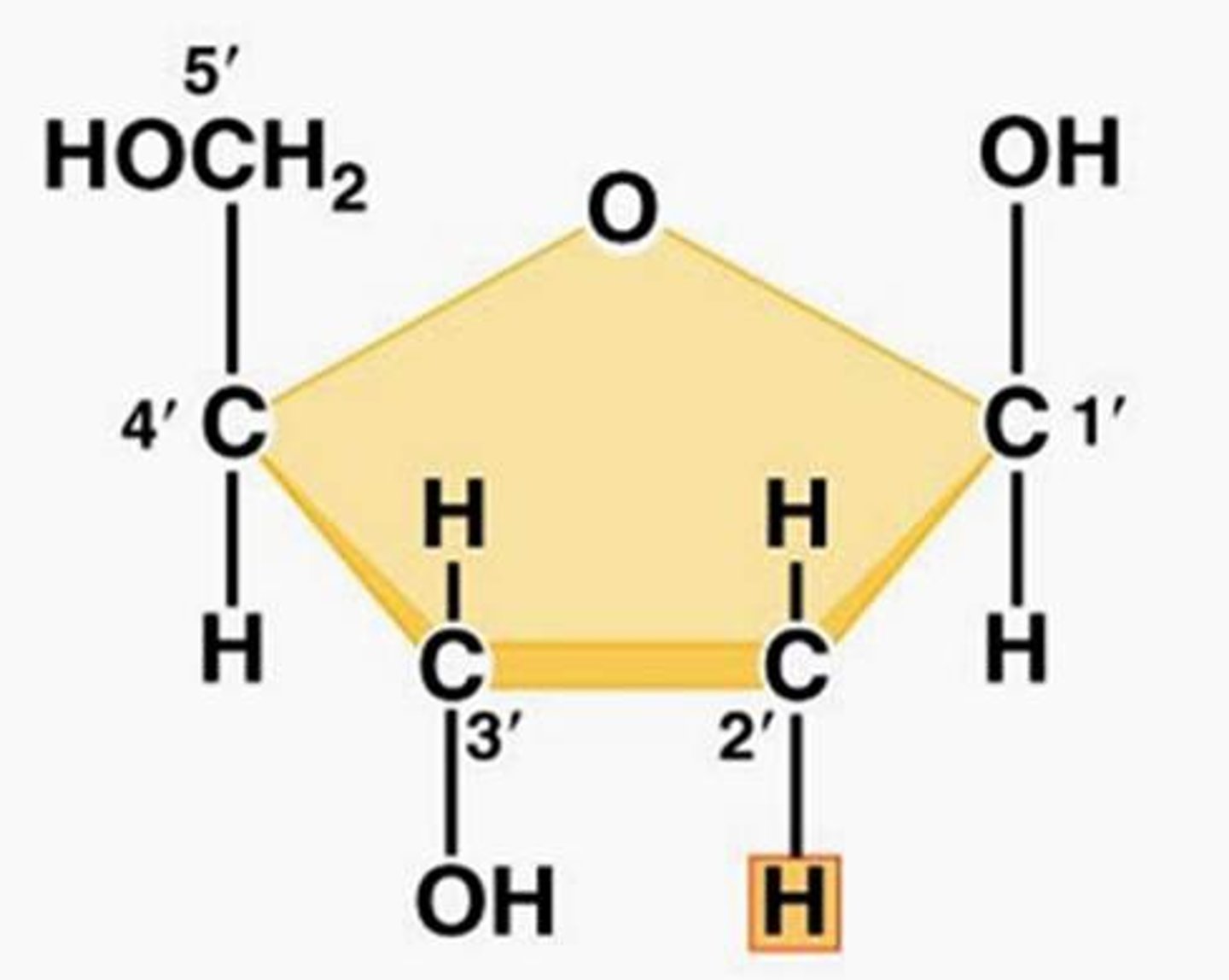
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
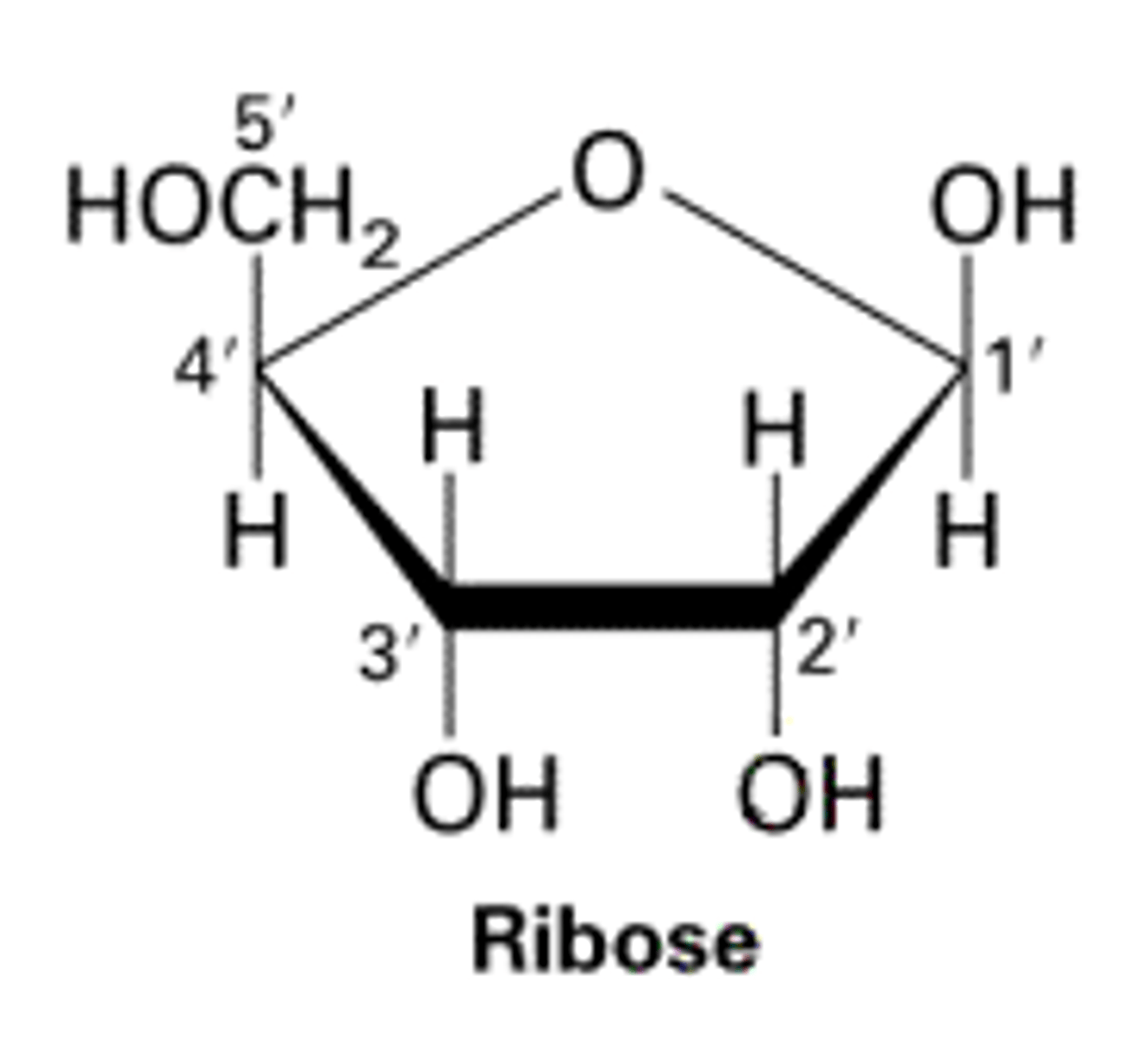
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
