Larynx and Phonation
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the larynx and phonation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Larynx Location
Lies in the anterior of the neck posterior to the thyroid gland and the infrahyoids, but is anterior to the oesophagus.
Three Functions of the Larynx
1: provide an open airway for breathing 2: help route air and food to the correct location (epiglottis) 3: voice production (phonation)
Nine Cartilages of the Larynx
Connected by membranes and ligaments and forms the skeletal framework of the larynx.
Thyroid Cartilage
The largest cartilage, shield-shaped, formed by the fusion of 2 plates in the midline, known as the laryngeal prominence or the Adam’s apple.
Superior and Inferior projections
Projecting hours of the Thyroid Cartilage: Two superior, Two inferior – have a small facet articulation with cricoid cartilage – synovial joint
Cricoid Cartilage
Lying inferior to the thyroid cartilage. Single ring-shaped cartilage which sits between the thyroid and the top of the trachea.
Posterior Region of Cricoid Cartilage
Enlarged at the posterior region where smaller arytenoid cartilages attach. Inferiorly attached to the trachea via ligaments.
Epiglottis
Composed of elastic cartilage (more flexible), leaf-shaped, covered in a mucosal (epithelial) lining which contains taste buds.
Location of Epiglottis
Attached to the internal anterior part of the thyroid cartilage and enclosed in membranes of the larynx. Closely related to the posterior part of the tongue.
Epiglottis Movement During Swallowing
Movements of the laryngeal muscles and associated muscles during swallowing allows it to tip backwards to cover and protect the laryngeal opening.
Small Paired Cartilages of the Larynx
Important for producing movements (adduction and abduction) of the vocal ligaments within the larynx and also for providing tension and support to the membranes of the larynx.
Arytenoid Cartilages
Pyramid shaped, sit atop the larger, posterior part of the cricoid cartilage. Apex (top), vocal process (vocal ligaments attach), muscular process (intrinsic laryngeal muscles attach).
Vocal Ligaments
Project from the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages forwards to the midline of the thyroid cartilage where they attach. Lie within the air-flow through the larynx. Moving and tensing these ligaments across the airflow allows different sounds and pitches to be created.
Corniculate and Cuneiform Cartilages
Lie in the folded edge of the quadrangular membrane (extends from the arytenoids and thyroid to the epiglottis). Help to provide support and tension for this membranous tube.
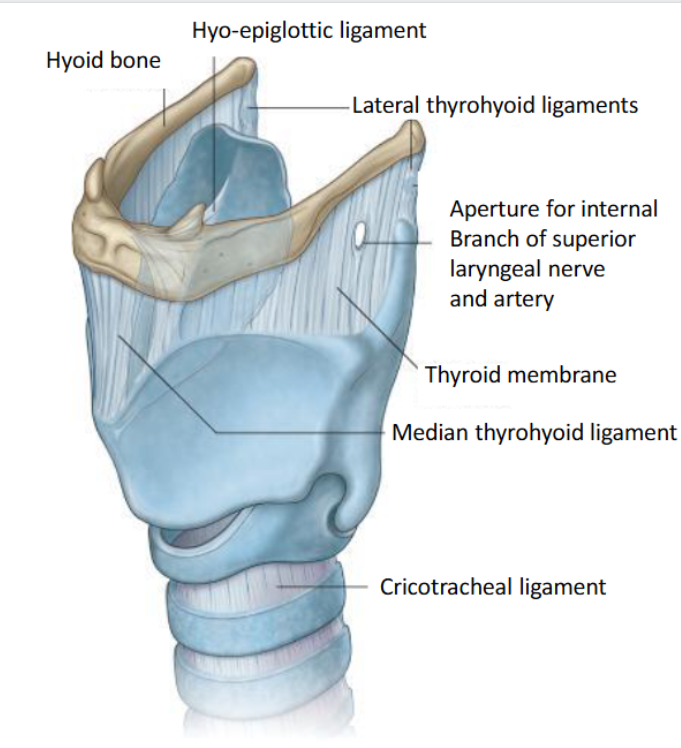
Framework of the Larynx
The framework is formed by the thyroid, cricoid and epiglottis cartilages in association with the cricothyroid and quadrangular membranes. Forms an elongated tube.
