Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms in Human Body
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Homeostasis
The way our body keeps a stable internal environment, even if the outside world changes.

Negative feedback
Constant adjustments to maintain setpoint; body counteracts a changing variable (stimulus).

Positive feedback
When the body intensifies the variable, such as during labor/delivery.
Stimulus
A variable that triggers a response in the body.

Response
The action taken by the body in reaction to a stimulus.
Regulation
The process of maintaining balance in the body.
Feedback loop
A system that uses feedback to maintain homeostasis.
Temperature regulation
The process of maintaining a stable body temperature despite external temperature changes.
Blood sugar control
The regulation of glucose levels in the blood to maintain homeostasis.
Childbirth
An example of positive feedback where contractions intensify to facilitate delivery.
Vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels to redirect blood flow, often in response to cold.
Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels to redirect blood flow, often in response to heat.
Shivering
A response to cold that generates heat to maintain body temperature.
Sweating
A response to heat that helps cool the body down.
Circulatory system
The system responsible for pumping blood through the body and distributing materials.
Respiratory system
The system responsible for inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide.
Setpoint
The ideal value or range that the body tries to maintain for various physiological parameters.
Oscillation around set point
The process of fluctuating around a setpoint due to negative feedback mechanisms.
Internal Steady State
A condition where internal variables remain stable despite external changes.
Importance of Negative Feedback
It is important to the body because maintenance of homeostasis is crucial for life processes.
Importance of Positive Feedback
It is important to the body because it helps complete short-term processes.
Blood Sugar Regulation
After eating, blood sugar levels rise, and the pancreas releases insulin to lower them; this is negative feedback because it is a corrective mechanism.
Childbirth Contractions
During labor, oxytocin release intensifies uterine contractions; this is positive feedback because it intensifies the response until the baby is born.
Body Temperature Regulation
When body temperature increases, sensors trigger sweating to cool down; this is negative feedback because it is a corrective mechanism.
Blood Clotting
When a blood vessel is injured, platelets attract more platelets to form a clot; this is positive feedback because it intensifies the response to stop bleeding.
Breathing Rate
When carbon dioxide levels rise, the brain signals the lungs to increase breathing rate; this is negative feedback because it is a corrective mechanism.
Insulin
A hormone that helps lower blood sugar levels after eating.
Glucagon
A hormone that raises blood sugar levels when they drop too low.
Oxytocin
A hormone that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth.
Platelets
Little cell fragments that help in blood clotting by attracting more platelets to the injury site.
Sensor
A part of the body that detects changes in the environment.
Short-term Processes
Processes that are completed quickly, often involving positive feedback.
Corrective Mechanism
A response that counteracts a change to restore balance.
Intensified Response
A response that increases in magnitude, often seen in positive feedback.
Lactation
When a baby suckles at the breast, it stimulates the release of the hormone prolactin, which increases milk production.
Example of negative feedback
When body temperature rises above normal, sweat glands release sweat, which cools the body as it evaporates.
Blood glucose regulation
When blood glucose levels are too high, insulin is released to drive glucose into cells; when too low, glucagon is released to break down glycogen to increase blood glucose to normal.
Childbirth feedback claim
This claim is false. Oxytocin increases contractions, pushes down baby, leading to more contractions.
Carbon dioxide levels during exercise
The increase in blood CO2 is the stimulus; the increase in breathing rate is the response to return to homeostasis.
Pain stimulus
You accidentally step on a sharp rock while walking barefoot. Stimulus: Pain; Response: Pull foot back.
Sound stimulus
A cat hears a loud noise and jumps away from the sound. Stimulus: Sound; Response: Jumps away.
Light stimulus
You walk outside on a bright, sunny day, and your eyes squint automatically. Stimulus: Light; Response: Squint.
Tropism movement
A sunflower turns to face the sun throughout the day as it moves across the sky. Stimulus: Light; Response: Tropism/movement.
Plant tropism
A plant's leaves bend toward a window where sunlight shines. Stimulus: Light; Response: Tropism/movement.
