iGCSE Geography Edexcel River Environments
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Source
The place where a river starts, usually in an area of highland.

Mouth
The place where the river ends, where it meets the sea.

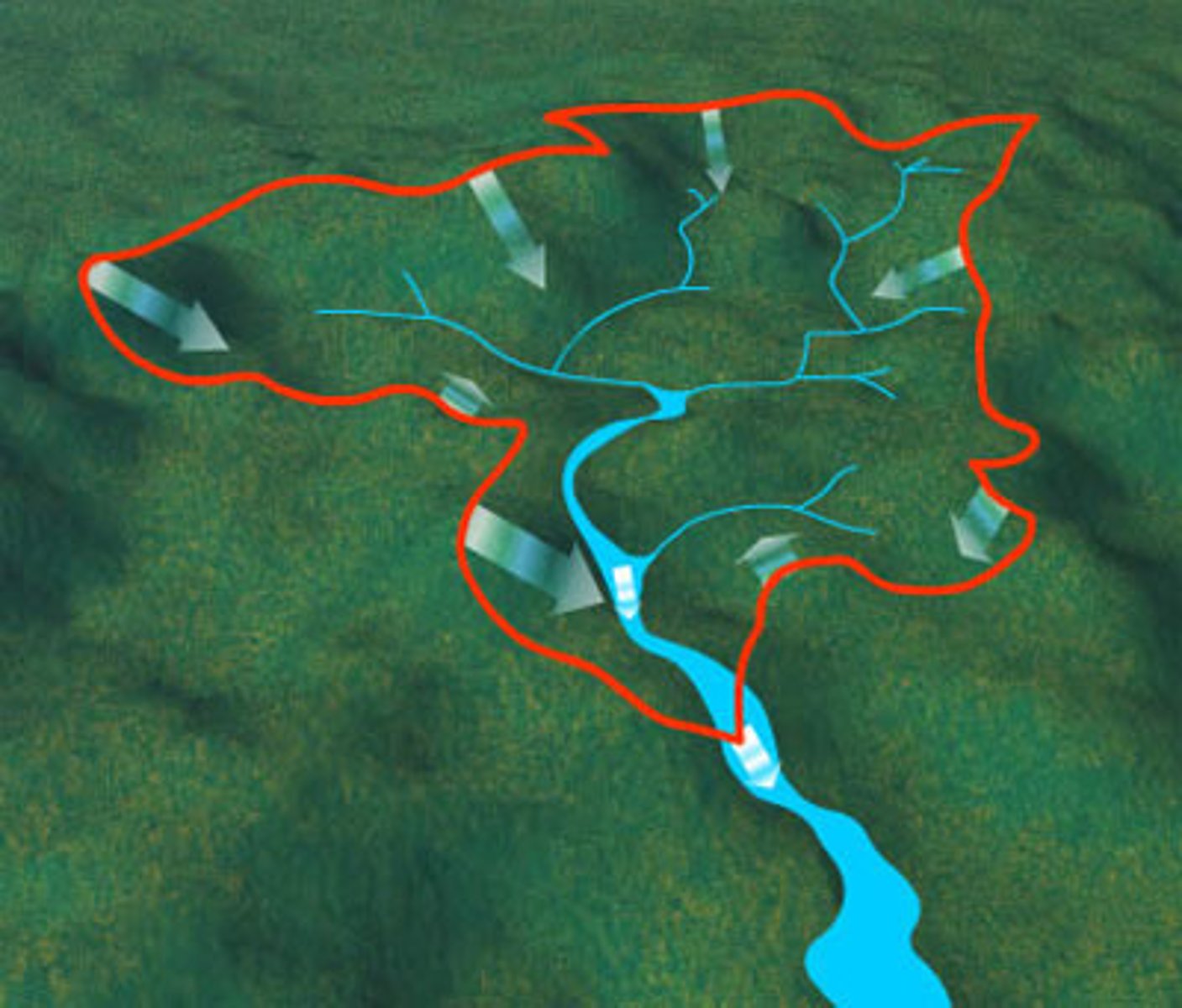
Watershed
An area of highland which separates 2 drainage basins, it marks the boundary between them.

Tributary
A smaller river which joins a larger river.

Confluence
The point at which 2 rivers meet.

Main channel
The main river.

Catchment
The area where water drains into a drainage basin.

Drainage basin
The area of land drained by a river.
Interception
When objects get in the way of a flow of water or rain.

Surface run-off
When water flows over a hard surface (e.g. a river)

Through-flow
When water flows through the rocks and underground.

Percolation
When water soaks through porous rocks or soil into the ground.

Condensation
When a gas cools and turns into a liquid. This forms clouds at high altitudes.

Transpiration
When plants release water vapour from their bodies (or more specifically the stomata in their leaves).

Precipitation
The fancy word for rain, sleet, snow, hail etc

Evaporation
When a liquid turns to a gas and rises.

The Hydrological (Water) Cycle
This cycle shows how water moves between the land, seas and atmosphere via precipitation, evaporation etc

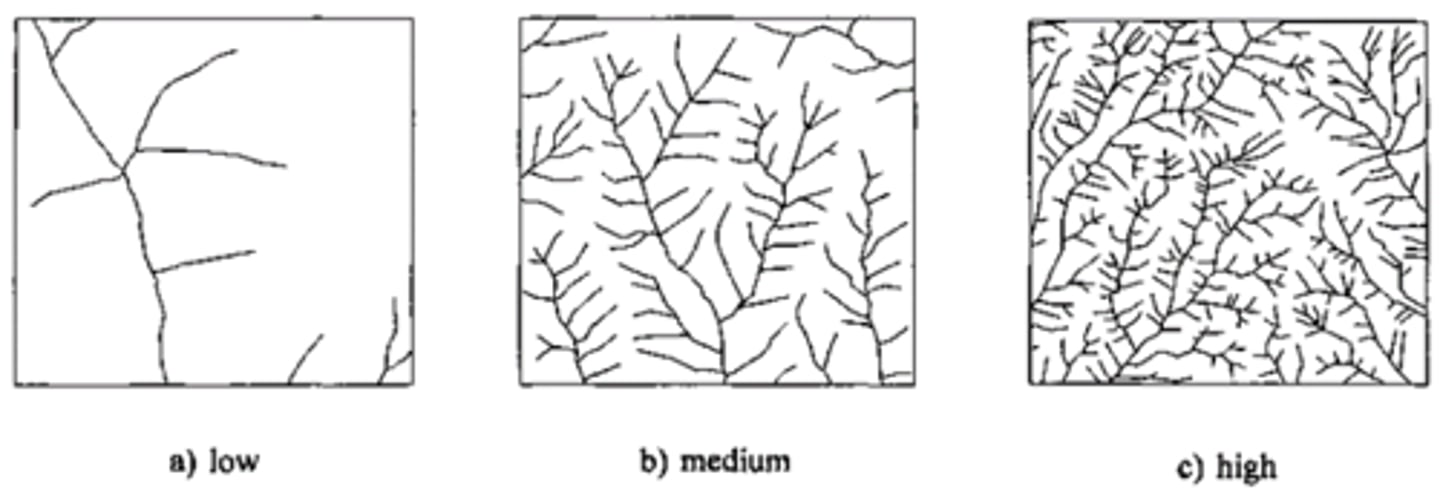
Drainage density
A measure of the amount of water in a drainage basin; it is calculated by adding up the length of all the rivers and streams and dividing it by the area of the drainage basin.
Velocity
The speed at which the river is travelling, measured in m/s.

Load
The sediment carried by the river.

Gradient
The steepness of the river.
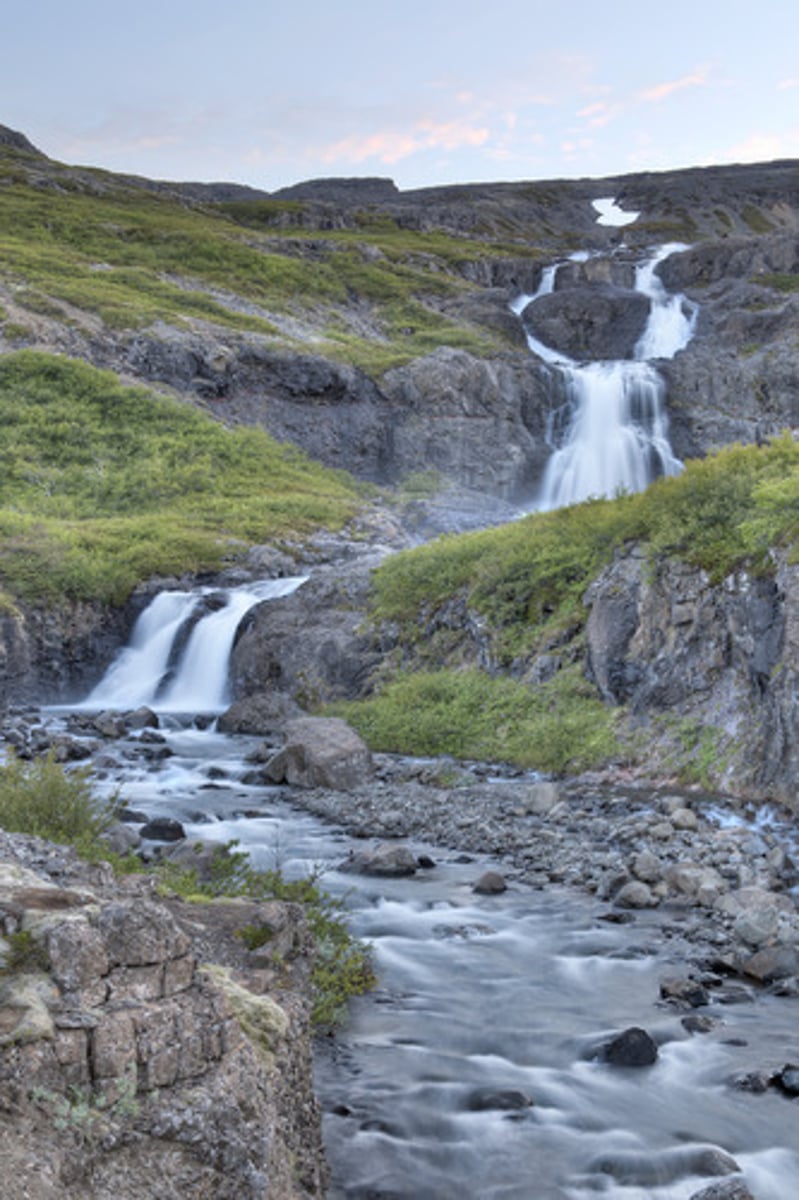

Discharge
The volume of water in the river, measured in cumecs (m3/sec).

Friction
The roughness of the bed and banks and how this impedes the water flow.

Load size
How big the sediment the river carries is called the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.

Load quantity
How much sediment the river carries is called the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.

Hydraulic action
This is a type of erosion; it is the force of the water as it slams against the bed and banks and rips chunks out of them.

