Greek Architecture
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Greek (800 - 300 B.C.)
Perfected proportions and refined treatment. Based the different proportions of their construction systems on mathematical ratios. Completed with sophisticated optical corrections for perspective. The first manifestation was a wooden structure of upright posts supporting beams and sloping rafters.
Rough and Massive
Characteristic of Aegan period.
Minoans
Bronze age civilization flourished in Crete.
Named after King Minos of Knossos.
Stone foundation walls, piers and lintels with Timber framework upper walls.
Gate buildings with multi-columnar porches provided access to unfortified compounds.

Palace of Knossos
Contains labyrinth for the son of King Minos, the Minotaur.
Architect is Daedalus.
The palace contained residences, kitchens, storage rooms, bathrooms, ceremonial rooms, workshops, and sanctuaries.
Mycenaeans
Flourished and defeated the Minoans at around 1600B.C.
Treasury of Atreus/ Tomb of Agamemnon Tholos
Beginning in the late Bronze Age, the kings were buried outside the city in great beehive—or tholos.
Treasury of Atreus
Unlike their Greek contemporaries who would cremate their dead, the Mycenaeans buried their deceased in tombs. In the Treasury of Atreus, a Mycenaeans king was buried with his weapons and enough food and drink for his journey through the Underworld.
Ossuary
A container or room in which the bones of dead people are placed.

The Lion’s Gate
Marks the entrance to the fortified citadel of Mycenae, part of the citadel palace of Agamemnon. About 10 feet wide and high and two lions under a triangle are inscribed on a stone above the entrance gate.
Hellenic Period (650 B.C. - 323 B.C.)
The period occurred before the death of Alexander the Great. This period also refers to Classical Greece, which is the Golden Age of Greece.
Characteristic of Hellenic Period
Columnar and Trabeated
Timber, stone and terracotta
Materials used by Hellenic Period
Entasis
Optical Illusions
Hellenistic Period (323 B.C. - 30 B.C)
The period after the death of Alexander the Great and the emergence of the Roman empire.
Symmetry and order
Characteristic of Hellenistic Period
Ovolo
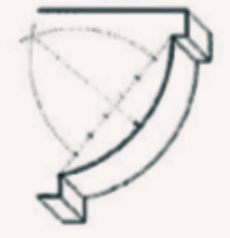
Echinus
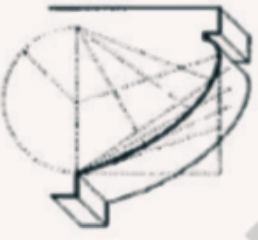
Scotia

Cavetto

Fillet
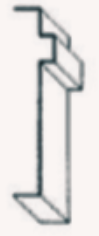
Cyma Recta
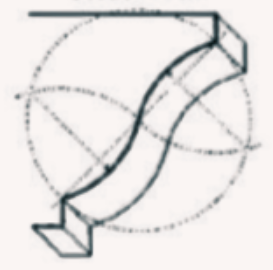
Cyma Reversa
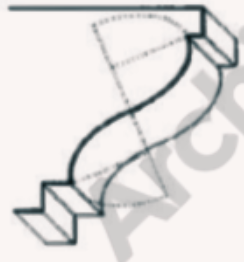

