Automated analyzers, sample collection, and sample handling (Vet 152)
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering automated analyzers, collection methods, anticoagulants, sample handling, and basic hematology concepts from Vet 152 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
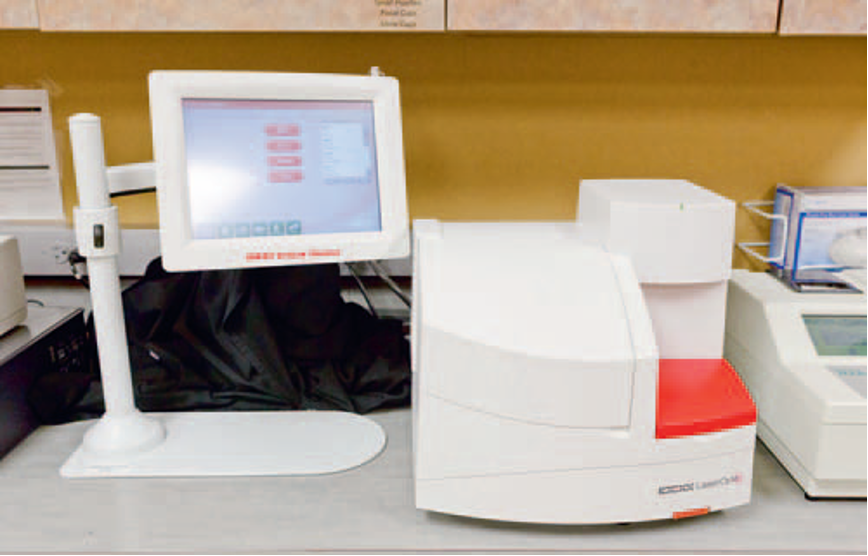
Automated hematology analyzers
Cost-effective devices that perform CBCs daily, reducing labor and improving data reliability.
CBC
Complete Blood Count; a routine hematology test run by analyzers.
RBCs
erythrocytes, red blood cells
WBCs
leukocytes, white blood cells
Platelets
thrombocytes, involved in blood clotting.
Impedance analyzer
Counts cells by measuring changes in electrical conduction as cells pass between electrodes.

Quantitative Buffy Coat (QBC) system
Uses centrifugation to separate cells by density
Uses fluorescence to differentiate cell types

Laser flow cytometry
Analyzes cells using focused laser beams to evaluate size, density, and light scatter.

RBC indices
Hct, MCV, MCH, and MCHC used to describe red blood cells.
Hematocrit (Hct)
Percentage of blood volume occupied by RBCs; often calculated from CBC.
MCV
Mean Corpuscular Volume; average size of red blood cells.
MCH
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin; average hemoglobin per RBC.
MCHC
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration; average hemoglobin concentration in RBCs.
Electronic Cell Counters Used to determine:
RBC indices
Partial WBC counts
Platelet counts
Reticulocytes
Reticulocytes
Immature red blood cells referenced in CBC/indices.
Manual cell counts
Direct counting of cells (RBCs/WBCs) using devices like a Hemocytometer or Leukochek.
Hemocytometer
Counting chamber used to determine cells per microliter of blood.
Chemistry Analyzers
Wet analyzers
Uses liquid reagents
Dry analyzers
Pre-measured reagents on strips or pads
Electrolytes
Glucometer
Device used to measure blood glucose concentration.
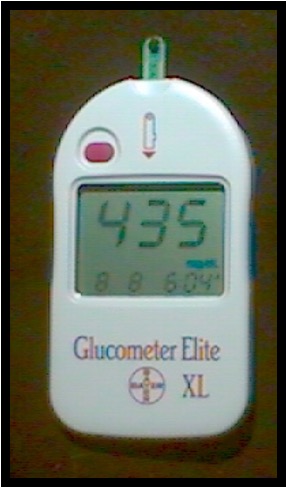
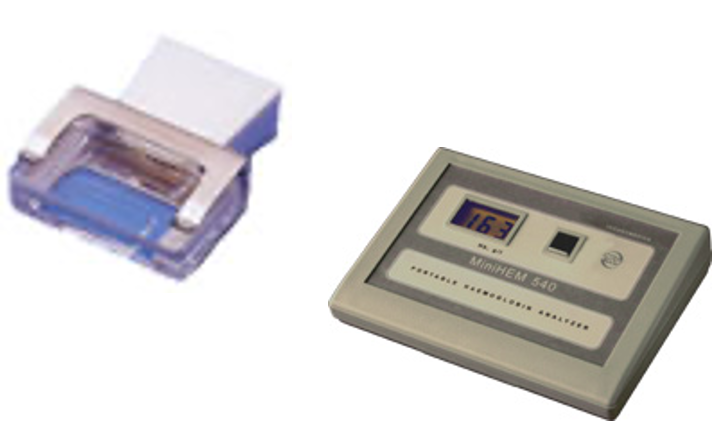
Hemoglobin testing hemoglobinometer
Assesses hemoglobin content by lysing cells and comparing color to a standard; often with automated analyzers.
Low hemoglobin: anemia
high hemoglobin: dehydration or polycythemia

