elgawly- final spring 2022
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Opportunity Cost
Whatever must be given up to obtain some item
Normal Good
Demand increases as income increases
Inferior Good
Demand decreases as income increases
Substitutes
Price of Good X decreases as demand of Good Y to decrease
Complements
Price of Good X decreases as demand of Good Y increases
Equilibrium effect when demand AND supply shift left
Quantity decreases, price is constant
Equilibrium effect when demand AND supply shift right
Quantity increases, price is constant
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
Price Floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold
Price Ceiling is effective when ______ the equilibrium
below
Price Floor is effective when ______ the equilibrium
above
Price Ceiling produce a ______
Shortage
Price Floor produce a ______
Surplus
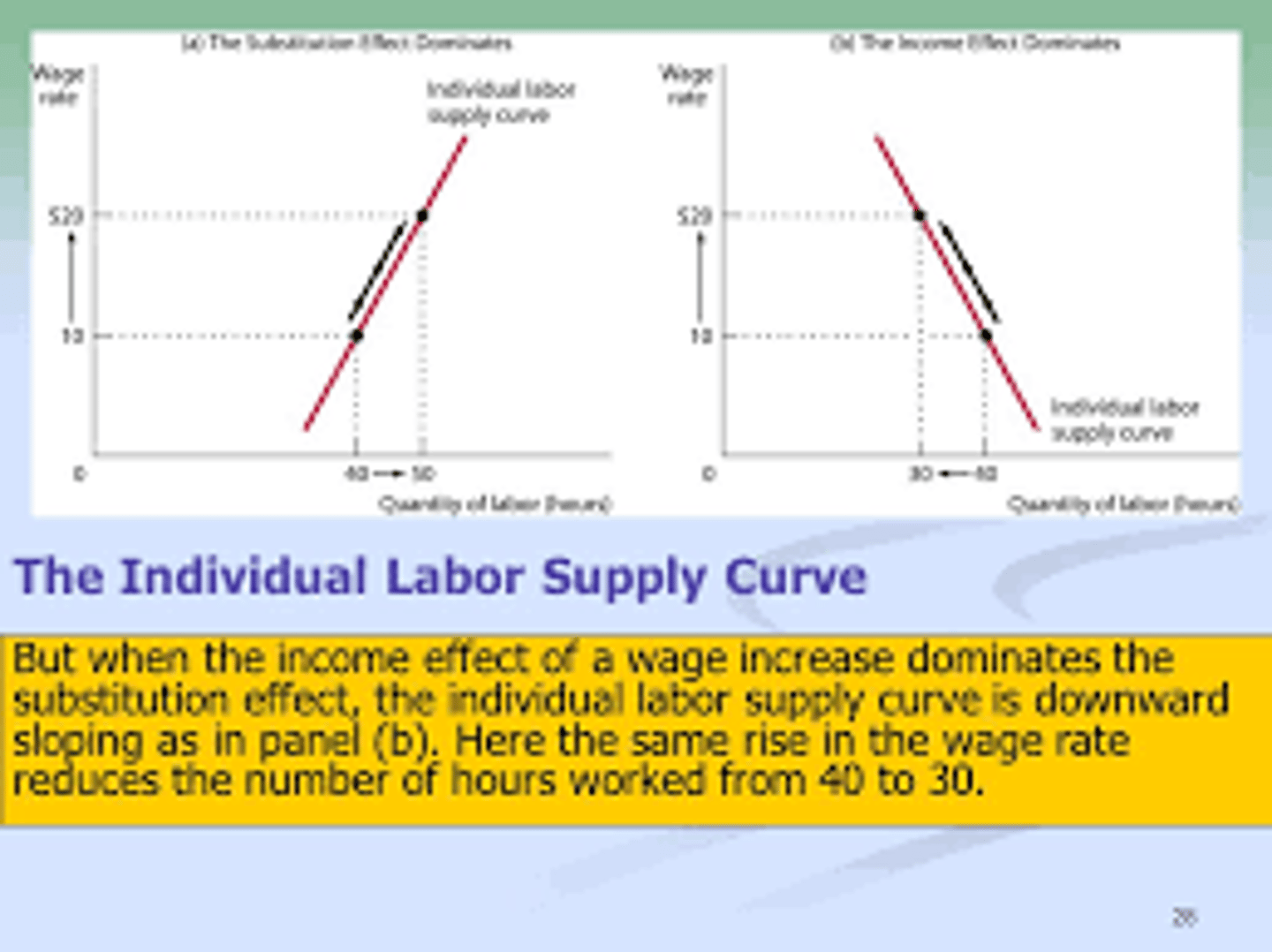
Individual Labor Supply Curve
shows how the quantity of labor supplied by an individual depends on that individual's wage rate
Elasticity of Demand
Percentage change in quantity demanded divided / Percentage change in price
The relationship between total revenue and price when a product is elastic
As total revenue increases, the price decreases
The relationship between total revenue and price when a product is inelastic
As total revenue increases, the price increases
When does a firm start to minimize losses?