Vocal and Vestibular Ligaments
Lie inside the framework of the larynx and are formed by the cricothyroid membrane and the quadrangular membrane.
Function of the 3 Paired Cartilages
Help to support and strengthen the membranes of the framework and to aid in the movements of the vocal and vestibular ligaments in and out of the airflow through the larynx.
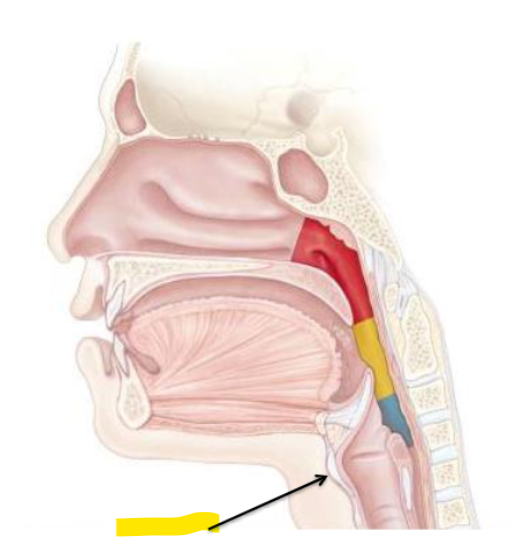
What is this part of the neck?
What are the 9 cartilages of the larynx
3 unpaired:
• Thyroid
• Cricoid
• Epiglottis
3 paired:
• Arytenoid
• Corniculate
• Cuneiform
What are the 3 functions of the larynx
1: provide an open airway for breathing
2: help route air and food to the correct location (epiglottis)
3: voice production (phonation
What is the largest cartilage of the larynx
Thyroid
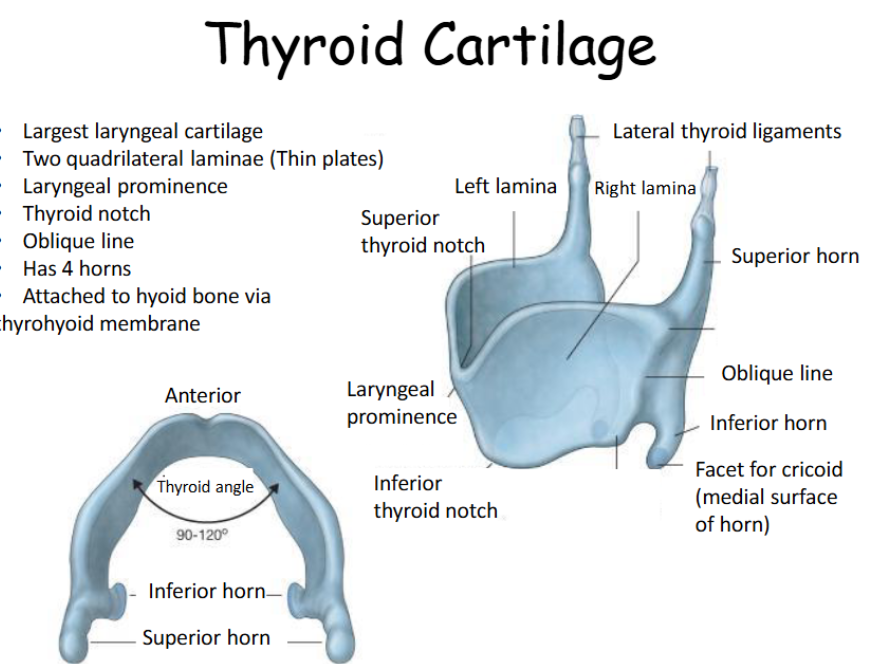
How is the thyroid cartilage formed?
It is formed by the fusion of 2 plates in the midline and this midline
region is known as the laryngeal prominence or the Adam’s apple.
