Topic 7: Human Nutrition
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is a balanced diet?
A meal or diet consisting of all food groups; carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, vitamins, and water in the correct amount and proportions.
Why are carbohydrates needed for a balanced diet?
Carbohydrates give energy to the body for various activities.
Why are proteins needed for a balanced diet?
Proteins are needed for growth and repair of damaged tissues.
Why are lipids needed for a balanced diet?
They provide long-term energy storage, insulation, and protect organs.
Why are mineral salts needed for a balanced diet?
Mineral salts are needed by the body to make certain cells, tissues, or organs to ensure proper functioning of the body.
Why is calcium needed for a balanced diet?
Calcium is needed to develop and build strong bones and teeth. It is also needed for blood clotting.
Why does the body need iron?
Iron is needed because they make haemoglobin, the red pigment which carries oxygen.
What happens when there is a lack of iron?
It leads to Anemia. Meaning that there are not enough red blood cells so the tissues don't get enough oxygen delivered to them.
Why is vitamin C needed for a balanced diet?
Vitamin C keep tissues in good repair as they make the stretchy proteins, collagen. They keep the body healthy as they help fight off diseases, and gives healthy gums.
What does fibre (roughages/dietary skin) do?
It helps in the movement of food through the alimentary canal, keeping it in a good working order. Lack of it can cause constipation.
Why is water needed for a balanced diet?
It provides a medium where chemical reactions occur. Its is a solvent that carries nutrients through the body, and regulates body temperature.
What are some examples of carbohydrates?
Maize, Bread, Pasta, Potatoes, Rice
What are some examples of proteins?
Meat, milk, eggs, cheese, fish
What is the deficiency of Vitamin C?
Scurvy, causes pain in joints and bleeding from gums
What is the deficiency of Vitamin D?
Rickets, causes soft and deformed bones
What are some examples of lipids?
Meat, nuts, milk, seeds
What are some examples of calcium?
Milk, fish, vegetables, cheese, yogurt
What are some examples of Vitamin C?
Orange, Limes, Raw Vegetables
What happens when the body has a lack of Vitamins?
Vitamin C leads to painful joints & muscles, bleeding gums (scurvy) & Vitamin D leads to soft & deformed bones.
Define ingestion.
When food and drink are taken into the body through the mouth, using the lips, teeth, and tongue.
Define digestion.
The process of breaking down large, insolubale food substances into small soluble food substances that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Define physical digestion.
The breakdown of food into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules. It occurs in the teeth and stomach.
Define chemical digestion.
The break down of large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules so they can be absorbed. This occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine.
Define absorption.
The movement of small nutrient molecules and mineral ions through the walls of the small intestine and into the blood.
Define assimilation.
The process of nutrients becoming part of the body. They are absorbed by individual cells and used for energy or to make new substances.
Define egestion.
The removal of undigested food from the body as feces.
Physical digestion increases…
The surface area of food for the action of enzymes in chemical digestion.
What is the function of the stomach?
To break down large insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble food molecules to provide the body with nutrients. They churn food by contracting its muscular walls, breaking it into smaller pieces and mixing it with digestive juices to increase the surface area for enzymes to act on, continuing the process of mechanical digestion. Protease enzymes begin protein digestion. Hydrochloric acid provides a suitable pH for the enzymes and also destroys any pathogens in food.
What is the function of the pancreas?
They produce amylase, protease and lipase enzymes and release it into the duodenum. They regulate blood sugar by producing hormones like insulin and glycegon.
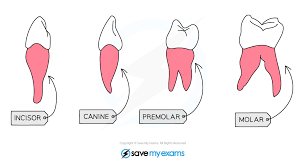
State the types of the teeth.
Incisors, canines, premolars and molars
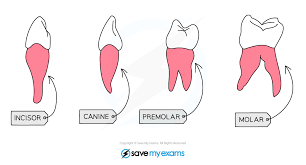
What is the structure & location of the incisors?
Chisel Shaped; Front part of the jaw
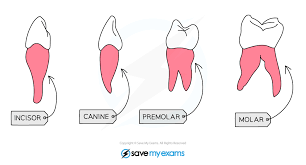
What is the function of incisors?
Biting and cutting into the food.
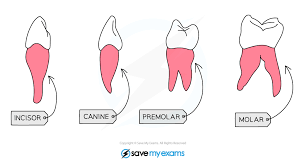
What is the structure & location of the canines?
Sharp and pointed; Front sides of the jaw
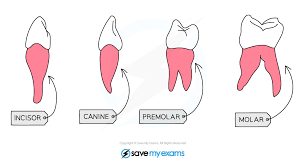
What is the function of the canines?
