Human Anatomy - Microanatomy (Histology Slides)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
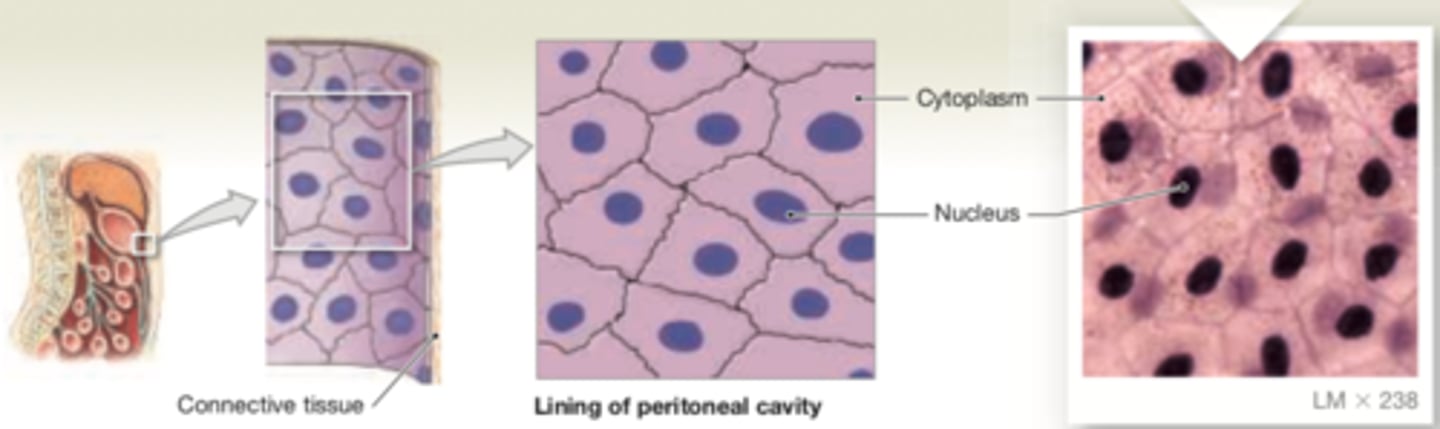
simple squamous
LOCATIONS: Mesothelia lining pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal body cavities; endothelia lining heart and blood vessels; portions of kidney tubules (thin sections of nephron loops); inner lining of cornea; alveoli of lungs
FUNCTIONS: Reduces friction; controls vessel permeability; performs absorption and secretion