Temple of Apollo Thermos
One of the oldest Doric temples in Greece. The temple of Apollo was the focal point for the ancient Greek sanctuary of Thermos. It was used to pay honor and respect to the Greek God Apollo.
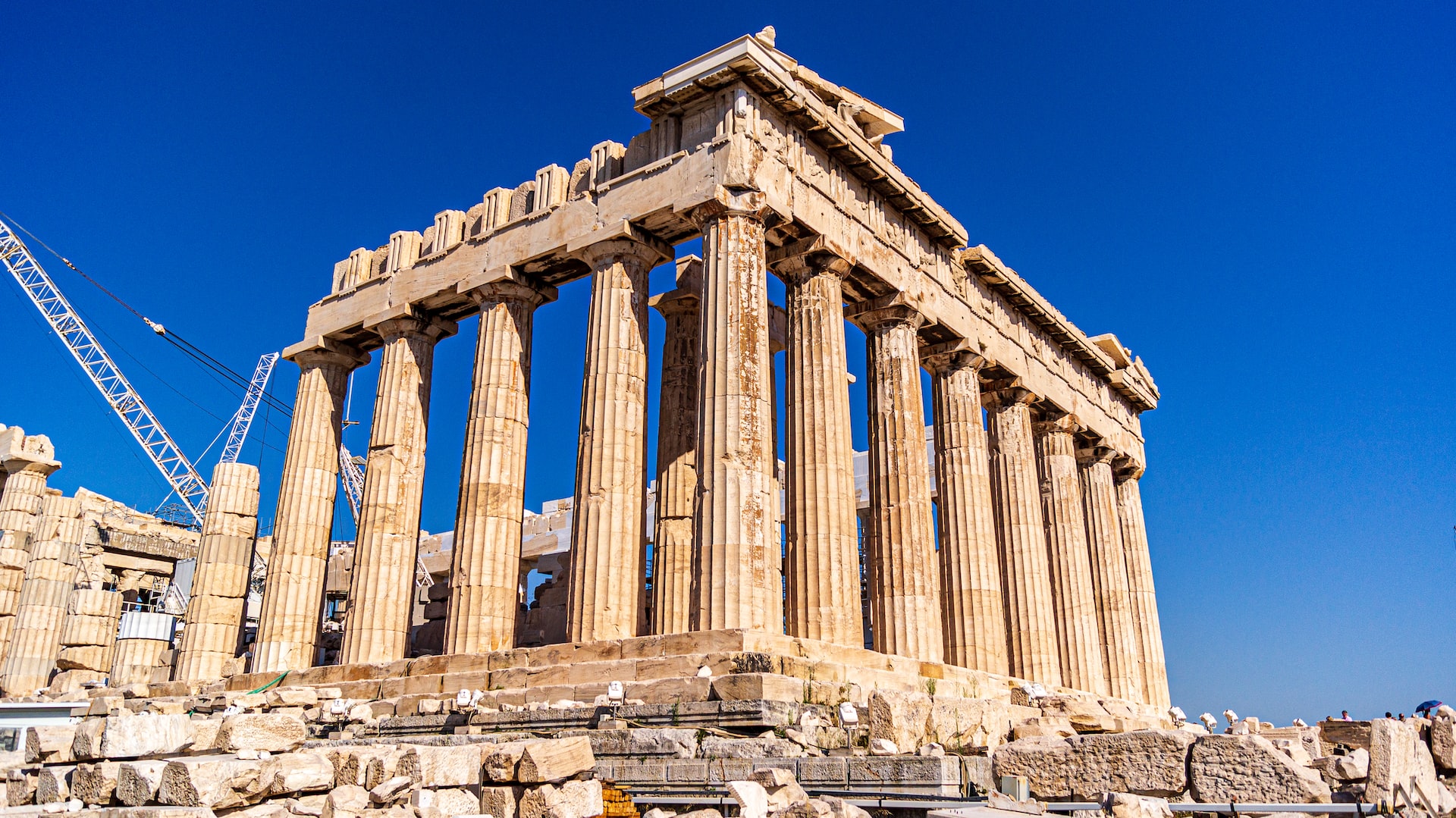

Acropolis
“City on the height" a city stronghold or fortress constructed on higher ground than surrounding. The most striking and complete ancient Greek monumental complex still existing in our times.

Propylaea
It is a monumental gateway that serves as a partition between the secular and religious parts of a city. Built by Mnesikles and it is his only known building.