Developmental differences between men and women (due to hormones) give men a much more prominent Adam’s apple and larger thyroid cartilage than women
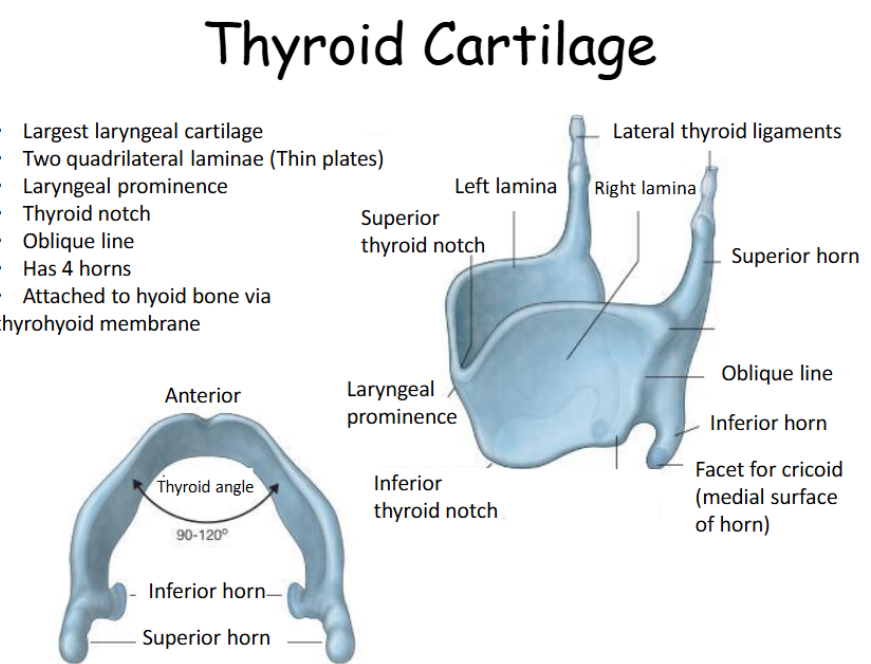
How many horns does thyroid cartilage have?
4
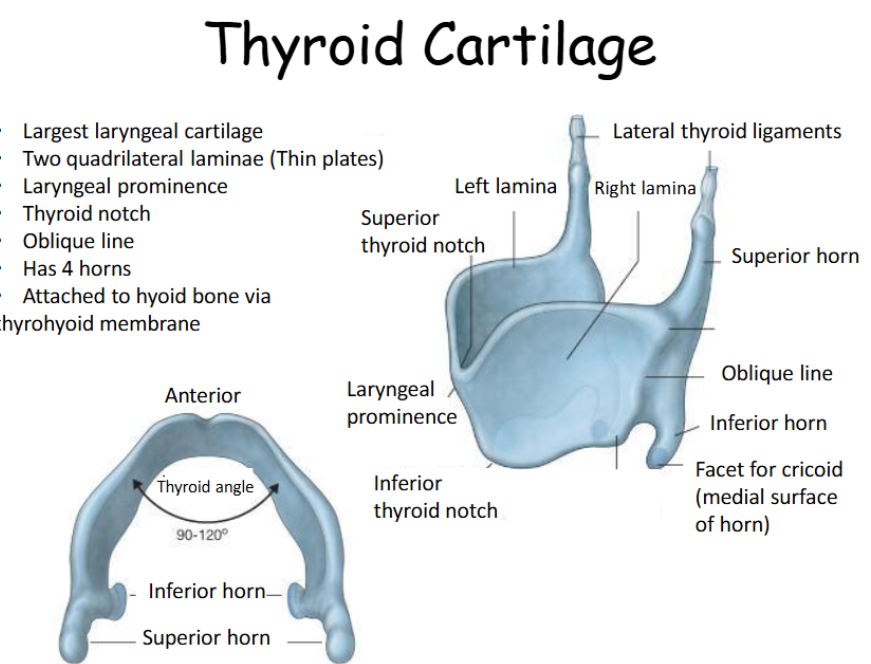
What is the thyroid attached too?
