ARTH 1162 Exam 1 - Monuments Images + Terms
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
holy fawk
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
The Vitruvian Triad
Commoditas — function / accommodation (what the building is for)
Firmitas — structural strength / stability (how the building stands up)
Venustas — beauty that delights (aesthetic appeal of the building; v. subjective)
plans, sections, façades and elevations
plan / floorplan — footprint of building
elevation —view of superstructure rising over plan
section — transverse slice / cross-section of building
façade — front of building
trabiated construction
post (like supporting members/columns) that keep the lintel (horizontal platform/segment) up
arcuated construction
arches and vaults
kinds of vaults
barrel vaults (has a lot of gravitational downward thrust)
groin vault (grav. weight distributed @ corners)
rib vault (seen in gothic architecture, v. pointed)
fan vault
masonry (regularly dress stone)
remove live rock, cut into smooth blocks to make walls, columns, etc
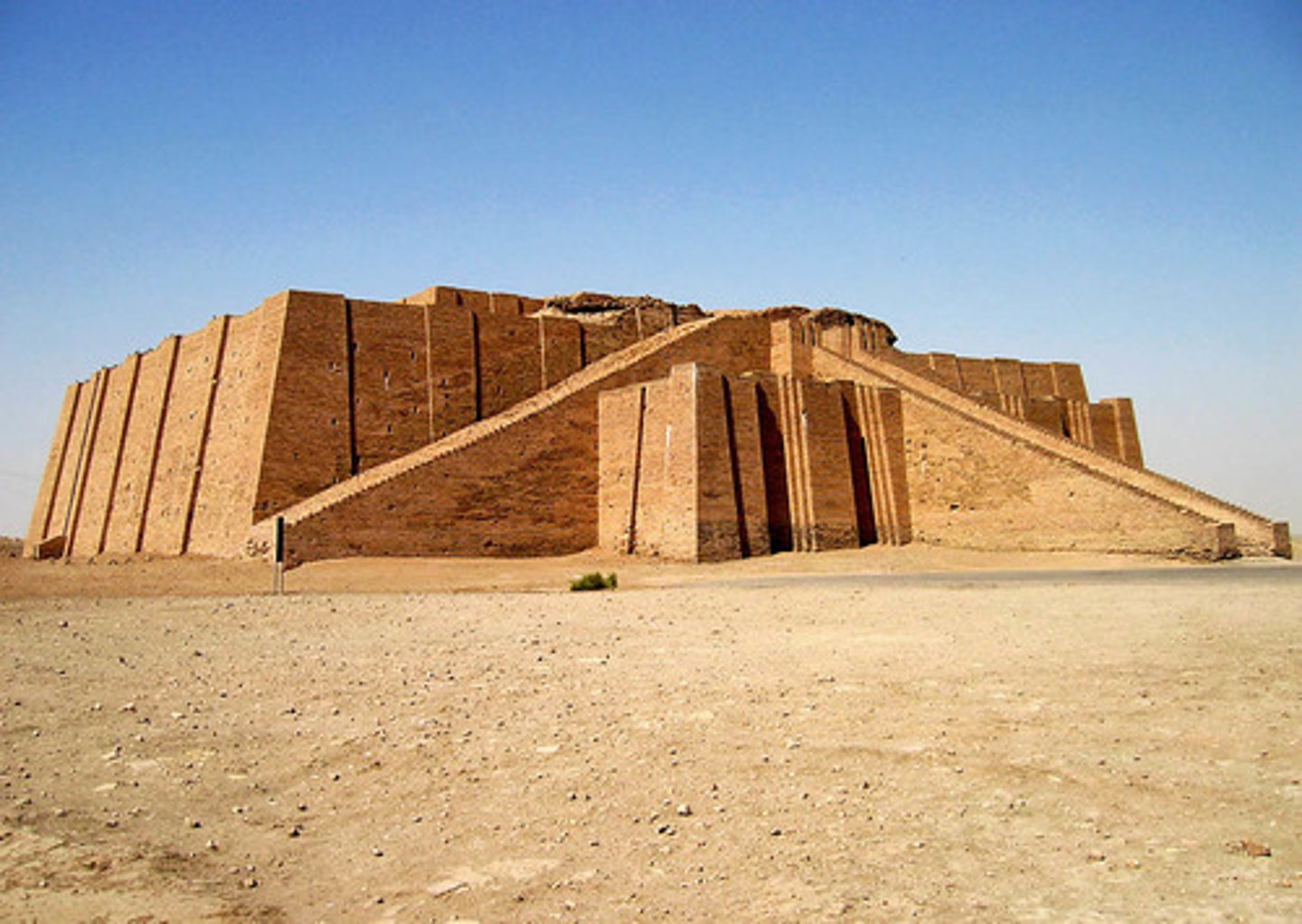
Ziggurat of Ur-Nammu
Sumer (@ Southern Mesopotamia) | Ur, c. 2000 BCE
ziggurat — religious structure; massive rectangular shaped staged tower from ancient Mesopotamia

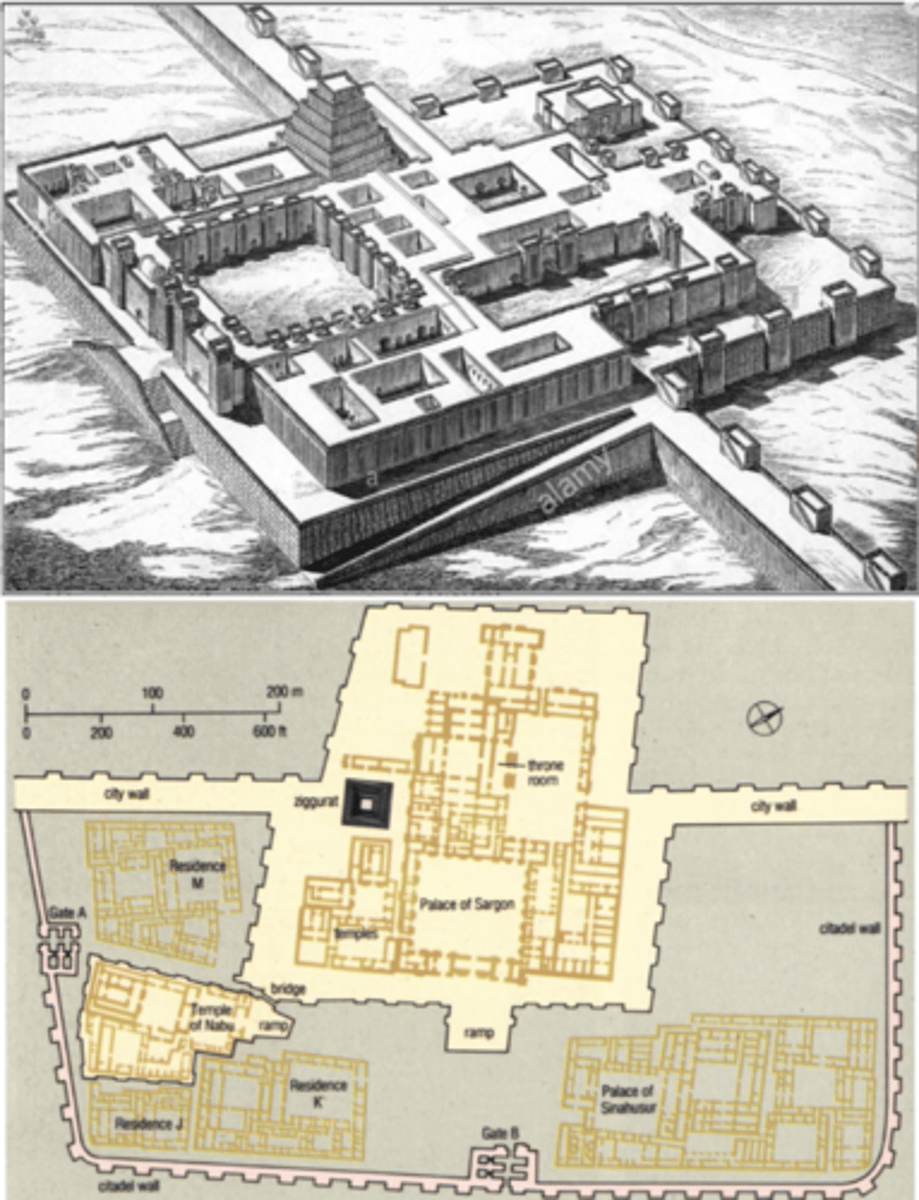
Khorsabad (Dur Sharrukin) — Citadel + Palace of Sargon II
(Assyria @ Northern Mesopotamia) | c. 700 BCE
crenellations — teeth-like structures on top of towers (where people shoot arrows)
buttresses — carry weight away from building; projecting structural support
casemates — defensive, double-walled fortification system that included chambers (in the case of the palace of Sargon II)
ziggurat — religious structure; massive rectangular shaped staged tower from ancient Mesopotamia
lamassu —— colossal statues of human-headed winged bulls that guarded the gates of the citadel of Sargon II; body of bull / lion, wings of eagle and head of human
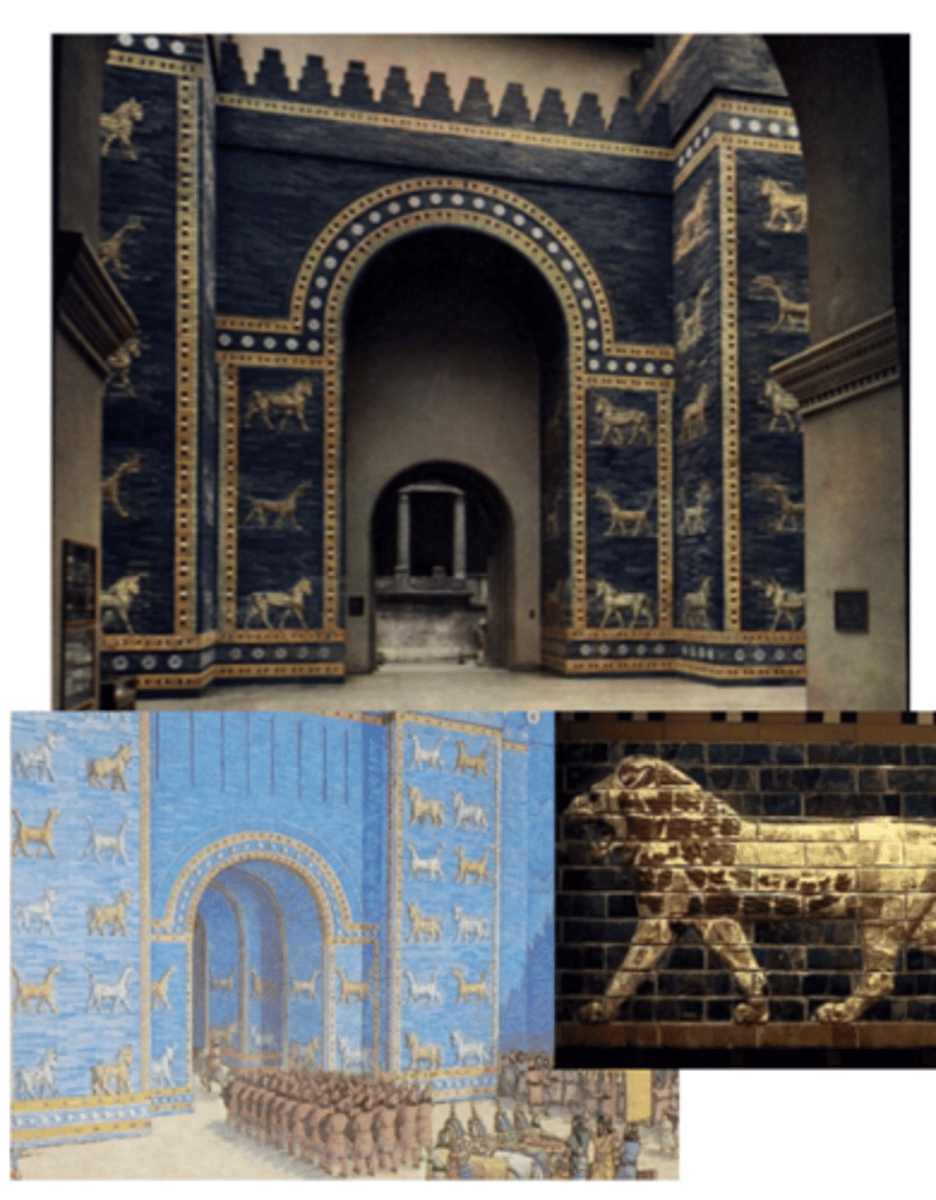
Ishtar Gate
@ Babylon | c. 575 BC | built by King Nebuchadnezar II
Lions — symbolize goddess Ishtar
crenellations
glazed bricks lined w/ animals walking in procession (bulls, dragons, lions → goddess Ishtar; goddess of fertility, love, war)

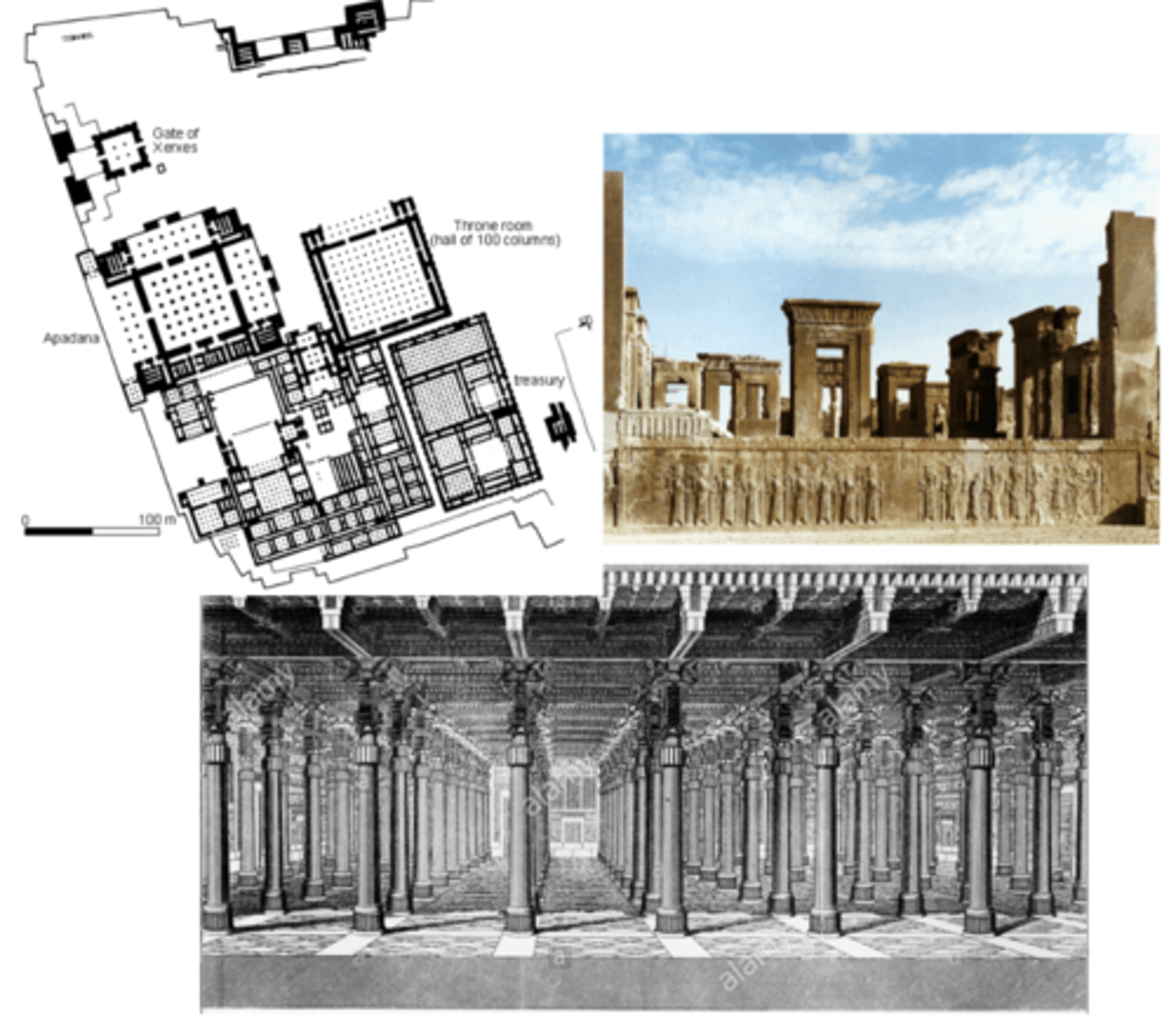
Persepolis (“Persian City”)
royal palace begun by Darius in 515 BC
apadana (throne room) w/ hypostyle hall
fortified military appearance
lamassu
royal architecture (powerful, overwhelming scale); v. volatile time (who had power was always changing)
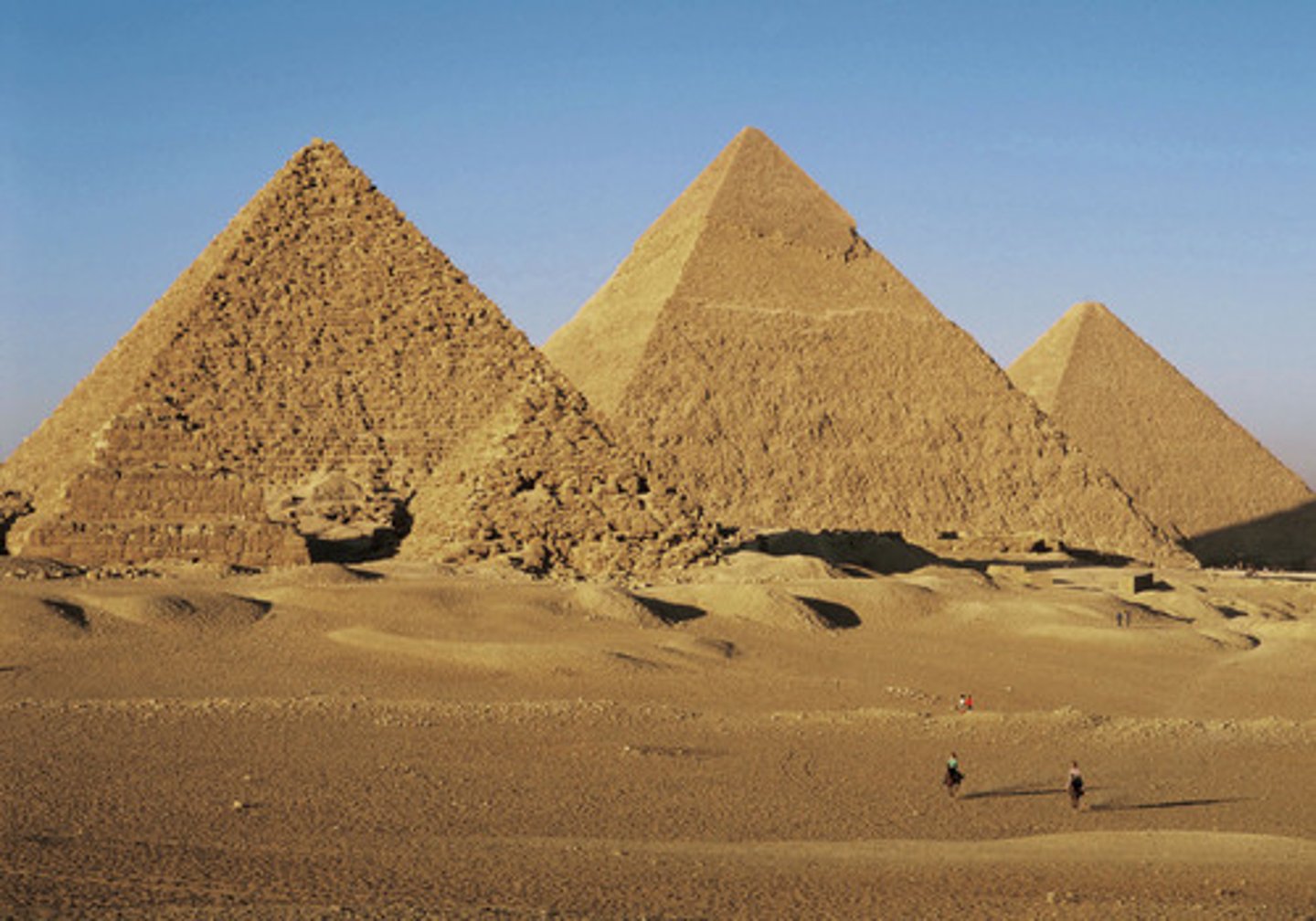
Giza Pyramids + Great Pyramid of Cheops
near Cairo | c. 2000 BCE
red limestone interior, polished higher grade limestone
pharaoh buried in granite sarcophagus alongside their worldly possessions, pets; pyramid was built around the tomb bc it was so narrow inside
prone to tomb raiders
pyramid shape = ramp/stairway to heaven
religious/social implications
gives civilians sense of loyalty, belonging; maintain social cohesion by creating drafts for people to called to help build the pyramids, helped create a sense of consistency and accountability for building

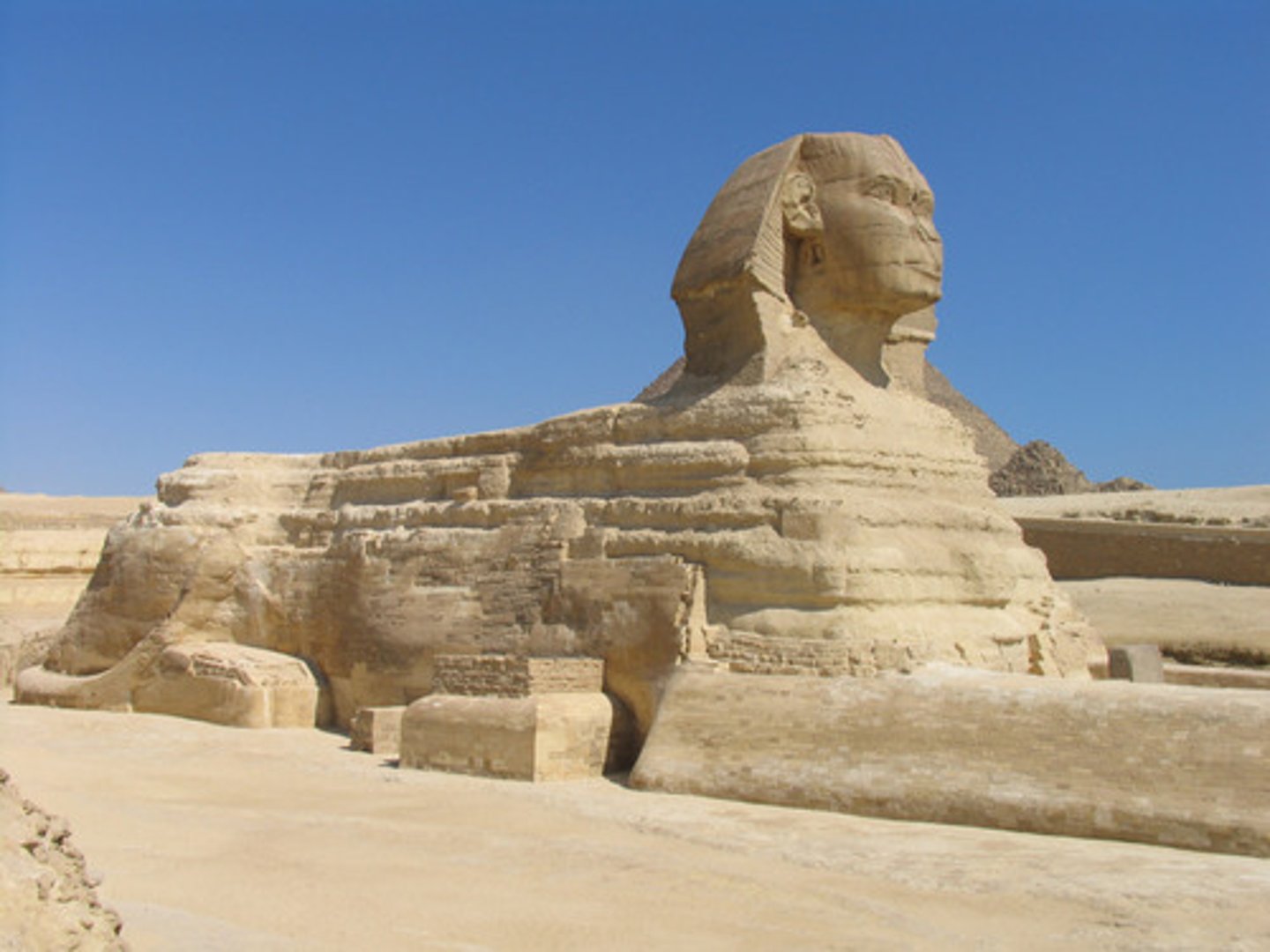
Sphinx
near Cairo | c. 2500 BCE
shows face of one of the pharaohs buried there (wearing the headdress thing)
granite interior, also used diorite
didn’t have wheels at this time so needed many people to build

