Resin-based Composites Restorative Materials
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
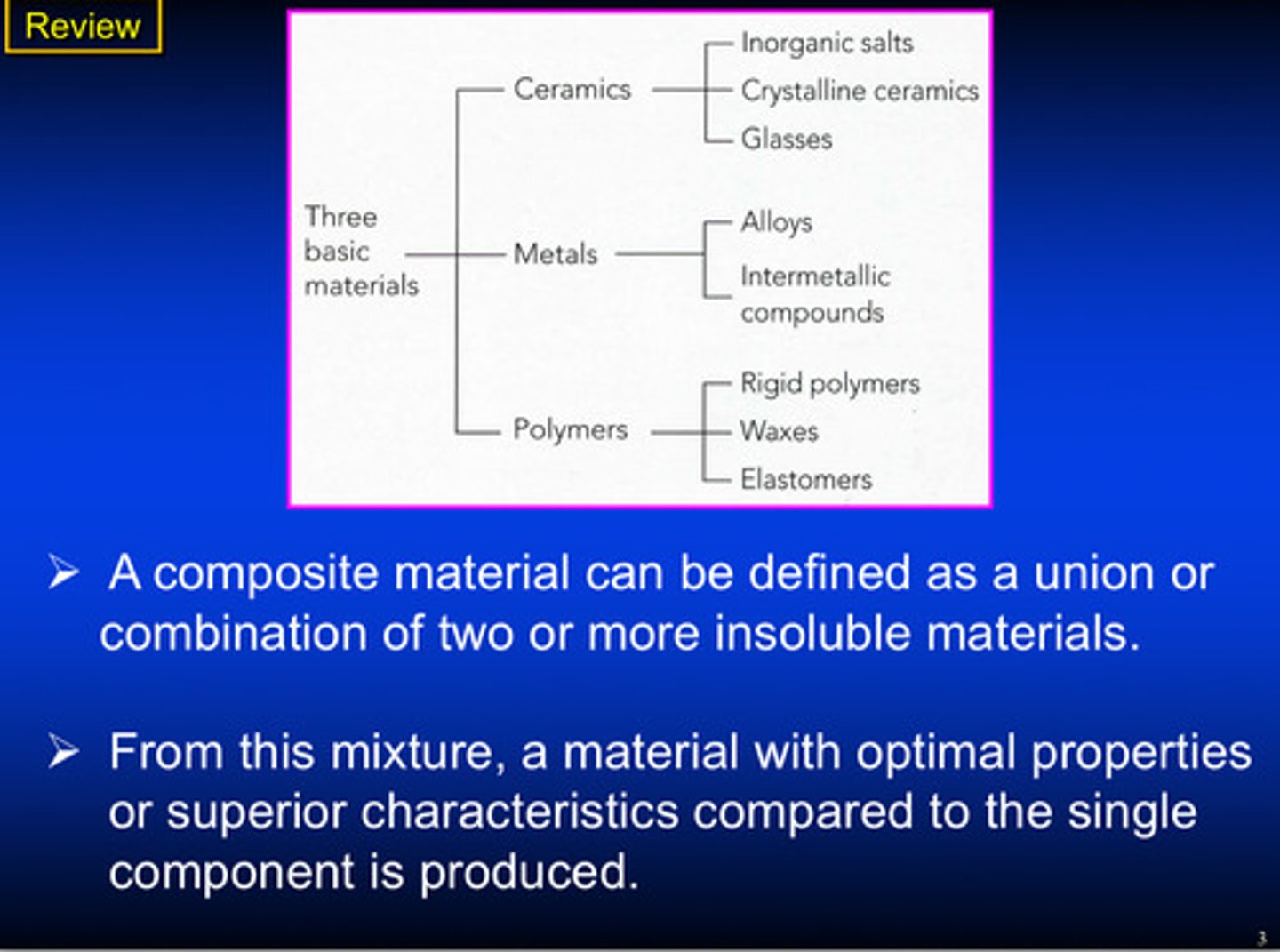
what is a composite material and what is produced from this mixture
A union or combination of 2 or more insoluble materials (from this mixture, a material with optimal properties or superior characteristics compared to the single component is produced)
what 2 things comprise dental resin-based composite (RBC)
organic resin matrix + inorganic filler particles

look at the from prep to polish slides again! slides 5-10
woohoo
application of dental composite to final result image
woohoo
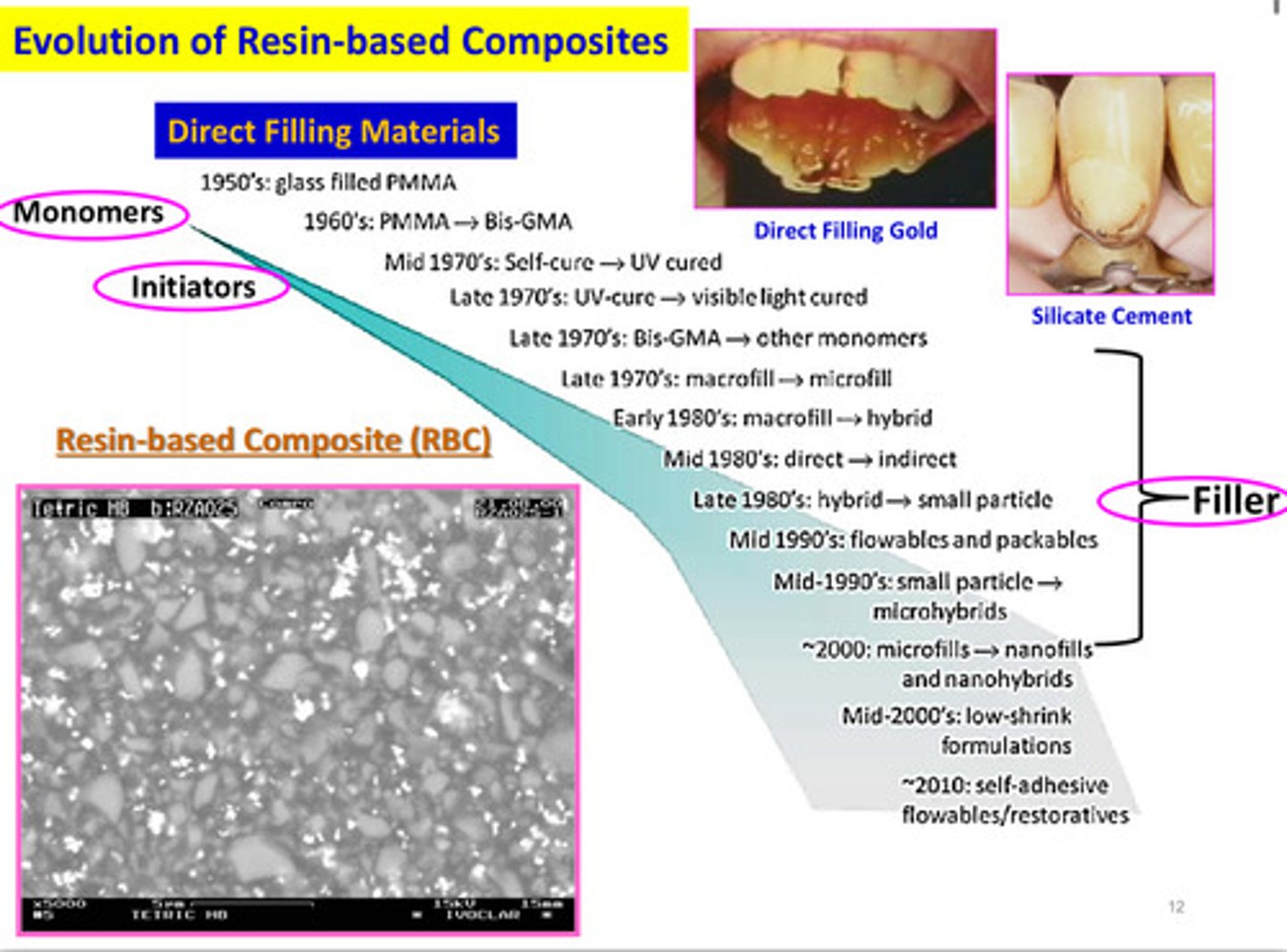
evolution of resin based composites
first just used monomers, then started to add initiators, and finally added filler in order to make modern day composites
what is PMMA, polymethyl methacrylate and when was it introduced
unfilled resin; introduced in the late 1940s to replace silicate cement
describe the 9 characteristics of unfilled resin
1) increased polymerization shrinkage
2) increased coefficient of thermal expansion
3) increased water absorption
4) increased solubility
5) decreased color stability
6) decreased surface texture
7) decreased wear resistance
8) decreased modulus of elasticity
9) decreased radiopacity

what is the method of polymerization of unfilled resin?
chemical-cured
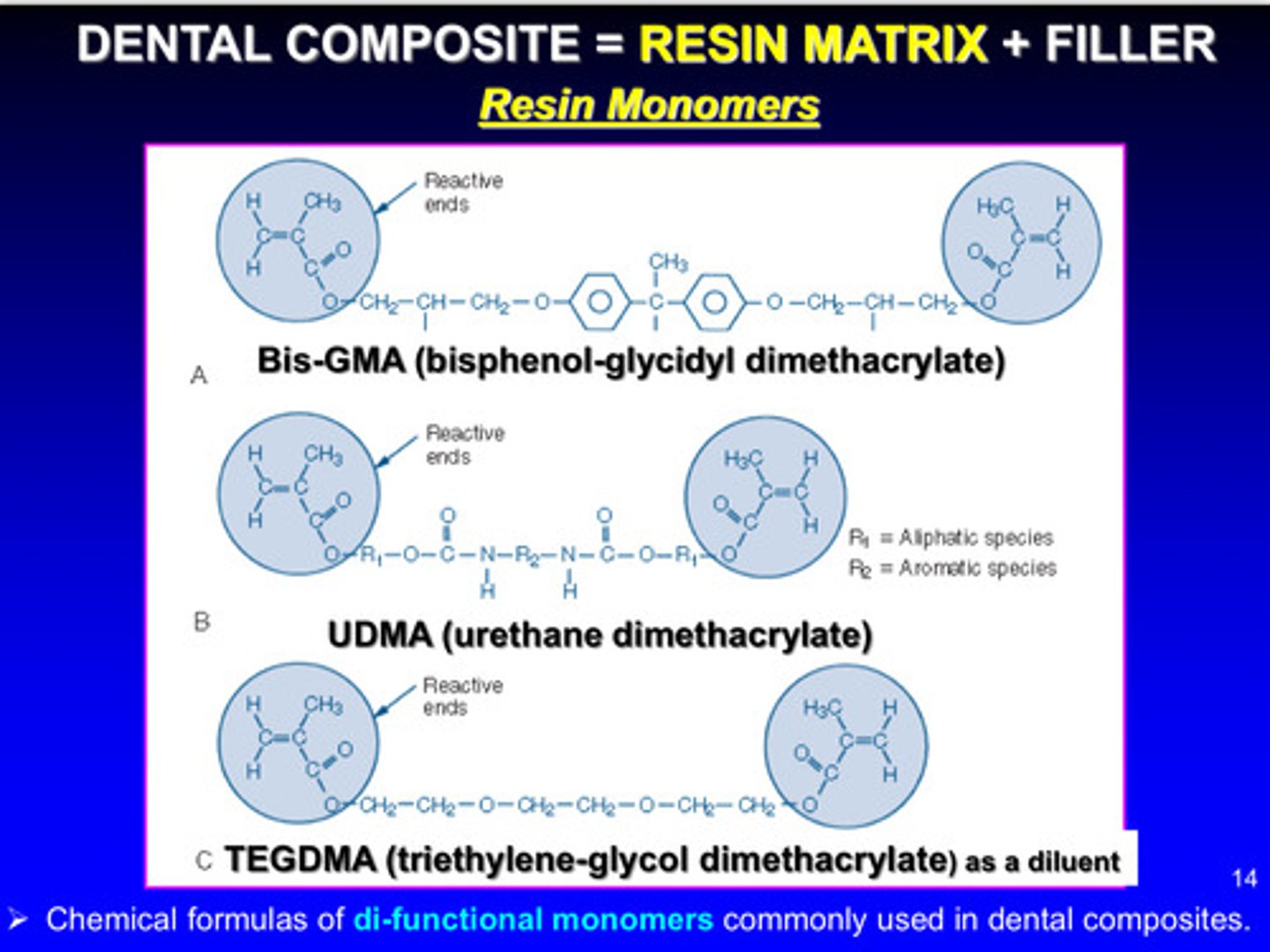
dental composites = resin matrix + filler; what are some commonly used resin matrices in dental composites
Bis-GMA, UDMA, TEGDMA: chemical formulas of di-functional monomers are commonly used in dental composites
these monomers have unsaturated double bonds on either end of the structure (allows them to react via free radical addition polymerization)
resin-based composite = resin matrix + inorganic fillers; what are some commonly used filler systems
1) silica, highly dispersed
2) barium glass
3) Ba-Al-fluorosilicate glass
4) mixed metallic oxide
5) yttrium fluoride
6) zirconia
7) hydroxyapatite

images of inorganic fillers: porous, friable nano-clusters vs solid particles
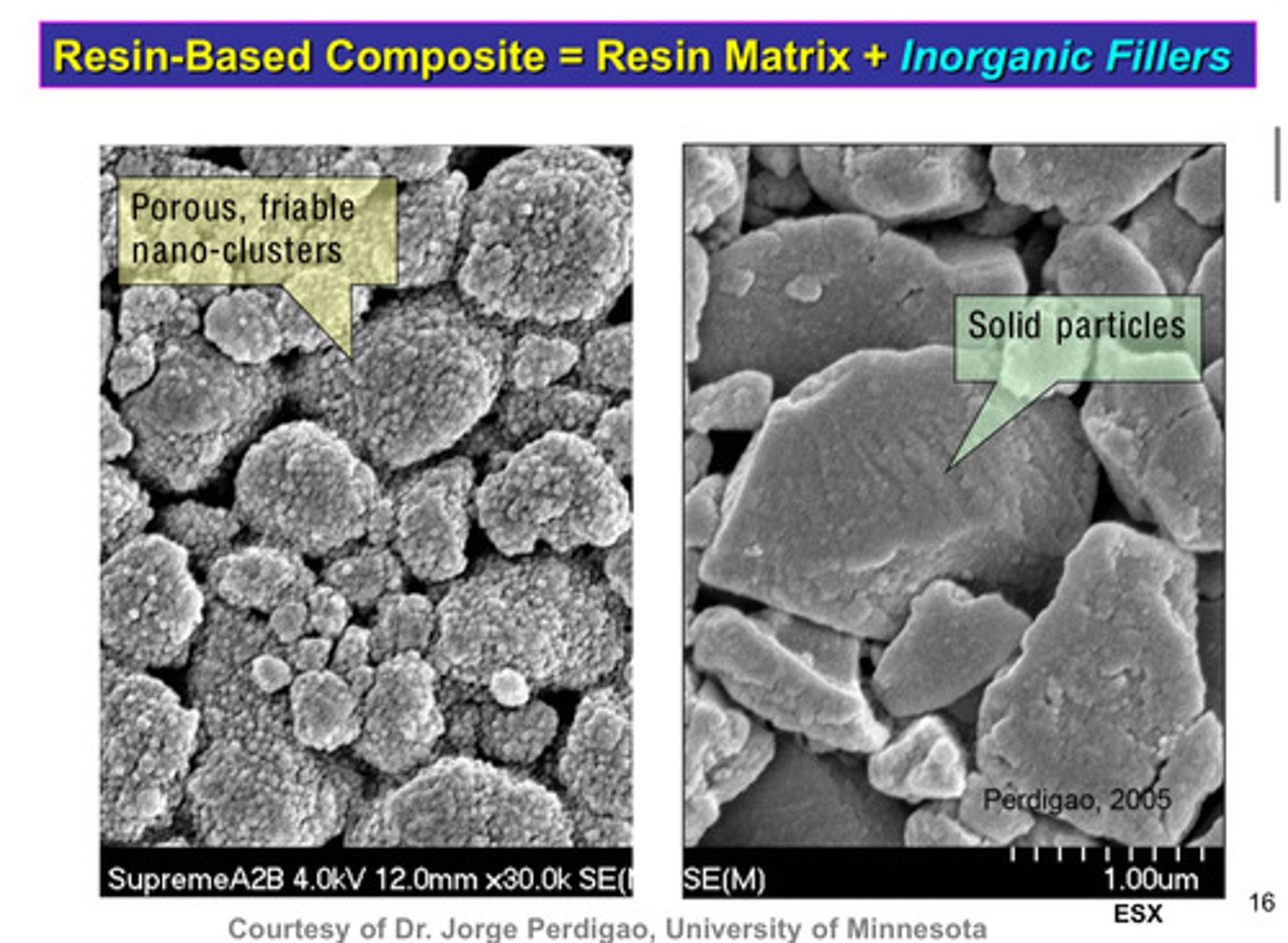
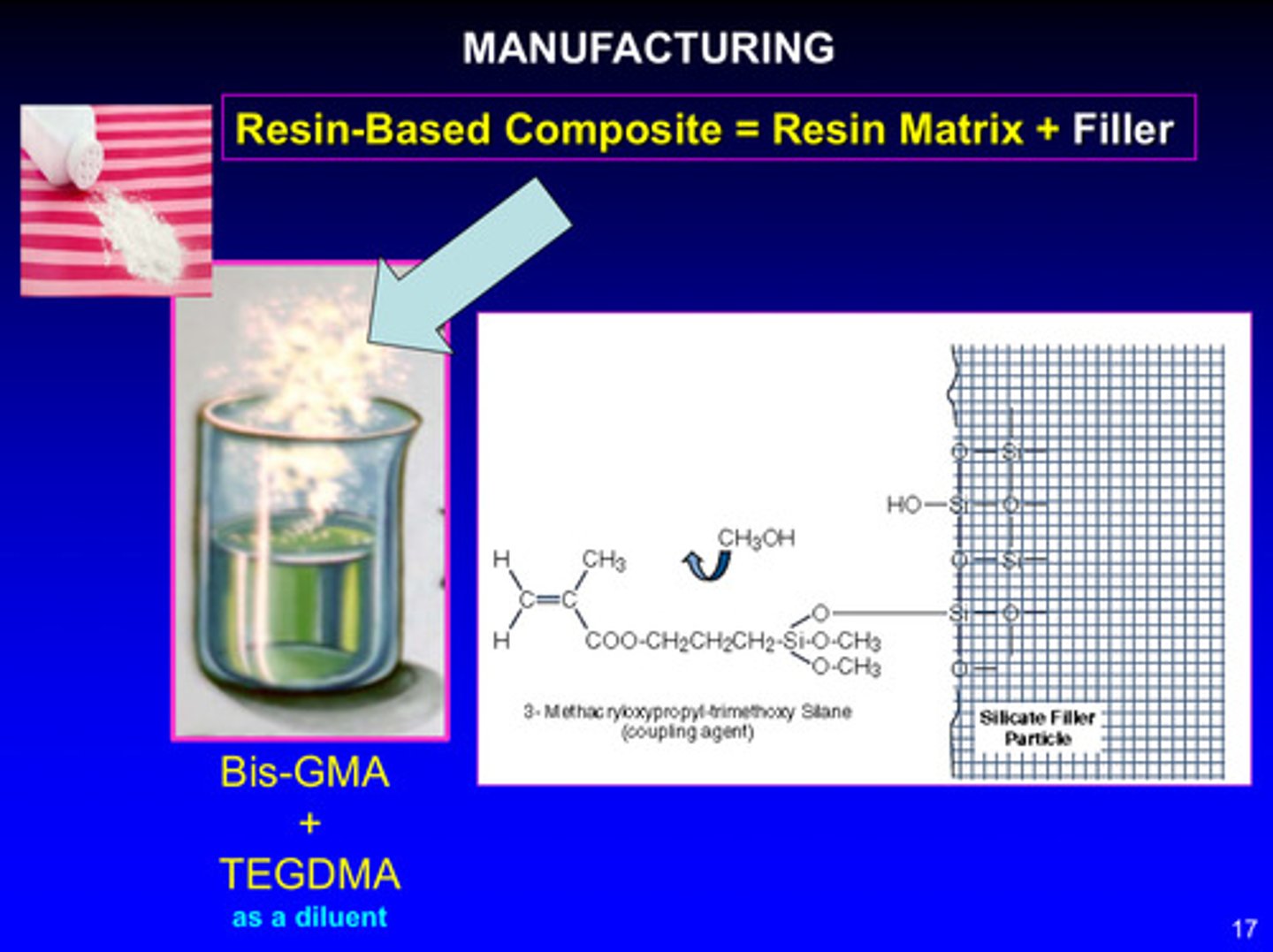
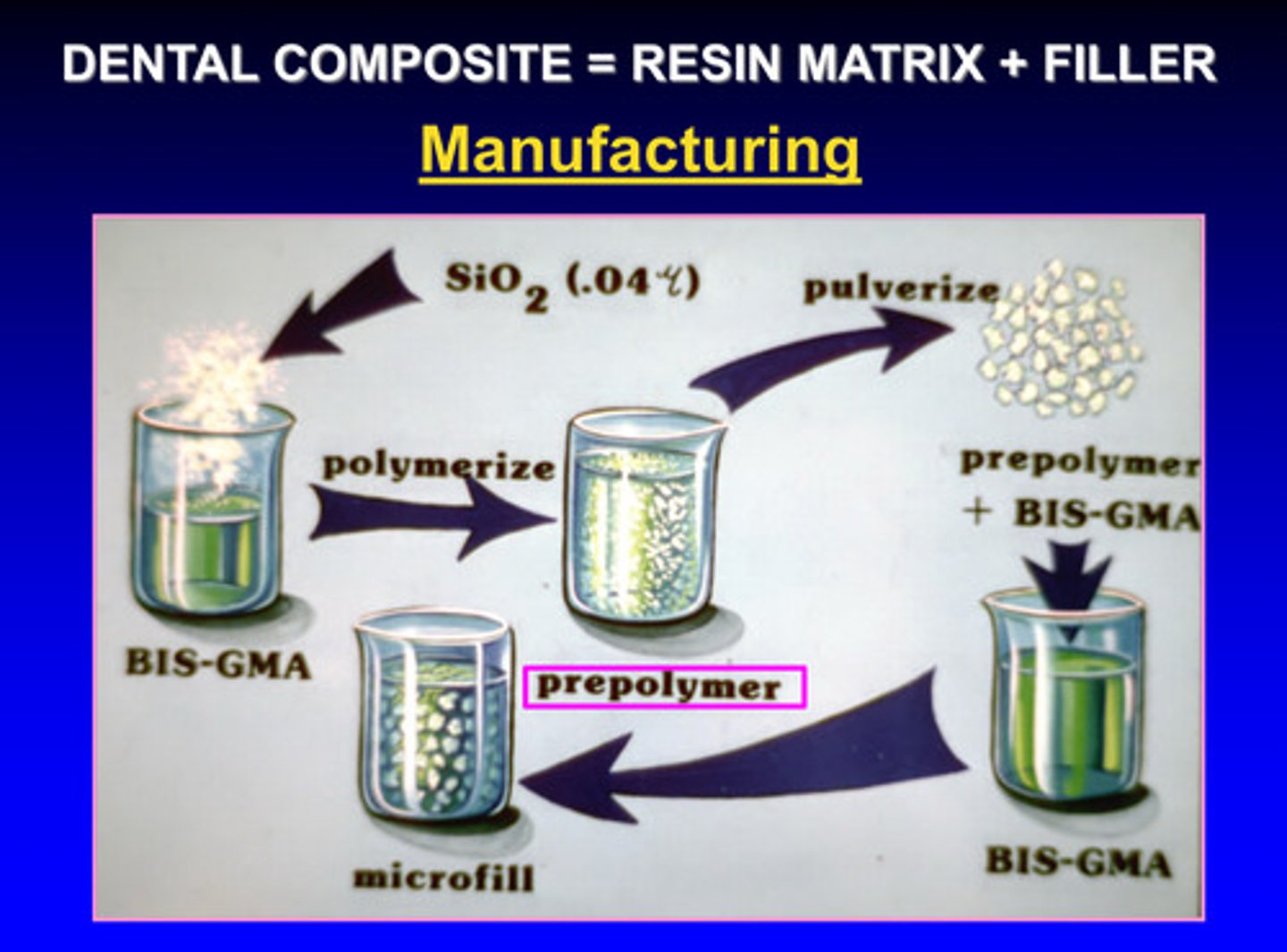
image of manufacturing of resin-based composite
bis-GMA + TEGDMA (as a diluent) are both resin monomers; when silica filler is added to the resin monomer system, a coupling agent is used to bond the resin to the filler: 3-methacryloxypropyl-trimethoxy silane
(this coupling agent is pre-applied to the surface of the silica filler during manufacturing to help chemically bond the filler to the resin matrix)
after the 3-methacryloxypropyl-trimethoxy silane coupling agent is produced, what can the methacrylate group on the other end of the silane molecule do?