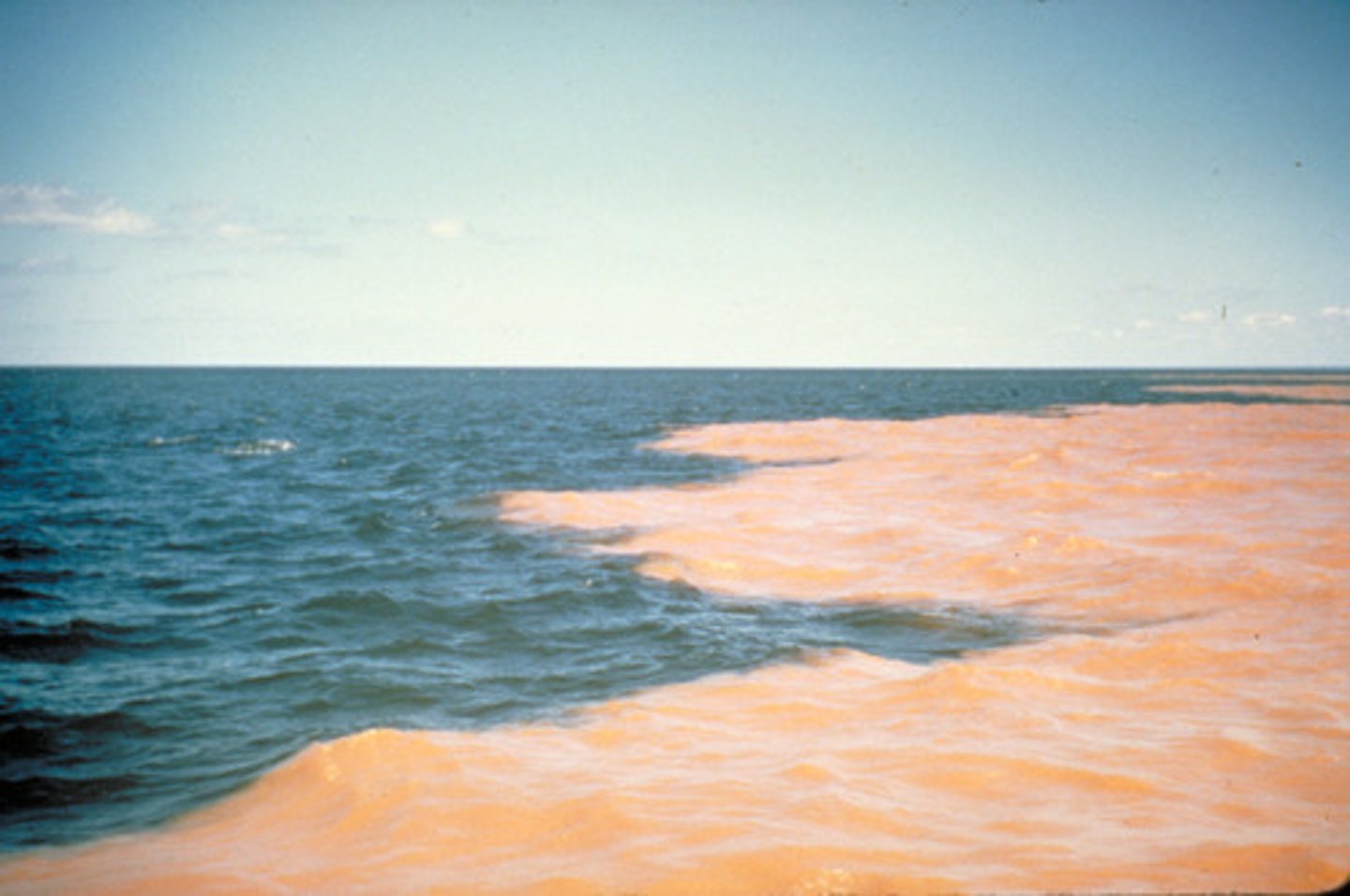
Corrasion (abrasion)
This is a type of erosion; it is when the river uses its load to scour the bed and banks which then erodes them.

Upper course
This is the name given to the start of a river's journey, here it is small, youthful and full of energy.
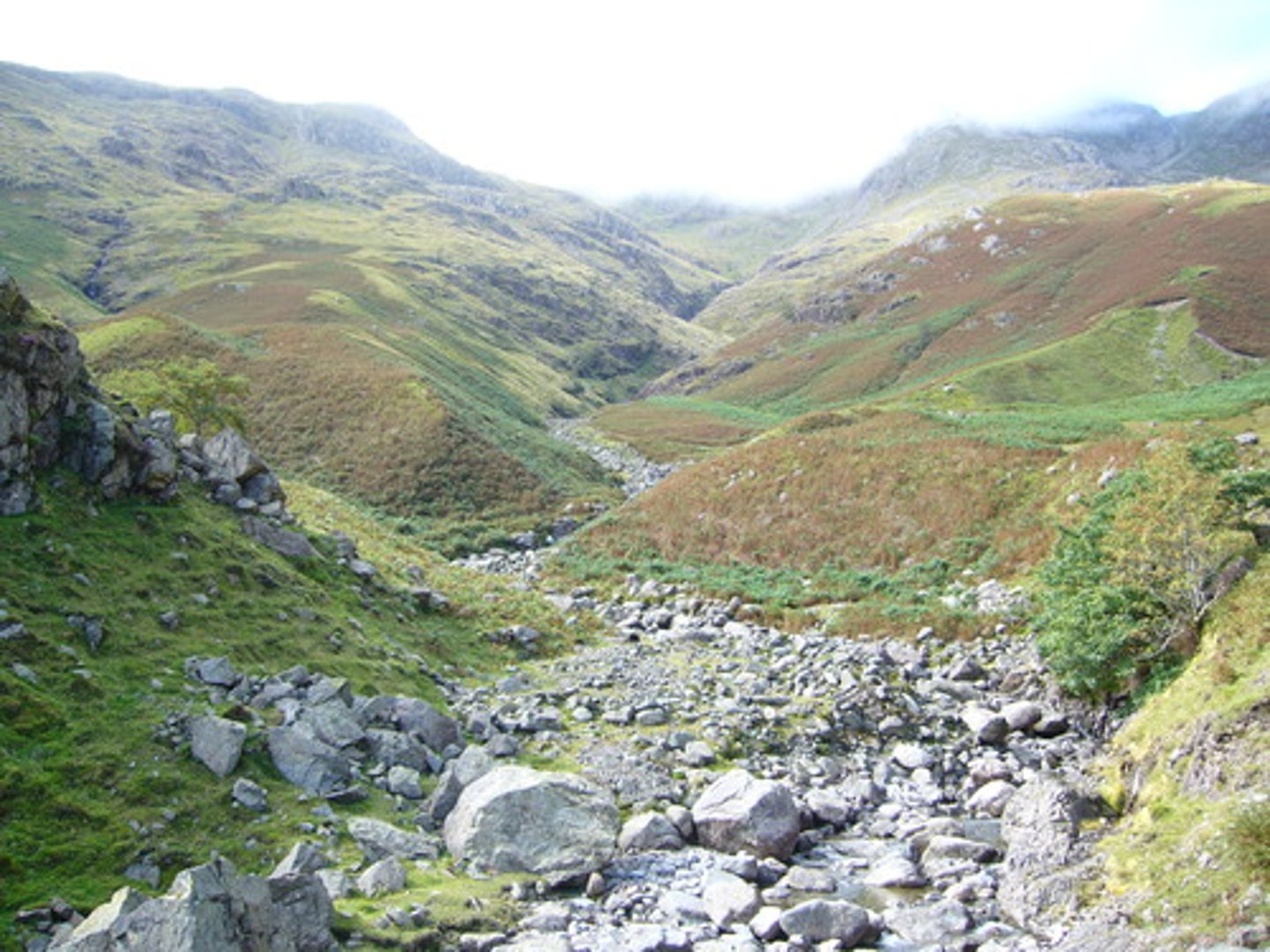

V-Shaped valleys
These are features formed in the upper course of a river due to downwards erosion. The characteristic shape of these features gives the name.
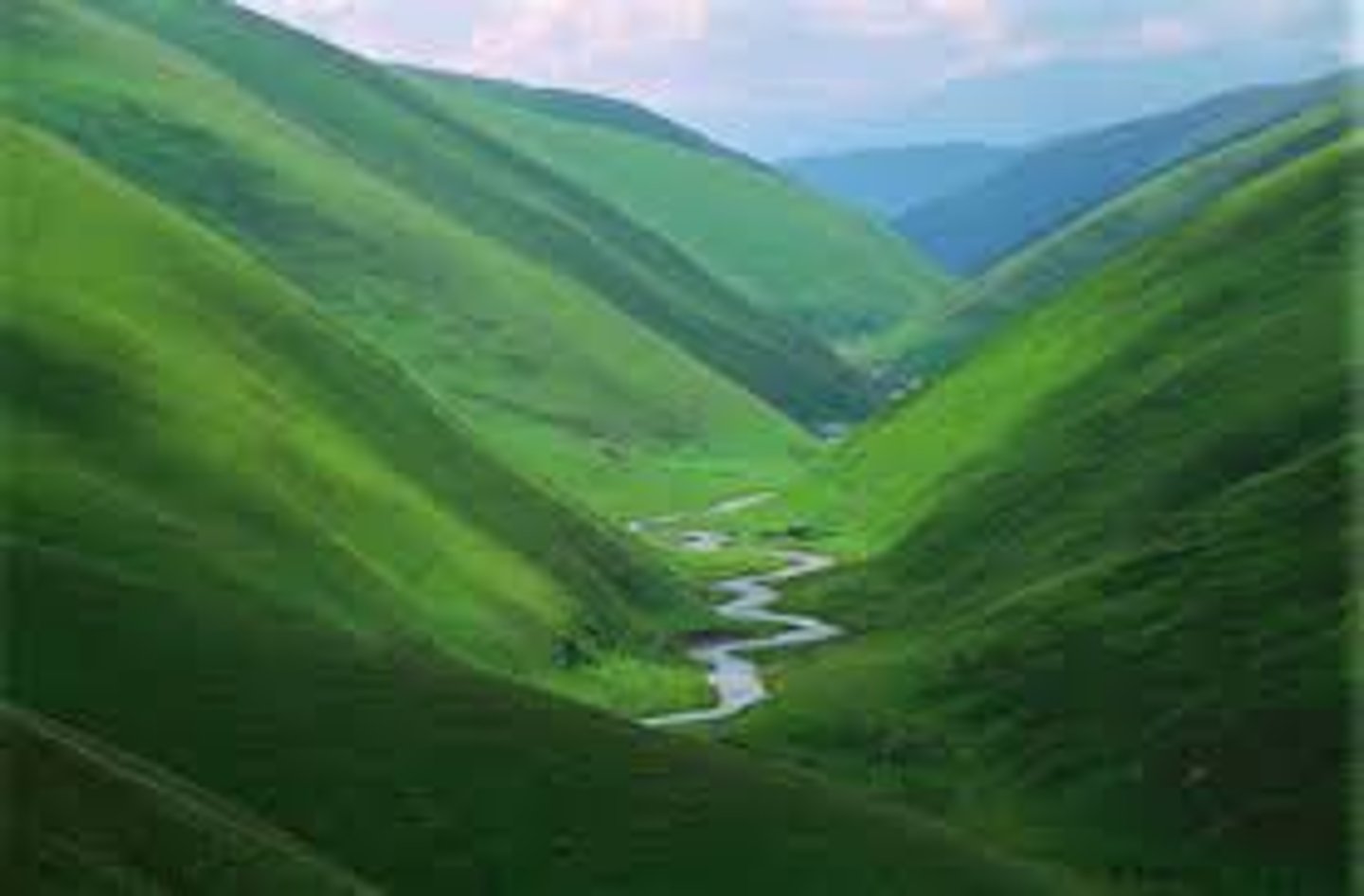

Interlocking spurs
These are features formed in the upper course of the river as it flows downhill and winds its way between more and less resistant rock.
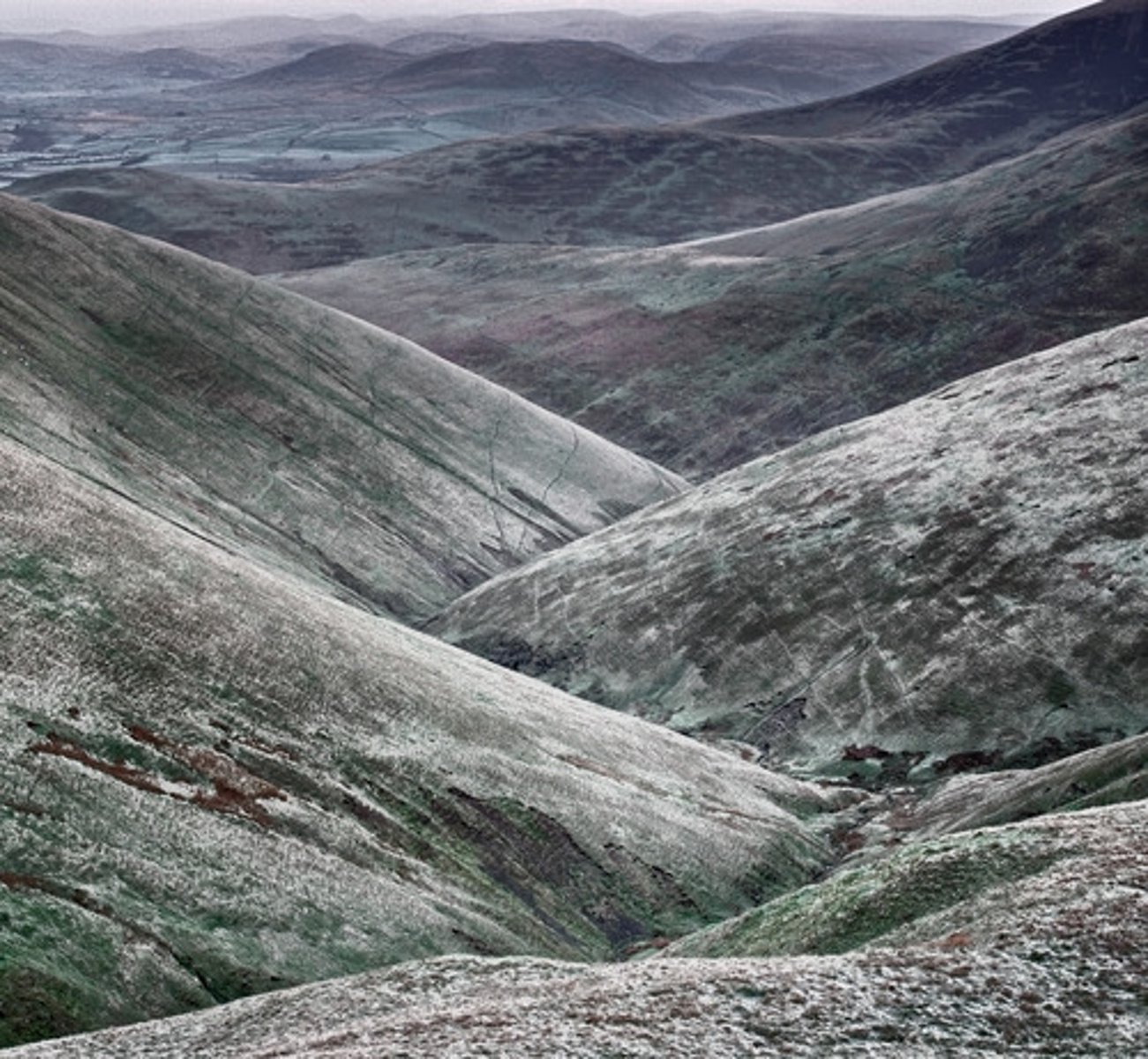

