Alkanes
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons
only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms and each carbon atom forms 4 single bonds
crude oil can be separated via fractional distillation
into smaller more useful hydrocarbons
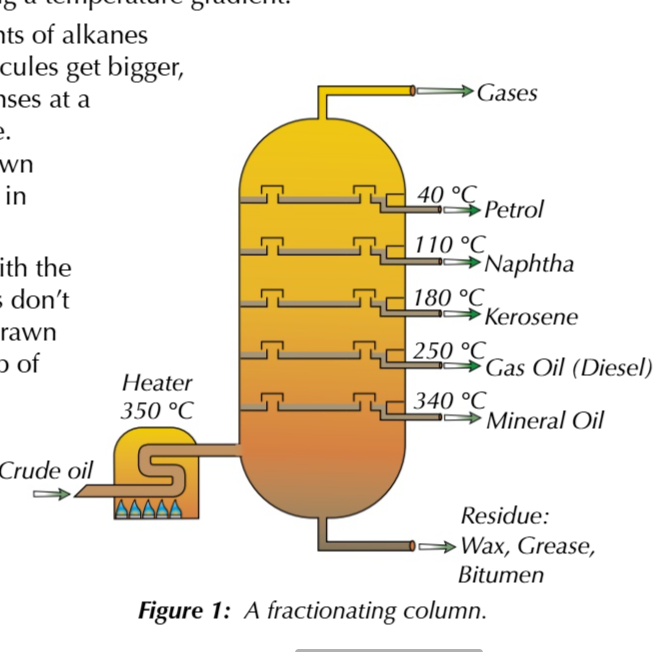
fractional distillation of crude oil:
crude oil is vapourised at 350℃
vapourised crude oil goes into the bottom of the fractioning column and rises up through the trays
the largest hydrocarbon chains are vapourised at all because their boiling point is too high
as crude oil vapour travels up the fractioning column it gets cooler creating a temperature gradient
because boiling points of alkanes increase as the molecule gets longer, each fraction condenses at different temperatures
hydrocarbons with the lowest boiling points dont condense, they’re drawy off as gases at the top of the column
long chain hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller pieces in a process called cracking
to meet the high demand of short chain hydrocarbons
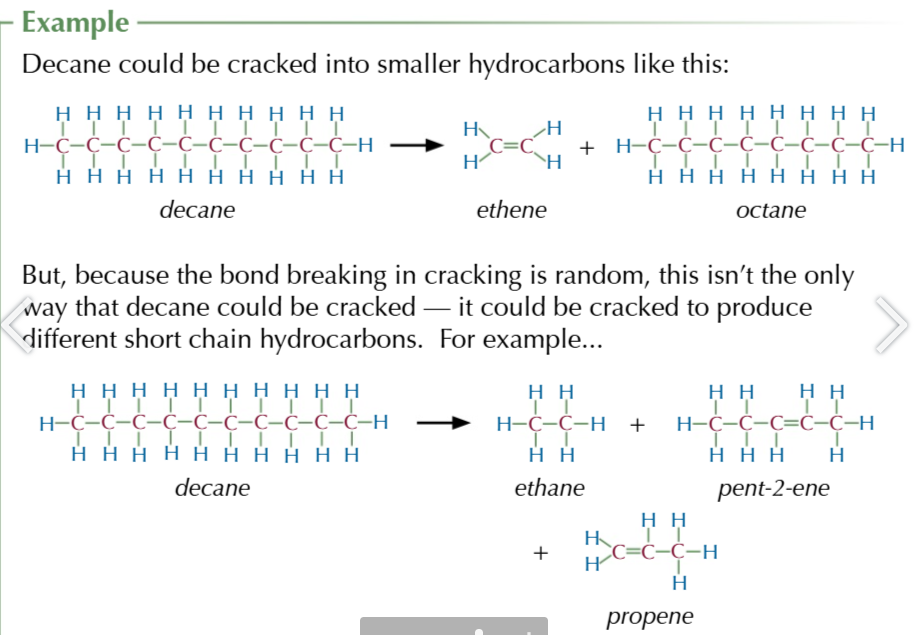
there are two types of cracking
thermal
catalytic
thermal cracking
occurs at temperatures up to 1000℃
high pressure up to 70 atm
produces lots of alkenes (useful for polymers)
catalytic cracking
zeolite catalyst
slight pressure
high temperature 500℃
produces lots of aromatic hydrocarbons and alkanes for motor fuels
using a catalyst cuts costs
because the reaction can be done at a lower pressure/temperature and saves time+money
complete combustion of alkanes
if you burn/ oxidise alkanes with plenty of oxygen, you get carbon dioxide and water