it can now react - via free radical addition polymerization - with methacrylate groups in subsequently placed adhesives and methacrylate-based resin cements (essentially: methacrylate group binds to resin monomers)
light cured RBC materials require what 2 things in order to achieve their intended physical, chemical, and optical properties
1) correct type (wavelength)
2) amount of light energy (J/cm^2)
the coupling agent plays a critical role in the composite, what are its 4 functions?
1) it forms an interfacial bridge that strongly binds the filler to the resin matrix
2) it enhances the mechanical properties of the composite and minimizes the plucking of the fillers from the matrix during clinical wear
3) the resulting interfacial phase provides a medium for stress distribution between adjacent particles and the polymer matrix
4) it provides a hydrophobic environment that minimizes water absorption of the composite
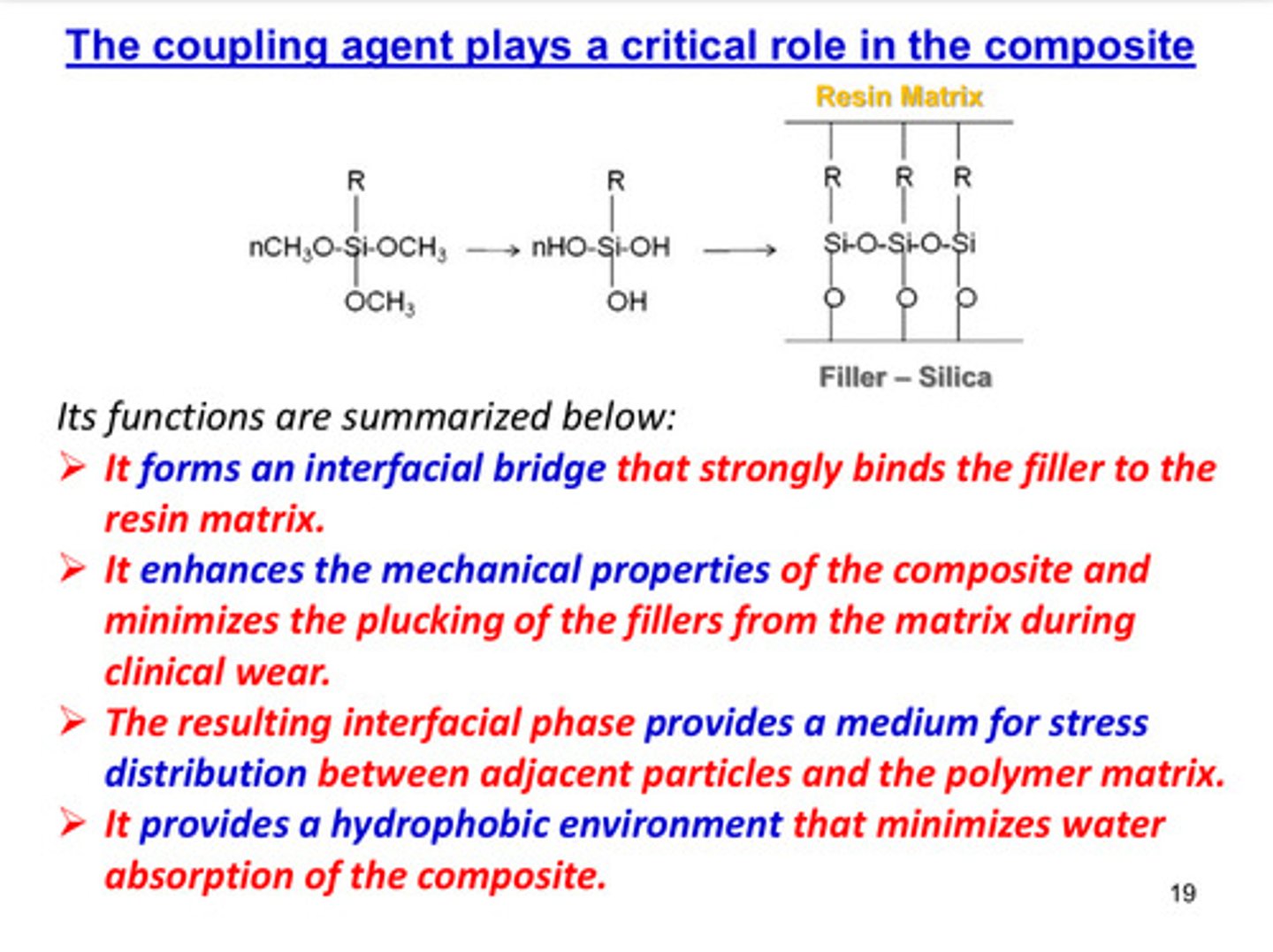
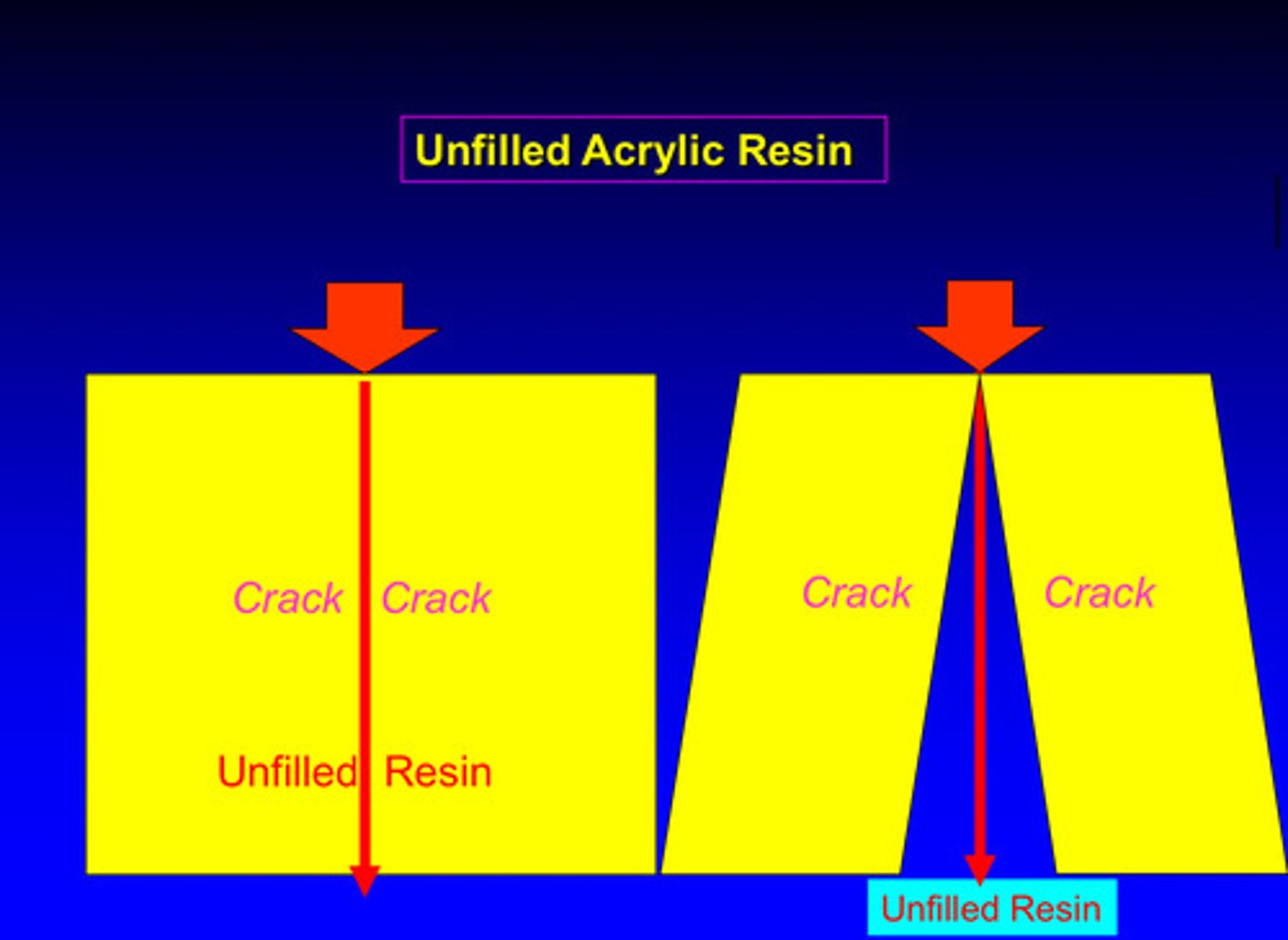
image of how cracks can propagate in unfilled resins
a composite structure can be defined as a set of ?