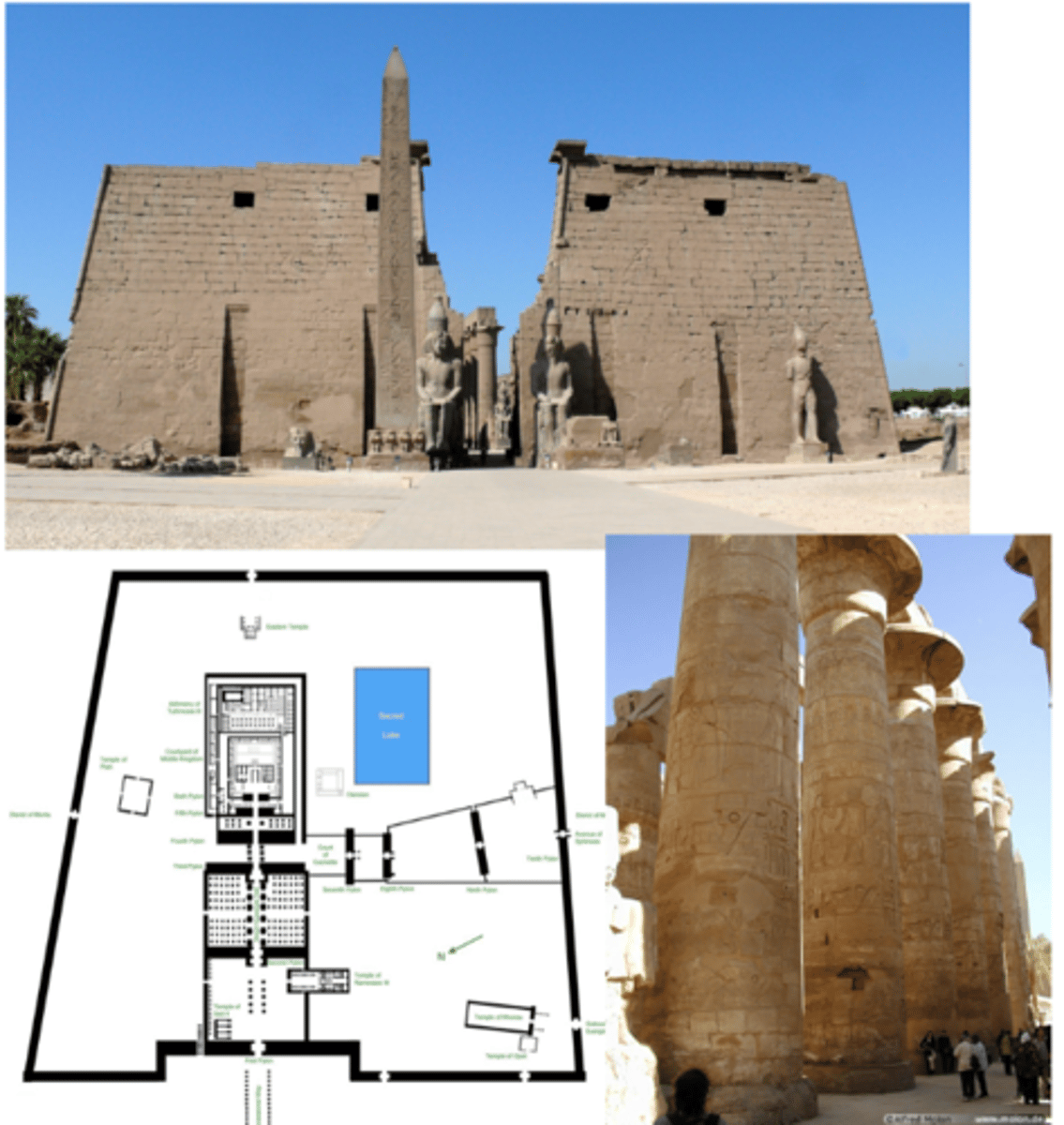
Temple of Amon-Re
Karnak | begun c. 2000 BCE and built over next 2000 years
hypostyle hall — 134 columns covered with hieroglyphic inscriptions
trabiated
pylon gates (tilted inwards)
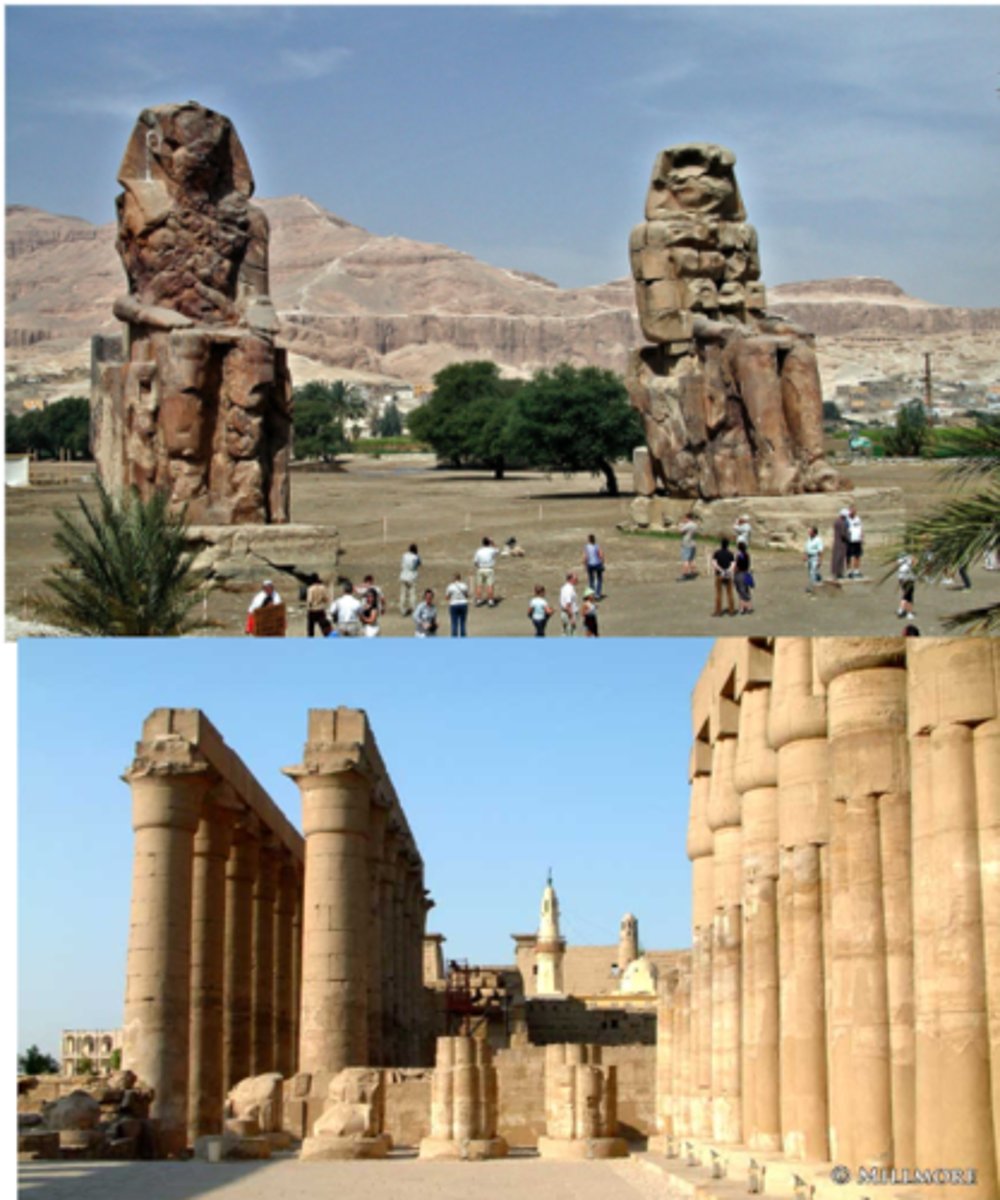
Temple of Amenhotep III
Temple of Amon-Re @ Karnak linked via mile long avenue lined with sphinxes to Temple of Amenhotep III @ Luxor (pylon c. 1250 BCE)
hypostyle hall
pylon gate (tilted inwards)
obelisks built w/ granite → sundial with hieroglyphics carved into it

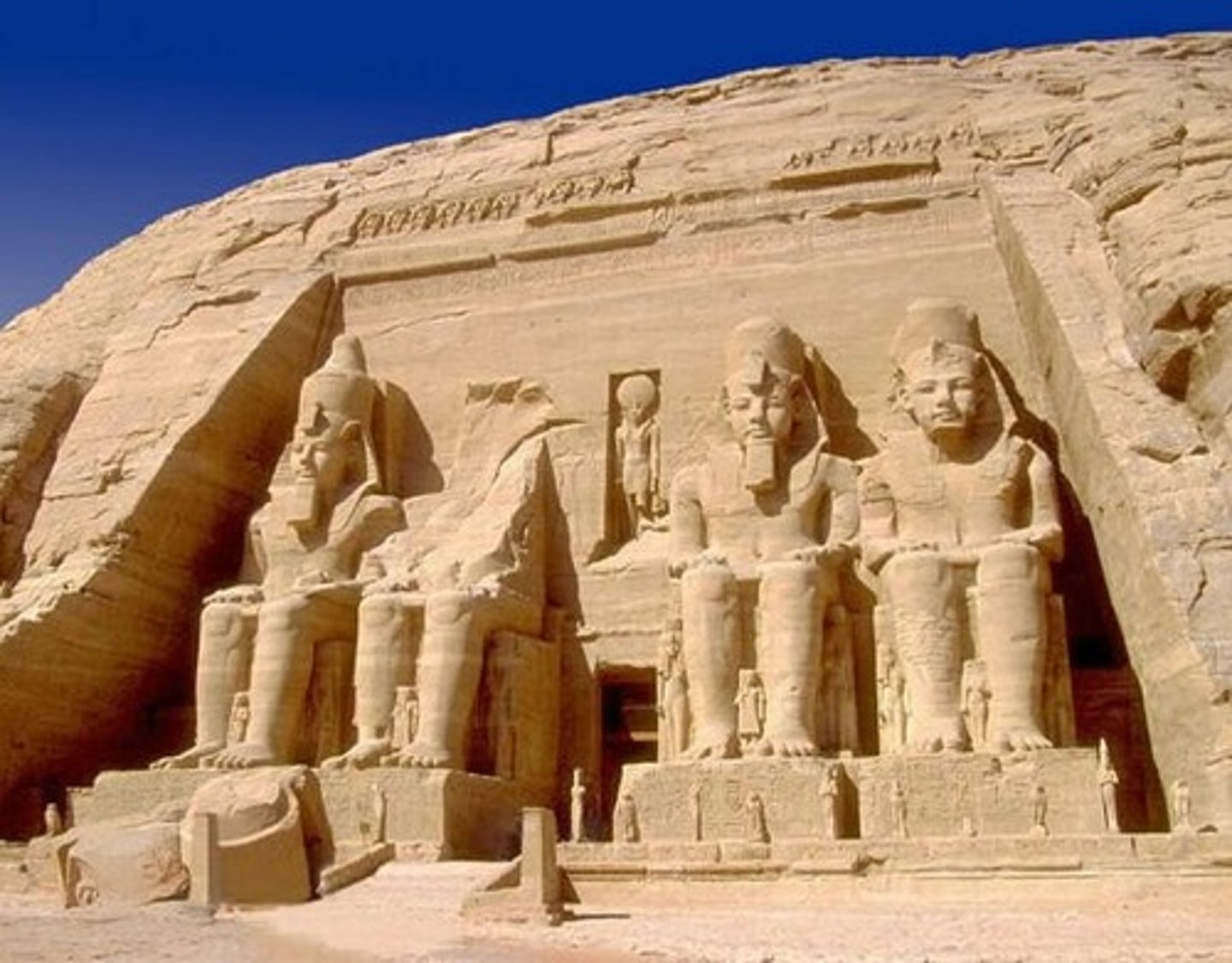
Abu Simbel Rock-cut tomb of Ramses II
(c. 1250 BCE) cf. Ptolemaic temples (Temple of Horus, Edfu, 237-57 BCE)) @ west bank of the Nile
masonry mimics construction of mudbricks (like from ziggurat @ mesopotamia)
pylon gate (tilted inwards) — monumental gateway @ entrance

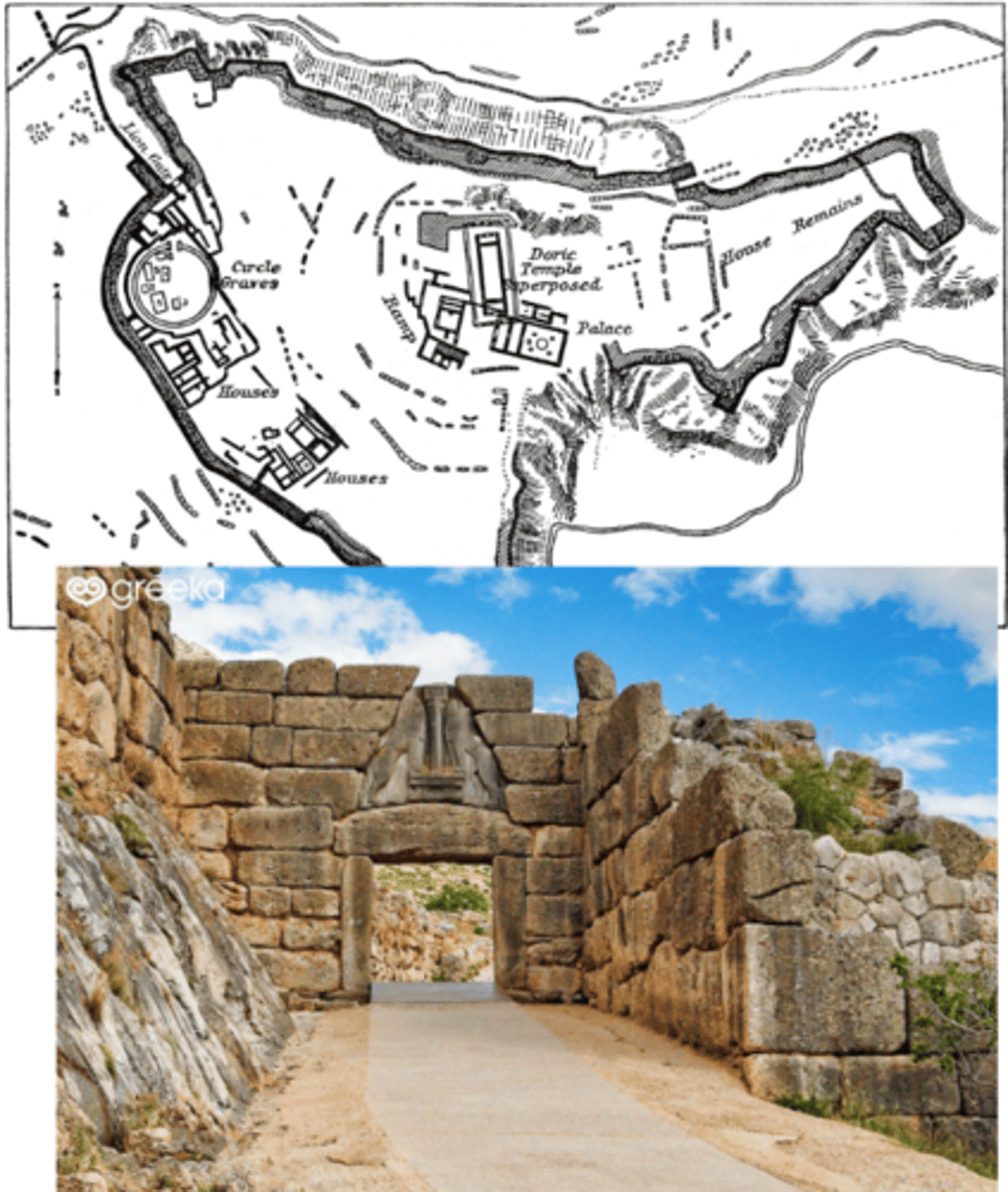
Mycenae Citadel + Lion Gate
Mycenae, c. 1250 BCE
Lion Gate — 2 lions with a column in the middle above an arch/vault (looks like a triangle above the gate); cyclopean masonry
Treasury of Atreus or Tomb of Agamemnon, c. 1300 BCE
has a ‘portal’ similar to Edfu (Mycenaens more open to foreign influence); also tilted inwards
Cyclopean masonry — stone fitted together that looks like it was done by a giant bc the blocks are so big)
Corbel Vault — “moving inward”; stones stacked horizontally to create an arch
Tholos — round structure with circular wall and domed ceiling/roof; tombs for Mycenaens
Dromos — a long, narrow corridor or passageway that leads to the entrance of a tomb or monumental structure
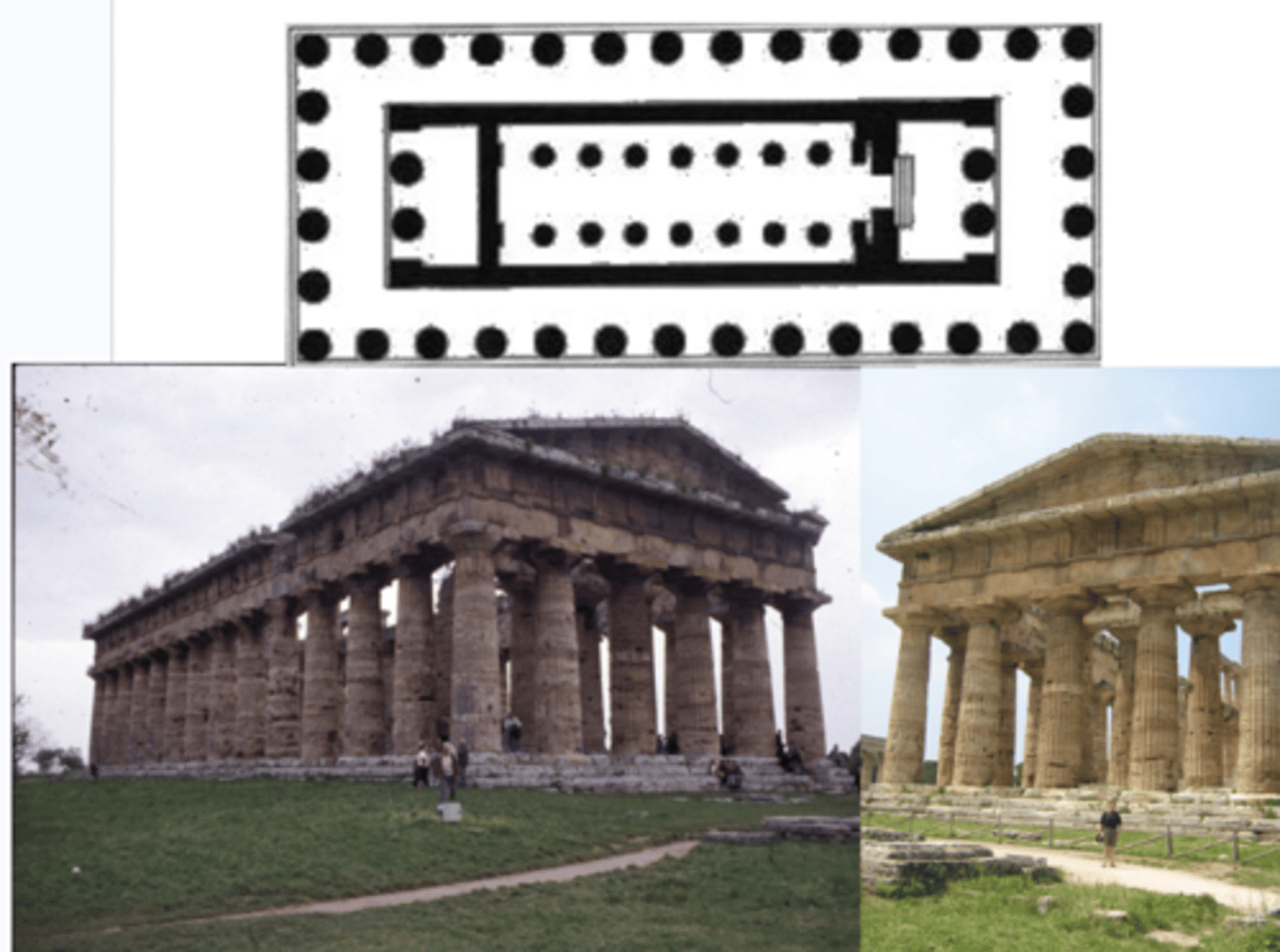
Temple of Hera II
Paestum | mid 5th Cent. BCE
doric order (no bases)
trabiated
anthropocentric — would be able to see sacrifices and athletic events at the same time bc of the gaps in the temples between the columns); communal architecture, focus on humans
house ‘cult image’ of Greek God
Athenian Acropolis
greek architecture inspo — external emphasis, trabiated
theater
greek / classical order (eg. ionic…)
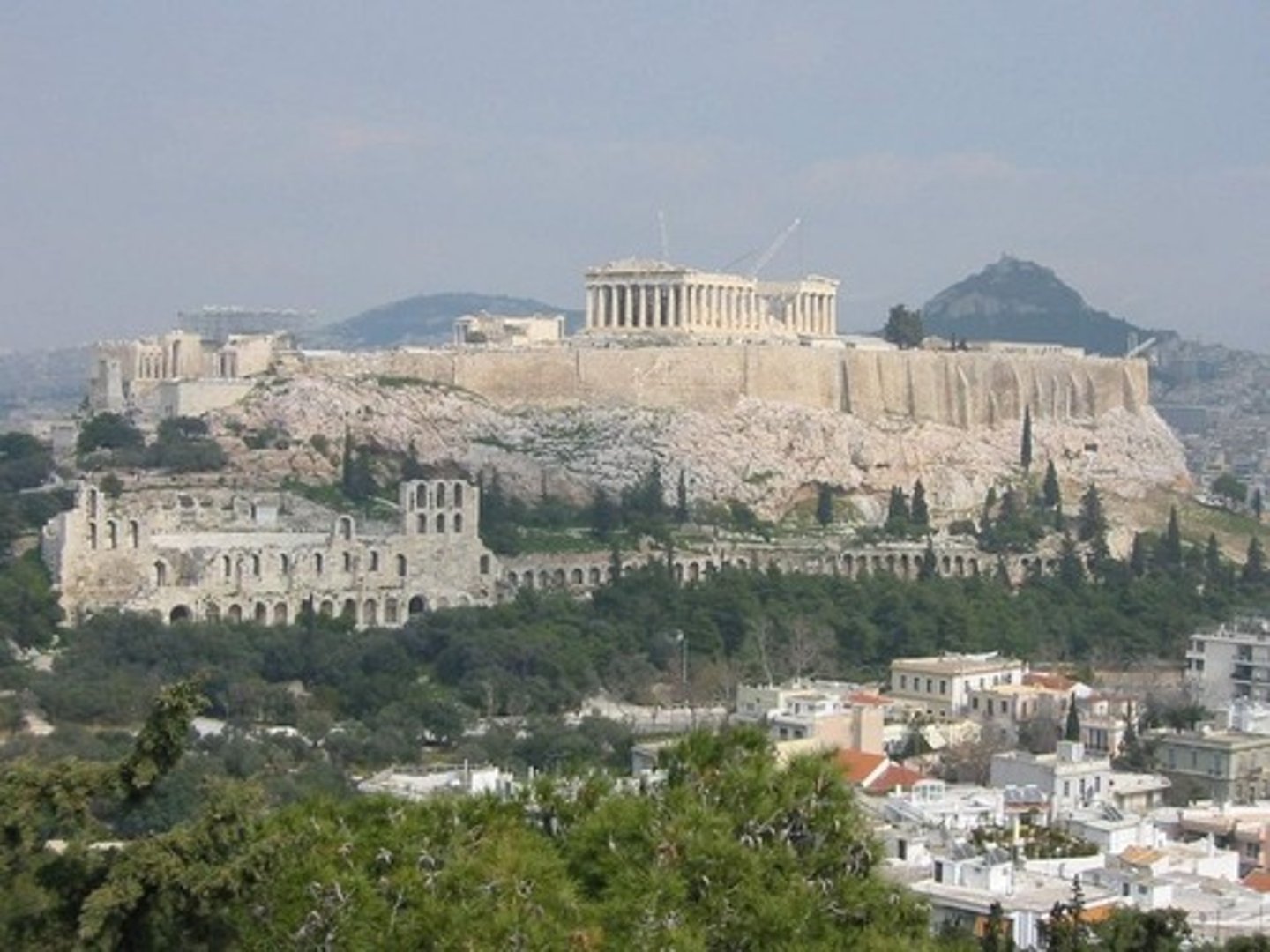