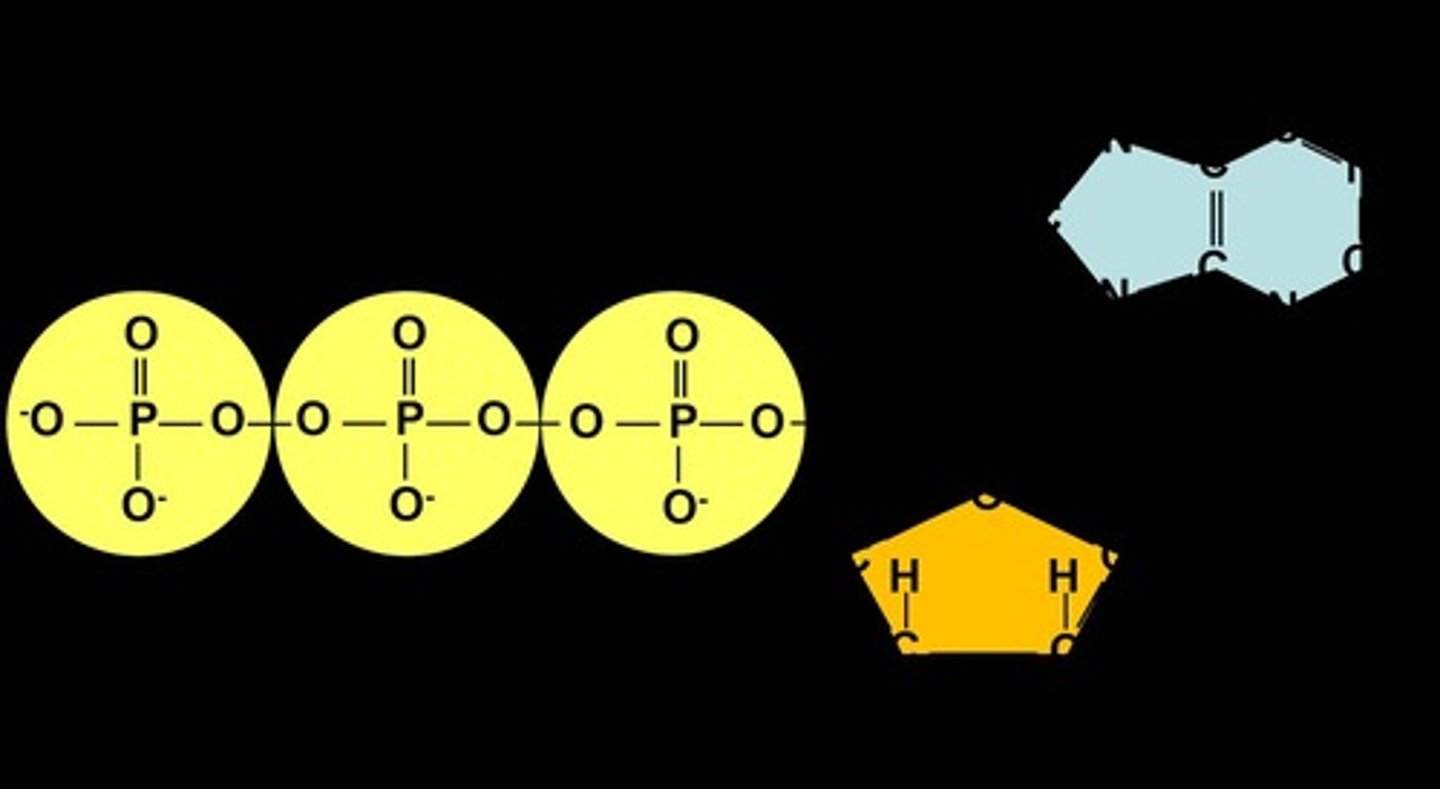
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
Carbon Dioxide
Gas molecule containing one carbon and two oxygens
Cellular Respiration
Process of converting glucose into ATP
Diffusion
Movement of substances based on concentration
Dynamic Equilibrium
Maintaining overall balance
Excretory System
System responsible for water balance
Gas Exchange
Inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide
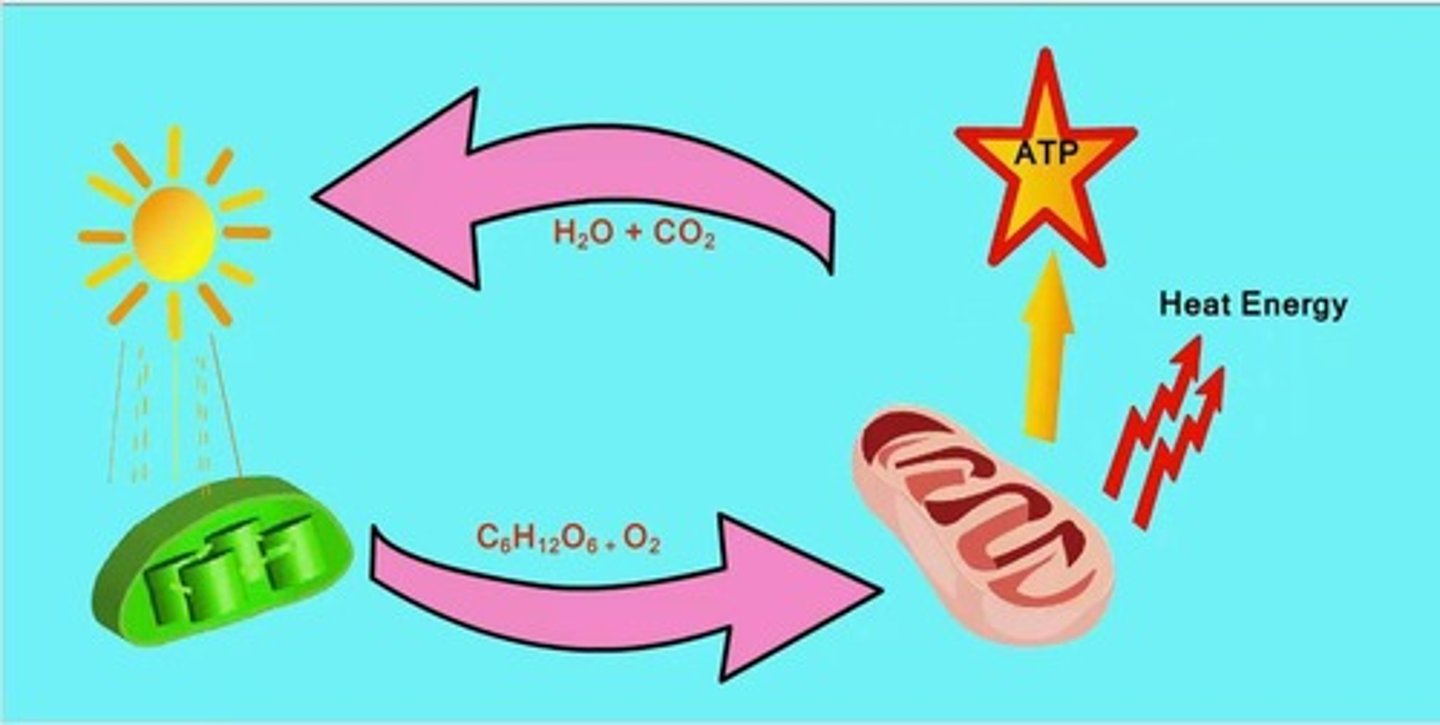
Glucose
Sugar
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Isotonic
A solution with an equal concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Metabolic Process
Chemical reactions that occur within a cell to maintain life
Mitochondria
Organelles known as the powerhouse of the cell, where ATP is produced