a set of interconnected elements that collaborate at runtime to achieve some properties (each element has some defined role in the collaboration)
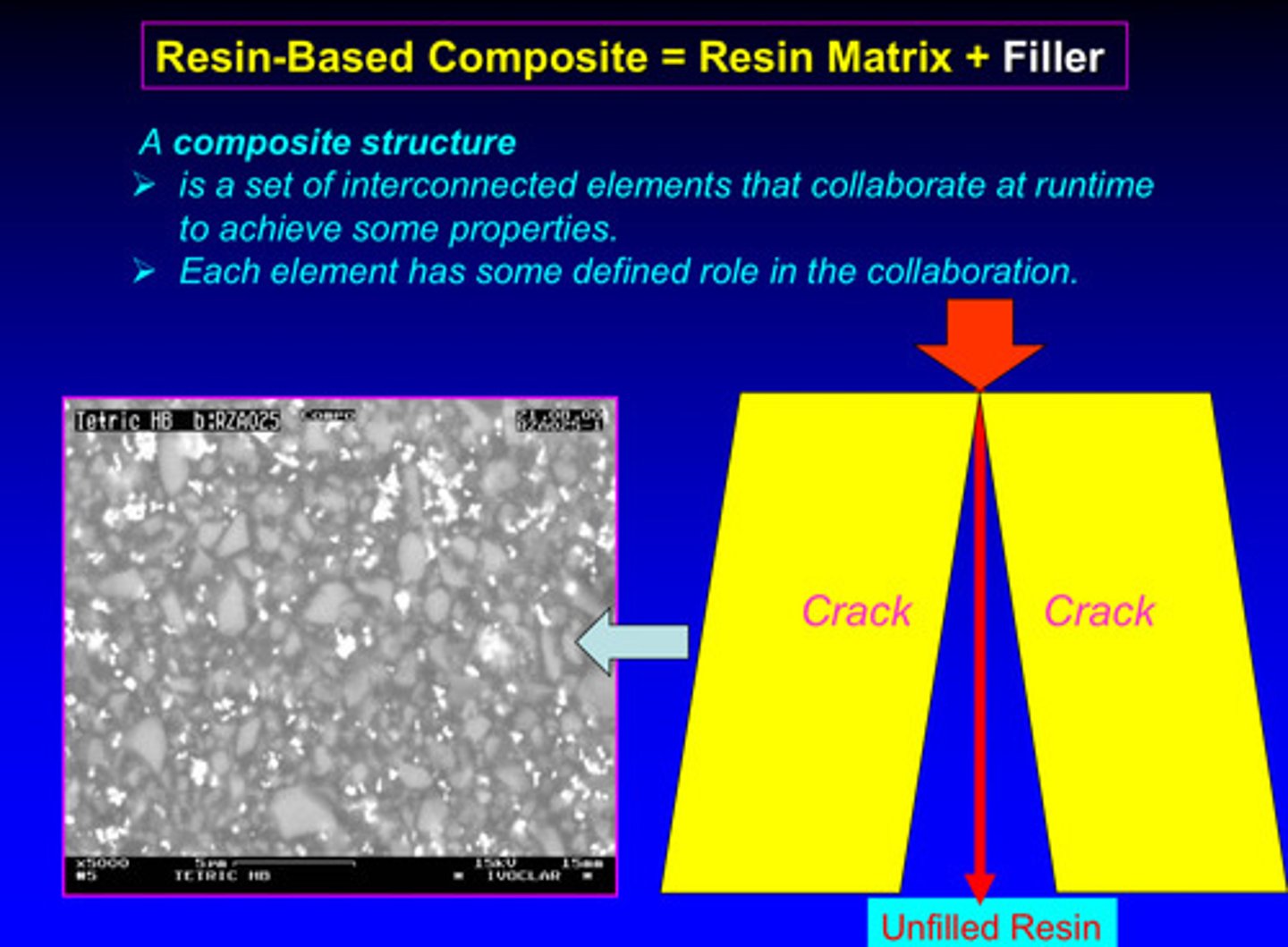
image of how addition of filler to a resin can delay the crack propagations
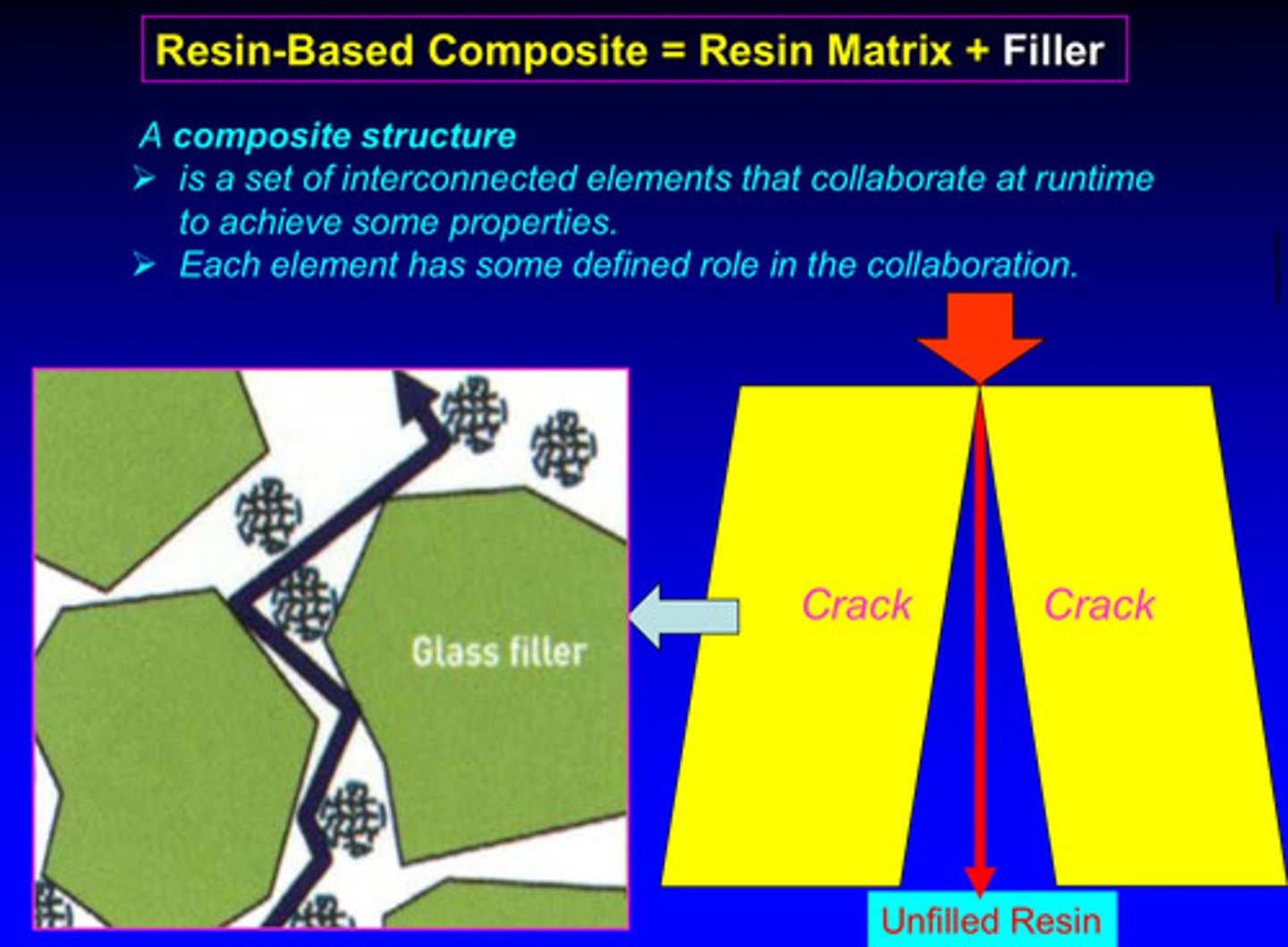
image of how different resin-based composites can delay crack propagation through the systems
biocompatibility of resin based composites is associated with less resin content —> composites with a lower amount of resin tend to be more biocompatible (cause less adverse reactions when used in the body) —> resin components (the monomers) can leach out and be toxic in nearby tissues so reducing the amount of resin and increasing the amount of inorganic filler (like silica or glass particles) means better biocompatibility
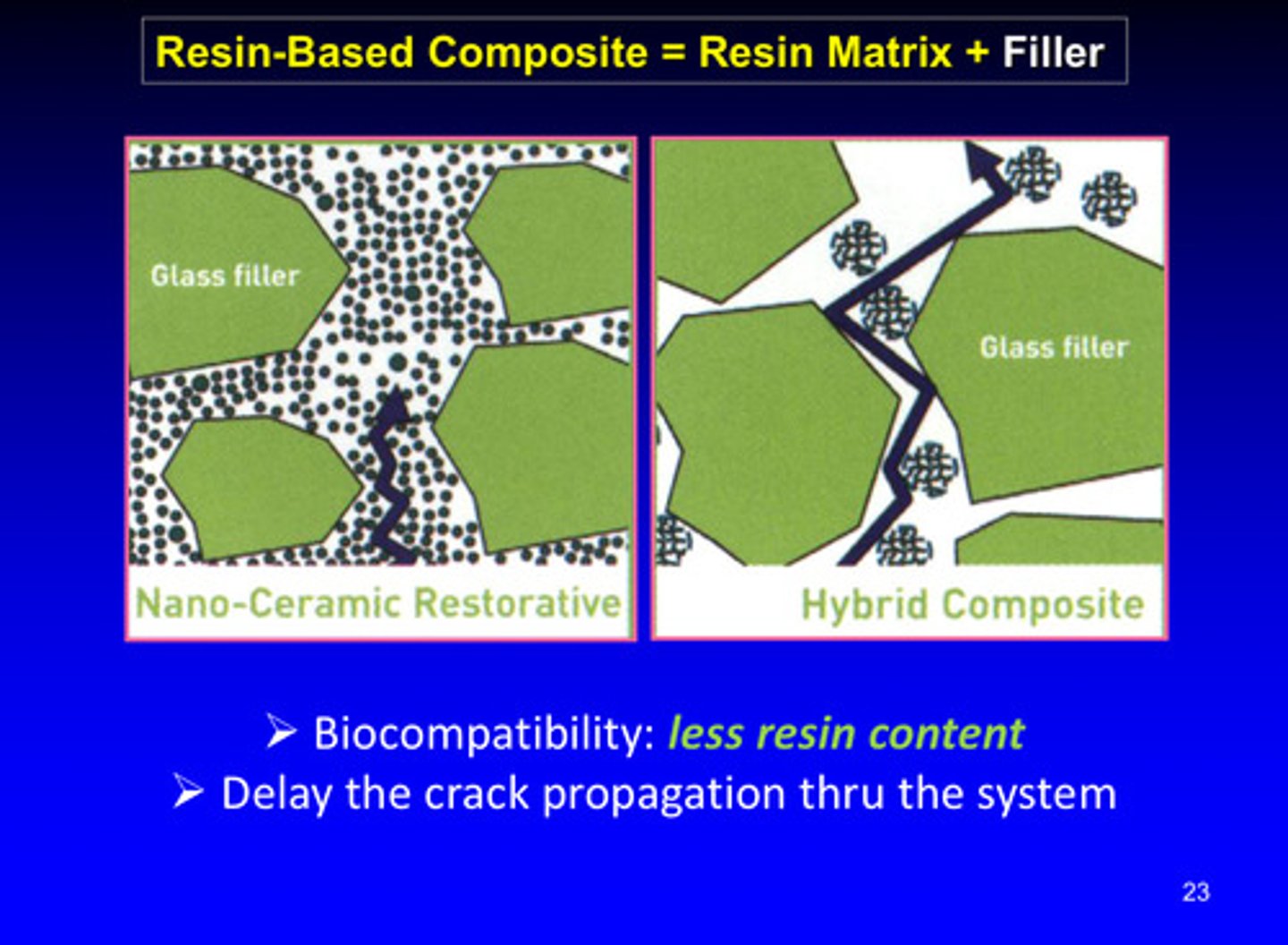
why are nano-ceramic restorative materials better than hybrid composites at delaying crack propagation?
1) nano ceramic restoratives contain nano-sized ceramic particles dispersed in a resin matrix and often have high filler loading and better filler-resin interaction —> this has better energy absorption and crack deflection due to uniformly dispersed, small fillers
2) hybrid composites have generally larger particles than nano-ceramics and may have lower filler loading and less effective dispersion
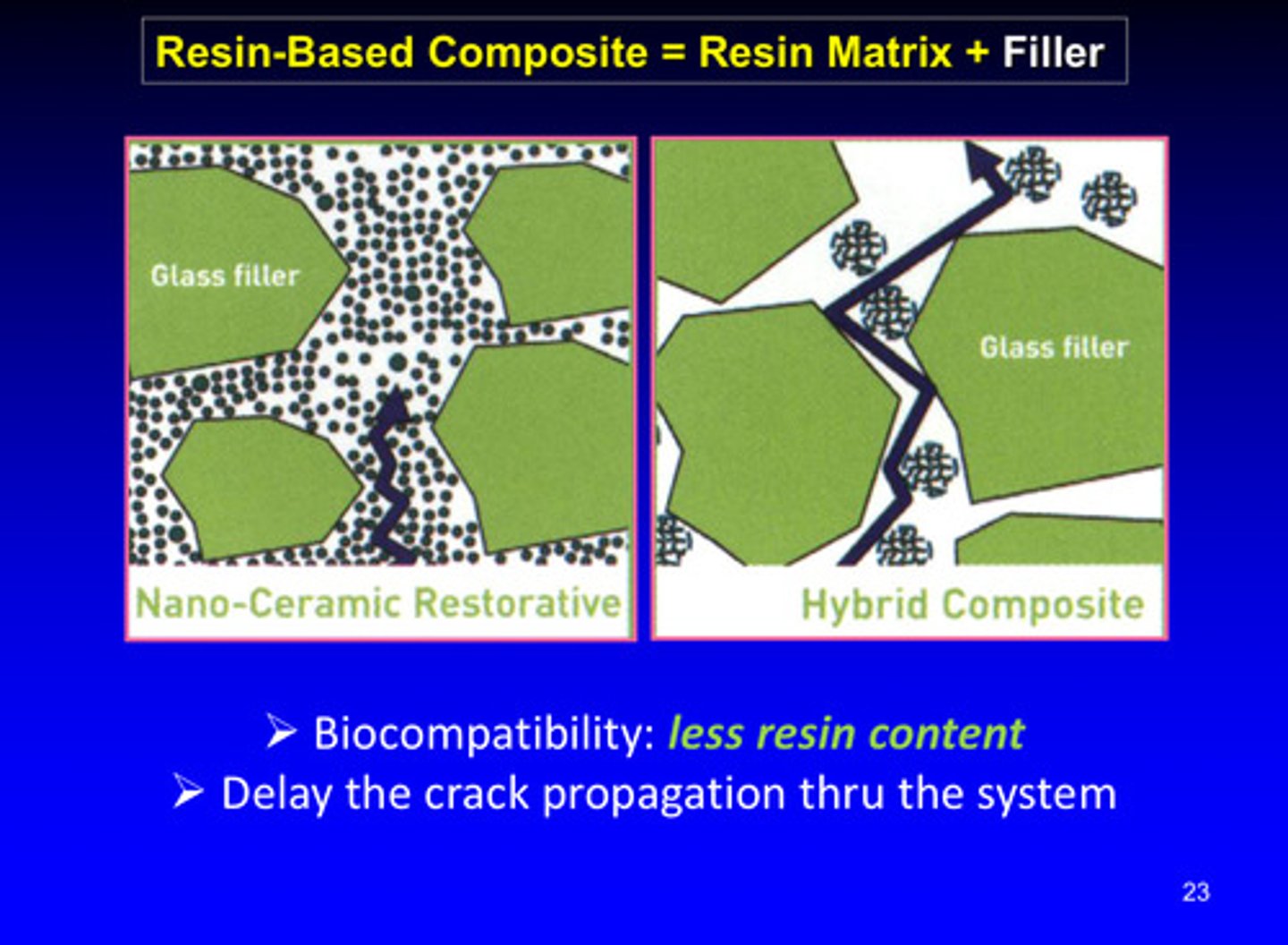
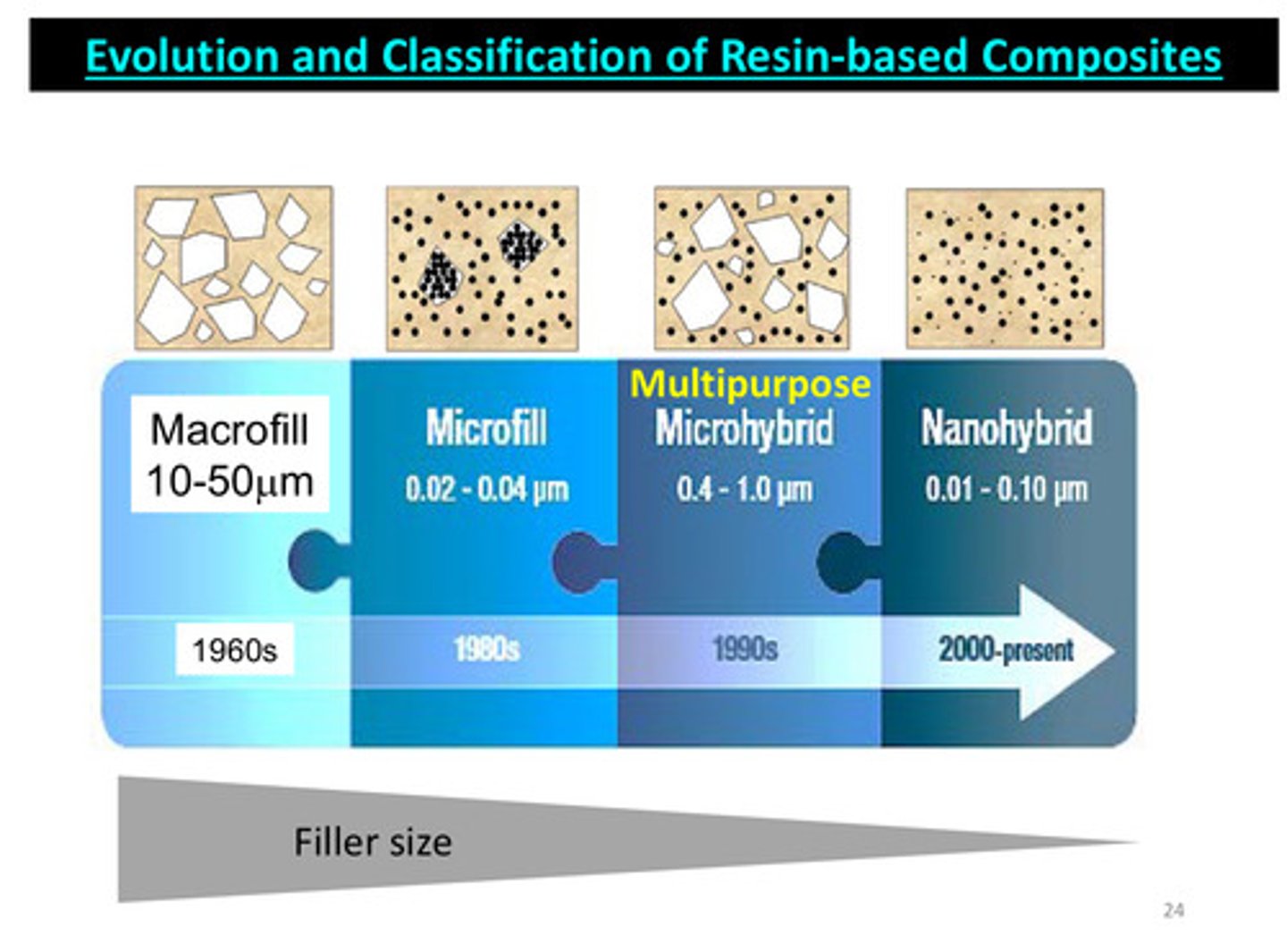
image of evolution and classification of resin based composites
nanohybrid is best due to smaller filler size but most common use is microhybrid (multipurpose use)
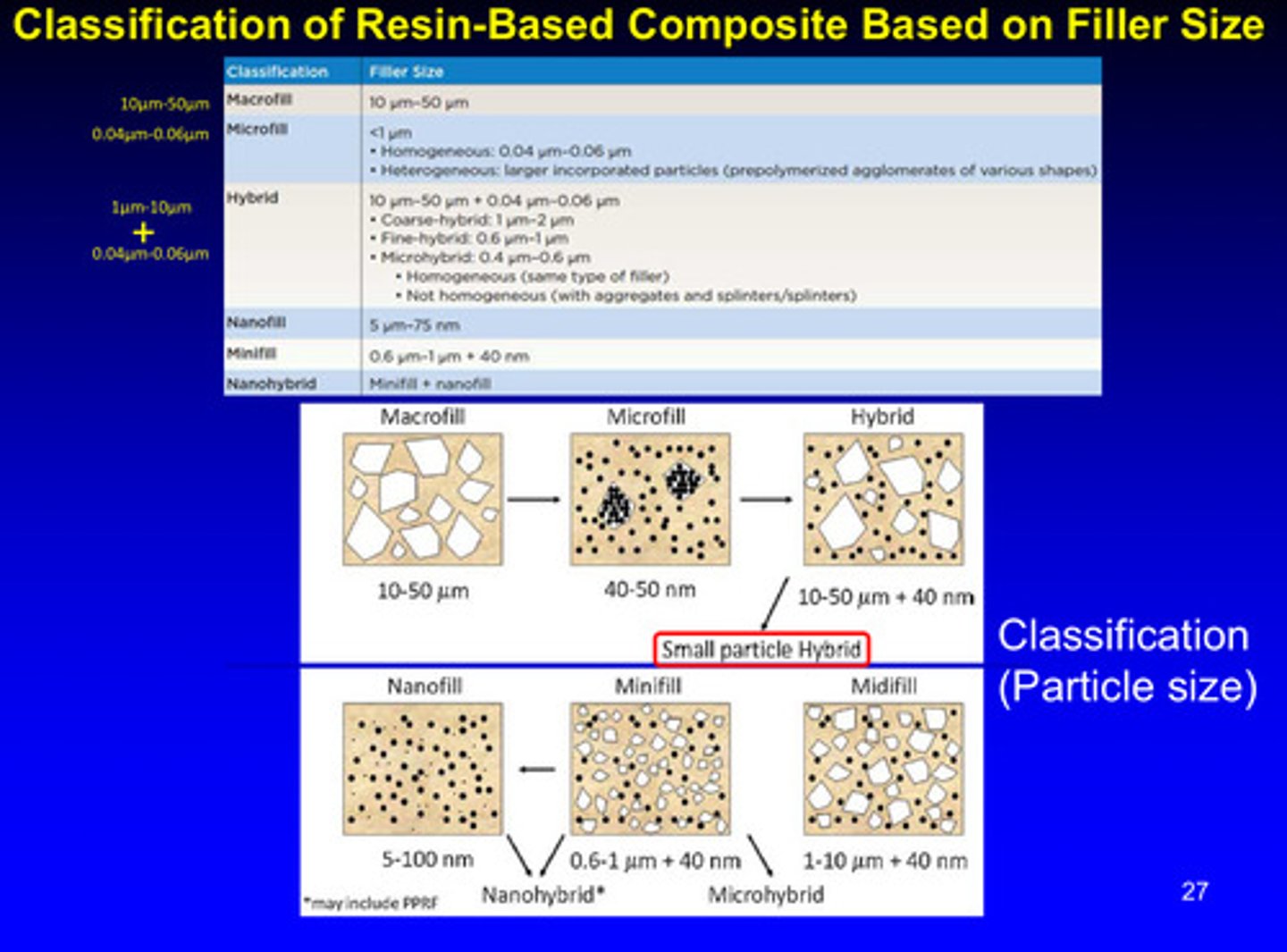
classification of resin-based composites is based on?
filler size!
