Quiz 15 med term- oncology (19) rad and nuclear medicine (20)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
mammography
uses low-dose x-rays to visualize breast tissue
barium sulfate
radiopaque substance that is mixed in water and used for examination of the upper and lower GI tract
upper GI series (UGI)
involves oral ingestion of barium sulfate so that the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum can be visualized
small bowel follow-through (SBFT)
traces the passage of barium in a sequential manner as it moves through the small intestine
barium enema (BE)
is a lower GI series that opacifies the lumen of the large intestine using an enema containing barium sulfate
double-contrast study
uses both radiopaque and a radiolucent contrast medium
iodine compounds
radiopaque fluids containing up to 50% iodine are used
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
procedure where contrast is being injected directly into the common bile duct
intraoperative cholangiography
where contrast is directly injected into the common bile duct during surgery of the gallbladder or biliary tract
digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
x-ray image of contrast-injected blood vessels is prodcued by taking two x-ray pictures and using a computer to subtract obscuring shadows from the second image
hysterosalpingography
x-ray record of the endometrial cavity and fallopian tubes is obtained after injection of contrast material through the vagina and into the endocervical canal
myelography
x-ray imaging of the spinal cord after injection of contrast agent into the subarachnoid space surrounding the spinal cord
urography
taking x-ray images if the urinary tract after injecting contrast
fluoroscopy
use of x-rays and a fluorescent screen to produce real-time video images
sonogram
the record produced by ultrasound imaging
echocardiography
sound waves are used to image the structure of the heart
doppler ultrasound