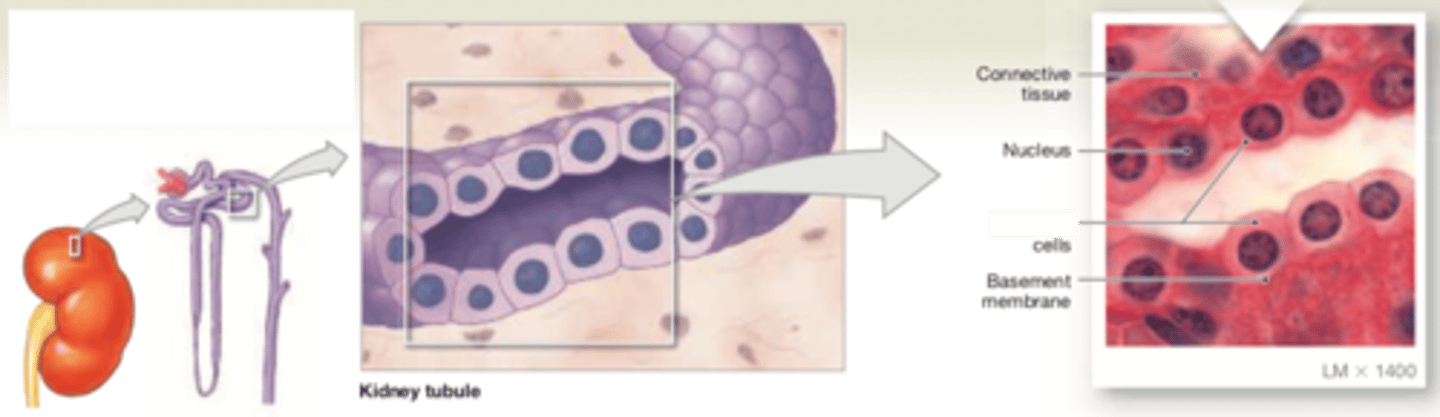
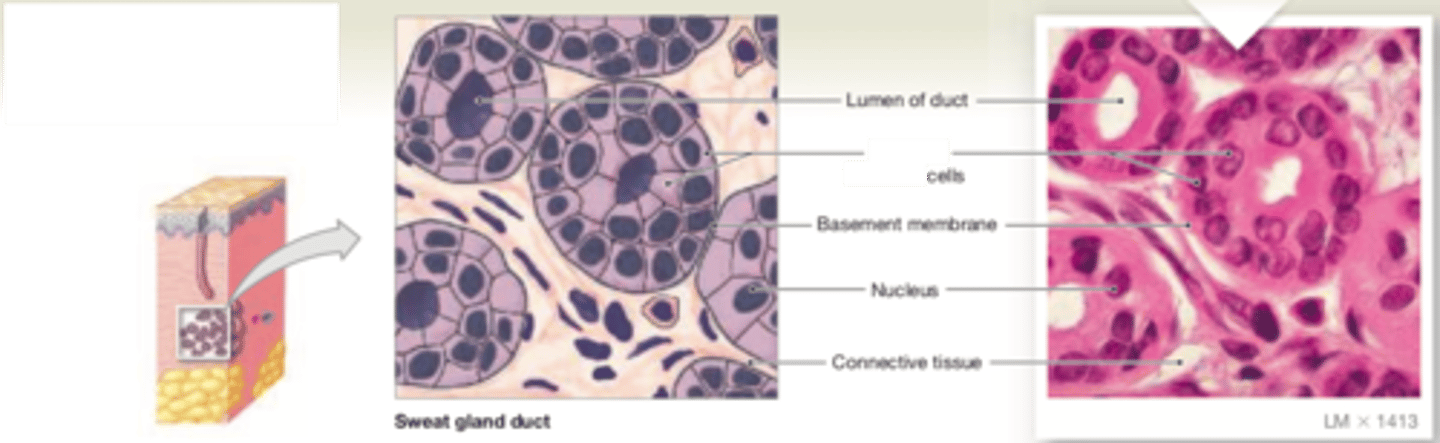
simple cuboidal
LOCATIONS: Glands; ducts; portions of kidney tubules; thyroid gland
FUNCTIONS: Limited protection; secretion; absorption
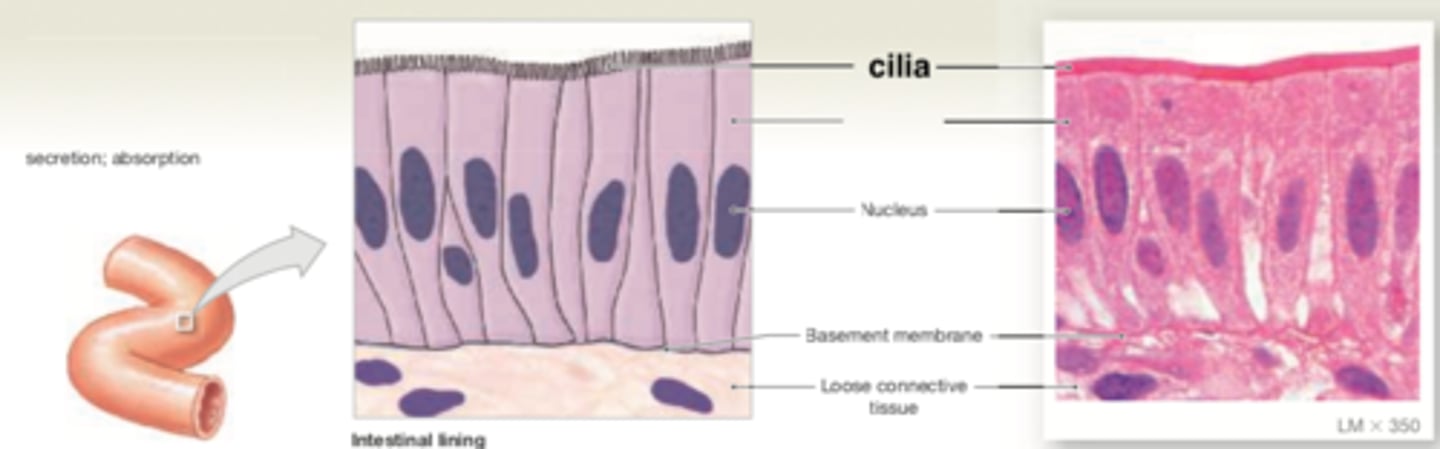
simple columnar
Location: in areas where absorption or secretion occurs, such as the lining of the stomach, intestinal tract, uterine tubes, and many excretory ducts
Functions: provide slightly more protection than simple cuboidal epithelia.
