Chapter 20 - special conditions and environments
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
mobile radiography
radiographic procedures performed at the patients bedside
requires a special mobile radiographic unit
seldon routine, may need a creative and innnovative approach
critical thinking is necessary
c-arm
mobile fluoro unit
dynamic imaging in real-time viewing
mobile radiography general guidelines
call nursing station before leaving image department unless responding to a stat request
ask nurse about patient’s condition
confirm order in patients’ chart if applicable
greet pt and explain procedure
check patient ID, DOB on wristband
inspect and prepare the room before bringing in the x-ray equipment
ICU and CCU
ICU and CCU are use to care for very ill patients who require frequent if not constant monitoring
chest radiographs is most common mobile exam requested
must maneuver and work around a lot of equipment - cables, pumps, tubing, lines
shield patient and provide aprons for personnel who cannot exit area to protect from exposure
post anesthesia care unit (PACU)
referred to as recovery room
located outside surgery for ease of transfer and access by surgeons and anesthesia personnel
check line placement
rule out pneumothorax or atelectasis
check orthopedic hardware placement
emergency trauma unit
mobile is used
to avoid interruption of care for very critical patients
assess injured of spine, pelvis and chest without removing immobilization or risking confounding injuries to patient
provide aprons for all essential ED personnel
use proper protection from blood and other bodily fluid - self and equipment
neonatal intensive care unit and newborn nursery
NICU - special unit for care of babies who are premature, low birth weight, or have health issue
mobile exams often must be performed while the infant is in an incubator (necessary to keep baby warm)
shielding is essential
gowns and gloves are often required when handling infants - low immune systems
special beds and mattresses
equipment provides continual position and pressure changes - decreases frequency requirements for turning patients
examples:
alternating pressure mattresses - rocking beds, wave, floatation, bead mattresses
air pattresses - must inflate for xray
warming/cooling devices
IR must be placed in front of those that use water or alcohol
IR must be on top of reflective blankets
orthopedic traction
provides constant pull on a part for therapeutic reasons
do not change or alter traction
ask patient to move as much as it is tolerable
ask nurse if unsure of allowed movements
chest and tube lines
endotracheal tubes (ET)
chest tubes (thoracostomy)
central venous lines
pulmonary arterial lines
endotracheal tube (ET)
placement of hollow tube un tracheal lumen
typically inserted through translaryngeal approach
commonly called intubation
tip of tube place just above carina - 1-2 in above bifurcation
chest radiograph required to verify position
most common mispositioning places tip in right main stem bronchus due to angle of carina
endotracheal tube indications
need mechanical ventilation or oxygen delivery
insufficient ventilation
inadequate arterial oxygenation
parenchymal diseases that impair gas exchanges
upper-airway obstruction
shock
impending gastric acid reflux or aspiration
tracheobronchial lavage
radiographic needed for placement and position
tracheostomies
a tube in the opening in the trachea to provide an open airway
sometimes hooked to a ventilator
