Psych 207 - Module 1: History, Methods, Paradigms
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Empiricism
Supported by john Locke, David Hume, and Stuart Mill Believe that knowledge comes from individual's own experience
Acquired from the observation and analysis of events that we experience
Humans are born with a blank slate and knowledge is acquired through their interactions with their environment
Nativism
Emphasizes roles of biological factors in determining one's cognitive abilities
View comes from traditions of Descartes and Kant
Attribute individual cognitive differences to innate abilities
Argue that many cognitive abilities and the processes that underlie them are hardwired in the brain and thus difficult to modify with experience
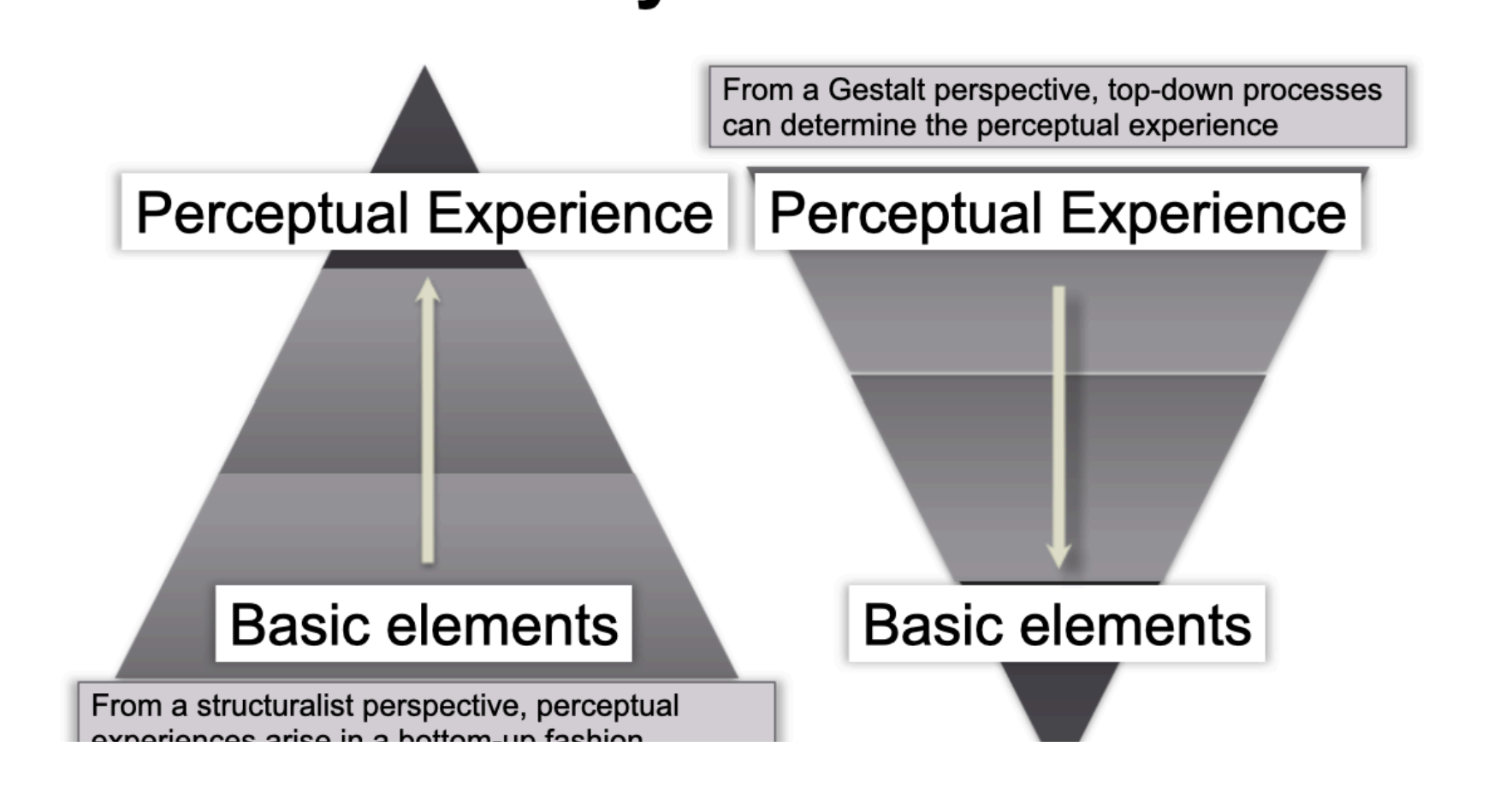
Structuralism
Wilhelm Wundt
Primary goal was to discover elemental components of human mind
Mode, quality, intensity, and duration = blocks of conscious experience
Once identified, could be used to understand how these units combine to produce complex experiences
Structuralists → laboratory
James Baldwin vs. William James
James Baldwin
Primarily used introspection: presenting highly trained observers with various stimuli and asking them to describe their conscious experience (but this is limited by consciousness)
William James
Polar opposite
Primary goal to describe the functions of the mind, instead of structural units (functionalism)
Functionalists → get out of lab and study organism in real life experiences
Behaviorism
Only study what is observable
Study of learning
Relationship between inputs and outputs
Unfashionable to talk about mental representations, consciousness or mental states
Responsible for the development of rigorous research methods
Gestalt Psychology
Phenomena had to be analyzed and studied in their entirety and could not be reduced to simple elements
Argued that observers did not construct a perceptual experience or conscious cog experience based purely on simple elemental sensory aspects of experience. But the total structure is perceived as a whole
Caption: (From a structuralist perspective, perceptual experiences arise in a bottom up fashion)
Sir Francis Galton
Intellectual abilities subject to same pressures of natural selection and thus inherited