Waterfalls
These are features formed in the upper course of a river when it flows over two types of rock with different resistances. The less resistant rock is cut back more quickly than the more resistant rock and a _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ is formed. These retreat upstream when the soft rock is eroded away, creating overhangs which collapse due to gravity.
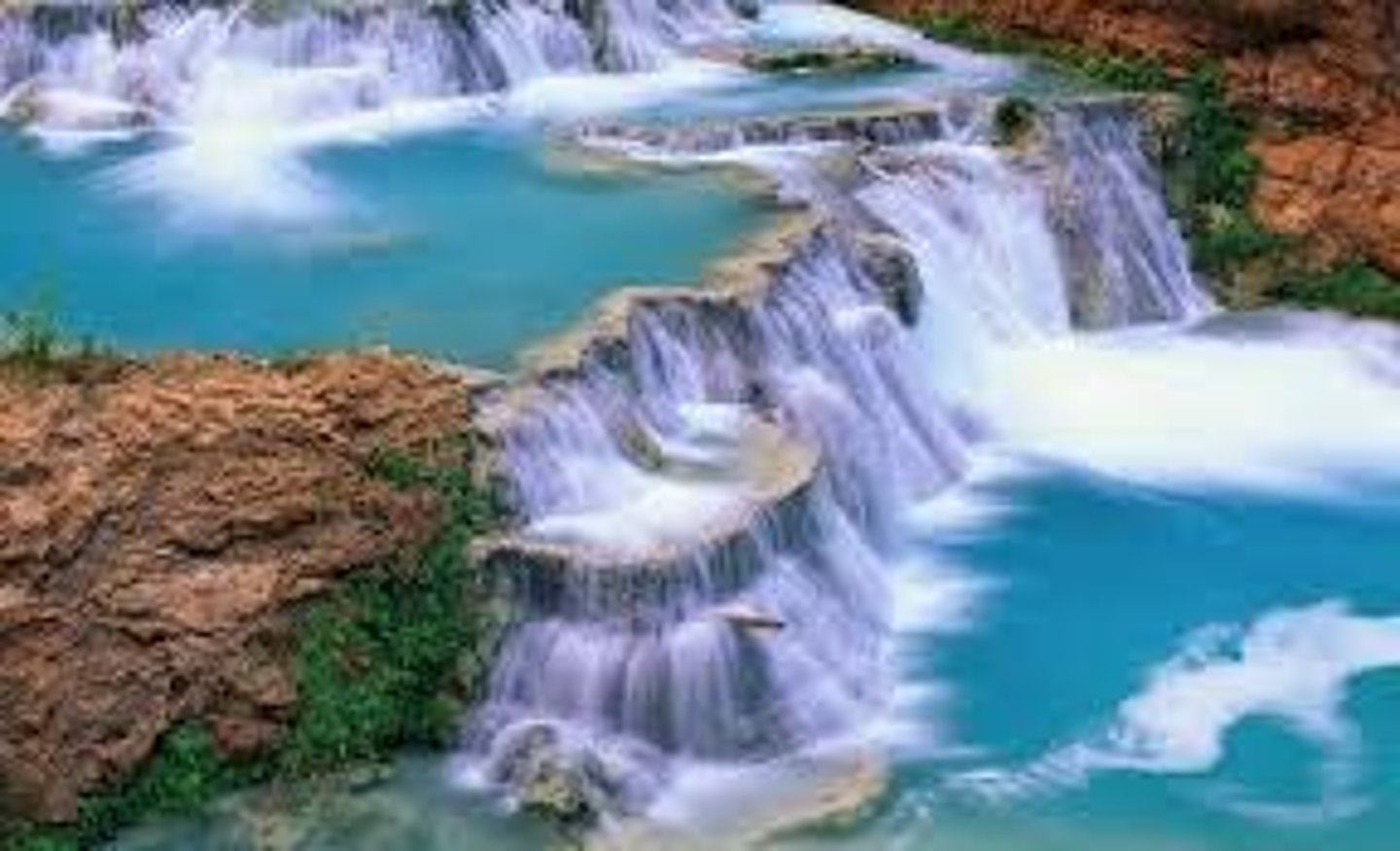

Plunge pool
This is a feature formed at the bottom of a waterfall, it is created by the force of the water hitting the riverbed. It is deepened by corrasion between the boulders.
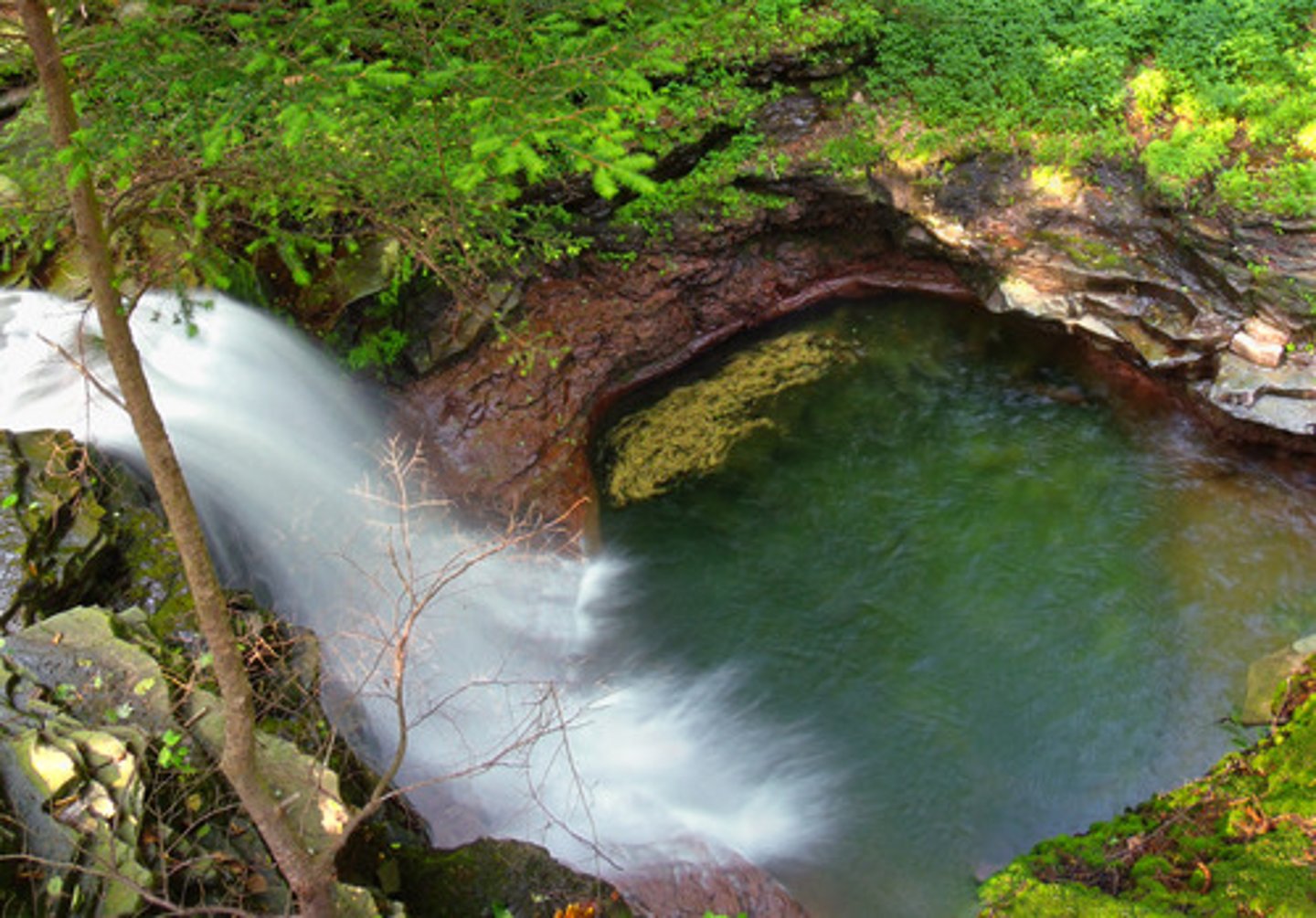

Steep-sided gorge
This is a feature left behind when a waterfall retreats upstream.

Attrition
This is a type of erosion between boulders in a river which causes them to become smoother.

Vertical erosion
This is the type of erosion that occurs mostly in the upper course of a river, after it has used most of its energy to overcome the force of friction.

Lateral erosion
This is the type of erosion that occurs mainly in the lower course of a river, it is erosion in a sideways direction.

Middle course
This is the middle section of the river's journey.
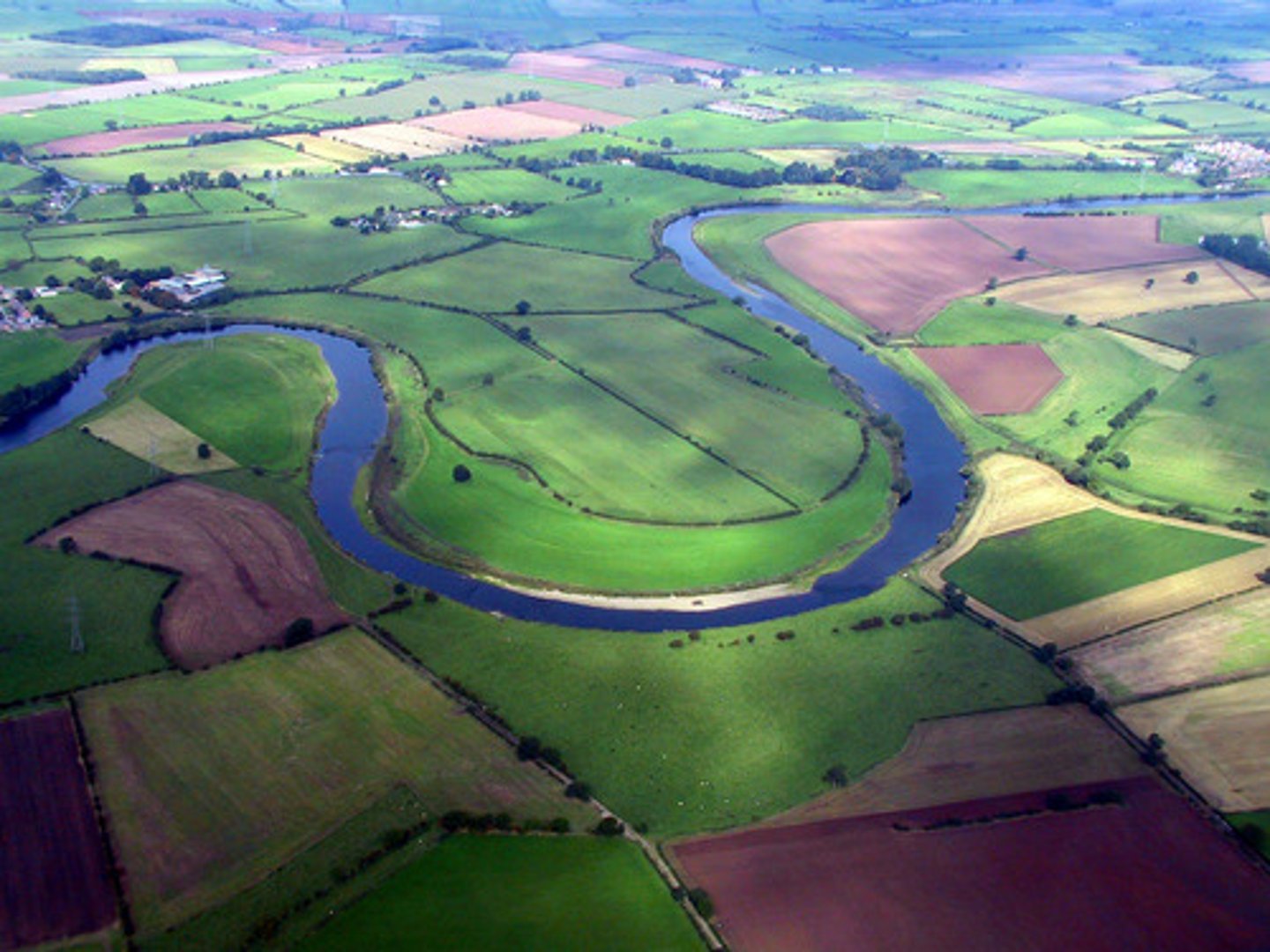