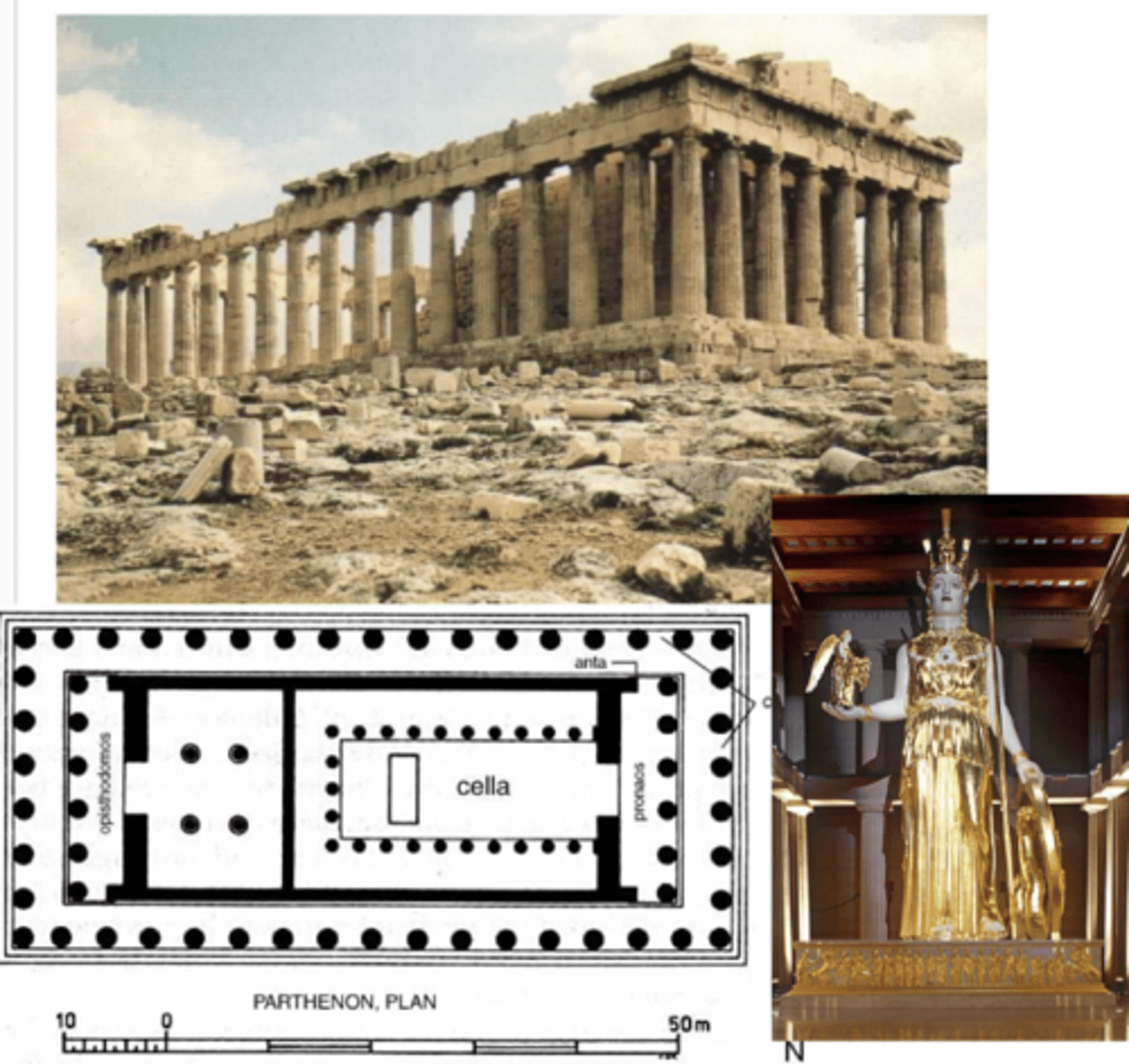
Parthenon
447-438 BCE | Architect Iktinus | Sculpture by Phideas Erechtheion, 421-405 BCE — Caryatid porch
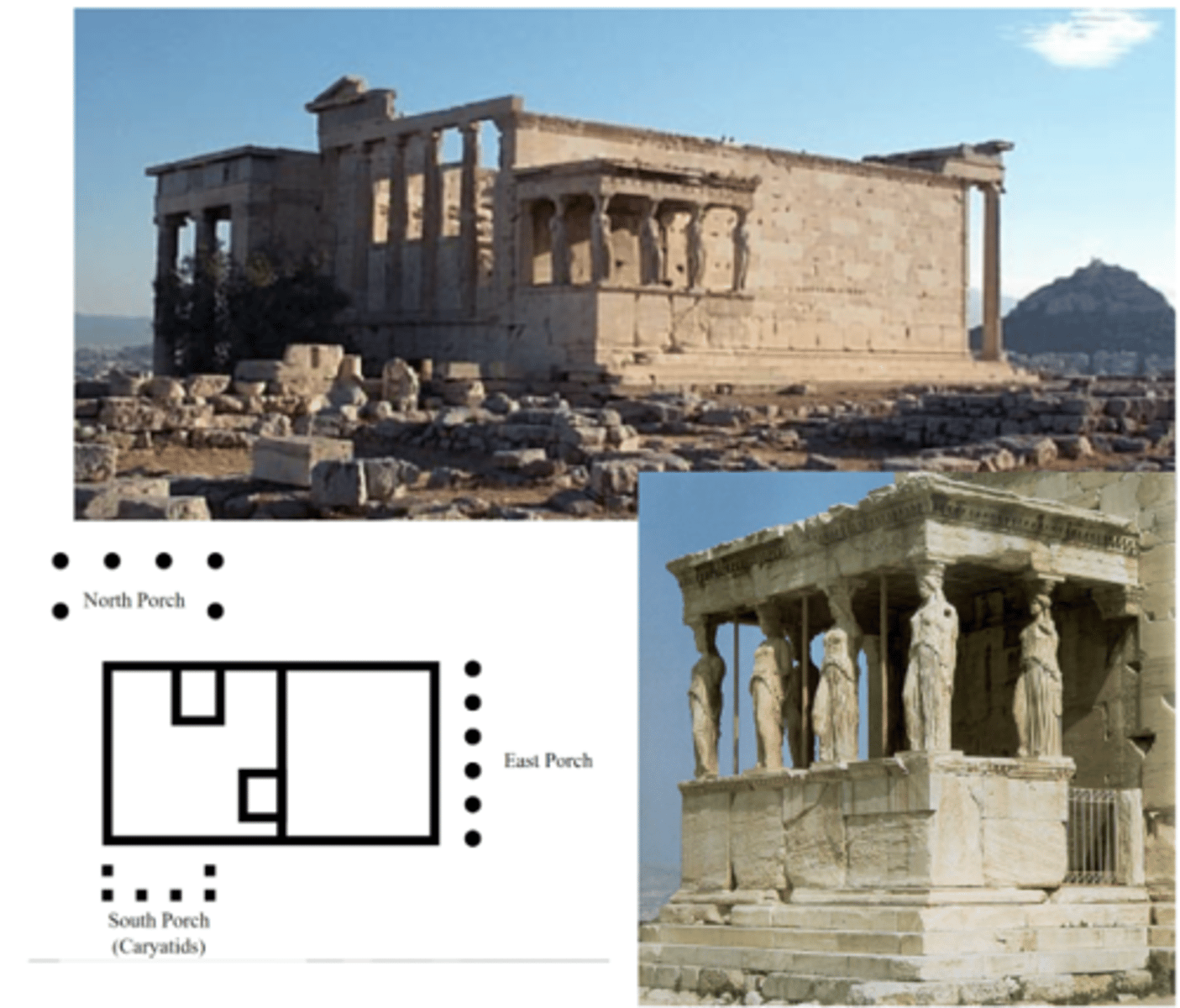
Caryatids — a stone carving of a draped female figure, used as a column to support the entablature of a Greek / Greek-style building.
Erectheion
@ Athenian Acropolis, 421-405 BCE
Ionic-style temple
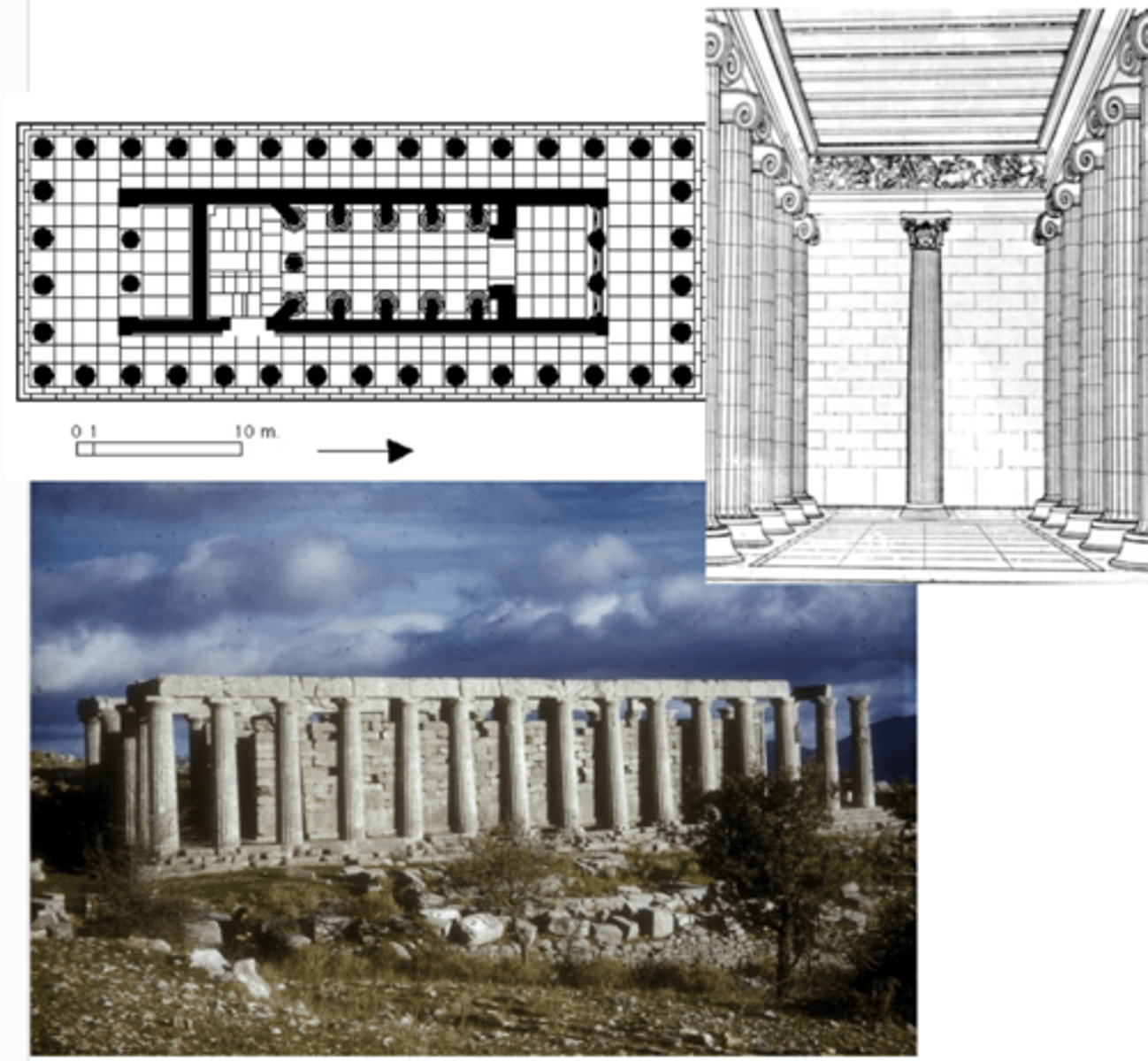
Temple of Apollo Epicurius
Bassae, 429-400 BCE | Architect: Iktinus
Corinthian order with acanthus capital in the middle, ionic order columns on the sides
communal architecture
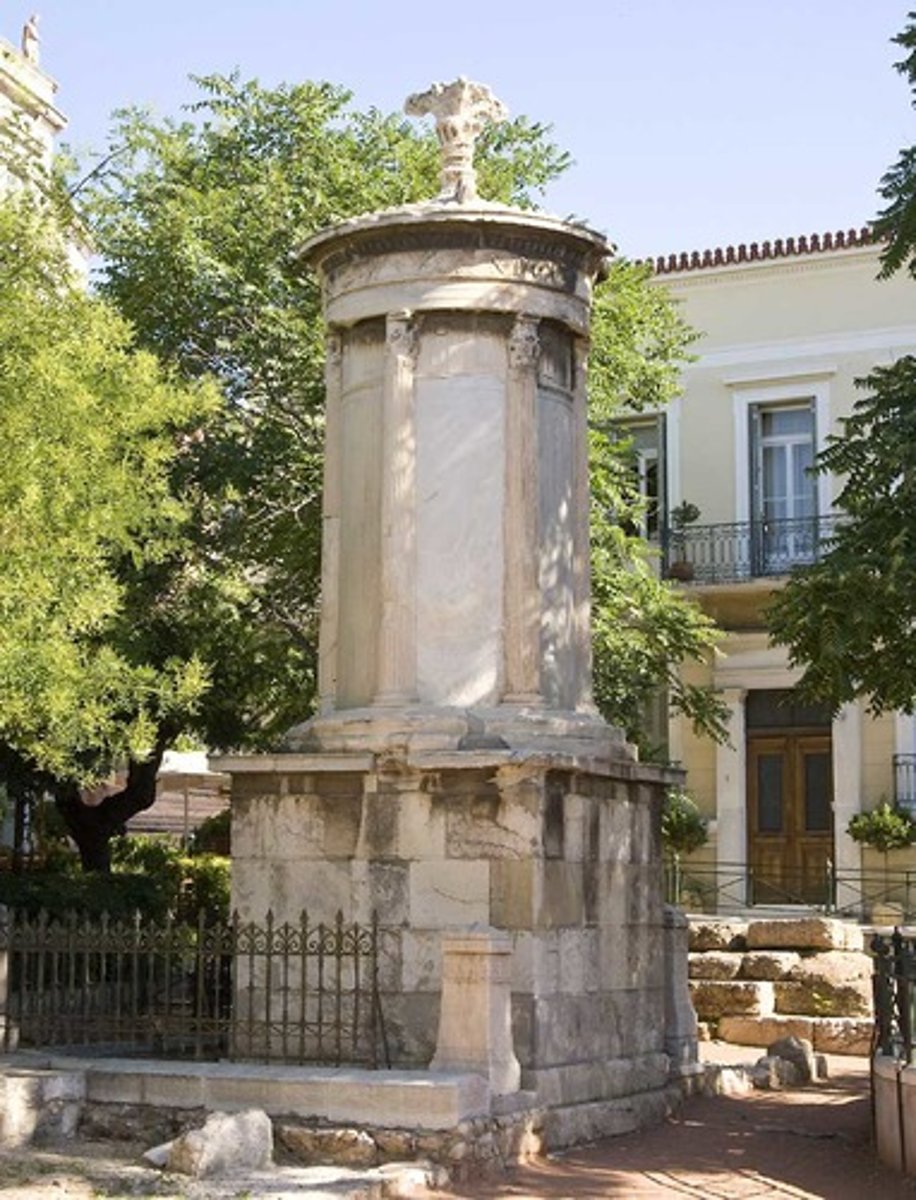
Choragic Monument of Lysicrates
Athens, 334 BCE
Corinthian order with ionic frieze, architrave

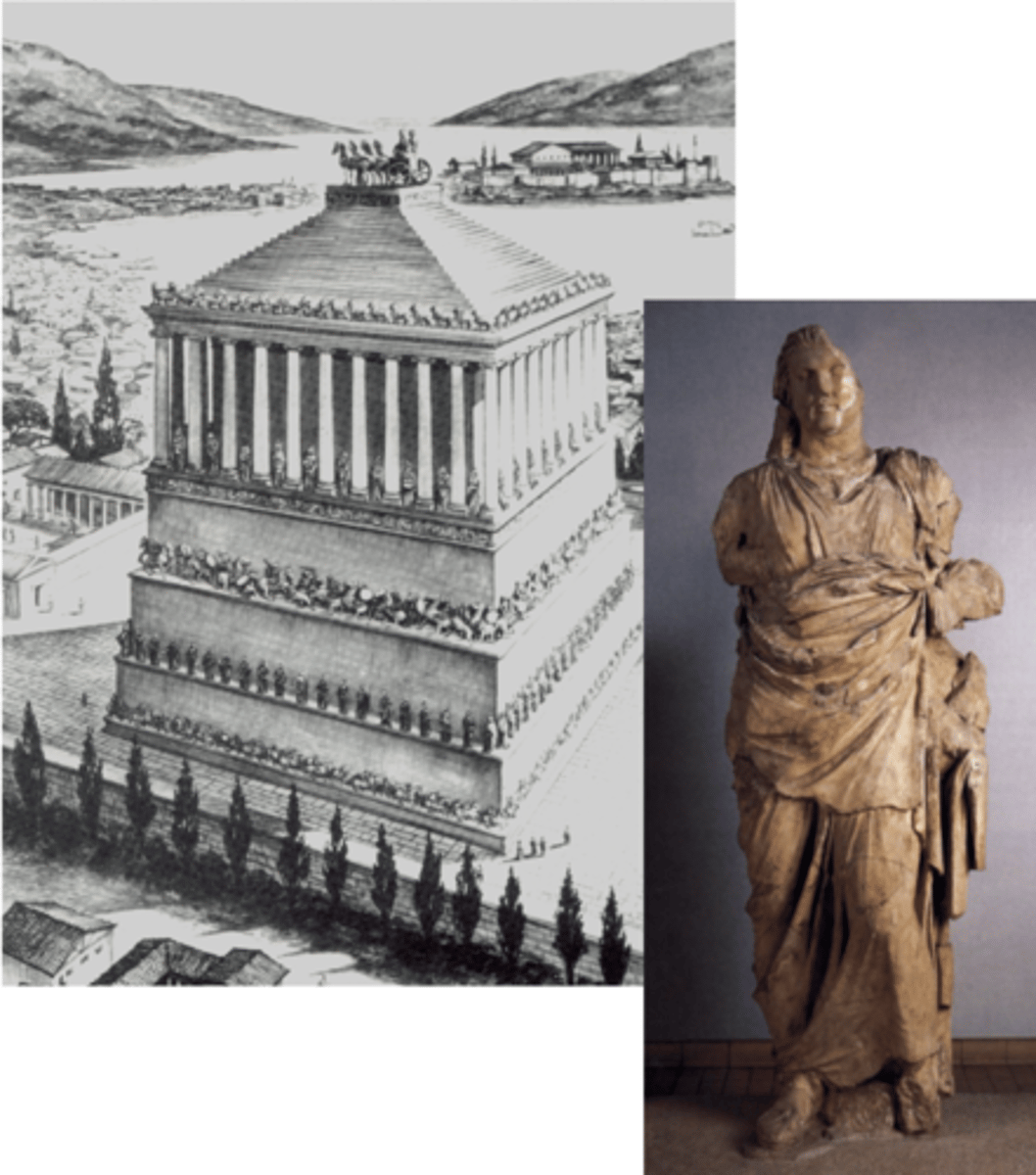
Mausoleum of Halicarnassus
350 BCE | Architect: Pythius
built for Mausolus and wife/sister Artemisia
royal architecture

Bouleuterion
Miletus, c. 170 BCE
engaged columns
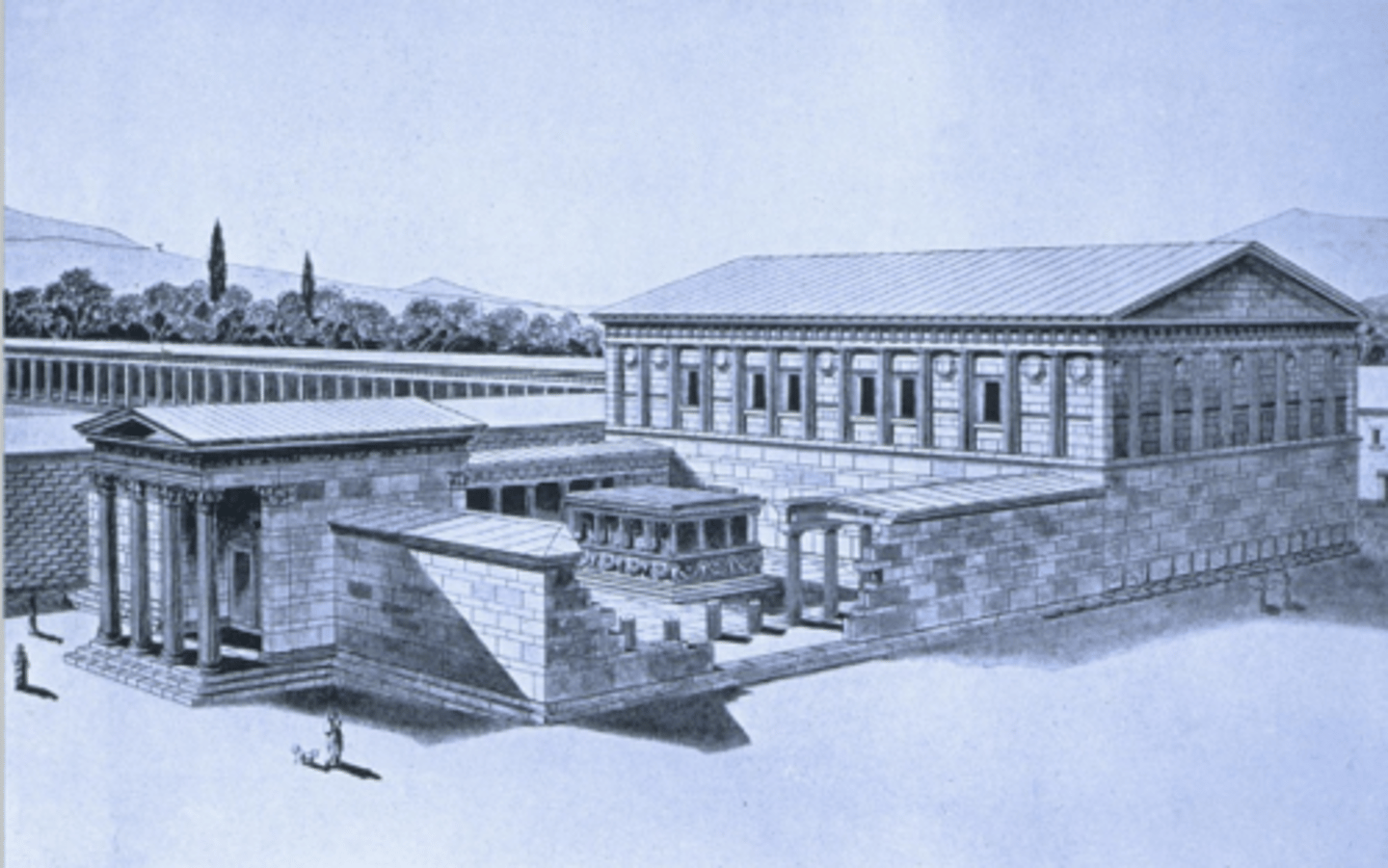
Priene
near Miletus, 300-400 BCE
orthogonal town plan (grid-like)
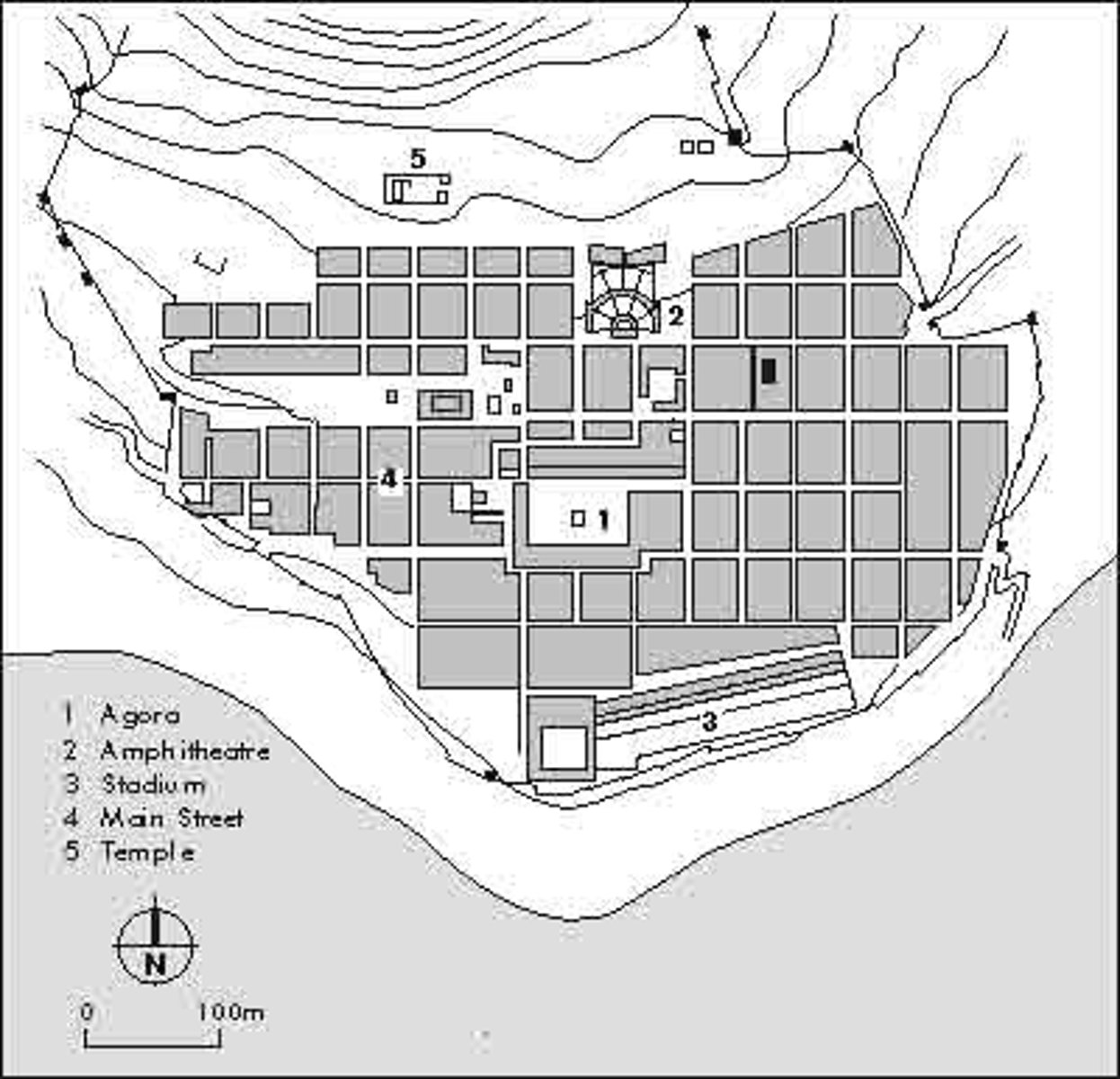
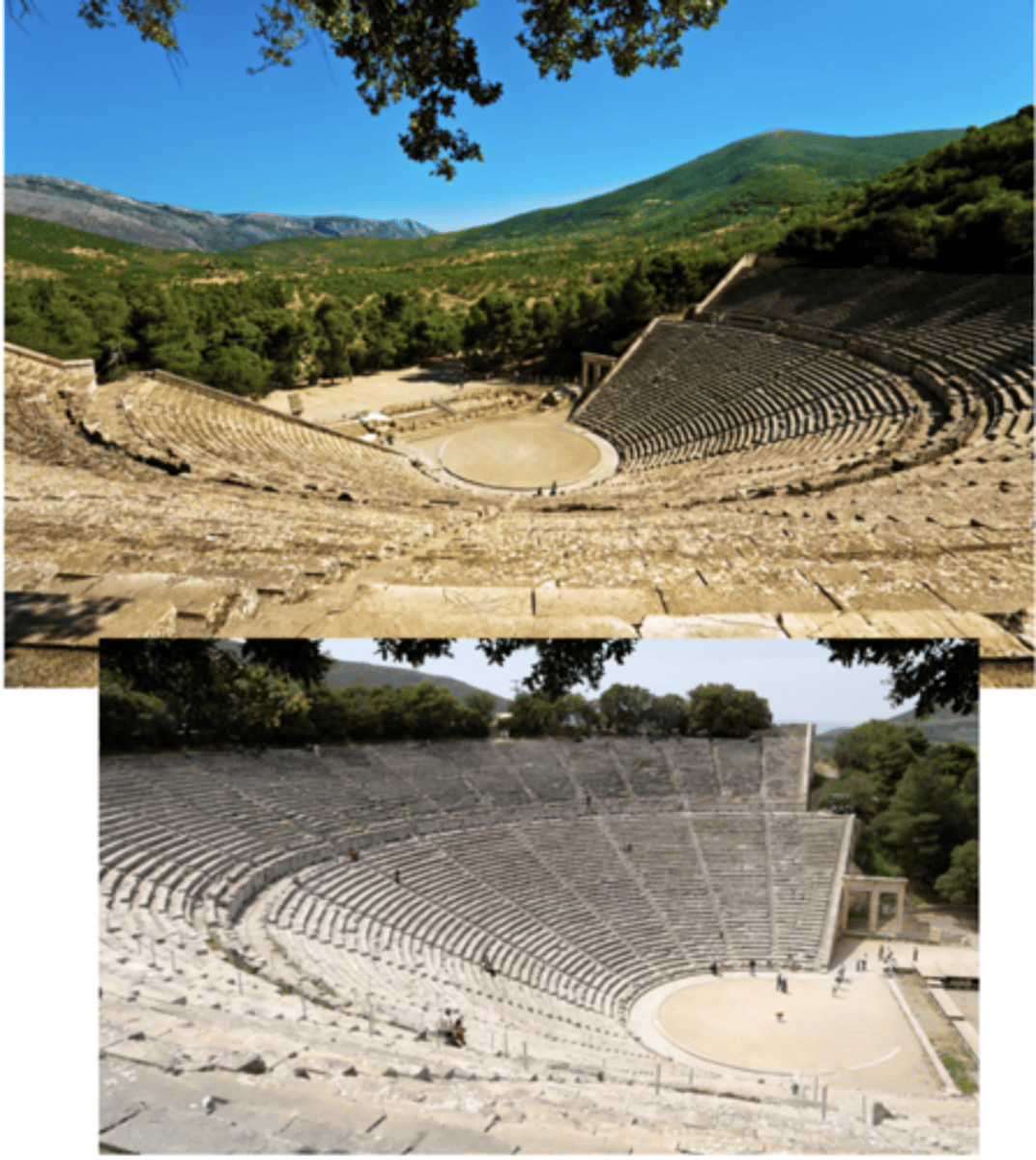
Theater at Epidaurus
c.300 BCE | Architect: Polykleitos
compare to roman theaters of pompey and marcellus
epidaurus uses natural disposition of landscape
made of stone, no concrete; using materials from surrounding environ.

