lf209 lecture 4 - blood cells, plasma & serum
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
white blood cells are known as
leukocytes
RBCs are flexible since they have ______ and ______ complex which forms a ___-like pattern on the surface of its inner plasma membrane
actin
spectrin
mesh
erythropoietin
a hormone which stimulates RBC production
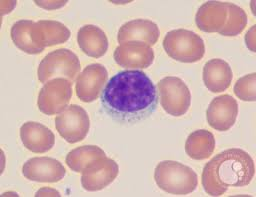
what cell is this?
lymphocyte
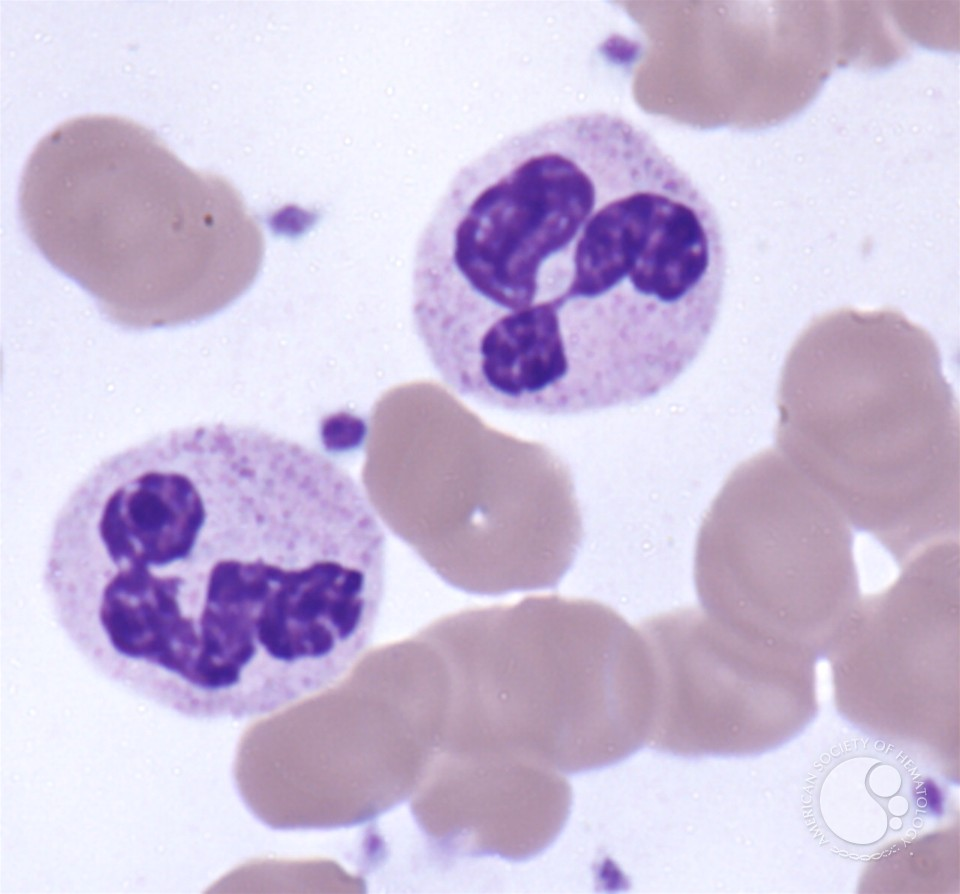
what cell is this?
neutrophil
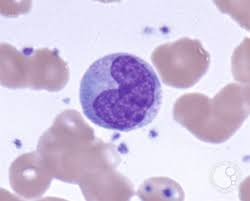
what cell is this?