incomplete combustion of alkanes
when there’s not enough oxygen present when you burn hydrocarbons you produce particulate carbon )soot) and carbon monoxide
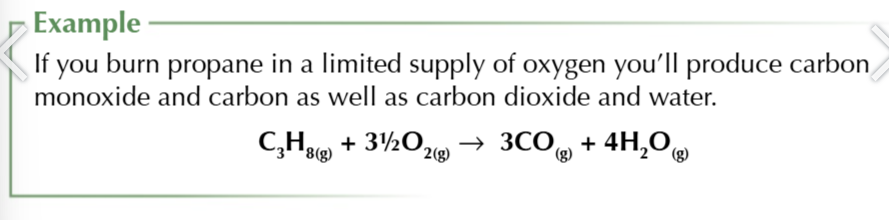
carbon monoxide is poisonous
carbon monoxide binds to the same sites on haemoglobin in RBCs as oxygen
this prevents oxygen from being carried around the body
carbon monoxide can be removed from exhause gases
by catalytic converters on cars
nitrogen odixes are a series of toxic and poisinous molecules with the general formula NOx
Nitroge monoxide is produced when at high temp/pressure in a car engine cause hitrogen and oxygen atoms in the air to react
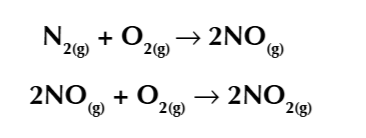
unburnt hydrocarbons can react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight to form ground level ozone O3
ground level ozone irritates people’s eyes, aggrivates respritory problems and causes lung damage
3 main pollutants from vehicle exchaust
nitrogen oxides
unhurnt hydrocarbons
carbon monoxide
catalytic converters can remove vehicle pollutants from the exhaust
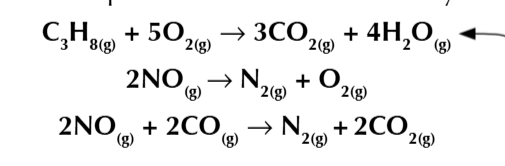
sulfur from fossil fuels reacts to form sulfur dioxide
sulfure dioxide dissolves the moisture in the atmosphere and is converted into sulfuric acid AKA acid rain
when nitrogen dioxide escapes into the atmosphere
nitric acid is created
acid rain
destroys trees, vegitation and corrodes buildings and statures and kills fish in lakes
sulfur dioxide can be removed before it gets into the atmosphere
using powdered CALCIUM CARBONATE/CALCIUM OXIDE MIXED W WATER
