MGT 101 - Organizational Structure: Concepts and Strategic Designs
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Organizing
the process of identifying activities to be done to accomplish a goal
grouping these activities into meaningful units
assigning authority and responsibility to people for their accomplishments
Why is Organizing Important?
divides work to be done into specific jobs and departments
assigns tasks and responsibilities associated with individual jobs
coordinates diverse organizational tasks
clusters jobs into units
establishes relationships among individuals, groups, and departments
establishes formal lines of authority
allocates and deploys organizational resources
Organizing Concepts
Organizational Designing
Organizational Structure
Organizational Chart
[Organizing Concepts] Organizational Designing
determination of the most appropriate organizational structure is important here
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Designing] 6 Elements of Organizational Design
Work Specialization
Departmentalization
Chain of Command
Span of Control
Centralization and Decentralization
Formalization
[6 Elements of Organizational Design] Work Specialization
also known as division of labor
the degree to which the work necessary to achieve organizational goals is broken into various units
increases efficiency but may lead to boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increased absenteeism, reduced performance, and increased turnover
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Work Specialization] Job Designing
specification of task activities associated with a particular job
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Work Specialization] Today’s View
most managers today continue to see work specialization as important because it helps employees be more efficient
[6 Elements of Organizational Design] Departmentalization
the clustering of individuals into units and units into larger units to facilitate achievement of organizational goals
large organizations are using a combination of the different forms of departmentalization
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Departmentalization] Today’s View
customer departmentalization has become a popular choice for better understanding of their needs and use of cross functional teams
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Departmentalization] Cross Functional Teams
composed of members from the various functional departments
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] mechanistic
traditional organizational designs tend to be more _____ in nature
[6 Elements of Organizational Design] Traditional Organizational Designs
Simple Structure
Functional Structure
Divisional Structure
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Simple Structure
an organizational design with little departmentalization, wide spans of control, centralized authority, and little formalization
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Functional Structure
the grouping of positions into departments based on similar skills, expertise, and resource use
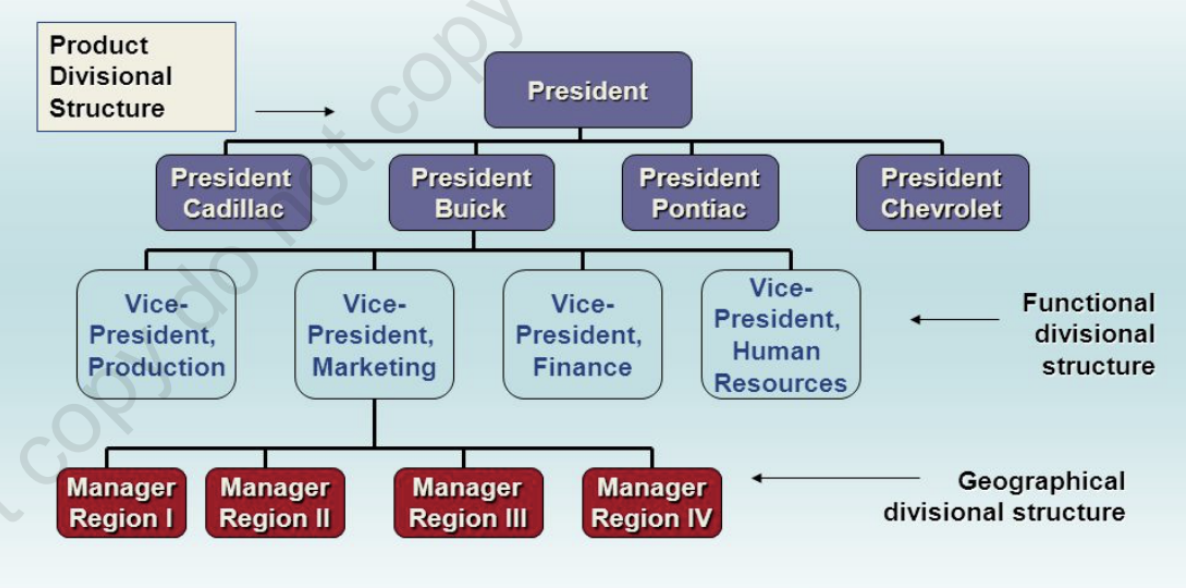
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Divisional Structure
the grouping of positions into departments based on similar organizational outputs such as product, process, and markets
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Functional Departmentalization Pros
efficiencies from putting together similar specialties and people with common skills, knowledge, and orientations
coordination with functional area
in-depth specialization
[6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Functional Departmentalization Cons
poor communication across functional areas
limited view of organizational goals
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Product Departmentalization Pros
more effective and efficient handling of specific regional issues that arise
serve needs of unique geographic markets better
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Product Departmentalization Cons
duplication of functions
limited view of organizational goals
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Geographical Departmentalization Pros
more effective and efficient handling of specific regional issues that arise
serve needs of unique geographic markets better
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Geographical Departmentalization Cons
duplication of functions
can feel isolated from other organizational areas
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Process Departmentalization Pros
more efficient flow of work activities
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Process Departmentalization Cons