attached to hyoid bone via thyrohyoid membrane
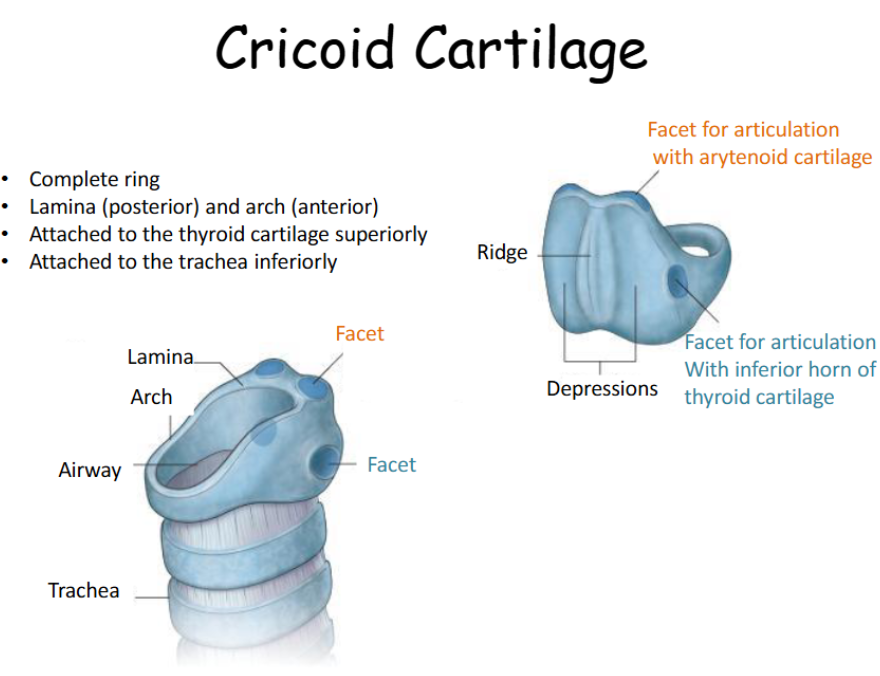
Where is the cricoid cartilage located?
This is a single ring-shaped cartilage which sits between the thyroid and the top of the trachea
Look at this diagram of the cricoid cartilage
Is the epiglottis more flexible than the thyroid?
The epiglottis is a composed of elastic cartilage and is therefore more flexible than the thyroid and cricoid cartilages.
What is the epiglottis shaped life?
A leaf and covered in a mucosal (epithelial) lining which contains taste buds.
What is the epiglottis attached too?
The epiglottis is attached to the internal anterior part of the thyroid cartilage and enclosed in membranes of the larynx
How does the movement of laryngeal muscles affect the epiglottis?
Movements of the laryngeal muscles and associated muscles (such as the tongue and soft palate) during swallowing allows the epiglottis to tip backwards to cover and protect the laryngeal opening. This helps to prevent food which travels through the oropharynx entering the larynx.
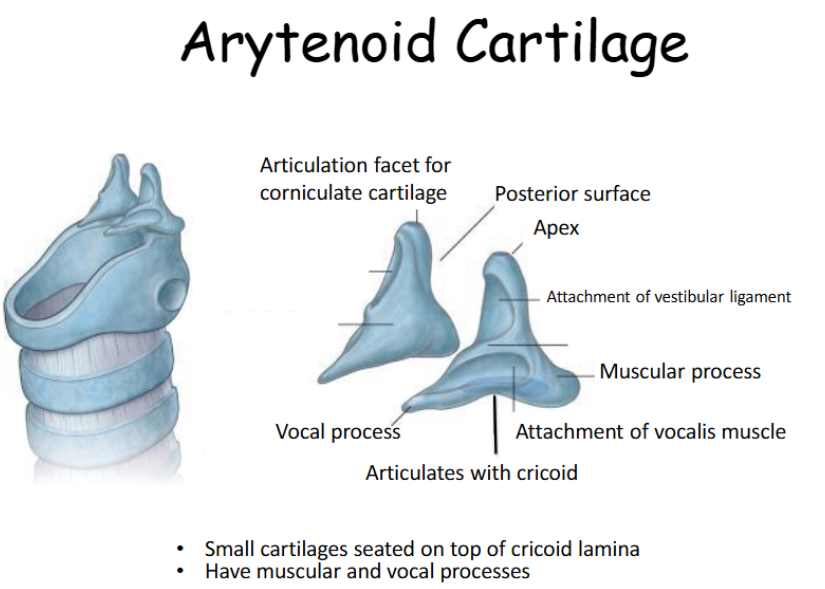