flue gases + alkaline slurry= harmless salt
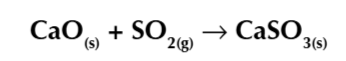
burning fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide
carbon dioxide is a green house gas
green house gases cause the green house gass efect
absorb infrared energy and emit some of the energy they absorb back towards the earth keeping it warm
halogens react with alkanes in photochemical reactions
forming halogenoalkanes
photochemical reactions
reactions started by ultraviolet light
a hydrogen atom is replayed by chlorine/ bromine
free radical substitution
free radicals
particles with an unpairewd electron
free radicals form when
a covalent bond splits equally giving 1 electron to each species
the unpaired electrons make them very reactive
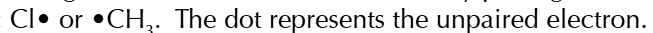
methene and chlorine exposed to UV light forms chloromethane
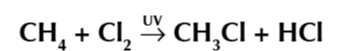
free radical substitution is split into 3 phases
INITIATION
PROPOGATION
TERMINATION
Initiation
produces the free radical via photodissocation
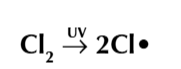
propogation
the free radical are used up in a chain reaction, first it will attack the normal molecule creating a new free radical which attack another molecule to for the origional free radical
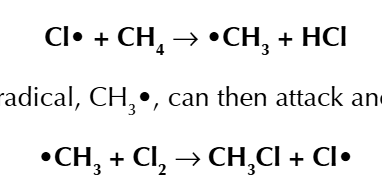
(substitution)
if there is excess reactants you get all sorts of reaction
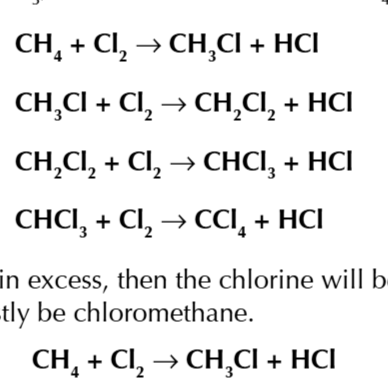
termination
all free radicals are mopped up to create stable molecules
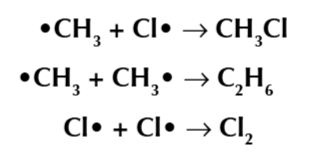
chlorofluorocarbons
halogenoalhakes when all the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by chlorine and fluorine

