Ch.4 - Tissues (Anatomy)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DT = defining trait (for ID practice)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Four Main Types of Tissues
Epithelial (covering), Connective (support), Muscle (movement), Nervous (control)
Epithelial Function
protection
diffusion
absorption/secretion
transport/filtration
forms slippery surfaces (i.e: cavities)
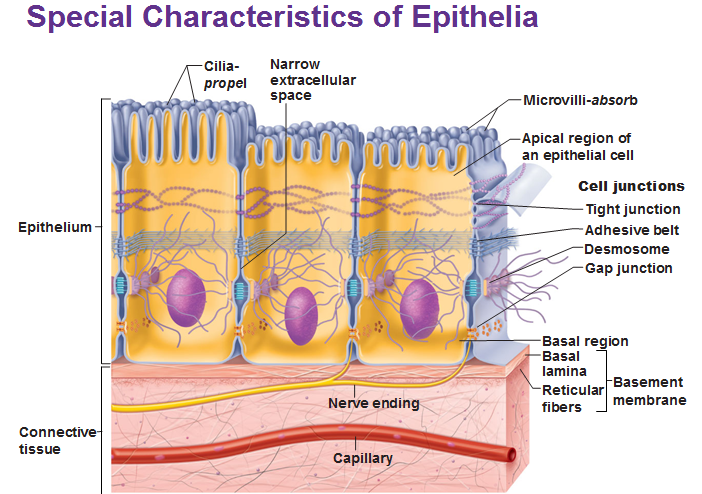
Epithelial
-densely packed w/cells
cell junctions in between cells
no blood cells → gets nutrients from underlying connective tissue @ lamina propria
Lamina Propria significance
carries blood supply to the epithelium + holds cells in place and binds them to smooth muscle below
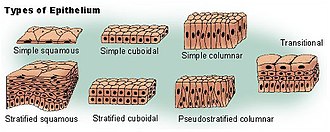
Naming system for Tissues
1st name = # of layers (simple: 1 or stratified 2/+)
last name = desc. shape apically (top)
Shapes of Cells (last name description)
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar
Squamous Cells
width > height (plate-like) + flattened, disc nuclei
Cuboidal
width = height, circular nuclei
Columnar
height > width + oval/elongated nuclei
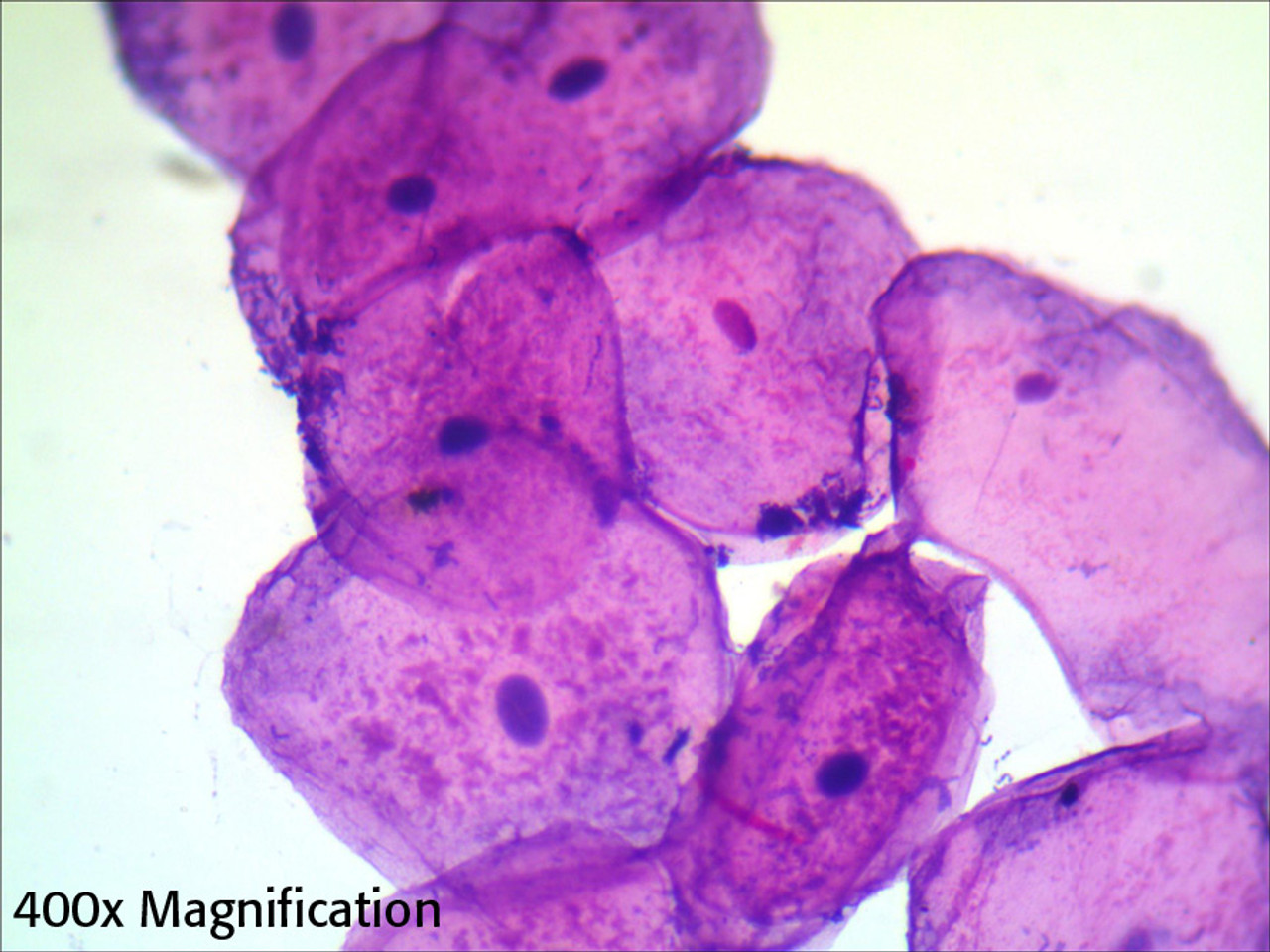
Simple Squamous Epithelium Cells
Function: secretes serous fluid → serous cavity + helps w/ passive diffusion, filtration
@ alveoli of Lungs, heart, blood + lymphatic vessels
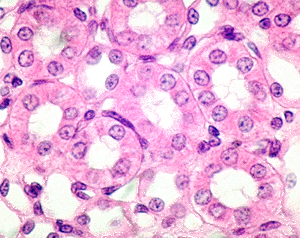