Low quality sample
hemolysis
unclean sample
not fasted
too much neg pressure
Sample quality
High-quality samples yield reliable results; avoid lipemia, icterus, hemolysis.
don’t use jugular when
collecting samples from patients with clotting disorders or anxiety.
why use vein more than artery
Veins are larger, easier to access, and typically have less pressure than arteries, making them safer and more suitable for sample collection.
75% in veins
when do we use an artery
Typically used for arterial blood gas analysis or when venous access is difficult.
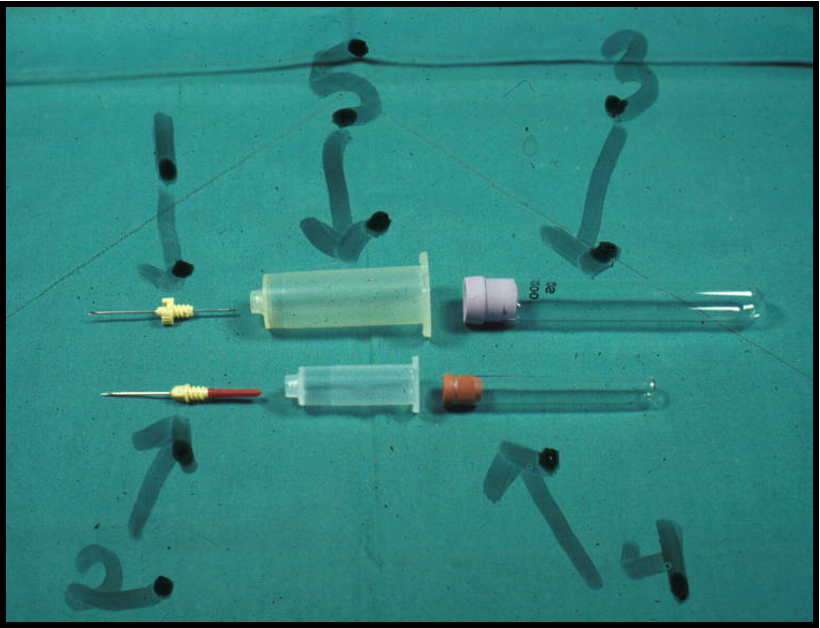
Vacutainer system
Vacuum blood collection system with needle(double needle), holder, and collection tubes.
1.Needle
2.Needle
3.Vacuum tube
4.Vacuum tube
5.Holder
can fill multiple tubes with one stick
Labeling and documentation
Record date/time, patient name/ID, owner; essential for accurate results.
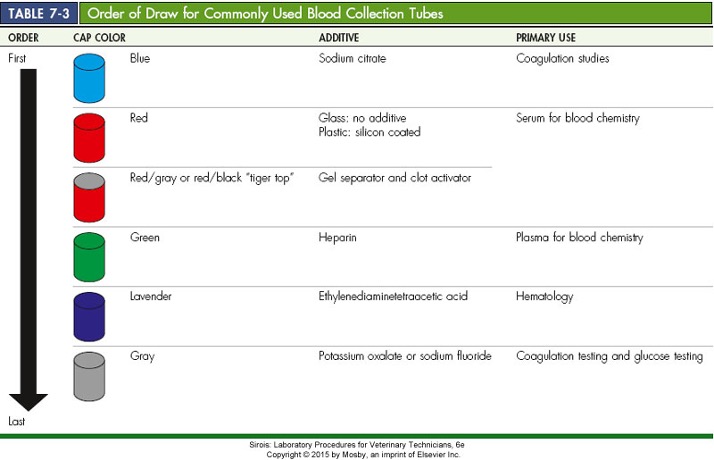
Order of draw
‒Vacutainers should be used and tubes collected in this order
•Citrate first BLUE
•Plain red top or white
•Tiger top – serum separator
•Green – heparin
•Lavender – EDTA
•Gray – potassium oxalate or sodium fluoride
Buffy coat
Whitish-gray layer of WBCs and platelets between plasma and RBCs after centrifugation.
Plasma
Fluid portion of blood with anticoagulant; contains proteins, electrolytes, etc.
Serum
Fluid from clotted blood; plasma without fibrinogen.
Anticoagulants
Substances that prevent clotting; chosen based on tests required.
There is NO one anticoagulant appropriate for all tests and there is NO one blood tube appropriate for all tests.
If unable to run test within 1 hour –refrigerate; do not freeze
Tubes with NO ANTICOAGULANT
Chemistries
Red top (plain or clot activator)
White top (plain)
Serum separator (SST)
Gel clot activator
Serum = plasma that has had fibrinogen removed (during the clotting process)
Tubes with ANTICOAGULANT
Hematology (CBC-RBC/WBC)
Purple top (EDTA)
Green top (Lithium heparin)
Others
Plasma = fluid portion of whole blood that has not been allowed to clot.
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; lavender top; preserves cell morphology for hematology.