monocyte
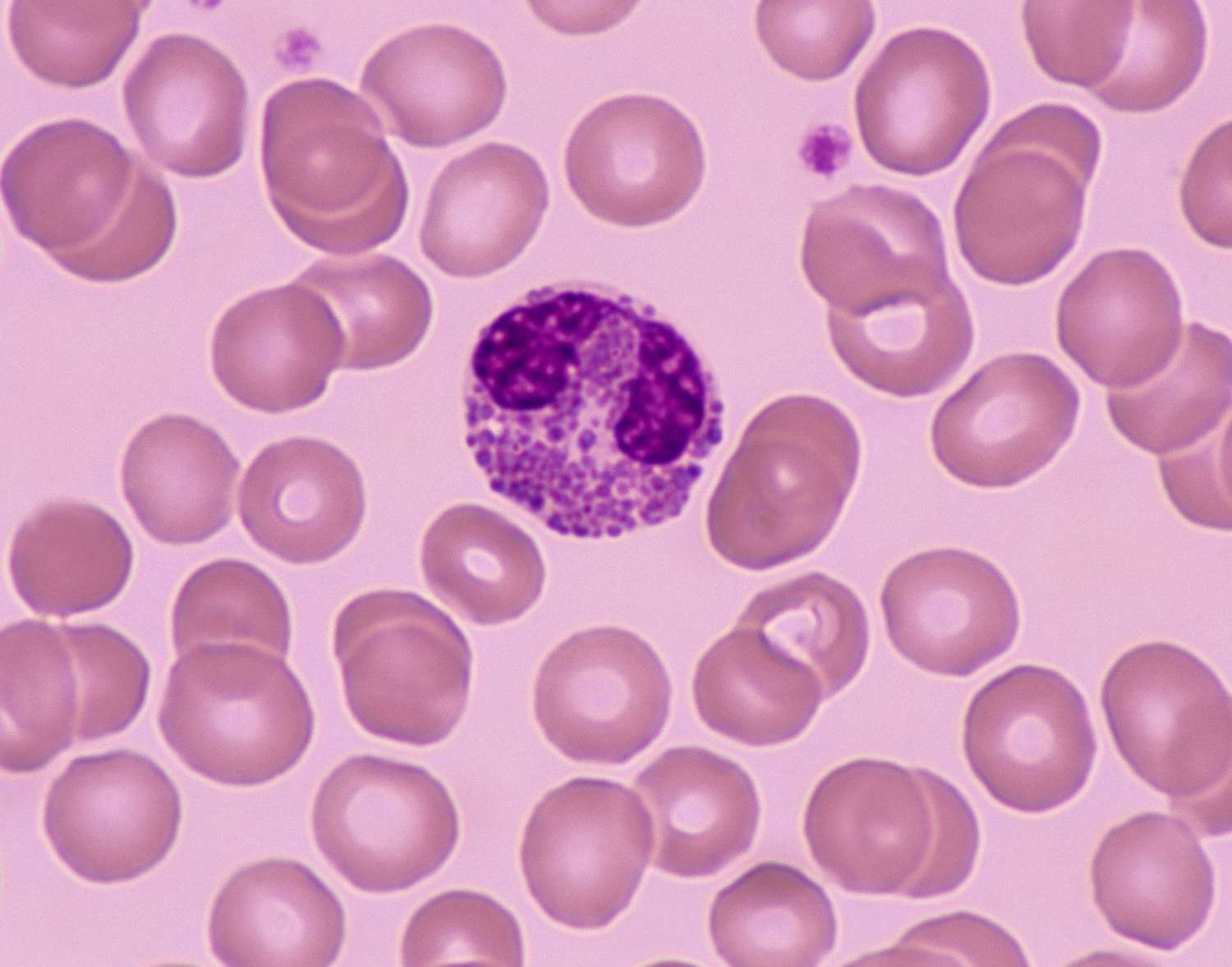
what cell is this?
eosinophil
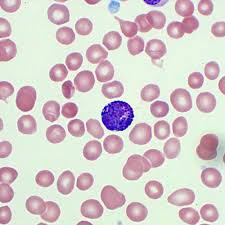
what cell is this?
basophil
cells in suspension are always ______ but when in tissue have more of a charcteristic shape i.e. dendritic
rounder
H&E (_________ & _____) is the most common blood stain
E____ is a pink ______ dye that binds to proteins and stains ______ pink.
H_______ is a blue-purple ____ dye that binds to _____ acids
haematoxylin & eosin
eosin, acidic, cytoplasm
haematoxylin, basic, nucleic
histochemistry
exploitation of specific enzymes within cells converting the colourless substrate into a coloured product
histochemistry test for leukaemia
using non-specifc esterases to cleave a-napthyl acetate to a-napthol.
a-napthol reacts with pararoasaniline (Schiff’s base) = red-brown colour.
is counterstained with haematoxylin
red-brown = positive for leukaemia
immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry
both are staining techniques by binding specific antibodies to intra/extracellular antigens
cyto → antibodies linked to fluorescent chromophores
histo → antibodies linked to enzymes that convert a substrate (can get a colour change)
flow cytometry
take cells into single cell suspension after being stained through tube, has detector to detect the fluorescence.