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Cells
Function: secretion/absorption
@ kidney tubules, ovary surface, secretory portions at small glands
DT: two rings, outer filled with nuclei
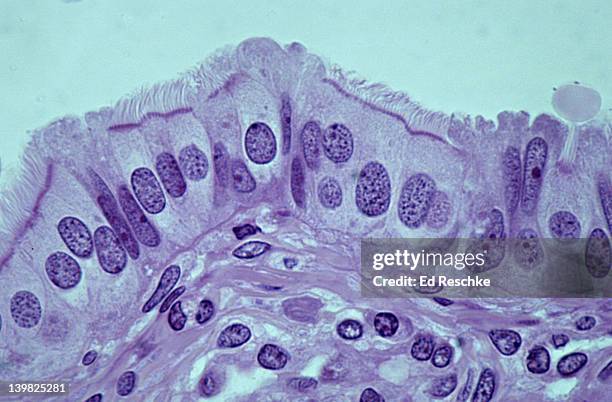
Simple Columnar Epithelium Cells (Ciliated)
Function: propels mucus/reprod. cells +secretion of mucus
@ lining of small bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus
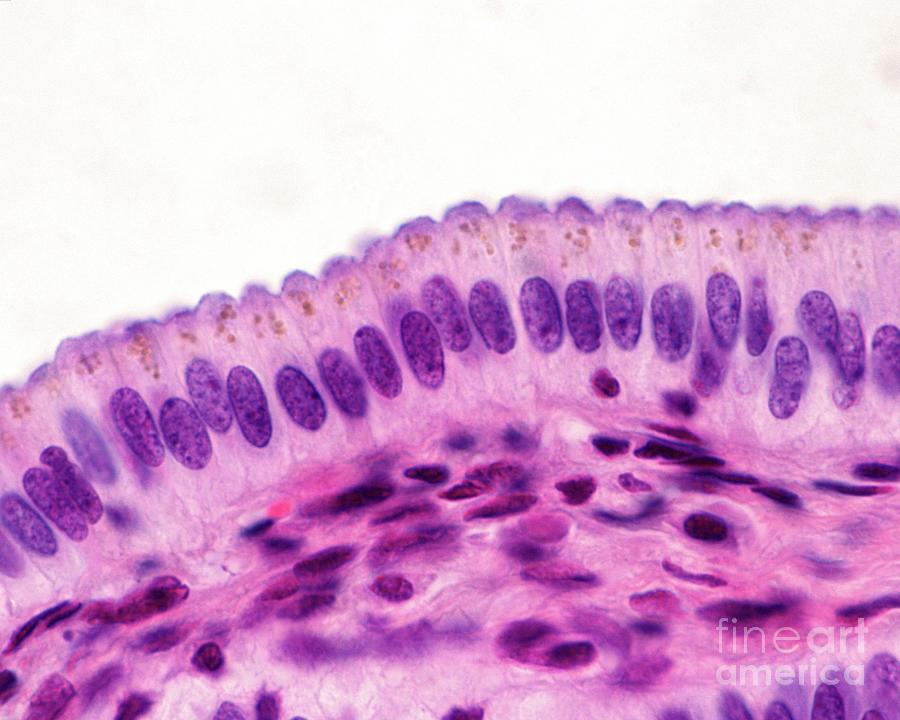
Simple Columnar Cells Epithelium (Non-Ciliated)
Function: absorption/secretion by using microvilli to UP surface area for nutrients
@ lines digestive tract, gall bladder, ducts
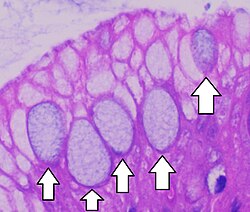
Goblet Cell
@ simple epithelia + pseudostratified epithelia
Function: protect epithelium, secret mucin (that’ll → mucus) and trap dust
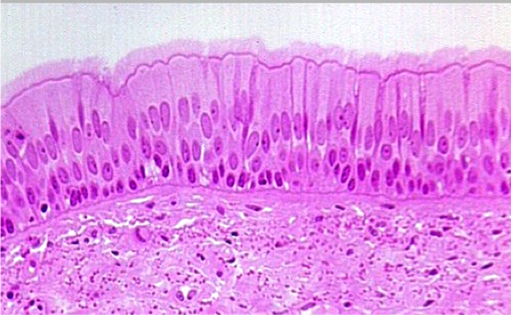
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial Cells
*appears to be multiple kinds of cells, but is actually just columnar nuclei seen at different levels
Function: same as columnar epithelial cells
non-ciliated: @ sperm-carrying + large glands’ ducts
ciliated: lines trachea and most of upper respiratory tract
Stratified Epithelia Properties
2/+ layers of cells
name based on shape of cell at APICAL layer
regenerate from basal layer
major role protection
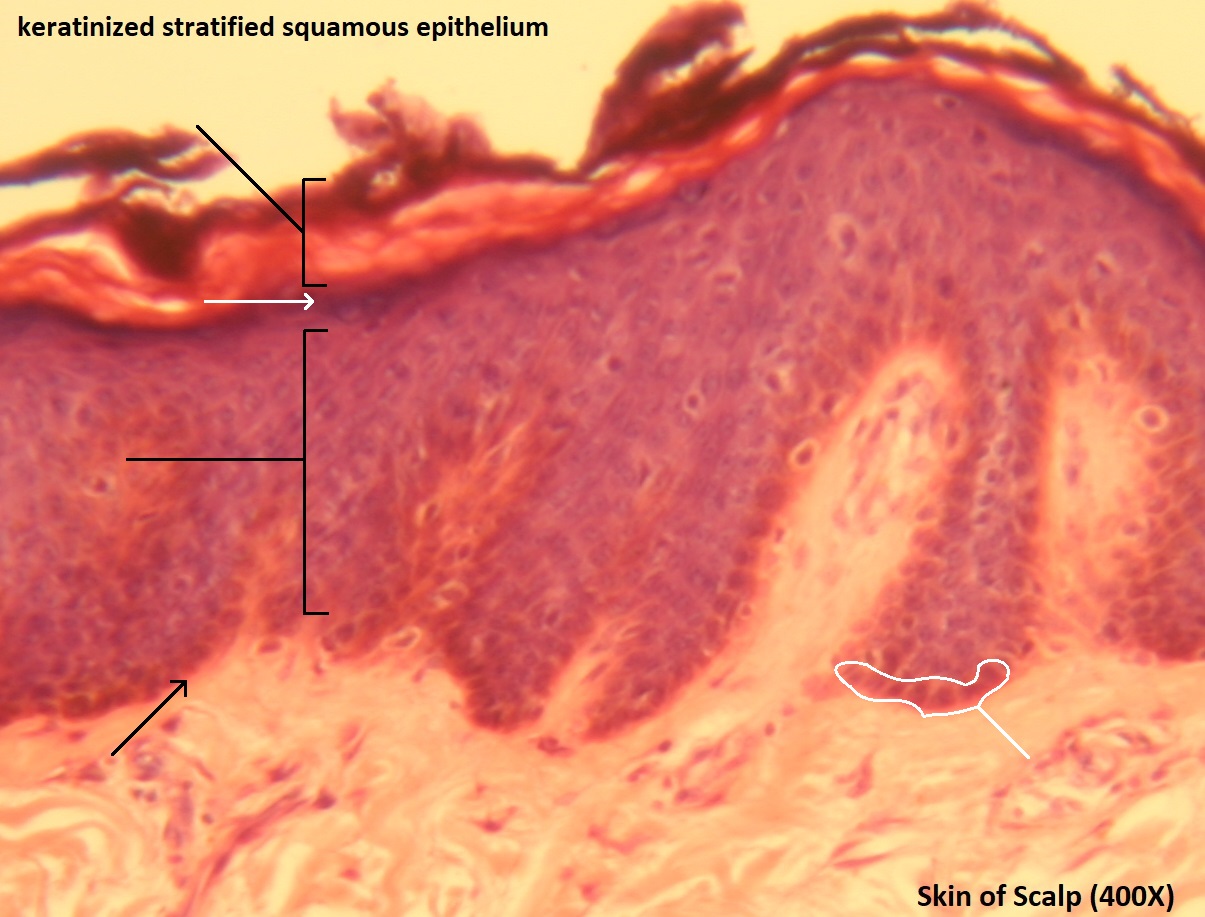