Erechtheion
Also known as Temple of Athena Polias it is an ancient Greek Ionic temple on the north side of the Acropolis of Athens built for the goddess Athena.
Odeon of Herodes Atticus
It is an Odeon, or a theatre having a roof, located on the southwest slope of the Acropolis of Athens, Greece. The building was completed in AD 161 and then renovated in 1950. Built by Herodes Atticus in memory of his Roman wife, Aspasia Annia Regilla.
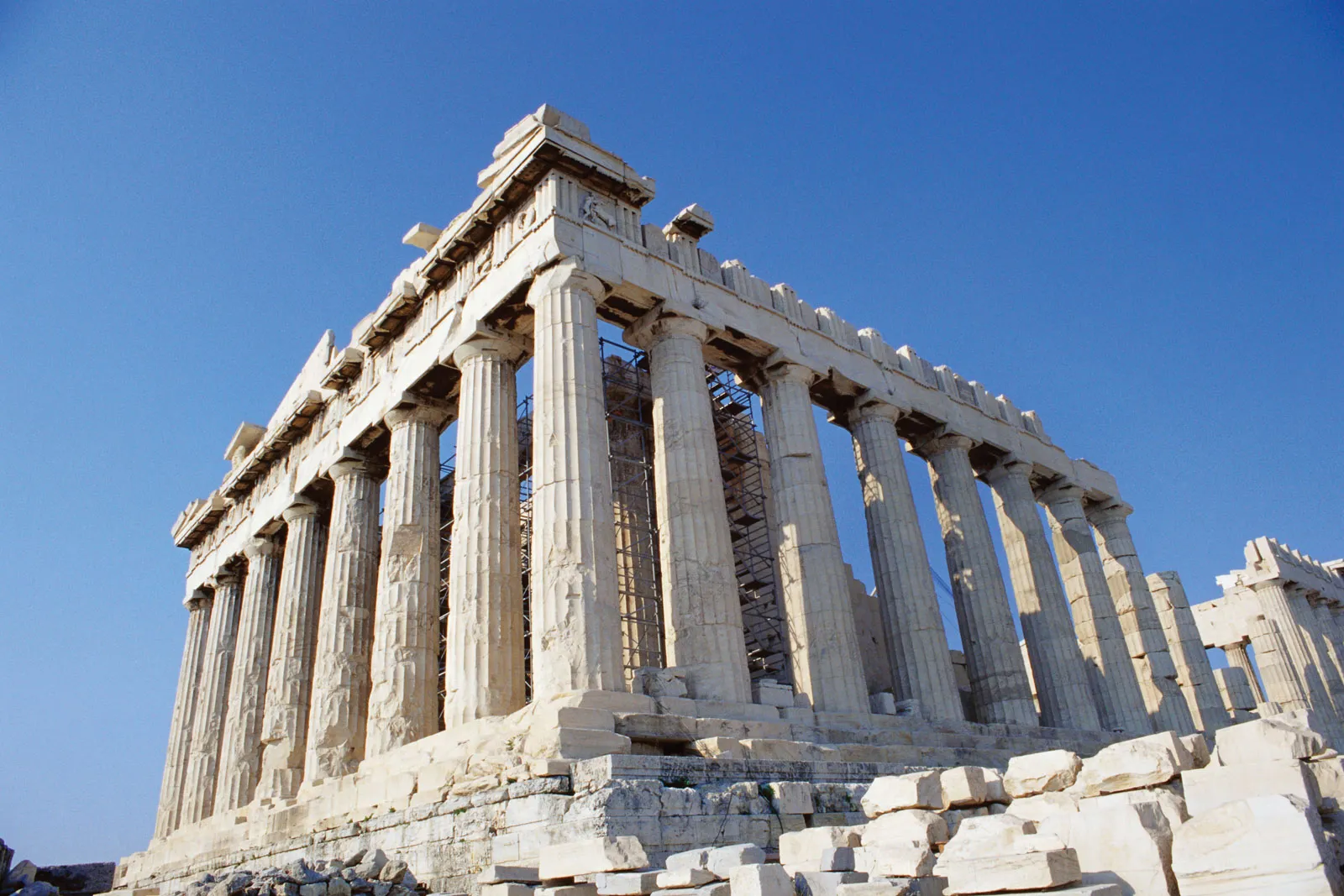

