Physics Ch19 and Ch 20 Multiple Choice
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bridge, homework, and textbook GTC questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms

B. electric forces but not magnetic forces
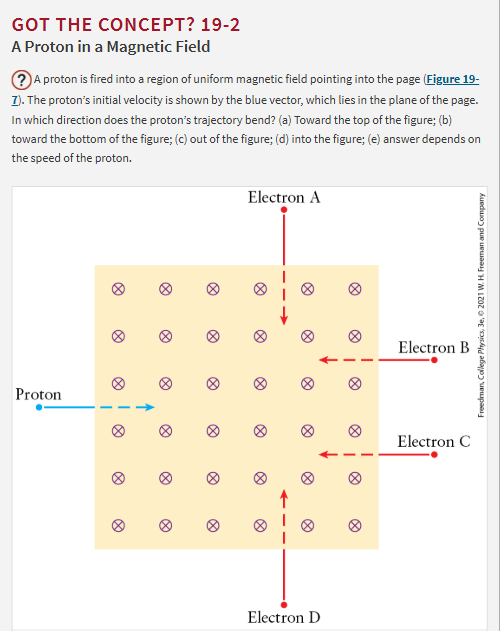
A. toward the top of the figure.

A and C
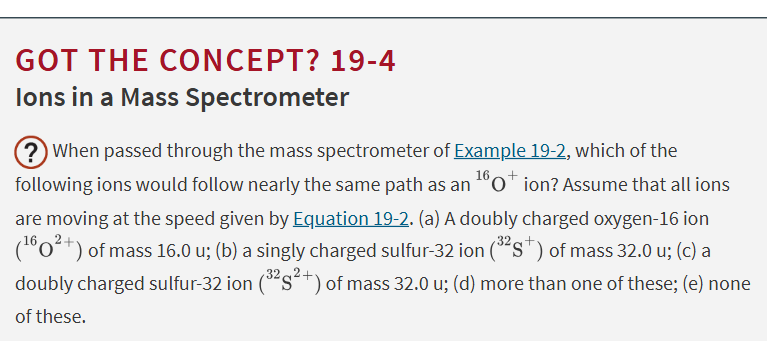
C. a doubly charges sulfur-32 ion
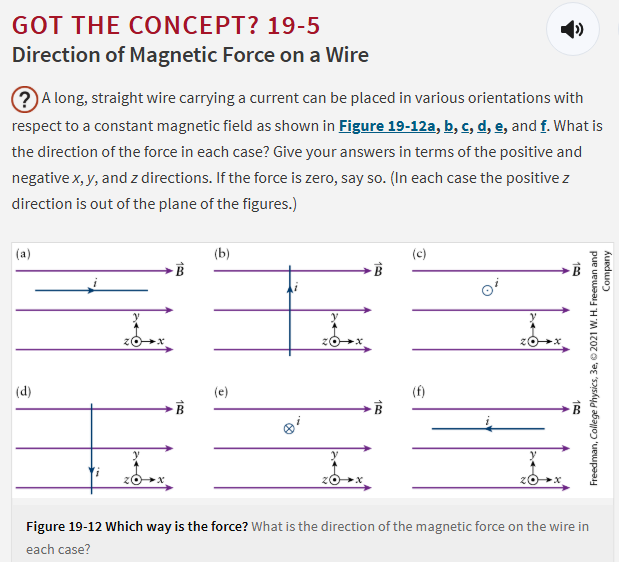
A. force is 0
B. -z
C. +y
D. +z
E. -y
F. force is 0

E. none of these
doubling the turns would double the magnetic torque but it also double the mass and moment of inertia