method of focusing sound waves on blood vessels to measure blood flow
gadolinium
most commonly used contrast agent in MRI
posteroanterior (PA) view
in this most commoly requested chest x-ray view, x-rays travel from a posteriorly placed source to an anteriorly placed detector
anteroposterior (AP) view
x-rays travel from an anteriorly placed source to a posteriorly placed detector
lateral view
x-rays travel from a source located to the right of the patient to a detector placed to the left of the patient
oblique view
x-rays travel in a slanting direction at an angle from the perpendicular plane
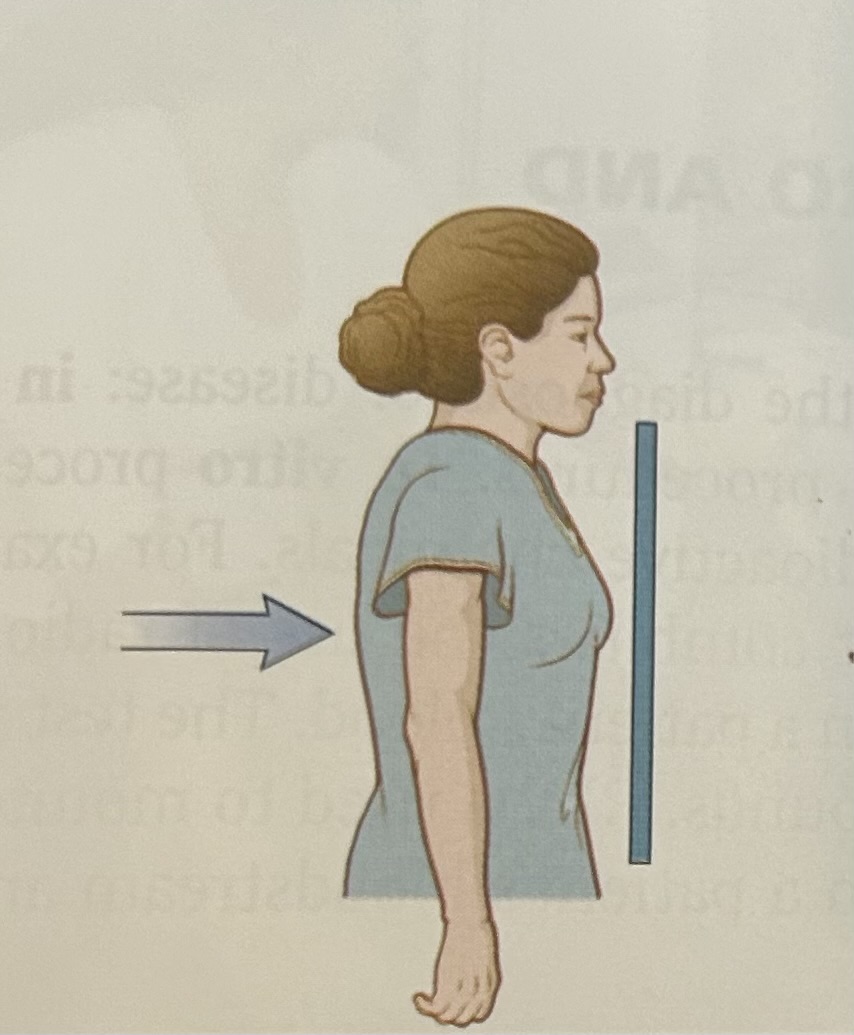
posteroanterior (PA) view
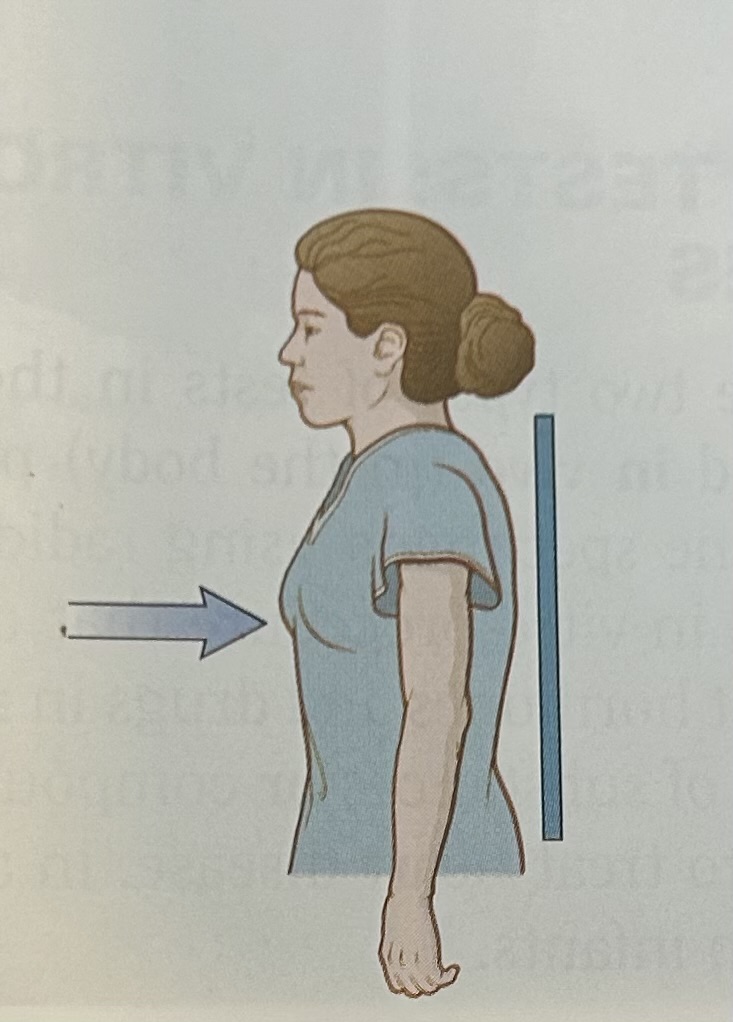
Anteroposterior (AP) view
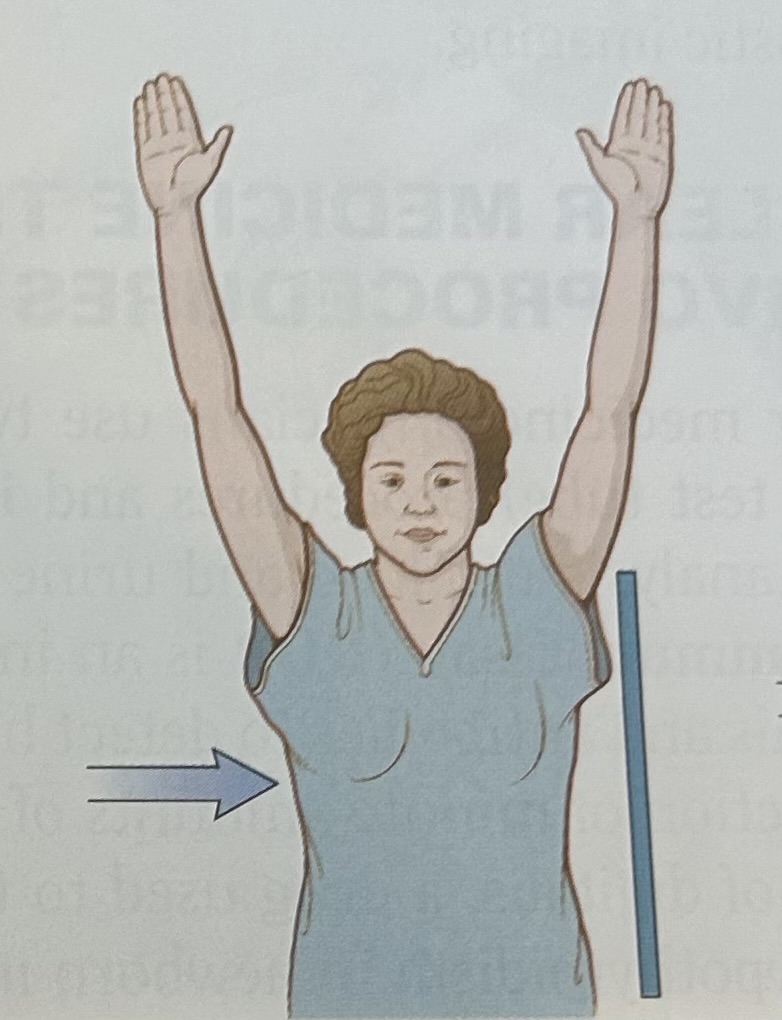
Left lateral view
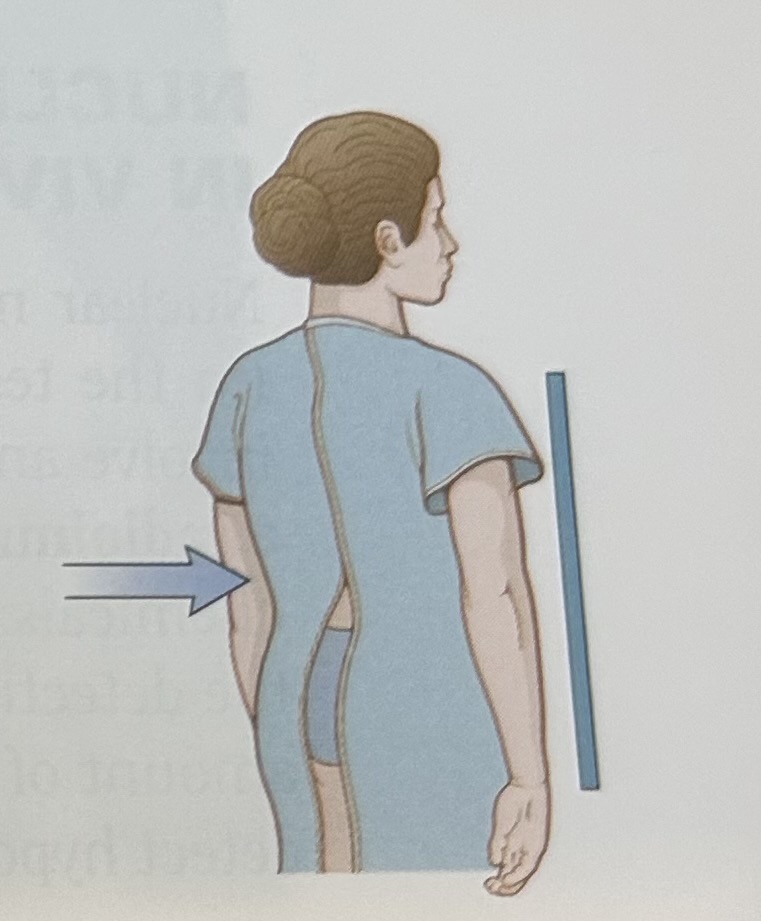
Oblique view
decubitus
lying down. a lateral decubitus position is lying down on the side
eversion
turning outward
inversion
turning inward
recumbent
lying down (may be prone or supine)
PET-CT scan
combines PET and CT techniques to produce a more accurate image than a PET or CT alone
PET-MRI scan
combine magnetic resonance imaging with positron emission tomography
computed tomography (CT)
diagnostic x-ray procedure whereby a cross-sectional image of a specific body segment is produced
contrast studies
radiopaque materials are injected to obtain contrast between tissues that would be indistinguishable from one another
gamma camera
machine to detect gamma rays emitted from radiopharmaceuticals furing scanning for diagnostic purposes
half-life
time required for a radioactive substance to lose half its radioactivity by disintegration
interventional radiology
therapeutic or diagnostic procedures performed by a radiologist
ionization
transformation of electrically neutral substances into electrically charged particles. x-rays cause ionization of particles within tissues
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