macrofill: 10-50 micrometers
midifill: 1-10 micrometers + 40 nanometers
minifill: 0.6-1 micrometers + 40 nanometers
microfill: 40-50 nanometers
nanofill: 5-100 nanometers
he said not to pay too much attention to this lol just know the differing filler sizes = different classification
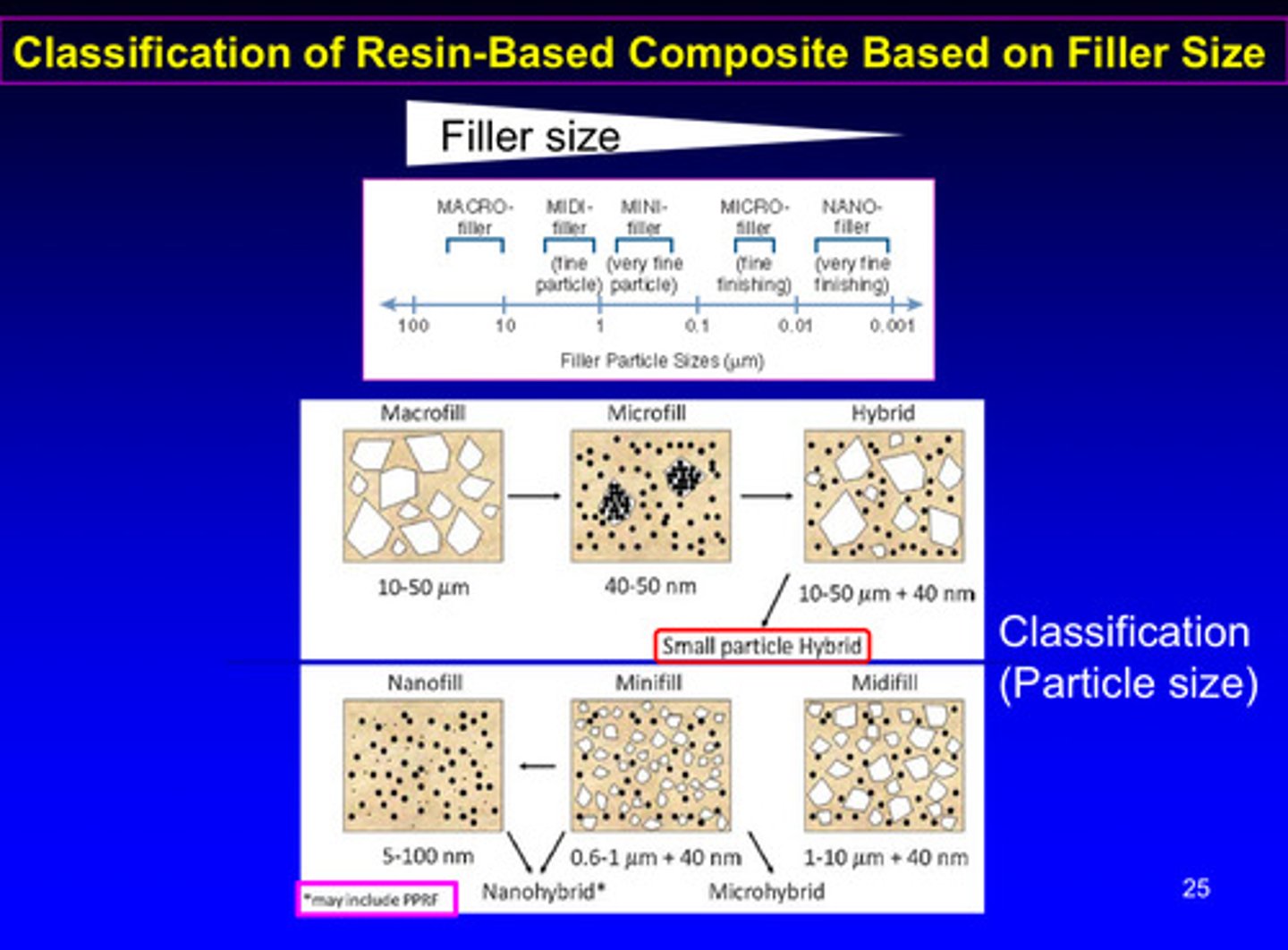
image of manufacturing of dental composite = resin matrix + filler check this
adding the tiny particles to the resin monomer is very difficult; manufacturers will prepolymerize it first. essentially they make a resin composite, grind/pulverize it, and create another composite using that; this helps increase filler content and decrease resin monomer content
another image of classification of resin-based composites based on filler size
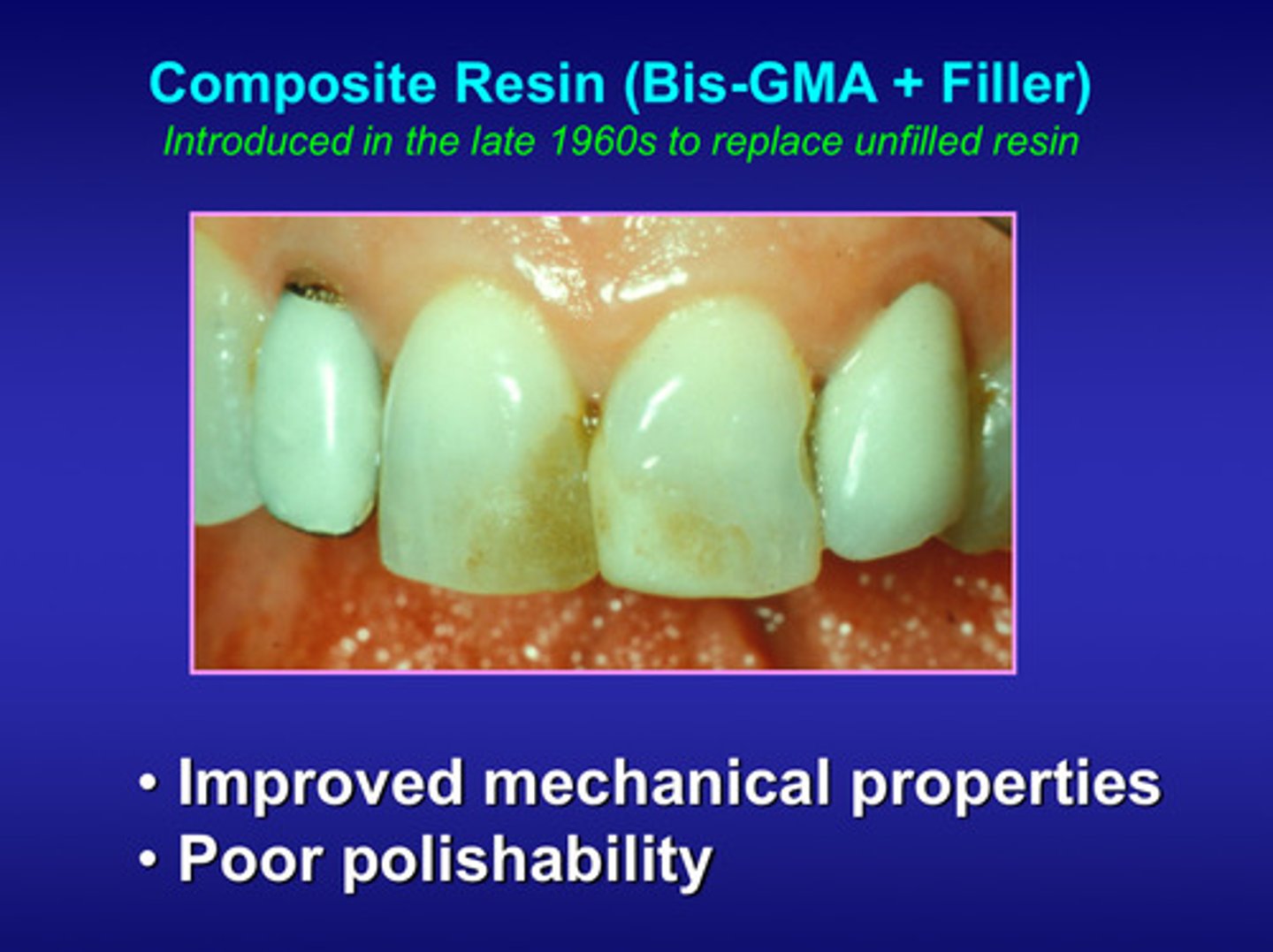
compare the characteristics of unfilled resin vs composite resin
composite resin has opposing characteristics of unfilled resin besides color stability and surface texture

what are the 2 things we discovered once switching to composite resin in the late 1960s? (bis-GMA + filler)
1) improved mechanical properties
2) but still has poor polishability due to color stability and surface texture
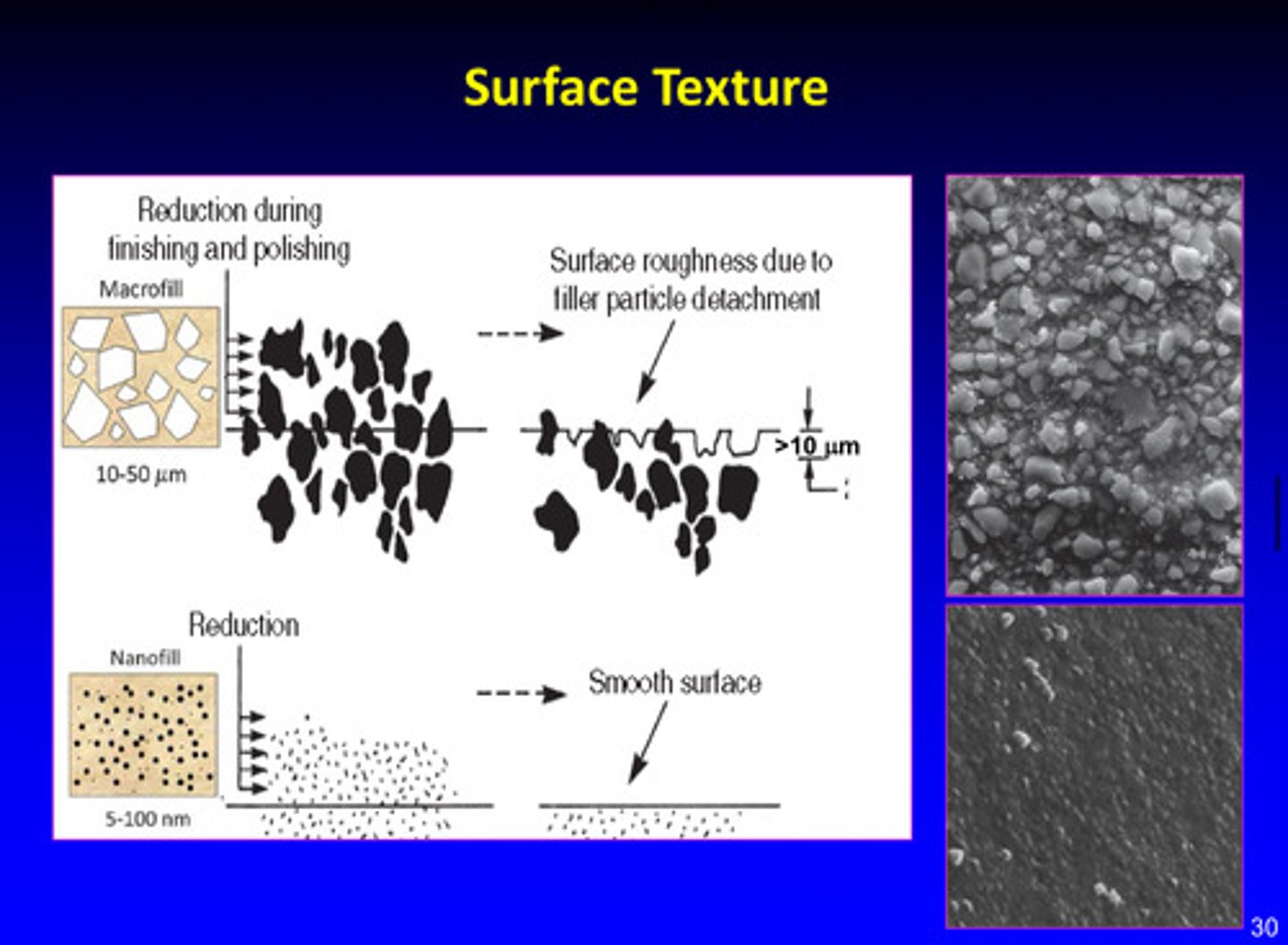
images of surface texture differences
there is surface roughness in macrofill material due to filler particle detachment; nanofill has smooth surface