Parthenon
The marble temple built in honor of Athena, the city’s patron goddess. Used the proportion2n+1in determining the number of columns on the sides of a temple (n=number of columns at front) Built by Ictinus and Callicrates.
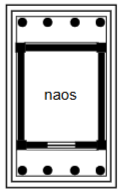
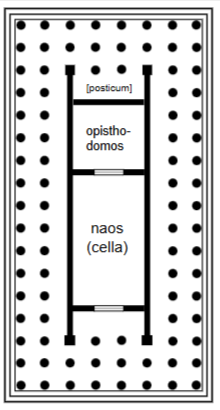
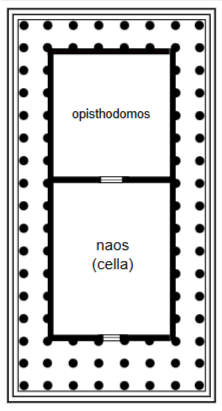
Naos or Cella
Principal chamber: enclosed part of the temple where the cult image was kept.
Pediment
A wide, low-pitched gable surmounting a colonnade or a major division of a facade.
Tympanum
The triangular space enclosed by the horizontal and raking cornices of a pediment; often recessed and decorated with sculpture.
Stylobate
A course of masonry forming the foundation for a row of columns, esp. the outermost Collonade of a classical temple.
Stereobate
A solid mass of masonry visible above ground level and serving as the foundation of a building esp. the platform forming the floor and substructure of a classical temple. Alos called crepidoma podium.
Acroterium
A pedestal for a sculpture or ornament at the apex or at each of the lower corners of a pediment. Also called acroterion.
Entasis
A slight curvature of a Classical column to serve as a kind of correction to optical illusions.
Antis
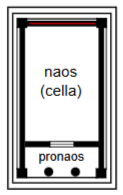
Amphi-antis
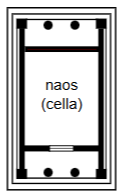
Prostyle
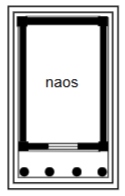
Amphiprostyle
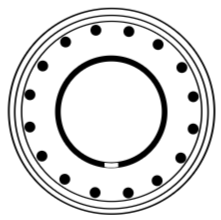
Tholos
Dipteral
Pseudodipteral
Apteral
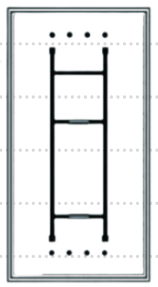
Pyconstyle
1.5 D
Systyle
2 D
Eustyle
2.5 d
Diastyle
3 D
Areostyle
4 D
In-antis
Columns are between anta and at front
Amphi-antis
Double anta at front and rear
Peripteral
On all sides
Pseudo-peripteral
Columns attached to naos.
Dipteral
Double line of columns surrounding the naos.
Pseudo-dipteral
Like dipteral but inner columns are attached to the naos.
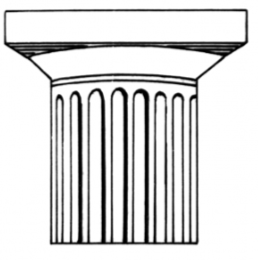
Doric
Oldest, simplest and most massive of the three Greek orders.
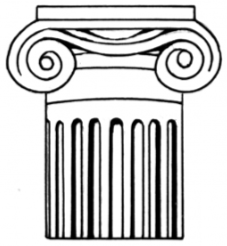
Ionic
Used for smaller buildings and interiors and volutes.