When price is less than the average total cost.
When does a firm shut down?
When price is less than the average variable cost.
Ricardian Model
The level of a country's technology affects the wages paid to labor, such that countries with better technologies have higher wages.
How do you determine comparative advantage on a graph?
Set the intercepts equal to each other. Whatever variable you're isolating is what you are producing (Ex: 1C = 20P indicates that for every C you produce, you give up 20 P). Whichever one gives up less is the one that the country specializes in.
Comparative Advantage
The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Where does a firm determine its maximum output?
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
Increasing returns to scale
When long-run average total cost declines as output increases
Constant returns to scale
When long-run average costs remain constant as output increases
Decreasing returns to scale
When long-run average total cost increases as output increases
Economic Profit
Profit = Total Revenue - Explicit Costs - Implicit Costs (Remember that the word economic has E and I in it, hence Explicit and Implicit Costs are factored in!)
Accounting Profit
Profit = Total Revenue - Explicit Costs
Average Variable Cost
Variable Cost / Quantity
Total Cost
Fixed Cost + Variable Cost
Fixed Cost
A cost that does not change, regardless of quantity
Barriers to Entry of the market
Patents and copyrights,
Increasing returns to scale
Network Externality
Technological superiority
Control of natural resources
Perfect Competition Curve is at the profit maximizing point when...
P = MC
Perfect Competition in the Long Run
Price is equal to the ATC
Oligopolies and Monopolies in the Long Run