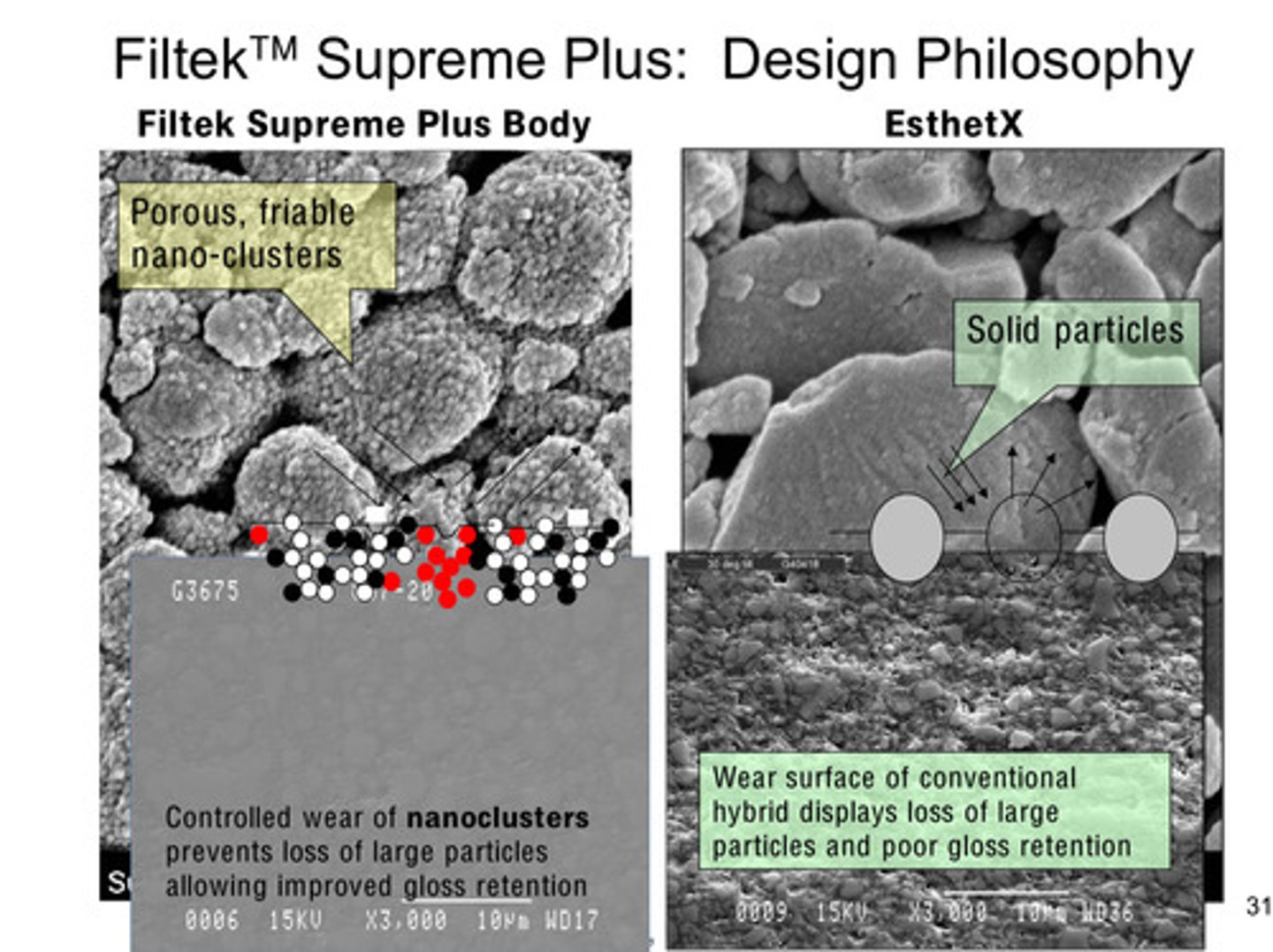
filtek supreme plus: design philosophy image
filtek supreme plus uses nanoclusters —> this controlled wear of nanoclusters prevents loss of large particles, allowing improved gloss retention
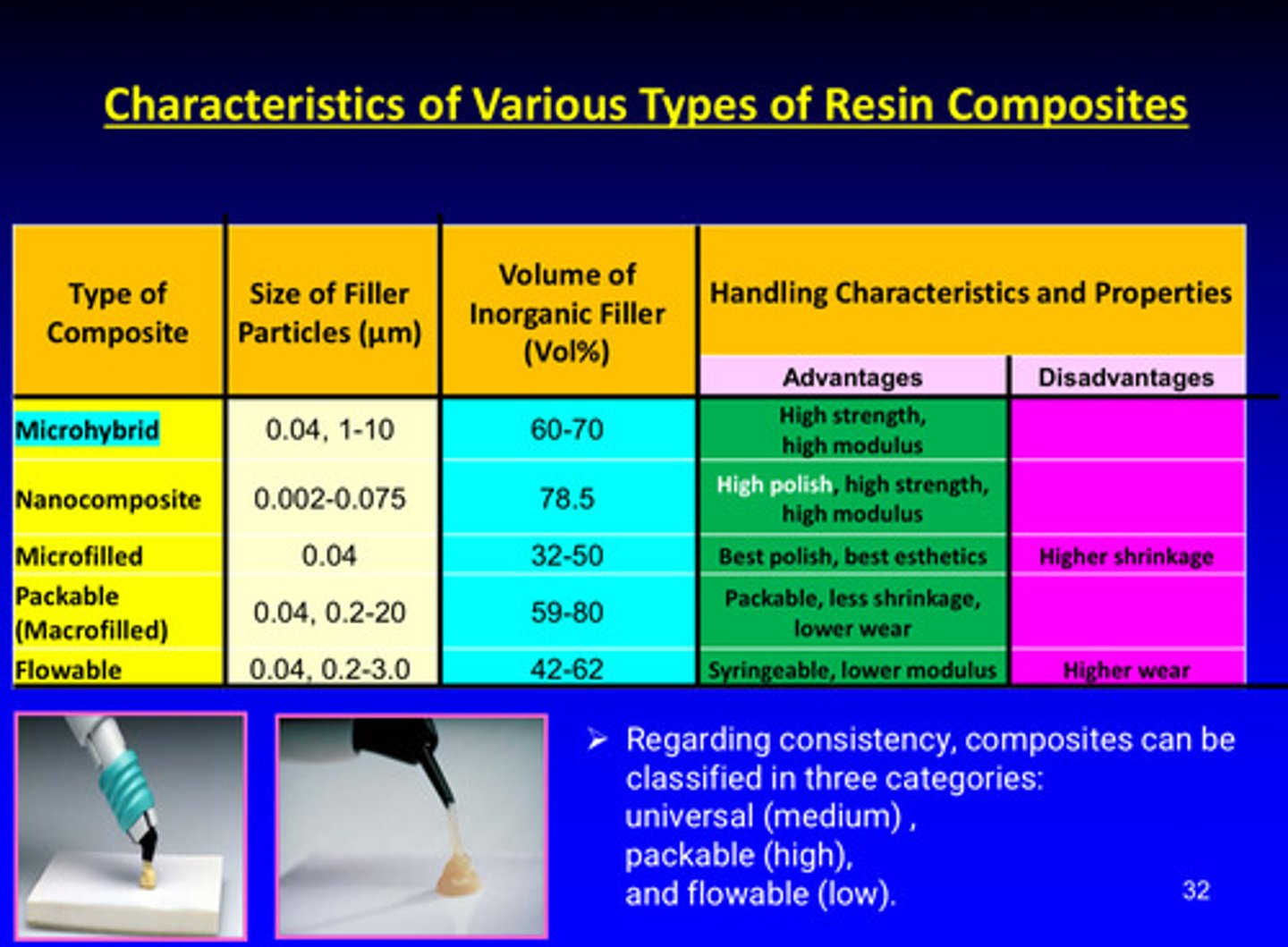
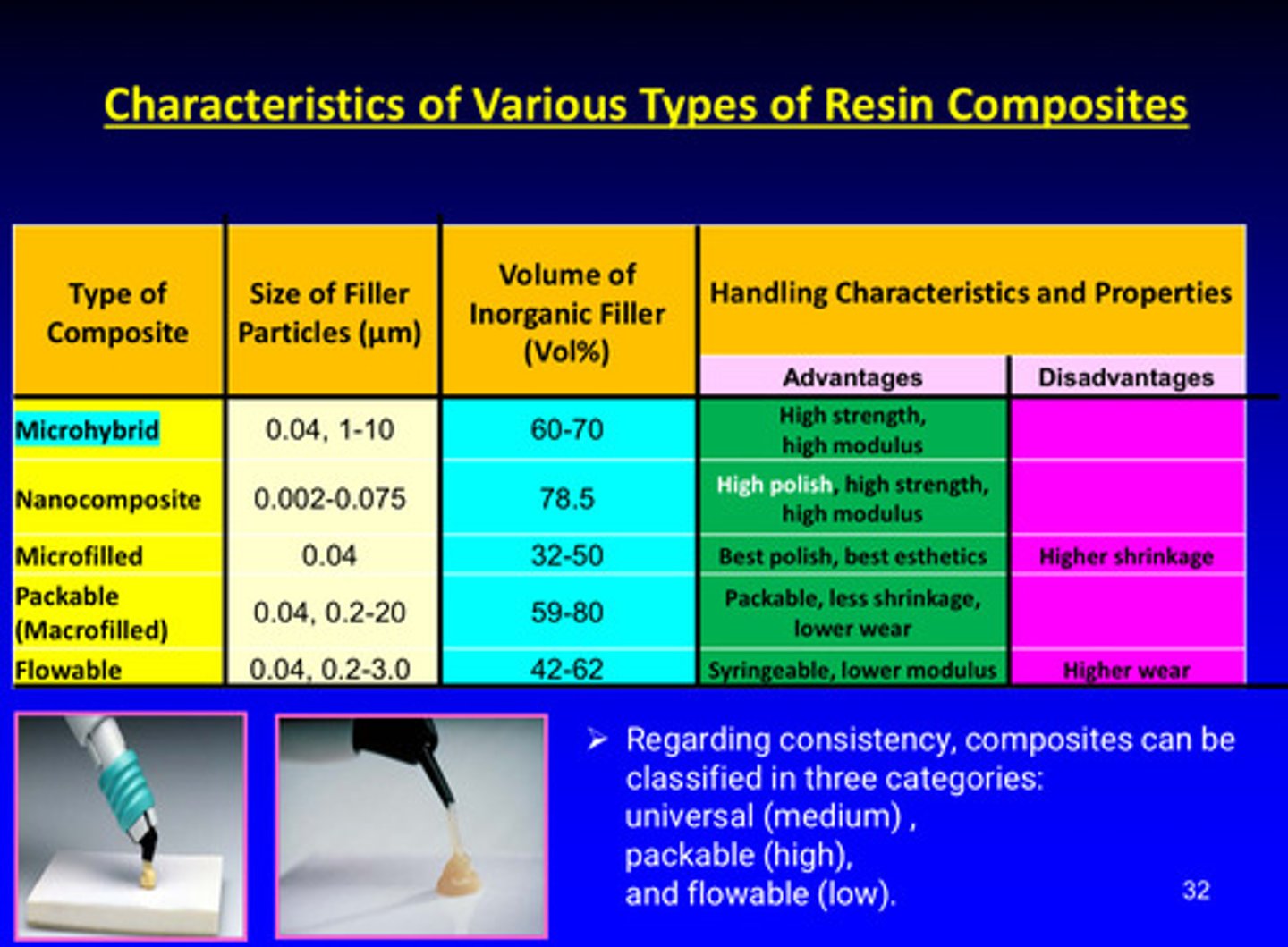
summary table of classification of resin composites w advantages and disadvantages
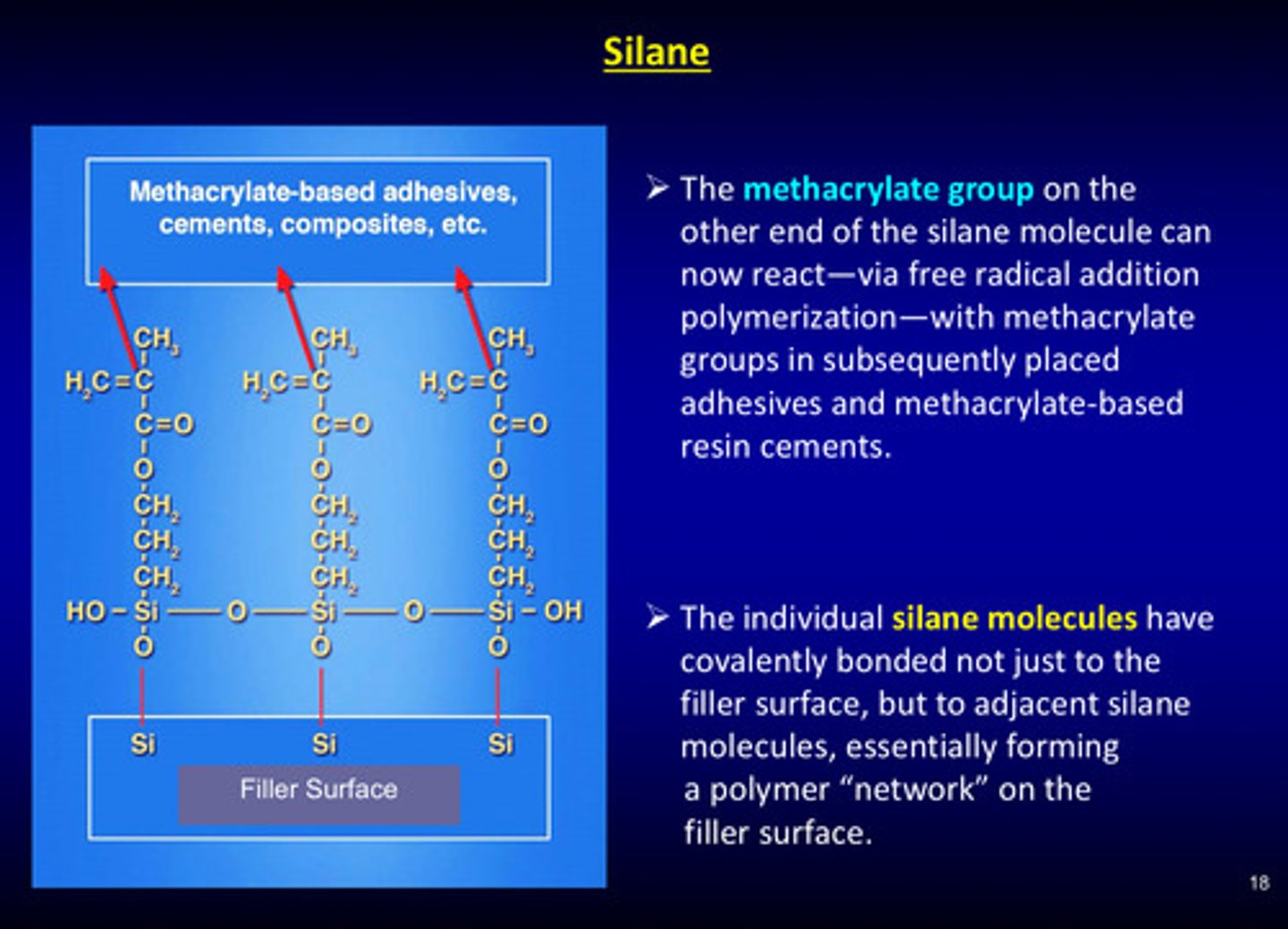
what do the individual silane molecules do?
they covalently bond not just to the filler surface, but to the adjacent silane molecules, essentially forming a polymer "network" on the filler surface (essentially: silane groups bind to silica filler)
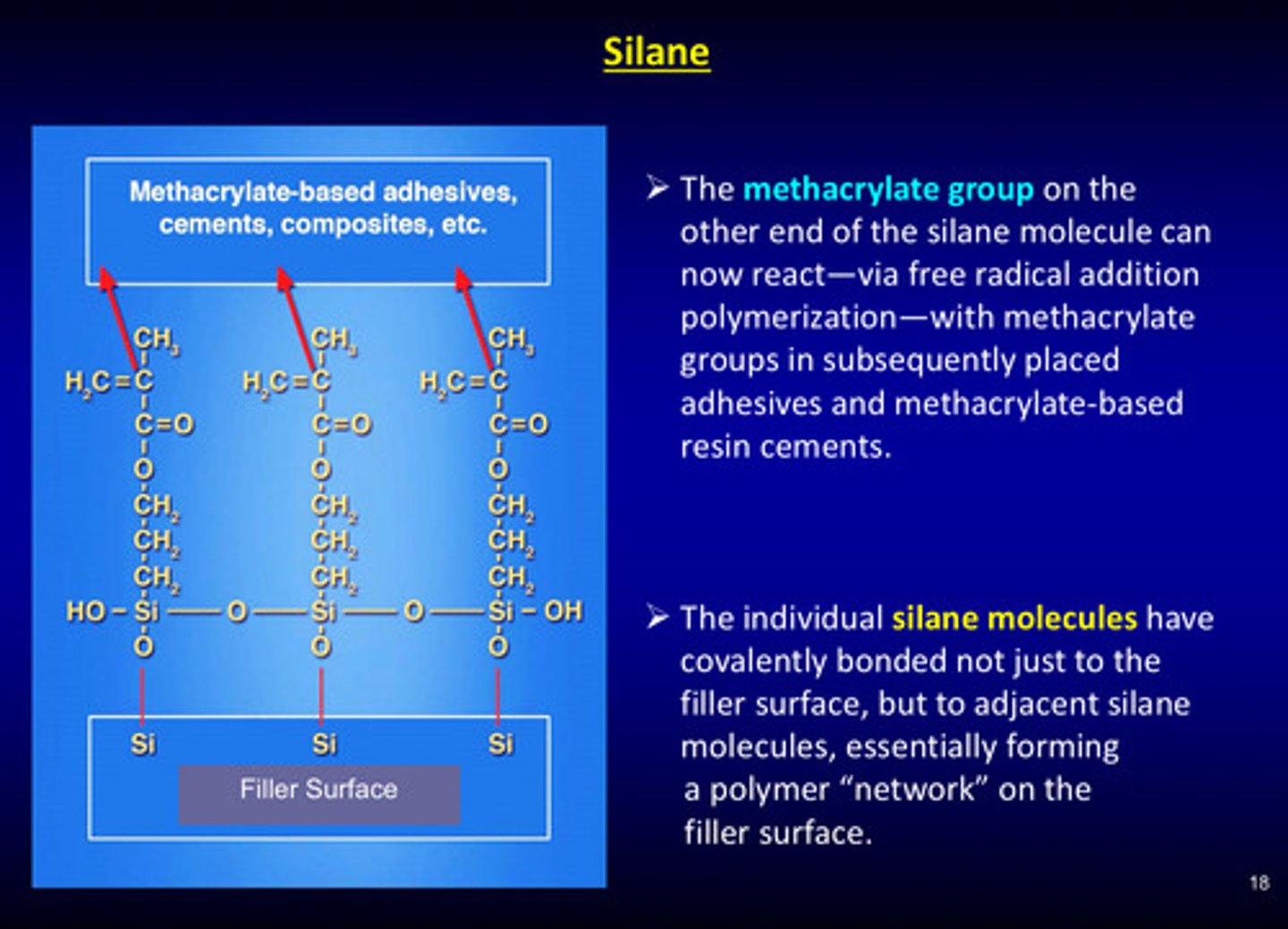
image of composite systems: high viscosity
harder to push out; more "sturdy" —> high viscosity by having high filler content (19 vs 80)
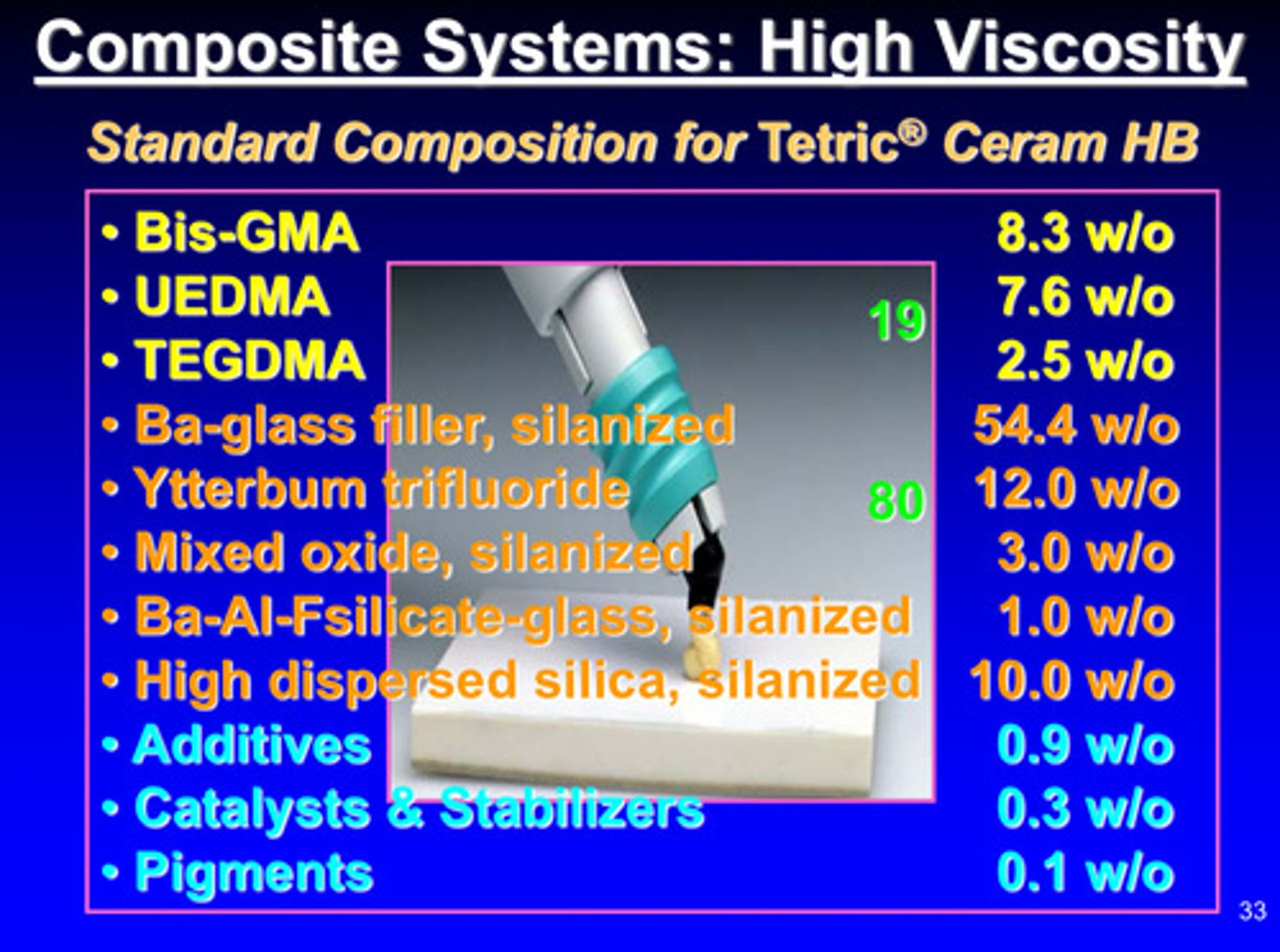
image of composite systems: low viscosity
you can push it out easily (more viscous) but remains fixotropic (maintains its shape) —> low viscosity by having less filler content (31 vs 68)
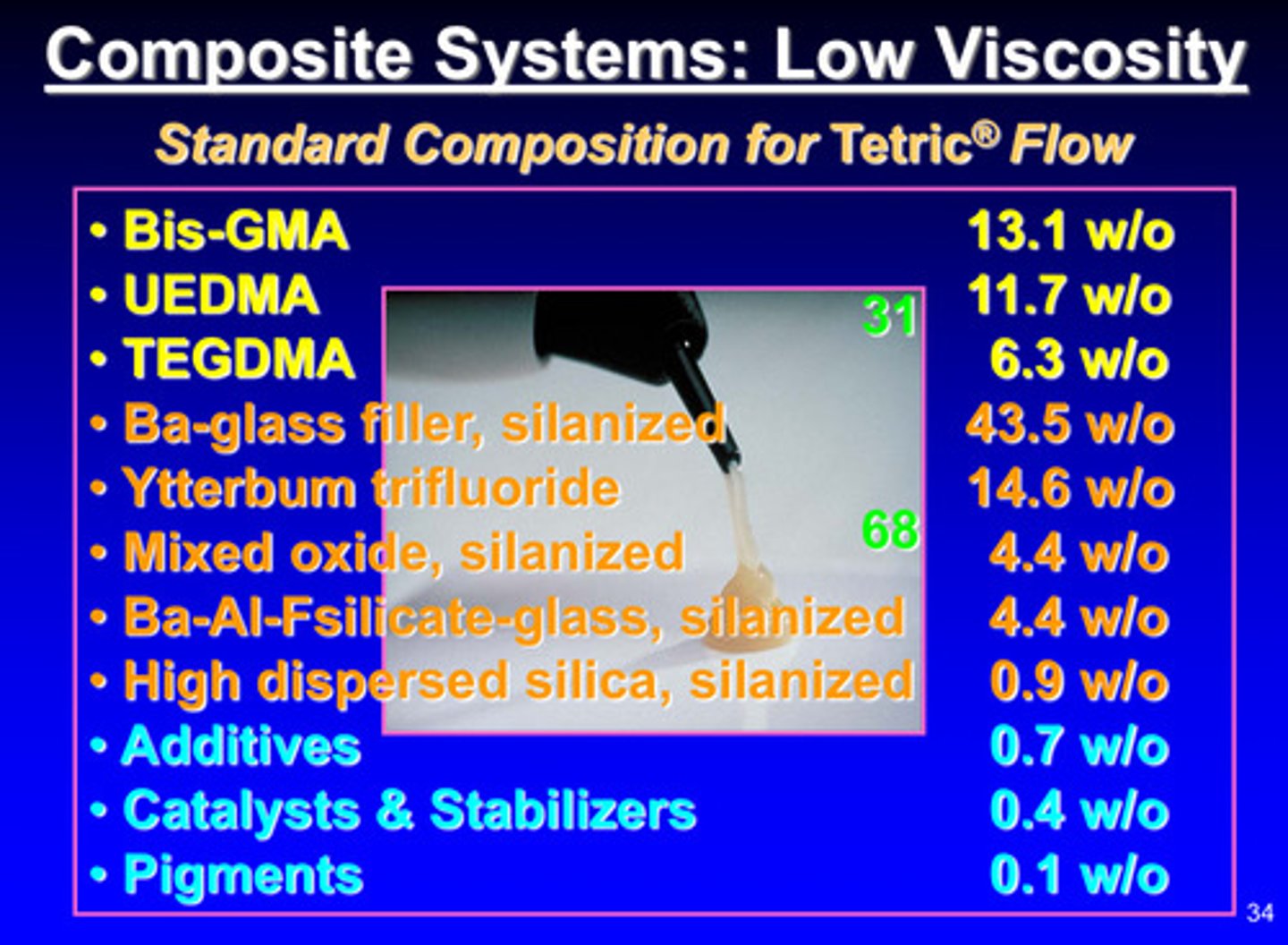
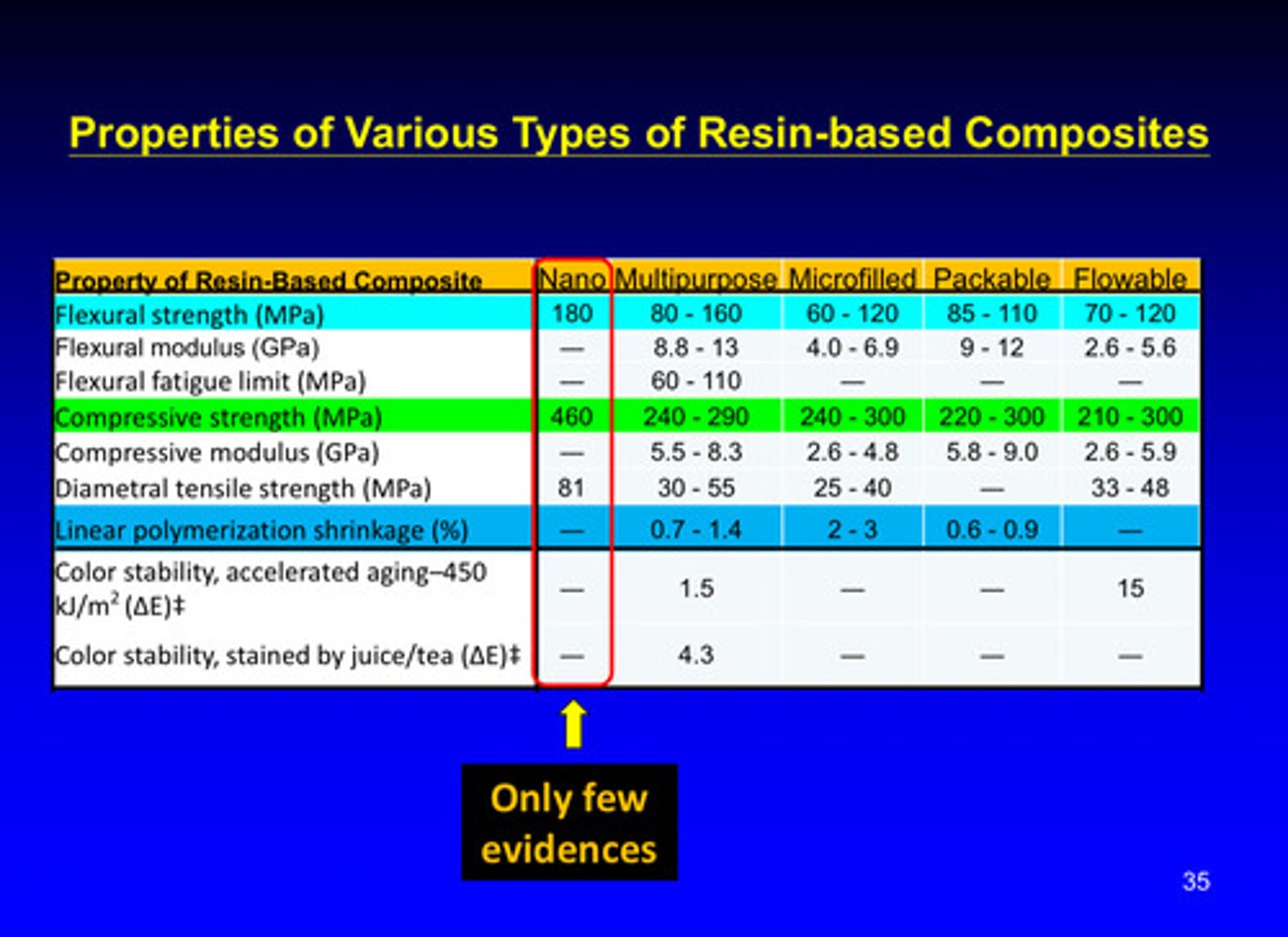
image of properties of various types of resin-based composites
review polymerization mechanism
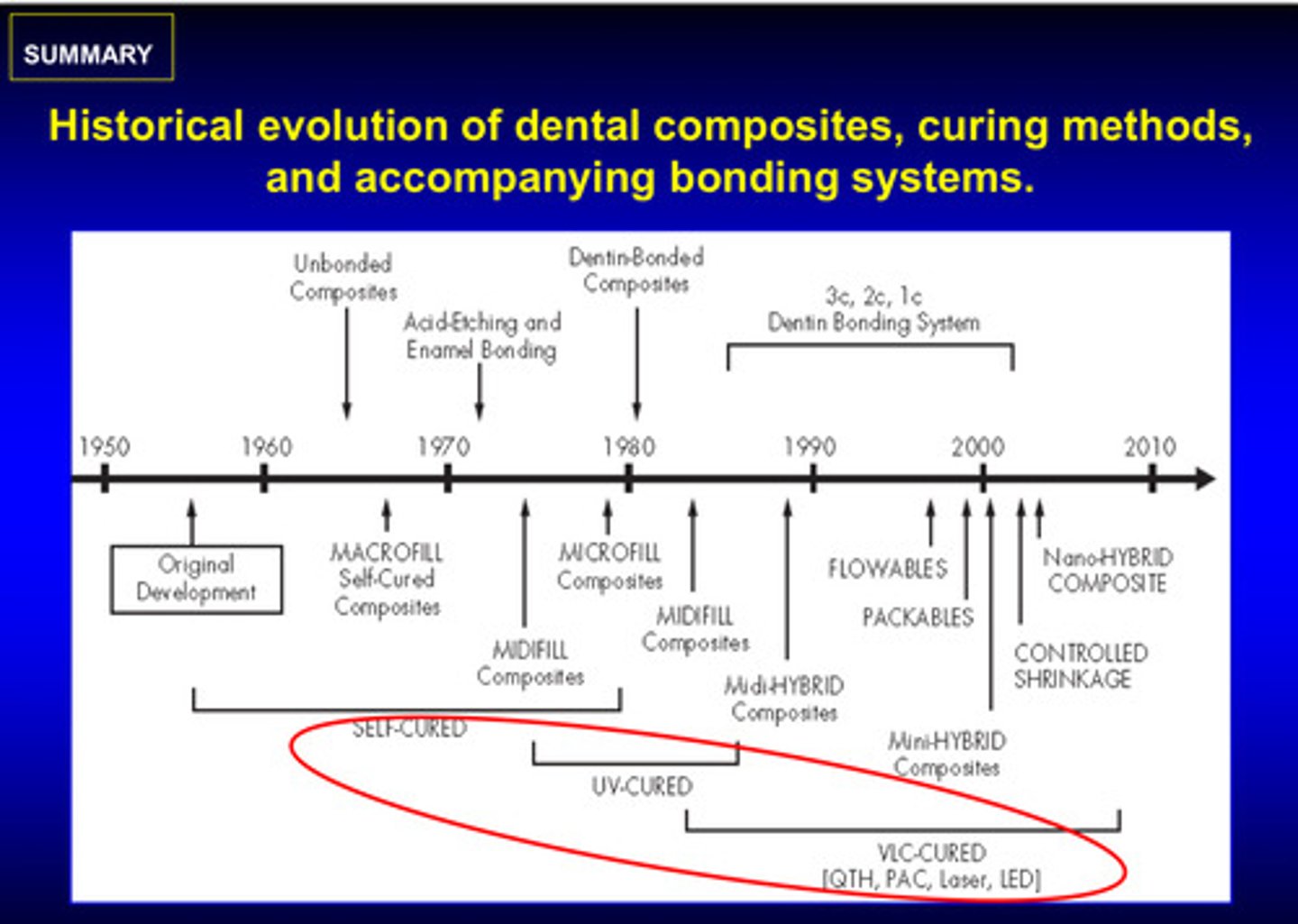