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
*surface cells are dead and full of Keratin
Function: protective protein of Keratin + waterproof
@ Epidermis
DT: tissue appears like an ocean wave + layers of dead skin on top w/o nuclei (b/c dead)
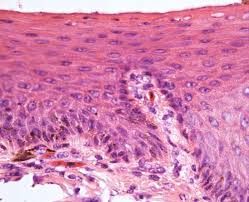
Stratified Squamous (Non-keratinized)
Function: moist lining of body openings
@ vagina, mouth, esophagous
DT: wavy, thin cells on top with cuboidal cells at the basal layer
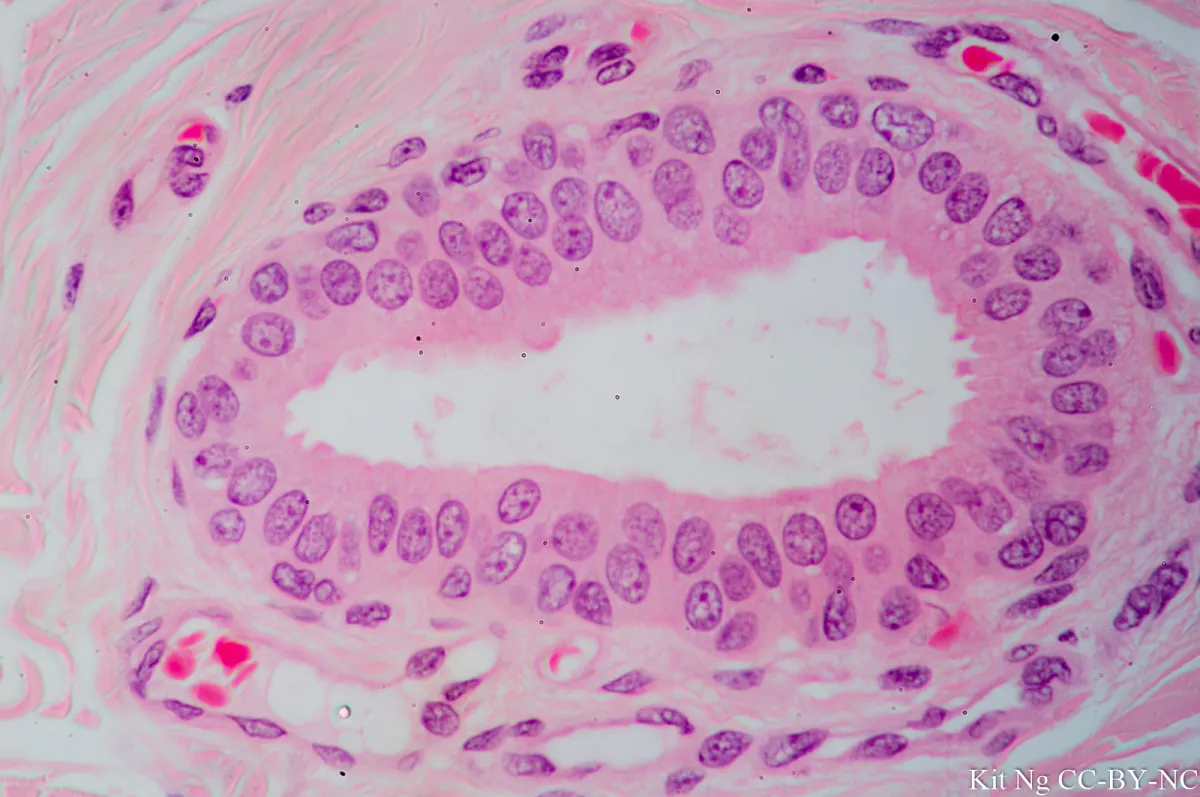
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Function: protection
@ mammary/salivary/sweat glands
*note the multiple layers in close prox.
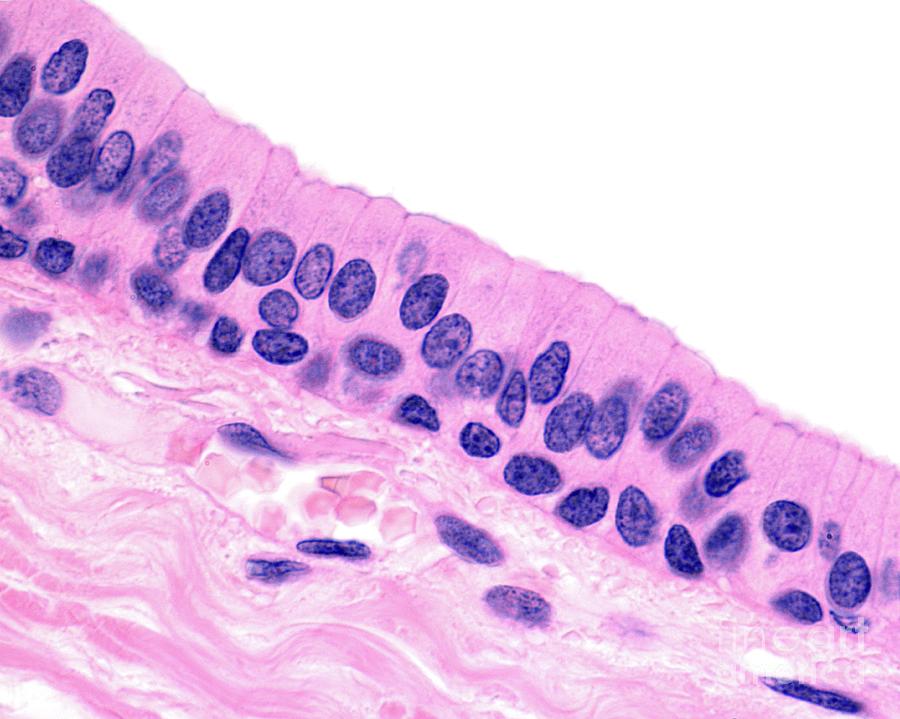
Stratified Columnar Epithelia
Function: protection + secretion
@ male urthera and large ducts of some glands (rare)
*DT: basal levels usually cuboidal w/ superficial cells looking columnal
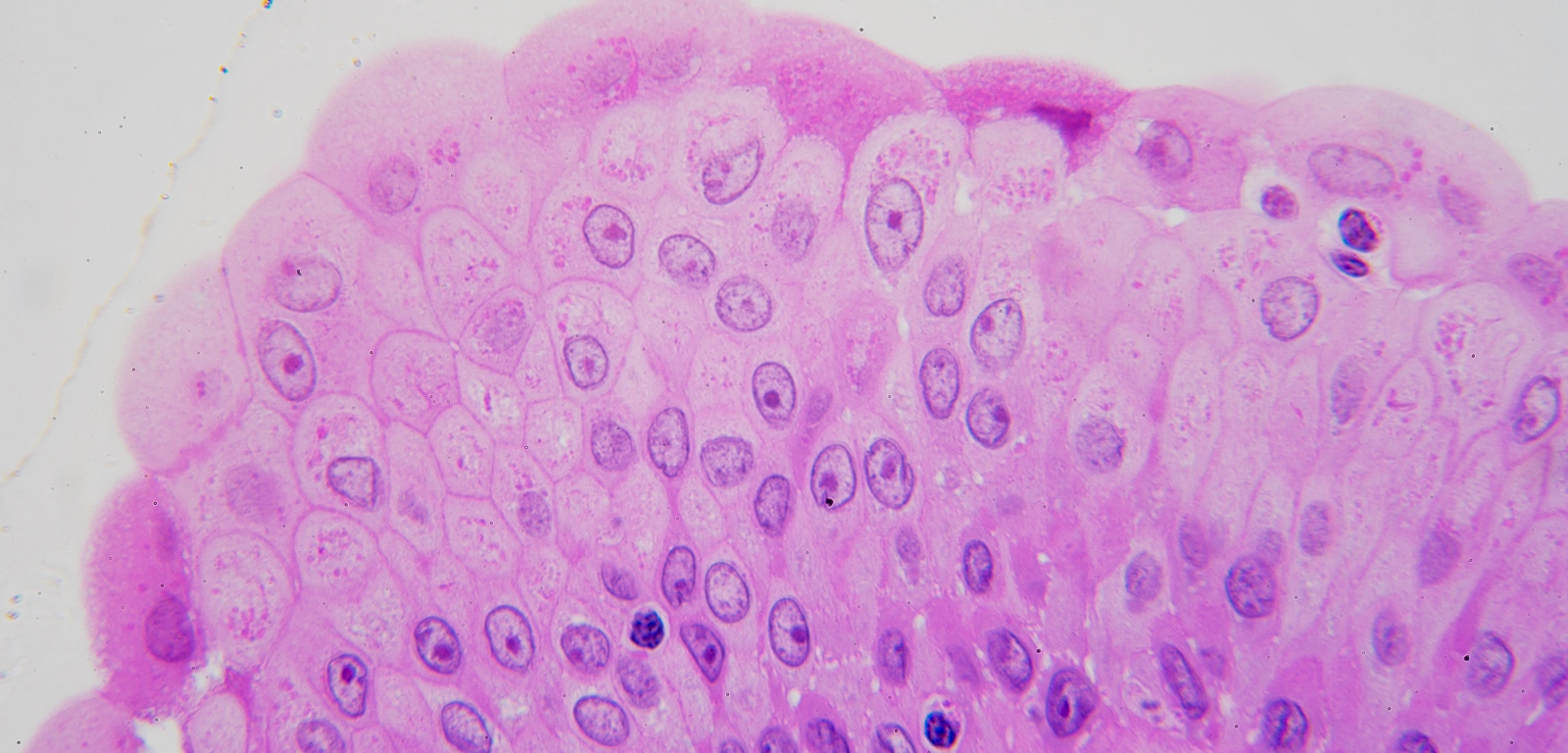
Transitional Epithelium
Function: stretches readily for distension
@ uterus/bladder
DT: bulbous cells on top of basal columnar cells
Types of Connective Tissue
CT Proper, Cartilage, Bone Tissue, Blood
*cells seperated by large amt. of extracellular matrix except blood, which doesnt have a matrix
(Extracellular) Matrix
made of ground substance (holds tissue interstitial fluid so gel-like) and fibers
*Blood has plasma engulf it instead
Structural Fibers found in CT
collagen , reticular, elastic
