14 - Ethernet
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a signal collision?
When more than one node sends to a shared link at the same time, resulting in an undecipherable transmission
What is Medium Access Control (MAC)?
A sub-layer of the link layer which manages how a shared physical medium is used by many devices at once. It is the MAC’s responsibility to ensure availability while mitigating collisions
What is Full-Duplex?
Full-Duplex means that two ends of a link can send simultaneously (e.g., Ethernet cable.
What is Half-Duplex?
Half-Duplex means both ends of a link can send, but not at the same time (e.g., Walkie-talkie, WiFi)
What is Simplex?
Simplex means only one end of a connection can send (e.g., Broadcast TV, radio)
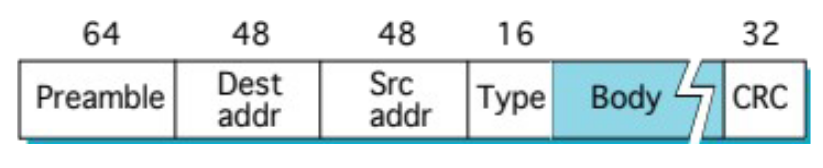
Describe the different fields of an Ethernet Frame and what they are for
Preamble (64 bits) - Used to help receiving device synchronize with incoming signal
Dest Addr (48 bits) - Destination address of 48-bit unicast address (the MAC address of the network interface card/hardware on a computer)
Src Addr (48 bits) - Same as dest addr but for sender
Type (16 bits) - Indicates the protocol of payload at the network layer, e.g., IPv4, IPv6, ARP, etc.
Body (var bits) - Payload data, minimum of 46 bytes, max of 1500
CRC (32 bits) - Cyclic redundancy check
What is unicast, broadcast, multicast communication? How does a node “send” to each?
Unicast - The intended receiver is a single host (one-to-one), sends via addresses configured on network interface
Broadcast - The intended receivers are all hosts in a network (one-to-all), sends via well-known address like FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF for Ethernet
Multicast - The intended receivers are a group of nodes in the network (one-to-some), sends via address assigned to destination group which nodes can join and leave
How does Ethernet receive frames
By default, Ethernet accepts all frames transmitted on the wire, but only gives to the OS the frames intended for the host (determined through unicast, broadcast, or multicast address), otherwise the frame is discarded.
Note: All frames can be accepted if an Ethernet adapter is put in promiscuous mode (think wireshark or tcpdump)
What is a collision domain?
A collision domain refers to a shared link by which multiple hosts compete for access to (and which sent frames can possibly “collide” with one another)
Describe CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD stands for “Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection”
CSMA: Sender listens before transmitting: if link busy, waits. Otherwise, sends, and waits 9.6 microseconds between each sent frame (to allow link to be used by others)
CD: Sender compares what it sent to what it is receiving on the Ethernet link, and if any collisions occur, a 32 bit jam signal is sent out to alert other devices of a collision, and then backs off (Binary Exponential)
Describe how Binary Exponential Backoff works (Ethernet back off)
After a collision occurs, the sender waits a random amount of time before transmitting again:
1st time: between 0 and 51.2us (randomly picked)
2nd time: between 0, 51.2us, 102.4, or 153.6us (randomly picked)
nth time: k x 51.2us for some random k in range 0 → 2n-1
Then, give up after some # of tries (default = 16)
Which does Ethernet work best under, lightly or heavily loaded networks, and why?
Ethernet works best under lightly loaded networks due to the network’s capacity is otherwise wasted at higher loads due to frequent collisions
What is the maximum number of connected hosts using Ethernet?
1024
Why are switches so useful in an Ethernet-backed network?
They completely remove collisions by packet-switching
Describe the basic idea behind Token Ring
All nodes in a network are connected in a ring topology
Frames are sent in one direction only
All frames are forwarded downstream, and when a frame reaches its destination in the ring, the host saves it and then sends the token frame back around the ring
When the token reaches the original sender, they remove their frame from the token and forward the empty token along
Summary: Hosts take turn transmitting data on the ringed network by having a circulating token dictate who can send data. Result is that hosts get round-robin access to the link
What are the general pros/cons of Token Ring?
Pros: Collisions should never occur and token is shared uniformly
Cons: Sensitive to failure points (node goes offline, token duplicates itself, etc.), not efficient for bursty traffic (all frames have the overhead of going across the entire network)