IB Biology 2025 - Cell Signaling
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Signal molecules bind to
receptor proteins
ligand
A signal molecule that binds specifically to another molecule, usually a larger one.
The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________.
cAMP
Endocrine
long distance signaling occurring in the body
autocrine
term for hormones that act on same cells that secrete them
paracrine signaling
Signal released from a cell has an effect on neighboring cells.
transduction pathway
A series of molecular changes that converts a signal on a target cell's surface to a specific response inside the cell.
reception
The target cell's detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell.
Insulin released by the pancreas signals the liver to store glucose.
endocrine response
Stage of cell signaling when a transcription protein is activated for gene regulation.
cellular response
steroid
type of cell signaling molecule that can bind to an intracellular receptor.
enzymes that transfer the terminal phosphate from ATP to an amino acid residue on the target protein.
protein kinases
Apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
target cells
cells that have receptors for a particular hormone
The antagonistic functions of the direct and indirect pathways are often regulated by
hormones
negative feedback system
a process that results in a response that reverses the original stimulus
positive feedback mechanism
Feedback that tends to cause the level of a variable to change in the same direction as an initial change (more gives more, less gives less)
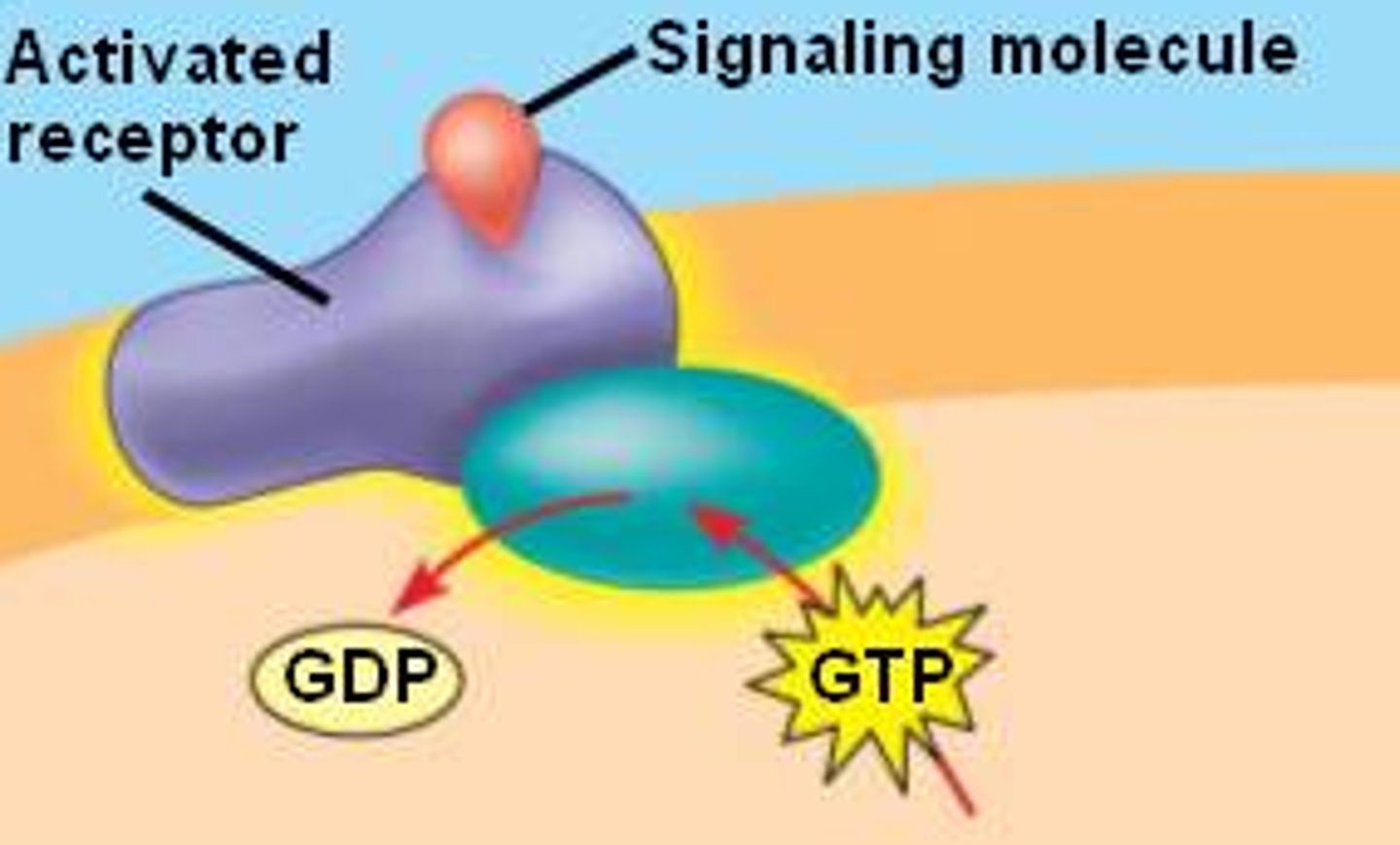
G-protein coupled receptors
A special class of membrane receptors with an associated GTP binding protein; activation of a G protein-coupled receptor involves dissociation and GTP hydrolysis
G-protein-linked receptor
A plasma membrane receptor that works with the help of a G-protein.