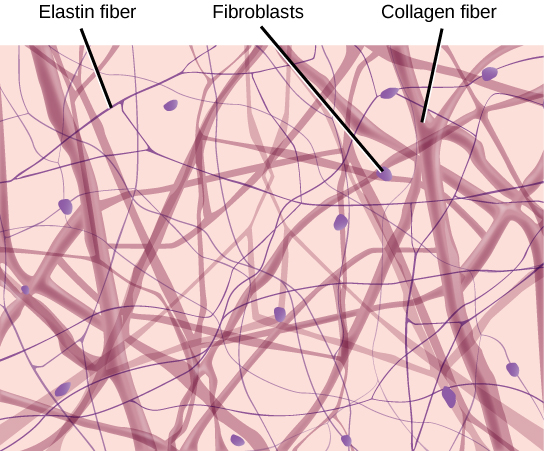
Collagen Fibers
function: strongest of all fibers, resists tension and prevents scurvy
structure: a network of crosslinks made of Vitamin C
Reticular Fibers
function: covers/support structures
structure: bundles of special collagen
* NOT VISIBLE UNDER MIROSCOPY BUT IS PRESENT
elastic fibers
made of elastin
function: recoils after stretching
Connective Tissue Proper’s Subclasses
Loose Connective Tissue: areolar, adipose, reticular
Dense Connective: Irregular, regular, elastic
Connective Tissue Proper:
cells: fibroblast, fibrocytes, fat cells
contains all 3 fiber types
function: binding tissue + resists tension

Areolar CT:
function: helps immune cells like WBC + wraps/cushions organs + holds interstitial fluid
@ underneath epithelia (highly vasculized to give nutrients and help excrete waste)
DT: elastic + collagen fibers all over
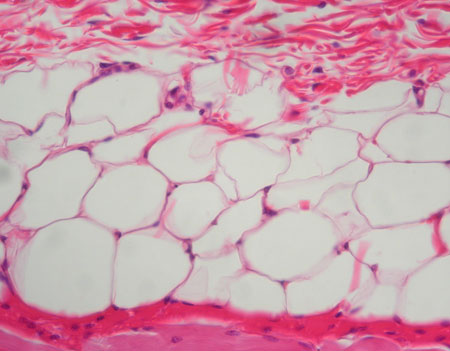
Adipose Tissue
Function: warmth + reserve food storage + protects organs and storing energy
@ hypodermis (fatty layer) + kidney, eyeballs, w/in abdomen and breasts
DT: fatass cells pushing their nuclei to the edges
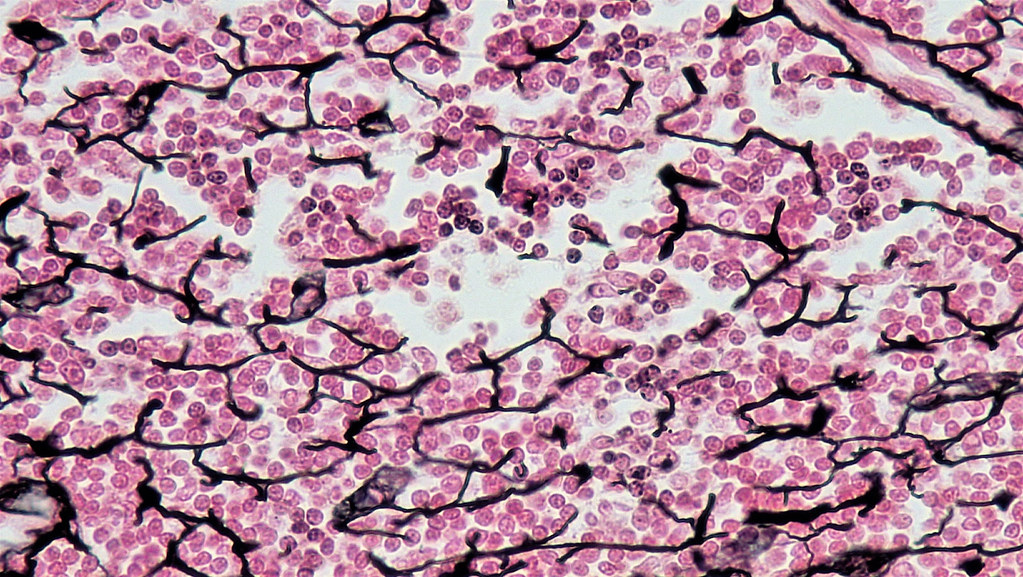
Reticular CT
structure: network of reticular fibers in loose ground substance
function: fibers form soft internal skeleton to support other cell types
@ lymphoid organs (bone marrow, spleen, etc.)