Acropolis of Pergamon
Asia Minor, mid-3rd-mid 2nd Cent. BCE
developed by King Attalus and later on
King Eumenes II
King Eumenes II built Altar of Zeus in honor of his father Altar of Zeus (now in Pergamon Museum, Berlin), c. 170 BCE
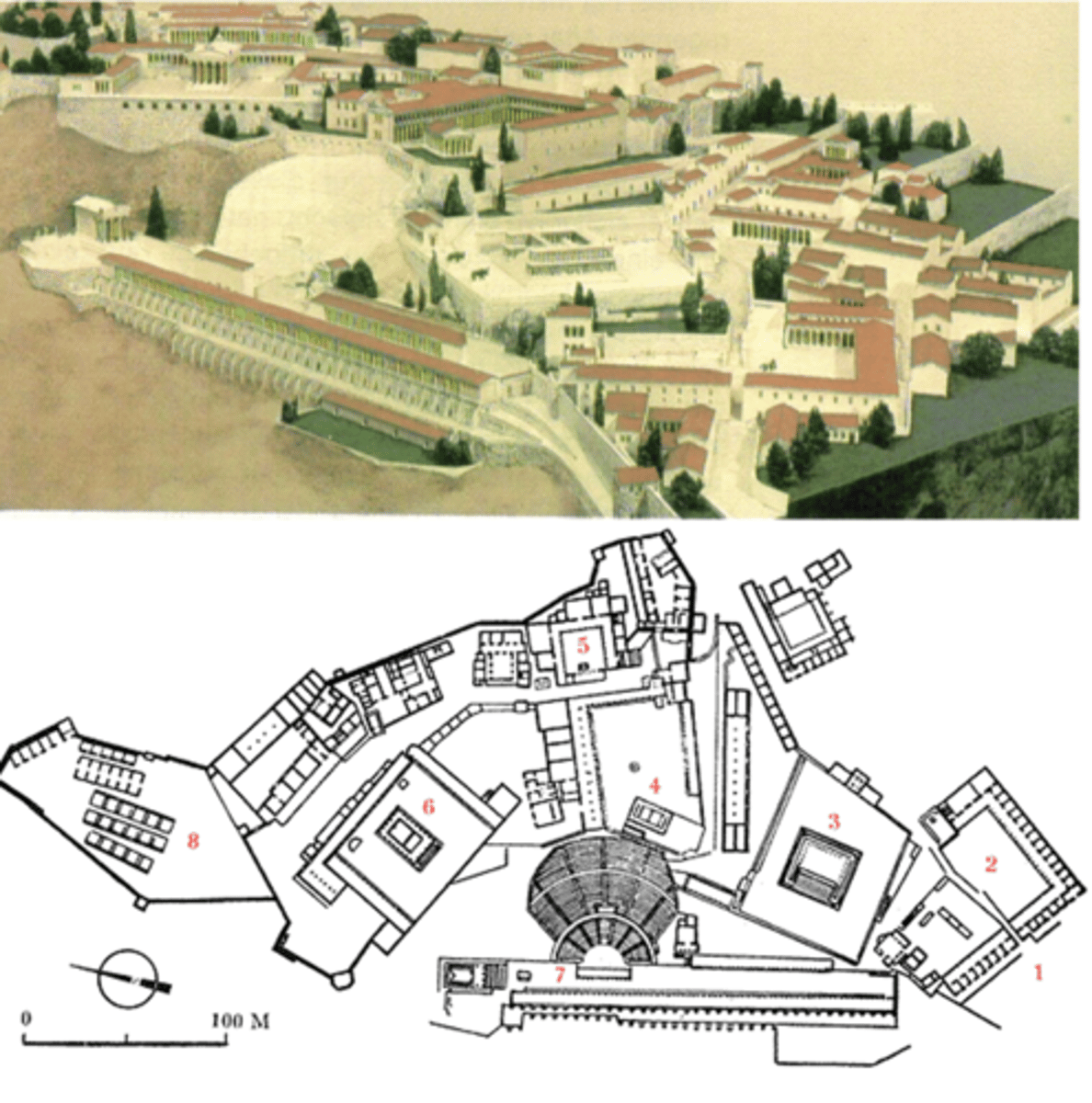
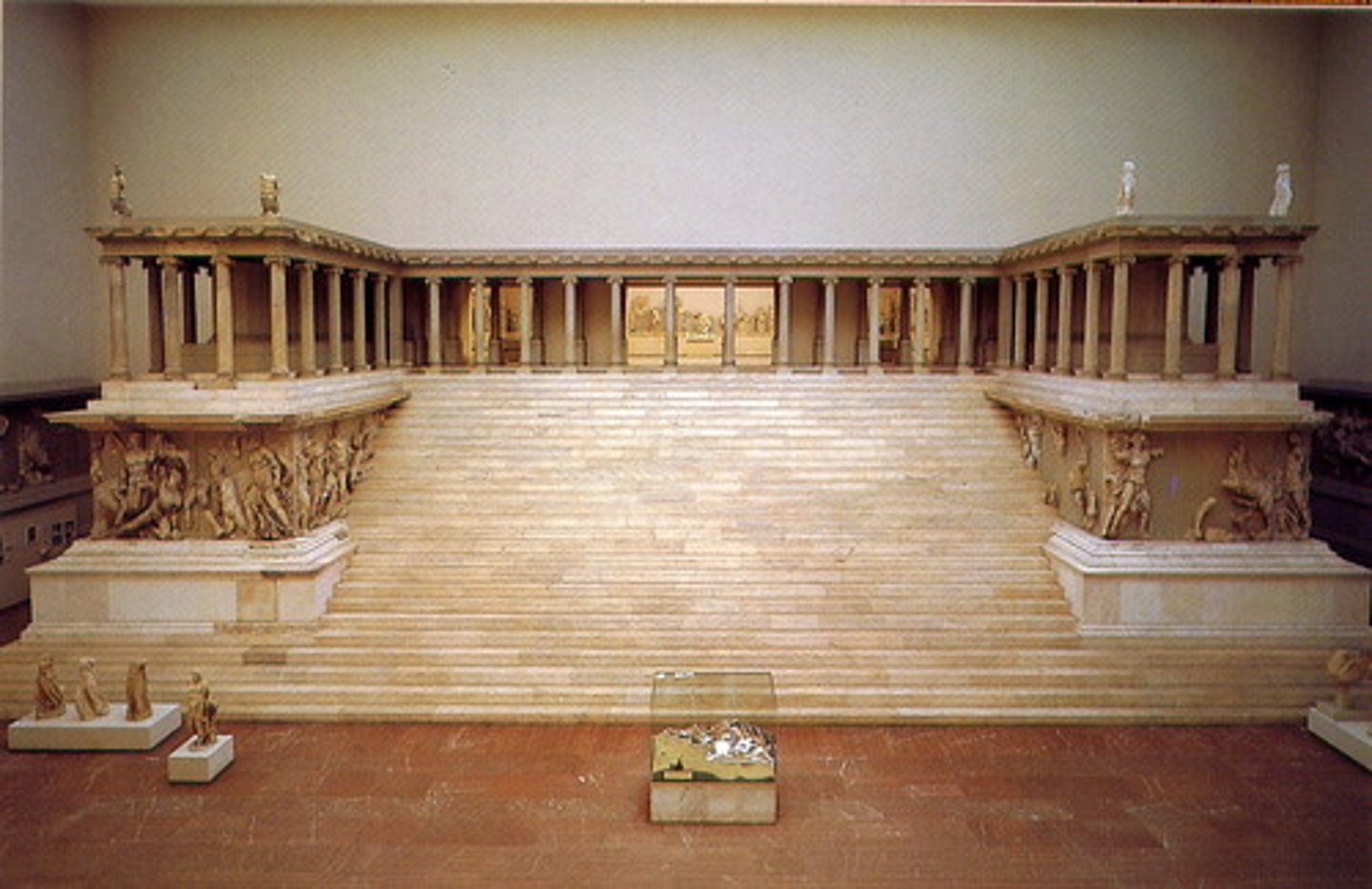
Altar of Zeus
Asia Minor, c. 170 BCE
King Eumenes II built Altar of Zeus in honor of his father Altar of Zeus (now in Pergamon Museum, Berlin)

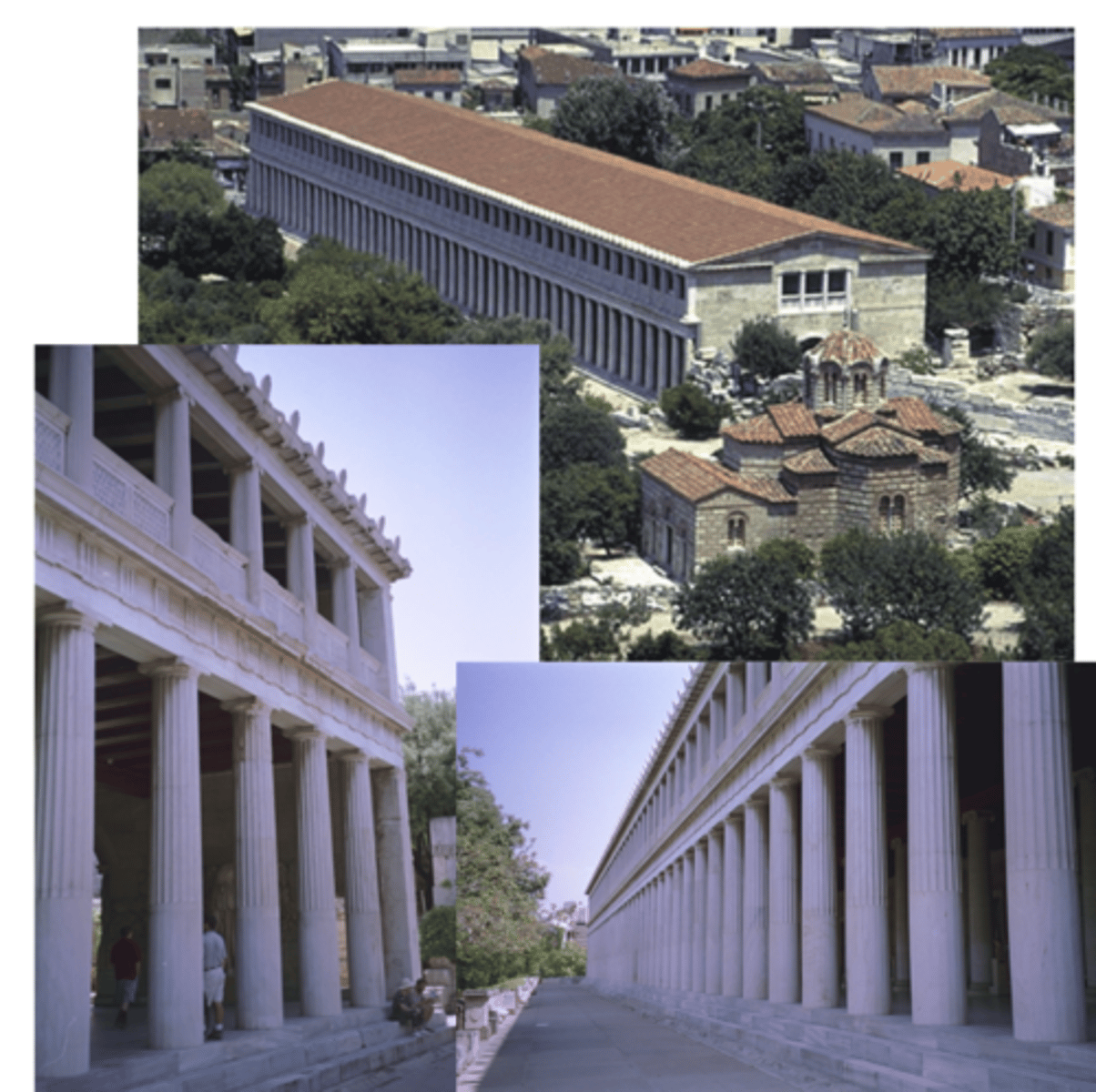
Stoa (roofed colonnade) of Attalos II
Agora, mid 2nd Cent. BCE
2 orders (doric and ionic) used in 1 building (relaxing of Classical rules)

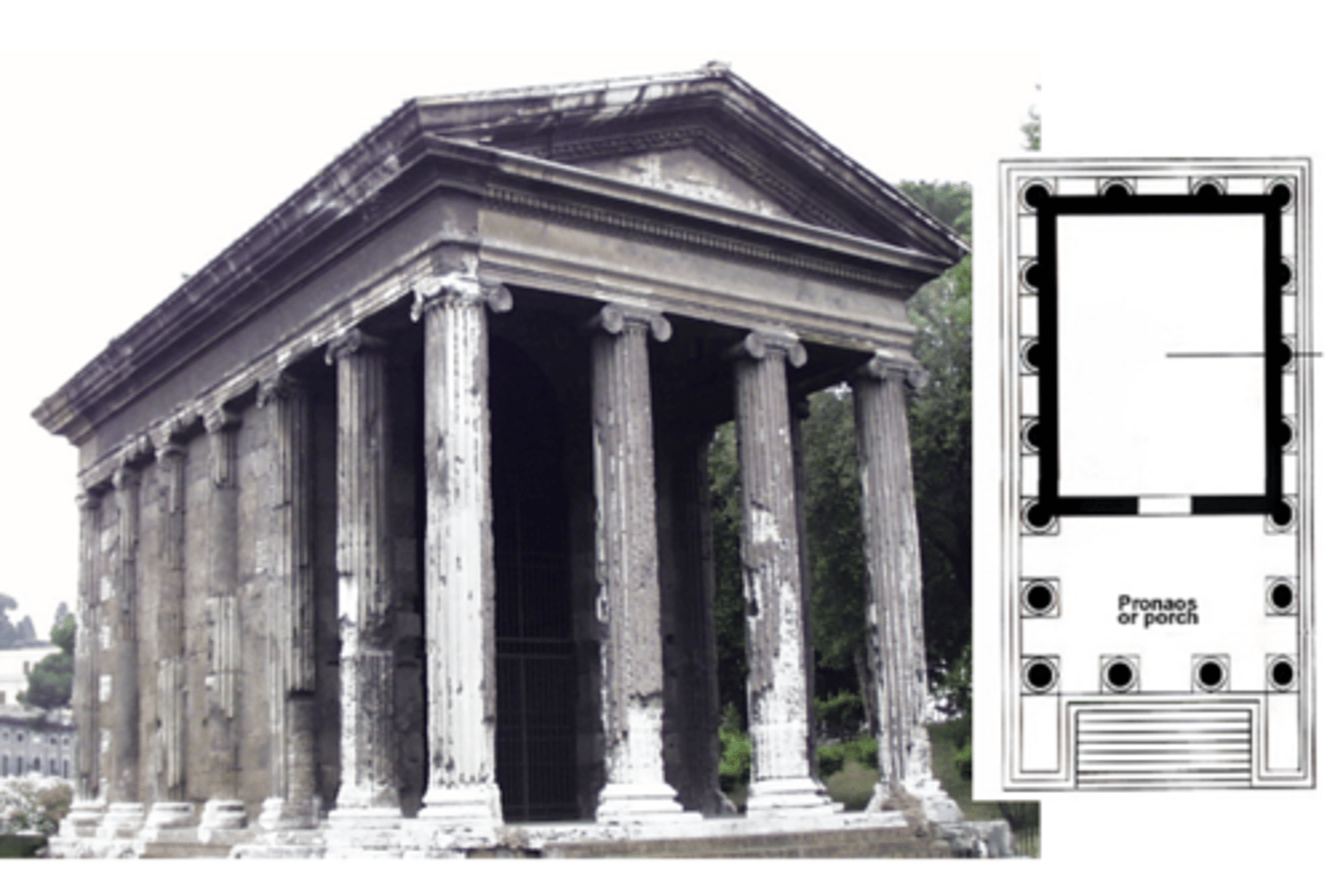
Temple of Fortuna Virilis/Portunus on Forum Boarium
Rome, early 1st Cent. BCE
Ionic order
engaged columns on side but free-standing columns @ front (front-emphasis in roman architecture)
elevated on high podium

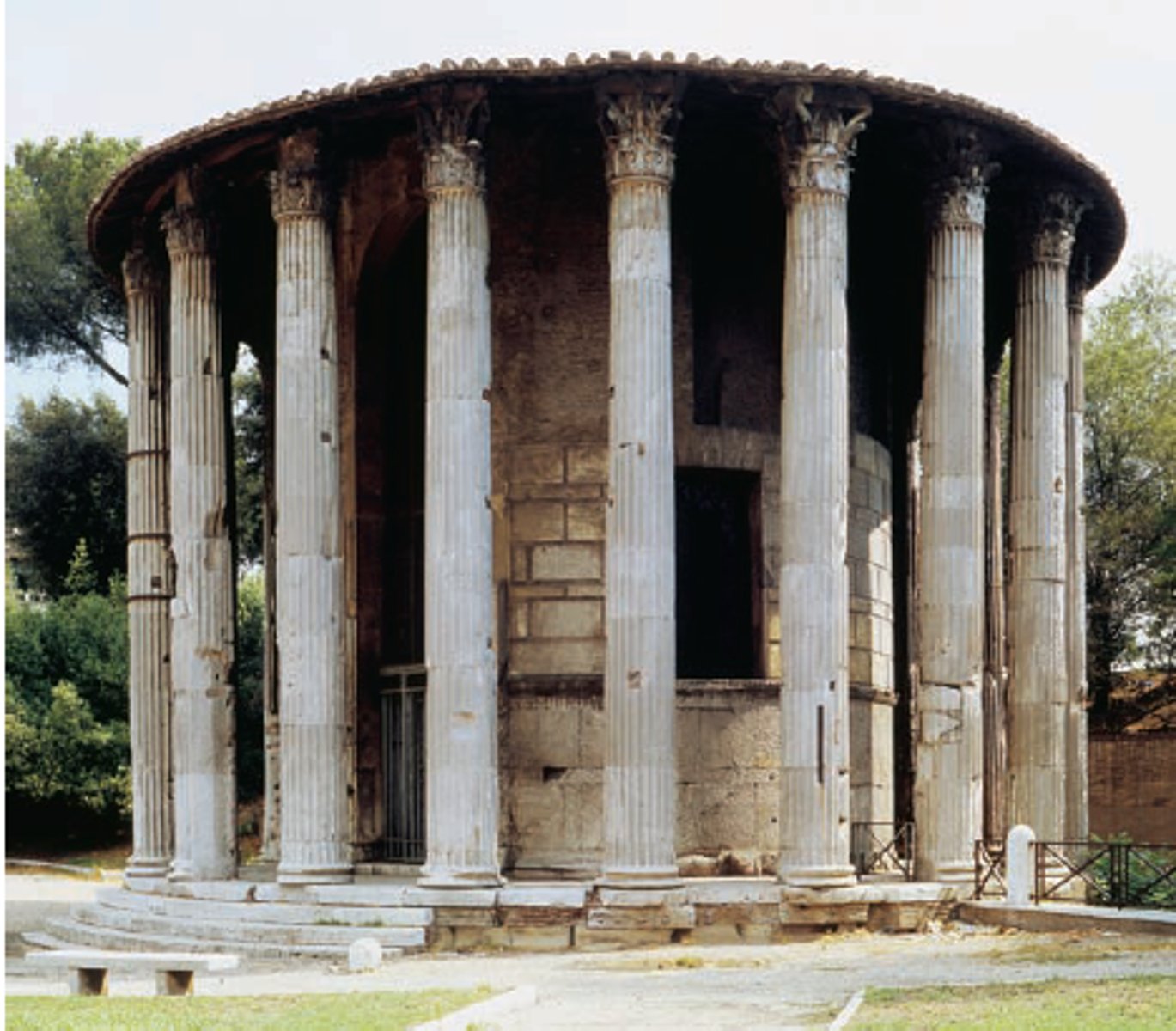
Round "Temple of Vesta" on Forum Boarium
Rome, late 2nd Cent. BCE