image of historical evolution of dental composites, curing methods, and accompanying bonding systems
self cured —> UV cured —> visible light cured (VLC)
what are the 3 methods of polymerization
1) chemical cured
2) UV light cured
3) visible light cured
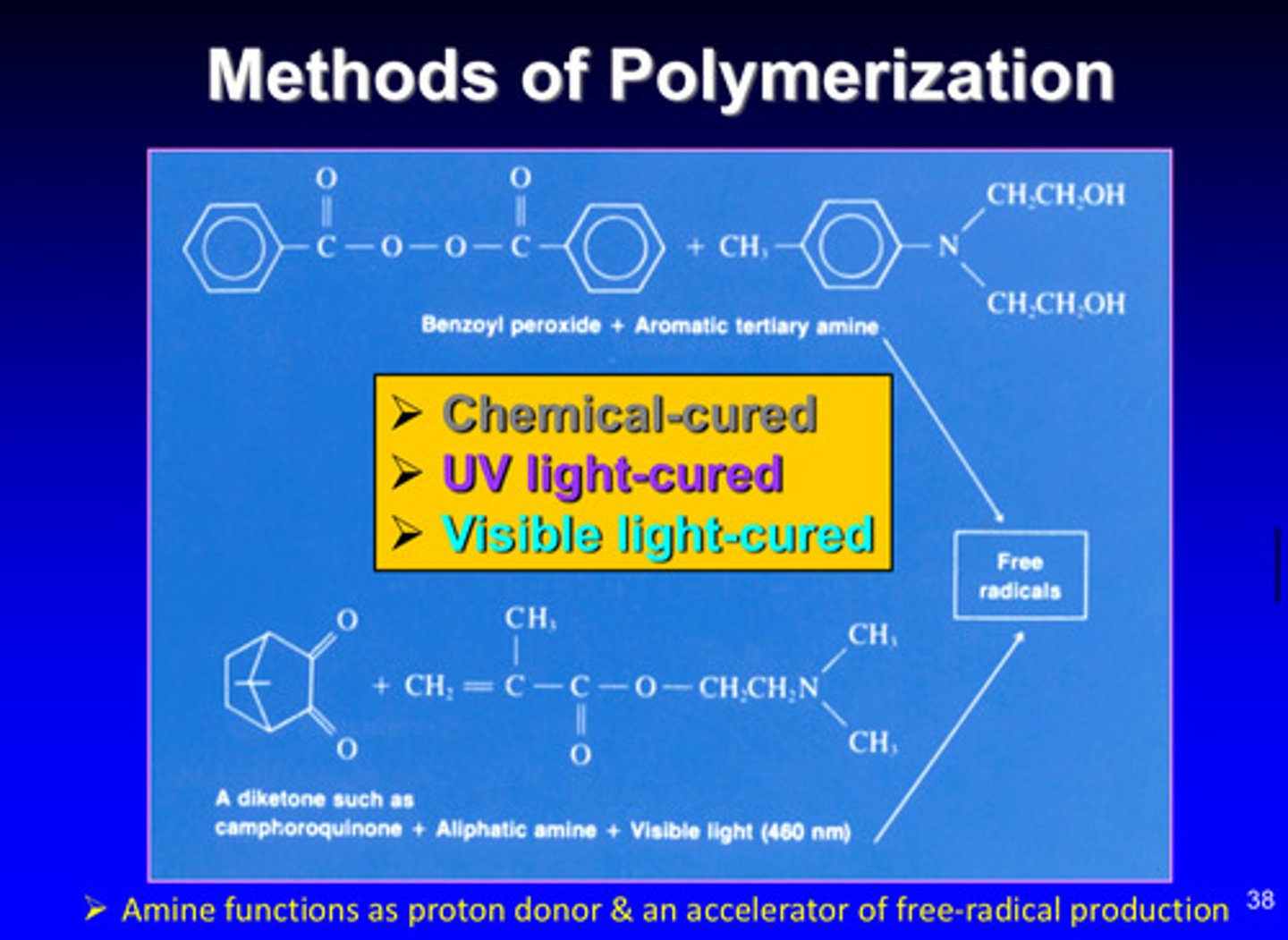
how do amines function in visible light cured polymerization
functions as proton donor & an accelerator of free-radical production
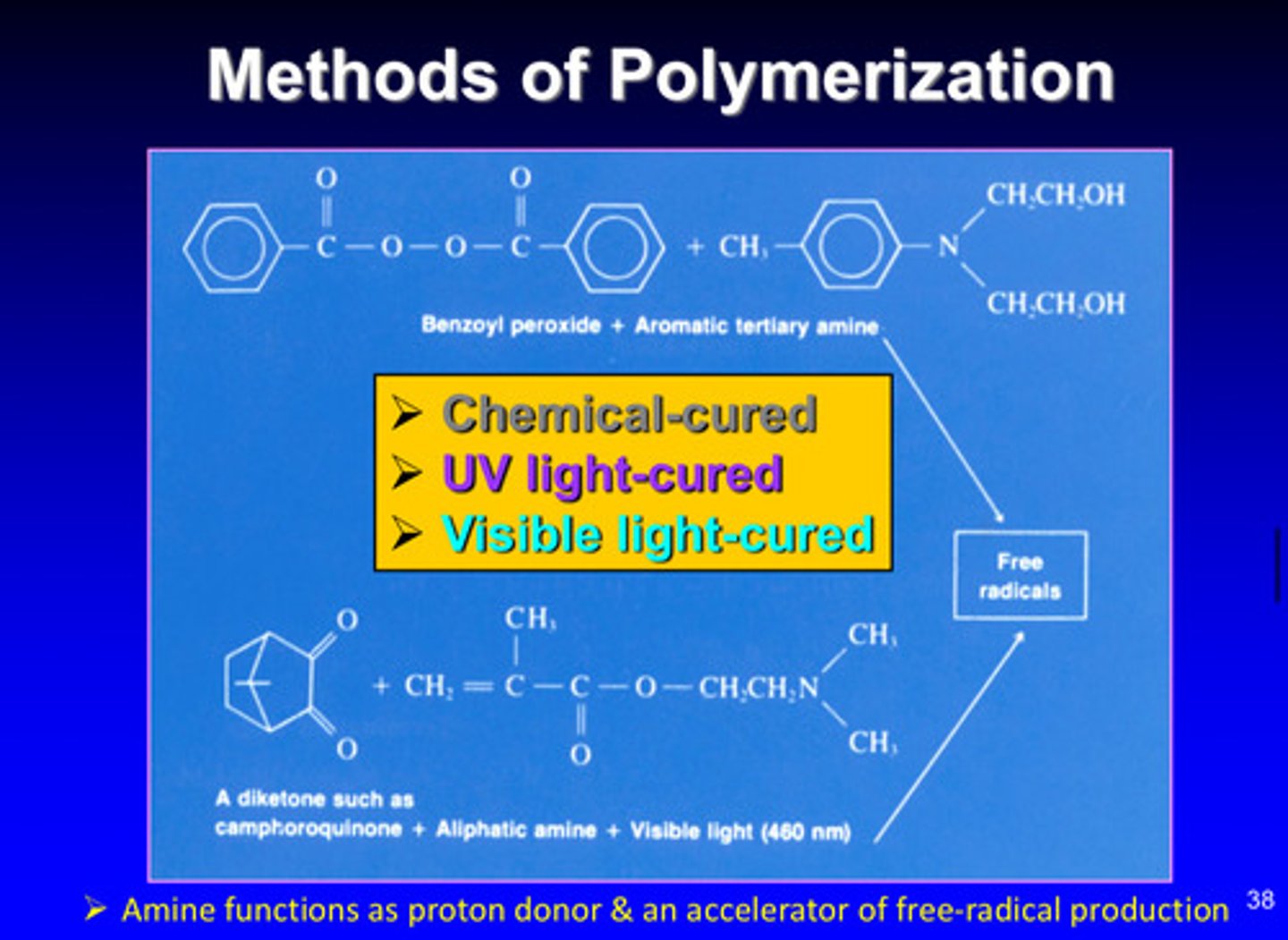
image of composite resins composition + functions (base paste vs catalyst paste)
base/universal paste:
monomer = primary reacting ingredient
treated inorganic particles = add glint and strength
catalyst paste:
monomer = primary reacting ingredient
treated inorganic particles = add glint and strength
barium compounds = radiopacity
catalyst = starts and accelerates polymerization
tldr: had to mix these things together in order to have the reaction
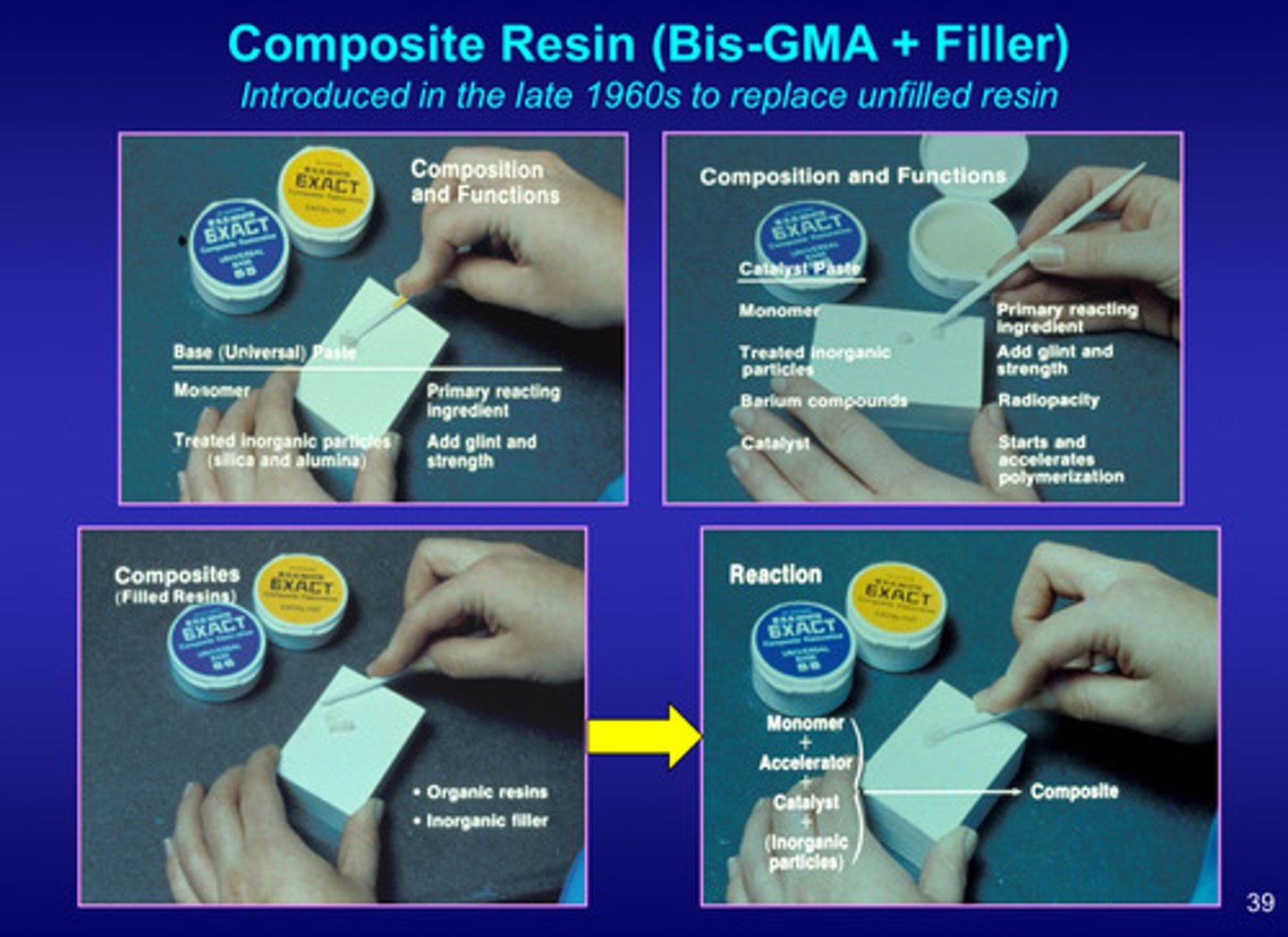
image of resin based composite filling materials and instruments
no longer have to mix because already mixed which means no void or air trapped inside the material

what are the advantages of visible light curing composite (photopolymerization)
1) no mixing, less porosity, better shade control
2) less finishing time, contoured before curing
3) more color stable and wear-resistant

why is delivering sufficient energy to resin-based composites important?