Corinthian
More ornate, carved with two tiers of curly acanthus leaves.
Caryatid
A carved statue of a draped female figure which functions as a column.
Canephora
basket-carrying; a carved statuesque column of a |draped female figure carrying a basket, or with a basket on her head.
Atlas
A massive carved statuesque stooping male figure, often serving as a columnar support for a pediment.
Herm
A square tapered column capped with the carved head, bust or torso of a figure, usually Hermes; originally used by the Greeks as a boundary marker, later as decoration.
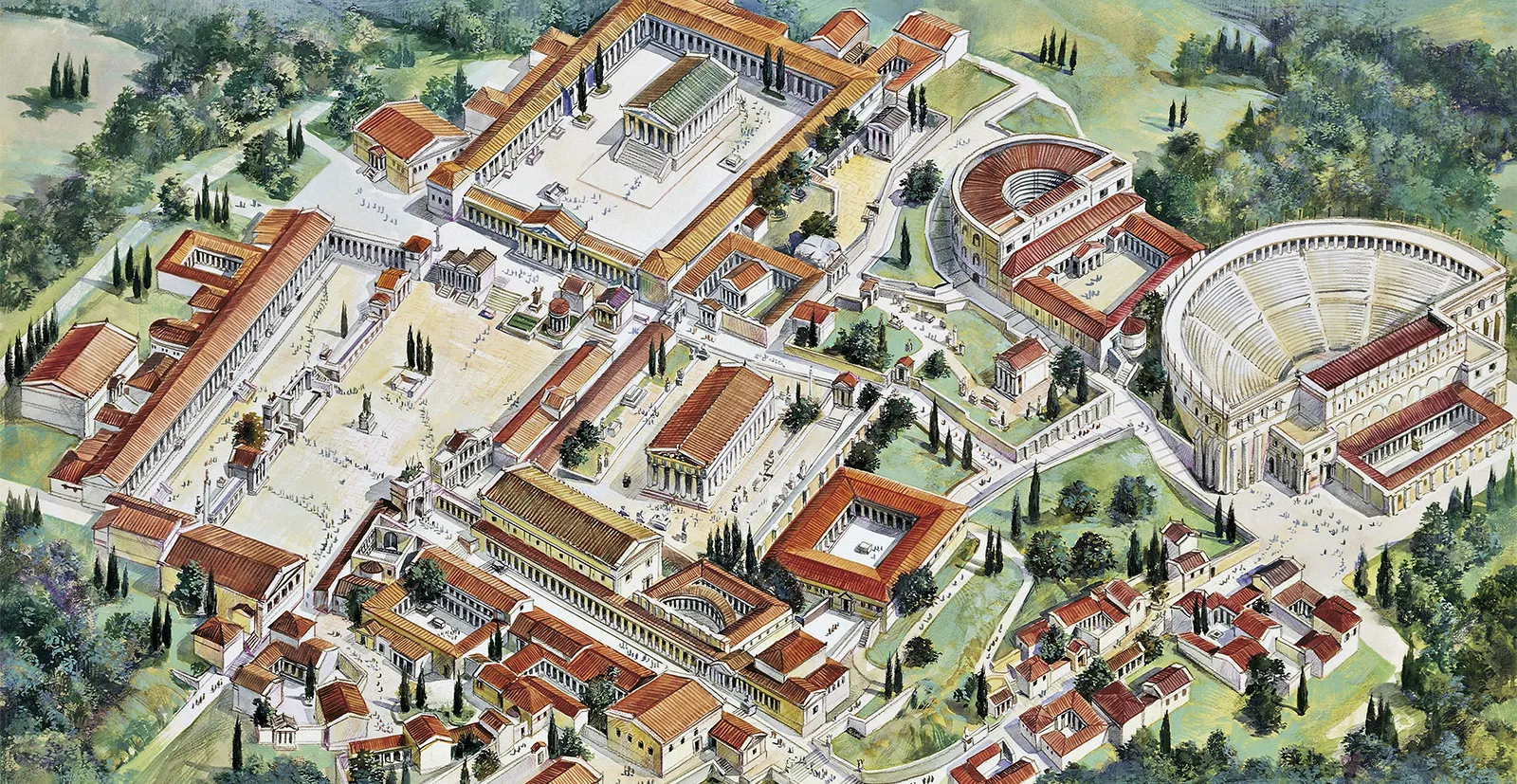