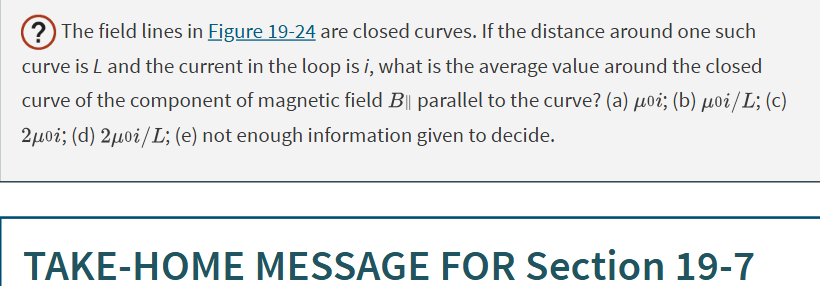
B. ui/L
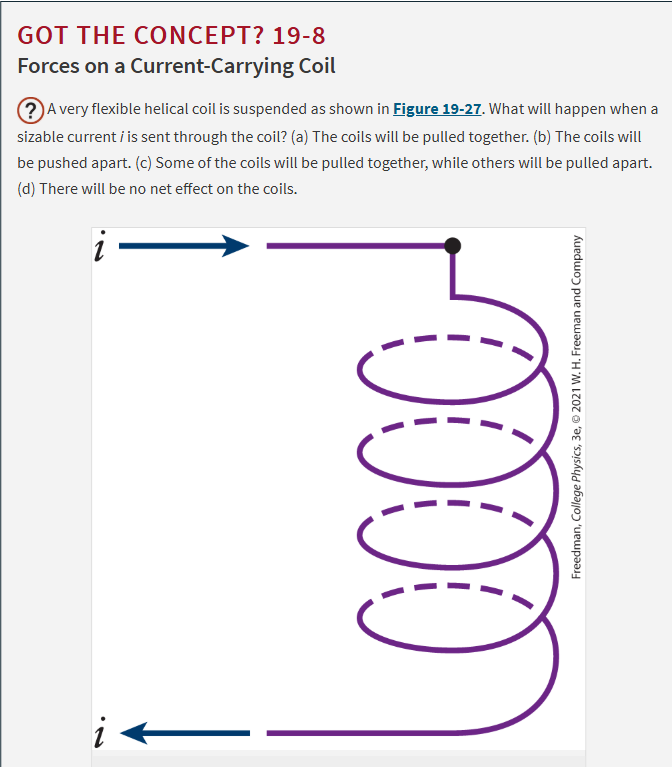
A. The coils will be pulled together
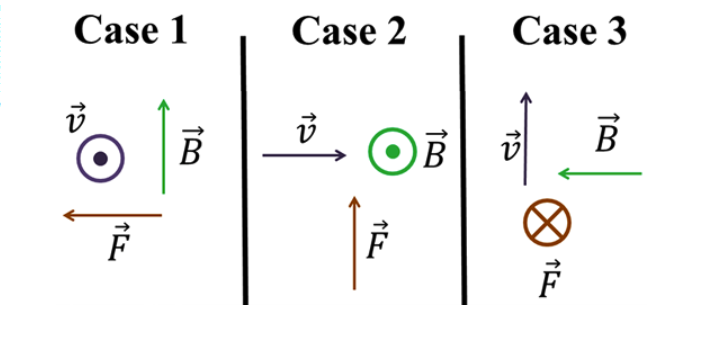
A moving charge experiences a force in the presence of external magnetic fields. The velocity, external magnetic field, and resultant magnetic forces on different charges are shown.
Which set(s) of vectors represent the magnetic force on a negative charge.
Case 2 and 3
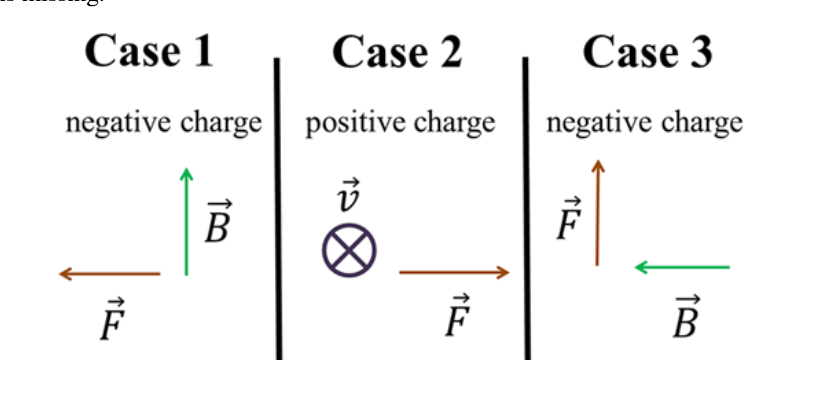
In which case is the missing vector pointing out of the plane?
