Atomic structure and periodic table CP1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Protons relative mass
1
Neutrons relative mass
1
Electrons relative mass
very small, specifically 2000x smaller
Protons charge
+1 - P for positive charge
Neutrons charge
0 - N for no charge
Electrons charge
-1
Atoms radius
Around 0.1nm
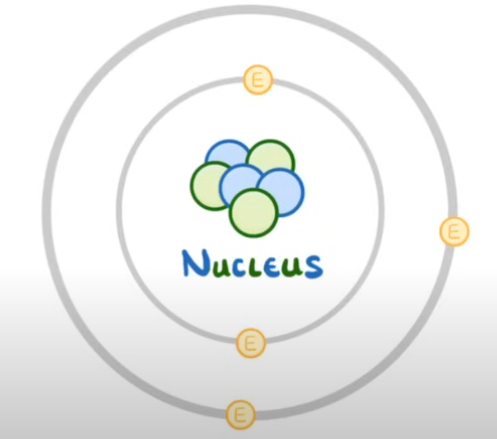
What is an ion?
An atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, meaning charges will no longer balance.
Negative ion (3 protons, 4 electrons is a 1- negative ion)
When an atom has gained electrons outnumbering the protons.
Positive Ion (4 protons, 3 electrons is a 1+ positive ion)
When an atom has lost electrons meaning there are more protons.
What is an element?
A different type of atom, meaning the periodic table is filled with elements.
What is the atomic number and where is it found?
The number of protons the atom of an element has. It also tells us how many electrons the atom has. Determined by the bottom number of an element on the periodic table.
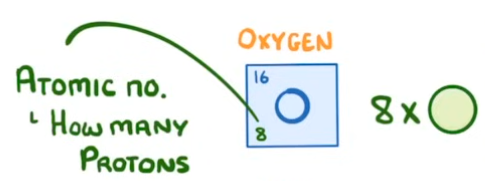
The number of protons in an atom determines…
which element that atom is.
What is the mass number and where is it found?
Tells us the total numbers or protons AND neutrons in an atom. Determined by the top number of an element on the periodic table.
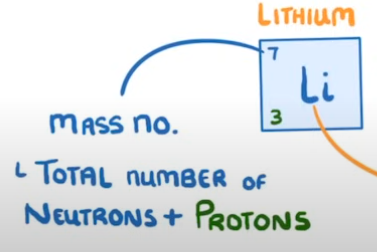
How would you work out how many neutrons an element has?
Mass number - Atomic number.
What is an isotope? (e.g. carbon-12 and carbon-13)
Different forms of the same element, that has the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.

What do we mean by the abundance in terms of isotopes?
How common or rare that isotope is.
What is the equation for finding out the relative formula mass?
Multiplied abundance x isotope mass divided by the sum of abundances of all isotopes.
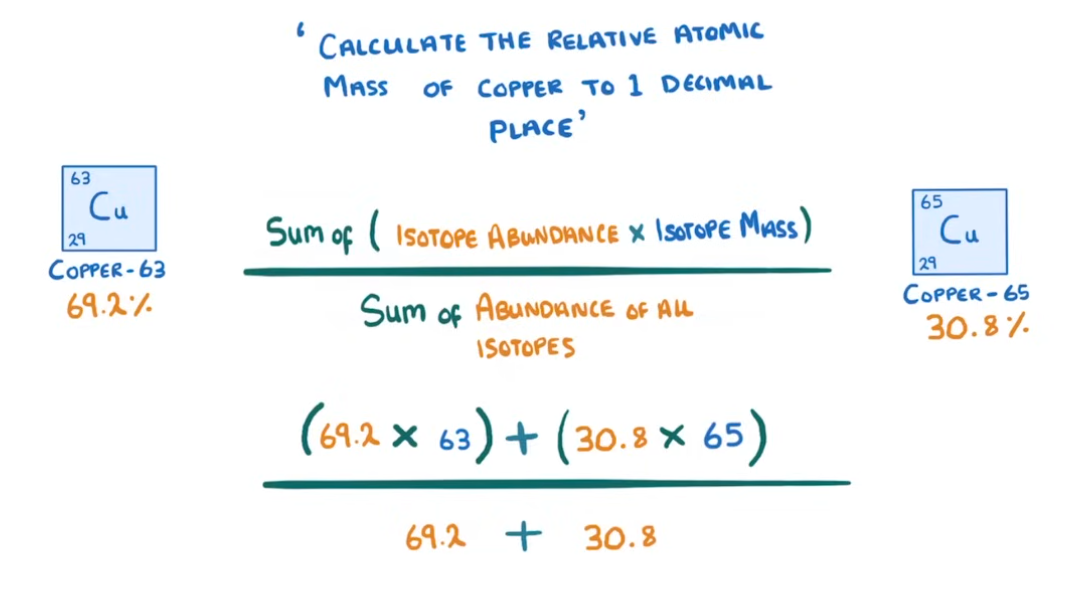
What is a molecule? (e.g. oxygen)
2 or more atoms chemically bonded together.
What is a compound? (e.g. water)
2 or more different elements chemically bonded together.