Tearing, holding, and biting into the food.
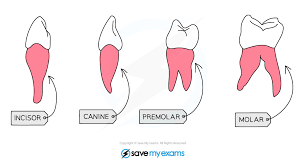
What is the structure & location of the pre-molars?
Large, flat surfaces with ridges/2-3 cups; The middle section of the jaw
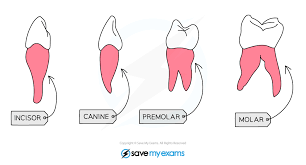
What is the function of the pre-molars?
Chewing & Grinding up Food
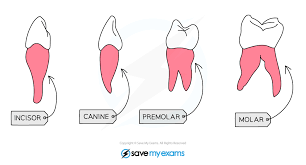
What is the structure & location of molars?
Large, flat surfaces with ridges/ 3 roots & 4 cusps; Back of the jaw
Define Bile.
A yellowish green, alkaline fluid produced by the liver, which helps with fat digestion and neutralizing the acidic mixture of food and gastric juices entering the duodenum from the stomach, to provide a suitable pH for enzyme action.
What is the function of amylase and where is it found?
They break down starch to simple reducing sugars in the mouth and duodenum, found in salivary glands and pancreas.
What is the function of protease and where is it found?
They break down proteins to amino acids in the stomach and duodenum, found in the stomach and pancreas.
What is the function of lipase and where is it found?
Breaks down lipids to fatty acids and glycerol in the duodenum, found in pancreas.
What is the function of hydrochloric acid?
Killing harmful microorganisms in food & providing an acidic pH for optimum enzyme activity.
How is starch digested in the digestive system?
Amylase breaks down starch molecules to maltose molecules. Then, maltase breaks down maltose to glucose molecules on the membranes of the epithelium lining the small intestine.
How are proteins digested in the digestive system?
Pepsin breaks down protein in the acidic conditions of the stomach. While, trypsin breaks down protein in the alkaline conditions of the duodenum
What are the functions of bile?
Its alkaline salts helps neutralize the hydraulic acid which comes from the stomach.
It emulsifies fats. It breaks up large drops of fat or oil into tiny droplets, increasing their surface area and allowing them to fully mix with watery liquids inside the digestive system, making a larger surface area allowing for lipids to chemically digest them into fatty acids & glycerol easier and faster.
What is the structure of enamel?
It is the hard, outer layer that protects the teeth.
What is the structure of the dentine?
It is the layer beneath the enamel that protects the nerves.
What is the structure of pulp?
It is the soft, internal tissue of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels.
What is the structure of the cement?
It is a hard layer around the root of a tooth that helps to anchor it within the jaw.
What are teeth embedded in?
In the gums and within the bone of the jaw.
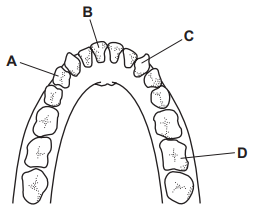
What is A?
Pre-Molar
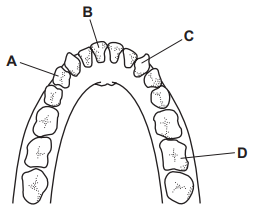
What is B?
Incisors
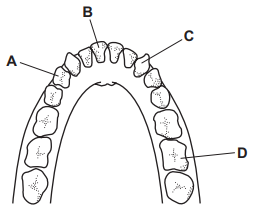
What is C?
Canine
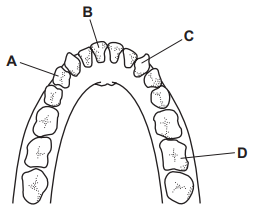
What is D?
Molars
Why is Vitamin D needed for a balanced diet?
Vitamin D helps calcium to be absorbed, for making bones and teeth. They develop the epitheral layer, tissues, and organs. Additionally, it supports immune function and may protect against certain diseases.
What are some examples of Vitamin D?
Butter, Salmon, Tuna, Egg Yolk
What is the deficiency disease for calcium?
Brittle bones and teeth; poor blood clotting
What role does chemical digestion play?
Large insoluble molecules are unable to be absorbed through the wall of the small intestines. With chemical digestion, enzymes catalyze these into small soluable molecules, making them to be easily absorbed through the wall of the small intestines.
The small intestine is the region…?
Where nutrients are absorbed.
Most water is absorbed from the small intestine but…?
Some is also absorbed from the colon.