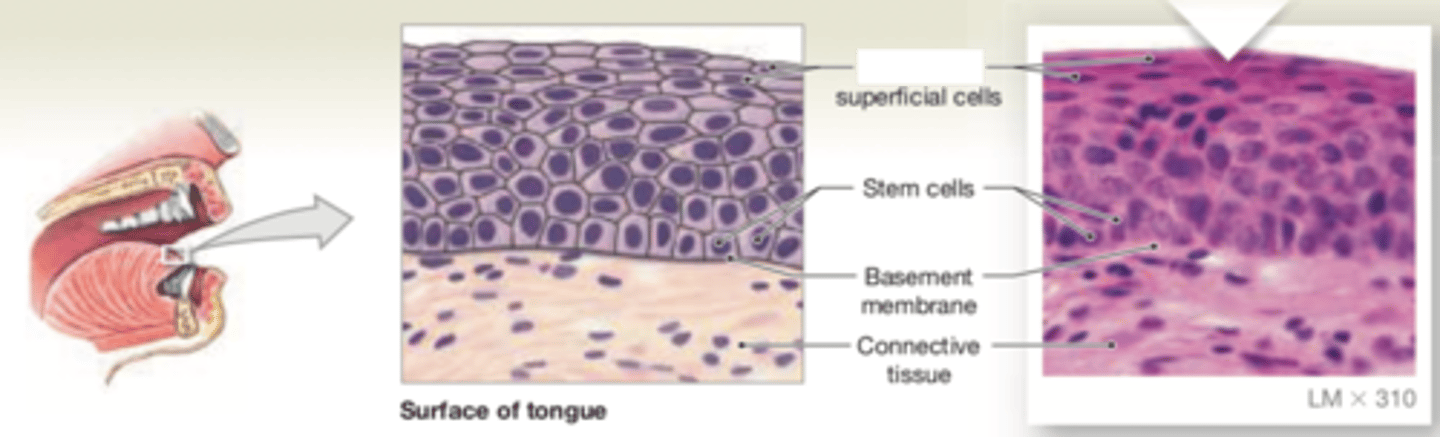
stratified squamous
LOCATIONS: Surface of skin; lining of oral cavity, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, and vagina
FUNCTIONS: Provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack
stratified cuboidal
LOCATIONS: Lining of some ducts (rare)
FUNCTIONS: Protection; secretion; absorption
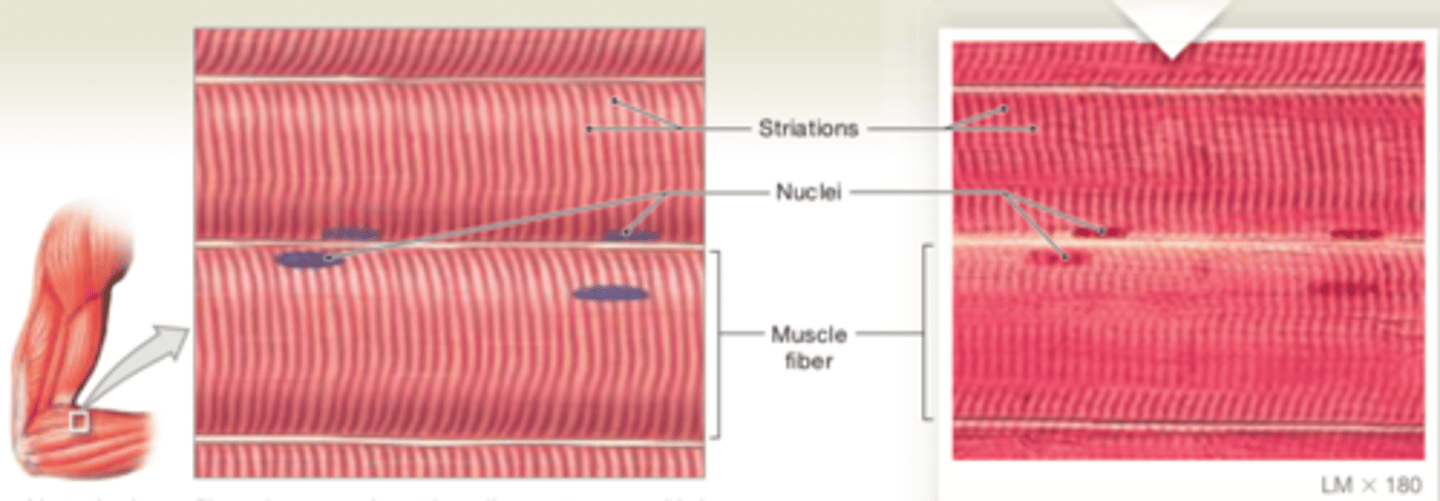
skeletal muscle tissue
Cells are long, cylindrical, striated, and multinucleate.