Lithium Heparin
Green top; preserves plasma for chemistry with minimal interference,
Disadvantage: may interfere with some chemical assays
Clumps WBCs

Sodium citrate
Blue top; anticoagulant for coagulation studies; requires correct fill volume.
clotting times
Specific coagulation tests require certain blue top tubes. For example, some are 3.2% and some are 3.8%. Using the wrong tube will invalidate any testing.
Most sensitive

Sodium fluoride
Glucose preservative (gray top); can interfere with some enzymatic assays.
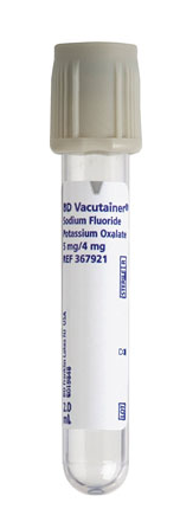
Oxalates
Sodium/potassium/potassium oxalate anticoagulants; may inhibit certain enzymes.
Citrates
Sodium or lithium citrate; anticoagulant for coagulation tests; binds calcium.
Sample Volume
Dependent upon quantity of serum or plasma needed
Well-hydrated animal (PCV 50%)
50% cells, 50% fluid
10 mL blood = 5 mL fluid
Dehydrated animals (PCV 70%)
70% cells, 30% fluid
10 mL blood = 3 mL fluid
Blood to draw (mL)= Plasma needed (mL) / Plasma Known as a fraction
PCV (Packed Cell Volume)
Measured hematocrit; percentage of blood that is RBCs after centrifugation.
Hematocrit vs PCV
Hematocrit is calculated; PCV is measured; values may differ if factors affect MCV.
Microhematocrit tubes
–Red ring – heparinized
–Blue ring – not treated
if already heprinized use blue
Buffy coat and plasma layers in PCV
Buffy coat is WBCs/platelets; plasma is the liquid layer above the slime; encourage accurate reading.
can see parasites in Buffy coat
–HW microfilaria
–Acanthocheilonema reconditum
Calculation for estimate of RBC count:
Divide PCV by 6
Polycythemia vera
A blood disorder characterized by an increased number of red blood cells in the bloodstream, often leading to increased blood viscosity and potential complications.
less oxygen in blood
Secondary or relative Polycythemia
is an increase in red blood cells due to a physiological response to factors such as hypoxia or dehydration, rather than a primary blood disorder.
Refractometer for TP
Measures total protein in serum/plasma; reading affected by lipemia.
need fasted
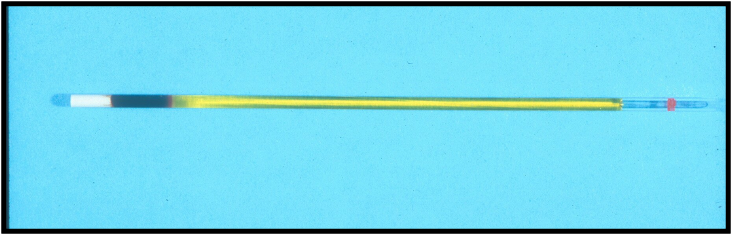
Lipemia/Icterus/Hemolysis
Interfering plasma/serum characteristics that can mislead results.
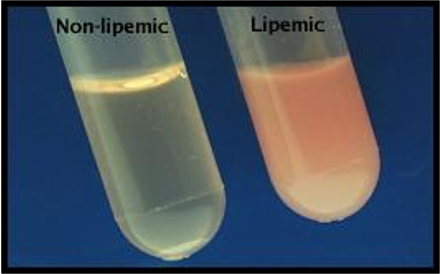
Plasma layer
–Normal – clear to pale yellow
–Cloudy – lipemic
–Reddish tinge – hemolyzed
–Deep yellow – icteric
Hemoglobin Testing
Rough estimate can be found by dividing the PCV by 3
Impedance Analyzers measure changes in electrical conduction as a solution of cells passes between two electrodes.
True
EDTA is not preferred for hematologic studies.
False
What is the correct order for collecting blood samples using Vacutainers?
Citrate, plain red top or white, tiger top, green, lavender, gray
Hematology samples should be processed immediately.
True
What is the purpose of the buffy coat layer in a blood sample?
layer contains white blood cells and platelets