Price is greater than the ATC
Dominant Strategy
A strategy that is best for a player in a game regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players
Dominant Strategy with collusion
Pick the highest payoff
Heckscher-Ohlin Model
a country has a comparative advantage in a good whose production is intensive in the factors that are abundantly available in that country (You will export that product).
When equilibrium is above autarky, you are _________
Exporting
When equilibrium is below autarky, you are _________
Importing
How to find how much something is imported or exported?
Find the difference in quantity when (Demand = World Price) - (Supply = World Price)
Tariff
Government tax on imports or exports
Neoclassical view on consumer behavior
Assumes that consumers are rational
Behavioral view on consumer behavior
Assumes that consumers are irrational
"How much" decision
Analyzes the marginal benefit of a decision
"Either or" decision
Pick one or the other, nothing in between.
Status Quo bias
Do nothing when faced with making a decision
Mental accounting
categorizing decisions into "accounts" mentally designated for specific consumption transactions, goals, or situations.
Loss aversion
We care more about losses than wins
Marginal Utility
Change in total utility / Change in quantity
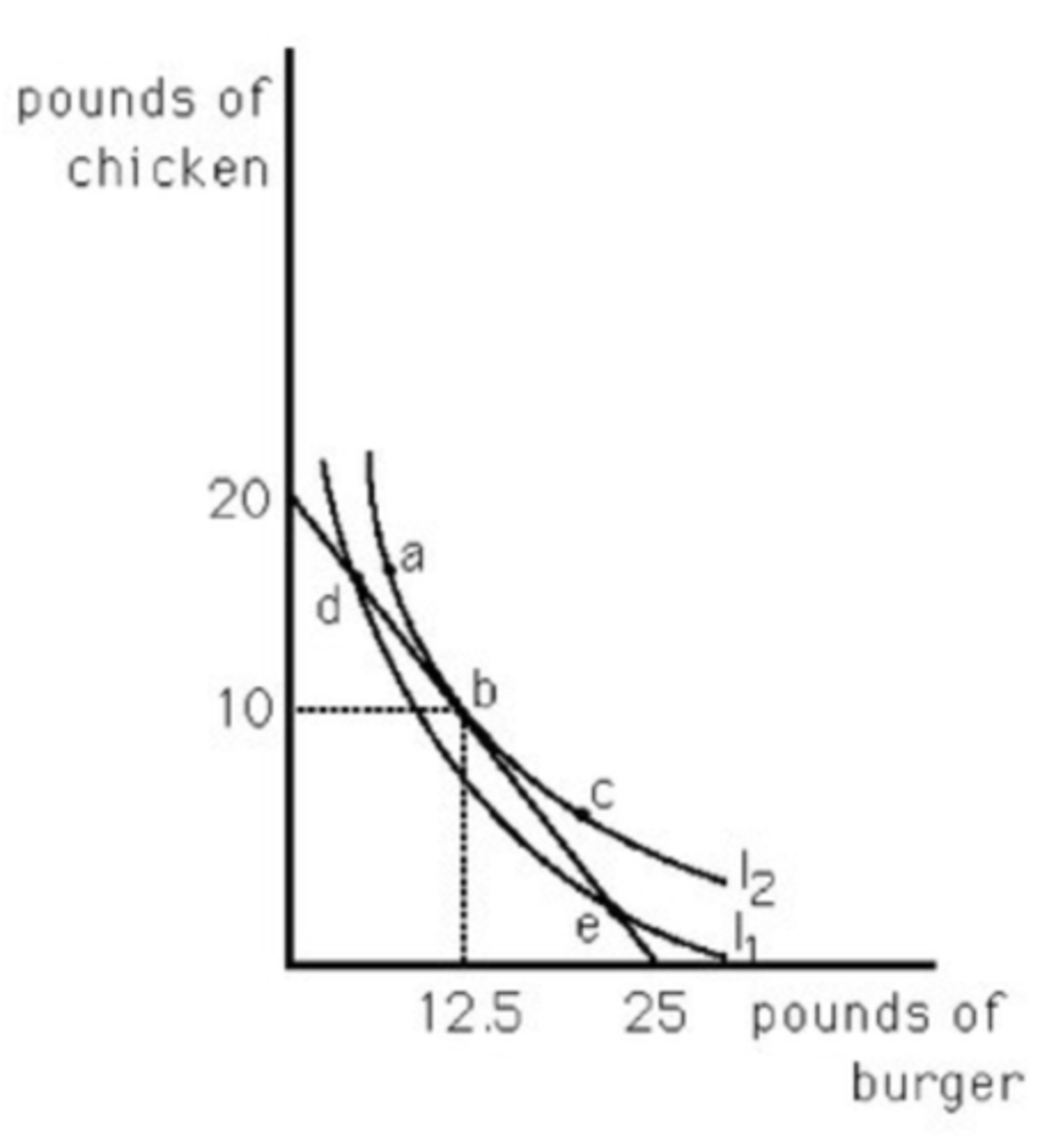
Properties of an indifference curve
Downward sloping, never criss cross, shows diminishing marginal utility, convex to the origin
Income effect (wages)
As wage increases, the labor decreases
Substitution effect (wages)
As wage increases, labor increases (to substitute labor for leisure)
Nonrival
One person's consumption does not interfere with another person's consumption
Nonexcludable