LOCATIONS: Combined with connective tissues and neural tissue in skeletal muscles
FUNCTIONS: Moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton; guards entrances and exits to the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; generates heat; protects internal organs
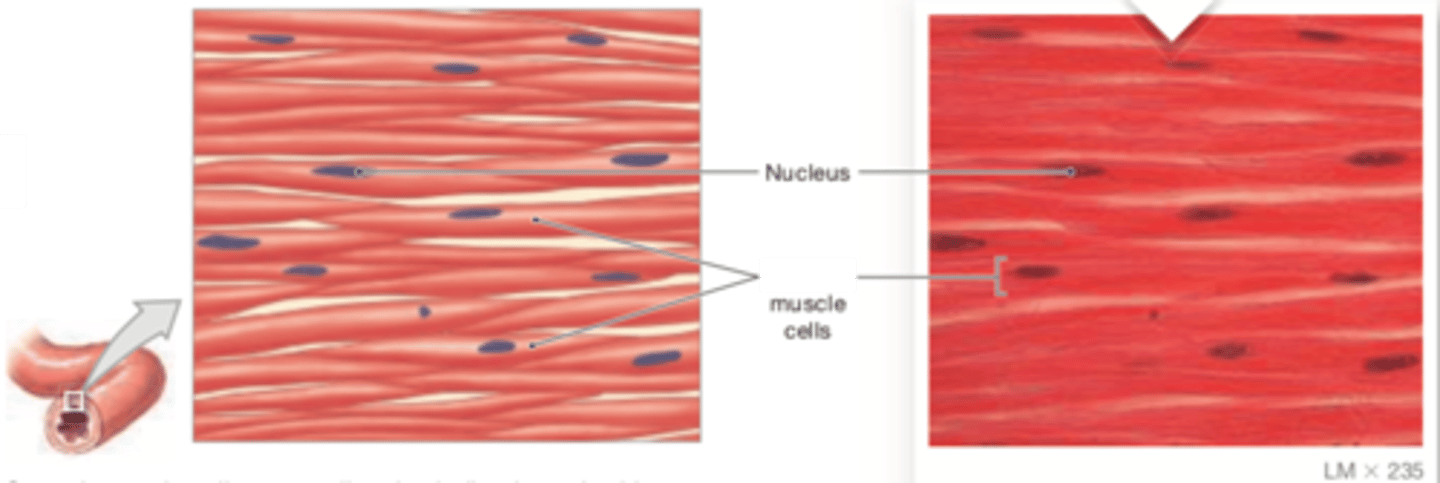
visceral muscle tissue (smooth muscle tissue)
Cells are short, spindle- shaped, and nonstriated, with a single, central nucleus
LOCATIONS: Found in the walls of blood vessels and in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive organs
FUNCTIONS: Moves food, urine, and reproductive tract secretions; controls diameter of respiratory passageways; regulates diameter of blood vessels
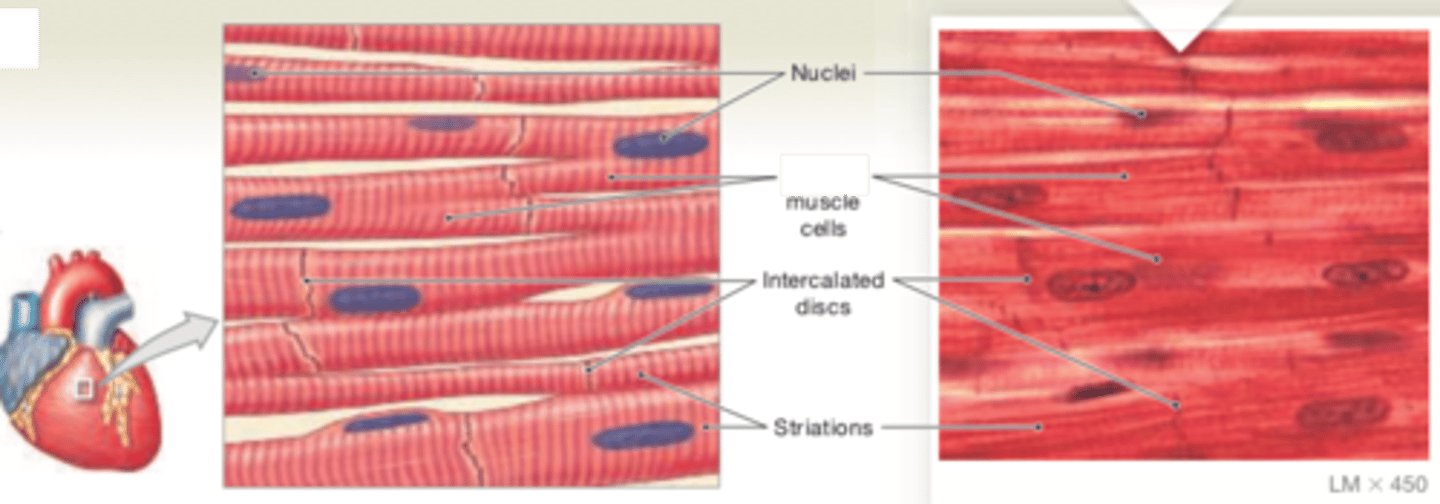
cardiac muscle tissue
Cells are short, branched, and striated, usually with a single nucleus; cells are interconnected by intercalated discs.