light cured RBCs must receive adequate light energy to achieve their intended physical, chemical, and optical properties

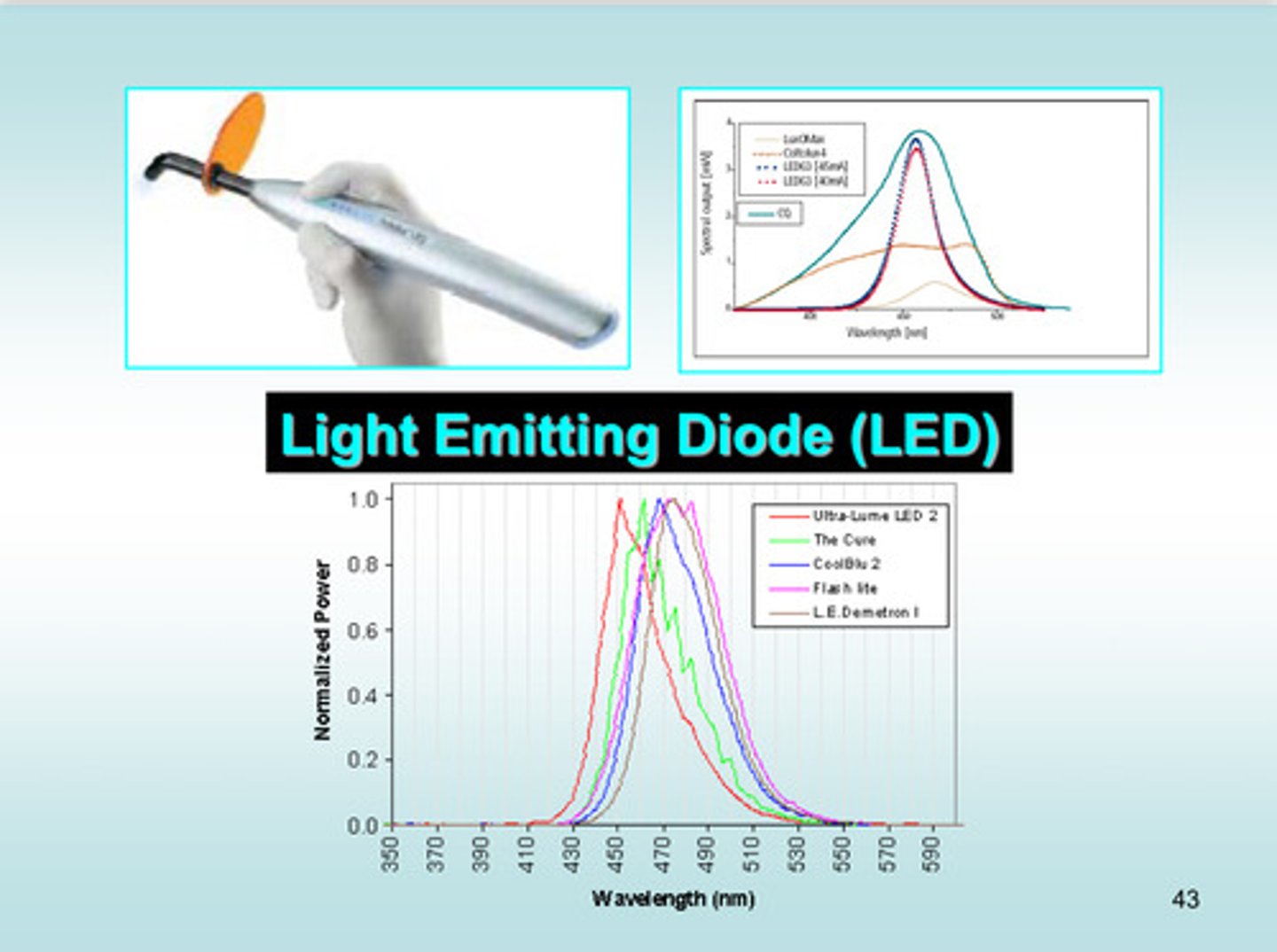
what are the 2 kinds of light curing units
1) quartz tungsten-halogen (QTH)
2) light emitting diode (LED)

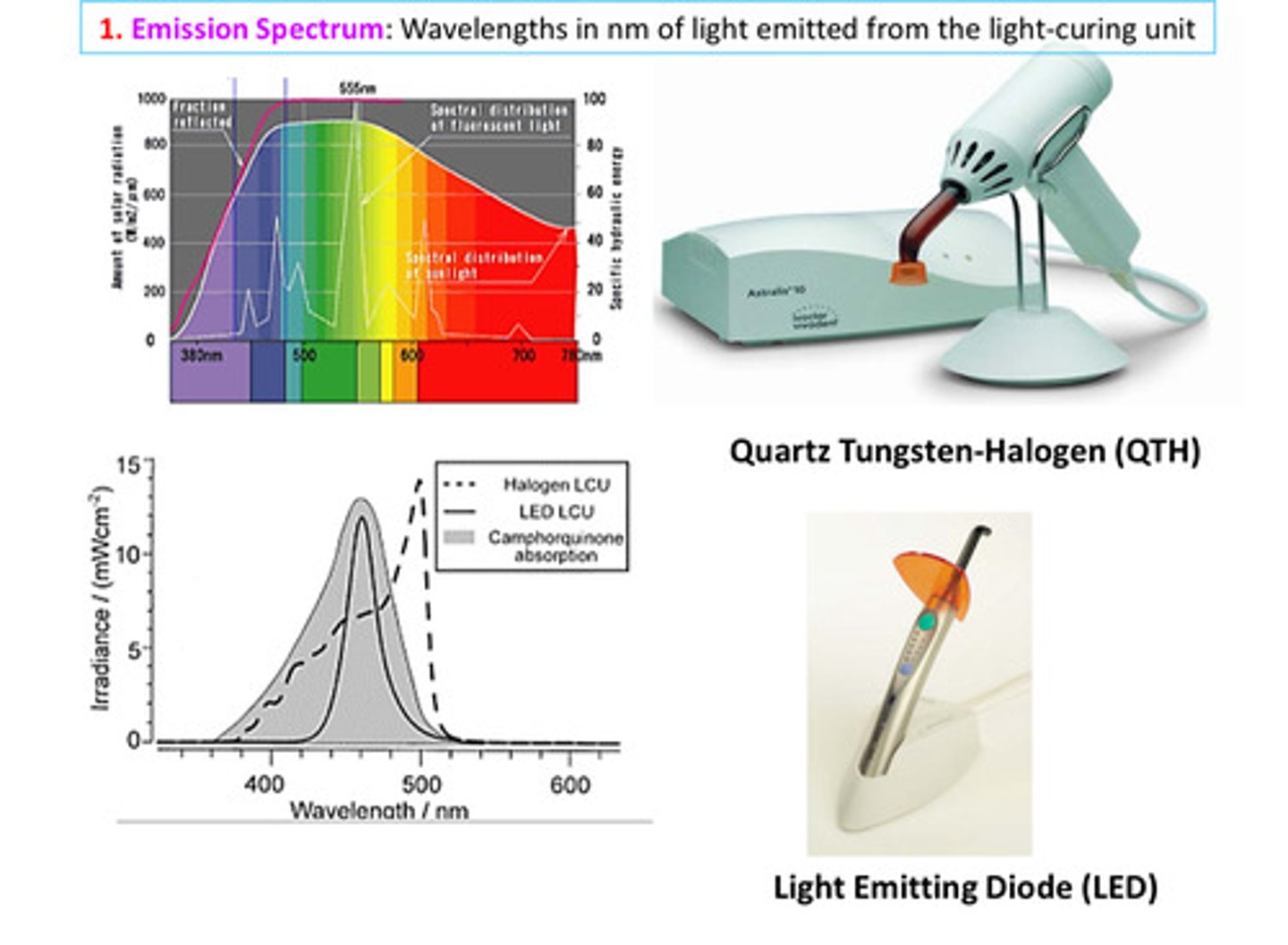
image of light emitting diode wavelengths
wavelength is usually between 430-490 (blue-green)
what are the 5 curing light considerations
1) emission spectrum: wavelengths in nanometers of light emitted from curing light
2) spectral radiant power: power at each nanometer of wavelength
3) radiant exitance: what comes out from light source
4) irradiance: what the surface receives from the light source
5) radiant exposure: radiant energy applied to a given surface area over exposure time

image of emission spectrum examples between QTH and LED
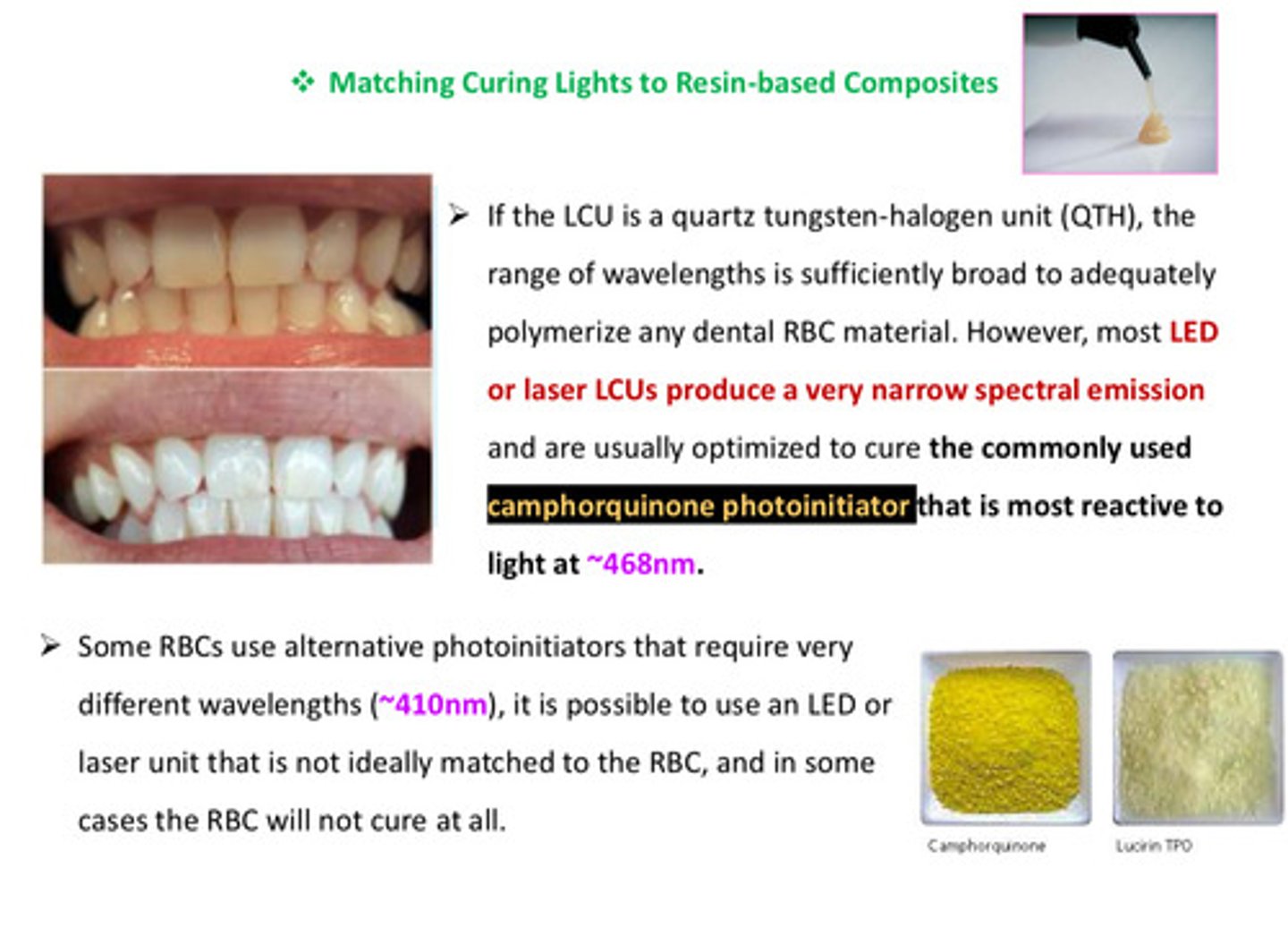
if the LCU is a QTH, the range of wavelengths is sufficiently broad to adequately polymerize any dental RBC material. however, most LED or laser LCUs produce a ____ ______ spectral emission and are usually optimized to cure ?
produce a very narrow spectral emission and are usually optimized to cure the commonly used camphorquinone photoinitiator (yellow material) that is most reactive to light at 468 nm
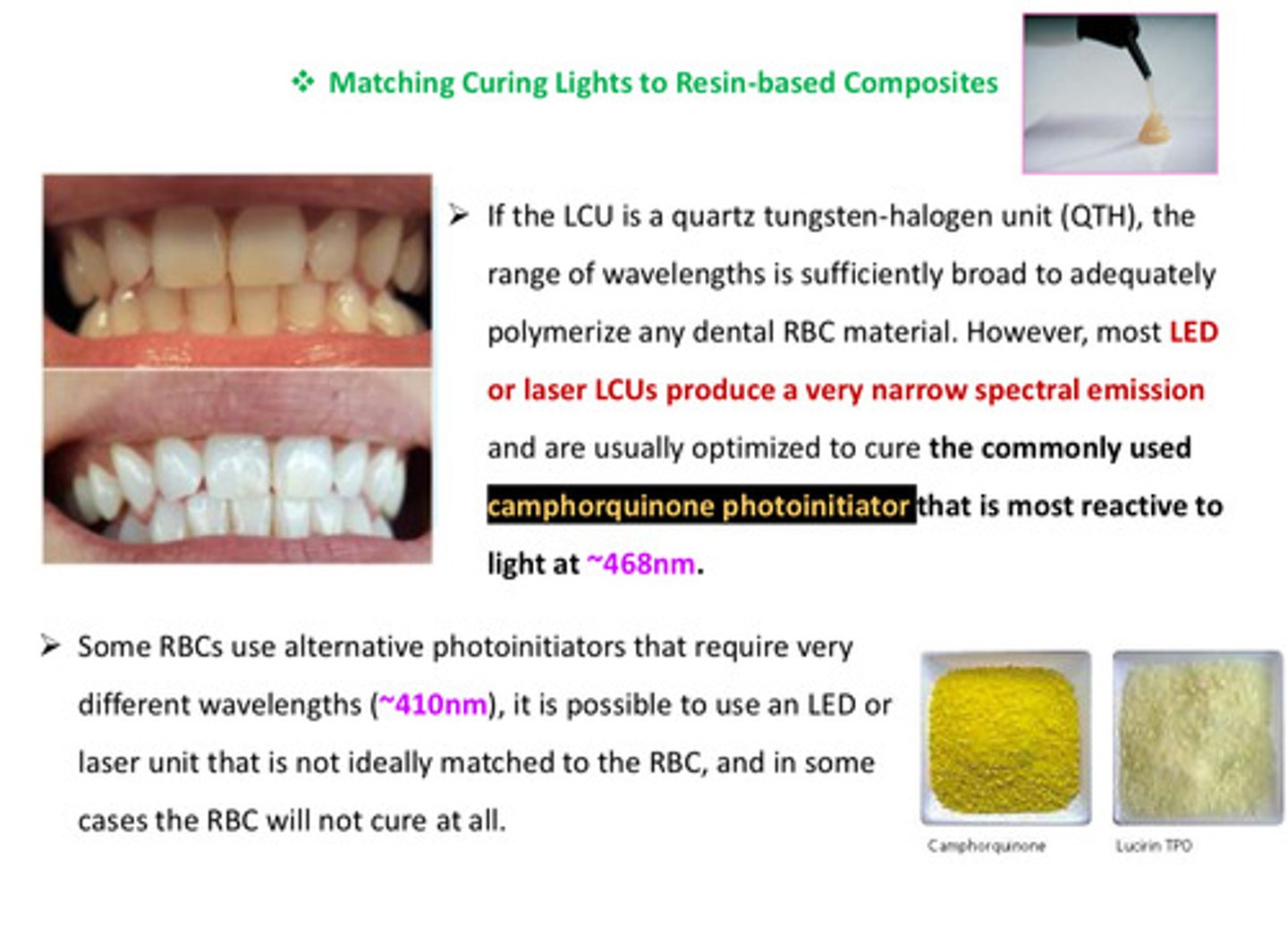
some RBCs use alternative photoinitiators that require very different wavelengths (~410 nm) which means?