DT: hella dots together with cells loosely together
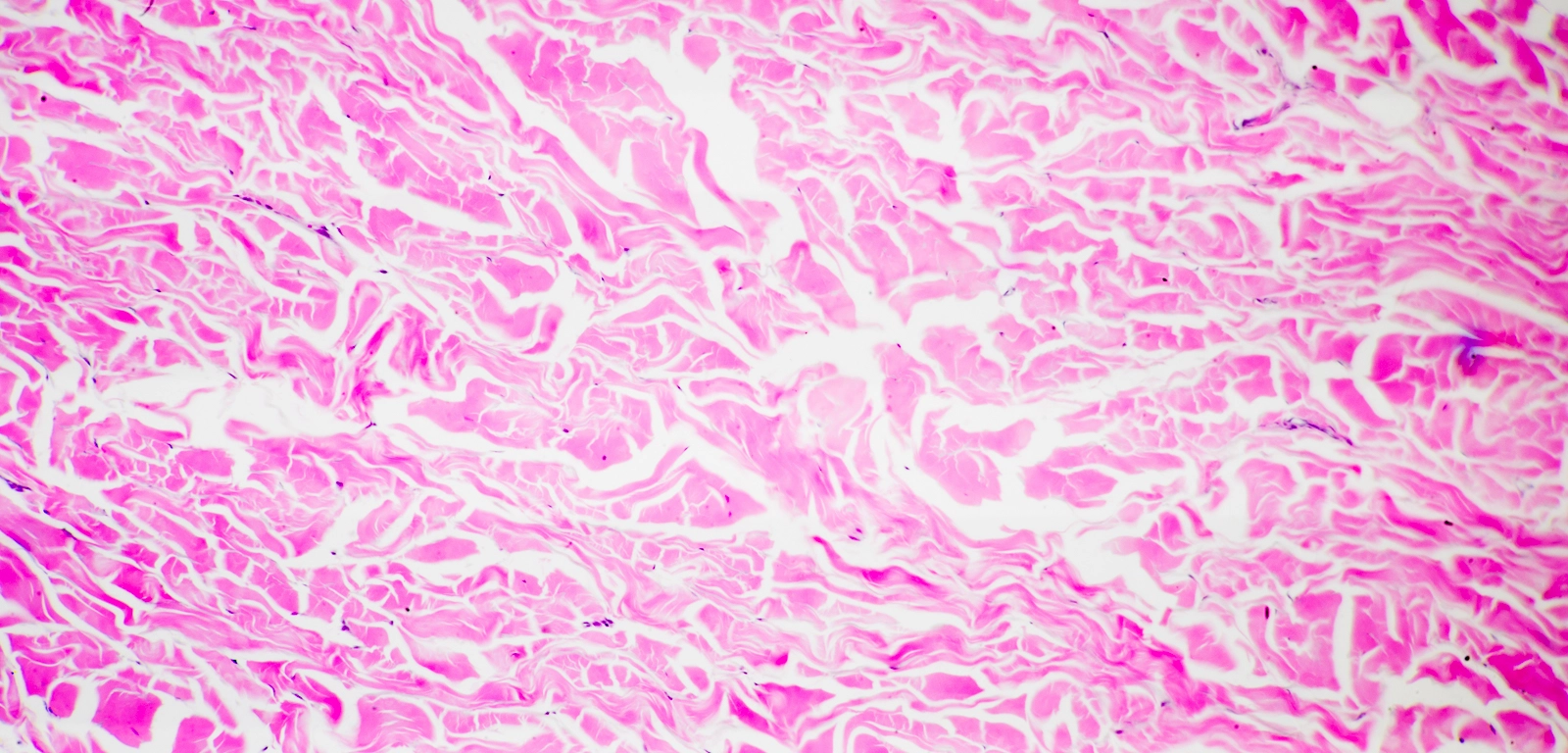
Dense Irregular Tissue:
function: withstand tension + structural strength
@ dermis of skin + submucosa of digestive tract
DT: collagen fibers in different directions + nuclei (dyed in purple) more visible comapred to dense regular tissue
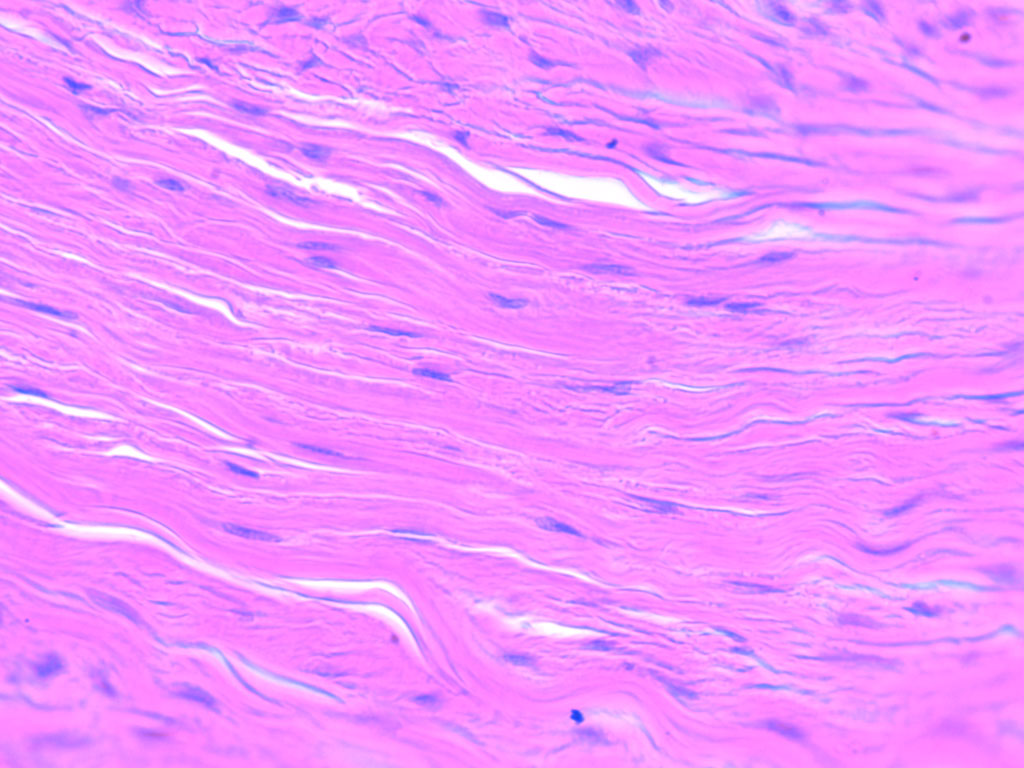
Dense Regular Tissue:
Function: reduce tension in ONE direction
@ tendons, fascia, aponeuroses, wrap skeleton like shoulder joint
DT: fibroblasts in 1 direction
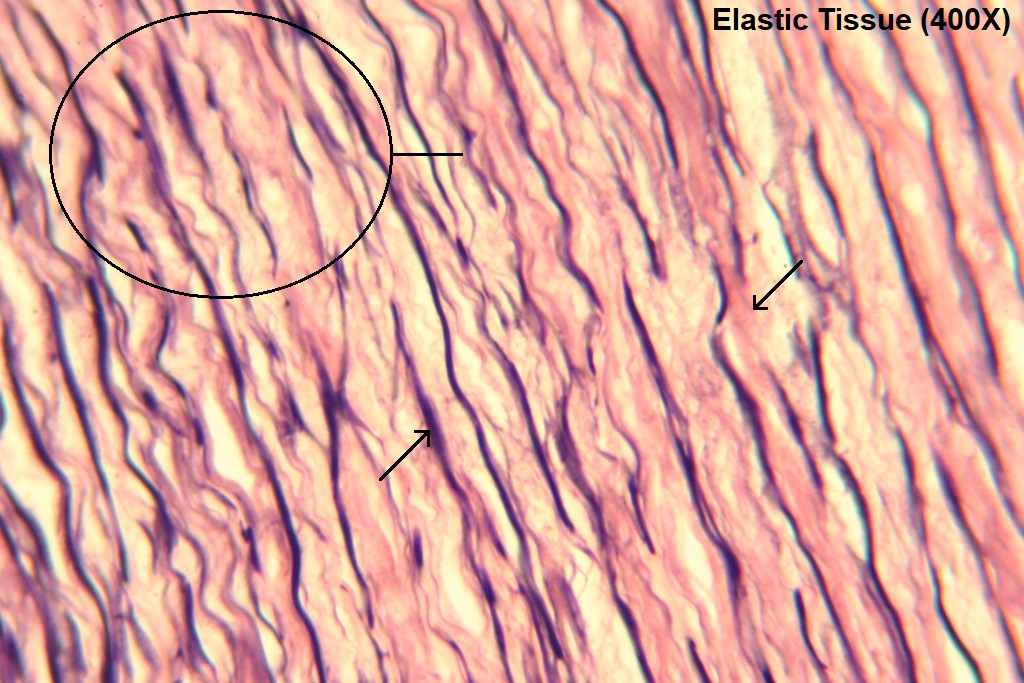
Dense Elastic:
Function: recoil tissue → pulsatile blood flow + help w recoil of lunges while breathing
@ walls of bronchial tubes + large arteries