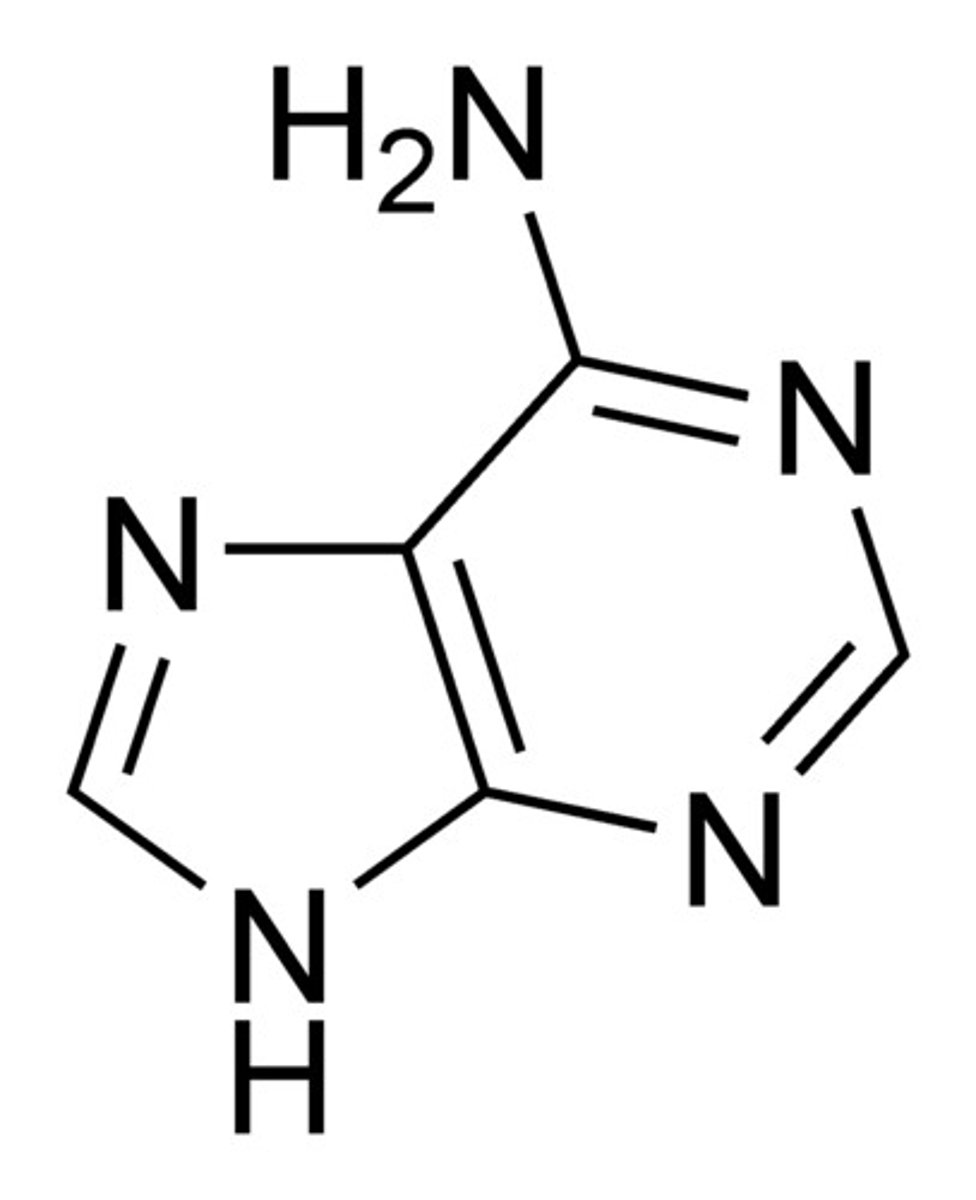
Adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA, and Uracil in RNA
purine
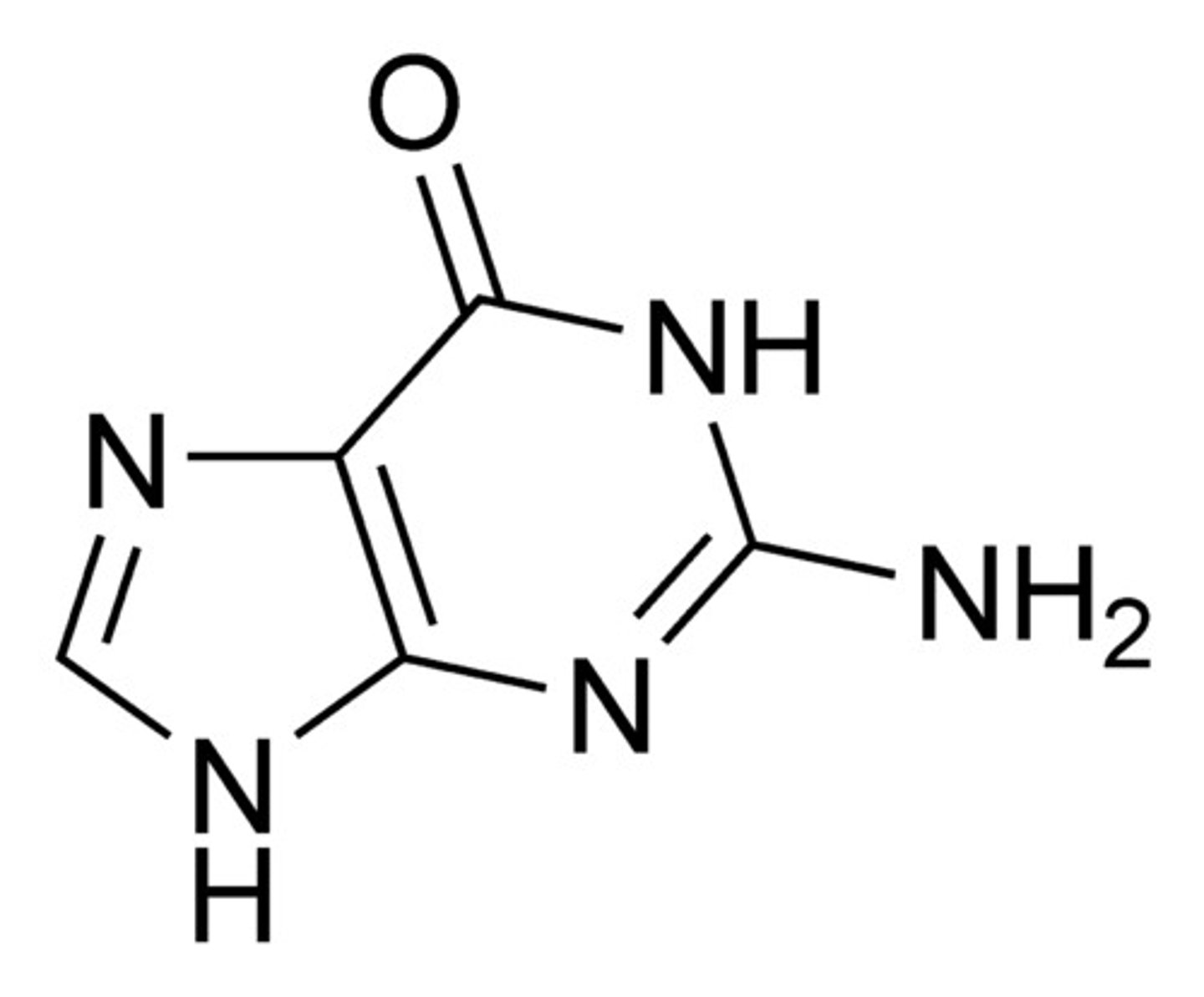
Guanine
