Chapter 5 test
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Smooth Muscle
muscle that has no striations and is involuntary
Motor Unit
group of muscle fibers under the control of one motor neuron
perimysium
covers fascicle
Cross Bridges
formed between actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction.
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane surrounding a muscle fiber that plays a key role in muscle contraction and excitation.
Insertion
movable end of a musclethat attaches to the bone it moves.
Origin
fixed end of a muscle
Peristalsis
The involuntary contraction and relaxation of muscles in the digestive tract that moves food along the gastrointestinal tract.
Aponeusrosis
serves as a fascia to bind muscles together or as a means of connecting muscle to bone
Muscle Fiber
Single muscle cells that make up skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle tissue
Action Potential
Causes entire motor neuron unit muscle fibers to contract in response to a stimulus, resulting in muscle contraction.
Fascicle
a bundle of structures, such as nerve or muscle fibers or conducting vessels in plants.
Supination
palms facing upwards
Pronation
palms facing downwards
When a muscle contracts it….. on the bones at the attachment site
pulls
The ability of a muscle to response to a stimulus
irritability
Extensibility - the ability of a muscle to be
stretched
Nerve that stimulates skeleton muscle
motor neuron
Muscle always shorten when they develop tension
False
An isometric contraction there is no change in muscle
True
Maysin heads create cross bridges
True
When stimulated to create tension muscle can only push
False
Skeleton Muscle contain nucleus
Multiple
All of the following are behaviors of muscle except
bendability
Which muscle is involuntary
A and C
Release of ion….
Calcium
Which of the following is not a muscle of head neck
Intercoastal
Which of the following is a major muscle in the back
Trapezius
Which of the following muscle is attached to the Achilles tendon
Gastrocnemius
All of the following are members of the hamstring group
Sartorius inseam
abduction
movement away from the central body
adduction
movement toward the body/toward midline
Agonist
moves bone
antagonist
opposes the movement of the agonist
concentric
agonist contracts, antagonist relaxes
Eccentric
agonist contracts while lengthening,
antagonist relaxes
Isometric
both agonist and antagonist contract
Planes

Sagittal
Dorsiflexion: toes pointed upward
Plantar: toes pointed downward
Flexion: hands up
Extension: hands down/to the sides
Hyperextension: hands a little to the back
Frontal
Abduction
Adduction
Radial deviation: toward radius
Ulnar deviation: toward ulna
Transverse
Lateral Rotation: moving the foot out
Medial Rotation: moving the foot inwards
Pronation
Supination
Multiplanar
Circumduction: in a circle
Opposition
Biceps brachial

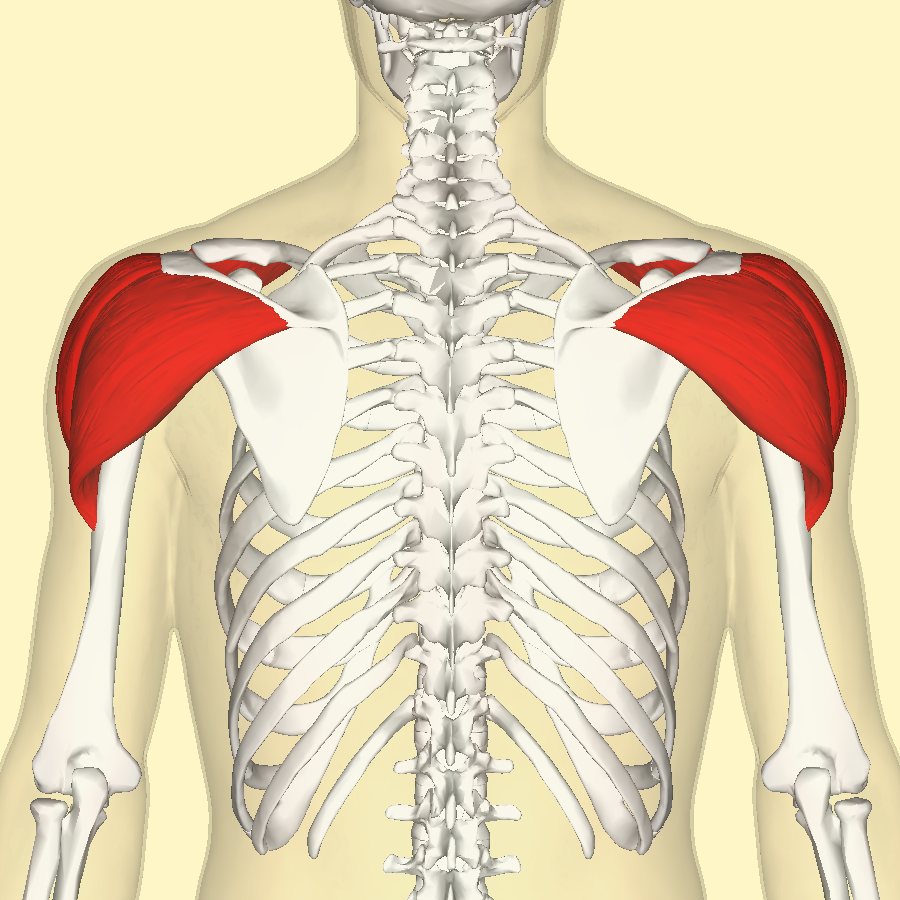
Deltoid
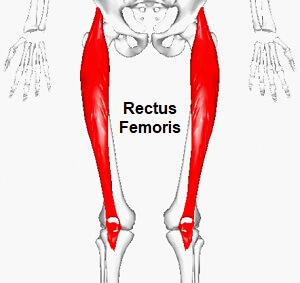
rectus femoris
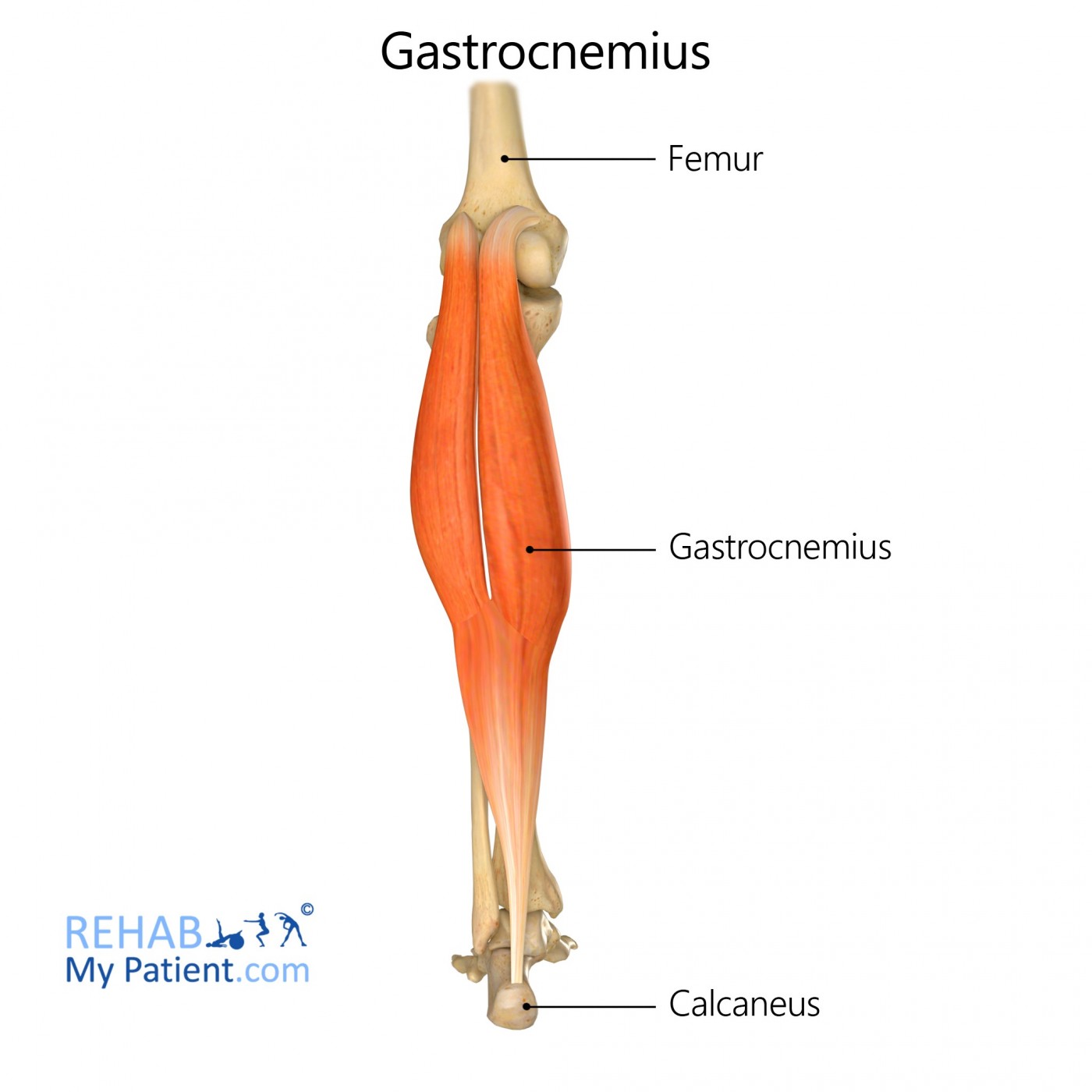
gastrocnemius
Sartorius