magnetic field and radio waves produce sagittal, coronal, and axial images of the body
nuclear medicine
medical specialty that uses radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
positron emission tomography (PET)
positron-emitting radioactive substances given intravenously create a cross-sectional image of cellular metabolism based on local concentration of the radioactive substance
radioisotope/ radionuclide
radioactive form of an element substance
radiology
medical specialty concerned with the study of x-rays and their use in the diagnosis of disease, includes other forms of energy, such as ultrasound and magnetic waves
radiolucent
permitting the passage of x-rays, appear black on x-ray images
radiopaque
obstructing the passage of x-rays, appear white on the x-ray images
single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
radioactive tracer is injected intravenously and a computer reconstructs a 3D image based on a composite of many views
ultrasonography (US, U/S)
diagnostic technique that uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of the body
ultrasound transducer
handheld device that sends and receives ultrasound signals
uptake
rate of absorption of a radionuclide into an organ or tissue
is/o
same
-graphy
process of recording
-lucent
to shine
-opaque
obscure
Ba
barium
DICOM
digital image communication in medicine
PACS
picture archival and communications system
inflammatory
having the features of inflammation- that is, redness, swelling, and heat
nectrotic
containing dead tissue
diffuse
spreading evenly throughout the affected tissue
cauterization
destruction of tissue by burning
core needle biopsy
placement of a large-bore needle that extracts a core of tissue
exicisional biopsy
removal of tumor and a margin of normal tissue
fine needle aspiration
placement of a very fine needle inside the tumor mass and extraction of cells for microscopic evaluation
incisional biopsy