Porticus Aemilia
ca. 179 BCE
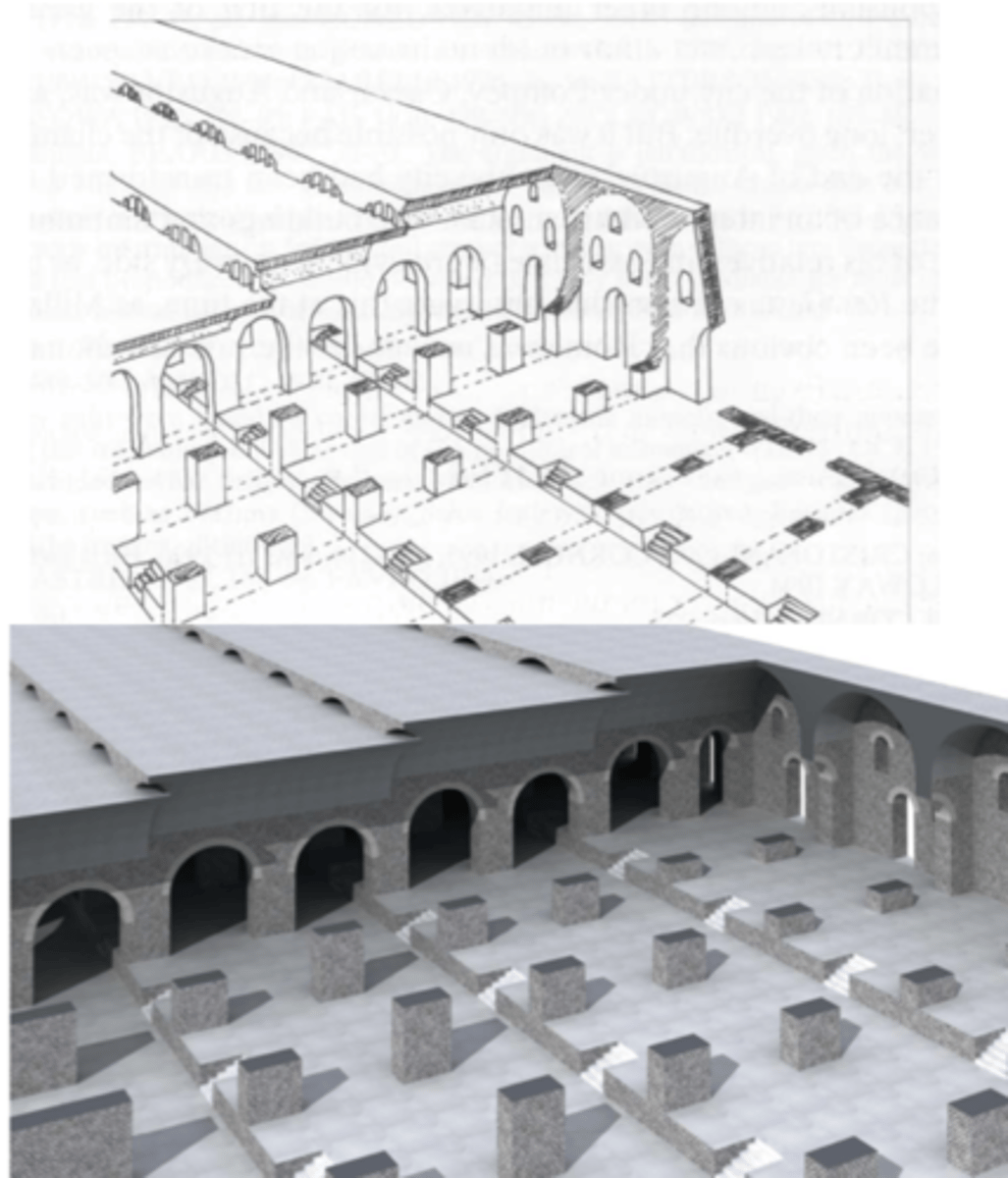
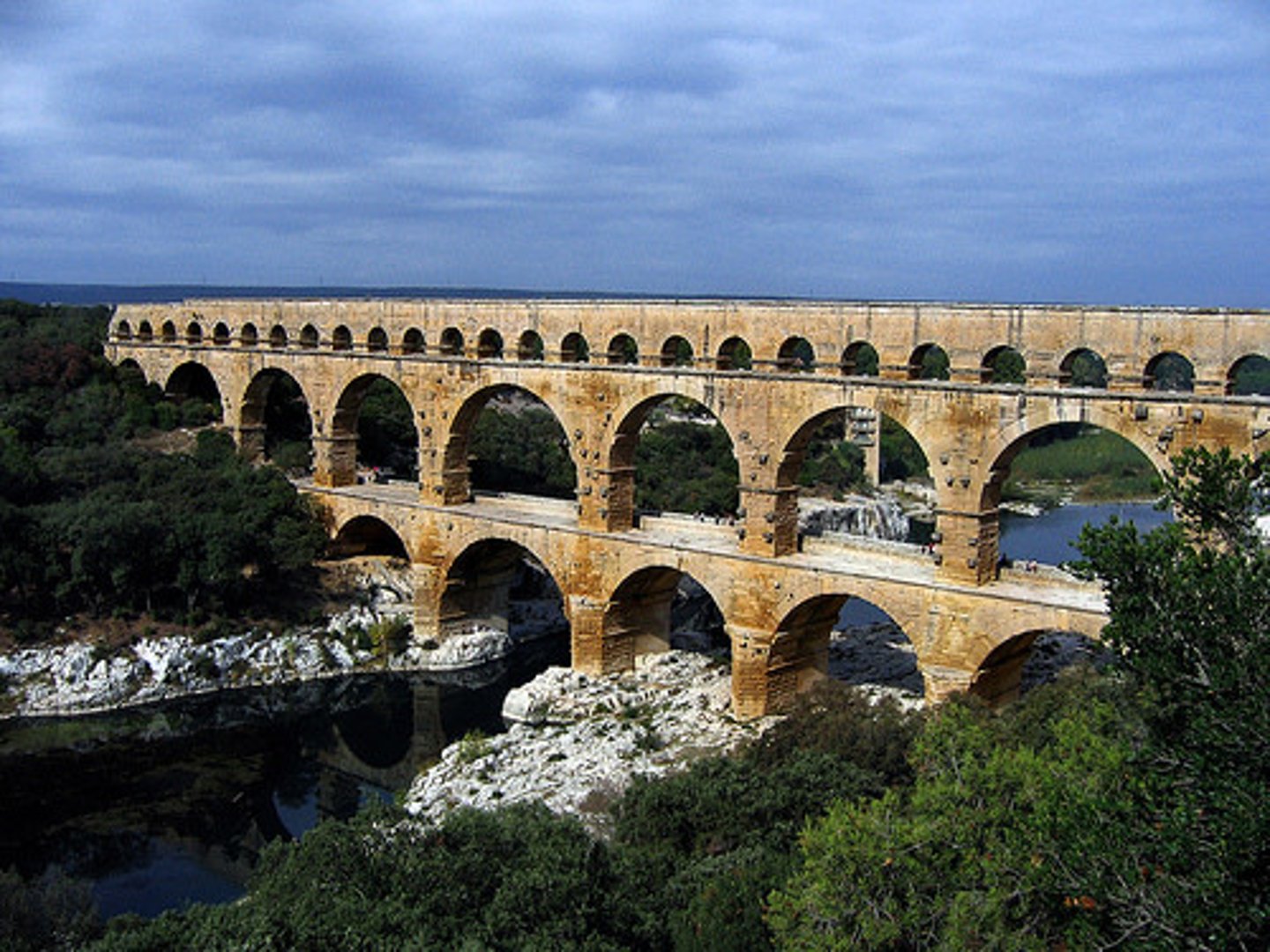
Pont du Gard (Aqueduct)
Nimes, France | late 1st Cent. BCE
arcuated; barrel vault

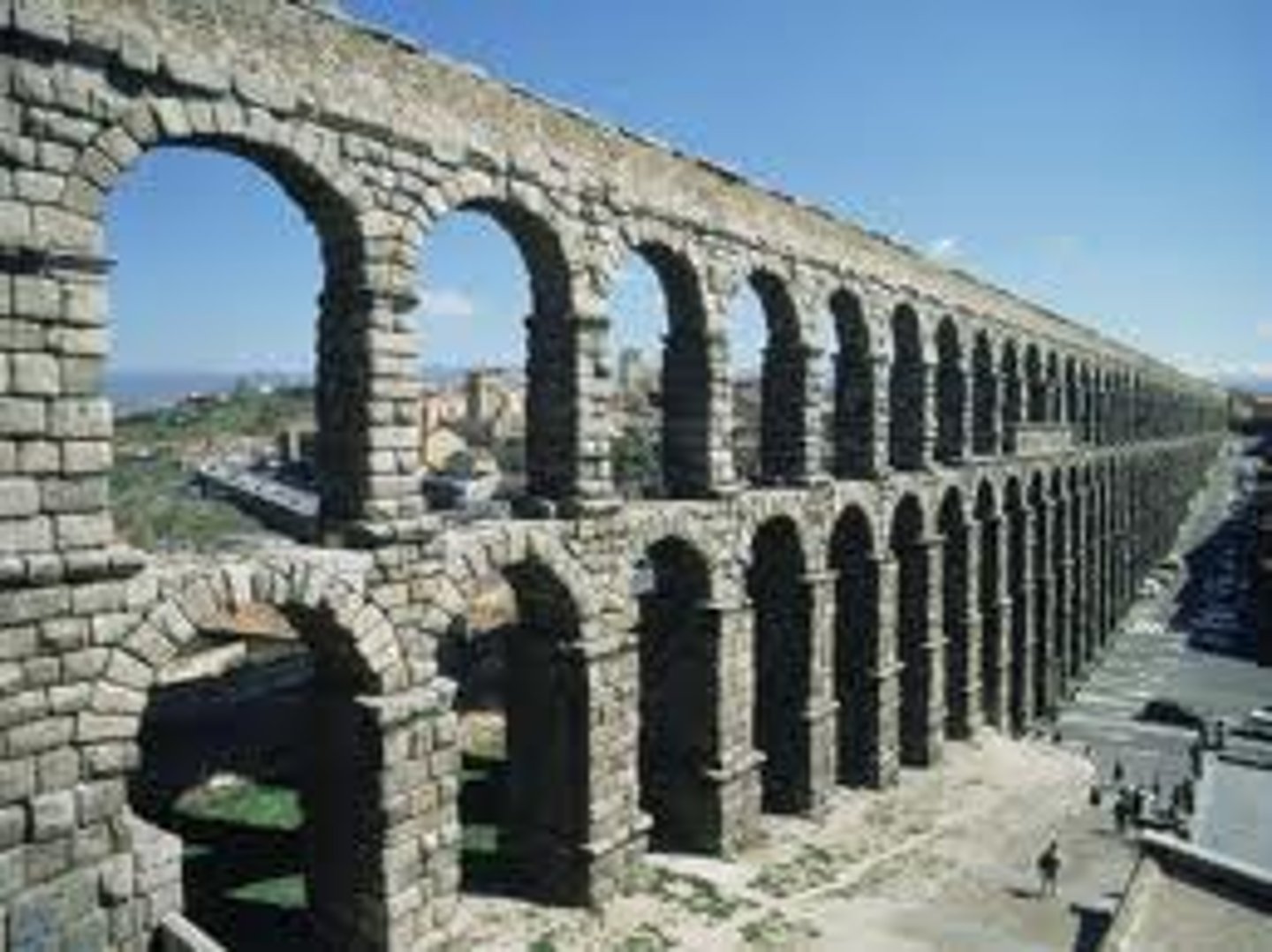
Aqueduct of Segovia
Segovia, Spain | 1st / early 2nd Cent. BCE
arcuated; barrel vault

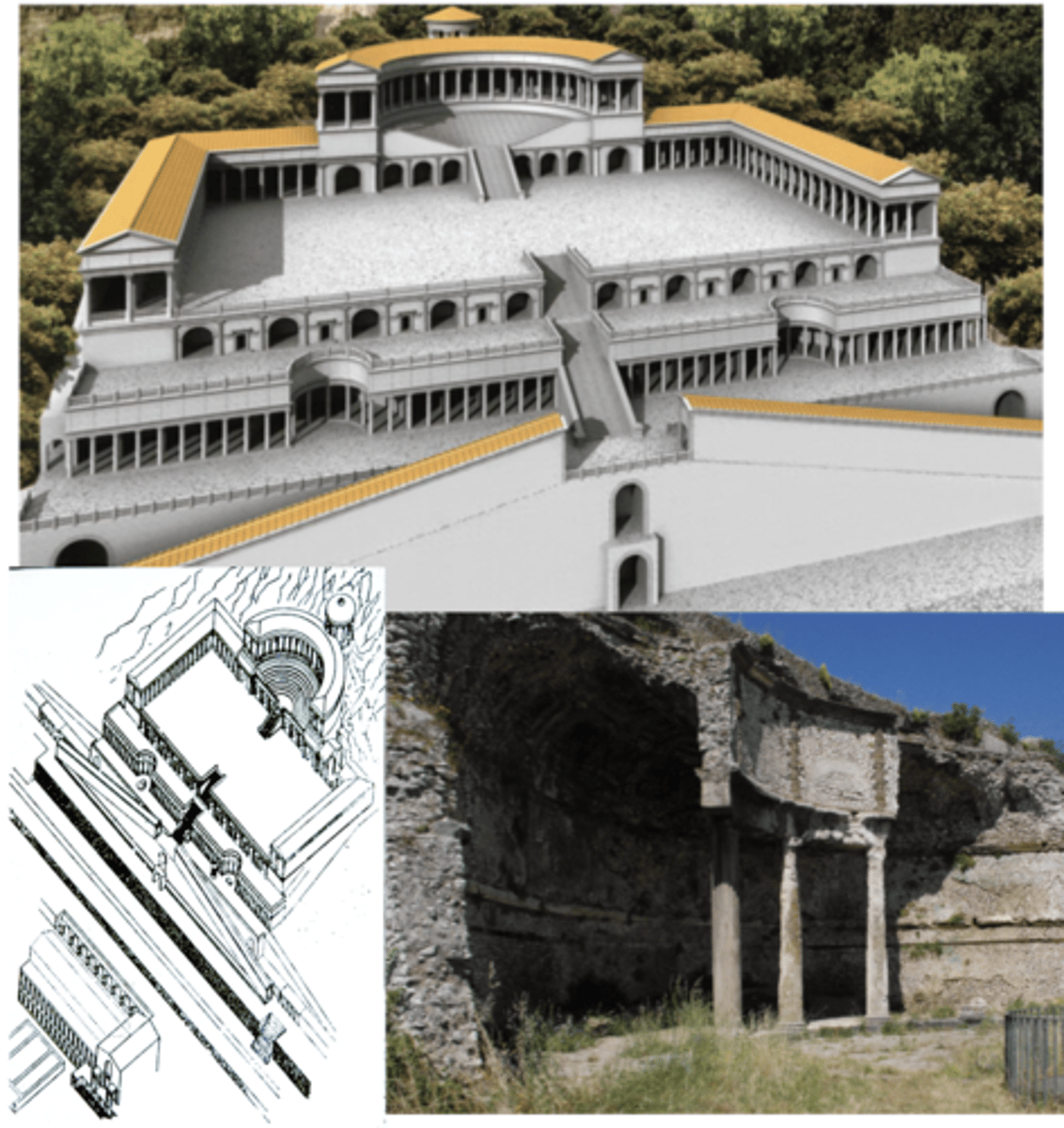
Sanctuary of Fortuna Primigenia (roman goddess Fortuna; god of luck and fate)
Praeneste (modern Palestrina, Italy), possibly late 2nd Cent BCE
pilgrimage site — travel there to increase chances of getting what you want
oracle @ top (like a psychic)
built to last (bombed and still remained)
hemicycle / exedra — semicircle
v. symmetrical (axiality of roman archi)
tholos @ top (round building w/ domed roof)
arcuated architecture made w/ concrete BUT w/ greek skin (marble plaster painted, tholos, theatre temple, columns there for deco. bc arches/vaults supporting everything)
egyptomania — has mosaic of the Nile
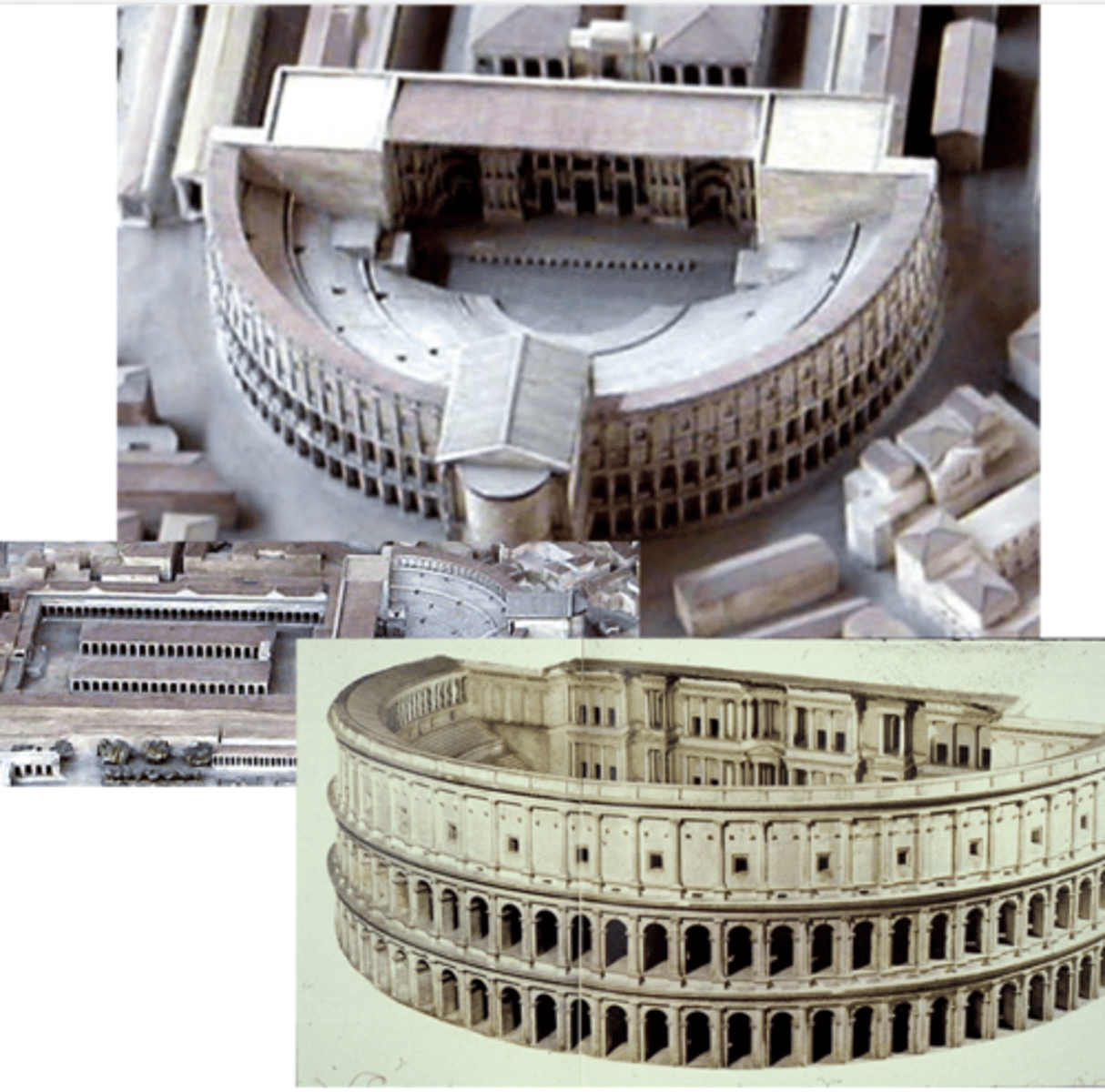
Theaters of Pompey and Marcellus
both @ Rome, Pompey — 55 BCE, Marcellus — 13-11 BCE
Pompey — roman general
built 1st monumental marble theater after victory
@ middle of the city (controversial) → added a temple
engaged columns
peristyle courtyard — open courtyard surrounded by columns
compare to Greek theater of Epidaurus
made of concrete
arcuated (uses arches and vaults)
self-supporting built on flat ground
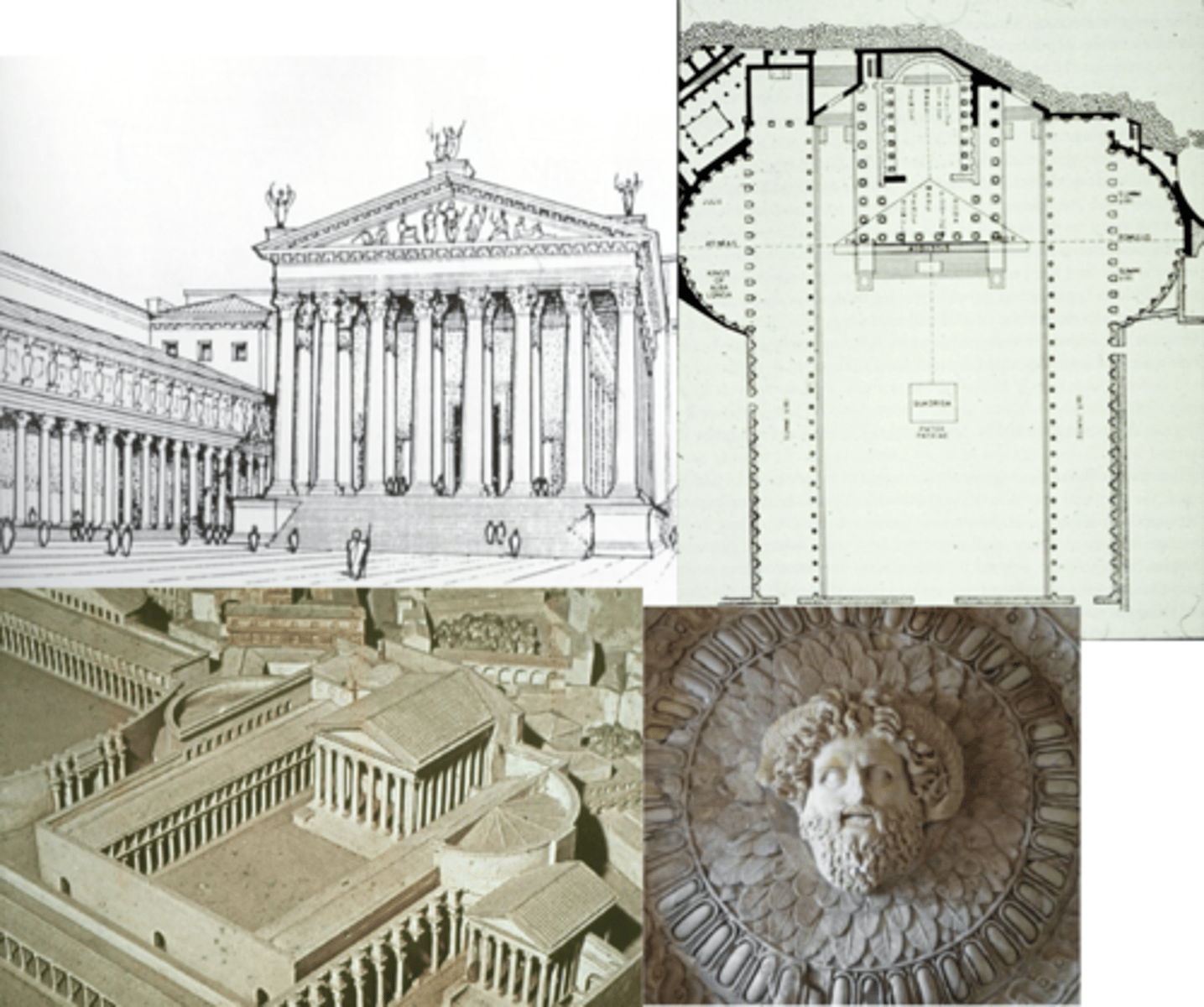
Forum of Augustus
Rome, Italy | 2 CE
Temple of Mars Ultor (Mars the Avenger)
Greek order — Corinthian w/ entablature, pediment, cornice w/ free-standing statues inside
collonades ; trabiated, v. conservative (Augustus bringing “golden age” by bringing back old trad. values)
combi. w/ roman features (raised podium, frontal emphasis, axiality/symmetry)
hemicycle
fountains (w/ perfume to make forum smell nicer)
statues along collonades and hemicycles (Juli, Augustus, Fortuna, Venus, etc.
*Caesar’s statue is naked = divinized
equestrian status of Augustus
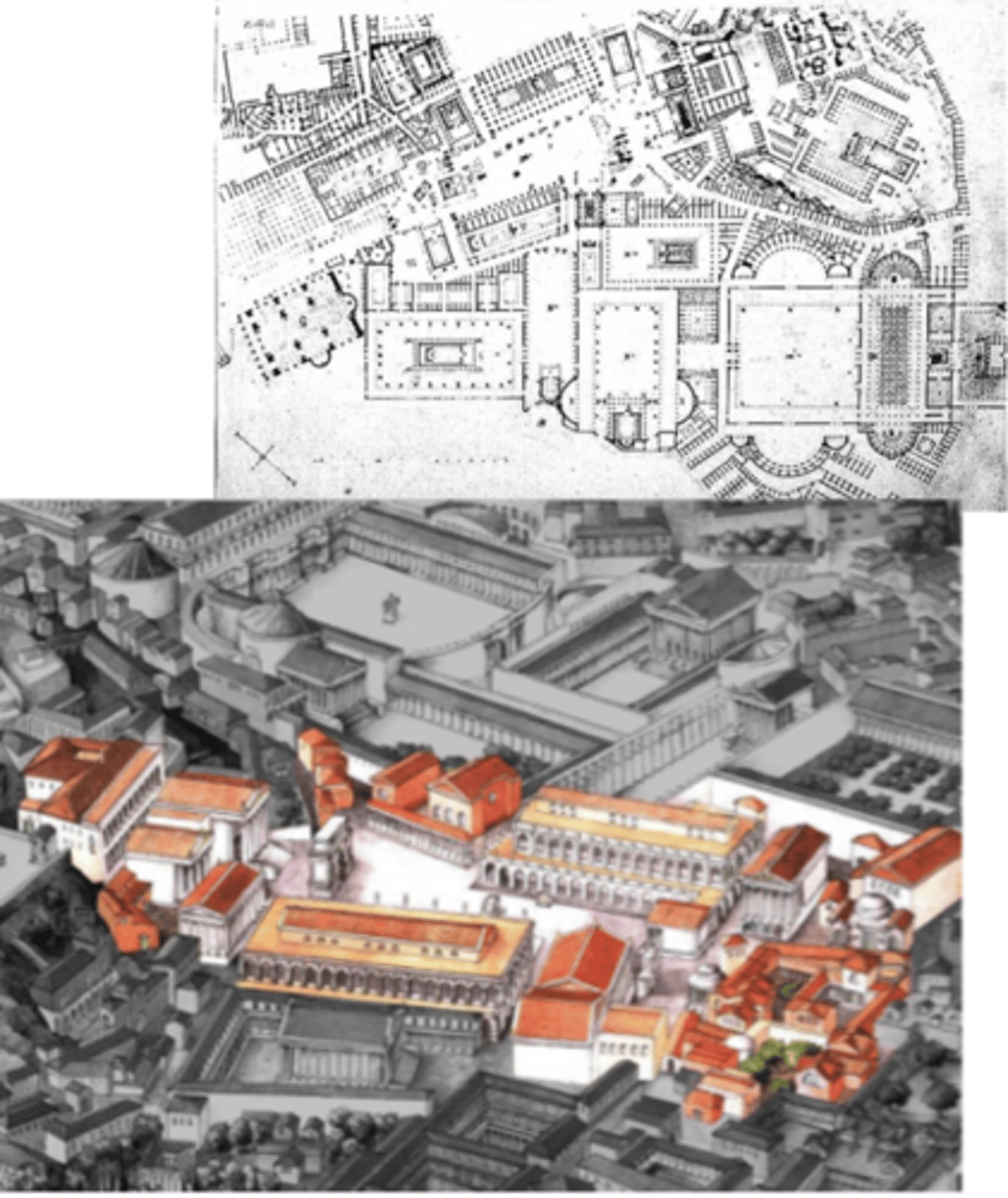
Roman Forum
Basilica Julia
rebuilt and named after Julius Caesar
rectangular-shaped building filled w/ columns
central aisle (knave) is wider
secular — law court, stock exchange, place to do impt. business
Basilica Aemilia
also rebuilt by Caesar
filled w/ diff color marble
marble columns — Corinthian order
knave is wider
roof of knave is higher than @ side aisles — clerestory windows
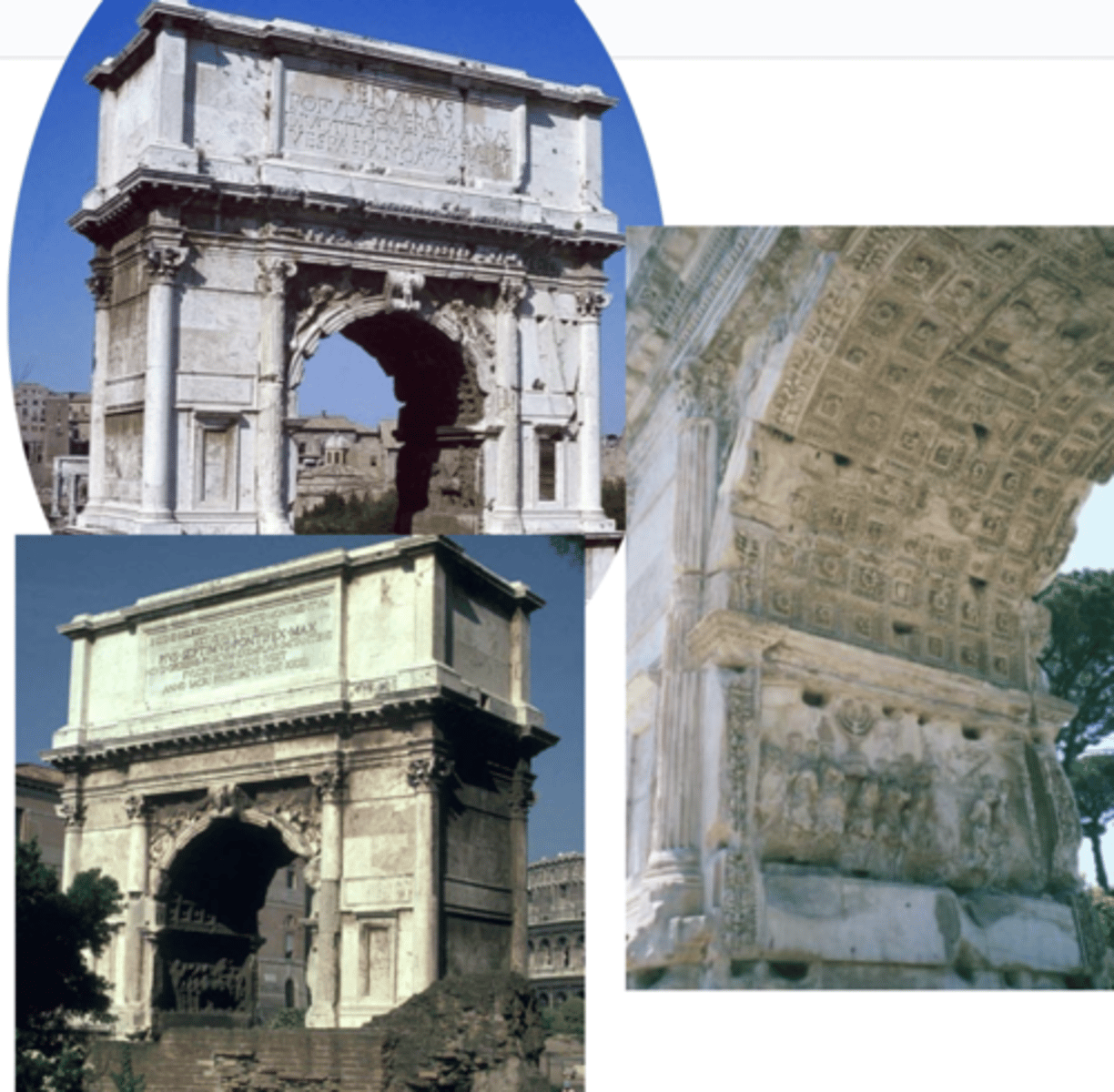
Arch of Titus
@ Roman Forum, after 81 CE
triumphant arch — commemorate divinized Titus; victory of roman armies vs jews in judaea revolting against roman rule (oh..!)
composite capital — engaged columns w/ Ionic volutes featuring Corinthian leaves; Ionic / Corinthian entablature)
victory figs holding military standards (poles with insignia) @ entrance of arch
coffers in vault