Case 3
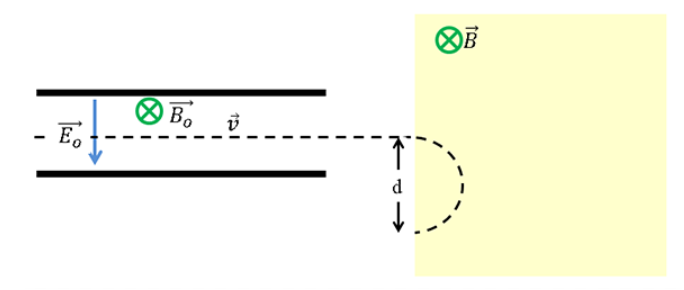
The figure shows a mass spectrometer in which negative ions that have passed through a velocity selector enter a region of uniform magnetic field.
Draw a free-body diagram of the negative ion when it is traveling inside the velocity selector.
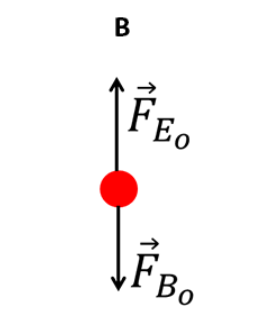
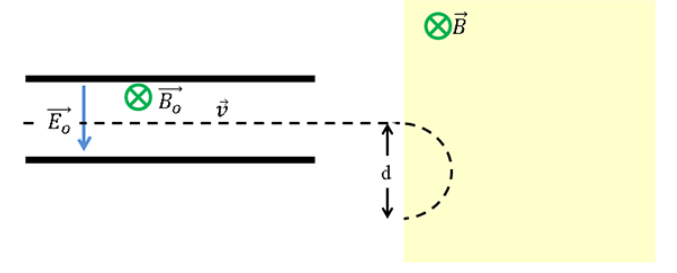
The figure shows a mass spectrometer in which negative ions that have passed through a velocity selector enter a region of uniform magnetic field.
Which of the following will decrease the distance where the ion lands after they have been deflected by the magnetic field?
A. decreasing voltage across the velocity selector
B. decreasing the strength of the magnetic field in the velocity selector.
C. flipping the direction of the magnetic field by 180 degrees in the region the ions enter after they leave the velocity selector.
A. decreasing voltage across the velocity selector
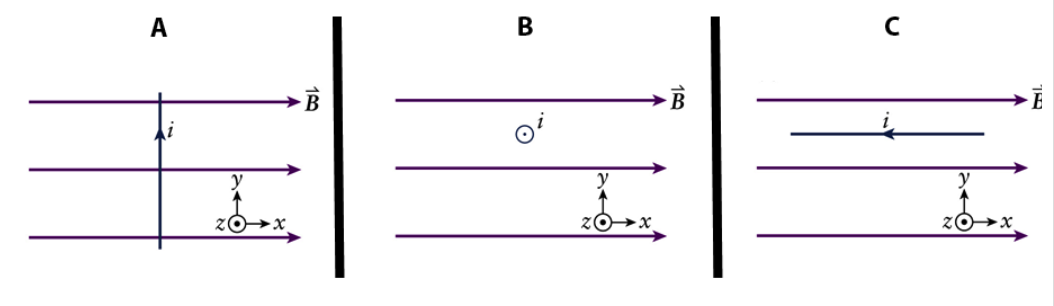
A long straight wire carrying a current in various orientation with respect to a uniform magnetic field as shown in the figures.
In which case is the direction of the magnetic force on the wire in the +y axis?