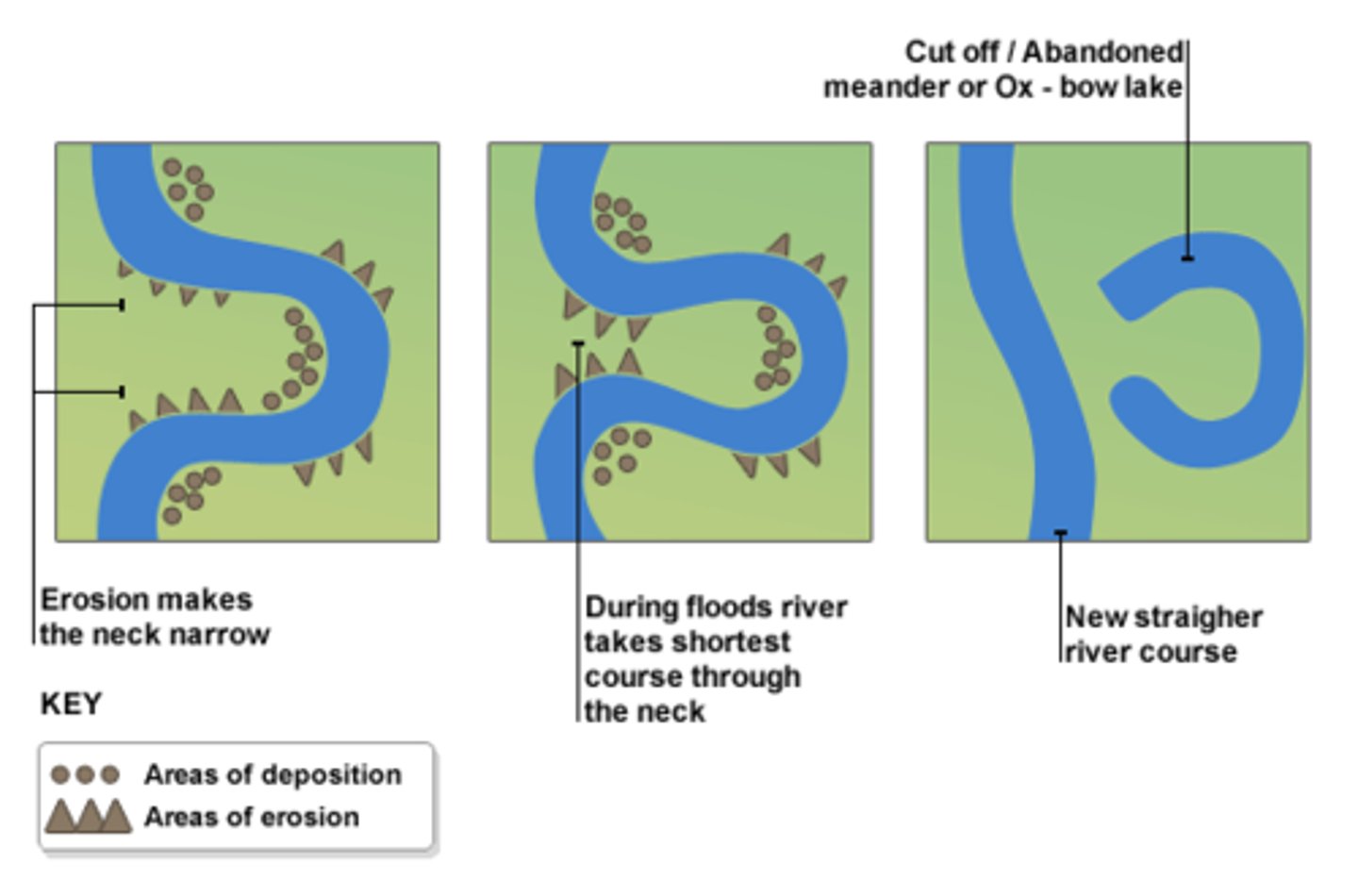
Meanders
Bends in the river that occur in the middle course.
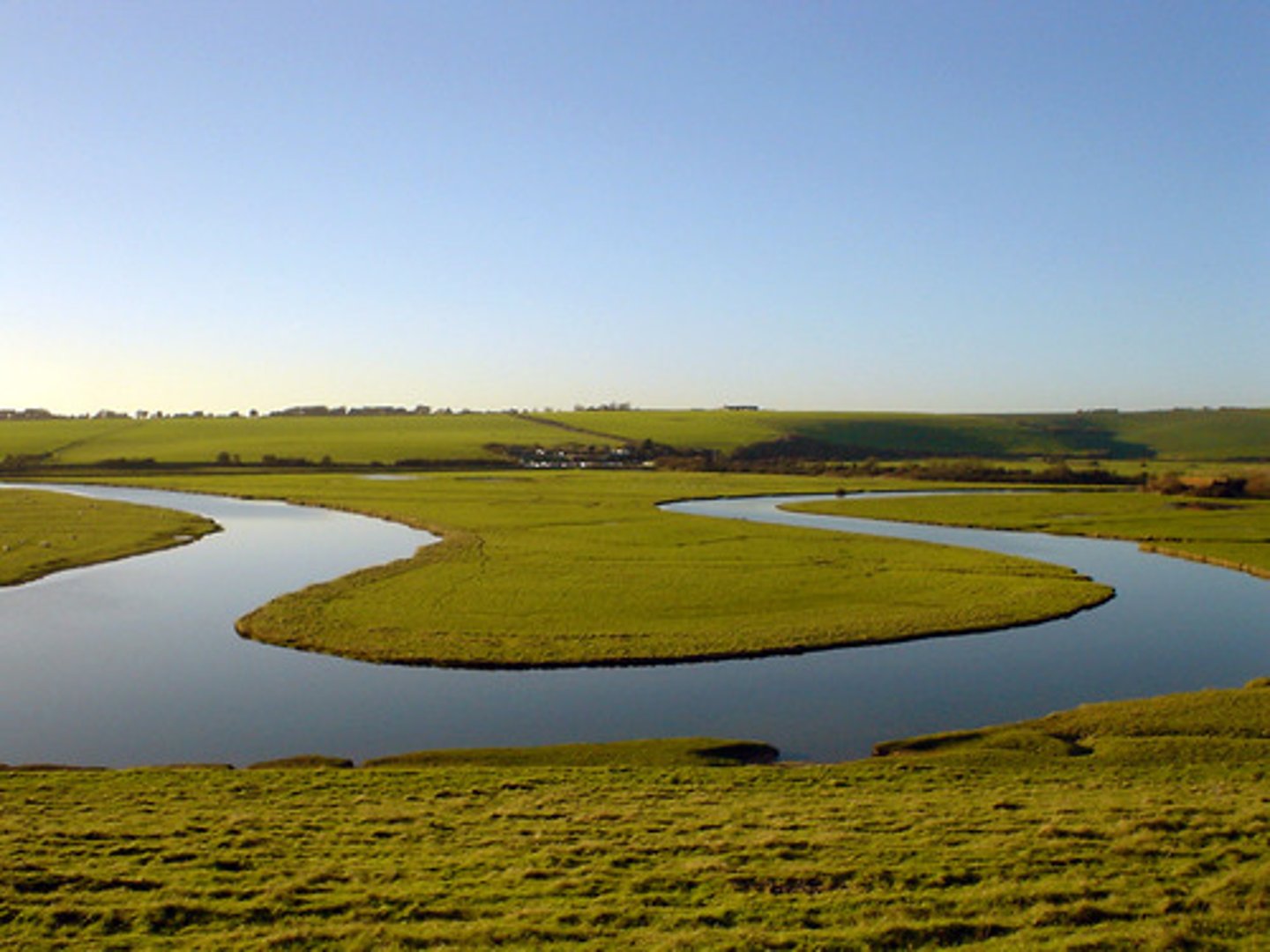

River beach/slip-off slope
This is a feature formed on the inside bend of a meander due to deposition (due to low velocity and high friction).
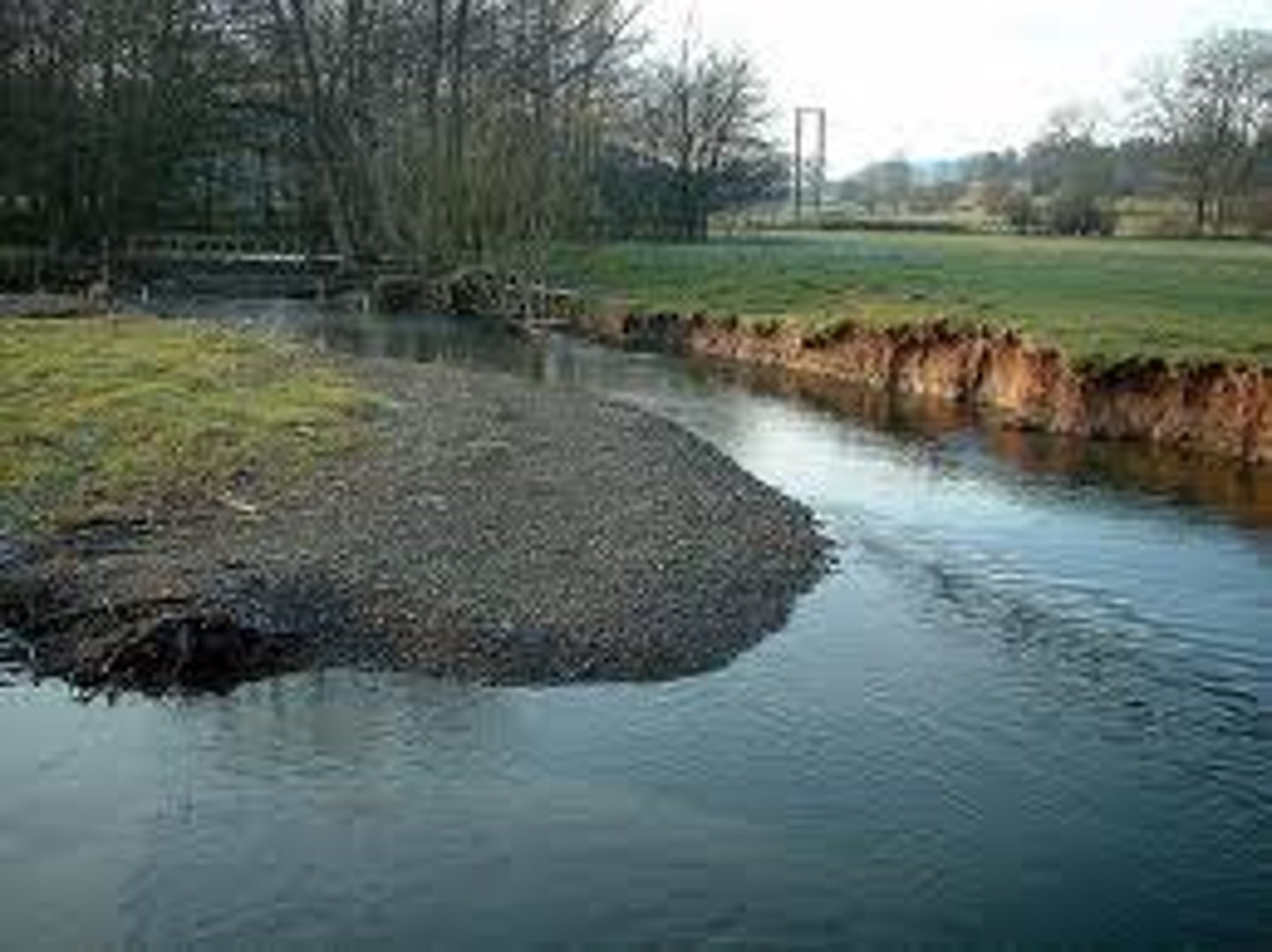

Thalweg
The fastest flowing part of a river.
River cliff
This is a feature formed on the outside of a meander where the thalweg erodes the banks through hydraulic action and corrasion.
Meander migration
This is the name of the process in which a meander moves and becomes more exaggerated due to constant erosion and deposition.
Erosion
This is the destructive action of the water in the river which wears away land.