B cells have what regions that are detected by ICC and IHC
CD38+ and CD138+
platelets are also known as
thrombocytes
megakaryocytes should never be found in ________ blood. this causes blood to rush past it forming _______
peripheral
platelets
plasma vs serum
plasma = liquid remaining after blood cells. contains proteins which are synthesised by the liver apart from gamma-globulins.
serum = liquid after blood has clotted
plasma proteins examples
polypeptide hormones
regulators of blood pressure
some enzymes
insulin
angiotensin
blood amylase
albumin, a plasma ________, is a _______ for substances with ___ solubility, ie.binds to Ca2+
protein
carrier
low
complement, a plasma ________, when activated performs o________, ch______, lysis and cl______.
proteins
opsonisation
chemotaxis
clumping
PLASMA PROTEINS
gamma-globulins are
a-anti-trypsin inhibts _____
haptoglobulin binds free _________
serum antibodies
trypsin (digests other proteins)
haemoglobulin
clotting cascade has 2 _______
ex______ - is stimulated by
in______ - is stimulated by
why have fibrinogen (insoluble) circulating in the blood instead of making fibrin when needed?
so we don’t have to wait for fibrin to be synthesised.
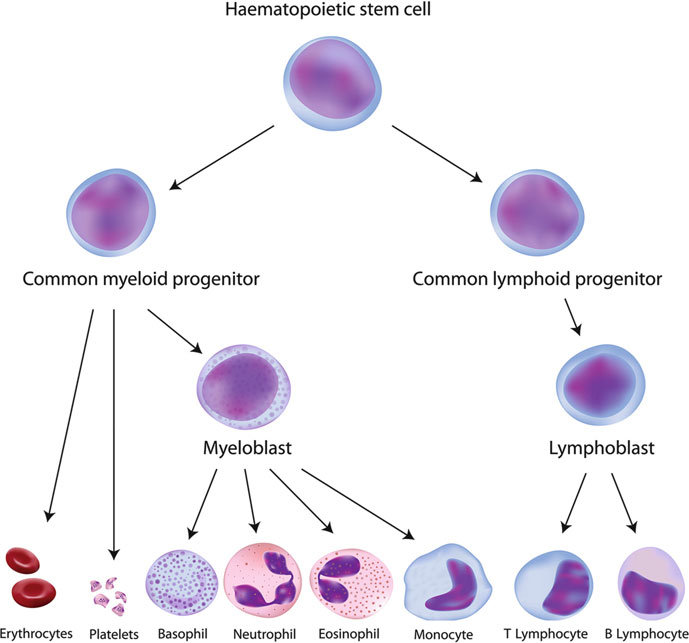
2 lineages of blood cells (draw it)
myeloid and lymphoid
haemostasis
mechanism that stops bleeding from a blood vessel - maintaining blood flow within the blood vessel.
HAEMOSTASIS STEPS:
injury exposes _______ in damaged vessel wall
__ ________ ______ (vWF) binds to collagen and ______ by GP Ib receptors on platelet
binding of integrins to vWF _______ platelets
activated platelets release ____ and ___________ (TXA2)
released ADP further activates platelets by binding to platelets ADP ______ (P2Y12)
TXA2 is a __________ which helps reduce blood flow and therefore limit blood ____
activated platelets ____ more to everything
________ are up-regulated on the platelet surface, these are pro-______ (stimulate clotting)
collagen
von Willebrand Factor, integrins
activates
ADP, thromboxane A2
receptors
vasoconstrictor, loss
bind
phospholipids, pro-thrombotic
MECHANISM TO PREVENT EXCESSIVE CLOTTING
thrombomodulin on the __________ binds to thrombin and activates protein C which ______ factors Va and ______
antithrombin in plasma inactivates _______
protease A_________ degrade ___
endothelium, inactivates, VIIa
thrombin
ADAMTS13, vWF
CLOT REMOVAL (fibrinolysis)
digestion of fibrin by the protease ______
it’s present in the ______ as inactive precursor _________
the precursor is activated by ______ _________ _______ (tPA)
plasmin
plasma, plasminogen
tissue plasminogen activator