Agora
An open place of assembly and area in a city where free-born citizens could gather for public activities or discuss politics. It later designated the open-air marketplace of a city.
Theatron
“The seeing place” where the audience sat to watch the performance of a Greek Play. Open-air, usually hollowed out of the slope of a hillside with a tiered seating area around and facing a circular orchestra backed by the skene, abuilding for the actor's use.
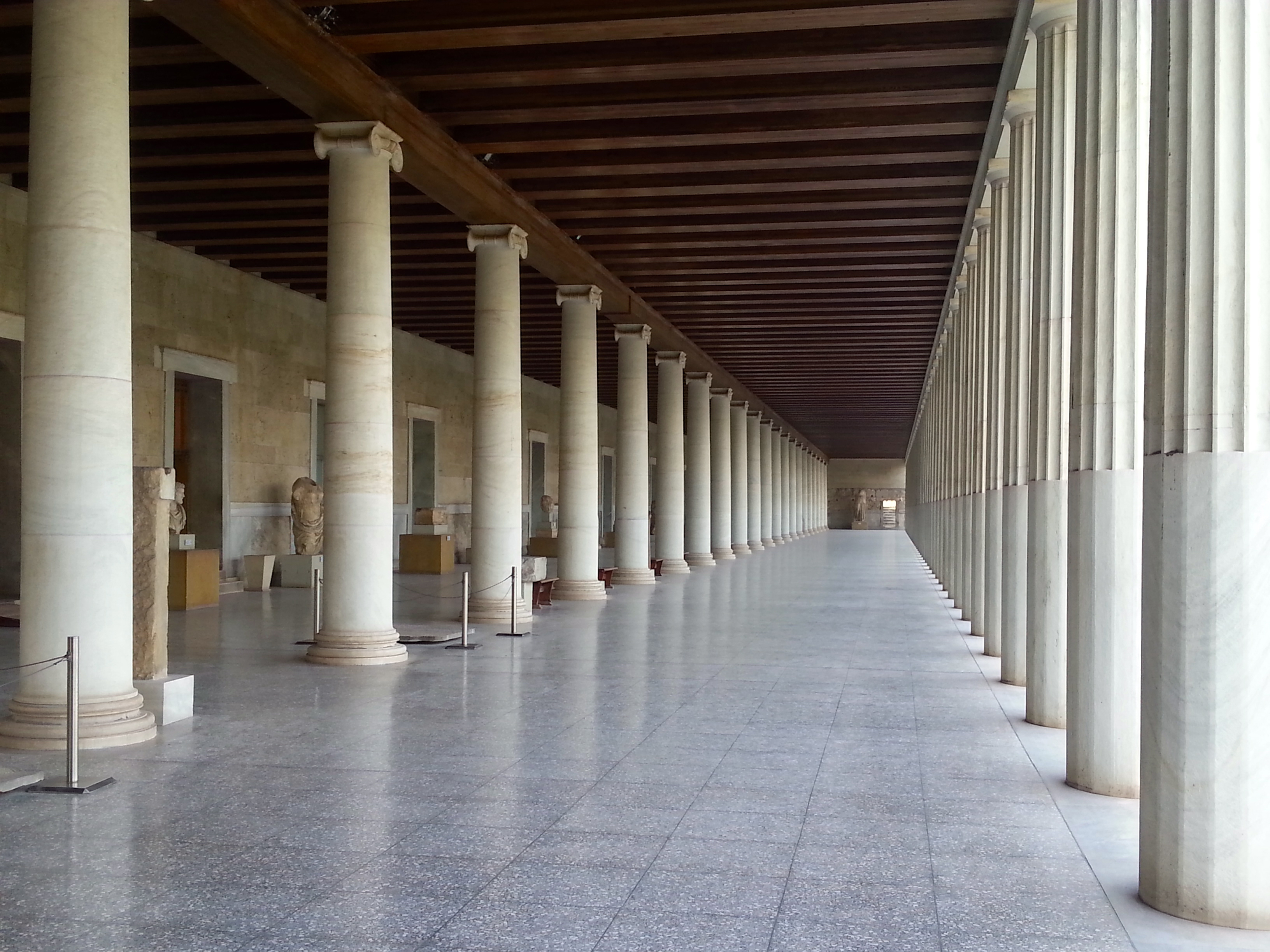