Deposition
This is the constructive action of water in the river where it drops sediment.

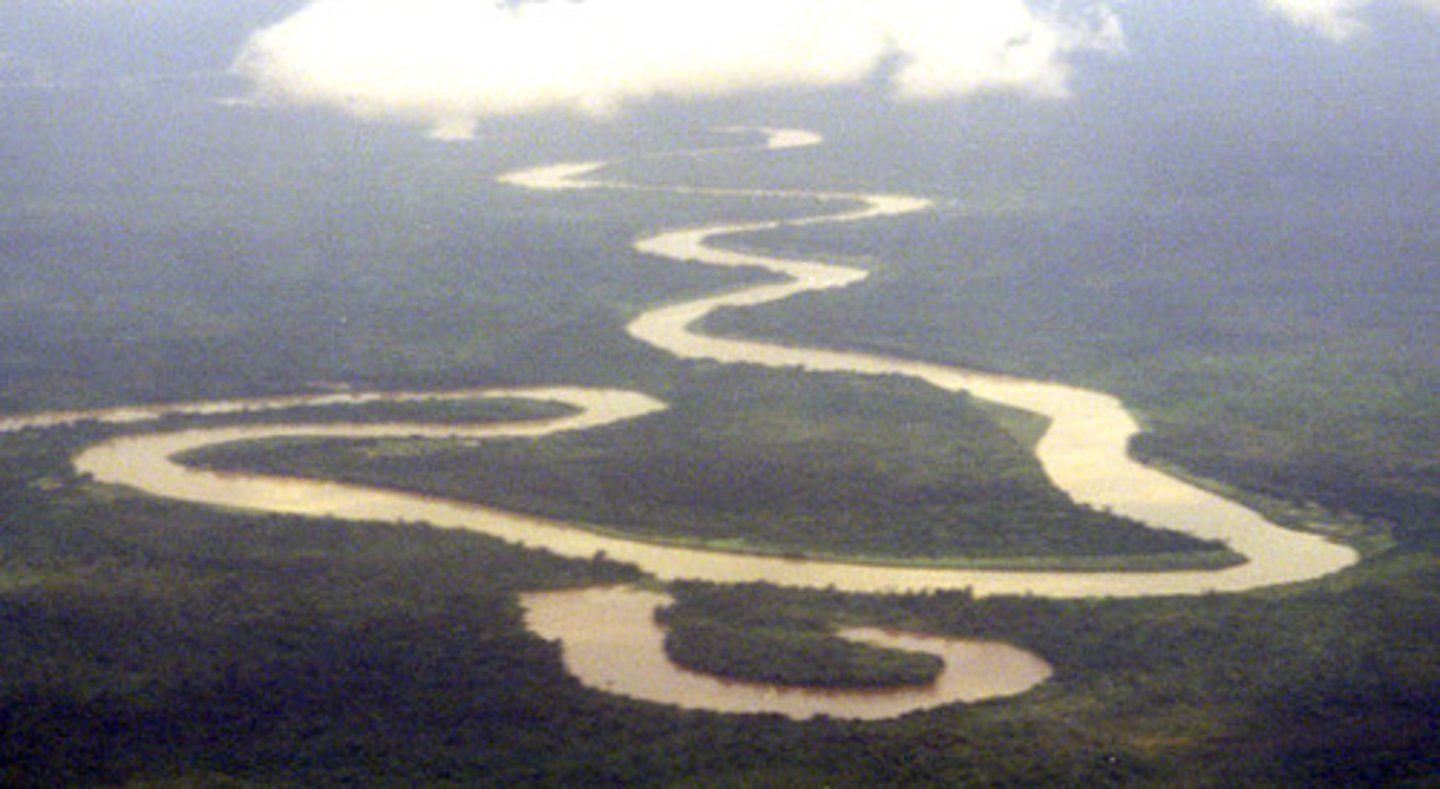
Ox bow lakes
This is a feature formed when the neck of a meander narrows so much that the river simply cuts through in times of flood (as it is a more direct route out to sea).

Lower course
This is the last section of a river's journey, here it is large and fast.

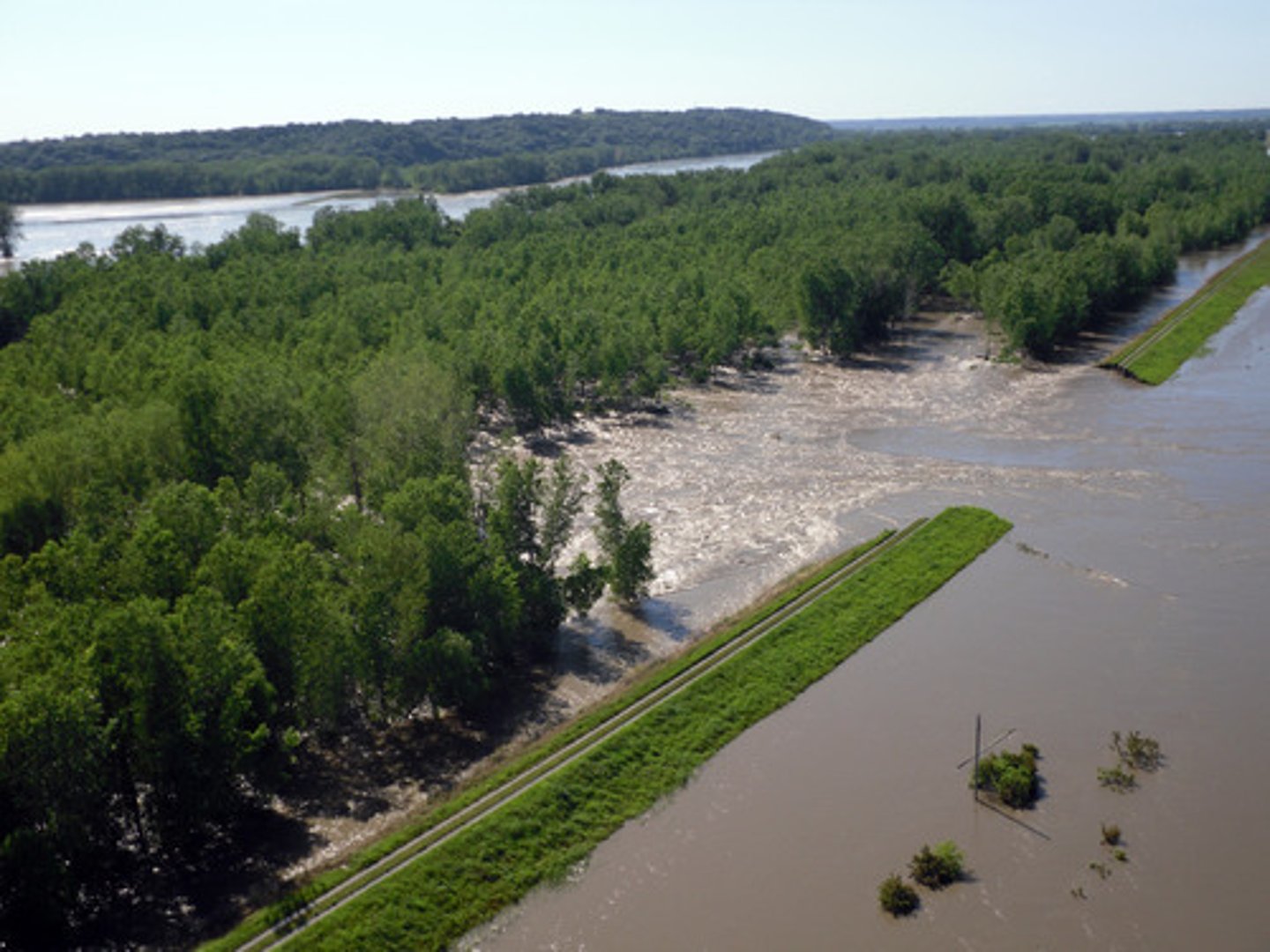
Levees
These are natural barriers formed by the continuous flooding of a river on to the flood plain. The river deposits heavier materials such as clays and the front and lighter materials like silt at the back. Over time, these features form.

Floodplain
This is a feature formed when the river floods and deposits sediment. These are usually very fertile.