can only be used with certain types of products
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Customer Departmentalization Pros
customers needs and problems can be met by specialists
6 Elements of Organizational Design | Traditional Organizational Design] Customer Departmentalization Cons
duplication of functions
limited view of organizational goals
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Structure] Definition
formal mechanism by which an organization is managed
way in which an organization’s activities are divided, organized, and coordinated
formal patterns of interaction, coordination, and linking of individuals and groups
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Structure] Advantages
efficiency gains from specialization
order arising from the clarity of job definitions
reduction of unintended gaps or overlaps in the conduct of the activities of the institutions
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Structure] Dimensions
the bases for grouping activities together
the type of authority relationships among organizational units
the coordination mechanisms used
[Organizing Concepts] Organizational Chart
a line that depicts the broad outline of an organization structure
show positions and titles, level of reporting relationship, and formal levels of communication
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Chart] each box
represents different work
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Chart] titles
represent the work performed
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Chart] solid lines
indicates reporting relationships
[Organizing Concepts | Organizational Chart] horizontal layers
indicates different levels of management
Chain of Command
unbroken line of authority that ultimately link each individual with top organizational position through a managerial position at each successive layer in between
line of authority extending from the top management to the lowest management to the lowest management level
defines who reports to whom
[Chain of Command] Authority
refers to the rights inherent in a managerial position to tell people what to do and to expect them to do it
[Chain of Command | Authority] Parity of Authority and Responsibility
if a person is responsible for accomplishing a certain task in the organization, he should be given sufficient authority to accomplish the task
[Chain of Command] Responsibility
an obligation to perform any assigned duties
[Chain of Command | Responsibility] Absoluteness of Responsibility
though a superior in an organization may delegate a portion of his authority to his subordinates, he does not reduce his responsibility or accountability for the performance of the tasks under his jurisdiction
[Chain of Command] Unity of Command
a person should report to only one manager
Span of Control
the number of employees a manager can effectively and efficiently handle
tall structure—narrow span, many hierarchical levels
flat structure—broader span, few hierarchical levels
[Span of Control] Narrow Span vs. Broad Span
close supervision and directed control
many levels of management, high cost of management staff
less independence and decision authority for subordinates
large distance between top management and bottom staff
poor executive communication and visibility
[Span of Control] Narrow Span vs. Broad Span
overloaded supervisors, loss of control
low management overhead, better operational cost and profit margins
encourages empowerment through delegation of authority and decision-making
employees have better communication with the top managements
[Span of Control] Factors Influencing the Number of Employees that a Manager can Manage Effectively and Efficiently
skills and abilities of managers and employees
characteristics and nature of work being done
similarity and complexity of employee tasks
preferred style of manager
experience level
physical proximity of subordinates
degree to which standardized procedures are in place
sophistication of organization’s information system
strength of organization’s culture
budget constraints
environmental stability
[Span of Control] Downsizing
process of significantly reducing the layers of middle management, expanding spans of control, and shrinking the size of the workforce
[Span of Control] Restructuring
process of making a major change in organization structure that often involves reducing management levels and possibly changing some major components of the organization through divestiture and acquisition
[Span of Control] Today’s VIew
The trend in the recent years is larger spans of control. With wider spans, the employees know their jobs well and when employees understand organizational processes.