Stoa
Greek Portico and promenade or meeting place.

Prytaneion
Senate house and a public town hall.

Bouleuterion
Council chamber with rows of stepped benches surrounding a central platform.

Odeion
A roofed theatre building for the performance of vocal and instrumental music.

Stadion
A Greek venue for foot races.
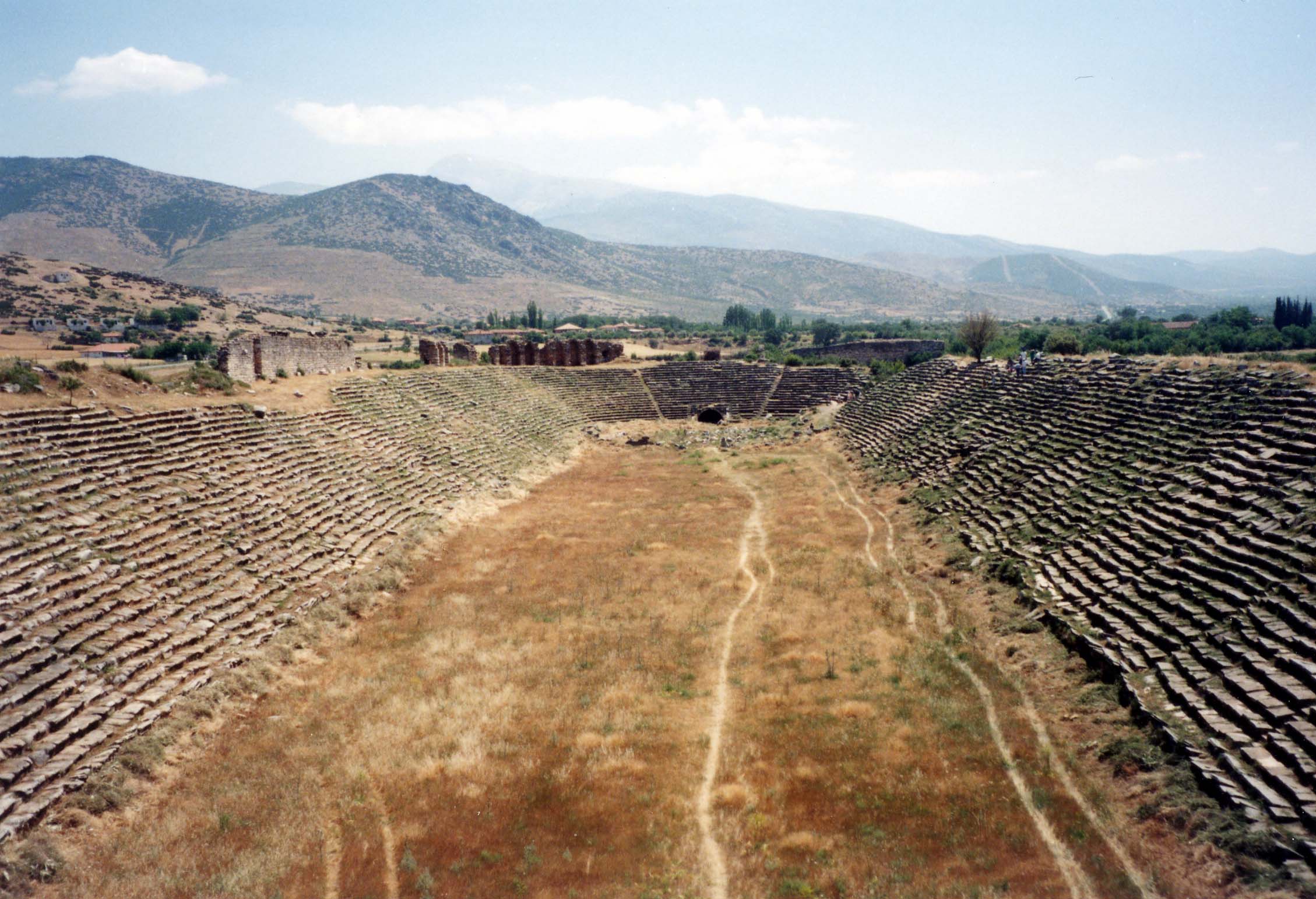

Hippodrome
Ancient Greek stadium designed for horse racing and especially chariot racing.

Palaestra
A Greek public area dedicated to the teaching and practice of wrestling and other sports; a wrestling school.

Gymnasion
Ancient Greek public training facility for competitors in athletic activities comes from the Ancient Greek term gymnés, meaning “naked” or “nude”.