What is the significance of villi and microvilli in increasing the internal surface area of the small intestine?
The ileum is very long and has a highly folded surface with millions of villi (tiny, finger like projections) and microvilli on the surface of the villus. This allows for absorption of nutrients to take place faster and more efficiently.
What is the structure of the villus?
Its one cell thick meaning that there is only a short distance for absorption to happen by diffusion and active transport
It is well supplied with a network of blood capillaries that transport glucose and amino acids away from the small intestine in the blood
It has a lacteal that runs through the center to transport fatty acids and glycerol away from the small intestine in the lymph.
What are the roles of the capillaries and lacteals in villi?
The villus is well supplied with a network of blood capillaries that transport glucose and amino acids away from the small intestine and transport them into the bloodstream. They help maintain a concentration gradient for diffusion by carrying absorbed substances away quickly.
Lacteal runs through the center of the villus to transport fatty acids and glycerol away from the small intestine in the lymph. Together, capillaries and lacteals ensure efficient absorption and transport of nutrients from the small intestine.
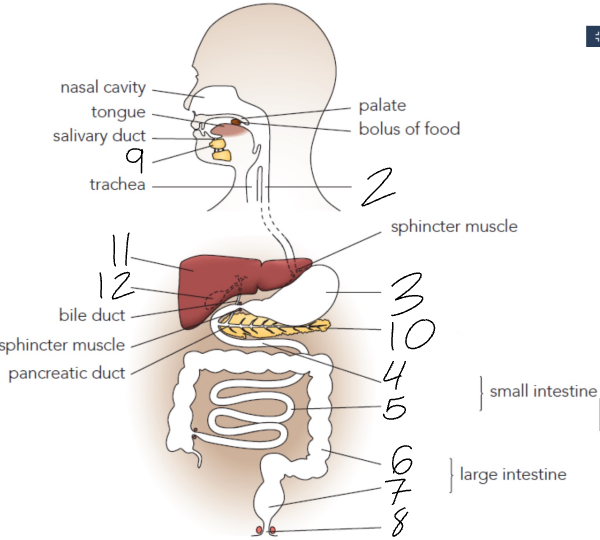
What is 2?
Oesophagus
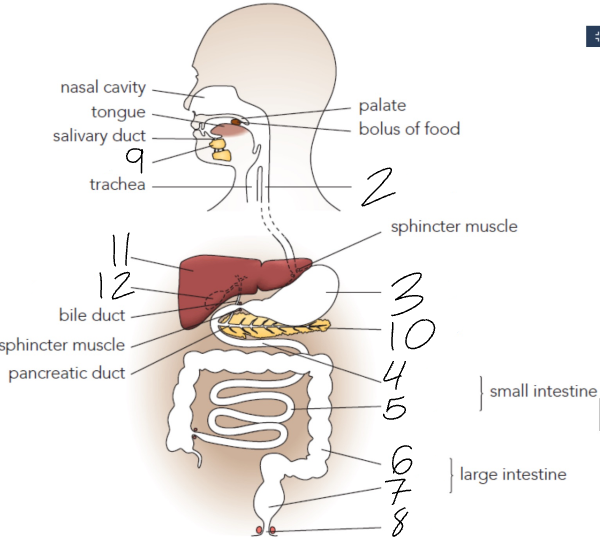
What is 3?
Stomach
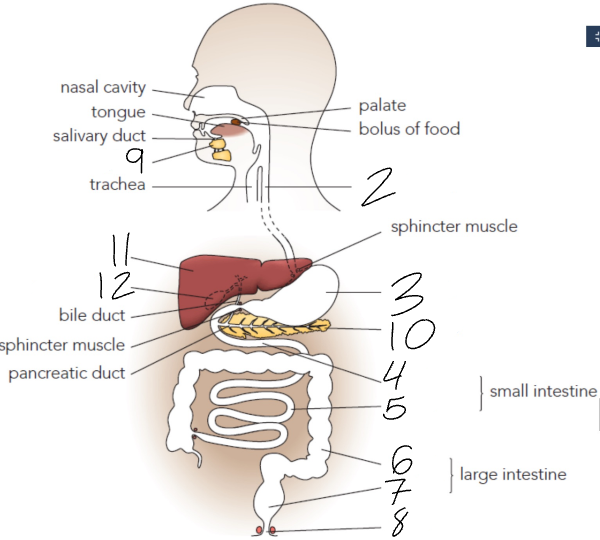
What is 4?