Example of antagonistic effect
insulin and glucagon
Yeast cells release mating factors that
bind to receptors on membranes of opposite sex only
Signaling across gap junctions
a cell targets a cell connected by gap junctions (cell signals to cell that is connected to it)
The order of cell signaling from shortest to longest distance.
autocrine --> signaling across gap junctions --> paracrine --> endocrine
functional categories of signaling chemicals
Hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines and calcium ions
Hormones
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
Cytokines
Hormone-like chemicals- small proteins - facilitating communication between brain and immune system.
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Chemical categories of hormones
steroids, amines, polypeptides, glycoproteins
chemical categories of neurotransmitters
amino acids, amines, peptides
structure receptor proteins in the cell membrane
intracellular receptors
hydrophobic Ligands move directly across the membrane to bind to the intracellular receptor.
Steps in signaling pathway
1. Recognition of hormone signal
2. Transduction of signal across membrane
- receptor conformational change (form weak interactions)
3. transmission to intracellular components
- receptor activates adaptor proteins
4. Modulation of the effector
- effector takes the inner molecule + makes it active
- 2nd messengers produced, target proteins activated
5. Response of the cell to the signal
6. Termination of the signal
- degrade 2nd messenger
- turn off target proteins
first messenger
A water soluble hormone that binds to its receptor at the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
transduction (cell signaling)
the binding of the signaling molecule alters the receptor and initiates a signal transduction pathway; transduction often occurs in a series of steps
signaling cascade/pathway
a series of chemical reactions that occur within a biological cell when initiated by a stimulus
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Produced by adrenal medulla. Targets liver, muscle, and adipose tissue to raise blood level of sugar and fatty acids; increases heart rate and force of contraction.
Melatonin function
maintains sleep/wake cycle; high during sleep
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
tyrosine kinase receptors
- transmembrane receptors - bind EC ligand (conformational change outside first)
- then internal part of receptor phosphorylates tyrosine sidechains (conformational change) induces:
- auto-phosphorylation = first step in signalling cascade
- eg Insulin R = 4 subunits (2 alpha EC + 2beta IC) disulfide bonds = outside cell
- platelet derived growth factors = single pass protein
tyrosine kinase
An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to the amino acid tyrosine on a substrate protein.
Phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
Kinase
an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specified molecule.
Outline how suprachiasmatic nuclei cells sense and respond to changes in light
Light Detection:
Retinal Photoreceptors: Specialized retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) containing melanopsin detect ambient light levels.
Signal Transmission:
Retinohypothalamic Tract (RHT): Signals from ipRGCs travel via the RHT directly to the SCN.
Neuronal Activity: Light exposure increases SCN neuronal firing rates, particularly during the daytime.
Gene Expression: Light induces expression of immediate-early genes in the SCN, influencing circadian rhythms
Outline the mechanism of action of epinephrine as a signaling molecule.
Receptor Binding:
Adrenergic Receptors: Epinephrine is a non-selective agonist, activating both alpha (α) and beta (β) adrenergic receptors.
Physiological Effects:
Cardiovascular System: Activation of β₁ receptors increases heart rate and contractility, enhancing cardiac output.
Respiratory System: Stimulation of β₂ receptors leads to bronchodilation, improving airflow in the lungs.
Vascular System: Binding to α₁ receptors causes vasoconstriction, which raises blood pressure and redirects blood flow to essential organs