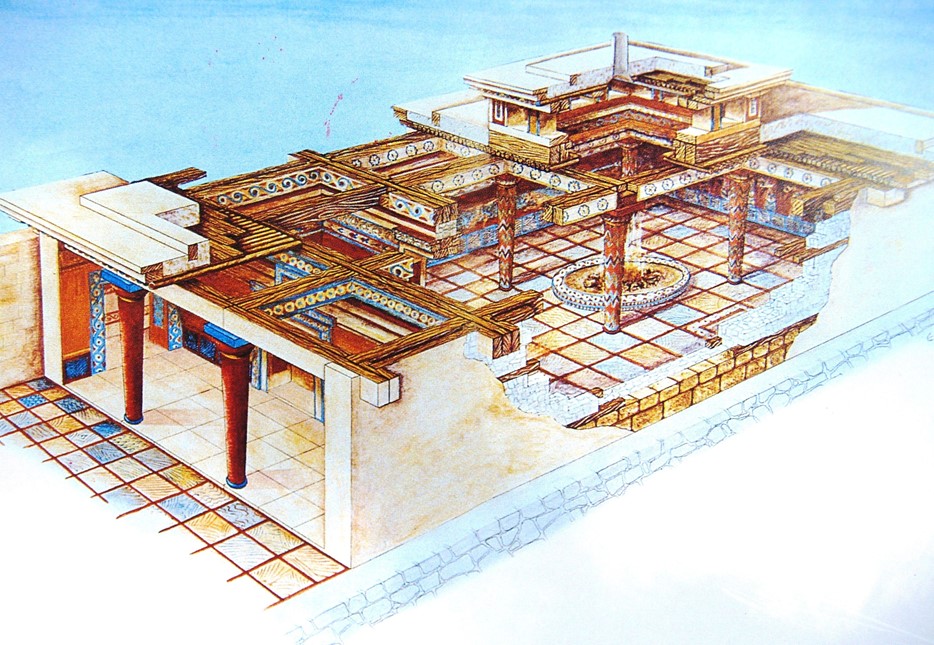
Megaron
A great rectangular hall that was surrounded by four columns, fronted by an open, two-columned portico, and had a central, open hearth that vented through an oculus in the roof.
Prostas
A Greek dwelling-type around which all spaces are arranged; the principal rooms are accessed via a niche-like anteroom or prostas. Entered from the street via a passage to an open courtyard,
Pastas
A dwelling-type with a courtyard in the center of the south side and deep columned veranda or pastas affording access to rooms.
Composite
A classical Roman order, a hybrid of Ionian and Corinthian.