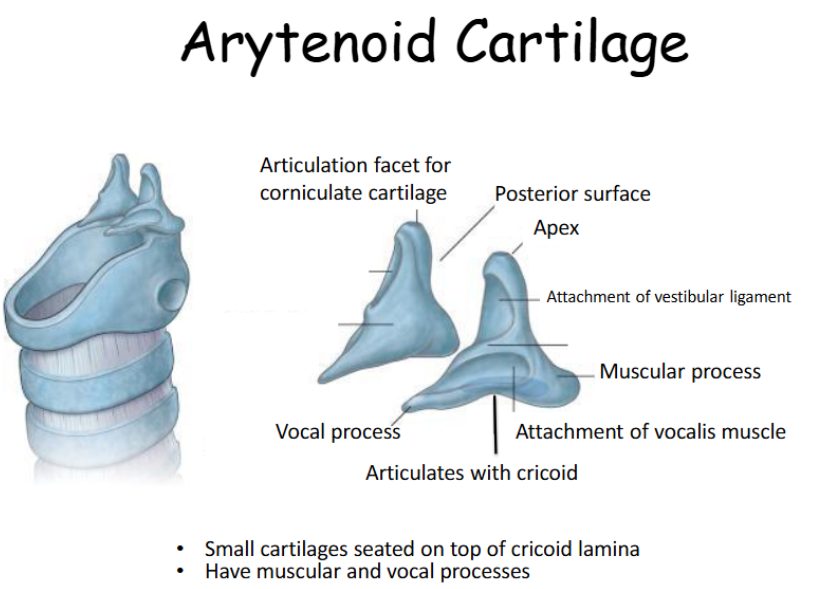
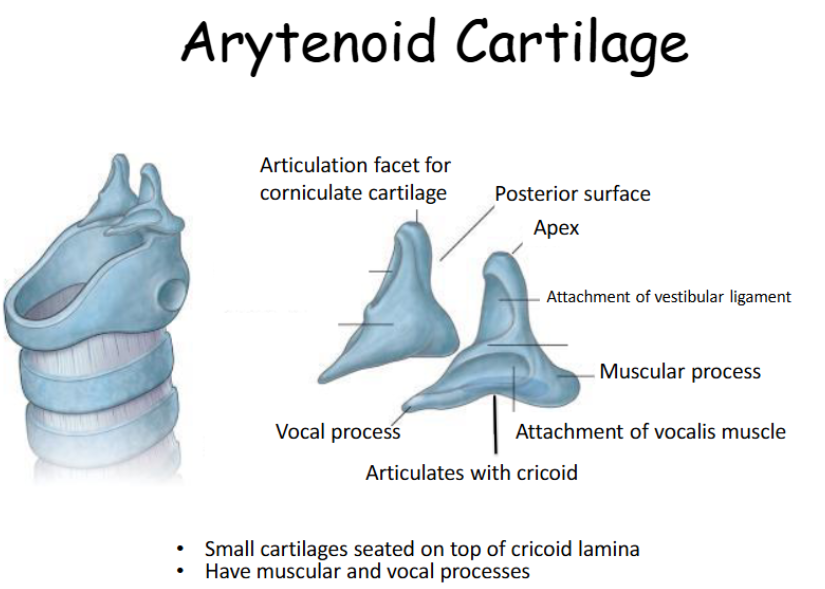
Look at this diagram of the arytenoids
What are the 3 smaller paired muscles of the larynx?
The three smaller paired muscles of the larynx are the thyroarytenoid, cricoarytenoid, and arytenoid muscles. These muscles assist in adjusting tension and position of the vocal folds during phonation.
What is the most important smaller paired muscle of the larynx
The most important of the small cartilages is the arytenoids. These are pyramid-shaped and sit atop the larger, posterior part of the cricoid cartilage.
They have an apex (top) a vocal process (onto which the vocal ligaments attach), and muscular process (onto which some intrinsic laryngeal muscles attach)
How does vocal ligaments produce noise?
The vocal ligaments stretch from the arytenoid cartilages to the thyroid cartilage, lying within the laryngeal cavity and in the path of airflow. When these ligaments are moved or tensed, they vibrate, producing different sounds and pitches—this is the basis of phonation (voice production).