B
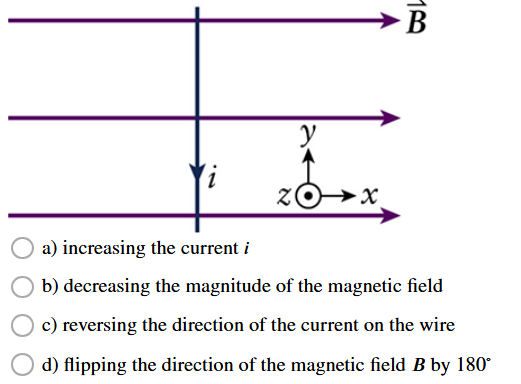
Which of the following will flip the direction of the magnetic force on the wire by 180 degrees?
either c or d
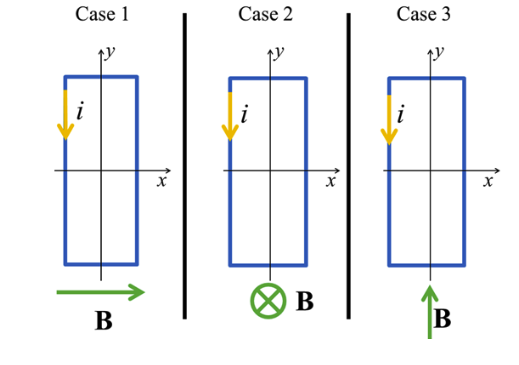
Rectangular loops of wire carrying current in the counterclockwise direction are each placed in an external uniform magnetic field as shown.
In which case will the loop rotate around the x-axis?
case 3
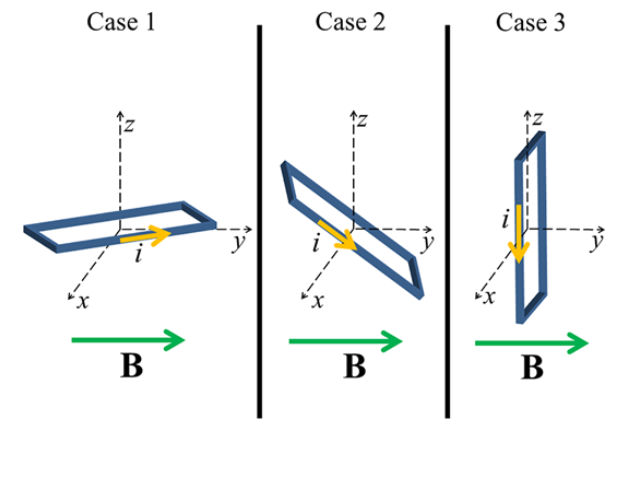
A rectangular loop of wire carrying current in the counterclockwise direction is placed in an external uniform magnetic field as shown.
In which case does the loop experience the largest net torque?
Case 1
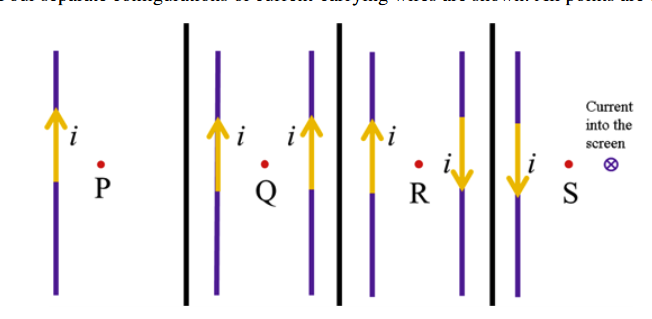
Four separate configuration sof current-carrying wires are shown. All points are equidistant with respect to the wires. At which point is the magnitude of the magnetic field the greatest?
R

Two solenoids have n windings per meter and current i. One has a diameter D and the other has a diameter of d=D/2. the direction of the current in each solenoid is shown in the figure. the small one is placed inside the larger one so that their long axes lie together. What is the direction of the net magnetic field at the center of the solenoids?
zero net field
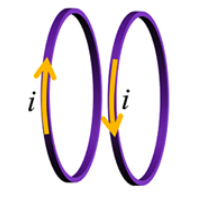
Two loops of the same dimensions carry current i in opposite directions. Will the loops repel or attract each other?
repel
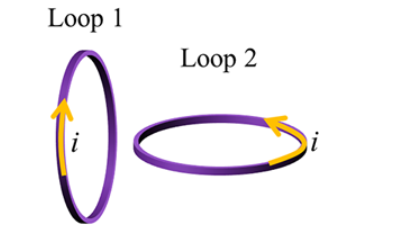
Will loop 2 rotate?
yes

No, the magnetic force always acts perpendicular to the displacement of each moving, charged particle, so the work done on each particle is always zero.