nasogastric and nasoenteric tubes
NG tubes - passed from nose to stomach
NE tubes- passed from nose to duodenum
OG - passed from oral cavity to stomach, often used along side ET tubes
uses:
feeding
decompression or draining
radiographic examination
medication administration
May also be called Naso intestinal tube (NI)
watch for artifacts such as safety pins holding tube to patient gown
thoracostomy tubes
also known as chest tubes
drain intrapleural space and mediastinum
fluid or air
create negative pressure
atelectasis
pneumothorax
hemothorax
pleural effusion
empyema
common insertion site (thoracostomy)
vary with intrapleural substances to be removed
usually inserted in 5th-6th intercostal space
laterally and midaxillary line
can be as high as 4th intercostal space and as low as 8th intercostal space
chest tubes
follow up chest radiographs should be taken with patient upright or semi-upright
to better demonstrate a pneumothorax, inspiration/expiration
specialty catheters
placed to help monitor and manage critical patients and patients requiring long-term care
placed in pulmonary artery, central vein, or peripherally
care must be used to avoid disruption of catheter
often requires c-arm during insertion
mobile images are often used to verify placement
central venous line
catheter that is inserted into a large vein - central venous catheter or venous access devices
wide variety of clinical applications
administer a variety of drugs
manage fluid volume
draw blood and blood transfusions
monitor cardiac pressures
sometimes referred to by developer - hickman, groshong, broviac, port-a-cath, mediport
inserted into a major vein - subclavian vein, internal jugular vein, femoral vein
if inserted into peripheral vein referred to as PICC line (peripherally inserted central catheter)
may be single, double, or multi-lumen
position should be superior vena cava, approximately 2-3cm above opening of right atrium
pulmonary arterial catheter (PA)
swan-ganz catheters
incorporates a small electrode at distal end, used to monitor pulmonary arterial pressure
access to left ventricle requires arterial approach
catheter placement in the left ventricle has major physiologic consequences
safest way to assess left-sided heart pressure is to extrapolate its value by monitoring right-sided heart and pulmonary pressures
distal tip will be in 1 of the 2 pulmonary arteries
has balloon on distal end, during pressure monitoring inflates balloon and allows tip to float and wedge in pulmonary artery
measures pressure, and then balloon deflates
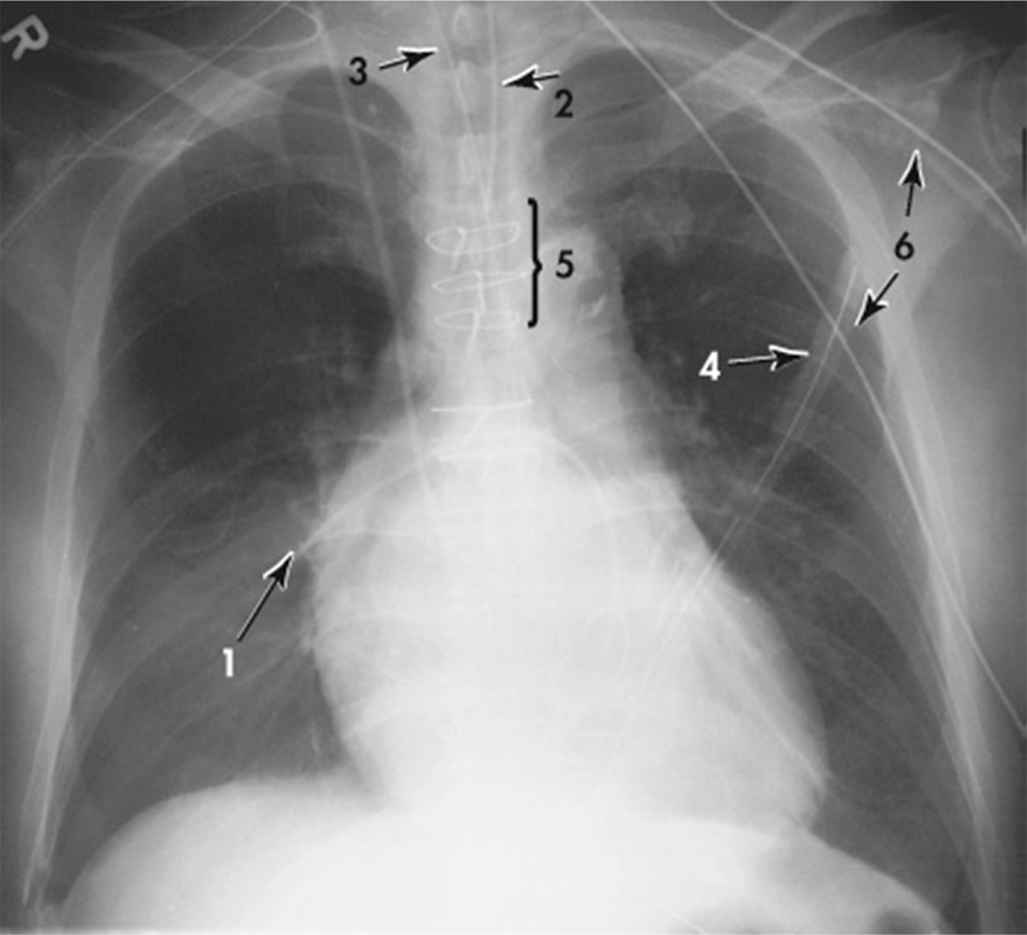
AP chest radiograph showing:
(1) tip of Swan–Ganz catheter advanced into right pulmonary artery
(2) endotracheal tube
(3) nasogastric tube
(4) chest tube
(5) sternal wires from open heart surgery
(6) monitor lines (external)
pacemaker
an electromechanical device that regulates the heart rate by providing low levels of electrical stimulation to the heart muscle
often inserted under c-arm guidance
technologist responsibilities
radiographic confirmation of line placement is essential at the time of insertion and thereafter as needed
recognition of catheter malposition requires thorough knowledge of CV structures and their branches
without any expectation of the radiographer to interpret the image from a pathological diagnostic standpoint, when mispositioning is thought to occur, alerting the appropriate authority is both appropriate and beneficial to patient