Refer to this diagram of the corniculate and cuneiform cartilage
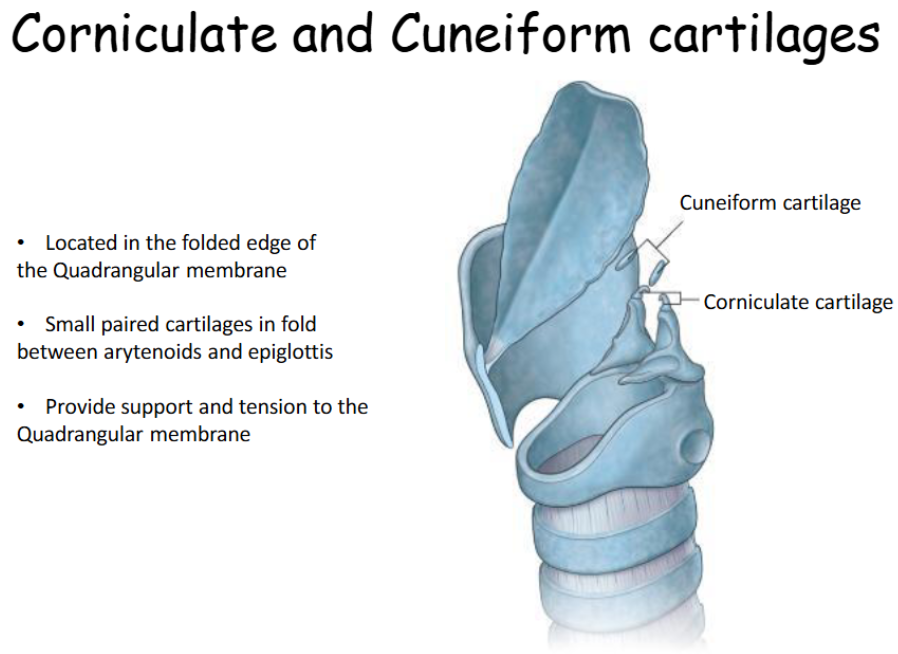
What is the function of the Corniculate and Cuneiform cartilages
Provide support and tension to the Quadrangular membrane
Where is the corniculate and cuneiform cartilages located?
The corniculate and cuneiform cartilages lie in the folded edge of the quadrangular membrane (which extends from the arytenoids and thyroid to the epiglottis.
What is the laryngeal framework made up?
The laryngeal framework is made up of the thyroid, cricoid, and epiglottis cartilages, along with the cricothyroid and quadrangular membranes, forming a 5 cm-long tube that allows air to flow into the trachea and lungs.