Invented cog ability tests
Mental imagery as a cog ability
Work on genetic basis of psychology inspired a great research boom in this direction
Precursors to the Cognitive Revolution
Human factors engineering presented new problems that needed solutions → machinery designed with human limits in consideration
Developments in the field of linguistics (importance of how people acquire, understand and produce language -behaviorism does not explain language, For example, children say sentences they never heard before as well as incorrect sentences/ innate capacity to acquire language
Developments in neuroscience, specifically the localization of function in the brain
Development of computers and artificial intelligence systems - Compute metaphor of the mind
Developments in neuroscience - Donald Hebb / Donald Hubel and Torsten Weisel
Donald Hebb --> visual perceptions and some otjher functions were constructed over time by building cell assemblies
Donald Hubel and Torsten Weisel --> specific cells in visual cortex of cats were specialized to respond to specific kinds of stimuli --> early experience shaped brain development
Together these showed cognitive functions can be localized in specific parts of the brain
Paradigms
Paradigm refers to a body of knowledge that is structured according to what its proponents consider to be important, assumptions investigators make in studying a phenomena, and what kinds of experimental methods and measures are appropriate for investigation
Four major paradigms of Cognitive Psychology
Information Processing, Connectionist, Evolutionary, and Ecological: used by cognitive psychologists to frame their research
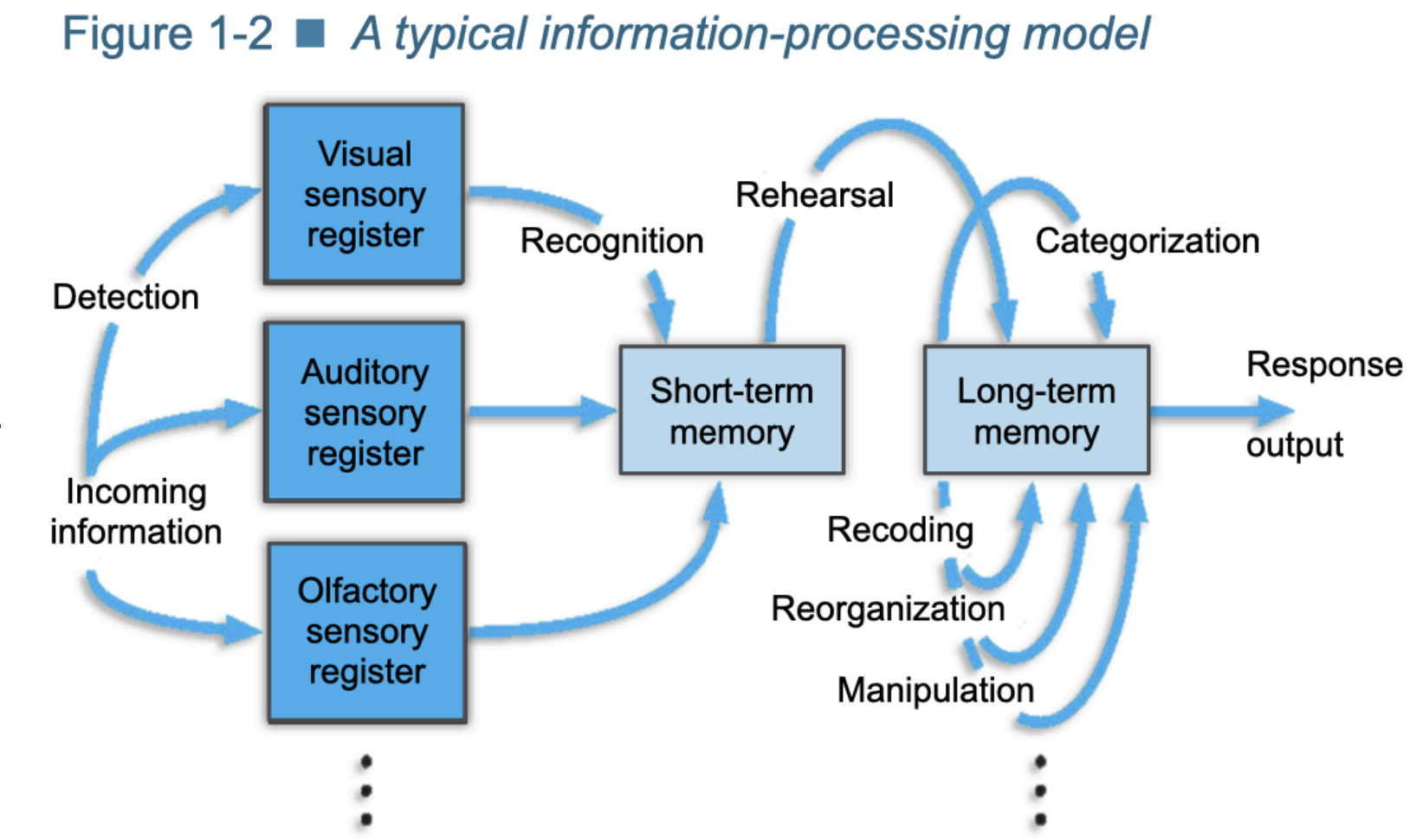
Information Processing: Mind as computer → cognition thought of as information that flows through a system (step by step)
Connectionism: cognitive machinery that underlies cognition is composed of interactions between processing units called neural networks (non-localist) (parallel)
Positively weighted connection between units → activation. Negative → inhibition
Evolutionary Approach: mind and cog processes have evolved through evolutionary mechanisms
Ecological Approach: culture and context shapes the cog processes under investigation (thus cog processes must be studied in their natural environments)