The base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA
purine
Cytosine
The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA
pyrimidine
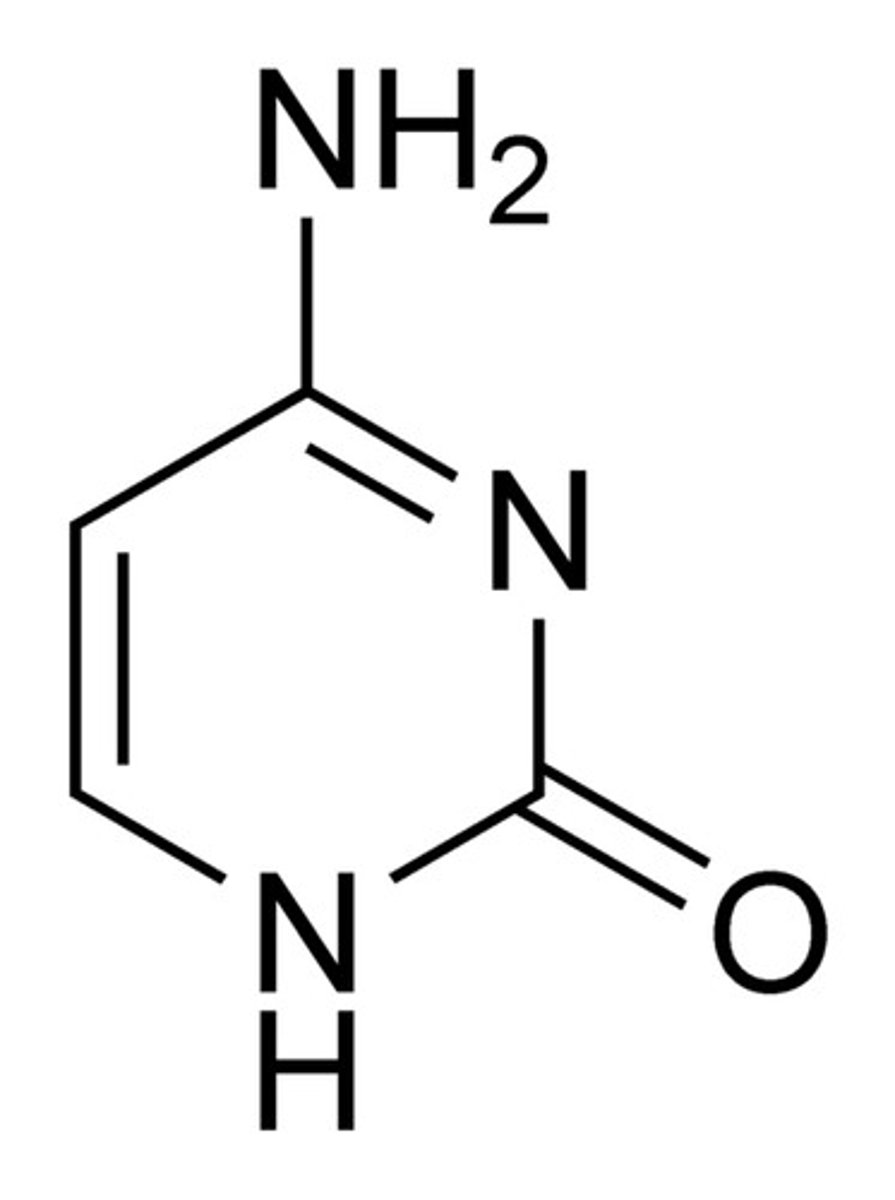
thymine