Centralization
upper level makes decisions
Decentralization
lower levels are also involved in decision-making
upholds employee empowerment—giving employees more authority (power) to make decisions
More Centralization vs. More Decentralization
environment is stable
lower-level managers are not as capable or experienced at making decisions as upper-level managers
lower-level managers do not want a say in decisions
decisions are relatively minor
organization is facing a crisis or the risk of company failure
company is large
effective implementation of company strategies depend on managers retaining say over what happens
More Centralization vs. More Decentralization
environment is complex
lower-level managers are capable and experiences at making decisions
decisions are significant
corporate culture is open to allowing managers a say in what happens
company is geographically dispersed
effective implementation of strategies depends on managers having involvement and flexibility to make decisions
[Centralization and Decentralization] Today’s View
the trend is decentralization, wherein organizations have become more flexible and responsive to environmental trends (employee empowerment)
Formalization
standardization of organization’s jobs
job descriptions
numerous organizational rules
clearly defined procedures
[Formalization | Clearly Defined Procedures] Highly Standardized
explicit job descriptions, numerous organizational rules, and clearly defined procedures covering work processes
[Formalization | Clearly Defined Procedures] Low Standardized
employees have more discretion on how they do their work
[Formalization] Today’s View
some formalization is necessary for consistency and controls but rely less on strict rules and
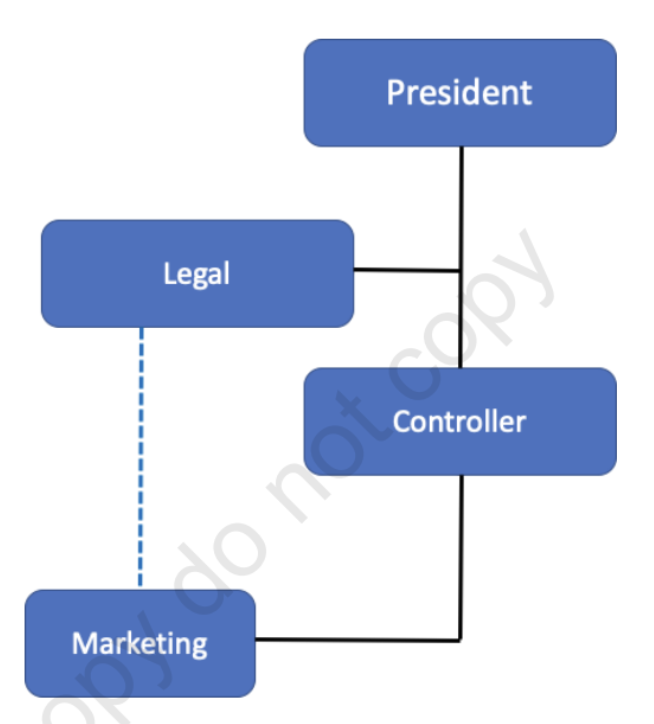
[Line and Staff Position] Line Position
a position that has authority and responsibility for achieving the major goals of an organization
[Line and Staff Position] Line Authority
authority that follows the chain of command established by formal hierarchy
such authority includes the power to supervise, direct and evaluate the work of his subordinates
[Line and Staff Position] Line Units or Departments
subdivisions or hierarchies which are directly involved in the production or distribution of the company’s products/services
[Line and Staff Position] Staff Position
a position where primary purpose is providing specialized expertise and assistance to line positions
do not exercise authority and command power over other units in the organization

[Line and Staff Position] Functional Authority
authority over other units in the organization in matters related directly to the staff department’s functions