DT: close together squiggly lines, much darker than other CT
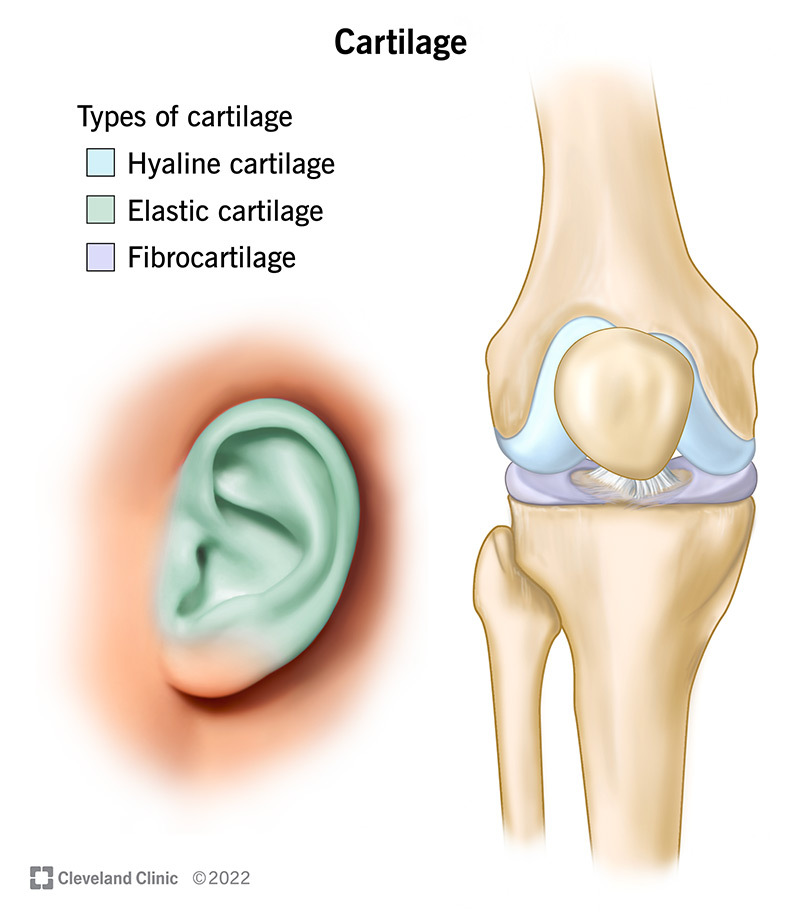
Cartilage:
structure: firm/flexible tissue + NO blood vessels/nerves + matrix made of 80% water
function: water resists compression
2* = Chondrocyte (no longer actively reprod. cells)
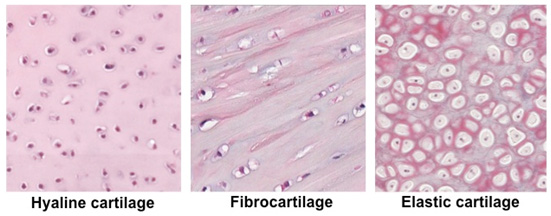
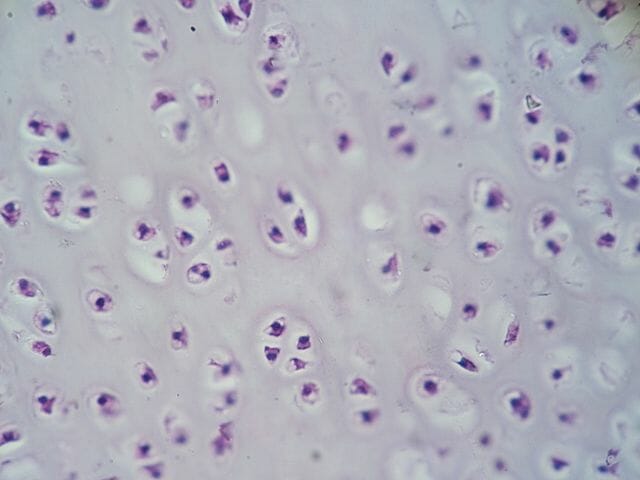
Hyaline Cartilage:
Function: supports/reinforces/cushions + resists compression NOT tension
@nose +trachea
DT: looks like model of ribsomal subunits together, tissue overall looks like frosted glass
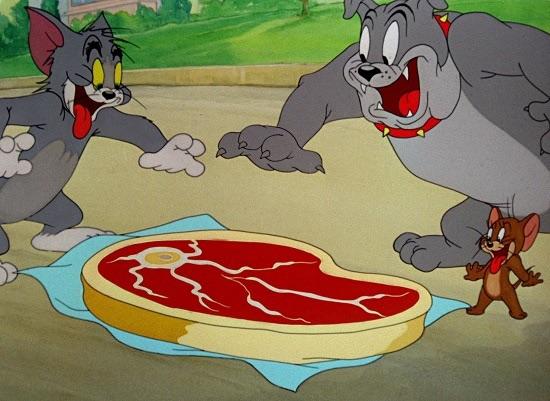
Elastic Cartilage:
*has more elastin than Hyaline cartilage
Function: maintain shape w/flexibility
@ helps external ear; epiglottis