The length of the wire is oriented either parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field lines at the location of the wire.

If equal but opposite magnetic forces act at separate points on an object, and do not lie along the same line, then the forces will sum to zero but the torques generated by them will not.
An electron is moving northward in a magnetic field. the force on the electron is towards the northeast. what is the direction of the magnetic field?
situation cannot exist
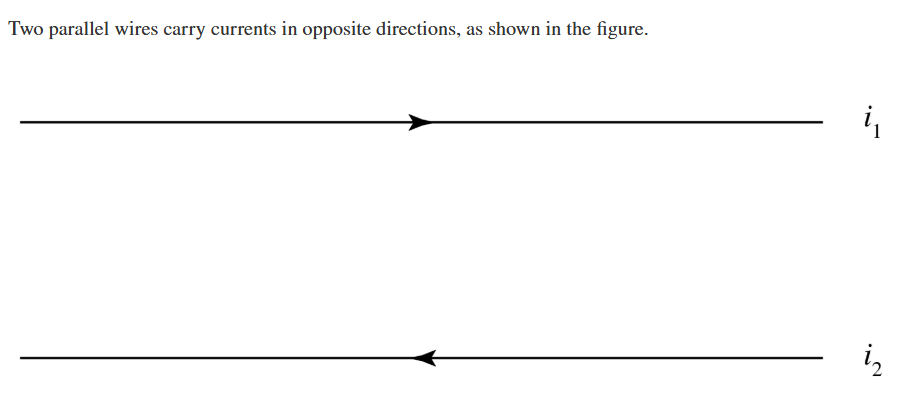
What is the direction of the forces on each wire?
The force on wire i2 is downward, and the force on wire i1 is upward
an electron moves with a velocity of 3×10^7 m/s at an angle 30 degrees above the +x axis. the magnetic field is 3T in the in the +y direction. what is the magnetic force and in which direction does it act?
F= e×v×Bsin60
F= 1.6×10^-19 C 3*10^7 m/s × 3Tsin60= 1.25×10^-11N
in the negative z-direction.
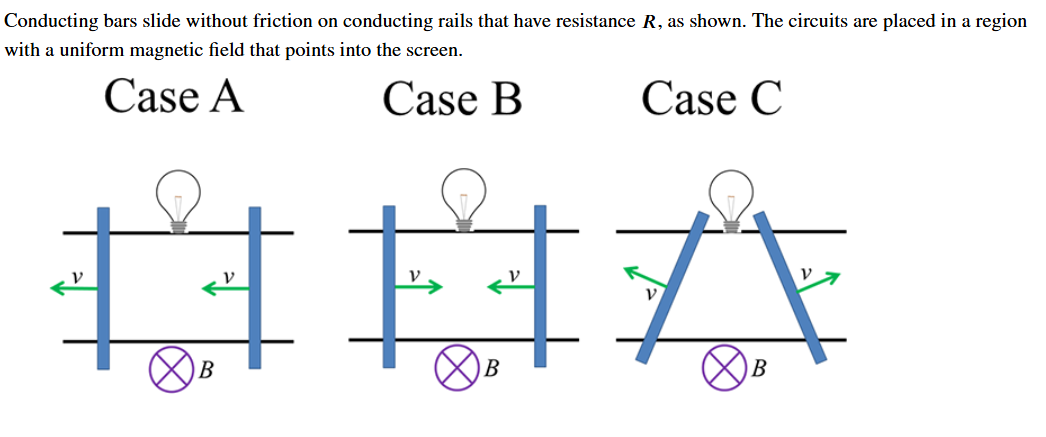
In which case/s will the bulb light?