A component of nucleic acid that carries hereditary information in DNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
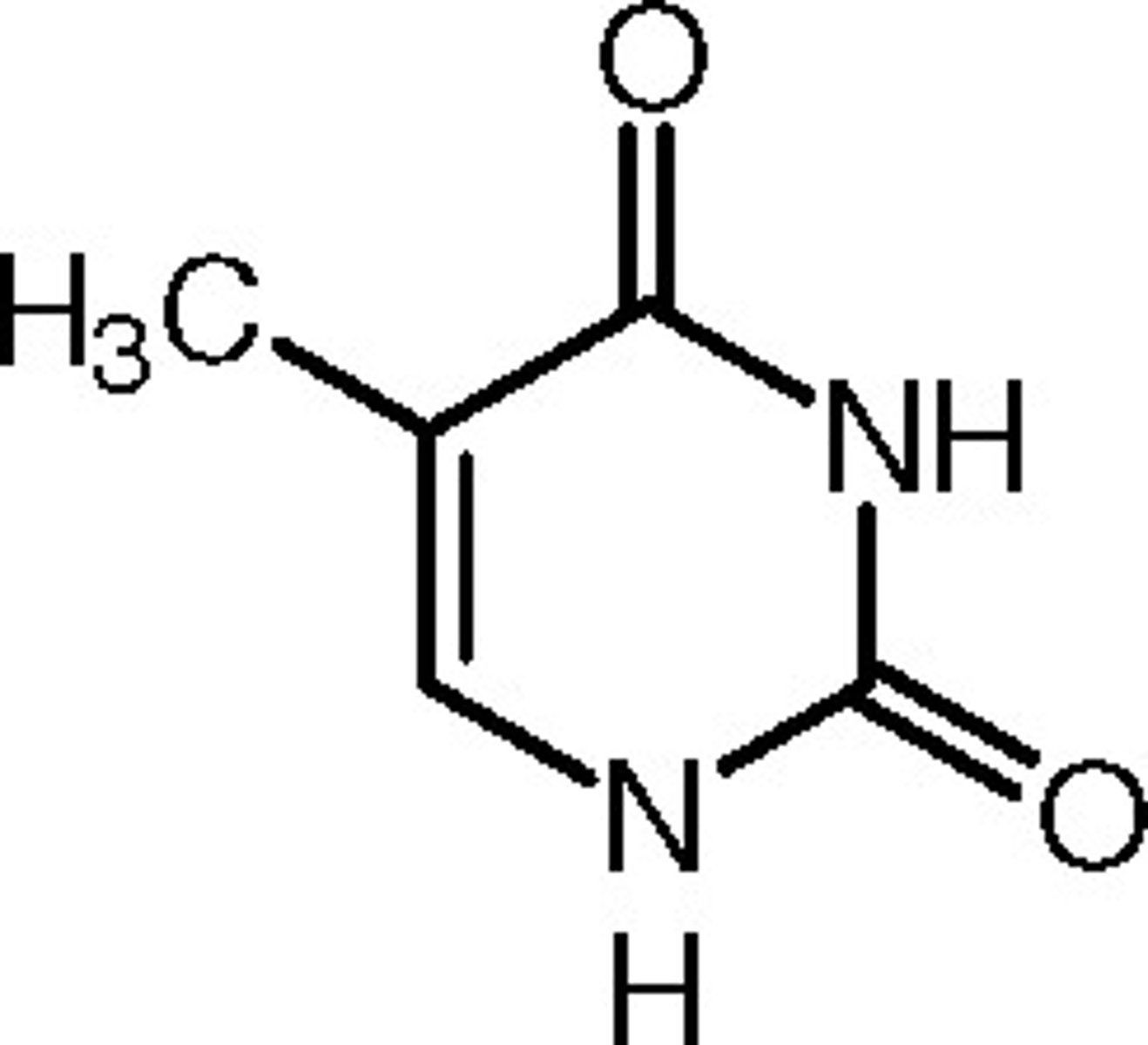
uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA) and derived from pyrimidine
clockwise
which direction are deoxyribose and ribose numbered where the fifth carbon is outside the ring
1'
which carbon is the nucleotide connected to
5'
which carbon are phosphate groups attached to
3'
which carbon has an OH group attached to it which is important in linking nucleotides to form covalent linkages.