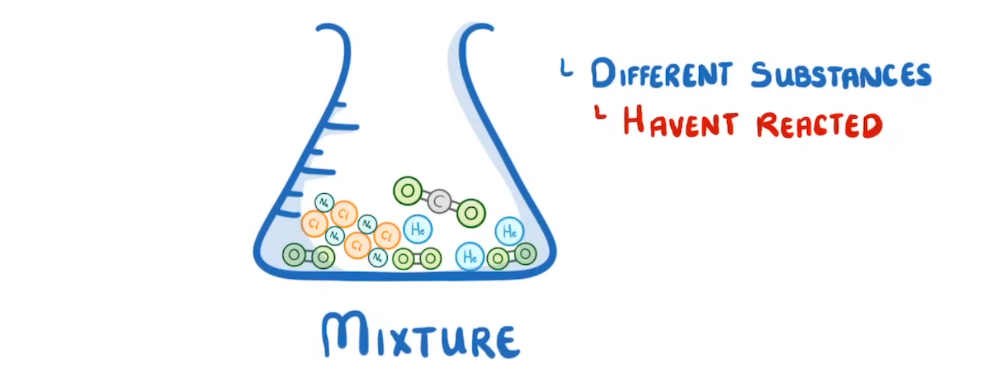
What is a mixture?
2 or more substances that are not chemically bonded meaning they can be easily separated through methods such as filtration.
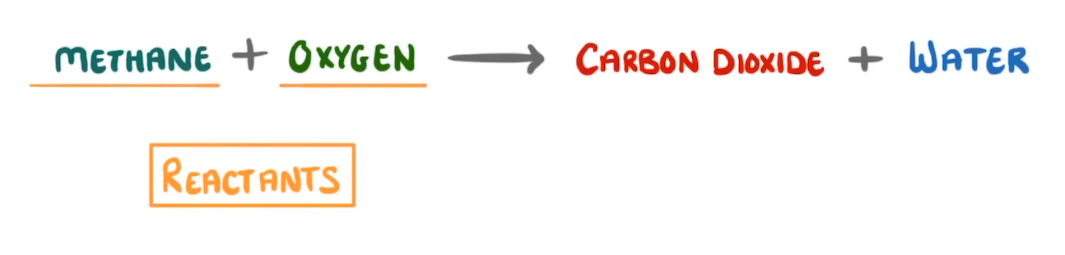
Where are the reactants typically found in an equation?
The left hand side of the arrow.
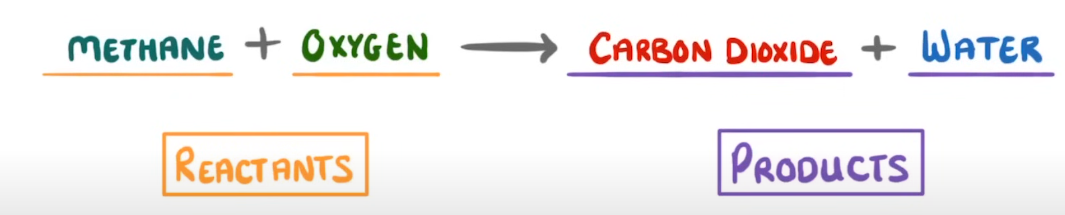
Where are the products typically found in an equation?
The right hand side of the arrow.
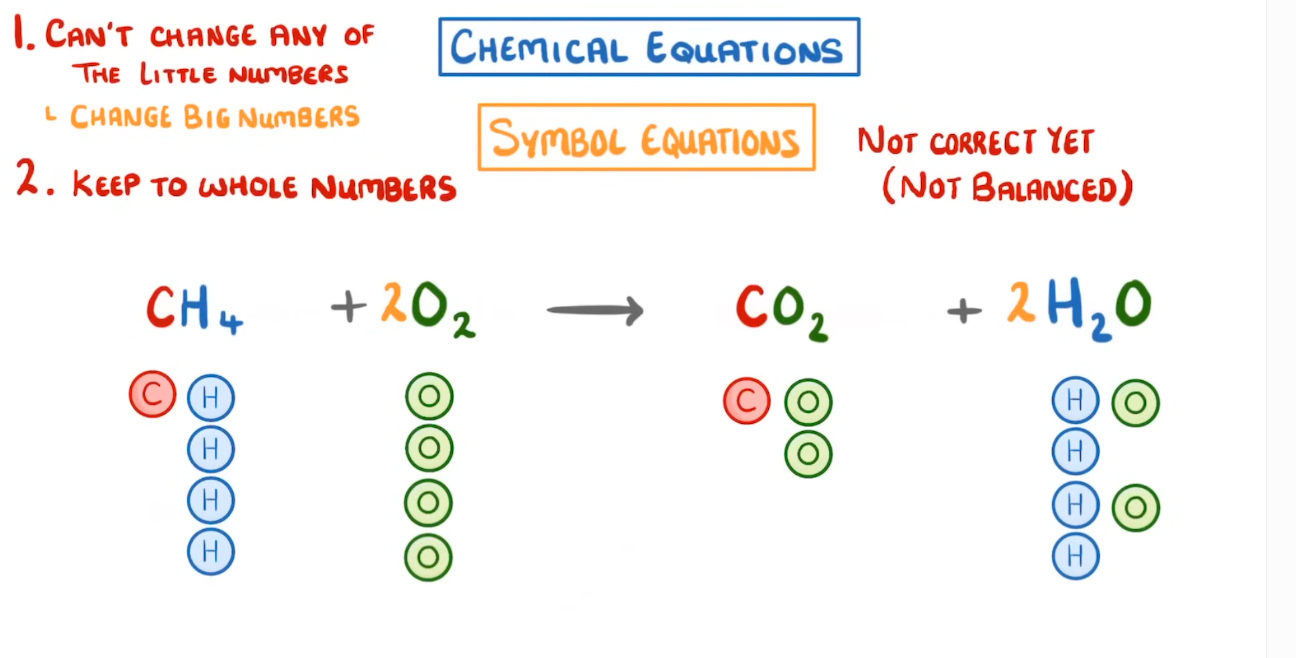
What is a balanced equation?
A balanced equation is an equation in which both sides, reactants and products, have the same total number of each type of atom.