B and C
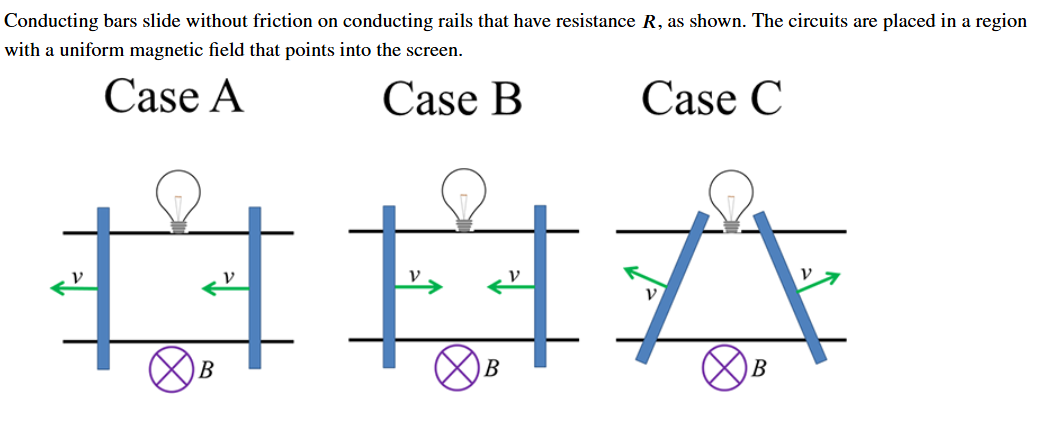
In which case will the current flow in the clockwise direction? why?
B; the magnetic flux is decreasing as the rails move towards each other. To resist this change, the current will flow in the direction that will produce a magnetic field in the same direction of the field already present.
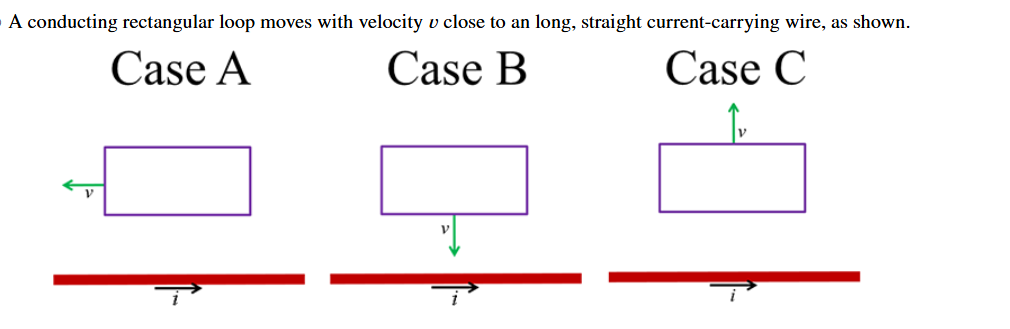
In which case does the magnetic flux increase through the loop?
B; it moved closer to the magnetic field- producing wire.
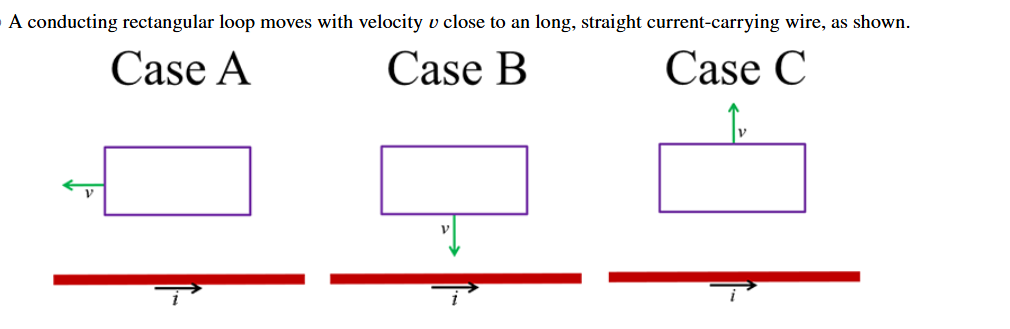
In which case does the induced current flow in the counterclockwise direction?