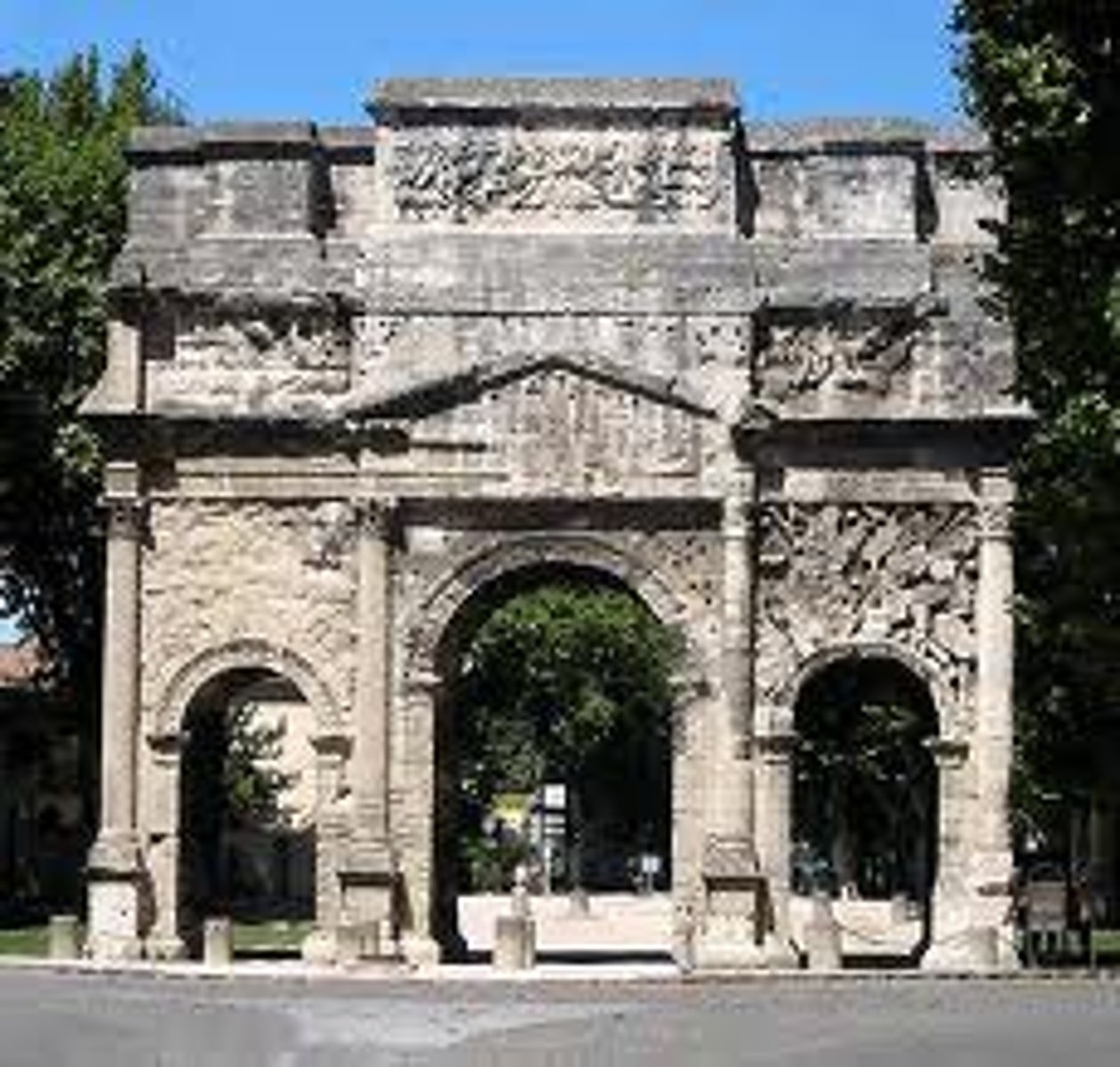
Arch of Tiberius
Orange, France | 26 CE
triumphant arch — celebrate victory over recovering roman standards
reliefs (has more sculptures than usual for romans)
3 arches
Corinthian engaged columns
rome’s arcuated construction + greek order and proportions