DT: looks like Tom and Jerry steak

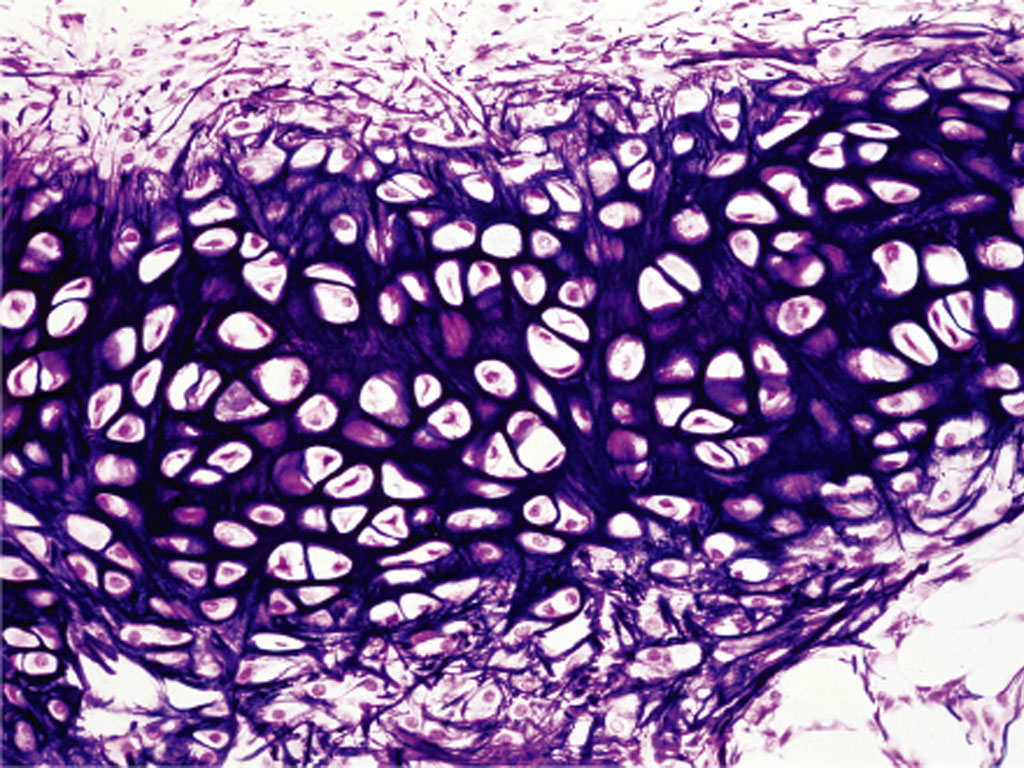
Fibrocartilage
Function: absorbs shock
@ between intervertebral discs, pubic symphsis,
DT: rows of chondrocytes
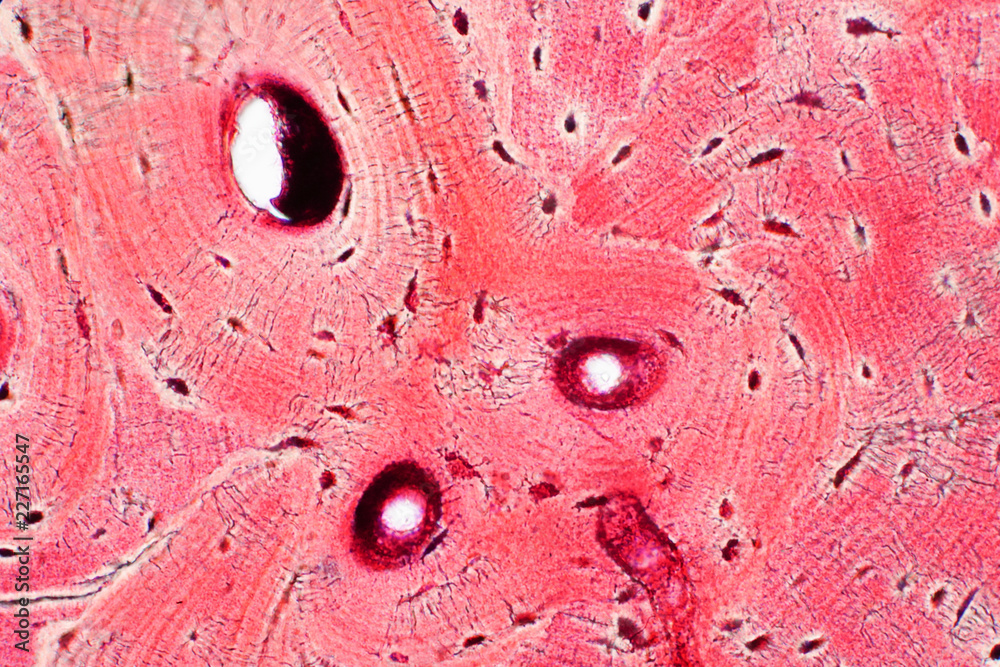
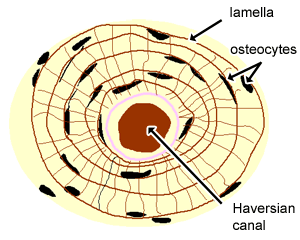
Bone Tissue:
Function: acts as levers for the muscles to pull at + stores calcium/minerals/fat + marrow inside for hematopoiesis
Structure: hard, calcified matrix with hella collagen fibers and wall vassalized with osteocytes that lie in lacunae
DT: looks like tree rings
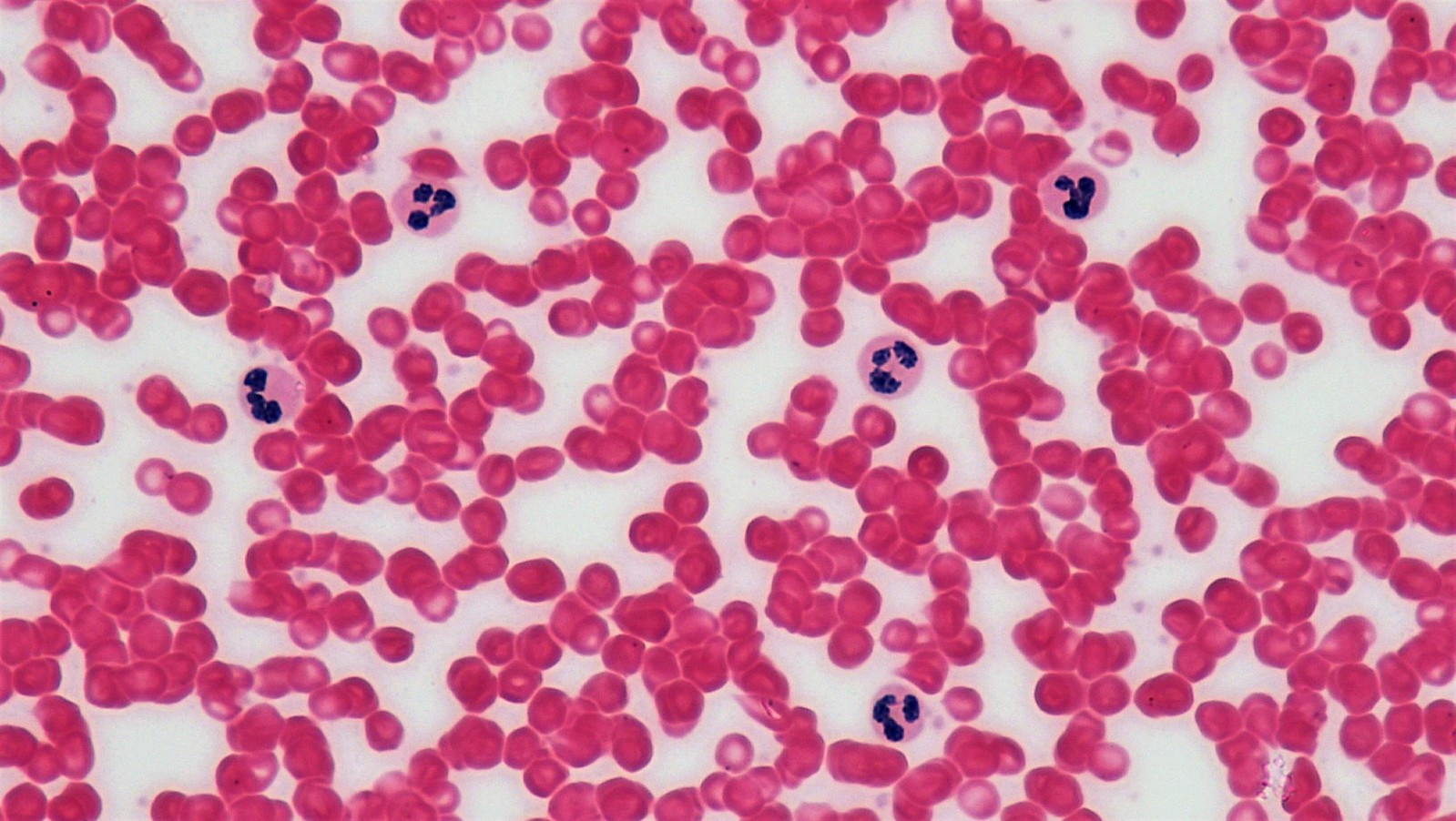
Blood Connective Tissue:
Structure: ANUCLEAR and NO ORGANELLES
Function: transport respiratory gases/nutrients/waters/etc.