C; the magnetic flux is decreasing and the magnetic field felt by the wire is out of the page. the loop will produce a magnetic field also out of the page to resist this change from a counterclockwise current
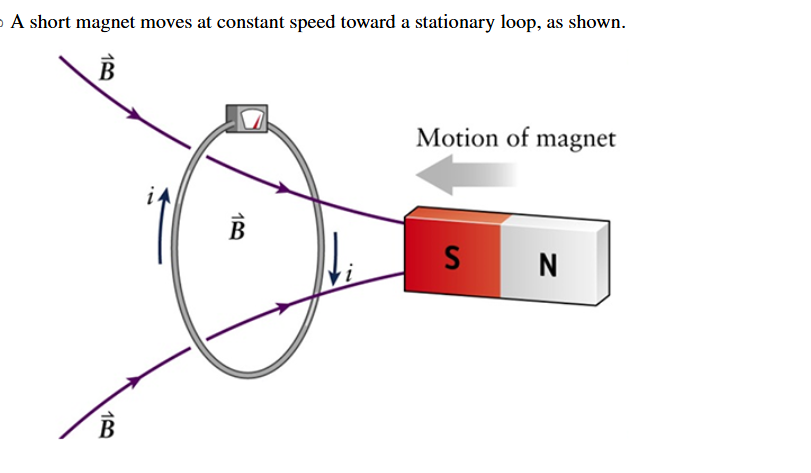
What does the plot look like of the current in the loop?
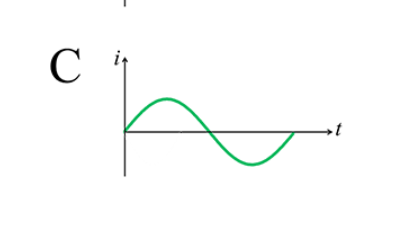
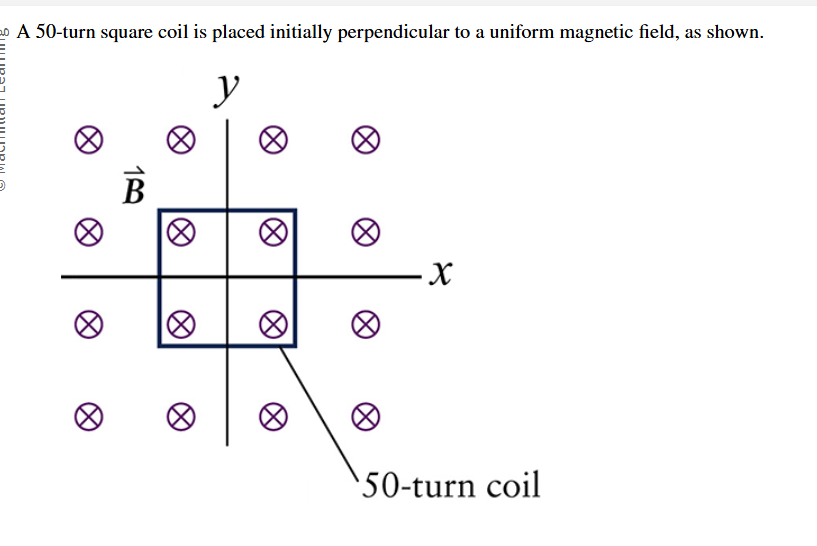
Which rotation/s will generate an alternating current in the coil?
x- and y-axis
On which variables does the magnetic flux depend?
magnetic field
area
orientation of field
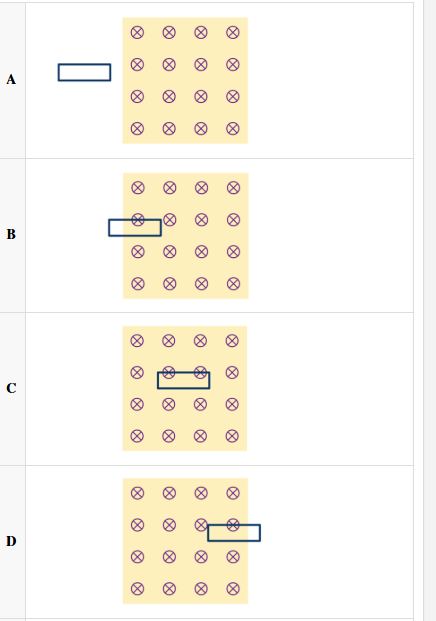
In which is the magnetic flux through the loop decreasing?
