biological molecules!!!
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
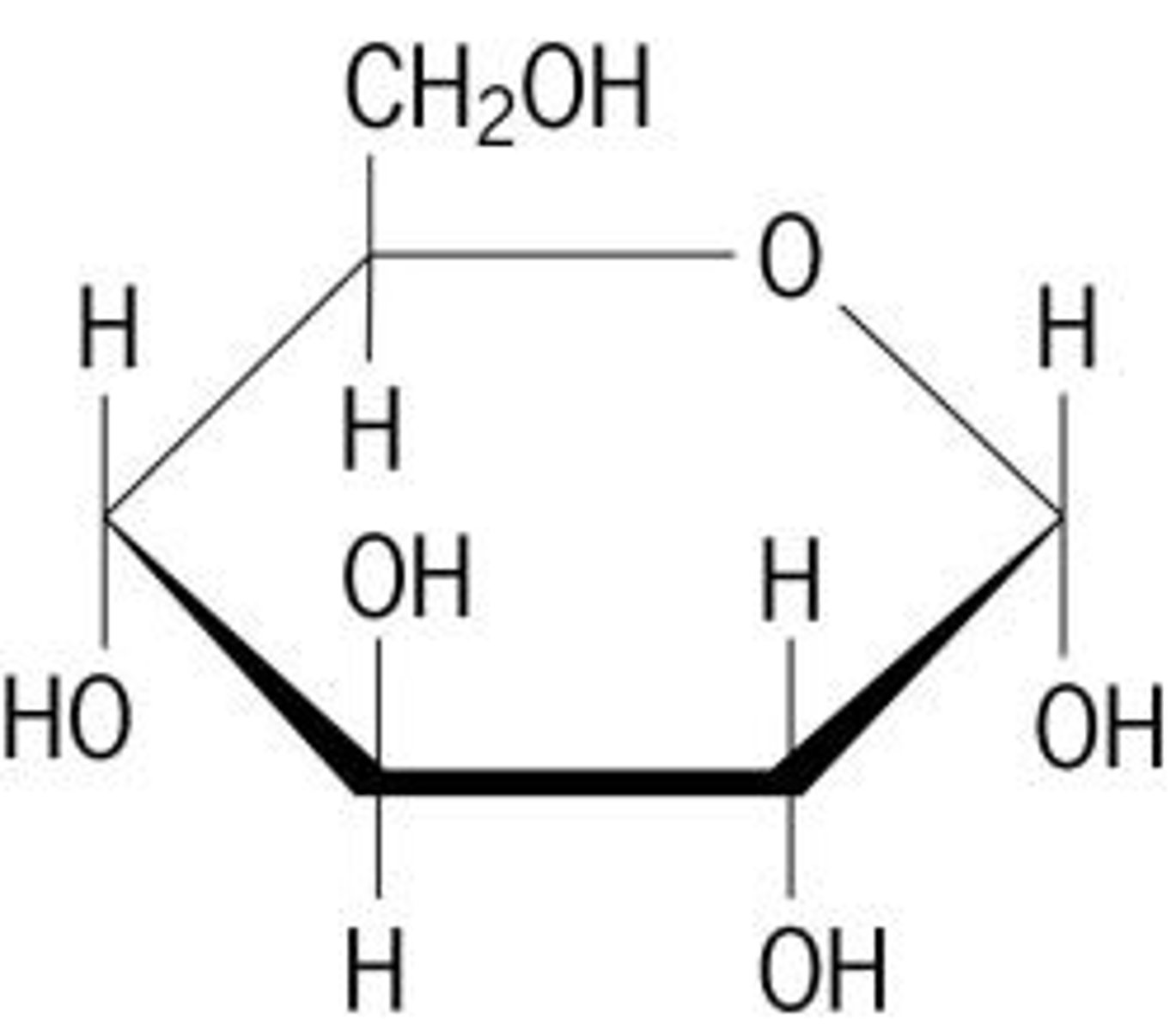
Carbohydrate- Monomer name and structure
Monosaccharide (Simple sugar), ring of carbon
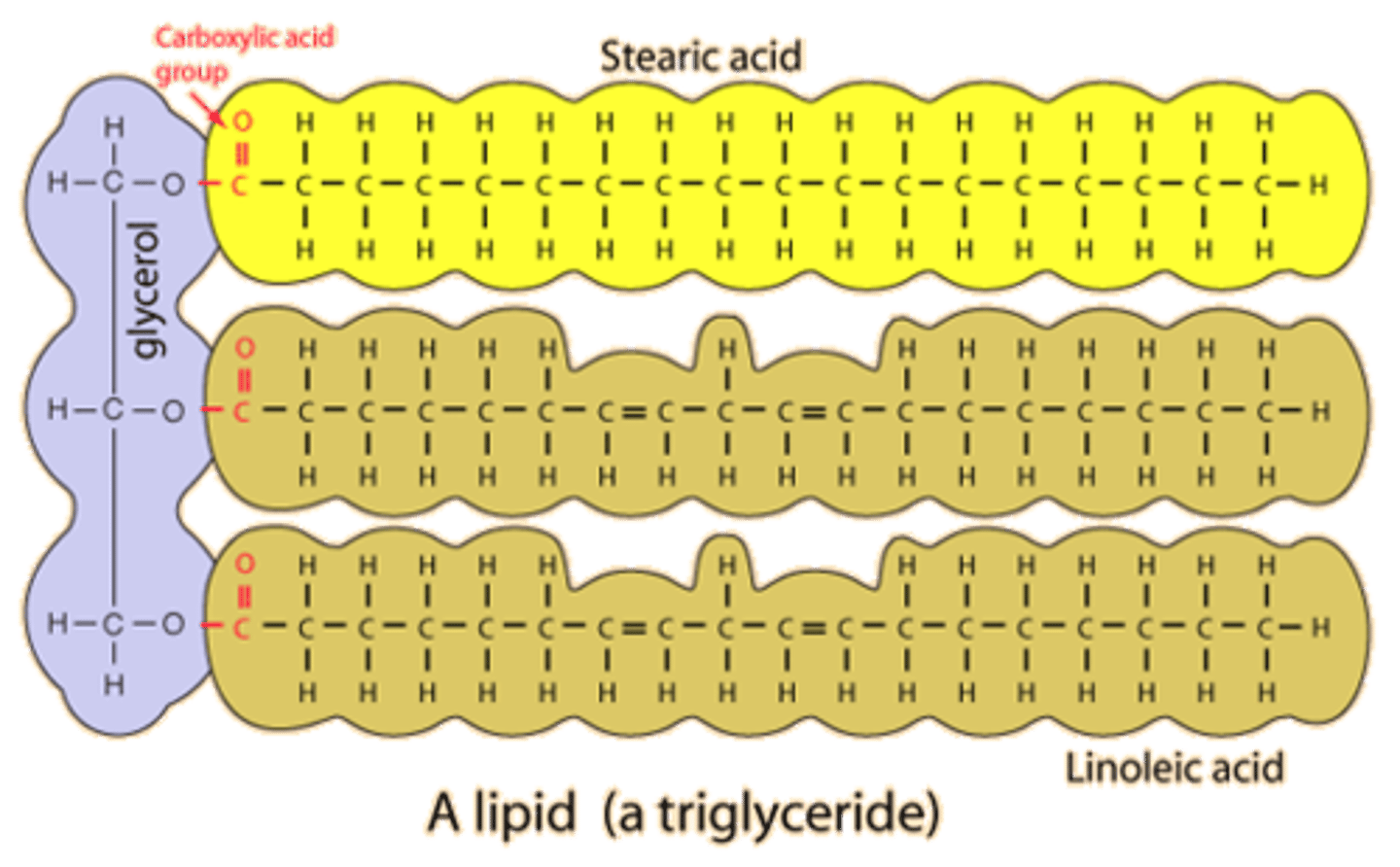
Lipids- monomer name and structure
fatty acids and glycerol
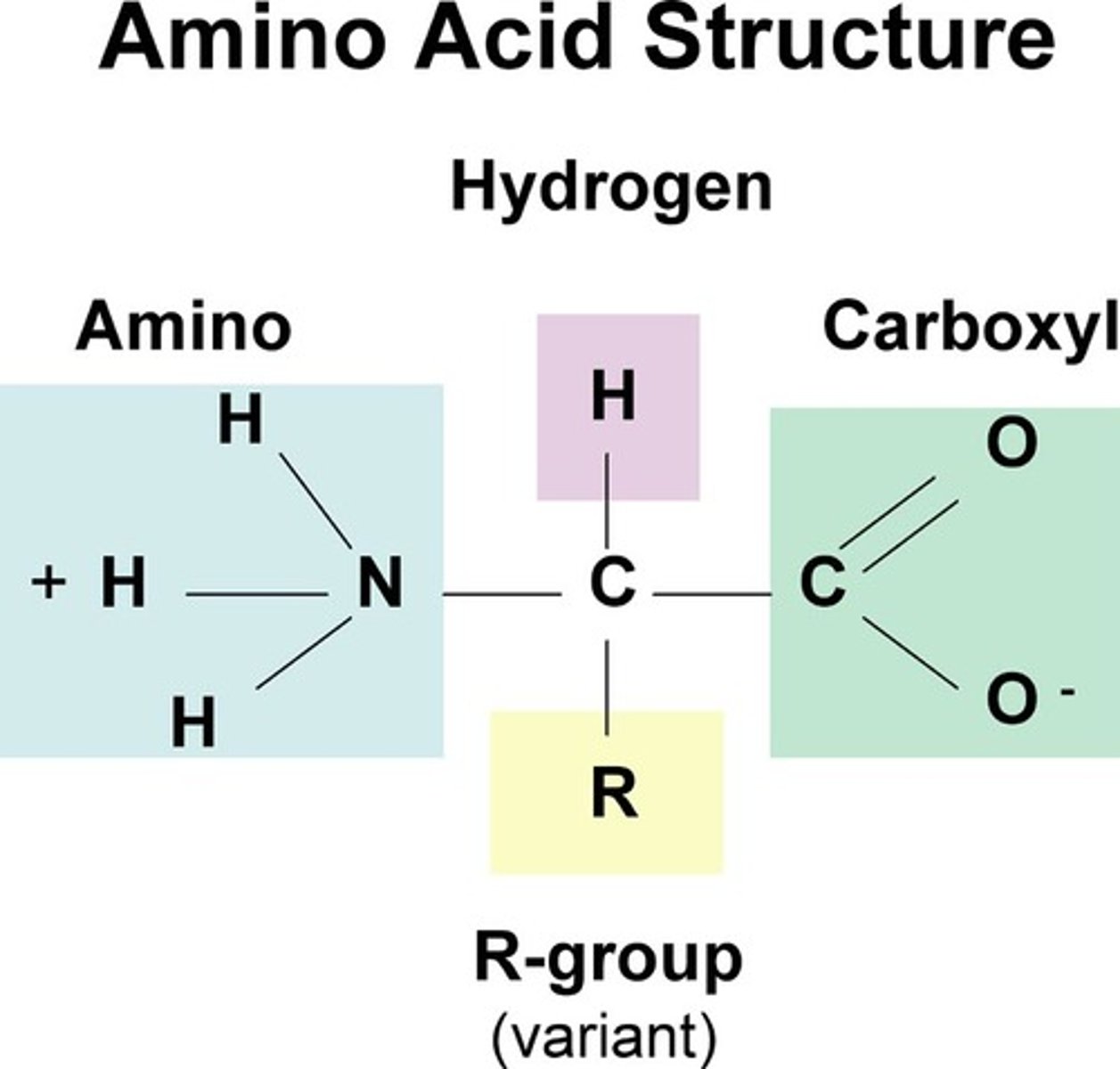
proteins- monomer name and structure
amino acids
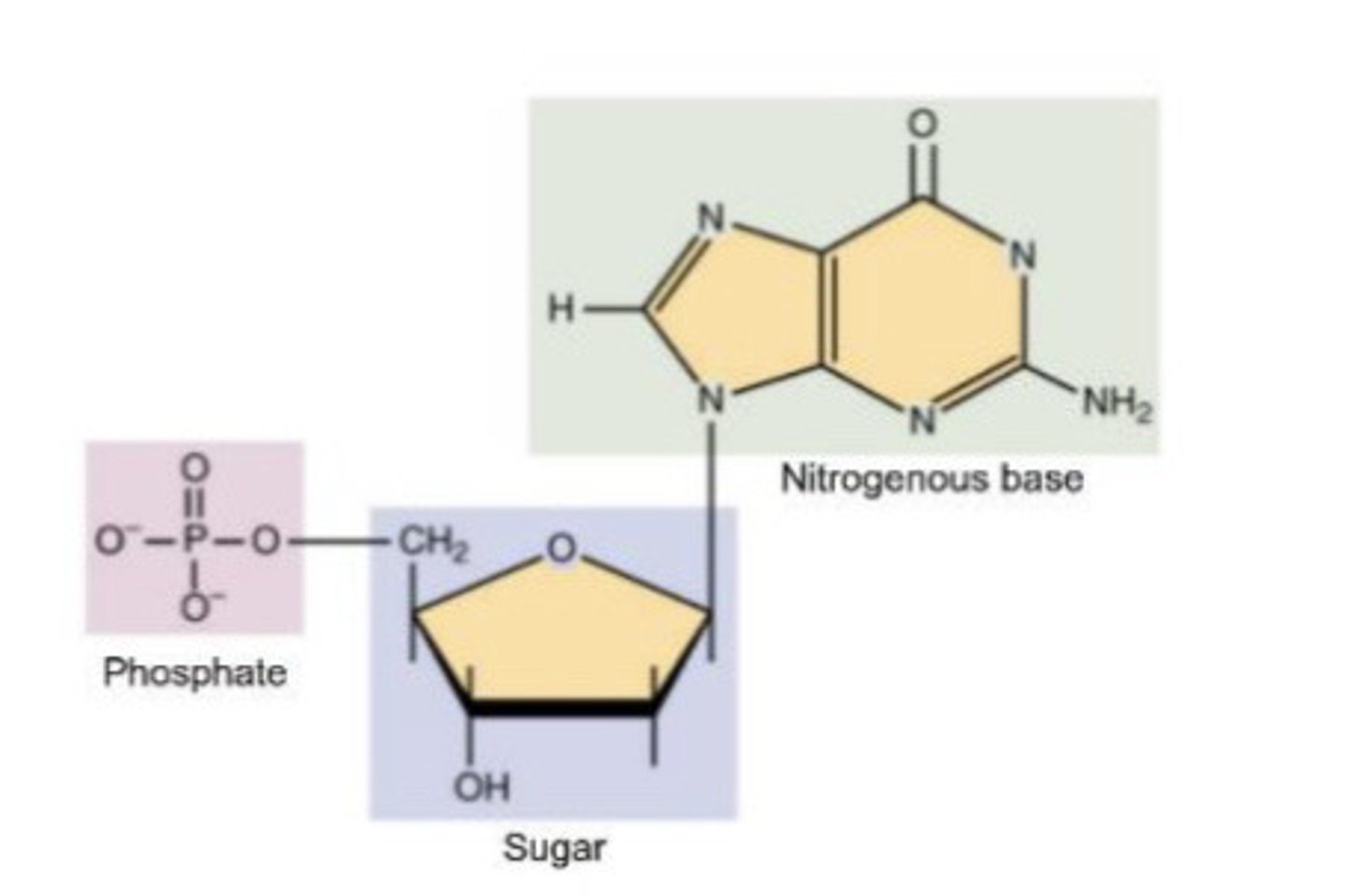
Nucleic Acids- monomer name and structure
nucleotides
Carbohydrates- monomer examples
glucose, fructose, galactose
Carbohydrates- Elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Lipids- Elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Proteins- Elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur (sometimes)
nucleic acids- Elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
All biological molecules have at the very least these three elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Monomer- Definition
A small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
4 valence electrons
why are carbon's valence electrons important?
1. they can form multiple covalent bonds with other atoms, making the bond very strong.
2. It can bond with other carbon atoms forming chains of unlimited length.
Polymers- Definition
molecules composed of many monomers
components of nucleotides
Phosphate, Nitrogenous base, 5 carbon sugar
Carbohydrate Polymer examples
Lactose, glycogen, starch, cellulose
Lipids Polymer examples
Oils, Wax, triglycerides
Proteins Polymer examples
Enzymes, hormones, hair, antibodies
Nucleic Acids Polymer examples
DNA, RNA, ATP
Carbohydrates function
short term energy, structural support
Lipids function
Long-term energy, insulation, cushioning organs, protective barrier
Proteins Function
facilitate reactions, regulate cell functions, transport materials, fight disease
nucleic acids Function
store and transmit genetic material, blueprint to make proteins, capture and transfer chemical energy.