LOCATION: Heart
FUNCTIONS: Circulates blood; maintainsblood pressure
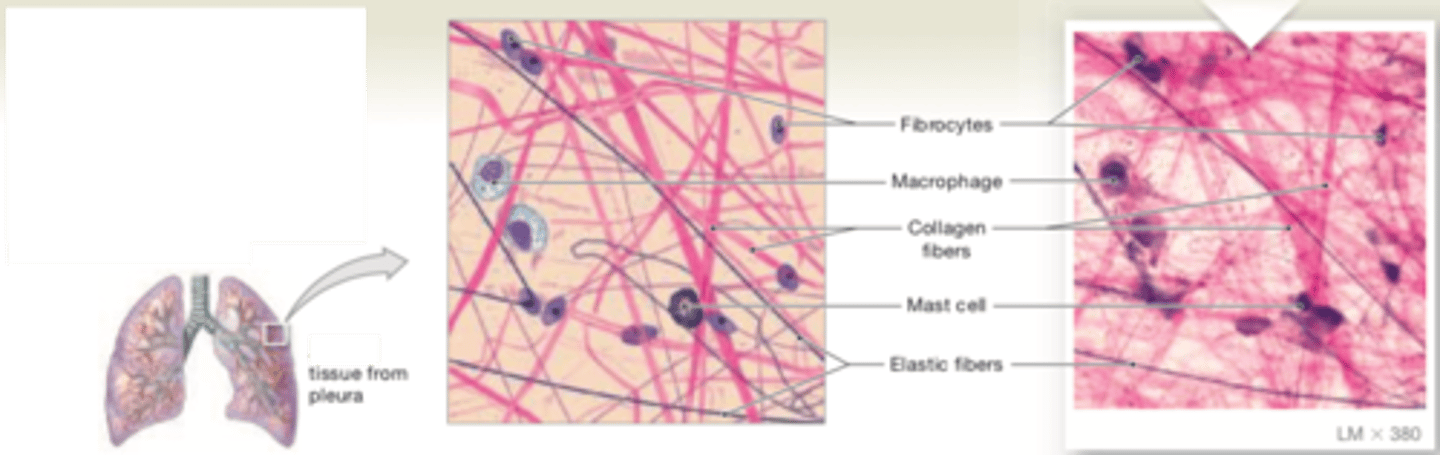
areolar connective tissue
LOCATIONS: Within and deep to the dermis of skin and covered by the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; between muscles; around blood vessels, nerves and joints
FUNCTIONS: Cushions organs; provides support but permits independent movement; phagocytic cells provide defense against pathogens
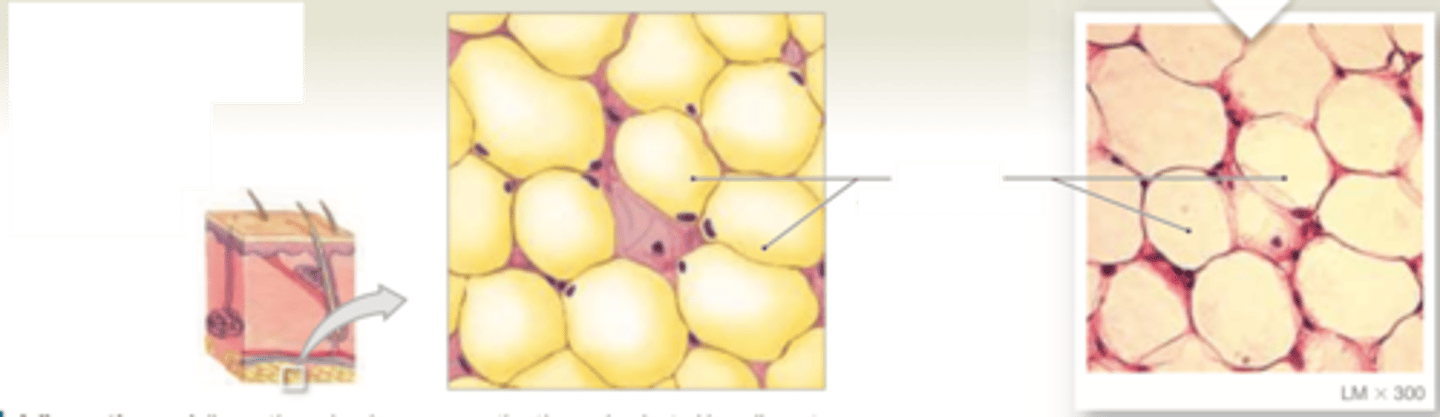
adipose tissue
LOCATIONS: Deep to the skin, especially at sides, buttocks, and breasts; padding around eyes and kidneys
FUNCTIONS: Provides padding and cushions shocks; insulates (reduces heat loss); stores energy