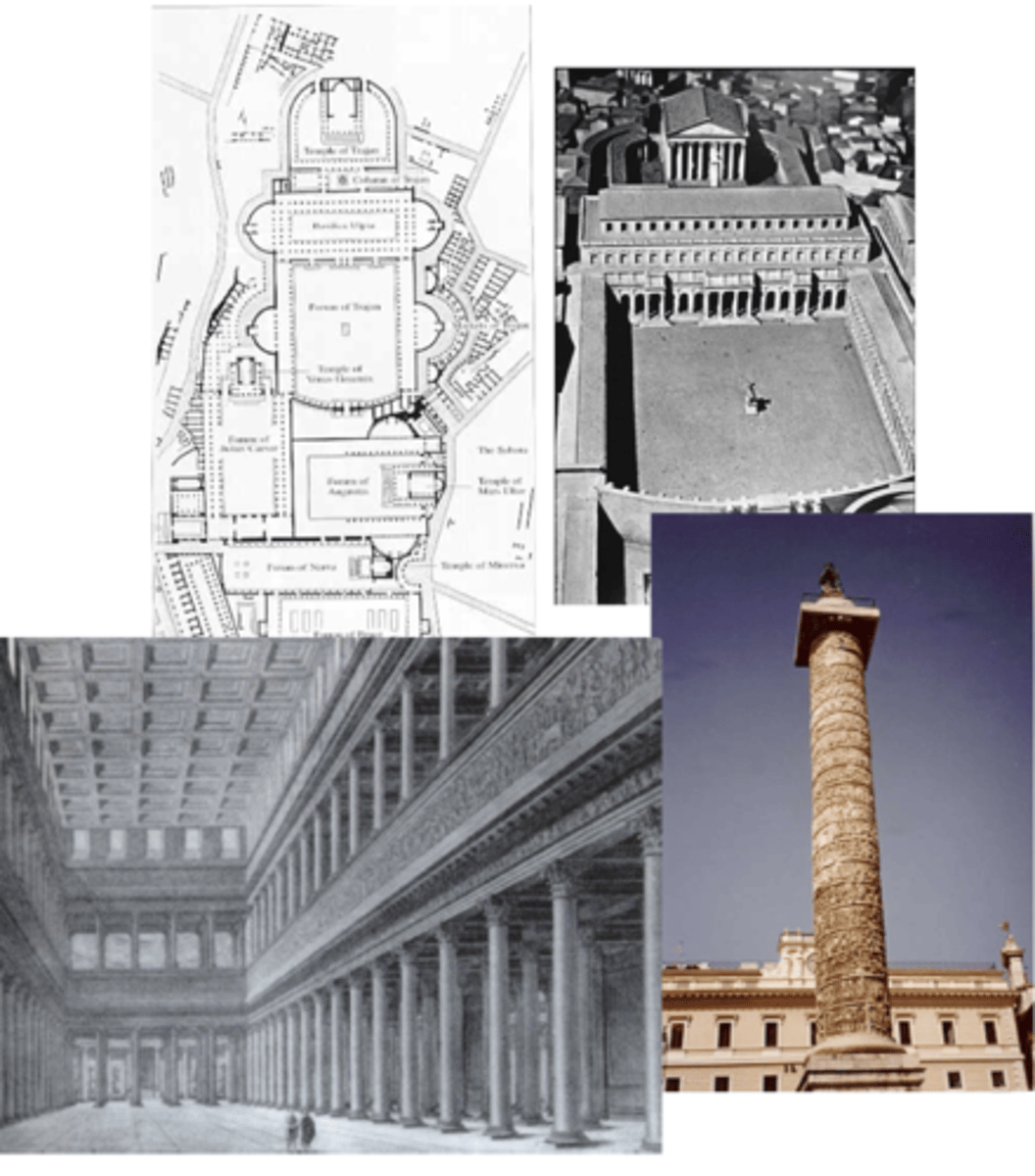
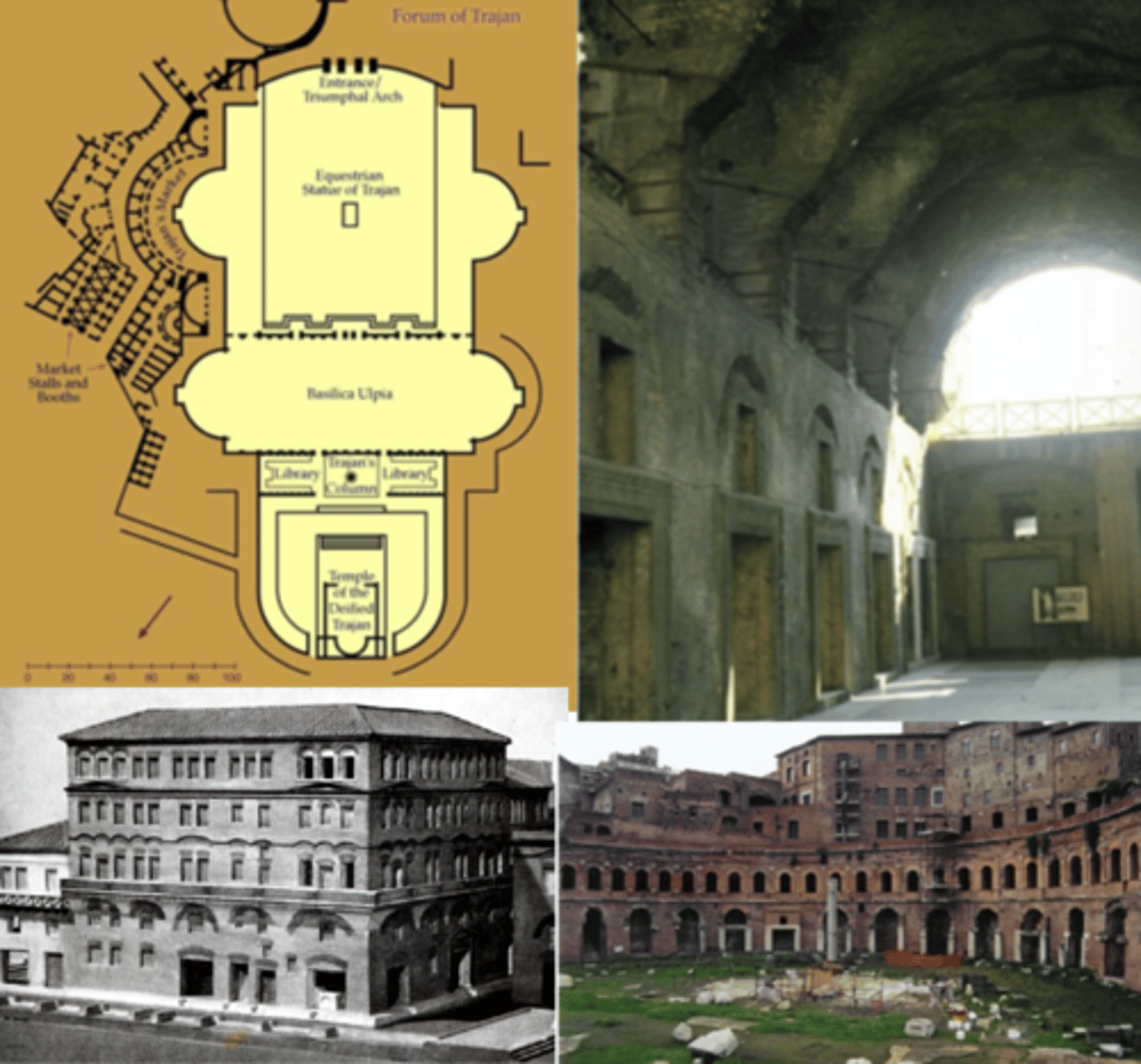
Forum of Trajan
Rome, Italy | 113 CE | Architect: Apollodorus of Damascus (from Greek East)
much larger than other forums
incorporated hemicycles like in other forums
Basilica Ulpia
rectangle-shaped
coffers
2 storey colonnade
clerestory windows
hemicycle
Trajan’s column — commemorates Trajan’s military victory in Dacian wars
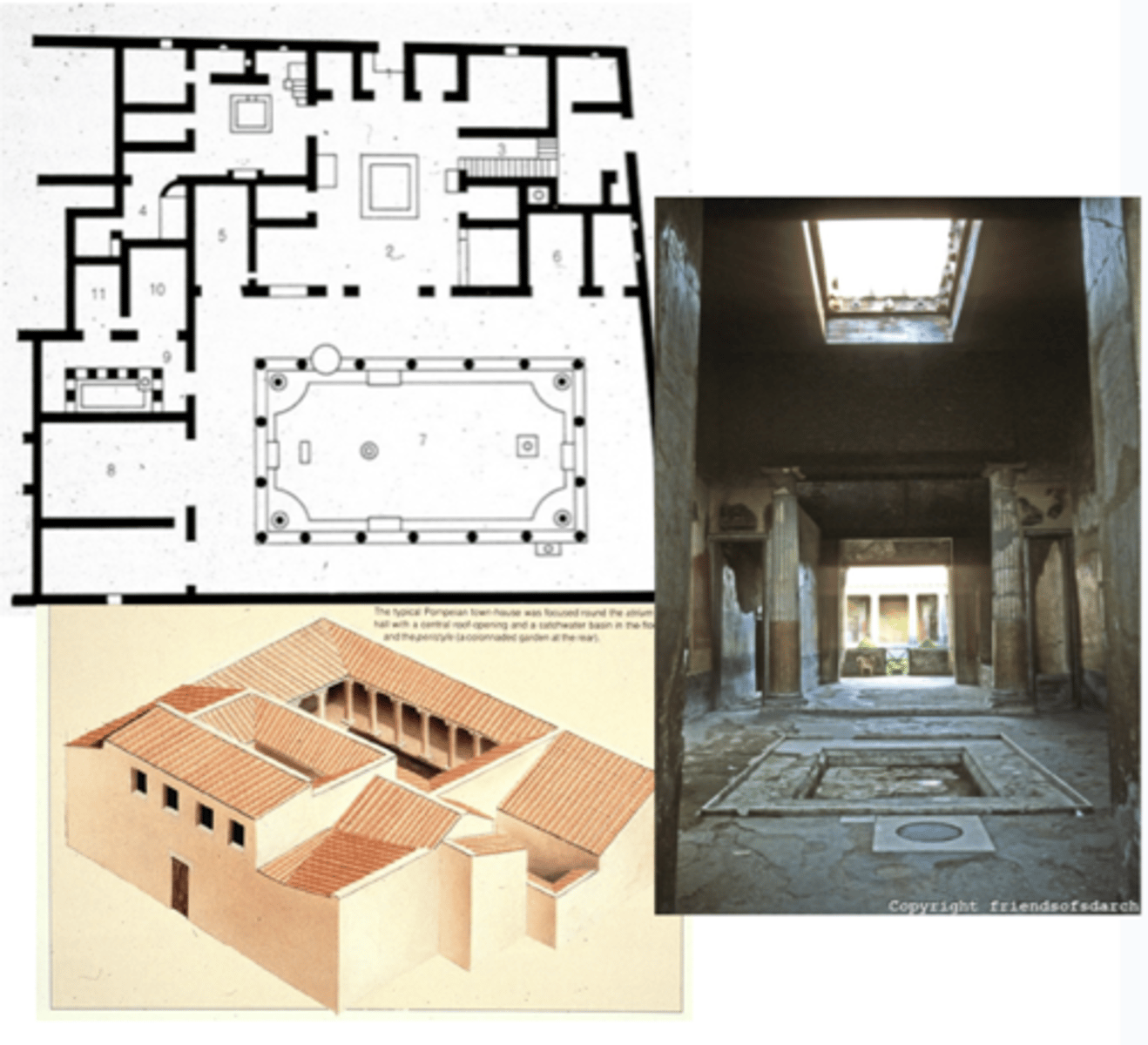
House of the Vettii
Pompeii, early 1st Cent. AD
atrium — central pt w/ opening in roof to collect water
peristyle (row of columns that goes all the way around) garden — filled w/ historical subjects
“tryphe” — Hellenistic luxury; luxurious looking wall paintings in house give illusion of being lavish
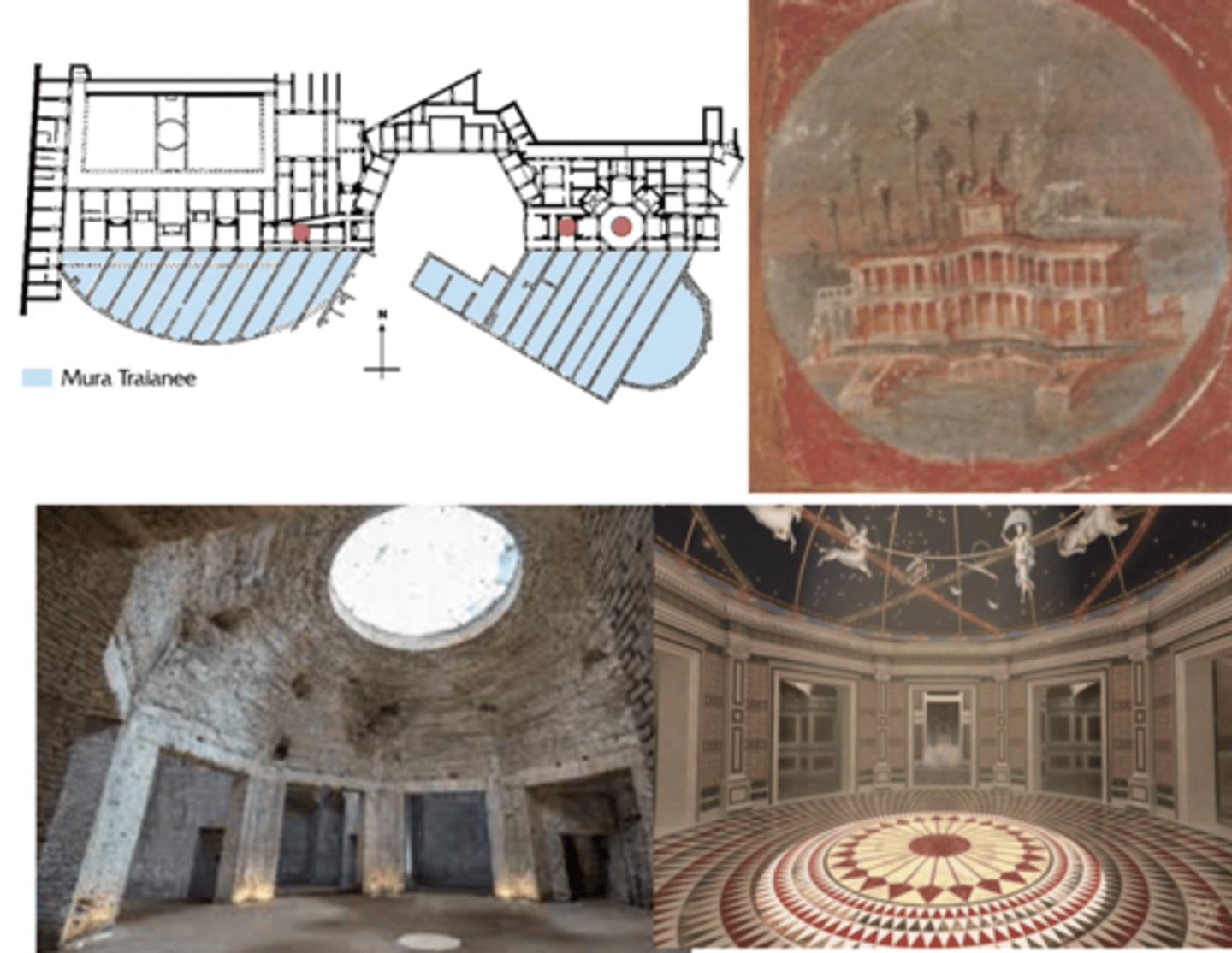
Emperor Nero's Domus Aurea (Golden House)
Rome, 64-68 CE | Architects: Severus and Celer
used pozzuolana (natural volcanic hydraulic cement found near Bay of Naples) to build maritime villa in the middle of the damn city
usually used for underwater construction; ancient roman concrete → Nero exploring using it in big, grand building
overhead lighting through oculus (circular opening in dome)
emphasis on interior space (roman)
wall paintings
marble
big ass statue of Nero (20x bigger than life)
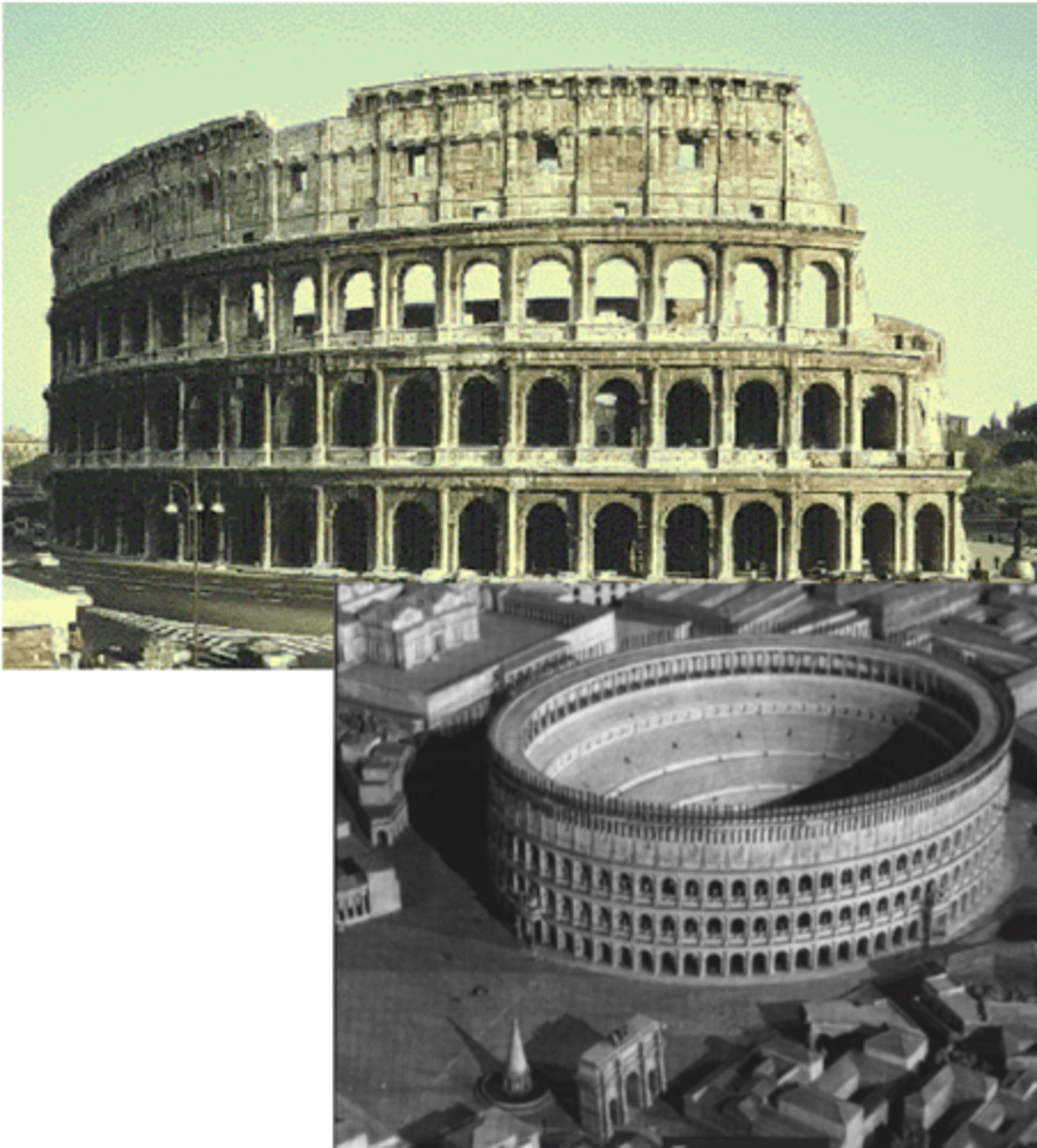
Flavian Amphitheater (Colosseum)
Rome, 70-80 AD
Emperor Vespasian tore down Golden House and replaced with Flavian Amphiteater lol (bc he’s for the ppl)
roman w/ greek skin
arcuated construction
made w/ marble
Trajan's Market
@ Forum of Trajan, Rome | AD 100-112
by the side of one of the hemicycles of Forum of Trajan
multi-storey buildings; shopping mall
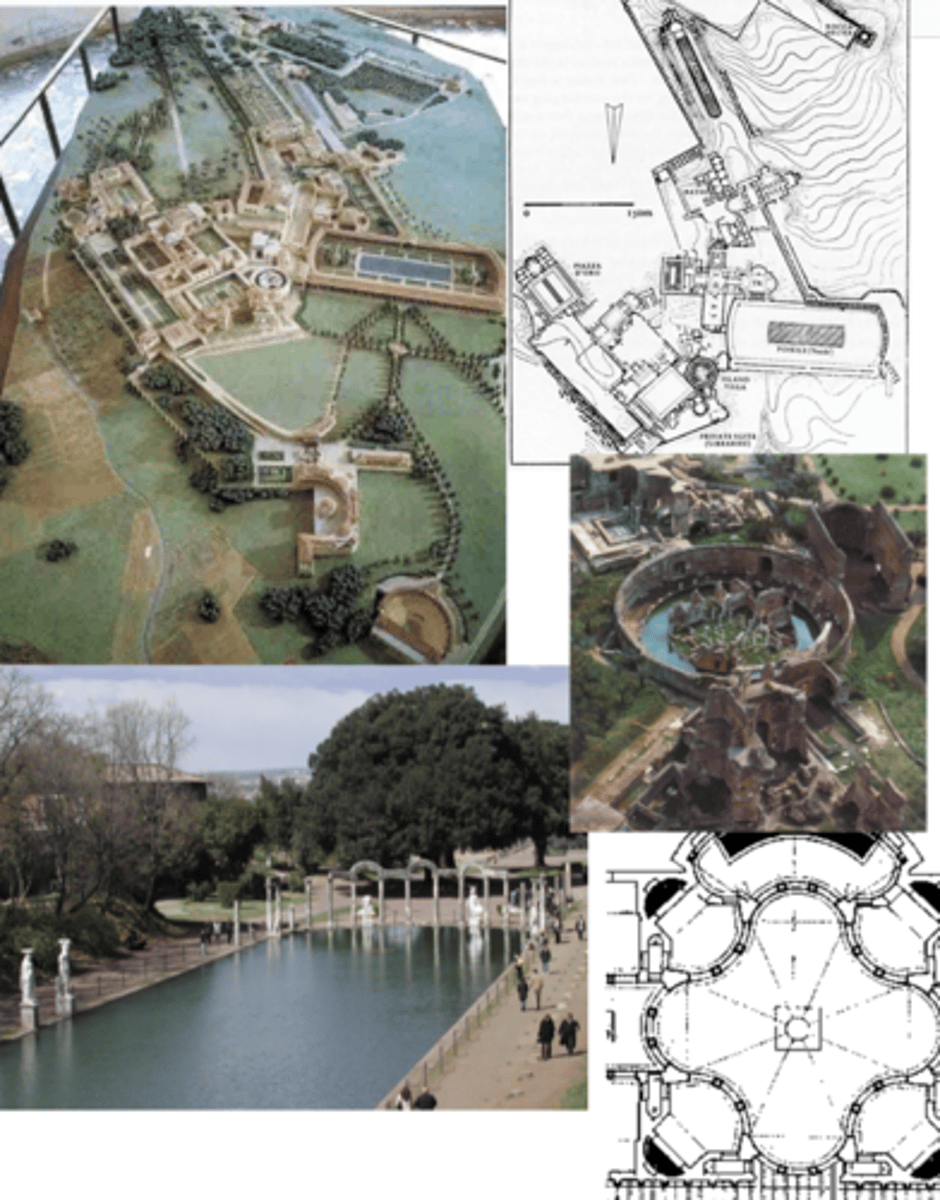
Hadrian's Villa at Tivoli (not in exam ? i think)
Tivoli, Italy | AD 120
canopus
has free-standing columns w/ arches on top as a ‘joke’ catering to ppl who know architecture well
end of canopus — pumpkin vaults
dining hall
baths
maritime theatre
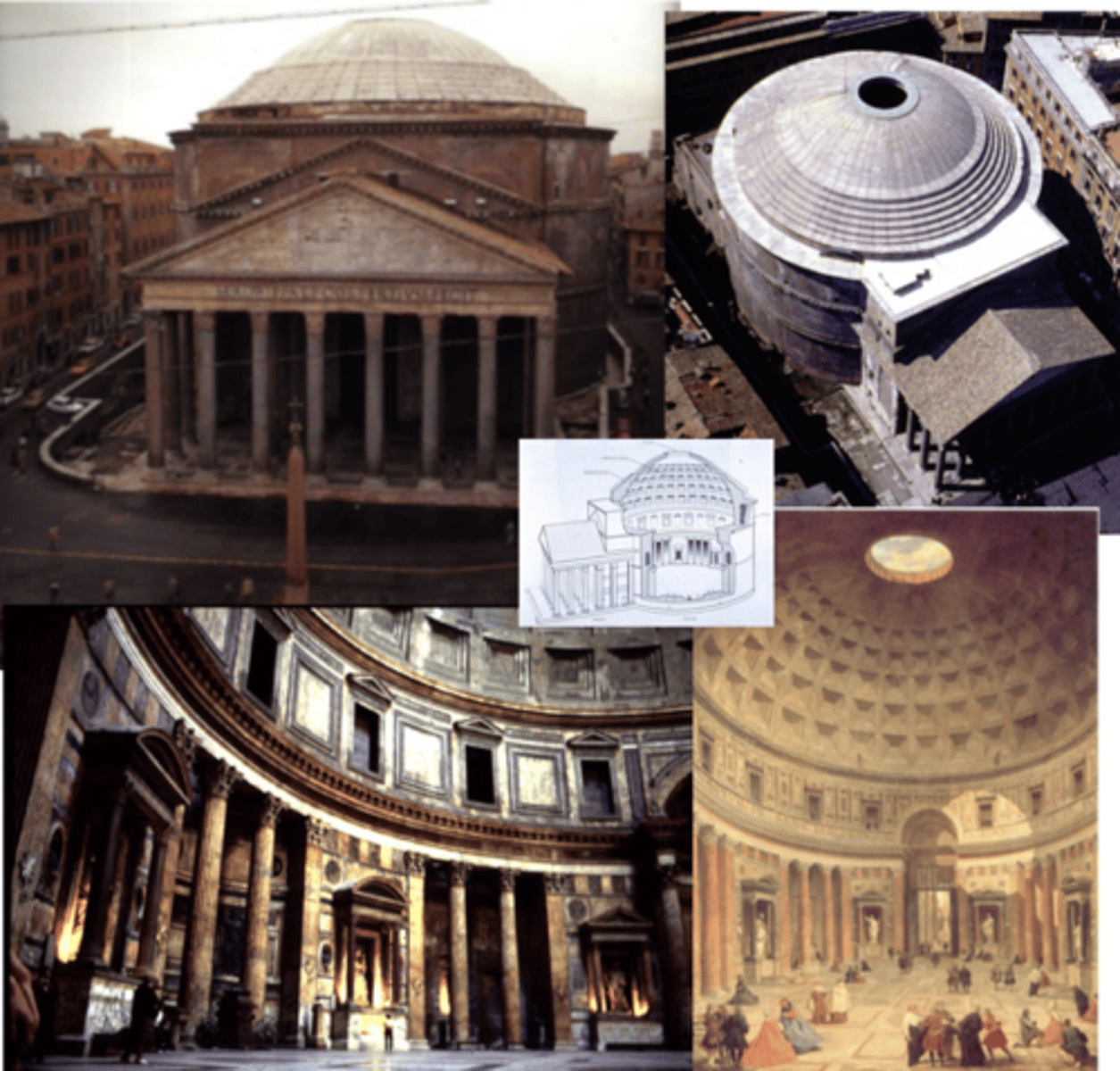
Pantheon
Rome, Italy | 118-128 AD | built by Emperor Hadrian
marble Corinthian capitals, granite columns
element of surprise — going from columns @ entrance → giant dome w/ interior emphasis
oculus (circular opening) @ roof of dome
built on travertine base; materials get lighter as we go up
Baths of Caracalla
Rome, AD 216-216
brick and concrete
has shopping area, place to exercise (NAKED!!!)
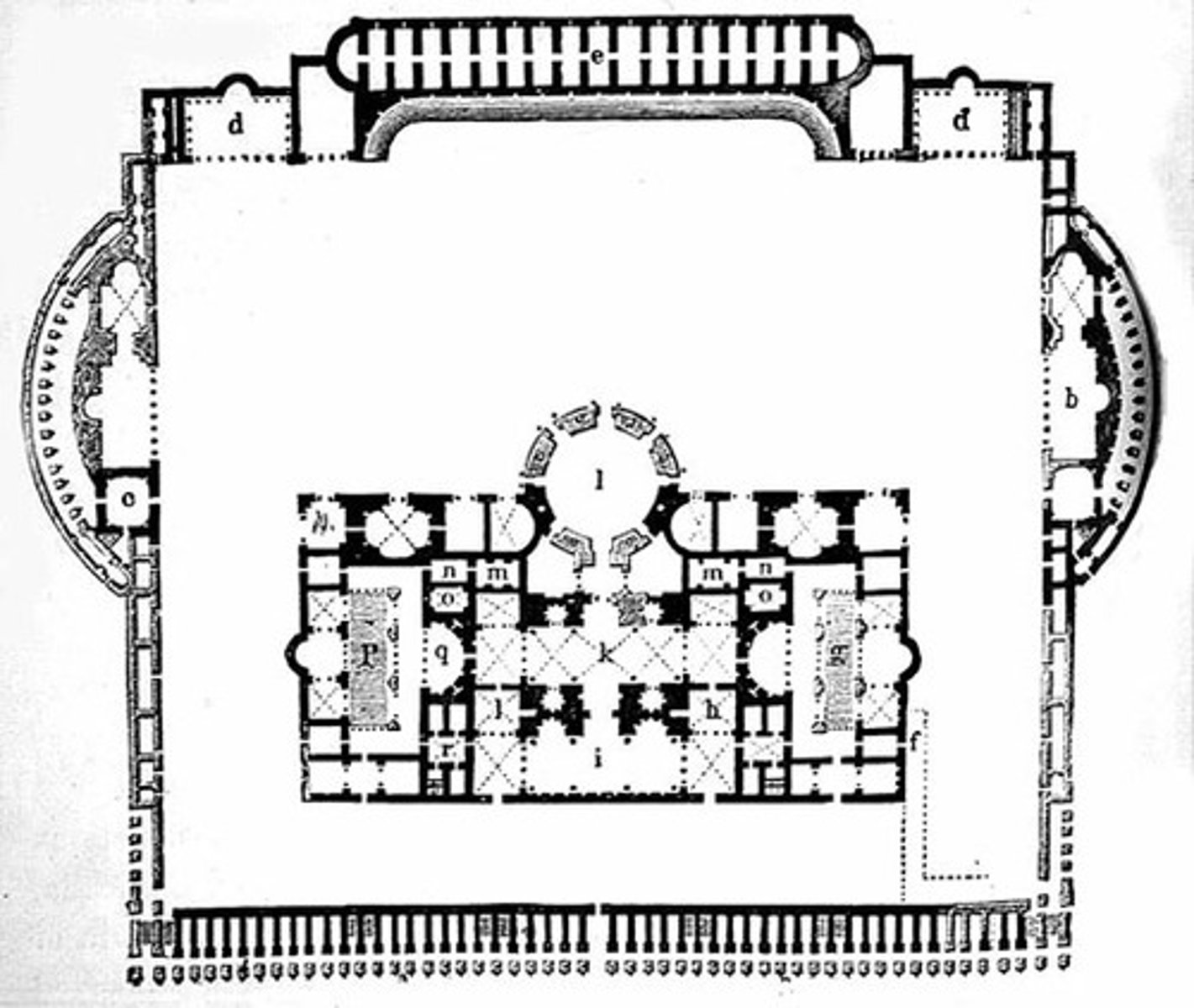
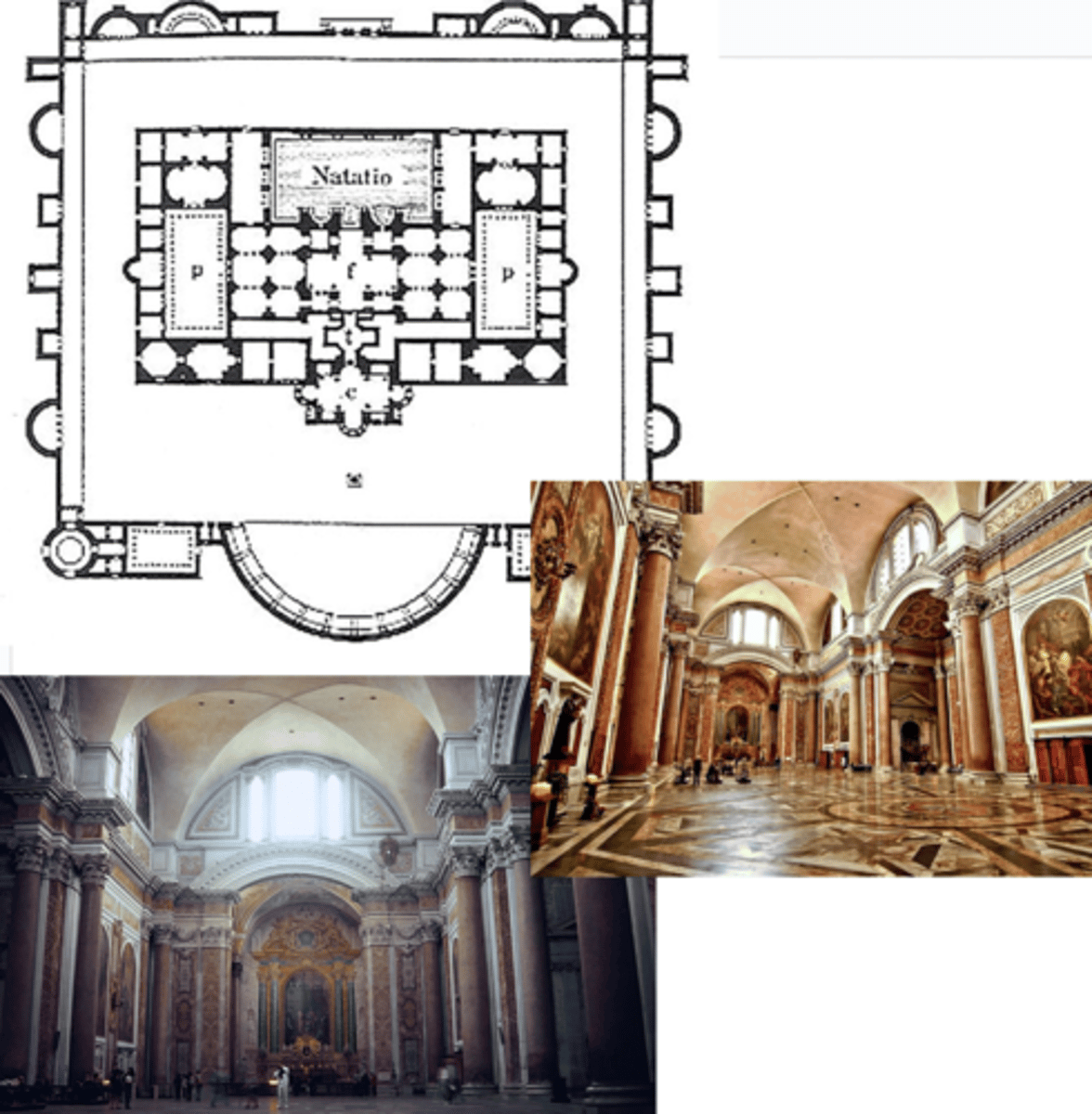
Baths of Diocletian
Rome, 298-306 CE
roman features
axiality / symmetry
interior emphasis
hemicycle / exedra
place for cultivated entertainment and exercise (shops, refreshments, concert hall etc.)
caldarium, frigidarium, temperatureum (pools of varying temps.)
groin vaults, windows act as vents (clerestory windows)
columns made of monolithic granite from Egypt
coffers pattern on ceilings; covered w/ plaster and stucco
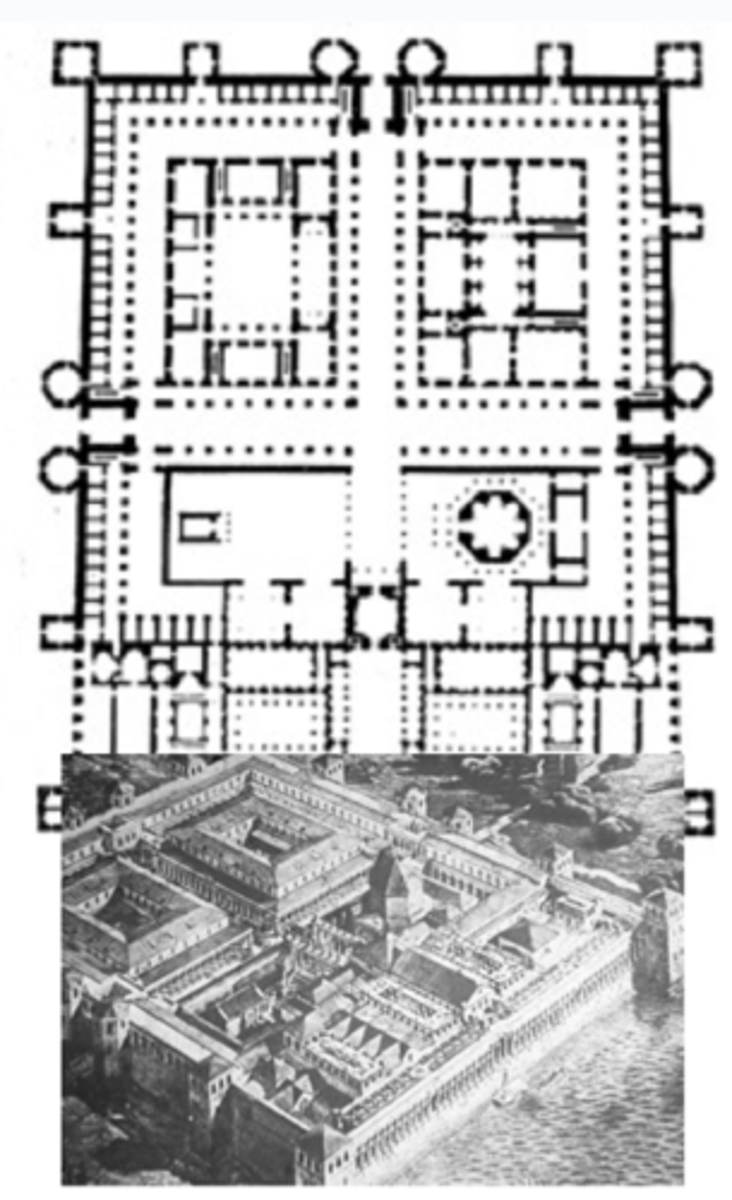
Dioceltian's Palace at Split (not in exam 1)
Basilica of Maxentius (not in exam 1)
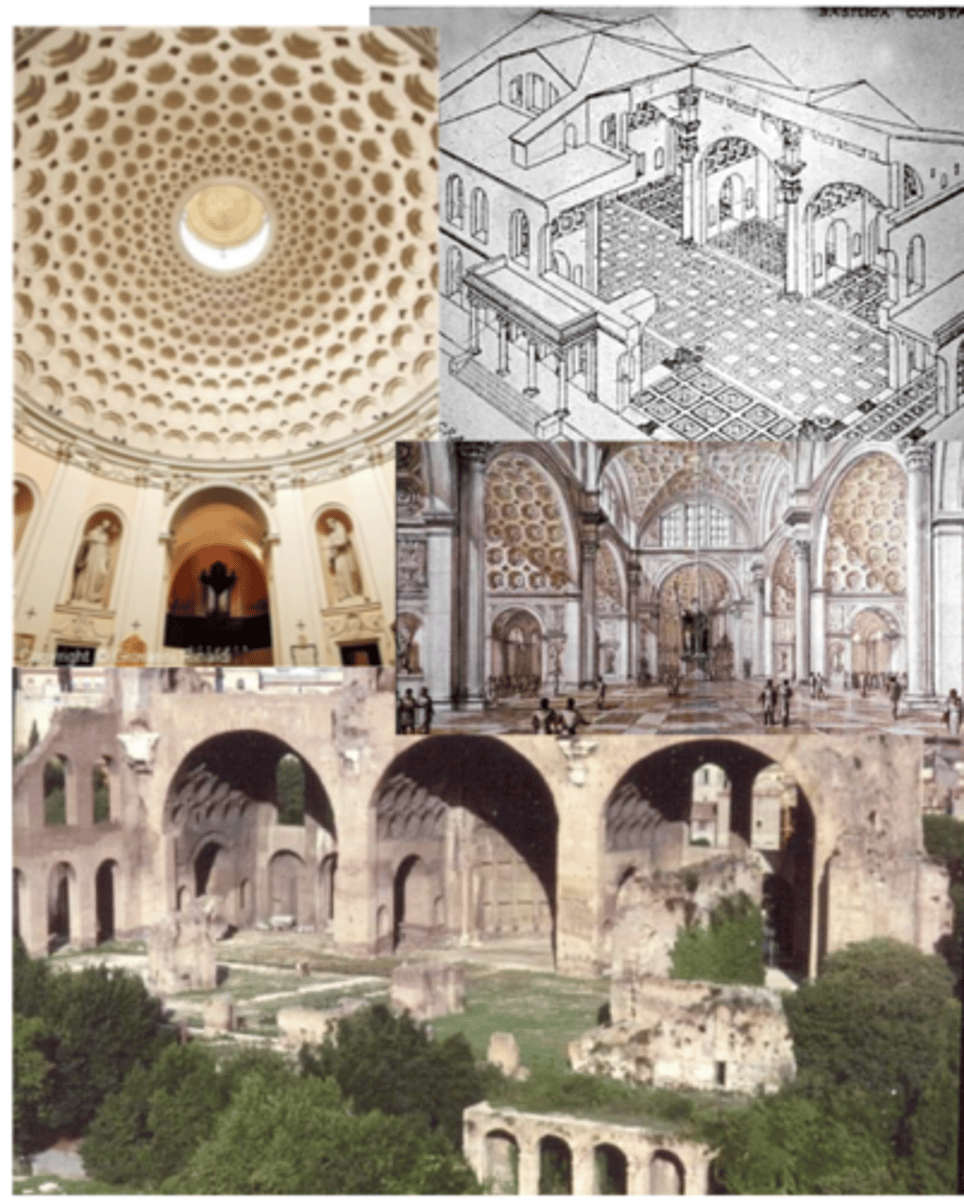
Arch of Constantine (not in exam 1)