Nucleoside
base + sugar
guanosine
guanine + ribose
cytidine
cytosine + ribose
uridine
nucleoside of uracil
adenosine
a nucleoside; a combination of ribose
deoxyadenosine
Adenine + deoxyribose
deoxyguanosine
Guanine + Deoxyribose
deoxythymidine
thymine + deoxyribose
deoxycytidine
cytosine + deoxyribose
ester bond
how are sugar groups attached to a phosphate group
phosphodiester linkage
a phosphate group connects two sugar molecules via two ester bonds
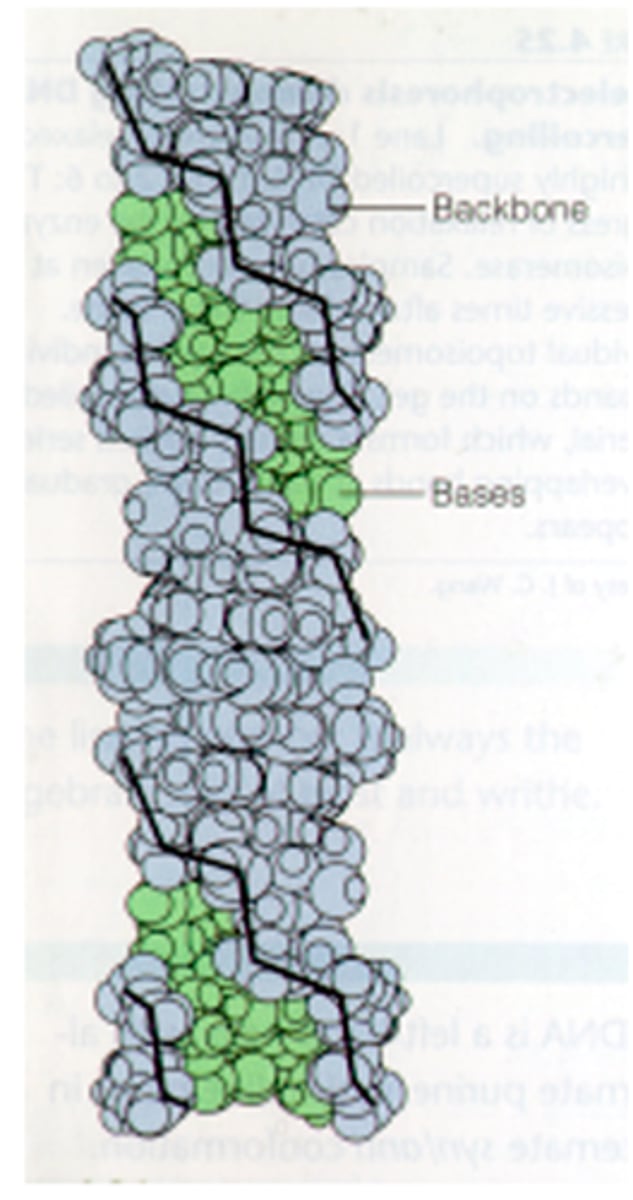
backbone
the phosphates and sugar molecules of a strand
directionality
all sugar molecules have the same orientation in a strand in the direction of 5' to 3'
ball and stick model
a molecular model that proved the alpha helix secondary structure of proteins which was a step in discovering the shape of dna
X-ray diffraction
when a purified substance such as dna is subjected to x-rays it produces a well defined diffraction pattern if the molecular structure has a repeating pattern
- helped discover the double helix shape of DNA
- determine 10 bp per rotation
AT GC rule
the number of A nucleotides = the number of T and G=C
2
how many hydrogen bonds are within A-T linkage
3
how many hydrogen bonds are between G-C
Chargaff's Rule
A=T and C=G
- helped determine the shape of DNA by helpind watson and Crick build a ball and stick model of DNA
Base pairs
stabilizes a double helix through hydrogen bonding
there are 10 of these in one 360 degree turn of a double helix
antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
Base Stacking
Stabilizing hydrophobic interactions between bases in the same strand of DNA.
- structural feature stabilizes the double helix by excluding water molecules which are polar.
- DNA molecules are oriented so that the flat sides of the bases are facing each other
Grooves
indentations where the atoms of the bases are in contact with the surrounding cellular fluid
minor groove
A smaller groove that spirals around the DNA double helix.
major groove
the larger of the two grooves in the DNA double helix
B DNA
Right-handed helical structure of DNA that exists when water is abundant; the secondary structure described by Watson and Crick and probably the most common DNA structure in cells.