D
Why should people with implanted medical devices not enter locations with large magnetic fields?
Electronic medical devices moving in the presence of large magnetic fields experience large changes in mag. flux. The resulting induces voltages and currents are large enough to interfere with the device’s operation
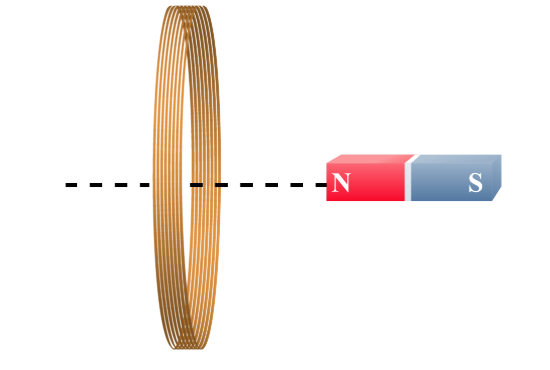
As the magnet moves to the left, in which direction will the resulting force on the magnet act?
to the right
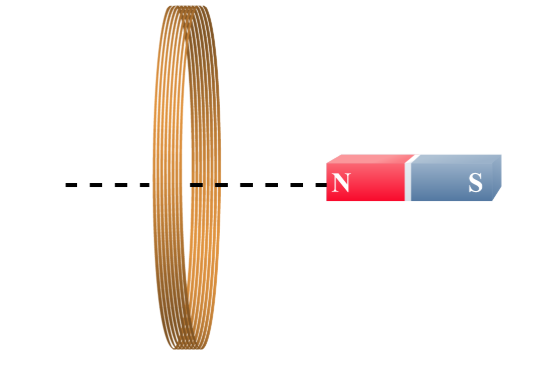
If the magnet moved to the right, in which direction will the resulting force on the magnet act?
to the left
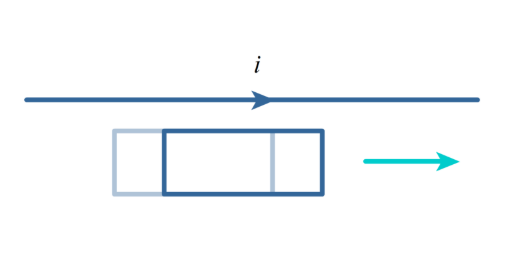
What is the induced current in the loop as it moves?
no current is induced
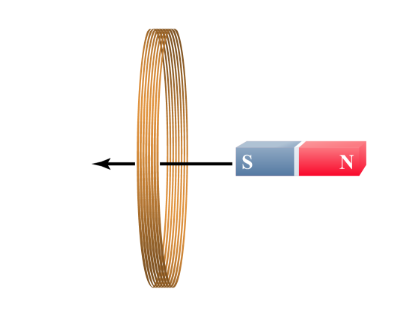
A bar magnet is moved through a stationary wire coil and an electric current flows through the wire.
What kind of force is responsible for making current flow around the coil?
electric force
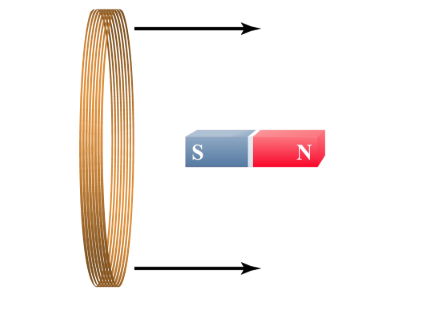
A wire coil is moved over a stationary magnet, and an electric current flows through the wire.
What kind of force is responsible for making current flow around the coil?
magnetic force