The supplier cannot prevent consumption by people who do not pay for it
Rival
One person's consumption interferes with another person's consumption
Excludable
The supplier can prevent consumption by people who do not pay for it
Two causes of income inequality
Single-Family housing and Education & Training
Private goods
Excludable and Rival
Public goods
Non-excludable and non-rival
Artificially Scarce goods
Excludable and non-rival
Common resource goods
Nonexcludable and rival
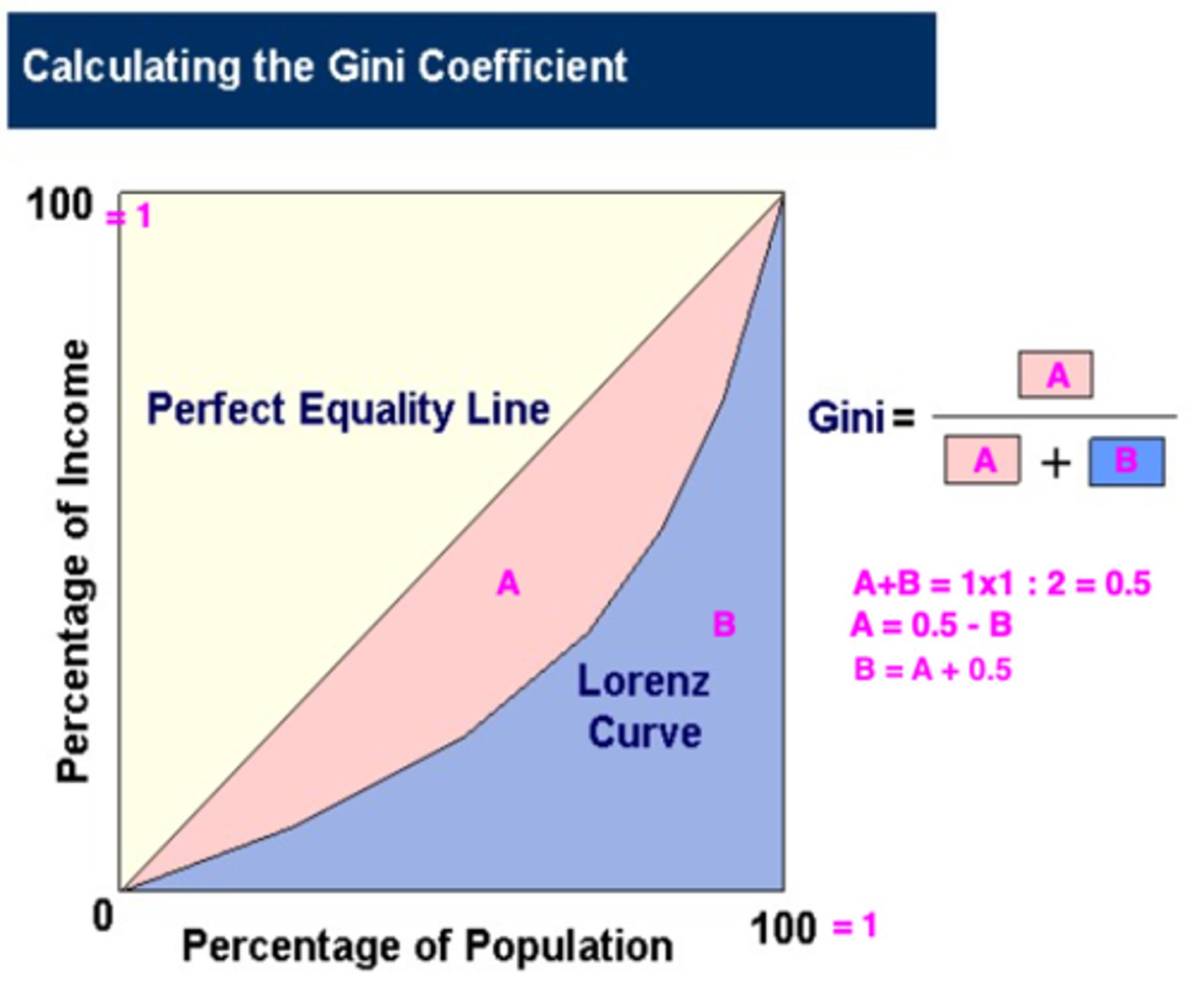
Gini Coefficient
A measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from zero for complete equality, to one if one person has all the income.
Gini Coefficient Formula
(Area A)/(Area A+B)
Transfer Payment
Government payments to individuals where no goods or services are exchanged.
Monetary transfers
money or a check transfer (There are no restrictions on how the transfer can be spent).
In-kind benefits
Goods and services provided for free or at greatly reduced prices
Means-tested program
A program in which an individual's income and assets must not exceed specified levels
Non-means-tested programs
Programs that provide cash assistance to qualified beneficiaries, regardless of income.
Poverty (welfare) programs
A government program designed to aid the poor. Always means-tested.
Social insurance programs
Programs to help the elderly, ill, and unemployed. NEVER means-tested.
Social welfare programs
Government programs that provide the minimum living standards necessary for all citizens. Means-tested
Median
The middle value in a distribution; half the values are above it and half are below it
Mean
The average value in a distribution
Negative income tax
A government program that supplements the income of low-income working families.