ozone forms naturally when a oxygen molecule is roken down into 2 free radicaks by ultraviolete radiation
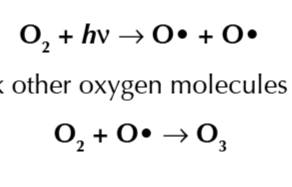
CFCs destroy the ozone by forming chlorine free radicals when C-Cl bonds break which react with ozone
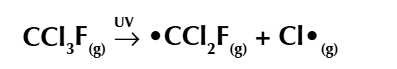
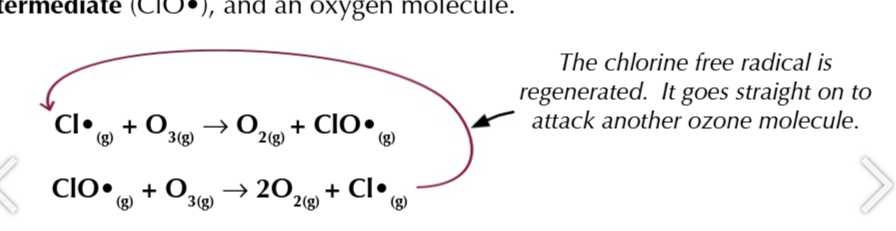
chlorine free radicals are catalysts
they react with ozone to form an intermediate ClO• and an oxygen molecules
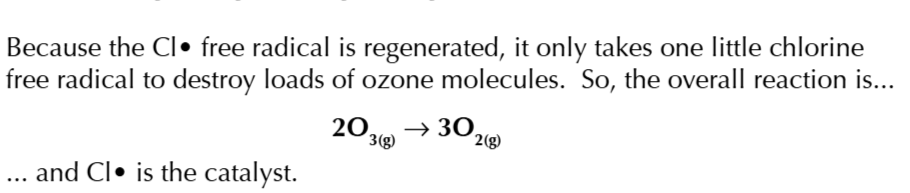
CFCs
unreactive
non fmamable
non toxic
CFCs used as
fire extinguishers
propellants in aresols
coolant gas in fridges
added to form plastics to make insulation and packaging materials
HCFCs created as a safer alternative to CFCs

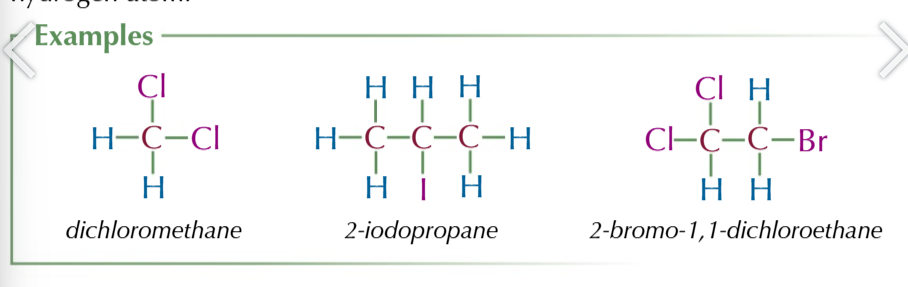
halogenoalkanes
alkanes with at least one halogen aotm in place of a hydrogen atom
halogenoalkanes are polar
because halogens are electronegative

δ+ carbon doesnt have much electrons
so it can be attacked by nucleophiles
nucleophiles
electron pair donors, attracted to positive regions
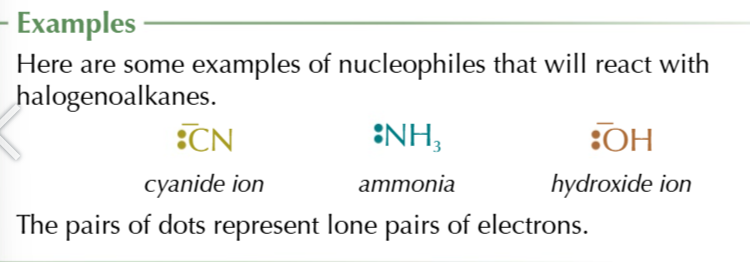
nucleophilic substitution
the mechanism for halogenoalkanes
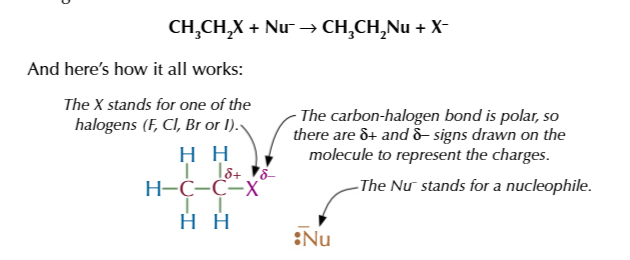
nucleophilic substitution step by step:
LPE on nucleophile attacks the slightly positive carbon attached to the halogen
the carbon can only form 4 bonds so the addition of the nucleophile breaks the bond between carbon and the halogen, the electron is attracted to the halogen as is electronegativity is high
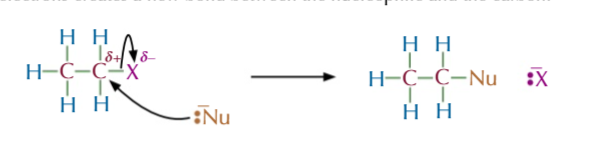
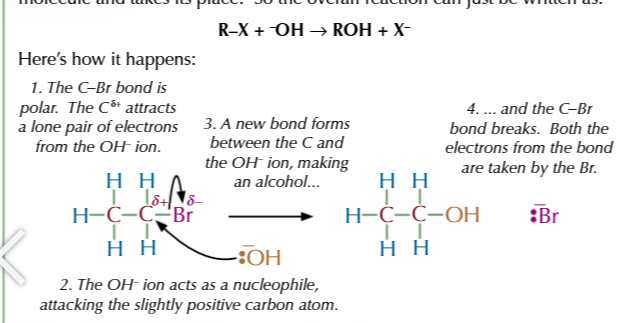