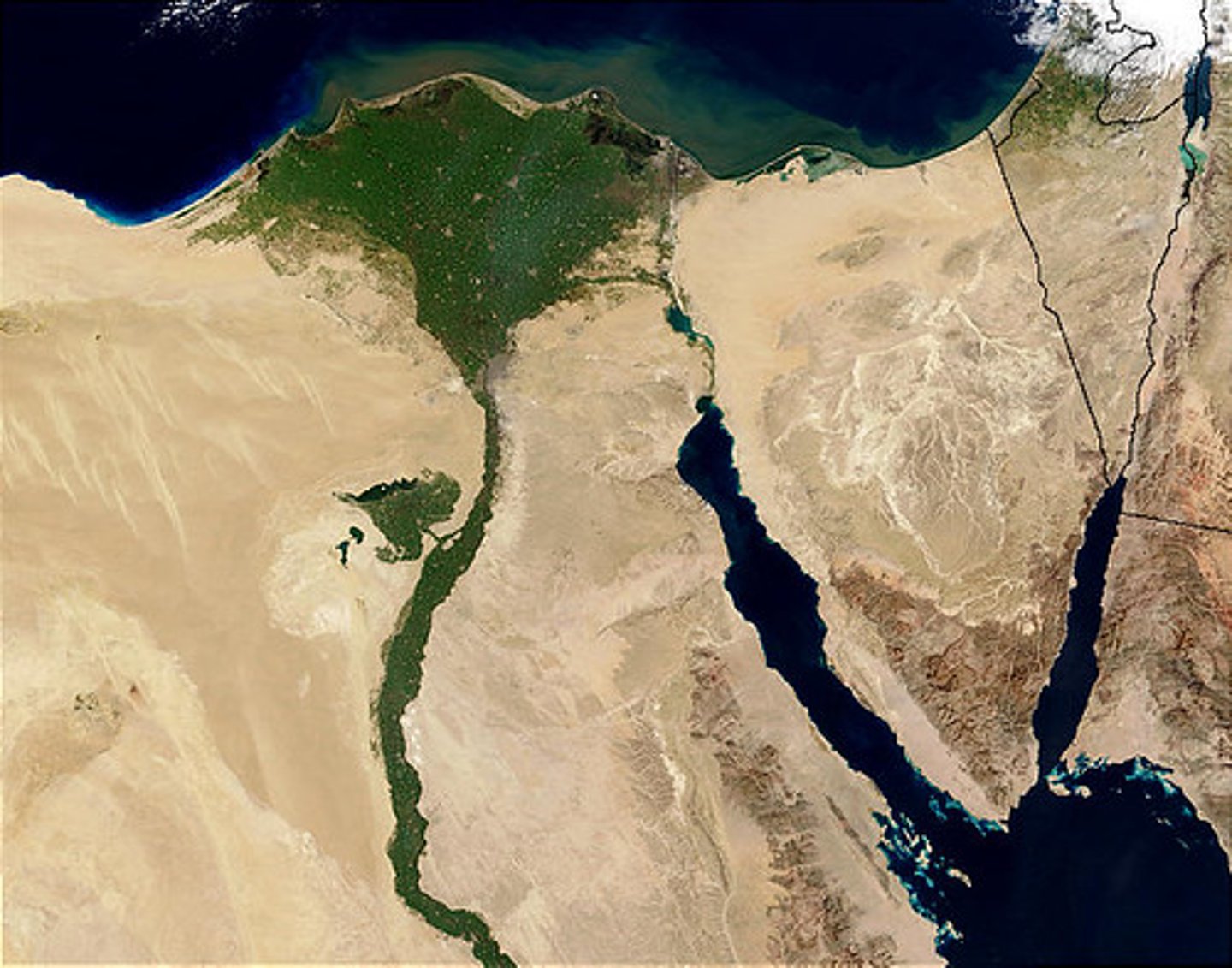
Deltas
These are features formed by huge quantities of sediment being deposited at the mouth of a major river such as the Nile. For these to form you need a small tidal range, low wave energy and large amounts of sediment.
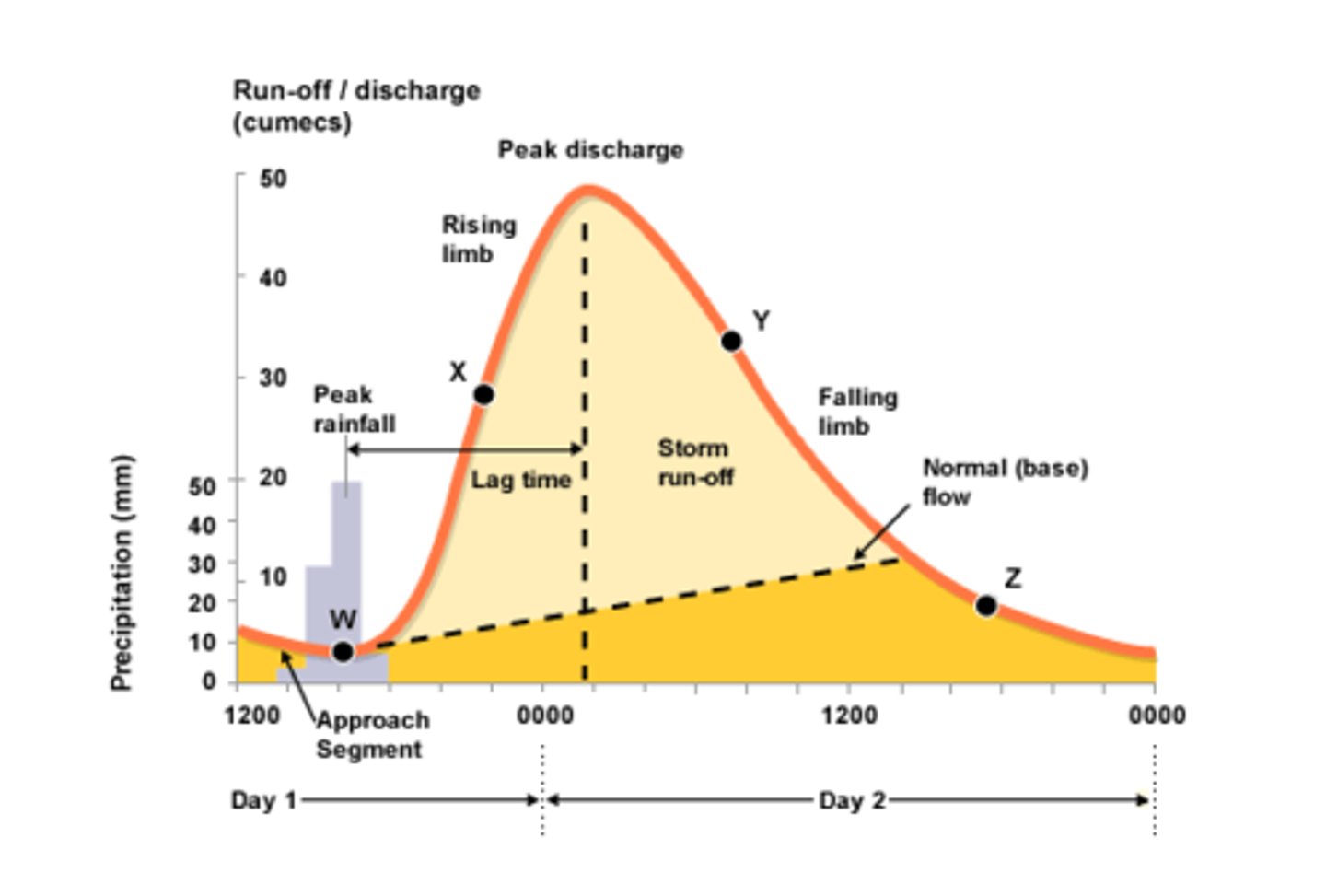
Hydrograph
This is a graph showing how river discharge changes in response to a rainfall event.
Bradshaw's model
This is a diagram showing downstream changes in rivers, the changes are shown by triangles which open out.
Lag time
The time between peak rainfall and peak discharge.
Rising limb
Increasing discharge on a hydrograph.
Falling limb
Decreasing discharge on a hydrograph.
Peak rainfall
Maximum rainfall on a hydrograph.
Peak discharge
Maximum discharge on a hydrograph.
Floods
An overspill of water caused when the discharge of a river exceeds its maximum capacity.

River capacity
How much water the river can hold.

Physical causes
These are natural causes of flooding to do with the environment.
Human causes
These are causes of flooding which are to do with us.
Bad ploughing
This is a human cause of flooding, when farmers accidently create artificial channels that the water can flow through so it reaches the river faster.

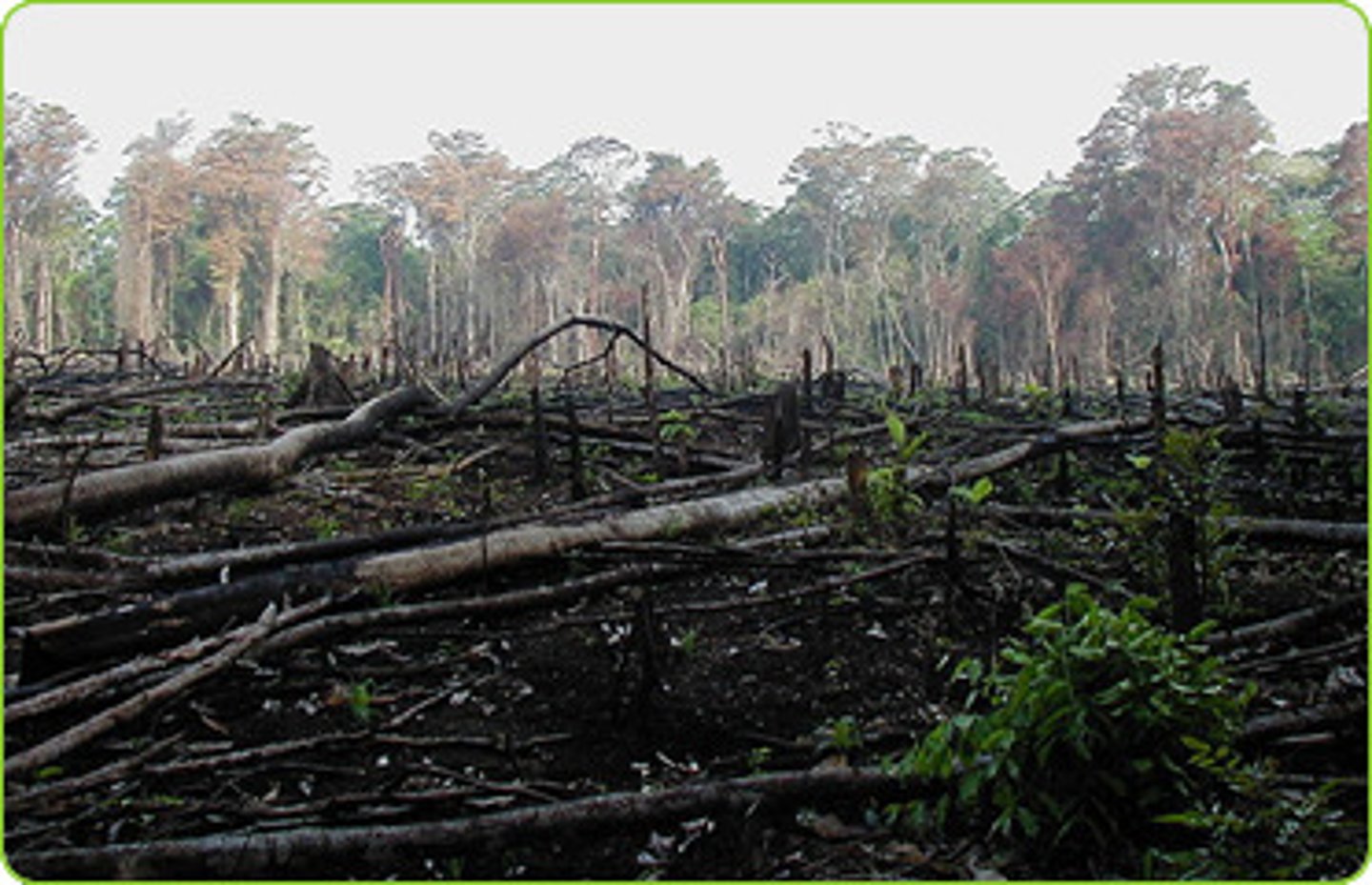
Deforestation
This is a human cause of flooding, when people remove trees and reduce interception.