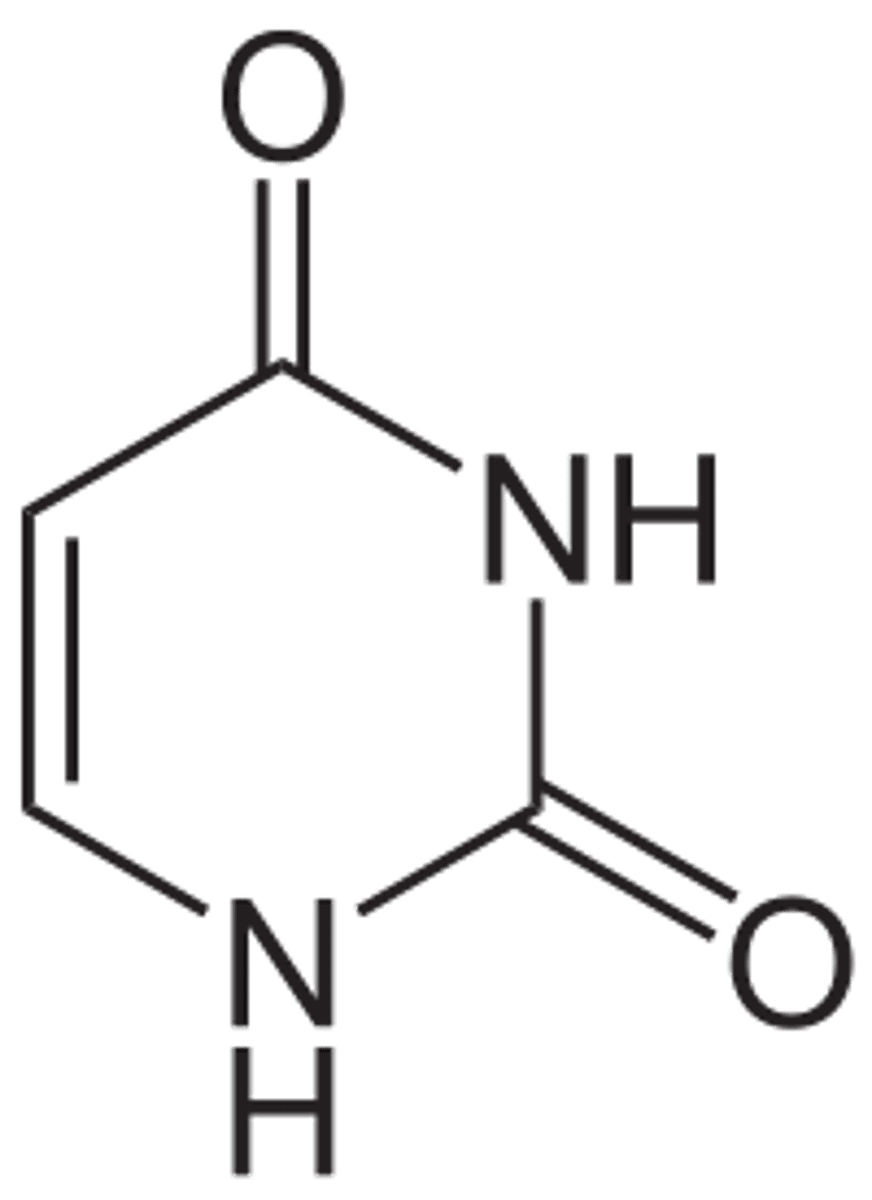
Z DNA
Secondary structure of DNA characterized by 12 bases per turn, a left-handed helix, and a sugar-phosphate backbone that zigzags back and forth.
- plays a role in transcription (certain proteins recognize it)
-affects level of compaction
Methylation
a biochemical process that influences behavior by suppressing gene activity and expression
- occurs when cytosine group attaches to a methyl group
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
acceptor site
binds incoming aminoacyl-tRNA
RNA world
period on earth in which RNA molecules but not DNA or proteins were replication and is carried out by three key functions
1- information storage in its nucleotide base sequence
2- self replication by functioning as a ribozyme and using RNA as a template to make complementary RNA molecules
3- Catalytic activity
glycocidic bond
bond between monosaccharides
- this is how base pairs are connected
three
how many atoms does it take to make a hydrogen bond
greater catalytic potential
why did proteins replace RNA
Glycocydic bond
bond between a base and a DNA or RNA sugar