@ blood vessels
DT: model is literally one big circle inside a circle

Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Function: voluntary movement + manipulation of environment + facial expression
@ skeletal muscles attaches to bones or sometimes skin
DT: striations (light/dark bands) are orderly and parallel w/e other + nuclei at edge of cell
* skeletal muscle cell = muscle fiber
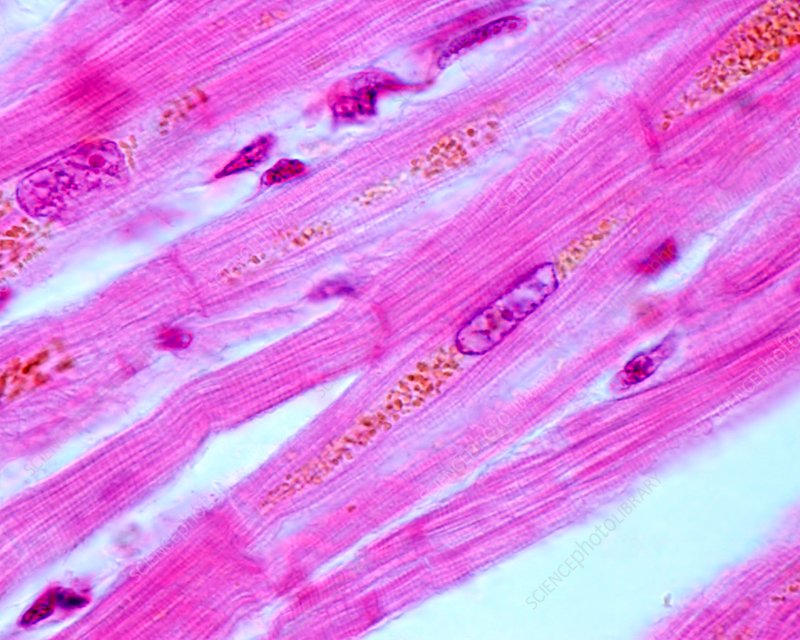
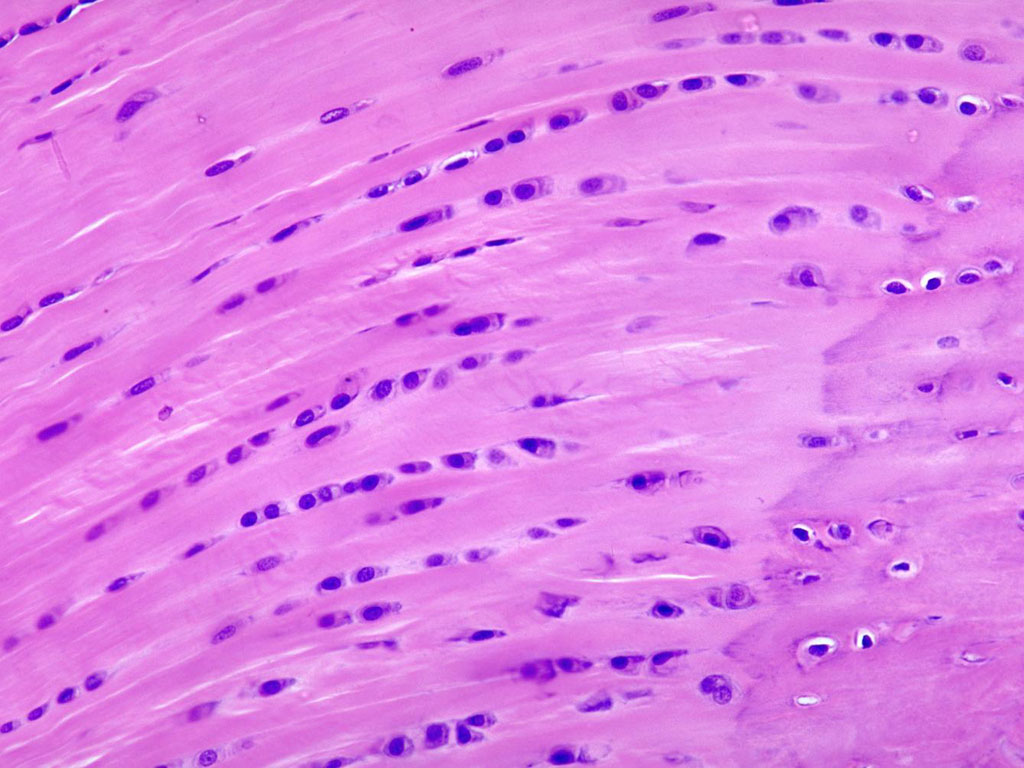
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Function: blood circulation
@ walls of the heart
DT: short, branching cells with striations (unterdigitated)
* can’t be called muscle fibers, instead called myocardial cell
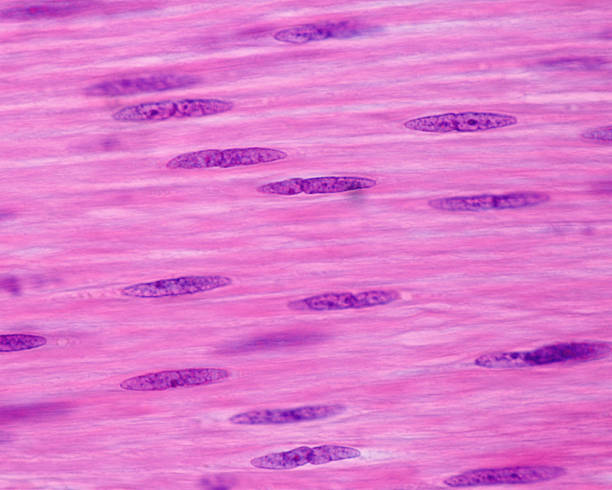
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Function: depends on location, helps move food/urea/etc. alongside passageways
@walls of hollow organs (like stomach, intestines, etc.)
DT: long nuclei in thin sheets + NO stritations