Mechanistic Organizations vs. Organic Organizations
rigid and tightly-controlled
high specialization
rigid departmentalization
clear chain of command
narrow spans of control
centralization
high formalization
Mechanistic Organizations vs. Organic Organizations
highly adaptive and flexible
cross-functional teams
cross-hierarchical teams
free flow of information
wide spans of control
decentralization
low formalization
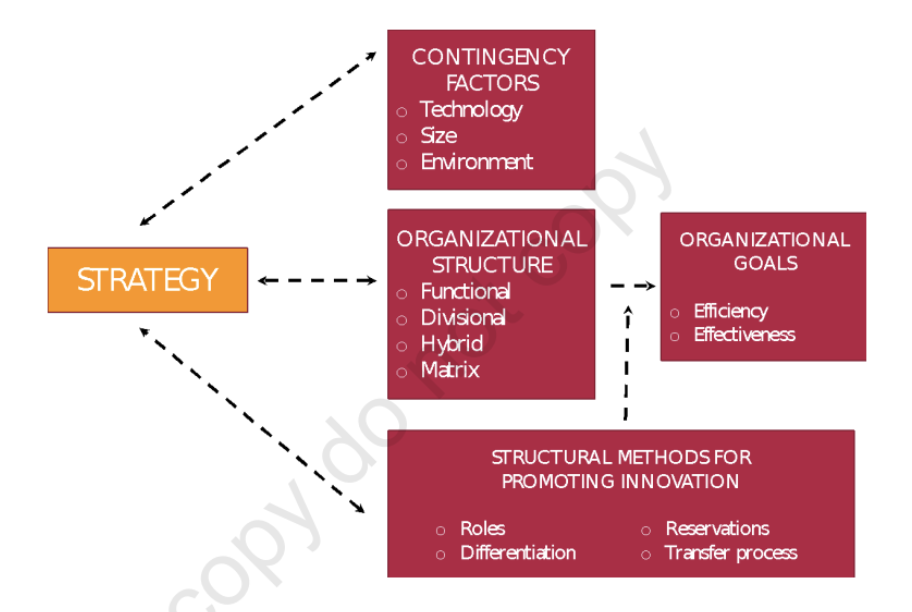
Contingency Factors to Structural Choice
strategy
size
technology
environmental uncertainty
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Strategy] Three Dimensions
innovation
cost minimization
imitation
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice] Strategy
traditionally structure follows strategy but there are modern theorists who believe otherwise
whatever the case is, structure should match strategy
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice] Size
an organization’s size affects its structure
large organizations tend to have more specialization, departmentalization, centralization, and rules and regulations than small organizations
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice] Technology
every organization uses some form of technology to convert its inputs into outputs
other studies also have shown that organizations adapt their structures to their technology depending on how routine their technology is for transforming inputs into outputs
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Technology] Unit Production
Definition: production of items in units or small batches
Model of Organizational Design: Organic
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Technology] Mass Production
Definition: large batch manufacturing
Model of Organizational Design: Mechanistic
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Technology] Process Production
Definition: continuous process production
Model of Organization: Organic
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice] Environmental Uncertainty
some organizations face stable and simple environments with little uncertainty; others face dynamic and complex environments with a lot of uncertainty
managers try to minimize environmental uncertainty by adjusting the organization’s structure
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Environmental Uncertainty] the environment-structure relationship
explains why so many managers today are restructuring their organizations to be lean, fast, and flexible
this is brought about by dynamic environmental forces such as worldwide economic downturns, global competition, accelerated product innovation by competitors, and increased demands from customers for high quality and faster deliveries.