Santa Costanza (not in exam 1)

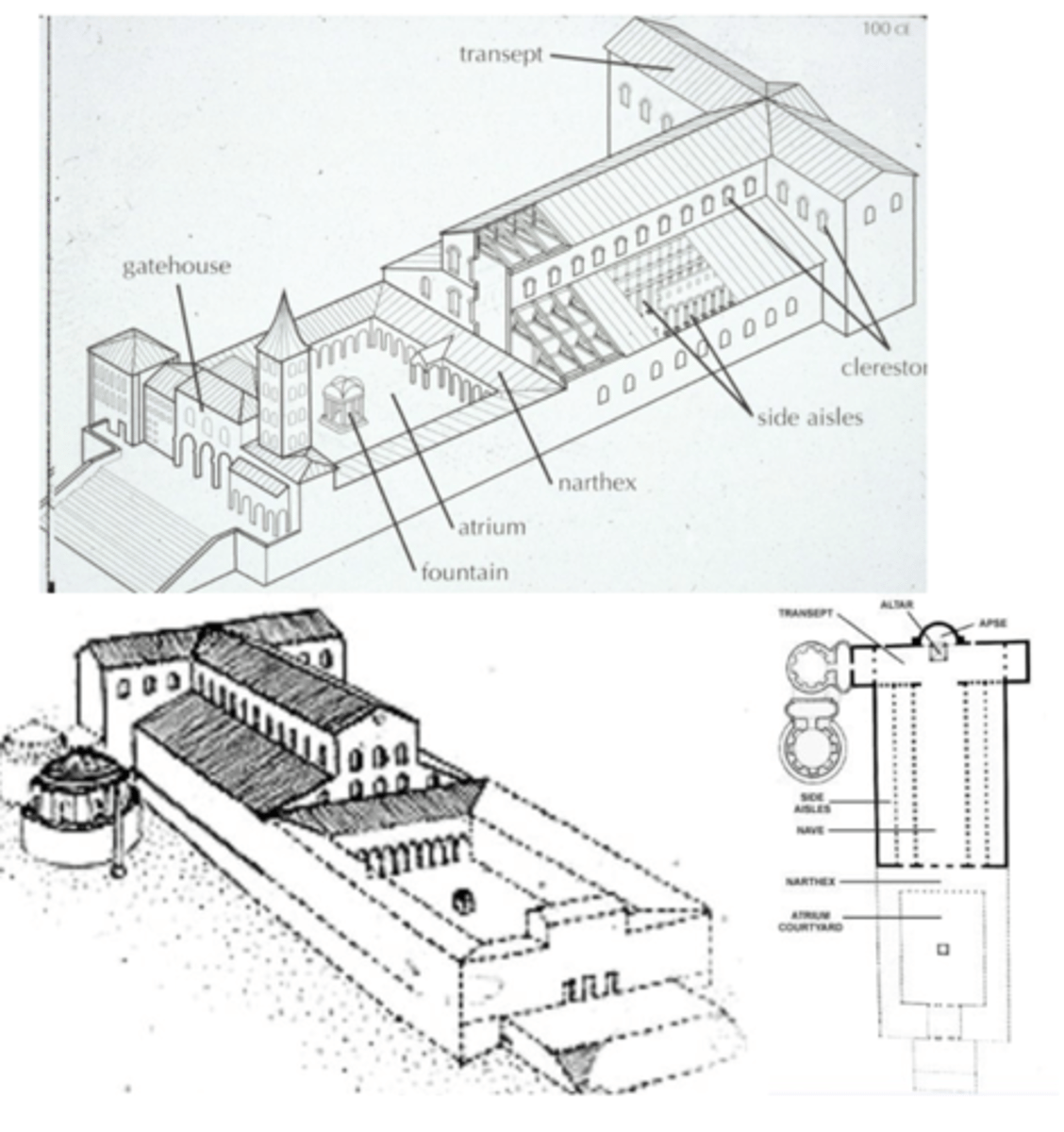
Old St. Peter's Basilica (not in exam 1)
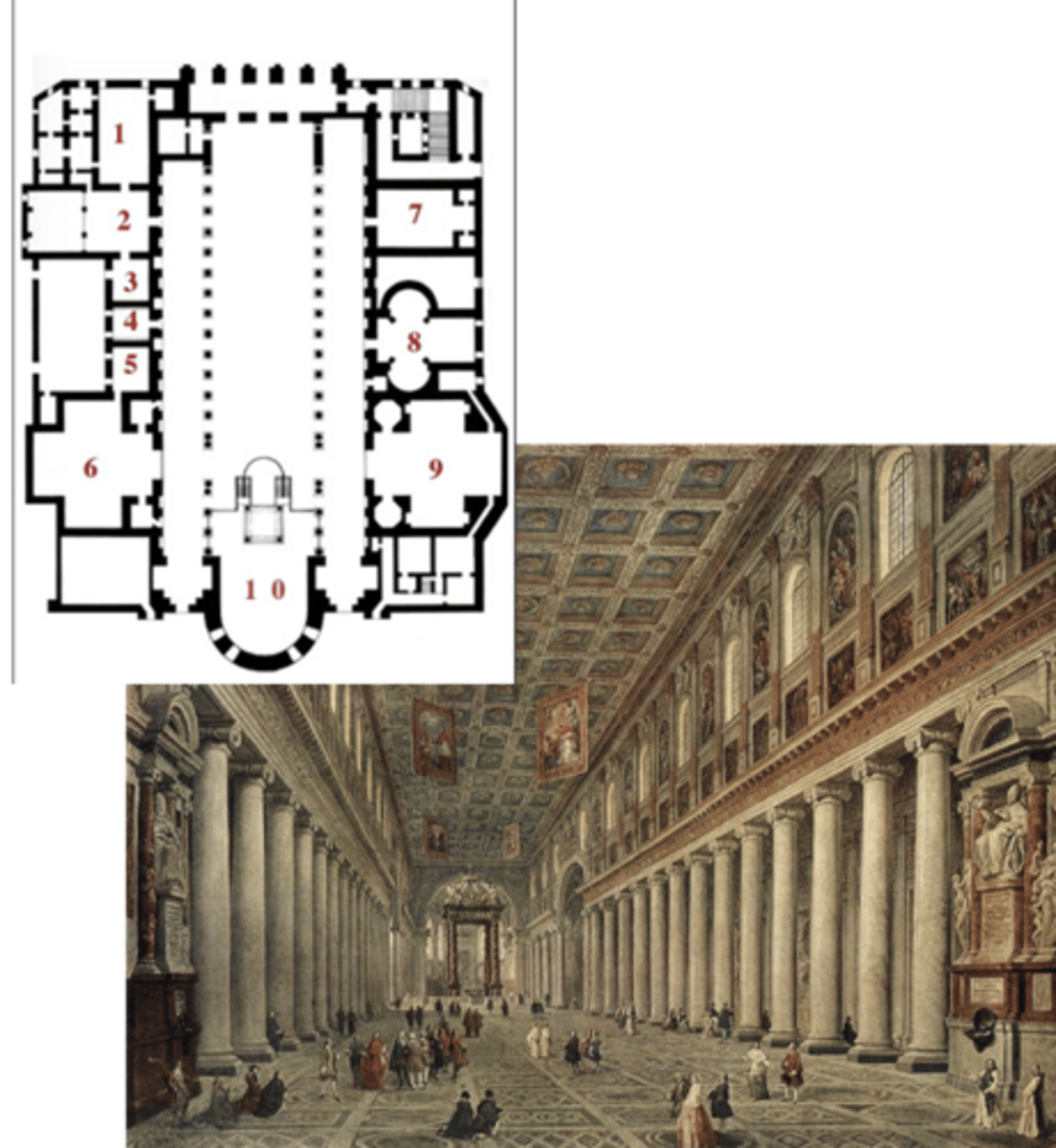
St. Maria Maggiore Basilica (not in exam 1)
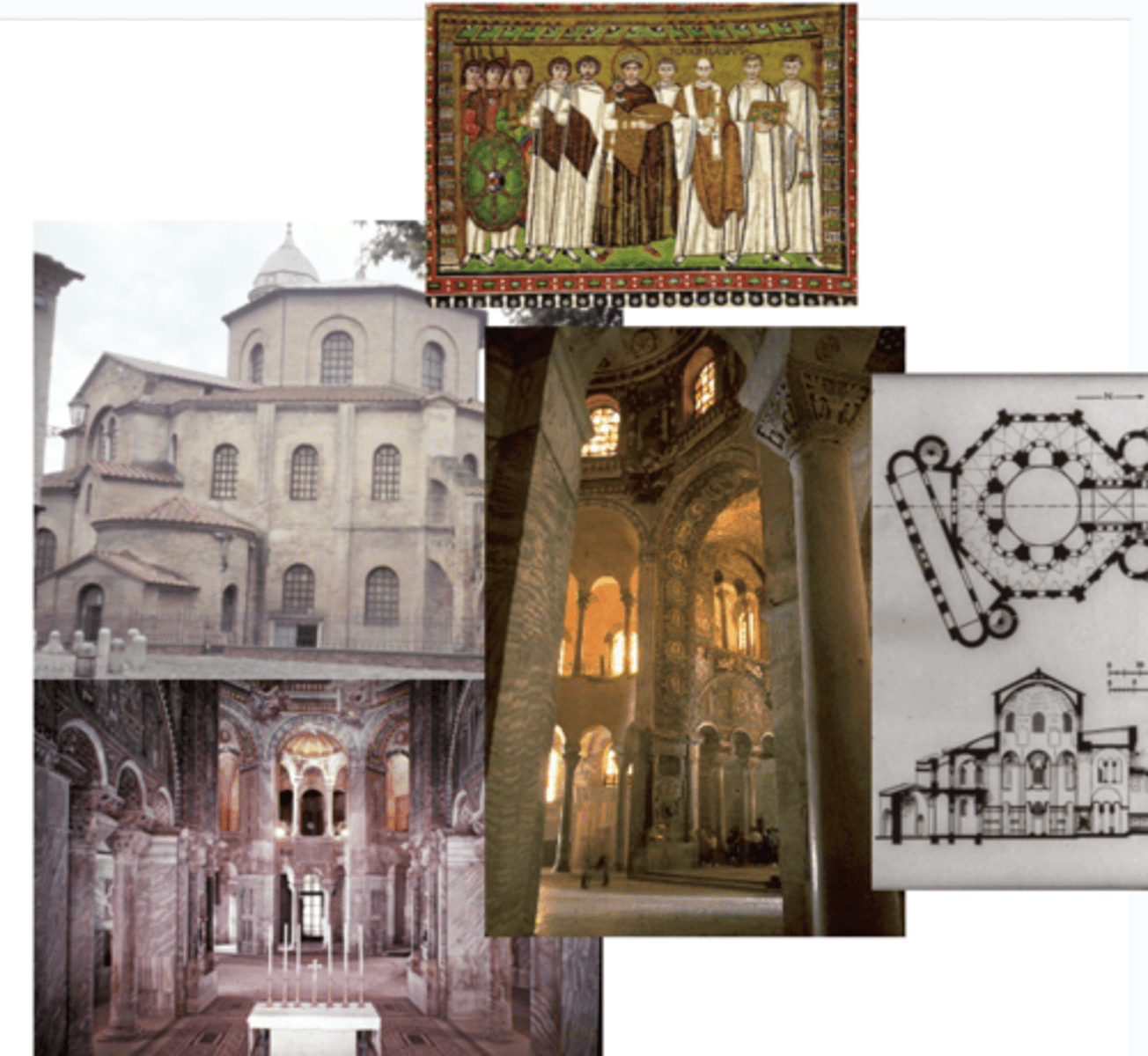
San Vitale (not in exam 1)
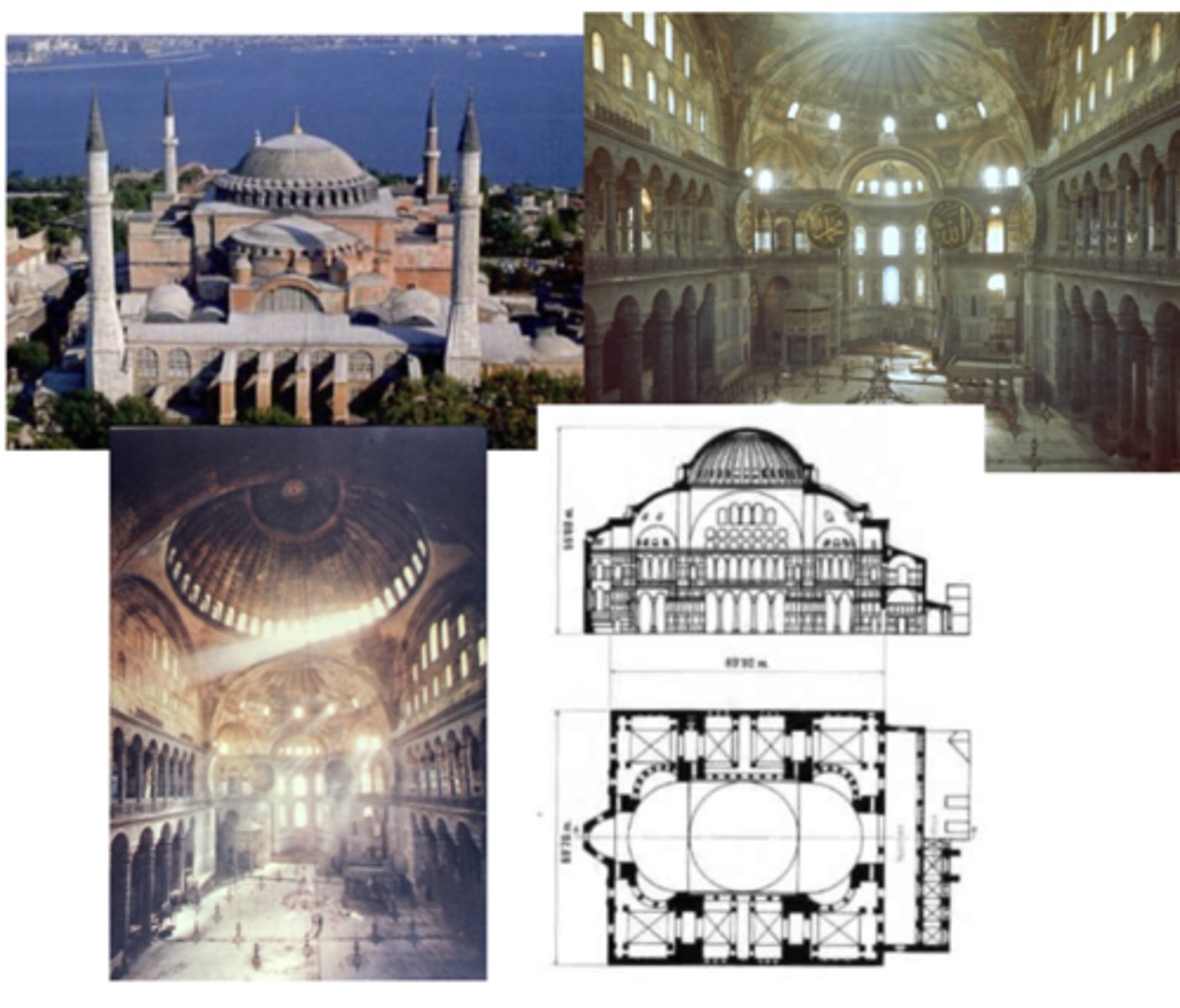
Hagia Sophia (not in exam 1)
Greek architecture
exterior emphasis (mass)
trabiated (post and lintel)
use natural disposition in landscape
greek orders
doric
ionic
corinthian
Roman architecture
interior emphasis (space)
arcuated (arch and vault)
Etruscan (frontal emphasis, raised on podium) + Hellenistic (orders and proportion) influences
masonry combi. w/ concrete
use of concrete — triumphing over adversities of nature
axiality and symmetry
order (trabiated form) applied to arcuated structure
ambivalent attitude to Greek culture (lowkey admired it and took inspo but acted like they viewed them as weak, effeminate, frivolous)
Hellenistic architecture
combines a lot of features from Greek and Egyptian architecture
communal architecture (temples)
mixing of orders — relaxation of canonical use
orthagonal town planning — grid like
ethos → pathos (sadness that comes from extreme exp; suffering)
Late classical architecture
royal architecture (tombs and palaces) — eg. Parthenon, Mausoleum of Halicarnassus
Roman town houses and villas
Pompeii
Roman town houses (“domus”)
eg. @ St of Abundance
lined w/ multi-storey buildings (bars, shops, etc.)
brick-faced concrete covered w/ plaster and decor
Roman villas (aka vacation houses)
@ countryside or seaside (maritime)
pastoral poetry — vision of life in countryside that wasn’t accurate to reality (villa urbana vs villa rustica)
ppl built villas based on these rich ppl views of countryside → roman villas
Civil Wars between Octavian and Ceasar’s enemies, and later between Octavian and Marc Anthony
Battle of Actium 31 BCE
Octavian become “Imperator” — Emperor Augustus 27 BCE, rules until 14 CE
Octavian (Caesar’s great nephew) — forms alliance w/ Marc Anthony post-Caesar assassination
start civil wars against enemies
Octavian avenges Caesar; kills assassins in 42 BC
Octavian and Marc Anthony basically divorce
Marc gets tgt w/ CLEOPATRA @ Egypt (who btw had a love affair w/ Caesar)
Battle of Actium (31 BCE) → Octavian defeats Marc + Cleopatra; ends civil war
Octavian becomes “Imperator” aka Emperor Augustus (27 BCE; rule until 14 CE)
Rome becomes monarchy (roman republic → roman empire)
builds Forum of Augustus (+ Temple of Mars Ultor)
Julius Caesar
assassinated 44 BCE
common ppl loved him for enacting reforms serving their interests (eg. restoring buildings like basilicas @ Roman Forum)
but feared and hated by ruling elite / ppl w/ power
entasis, stylobate, cella (naos) and peripteral colonnades
entasis — column diameter widest @ bottom, then taper as it reaches the top; corrects optical illusion of concavity from straight columns
anthropocentric view — reflects the weight distribution of how humans would carry weight (heavier @ bottom)
stylobate — upper steps to the temple
cella (naos) — inner chamber of temple
peripteral colonnades — 1 row of columns around naos
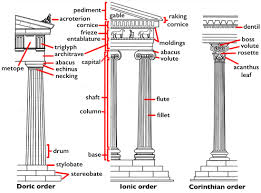
dipteral (double; 2 rows of columns around naos) colonnade orders
Doric
the simplest of the classical Greek architectural styles
unadorned columns with no base
fluted column shaft
Ionic
capitals with volutes (spiral scroll-like ornaments)
fluted columns, but deeper; meet @ smooth joint (fillet)
large base
Corinthian
Most ornate of the orders
a base
fluted column shaft
capital is elaborate and decorated with acanthus leaf carvings
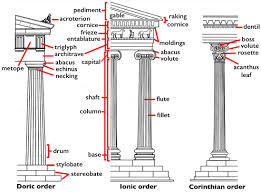
entablatures
frieze — made up of triglyphs and metopes
architrave — blank part
cornice — frame

pediment
pediment — triangle that features free standing, over-life-sized marble sculptures; basically a void since there’s no symbolism to them, just happen when built
painted/colored (polychrome) — red, blue, yellow
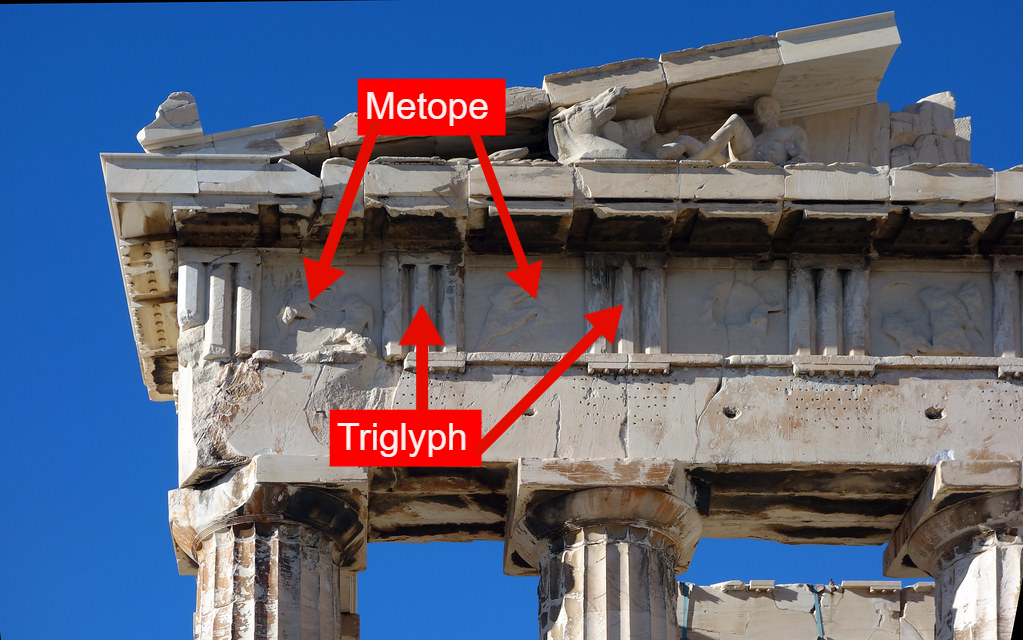
triglyphs and metope
triglyphs — vertical rectangles with grooves in them; kinda filler
metope — squares that can be decorated with painting or reliefs (molds in terracotta or carved into limestone / marble)
Hellenistic Civ. after Macedonian conquest of Philip of Macedon and Alexander the Great
Philip of Macedon (conquests of Greek world 359-336 BCE)
bro wanted to be Greek so bad (he’s actually Macedonian; couldn’t speak Greek)
Alexander the Great (died 323 BCE)
Philip’s son
REMEMBER 35(9), 33(6), 32(3) 9 6 3!!
Battle of Issus
333 BCE
battle between Alexander the Great (Macedonians) and Darius III of the Achaemenid Empire (Persians); part of Alexander’s conquest of Asia
From Polis to Cosmopolis
post-Alexander the Great’s death — Classical Greek period (polis) → Hellenistic period (cosmopolis)
Persian Wars
490 BCE (Battle of Marathon)
480 BCE (Battles of Thermopolae and Salamis)
479 BCE (Battle of Plataea)
490 marinara — marathon
480 thermometers and salami — thermopolae and salamis
479 plates — plataea
Delian League
Athenian hegemony (dominance of one grp above others) in Greece
Athens
Pericles (Strategos)
leader of the Athens
there was a democracy tho — council of 500