halogenoalkane + OH- (via warm aqueous sodium/potassium hydroxide)
=ALCOHOL

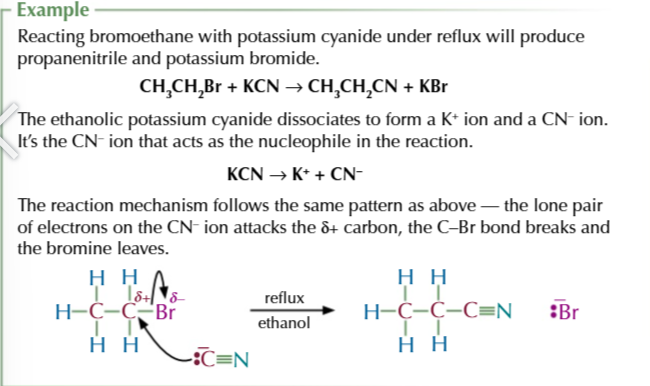
halogenoalkane + CN- (via warming halogenoalkane with ethanolic potassium cyanide/ potassium cyanide dissolved in ethanol)
=NITRILE
halogenoalkane + potassium cyanide dissolved in water
= the OH- could act as a competing nucleophile and you’d get some alcohol product
R3N, where R could be Hydrogens or another group
amine
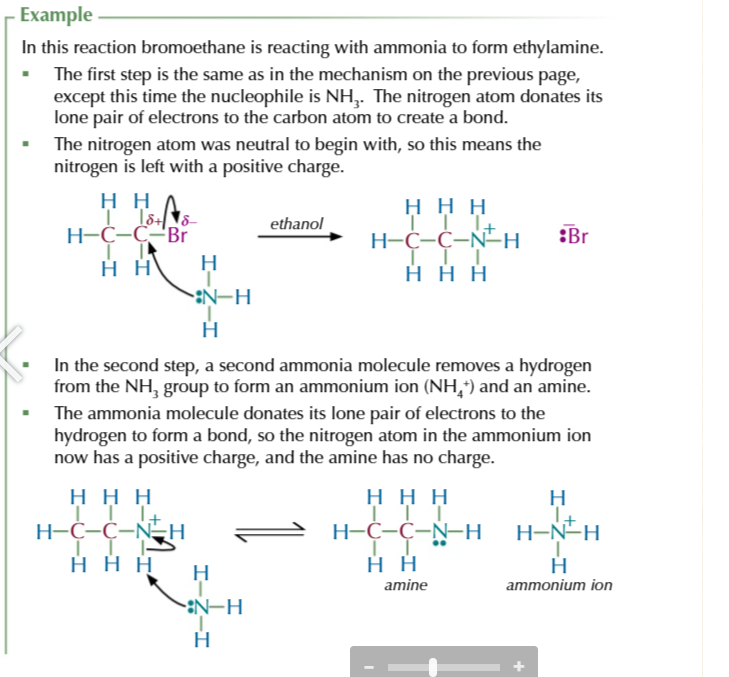
halogenoalkane + EXCESS ethanolic ammonia (ammonia dissolved in ethanol) in a sealed tube
= AMINE
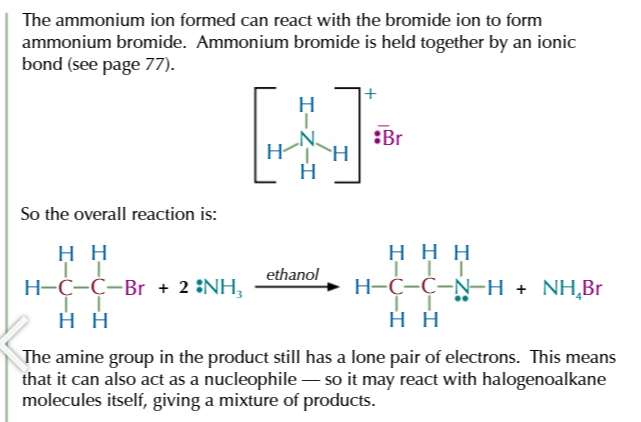
going down group 7, carbon-halogen bond strength DECREASES
therefore fluoroalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution slower than iodoalkanes, which undergo nucleophilic substitution the fastest
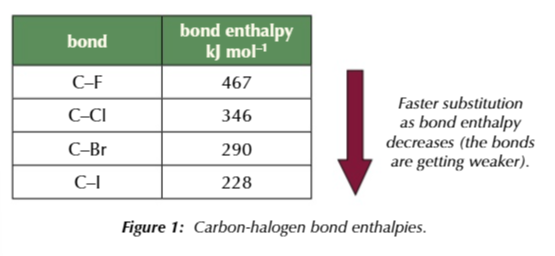
drawing mechanisms for nuceophilic substitution reactions
iys important to draw the curly arrows coming from the electrons (which come from either a bone/a lone pair on an atom or ion) and going to the atoms
make sure the charges are balanced at every stage of a mechanism
if you start with a negative charge you should end with a negative charge
halogenoalkane + OH- (warmed together with OH- from dissolved ethanol NOT water)
halogen elimination from a halogenoalkane produces ALKENES
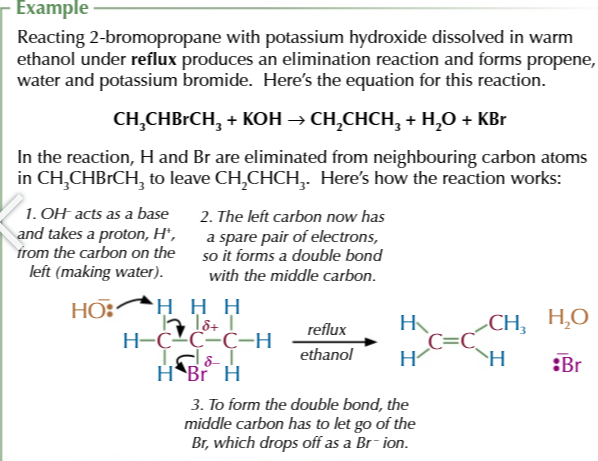
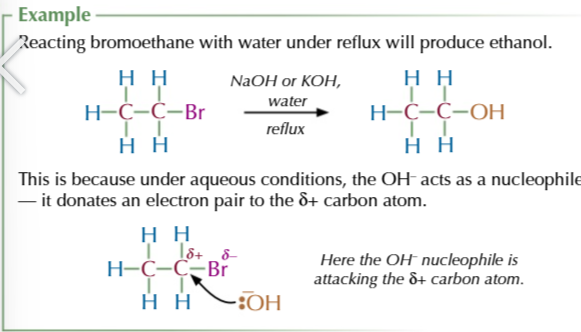
halogenoalkane + water under reflux
= ALCOHOL via nucleophilic substitution
halogenoalkane + ethanol under reflux
= ALKENE via elimination

halogenoalkane + water + ethanol
= ALCOHOL + ALKENE