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Strategy] Mechanistic
the mechanistic organization with its efficiency, stability, and tight controls works best for companies wanting to tightly control costs
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Strategy] Organic
flexibility and free-flowing information of the organic structure works well when an organization is pursuing meaningful and unique innovations
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Size] Mechanistic
large organizations
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Size] Organic
small organizations
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Technology] Mechanistic
more routine
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Technology] Organic
more nonroutine
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Environmental Uncertainty] Mechanistic
stable and simple environments
[Contingency Factors to Structural Choice | Environmental Uncertainty] Organic
rapid environmental change and environmental uncertainty
Strategy and Organization Structure
Contemporary Organizational Designs
Team Structure
Matrix Structure
Hybrid Structure
Virtual Organization
Network Organization
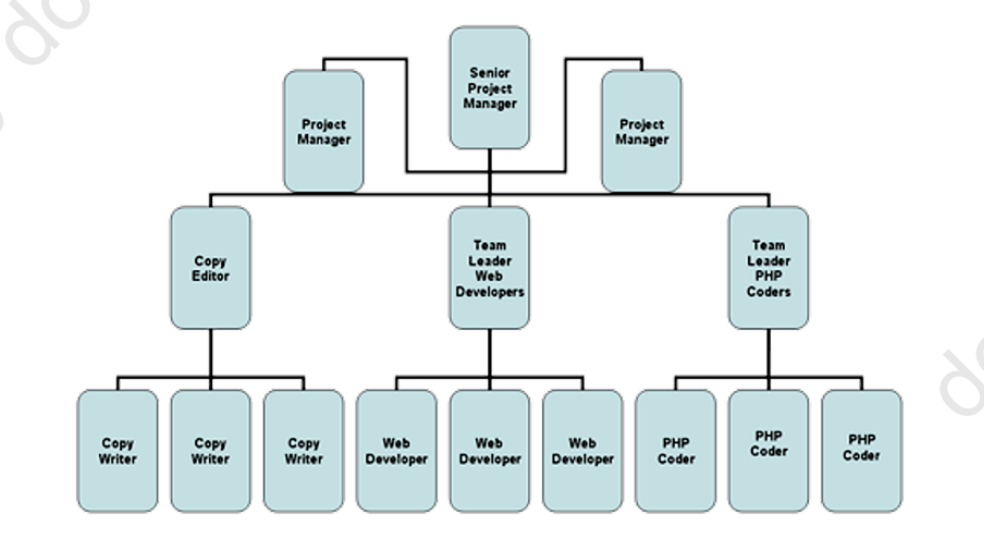
[Contemporary Organizational Designs] Team Structure
an entire organization of work teams
employee empowerment is crucial because no line of managerial authority flows from top to bottom
employee teams design and do work in the way they think is best, but the teams are also held responsible for all work performance results in their respective areas
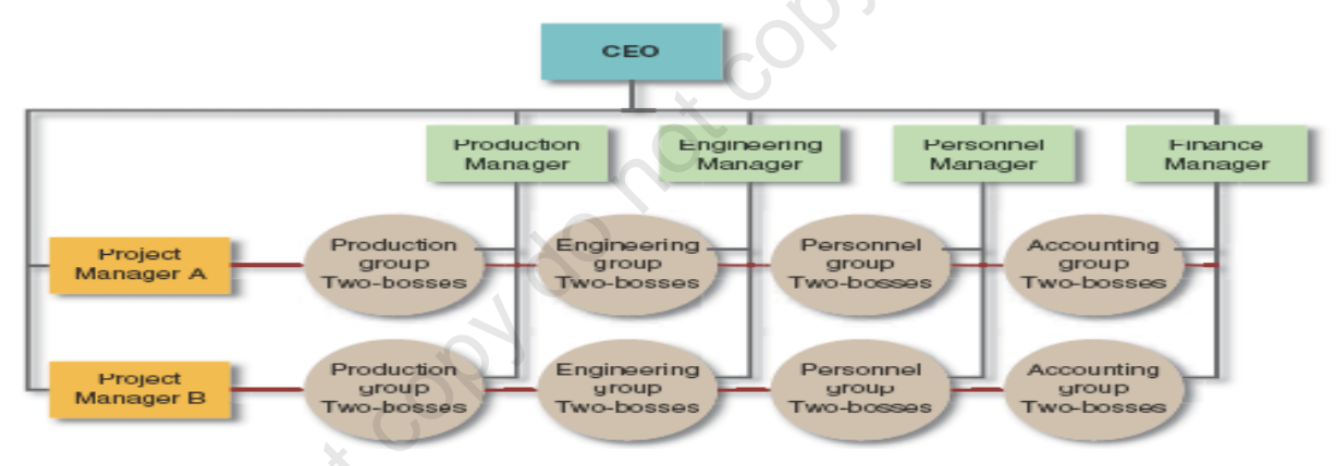
[Contemporary Organizational Designs] Matrix Structure
specialists from different functional areas are assigned to a project
functional and divisional forms overlap
managers and staff personnel report to two bosses: a functional manager and a divisional manager
[Contemporary Organizational Designs] Hybrid Structure
combines both functional and divisional structure but divides its activities into departments that can be either functional or divisional
this allows the utilization of resources and knowledge in each function, while maintaining product specialization in different divisions that makes it widely adopted by many large organizations
[Contemporary Organizational Designs] Virtual Organization
small core of full-time employees
