Biology - Gr.11 🦖 (UNIT 3: EVOLUTION) - Artifical Selection, Adaptation & Mimcry, Scientists' Contribution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Theory
a valid explanation for our observations, but it can always be revised if further evidence is discovered
How do populations change? How do new species form?
due to genetic mutations
genetic mutations
changes in the DNA sequence
mutations
changes in the nucleotide (DNA) sequence that alter a gene and ultimately modify or change the way an organism appears and functions
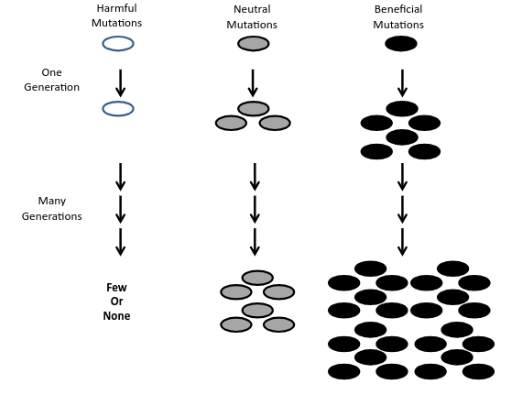
What are the THREE types of mutations? Explain.
Harmful: causes disorders or death
Indifferent: neither beneficial nor harmful
Beneficial: very rare, increase ab individual’s chance of sruvival and chances of reproductive success. These individuals have more children who carry the same mutations, therefore that mutation accumulates in the population.
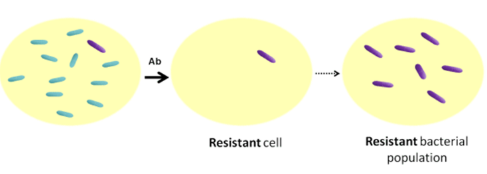
What is Antibitotic Resistance?
→ result of a random mutation
→ In an antibiotic environment, mutation is “good” for the bacteria
→ If successful reproduction, it will eventually outnumber non-resistant bacteria
artificial selection
→ use genetic variability of a population to artifically increase the abundance of a particular trait ex. dog breeding, agriculture
What are the consequences?* (provide examples)
→ can reduce genetic diversity and may contribute to biodiveristy lost
ex. english buldogs: selected for flat face, but prone to respiratory problems
ex. monoculture: lead to a loss of genetic diversity. If the organisms are genetically identical, they are prone to diseases or infestations
KEY IDEA:
→ organisms that live long enough to reproduce can pass on to their genetic info that allowed them to survive
adaptation
→ a structural element, behaviour or physiological process that allows an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment
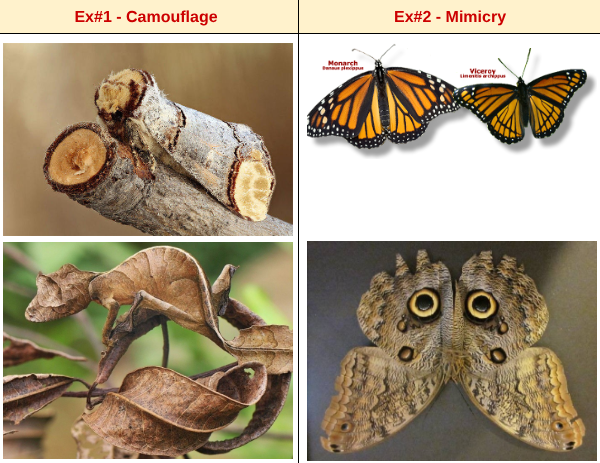
What are some examples of adaptation?
camouflage: allows organims to survive and reproduce (ex. chameleon)
mimicry: a structural adaptation in which a harmless species resembles a dangerous species in coloration or shape (ex. vicerays & monarchs)

What is an animal example of adaptation
→ peppermoths: started off ligh-colored, to blend in w/ birch wood in England. During the industrual revolution, the trees turned black, leaving the peppermoths unable to camouflage. Due to that, only dark ones (w/ advantageous varitations - mutationn) were able to survive

Who are the scientists that contributed to evolution?
Leclerc, Lyell, Cuvier, E. Darwin, Lamarck, Malthus, C. Darwin, Gould
Leclerc:
similar organisms all probaby have a common ancestor
E. Darwin:
proposed that all life could have a single source
Lyell:
proposed the theory of “uniformitariansim”
→ assumes that the same natural laws and processes that operate in the universes have always operated and can be applied everywhere.
Cuvier:
proposed the idea of “catastrophism”
→ complete extinction followed by a renewed creation of new species
Lamarck:
suggested “acquired traits” during the parents’ lifetime, such as stretching a giraffe’s neck to eat leaves from trees, could be passed to its offspring to produce a new generation of giraffes with longer necks (FALSE)
Malthus:
more offspring is born than nature' could supply. As offspring enter the population, fewer resources will be available to the populatioon. Potential for competition between organisms for survival due to lack resources
C. Darwin:
described the mechanism of evolution as “Natural Selection”
Gould:
proposed the theory of “Punctuated Equilibrium” developed with Niles Eldredge in 1972.
→ theory: most evolution is characterized by long periods of evolutionary stability, rarely punctuated by rapid periods of branching speciation
common ancestor
an ancestral organism shared by two or more descendant lineages
selective advantage
a characteristic or trait that allows an organism to have better chances of surviving or reproducing
immutable
unable to change
What is catastrophism?
theory → the pattern of fossils could be accounted for by a series of global catastrophes that wiped out most species on earth
ex. extinction of dinos
What is uniformitarianism?
theory → geological changes are slow & gradual and the natural laws & processes haven’t changed ove time
CRUCIAL FACTS about C. Darwin?
wrote the book “On the Origin of species by means of Natural Selection”
Theories were shaped on the 5 yr voyage on the HMS Beagle (1831-1836). Found lots of evidence in the Galapagos Islands & South America
Took 20 years to complete the book
Suggested the idea of “Natural Selection”