Duodenum
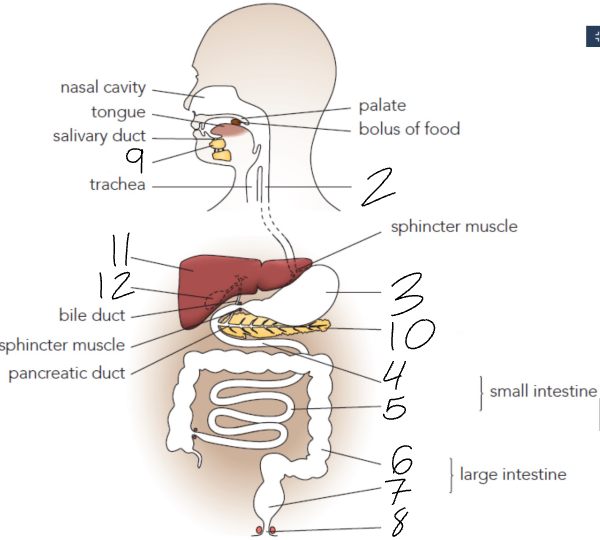
What is 5?
Ileum
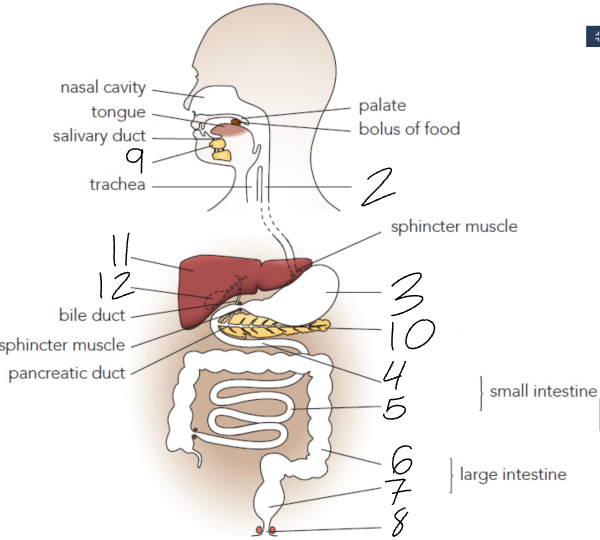
What is 6?
Colon
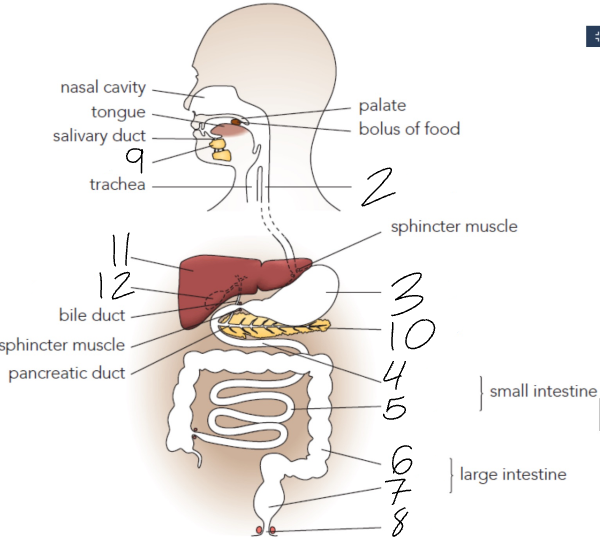
What is 7?
Rectum
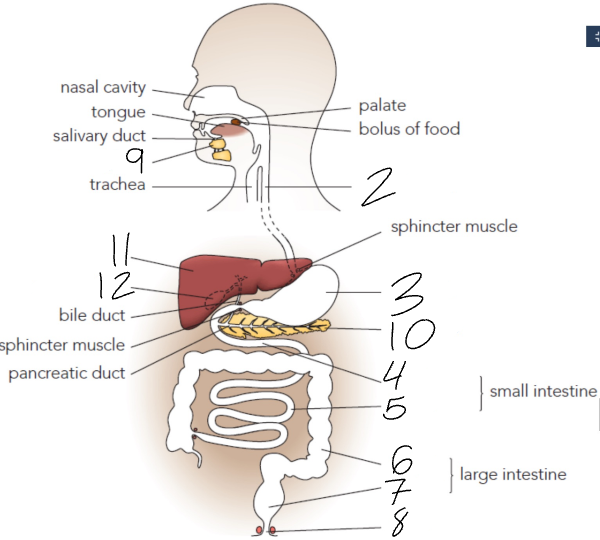
What is 8?