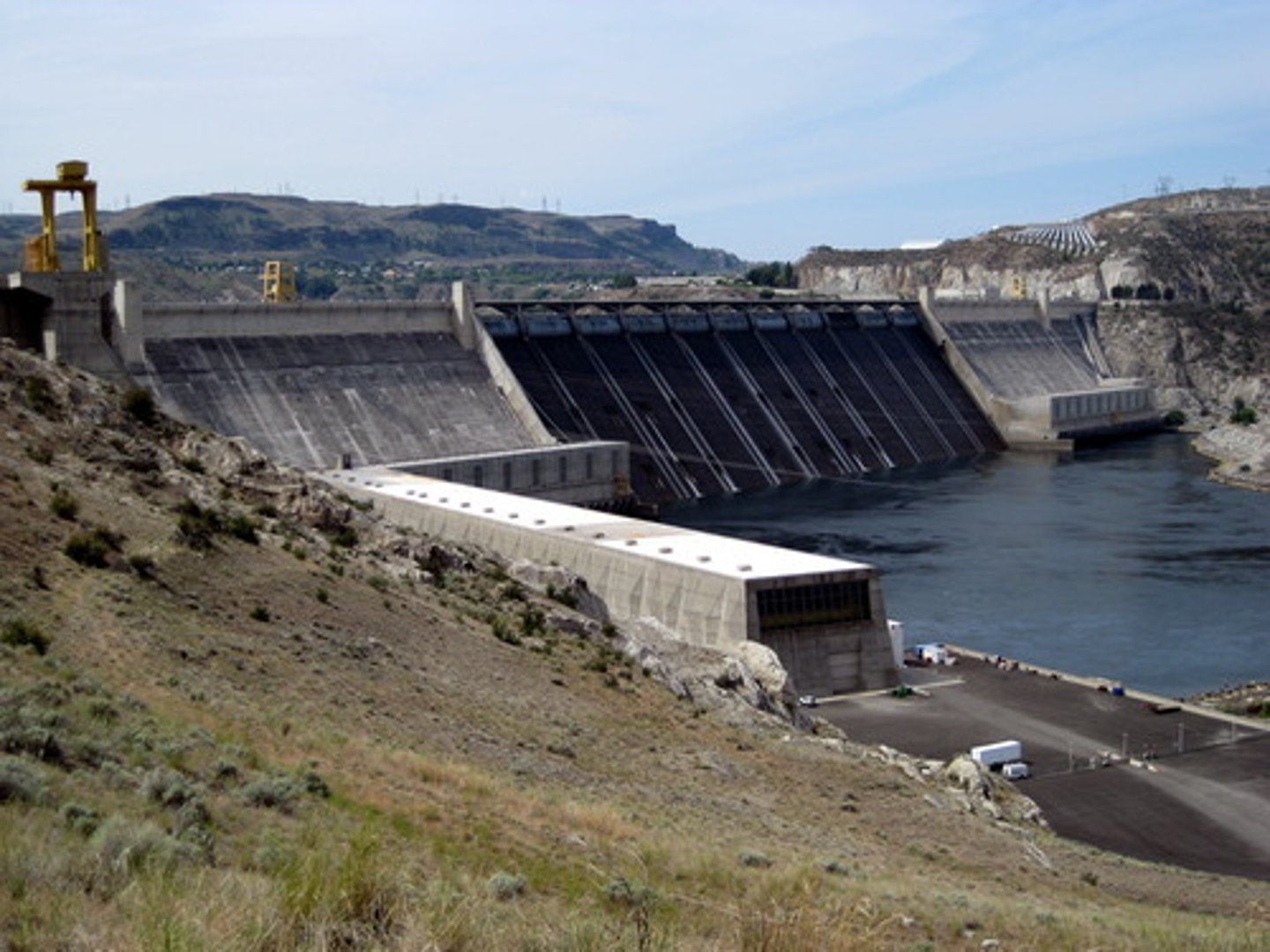
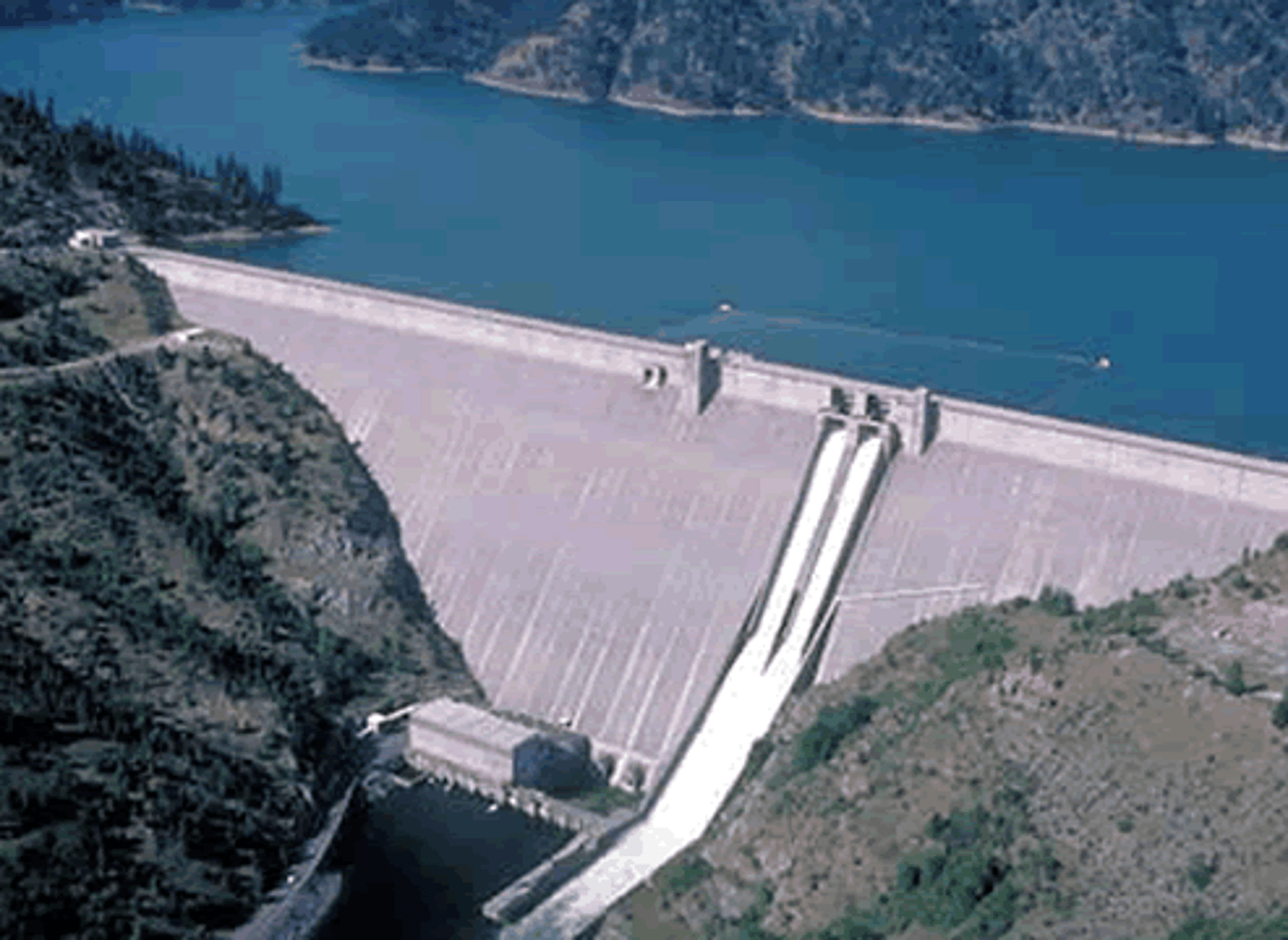
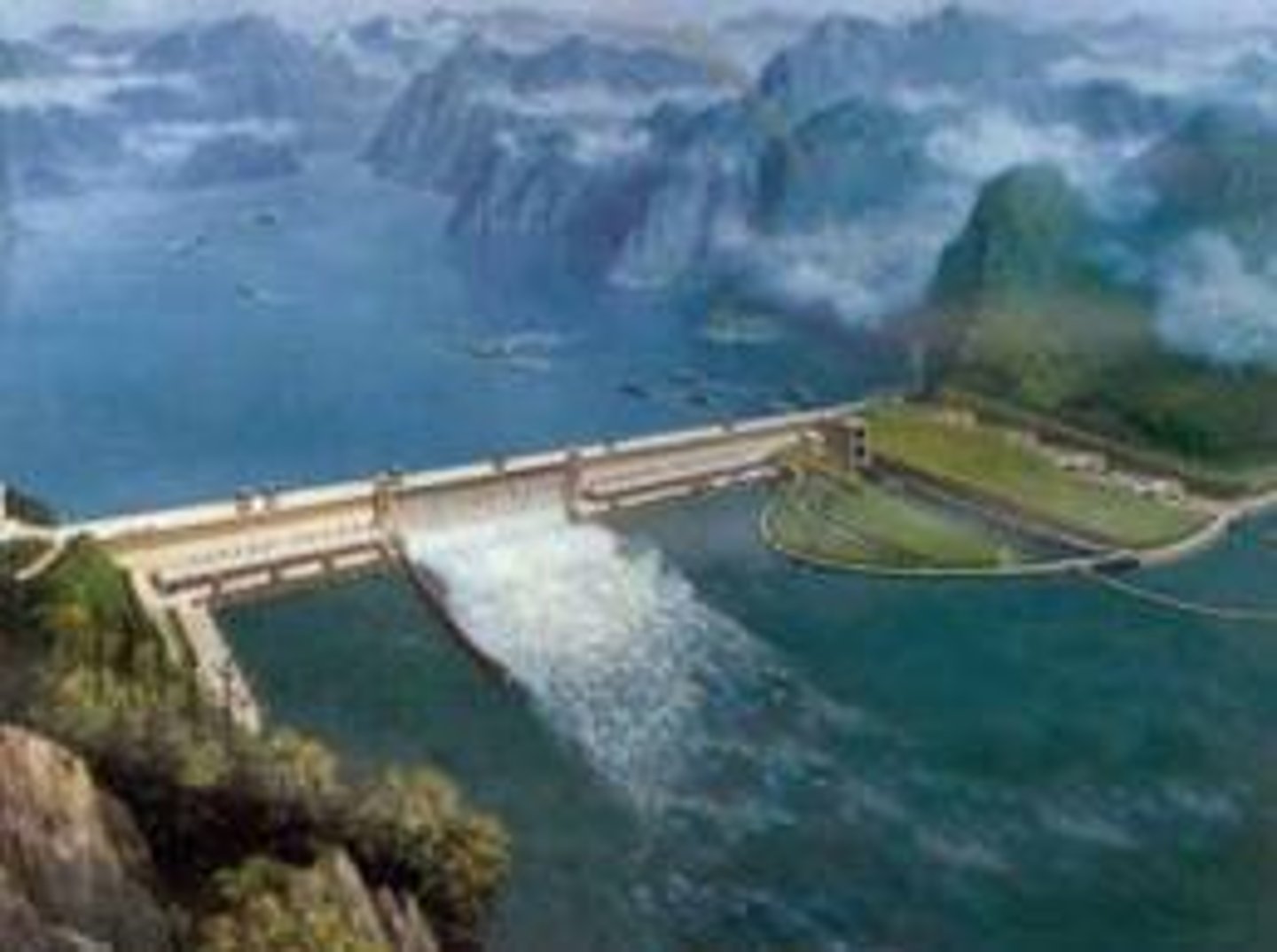
Dams
These are a device used to store water, if they burst it can cause a catastrophic flood. They are also a type of hard engineering technique which holds back water in times of flood.

Tarmac and concrete
These are examples of impermeable surfaces which humans create that can cause flooding.

Impermeable rock
This is a physical cause of flooding; it is a type of rock that does not allow percolation so increases surface run off.

Snow
This is a physical cause of flooding; this melts when the temperature rises and adds to the discharge of a river.

Saturated ground
This is a physical cause of flooding; this is when the ground becomes so soaked with water that it cannot hold any more and increases surface run off.

Hard engineering
A type of technique that interrupts and works against nature e.g. channelisation.

Soft engineering
A type of technique that uses nature against itself e.g. afforestation.

Flood relief channels
This is a type of hard engineering technique which alters the course of a river to divert flood water away from settlements. Is expensive but very effective.

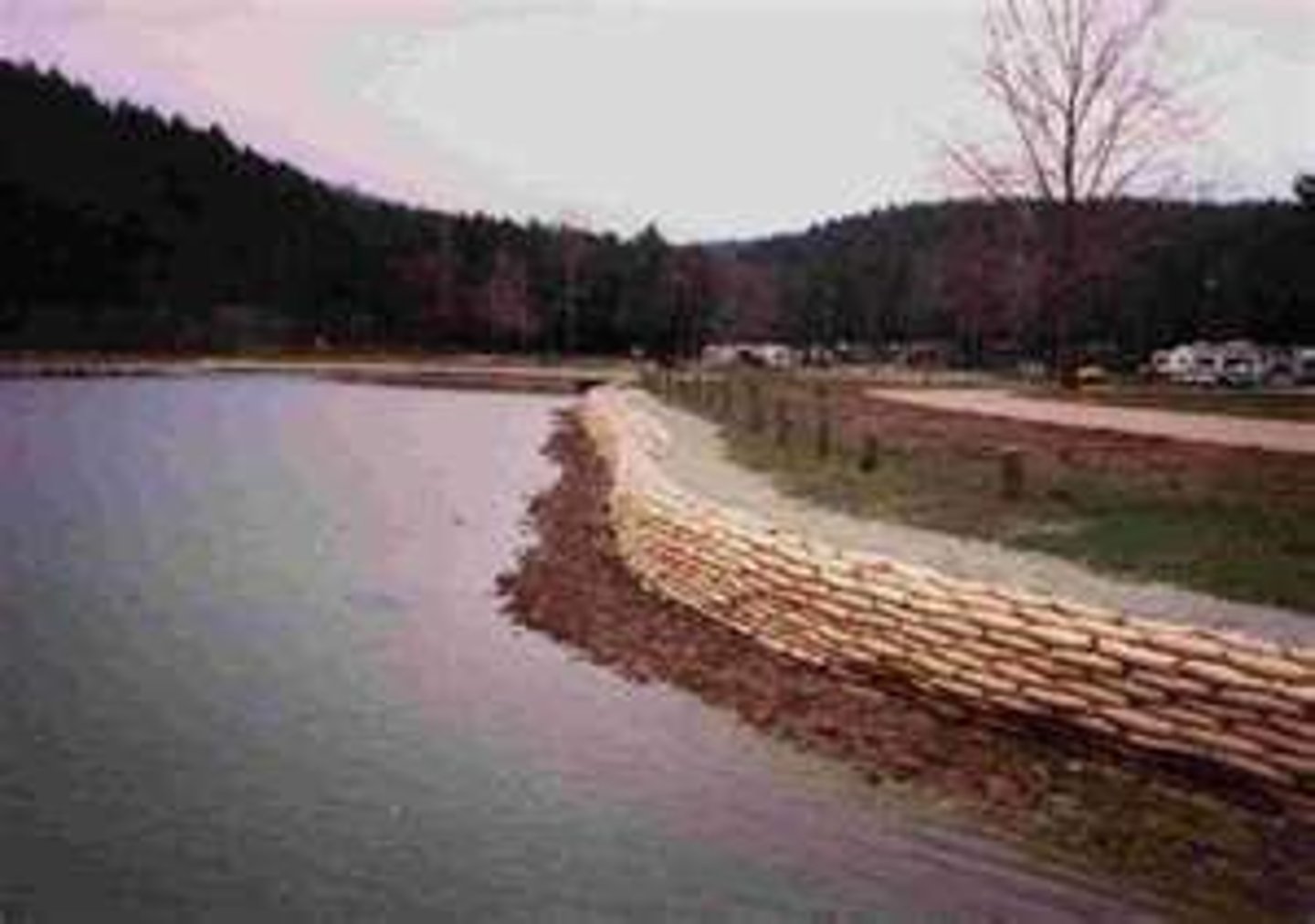
Embankments
This is a type of hard engineering technique, they are raised banks along the side of a river which increase channel capacity and prevent bank erosion. These can be used as walkways by pedestrians but can be ugly.