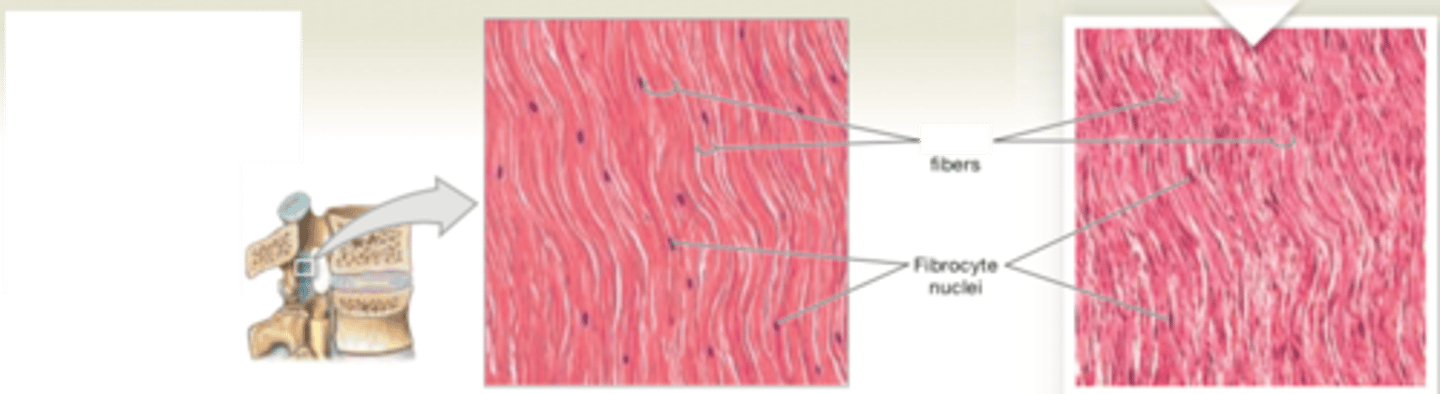
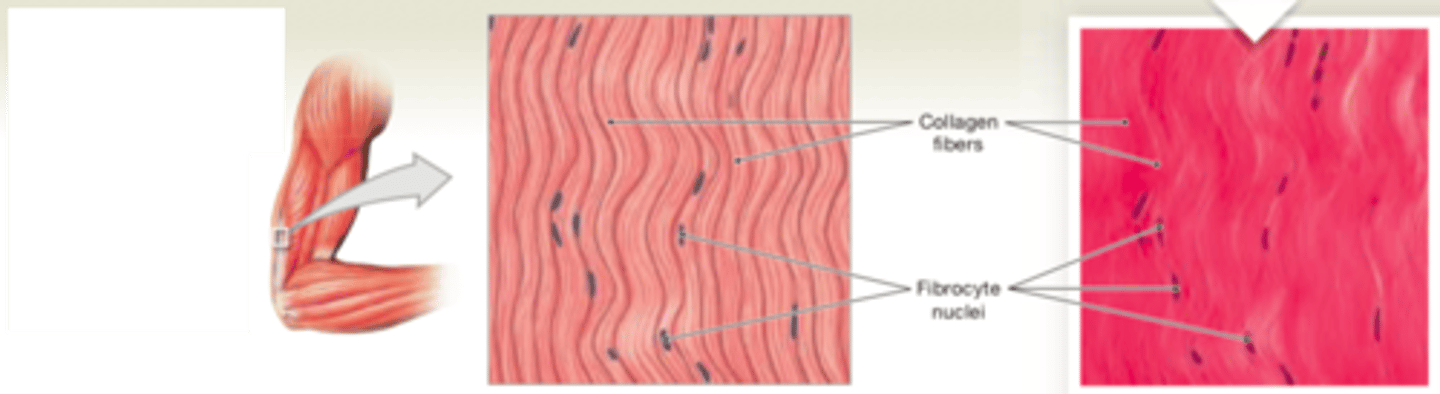
dense regular connective tissue (white fibrous)
LOCATIONS: Between skeletal muscles and skeleton (tendons and aponeuroses); between bones or stabilizing positions of internal organs (ligaments); covering skeletal muscles; deep fasciae
FUNCTIONS: Provides firm attachment; conducts pull of muscles; reduces friction between muscles; stabilizes relative positions of bones
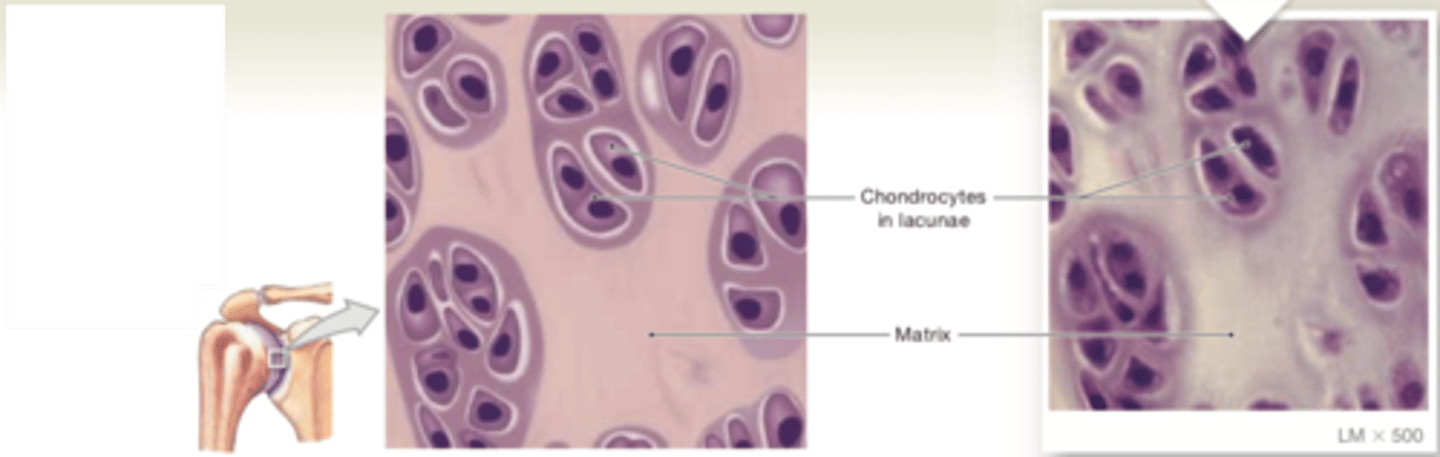
elastic cartilage
LOCATIONS: Auricle of external ear; epiglottis; auditory canal; cuneiform cartilages of larynx
FUNCTIONS: Provides support, but tolerates distortion without damage and returns to original shape