complementary resources existing in a number of co-parenting companies are left in place, but are integrated to support a particular product effort for as long as it is justifiable to do so

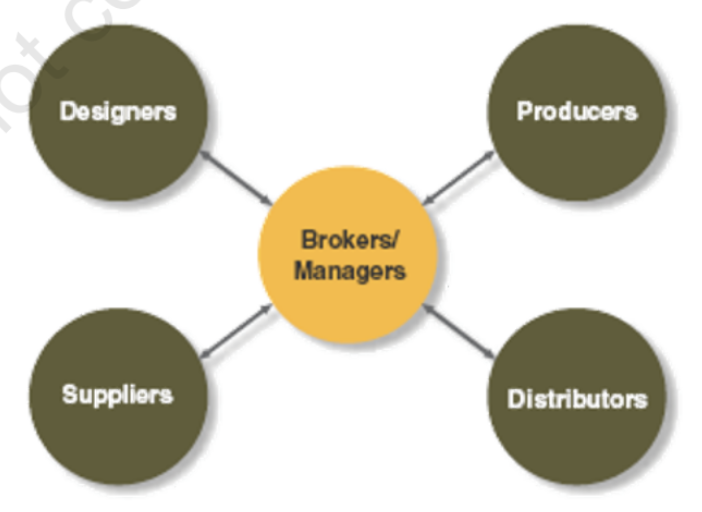
[Contemporary Organizational Designs] Network Organization
uses its own employees to do activities and network with outside employees to provide inputs and work processes
businesses driven by product development and customer service (i.e. electronics and software companies in particular), and often in smaller, younger organizations (where traditional boundaries are weaker) make use of this structure
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Team Structure] Advantage/s
employees are more involved and empowered
reduced barriers among functional areas
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Team Structure] Disadvantage/s
no clear chain of command
pressure on teams to perform
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Matrix Structure] Advantage/s
fluid and flexible design that can respond to environmental changes
faster decision-making
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Matrix Structure] Disadvantage/s
complexity of assigning people to projects
task and personality conflicts
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Hybrid Structure] Advantage/s
highly flexible and responsive
utilizes talent wherever it’s found
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Hybrid Structure] Disadvantage/s
lack of control
communication difficulties
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Virtual Organization] Advantage/s
hire many part-time workers
less expenses for office rentals, tax exemptions, facilities for your employees
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Virtual Organization] Disadvantage/s
communication with your workers
physical meeting, physical location of the business
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Network Organization] Advantage/s
strengthens linkages with other independent firms within the network
[Contemporary Organizational Designs | Network Organization] Disadvantage/s
may lead to dependence on other firms for the services being provided
Organizational Design Challenges
keeping control—how to coordinate activities of employees who are dispersed and mobile
building a learning organization—continuously learn, adapt, and change
managing global structural issues—applicability or organizational designs may vary across countries