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
state-run program that provides assistance and work opportunities to needy families; Means-tested Monetary Transfer
Food Stamps
Government coupons that can be used to purchase food; Means-tested In-Kind Benefits
Supplemental Security Income
Provides a minimum income to seniors and the disabled who do not qualify for social security; Means-tested Monetary Transfer
Medicaid
A federal and state assistance program that pays for health care services for people who cannot afford them; Means-tested In-Kind Benefit
Earned Income Tax Credit
Also known as the EITC, a refundable federal income tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and families, even if they did not earn enough money to be required to file a tax return; Means-tested Monetary Transfer
Affordable Care Act
Most of employers must provide health insurance, have insurance or face surtax, prevents rejection based on pre-existing condition; Means-tested In-Kind Benefit
Social Security
Federal program of disability and retirement benefits that covers most working people; Non Means-tested Monetary Transfer
Medicare
A federal program of health insurance for persons 65 years of age and older; Non Means-tested In-Kind Benefits
Unemployment Insurance
A government program that partially protects workers' incomes when they become unemployed; Non means-tested Monetary Transfer
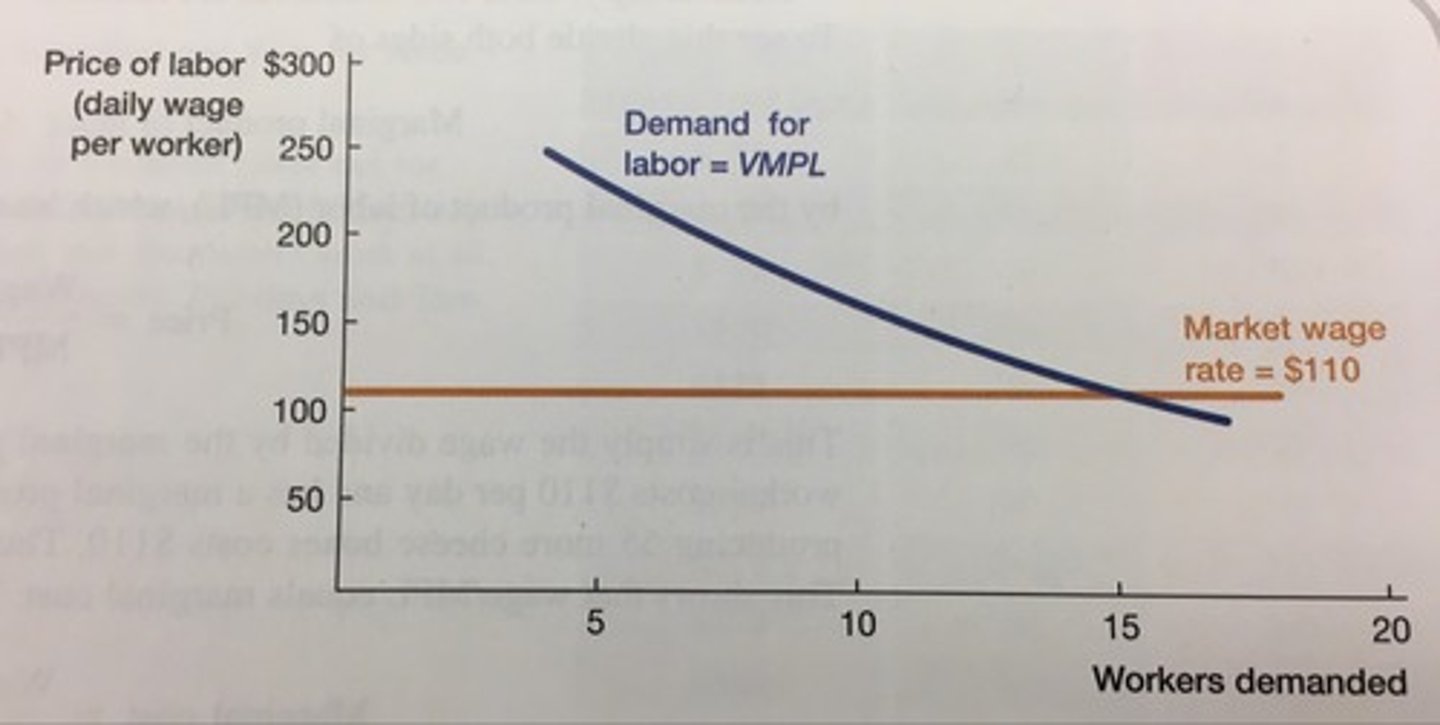
In terms of VMPL, when do we stop hiring?
Stop until VMPL = wage OR when VMPL < wage
Adverse Selection problem
a problem that occurs when buyers and sellers have different amounts of information about the good for sale and use that information to the detriment of the other.
Moral Hazard
When the act of insuring an event increases the likelihood that the event will happen
How to solve the adverse selection problem
Screening and Signaling
Screening
Describes the efforts of the less informed party to gather information about the more informed party.
Signaling
Describes the efforts of the more informed parties to reveal information about themselves to the less informed party.
How to solve the moral hazard problem
Require a deductible
Efficiency Wage
A wage that is deliberately set above the market rate to increase worker productivity. Less labor turnover, higher pool of workers, more productive workers, and productivity is higher.
Compensating differentials
Higher wages that compensate workers for unpleasant aspects of a job
Time Allocation Line
Determine the effects from A to B, then B to C, then A to C.