Channelisation
This is a type of hard engineering technique in which the river channel is straightened or deepened to allow it to carry more water out to sea faster. This is very long lasting and effective but can lead to a greater risk of flooding downstream.

Flood defences
These are techniques and devices installed to protect against floods.

Flood walls
This is a type of hard engineering technique in which a wall is constructed to form a barrier against the flood water.

Floodplain zoning
This is a type of soft engineering technique. The local council examine the flood risks in different areas and prevent buildings in theses areas (e.g. on a flood plain). This can aggravate the problem of housing shortage but lessens surface run off.

Warning systems
This is a type of soft engineering technique which warns residents of an imminent flood. This is a very cheap flood defence but can be vandalised.

Afforestation
This is a type of soft engineering technique. Trees are planted in the catchment area to increase interception. This is a cheap method of reducing flooding but can increase fire risk.

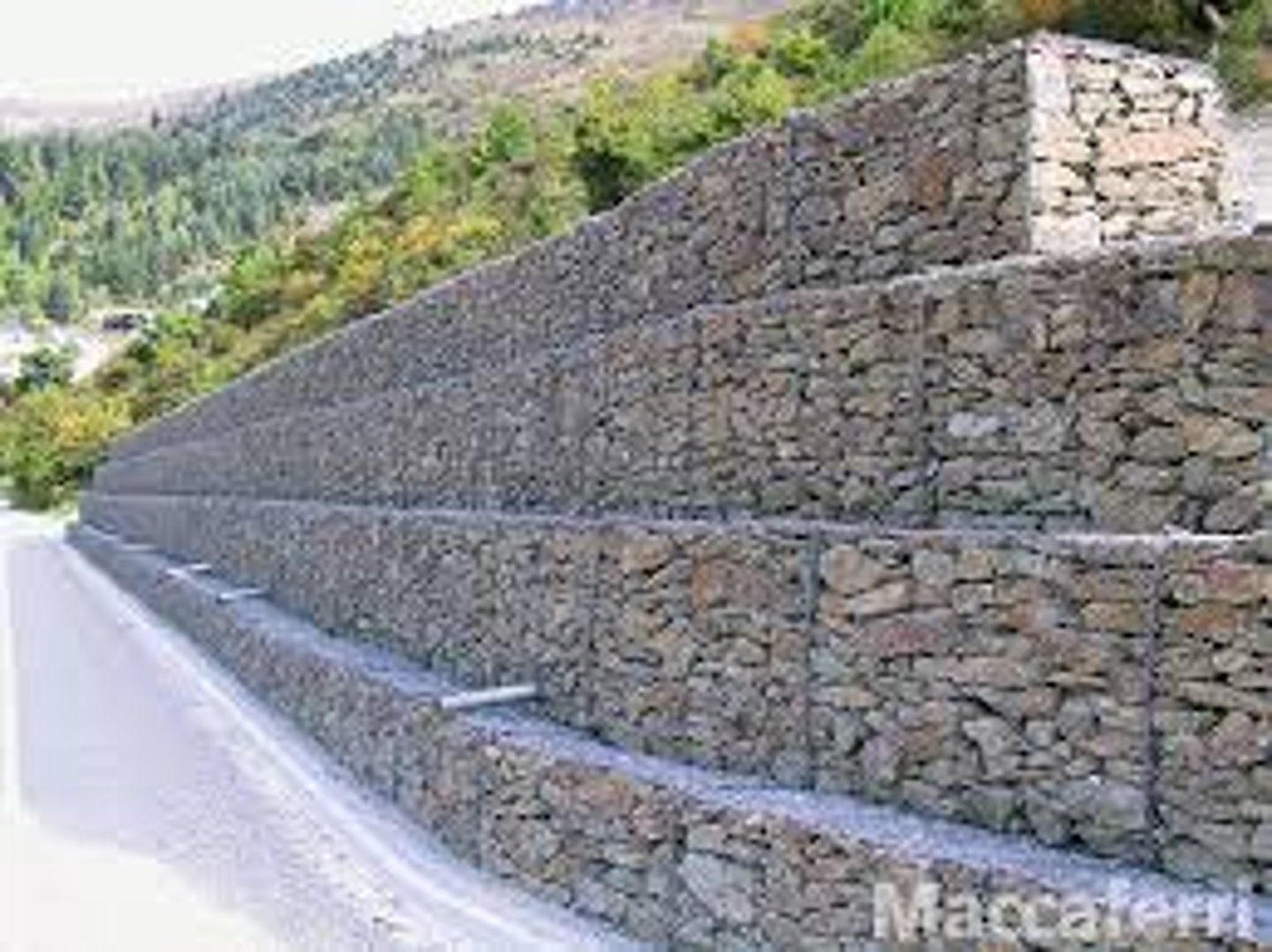
Gabions
These are a type of hard engineering technique. Wire cages are filled with rocks resistant to erosion and are placed along the banks of the river. They also reduce erosion but are ugly.

Arable land
The land which crops are grown on.

Suspension
This is a method of transportation in a river where the sediment is carried along.

Traction
This is a method of transportation in a river where the load is dragged or rolled along the riverbed.

Saltation
This is a method of transportation in a river where the load is bounced along the riverbed.

Bedload
The amount of sediment that is on the riverbed and the sediment that is carried.

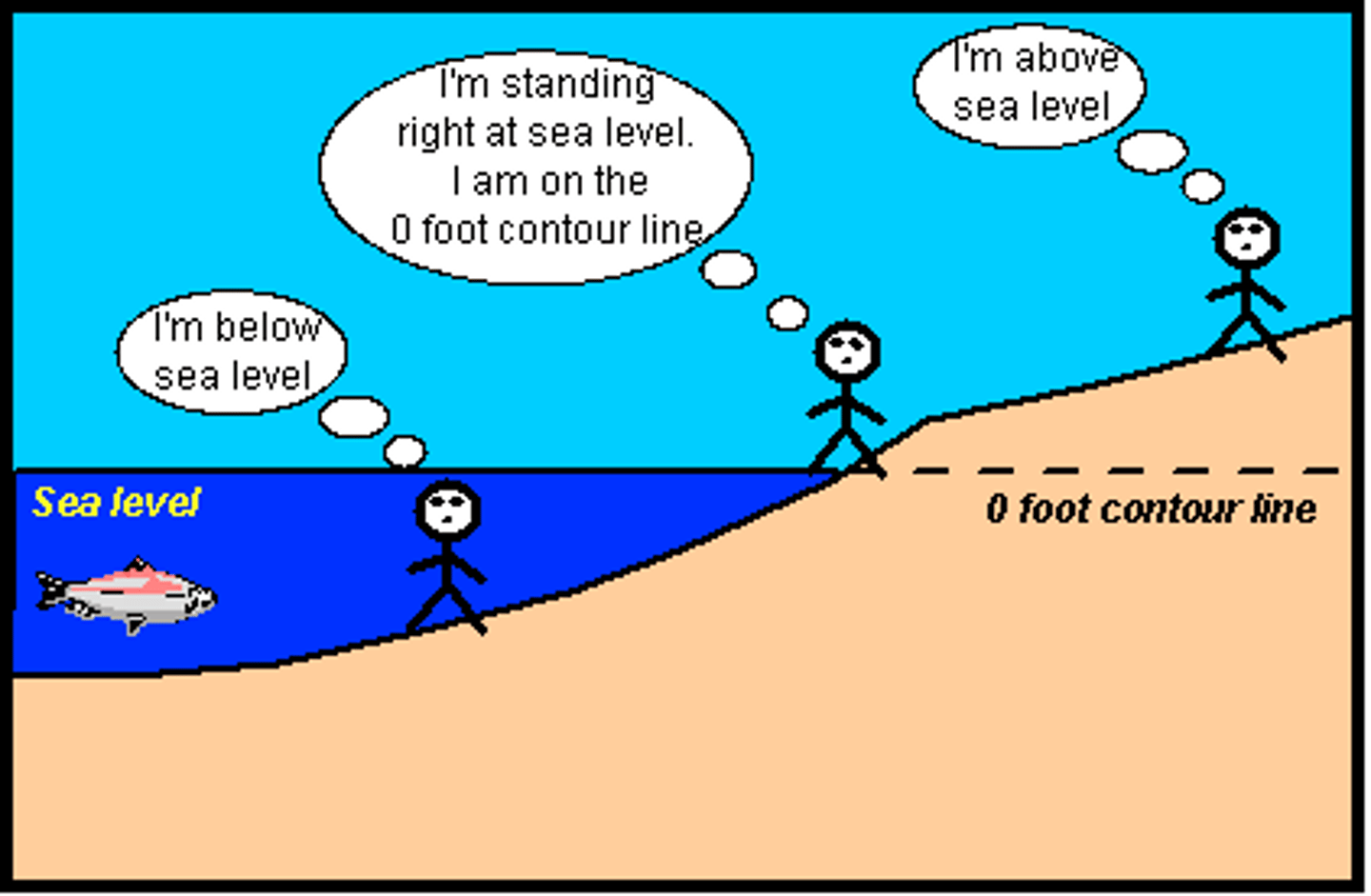
Base level
This is the level that the river tries to erode down to reach (sea level).
Bank-full
This is the level of water reached by the river when it is at maximum capacity.

Prediction
This is a way to reduce the effects of flooding- the MET office and the Environment Agency will issue warnings (through a series of codes) when a flood is imminent and alert residents.

Planning
This is a way to reduce the effects of flooding- local councils carry out a flood risk assessment before building is allowed.

Education
This is a way to reduce the effects of flooding- people are told how to act in a flood and the Government gives advice about what to do on its website.

Building design
This is a way to reduce the effects of flooding- buildings are made to withstand flooding e.g.by building them on stilts. This has happened in Doncaster after the 2002 floods.

Economic water scarcity
This is when water is available, but for some reason it is inaccessible or unusable. This might because it is groundwater that is expensive to extract or that the cost of transporting it is too expensive or simply that the supply of water has become polluted.
Physical water scarcity
This is when there is not enough water available. The most common reason for this is low precipitation rates.
Agricultural water use
E.g liquid from farm siliage and slurry from farm animals enters rivers. Fertilisers and pesticides seep into the groundwater. Deforestation - run off carries soil and silt into river, with serious effects on aquatic life and humans who drink the water.
Domestic water use
The discharge of untreated sewerage from houses - even treated sewage pollutes. Use of river for washing clothes and bathing contamiates water. Emptying highly chlorinated water from swimming pools contaminates water.
Industrial water use
Taking cooling water for an electric power station from a river and returning it to the source at a higher temperature upsets river ecosystems. Spillages from industrial plants such as oil refineries can enter rivers. Working of metallic minerals and the heavy use of water in processing ore - toxic substances from this eventually find their way into rivers
Infrastructure
The basic structure, framework, the system which supports the operation of an organization (e.g. the power and water supplies, the transport and communication facilities, the drainage system), which makes economic development possible, the basic capital investment of a country or enterprise
Weathering
Weathering is the break-up and decomposition of rocks in-situ (in their place of origin). Weathering does not involve the movement of material and this makes it different to erosion.
Chemical Weathering:
The break down of rocks caused by a change in their chemical make-up.
Physical or Mechanical Weathering:
The break down of rocks caused by physical processes with no change in the rocks chemical make up.
Biological Weathering:
Biological is sometimes included within physical weathering. Biological weathering is when flora and fauna break down the rock e.g. growing roots systems or burrowing animals.