piece of tumor is removed for examination to establish a diagnosis. A more extensive surgical procedure or other forms of treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, are used to treat bulk of the tumor
brachytherapy
small, sealed containers or seeds of radioactive material are inserted directly into the tumor or into a cavity of the tumor. An implant may be temporary or permanent
external beam irradiation (teletherapy)
radiation therapy applied to a tumor from a distant source
stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)
single large dose of radiation is delievered under precise, stereotactic 3D, performed at multiple angles to destroy vascular abnormalities and small tumors in the brain or other sites
cancer chemotherapy
treatment of cancer using chemicals, standard of treatment for many types of cancer, and is curative in a number or them, may be used alone or in combination with surgery and irradiation to improve cure rates
benign tumor
noncancerous growth (neoplasm)
carcinogens
agents that cause cancer; chemicals and drugs, radiation, and viruses
carcinoma
cancerous tumor made up of cells with epithelial origin
chemotheraphy
treatment with drugs that kill tumor cells
immunotherapy
cancer treatment using immune cells and antibiotics to kill tumor cells
malignant tumor
tumor having the characteristics of continuous growth, invasiveness, and metastasis
metastasis
spread of malignant tumor to a secondary site; literally, beyond control
morbidity
condition of being unwell or deficient in normal function
neoplasm
new growth; benign or malignant tumor
palliative
relieving but not curing symptoms
radiation
energy carried by a stream of particles
radiation therapy
treatment of tumors using doses of radiation
relapse
recurrence of tumor after treatment
remission
absence of signs and symptoms of disease
sarcoma
cancerous tumor dervied from connective or flesh tissue
virus
infectious agent that reproduces by entering a host cell and using the host’s genetic material to make copies of itself