Anus
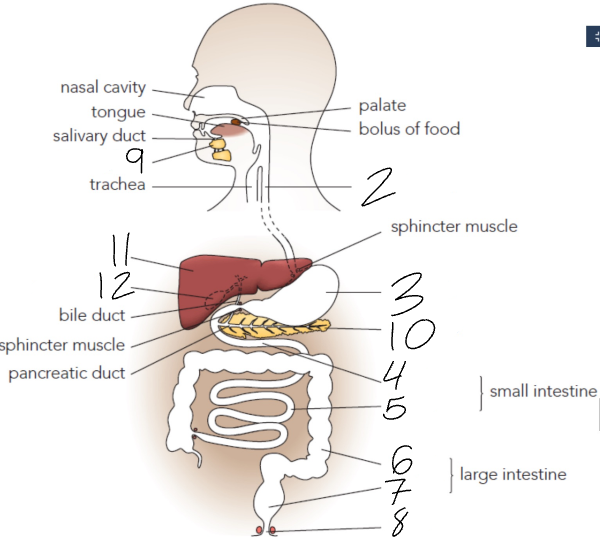
What is 9?
Salivary Glands
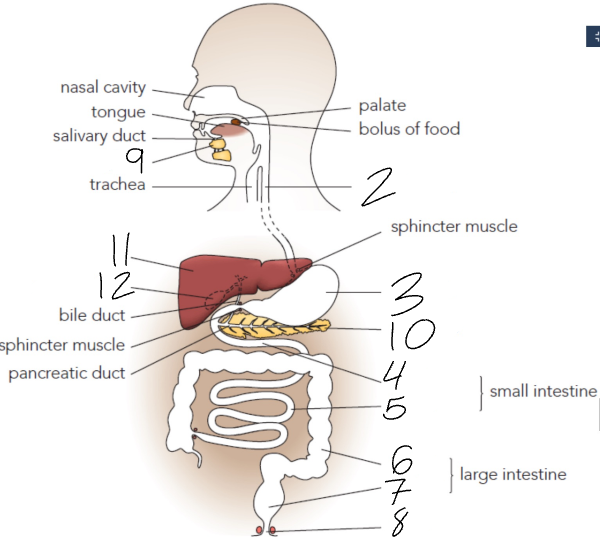
What is 10?
Pancreas
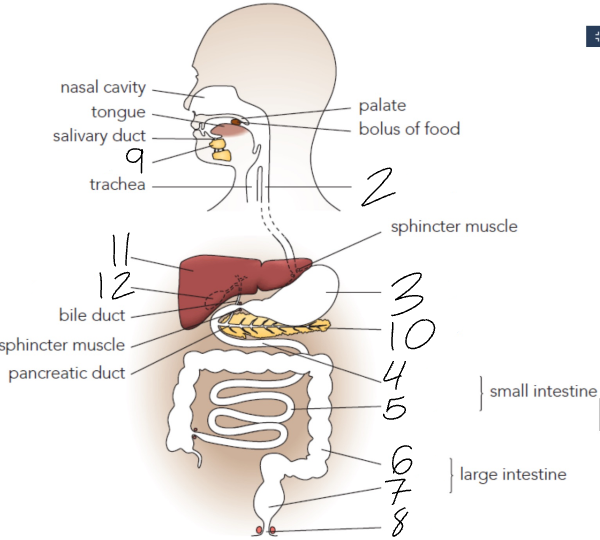
What is 11?
Liver
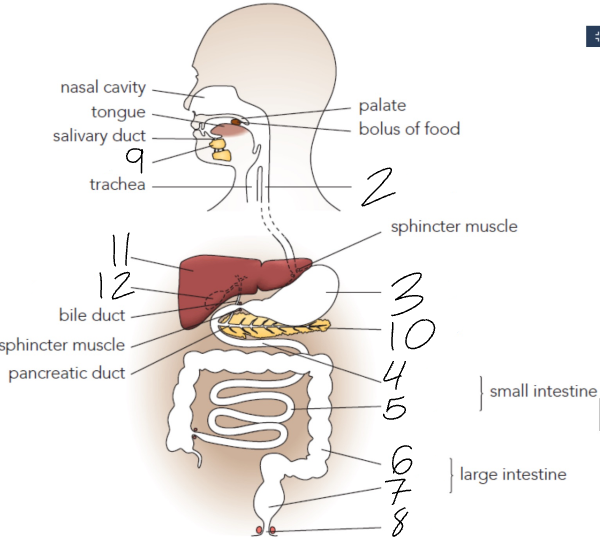
What is 12?
Gall Bladder