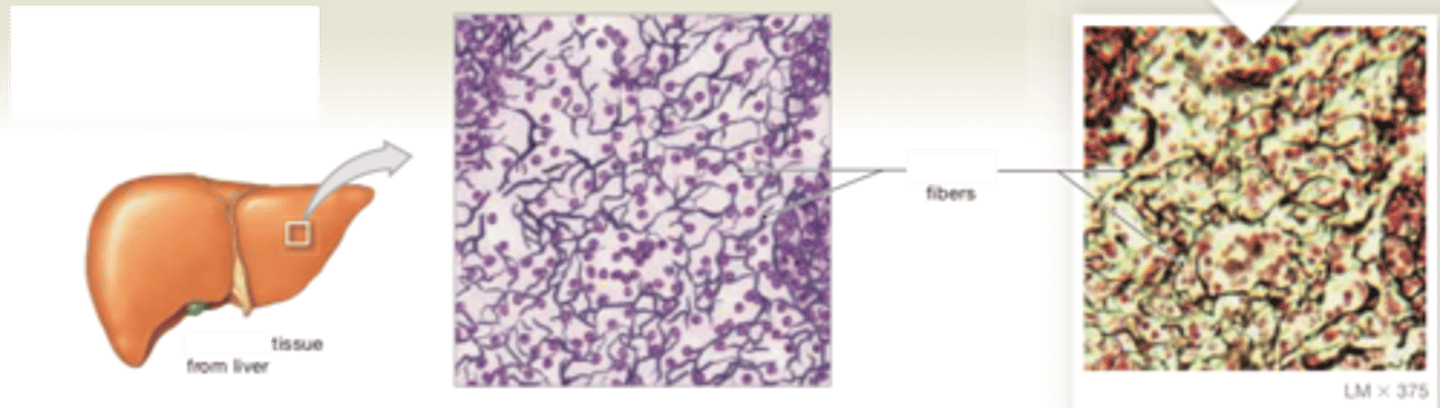
reticular tissue
LOCATIONS: Liver; kidney; spleen; lymph nodes; bone marrow
FUNCTIONS: Provides supporting framework
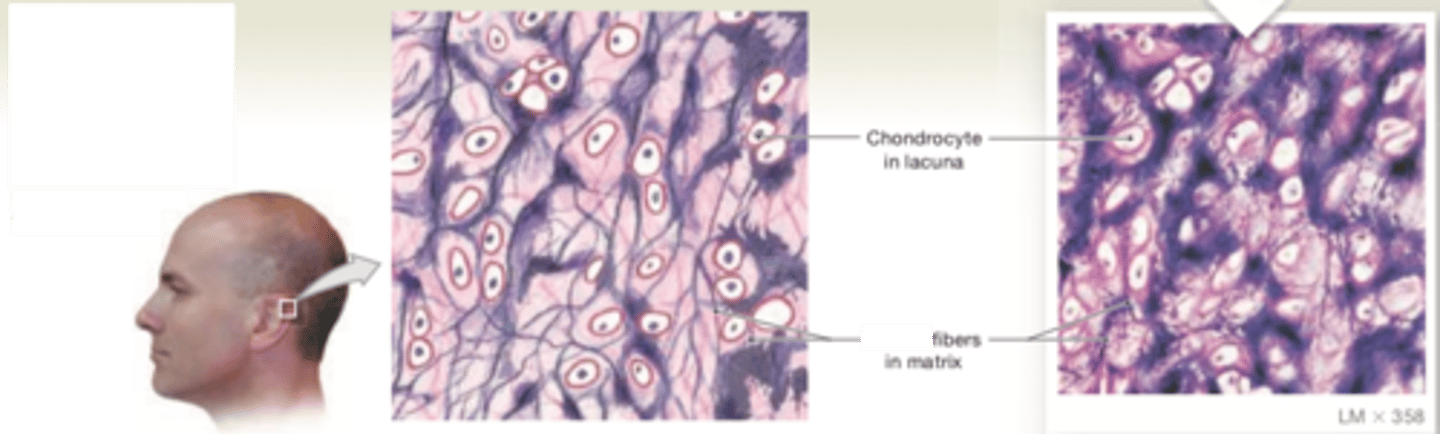
hyaline cartilage
LOCATIONS: Between tips of ribs and bones of sternum; covering bone surfaces at synovial joints; supporting larynx (voice box), trachea, and bronchi; forming part of nasal septum
FUNCTIONS: Provides stiff but somewhat flexible support; reduces friction between bony surfaces
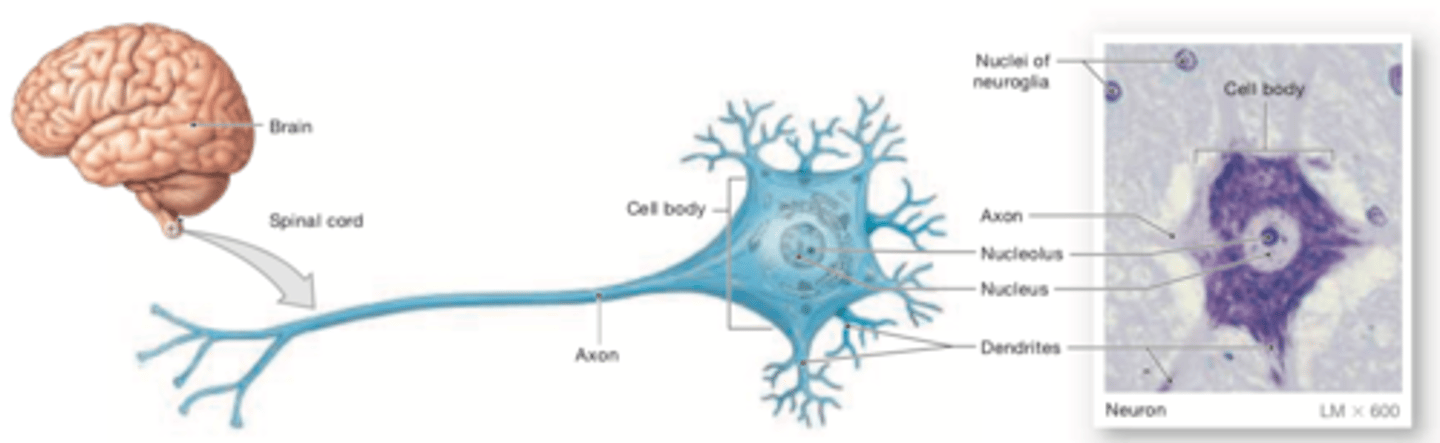
peripheral nerve
Locations: concentrated in the brain and spinal cord, the control centers for the nervous system.
Functions: Neurons, or nerve cells, transmit electrical impulses along their plasma membrane. All of the functions of the ner- vous system involve changes in the pattern and frequency of the impulses carried by individual neurons.
Neuroglia is a general term for several different kinds of supporting cells. Neuroglia have various functions, such as sup- porting nervous tissue, regulating the composition of the interstitial fluid, and providing nutrients to neurons.
Elastic tissue
LOCATIONS: Between vertebrae of the spinal column (ligamentum flavum and ligamentum nuchae); ligaments supporting penis; ligaments supporting transitional epithelia; in blood vessel walls
FUNCTIONS: Stabilizes positions of vertebrae and penis; cushions shocks; permits expansion and contraction of organs