Nervous System
The body system responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body
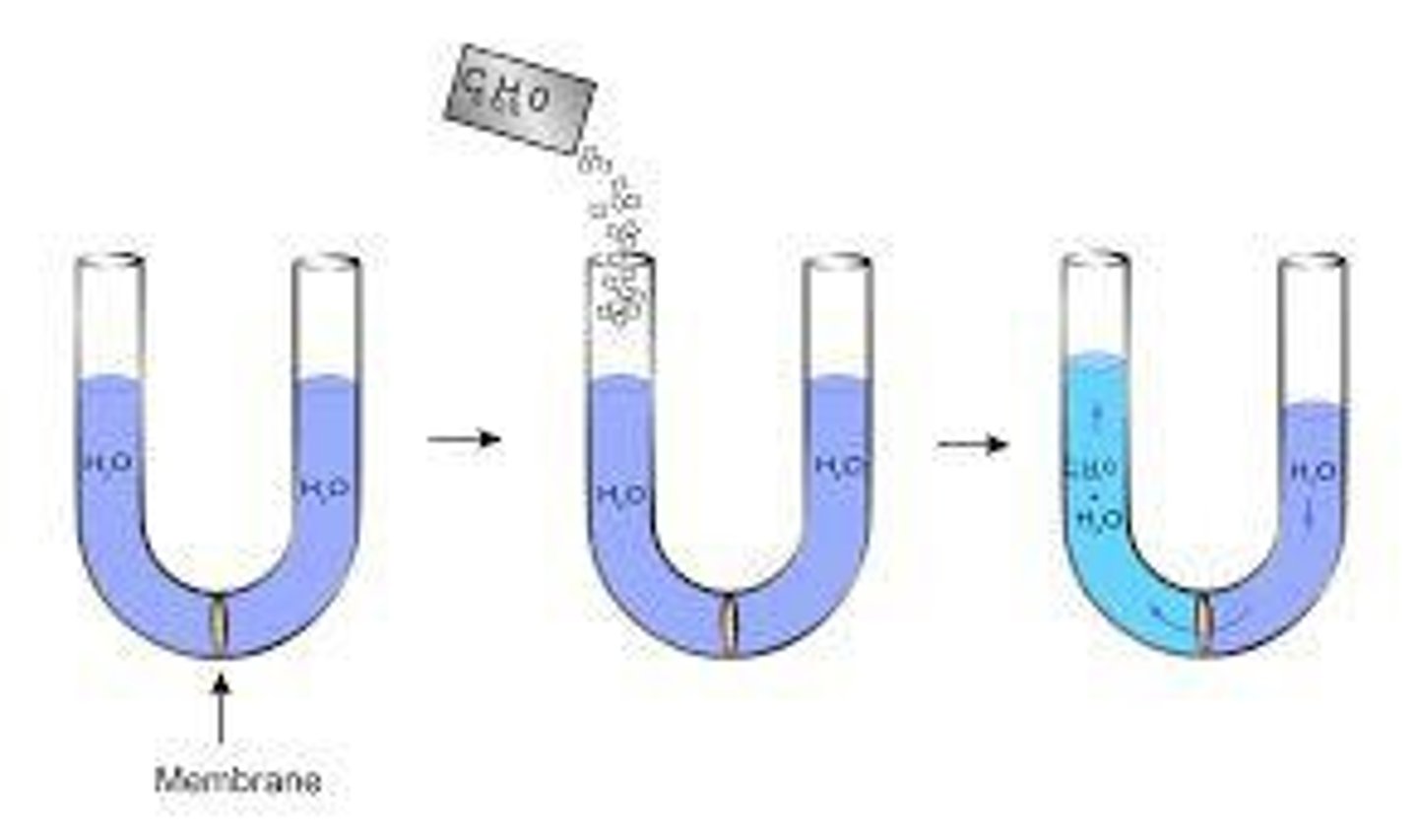
Osmoregulation
The process of maintaining water balance in the body
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Oxygen
A gas essential for cellular respiration
Thermoregulation
The process of maintaining an optimal body temperature