Inside this framework are two sets of ligaments: the vocal ligaments (from the cricothyroid membrane) and the vestibular ligaments (from the quadrangular membrane), both positioned within the airflow.
What are the 3 paired cartilages and their function as a whole
Three paired cartilages—arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform—support the membranes and assist in moving the vocal and vestibular ligaments to control airflow and sound
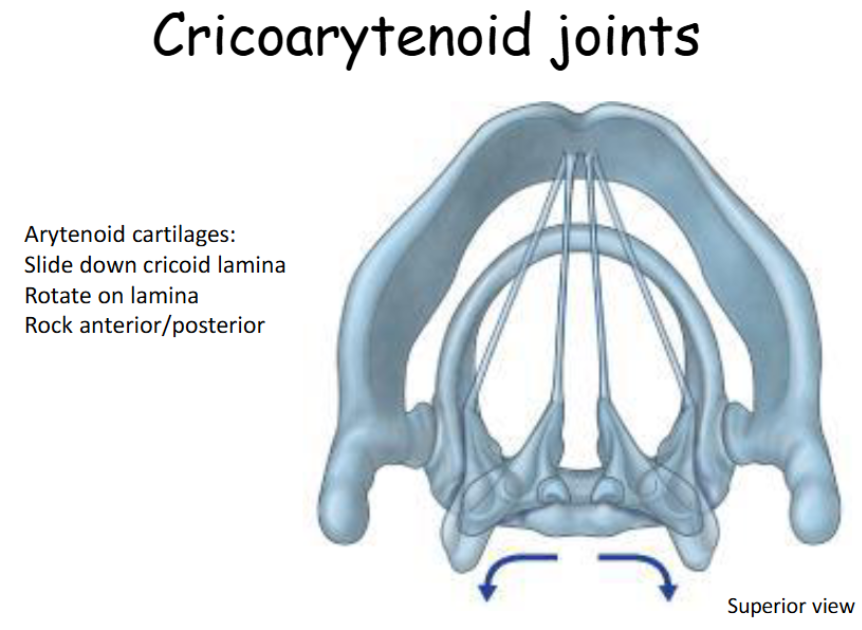
Look at this diagram of the cricoarytenoid joint
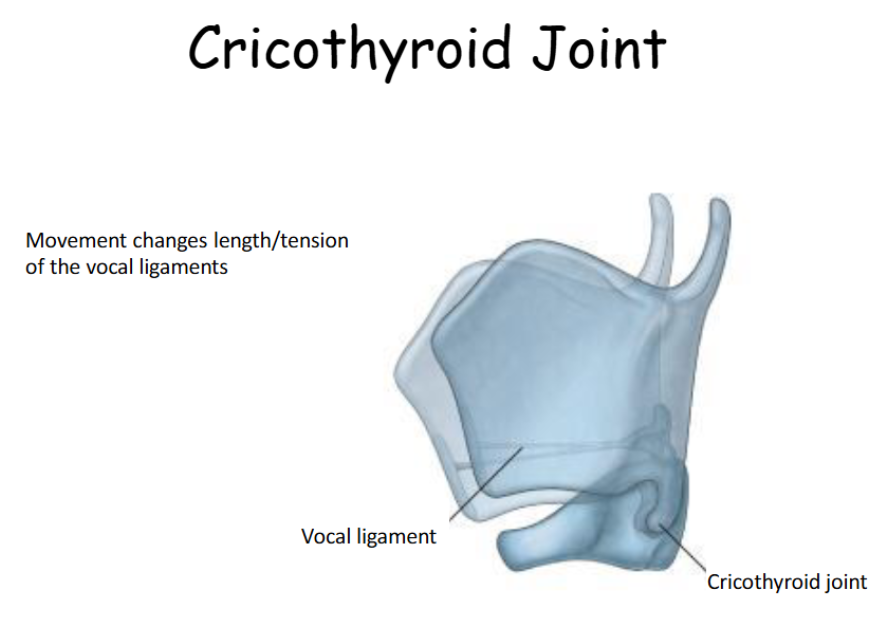
Look at this diagram of the cricothyroid joint
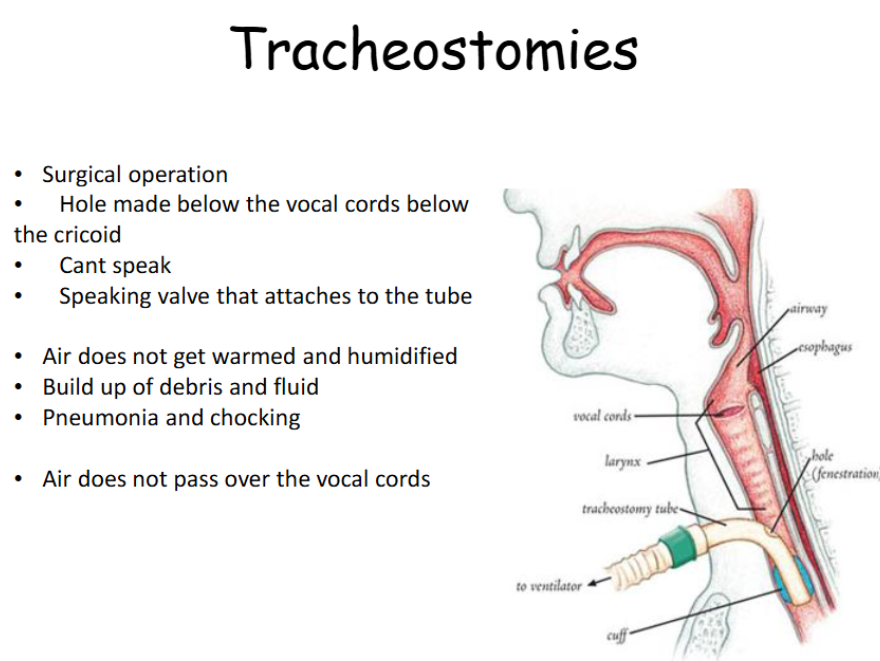
What is a tracheostimtracheostomomeome?
Surgical operationto create an opening in the trachea to facilitate breathing.