it is possible to use an LED or laser unit that is not ideally matched to the RBC, and in some cases the RBC will not cure at all
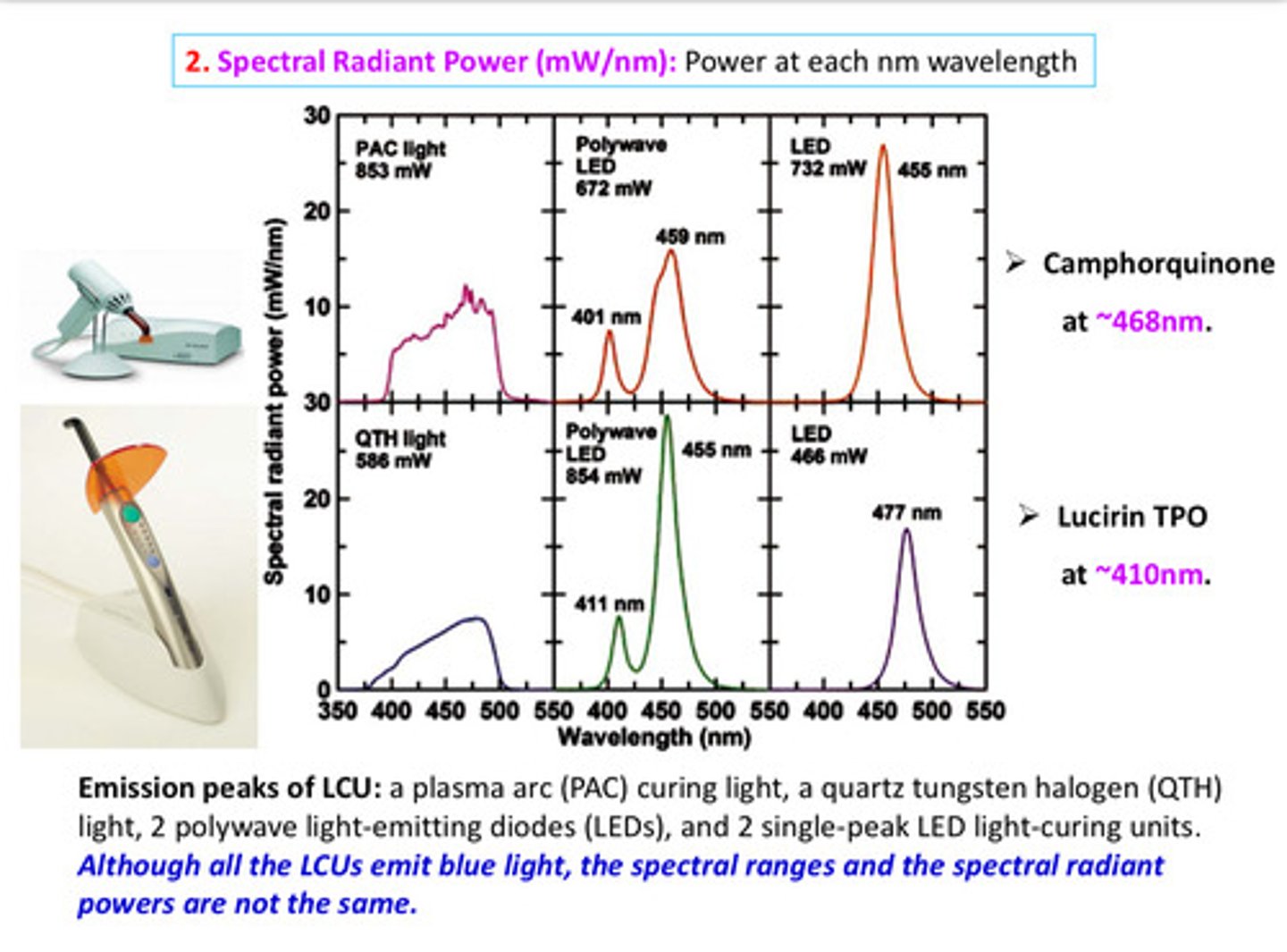
although all the LCUs emit blue light, the spectral ranges and the spectral radiant powers are ?
not the same!
in terms of radiant exitance, what should clinicians do?
should monitor the output from their LCUs using a radiometer on a regular basis to ensure that the LCU is functioning optimally, and take appropriate steps to remove adherent resin from tip-end surfaces

in terms of irradiance: the proximity of the curing light to the surface affects what?
the depth of penetration of light into the surface (there is an inverse relationship between distance and light intensity - as the distance increases, light intensity decreases)
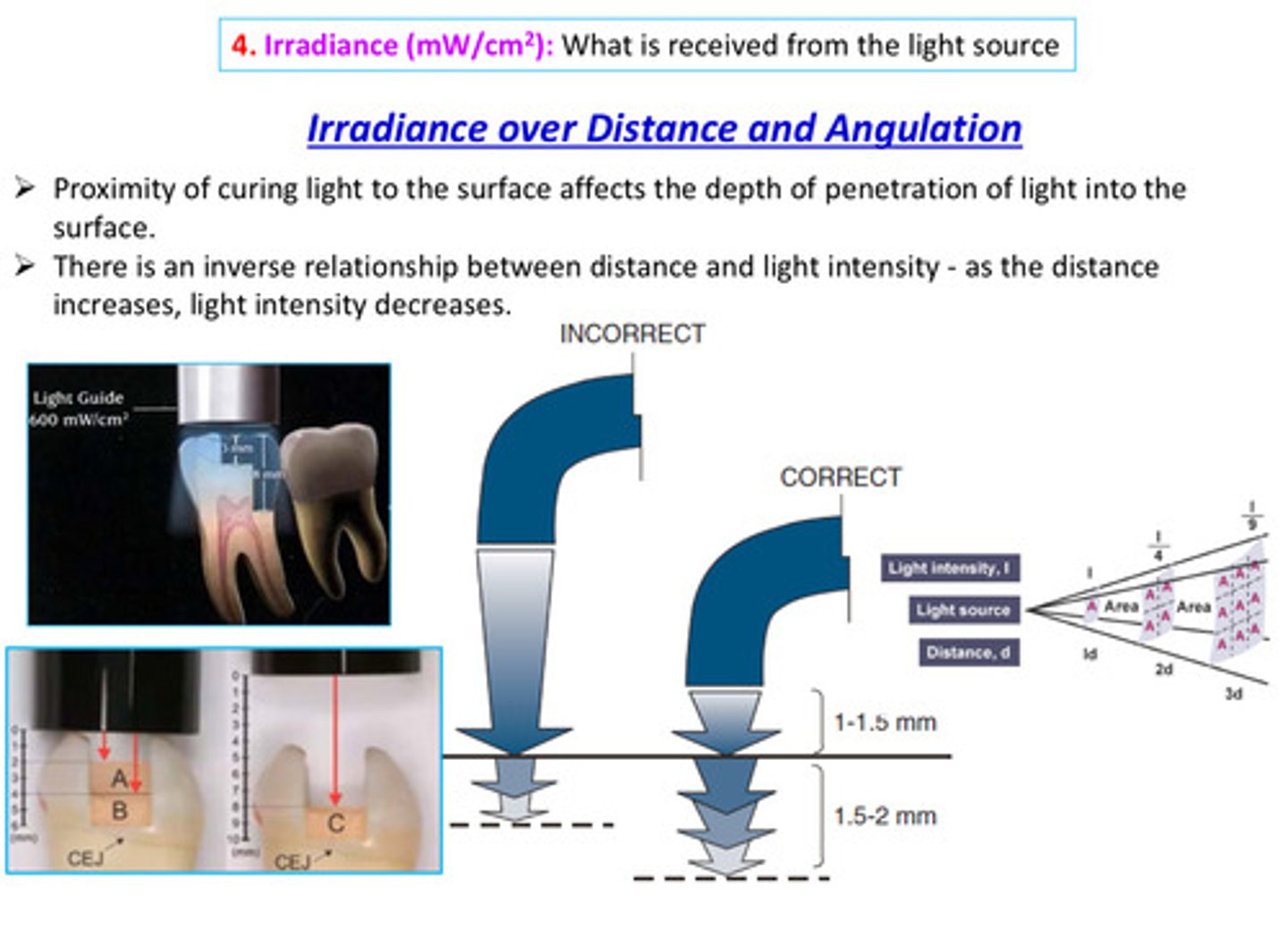
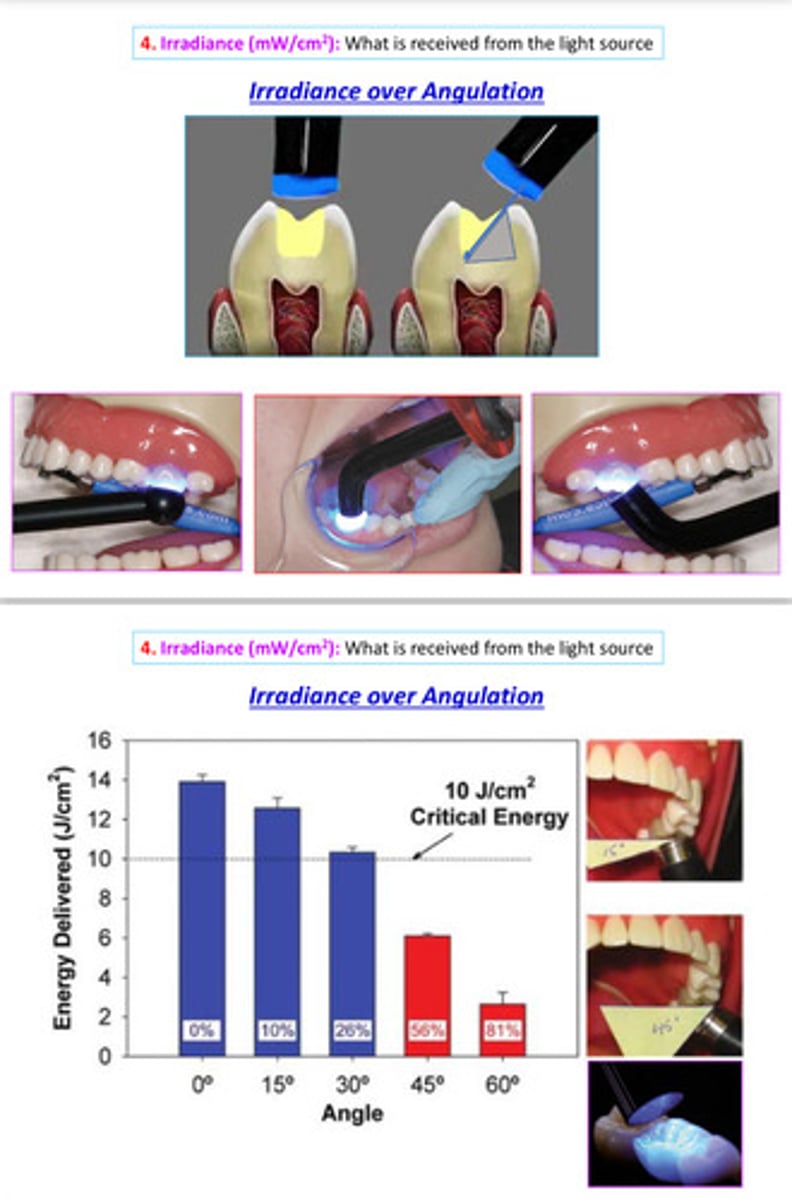
image of irradiance over angulation
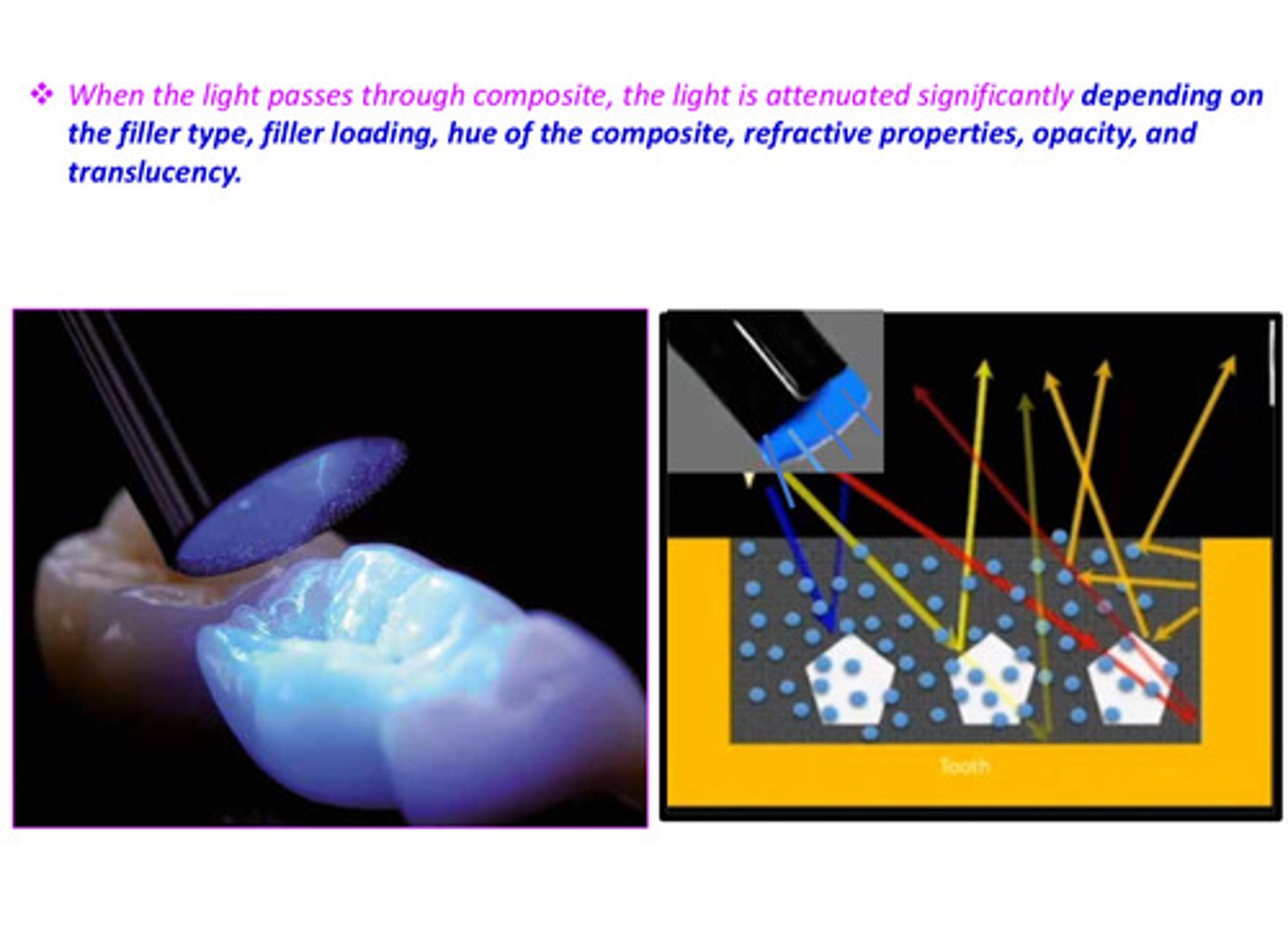
in terms of irradiance: when the light passes through the composite, the light is attenuated significantly depending on the ?
the filler type, filler loading, hue of the composite, refractive properties, opacity and translucency
describe the total energy concept (in regards to radiant exposure)
the light curing process depends on the energy; determined by the radiant exposure or energy density (E) received by the restoration (units are J/cm^2) and E is the mathematical product of the curing light irradiance (I units in mW/cm^2) and the exposure time (t in seconds): E = I x t

in terms of E = I x t, irradiance values ranging from at least _____ to ______ mW/cm^2 are recommended
600 to 1000

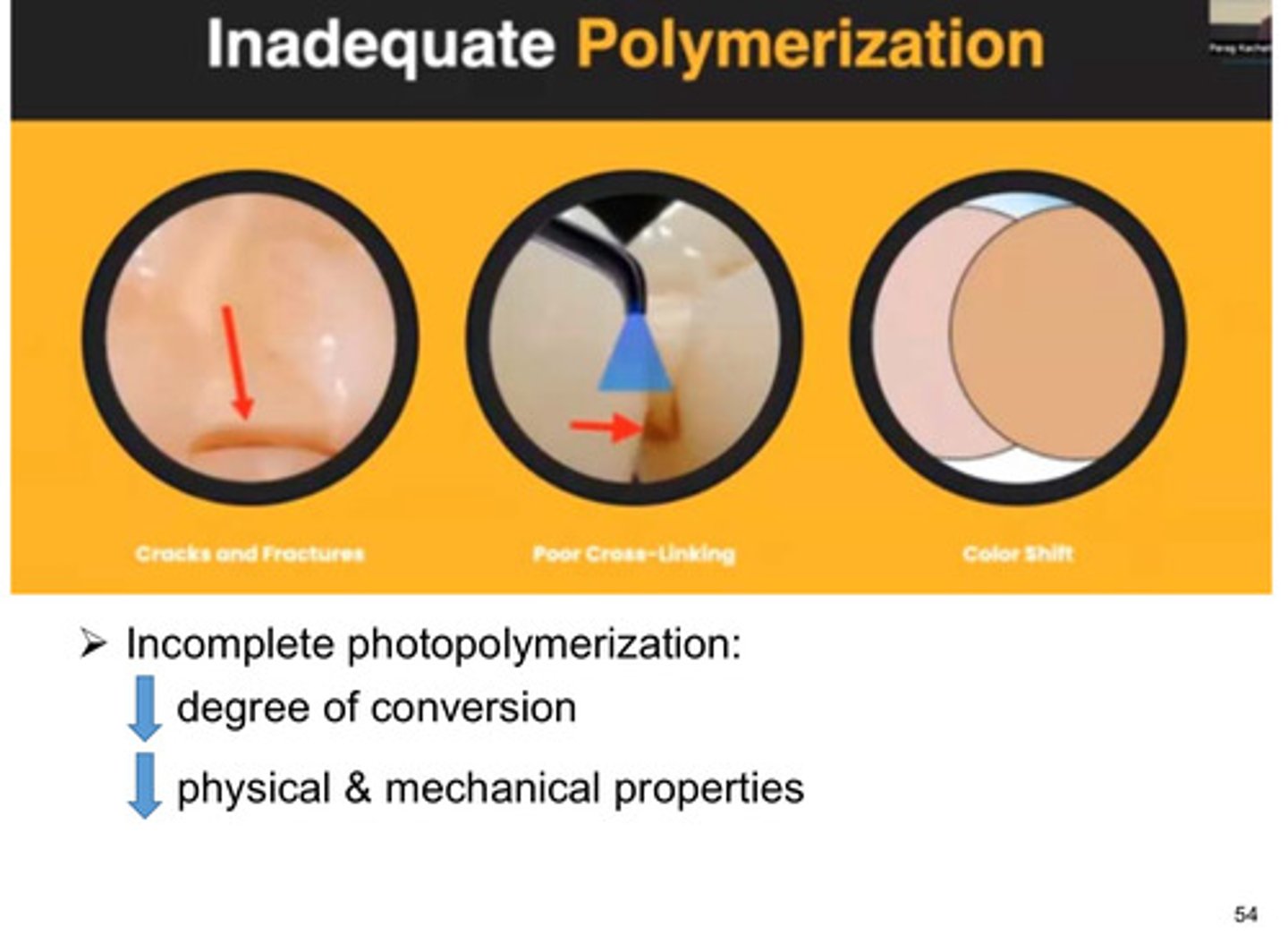
an incomplete photopolymerization can result in what 2 things
1) decreased degree of conversion
2) decreased physical and mechanical properties
regarding consistency, composites can be classified in 3 categories, what are they
1) universal (medium)
2) packable (high)
3) flowable (low)
how to effectively use dental curing lights
1) protect your eyes
2) position the patient
3) choose the appropriate LCU
4) examine the tip; place central axis of the tip
5) watch operative area through shield
6) stabilize the LCU and cure with the tip about 1 mm away from the RBC then after 1-5 seconds, when top surface of RBC is hard, move the tip of the LCU as close as possible to surface of RBC is hard
7) buccal lingual light exposures if needed
8) direct a stream of air over the tooth if needed

summary of to do in terms of clinical sequence of curing composites
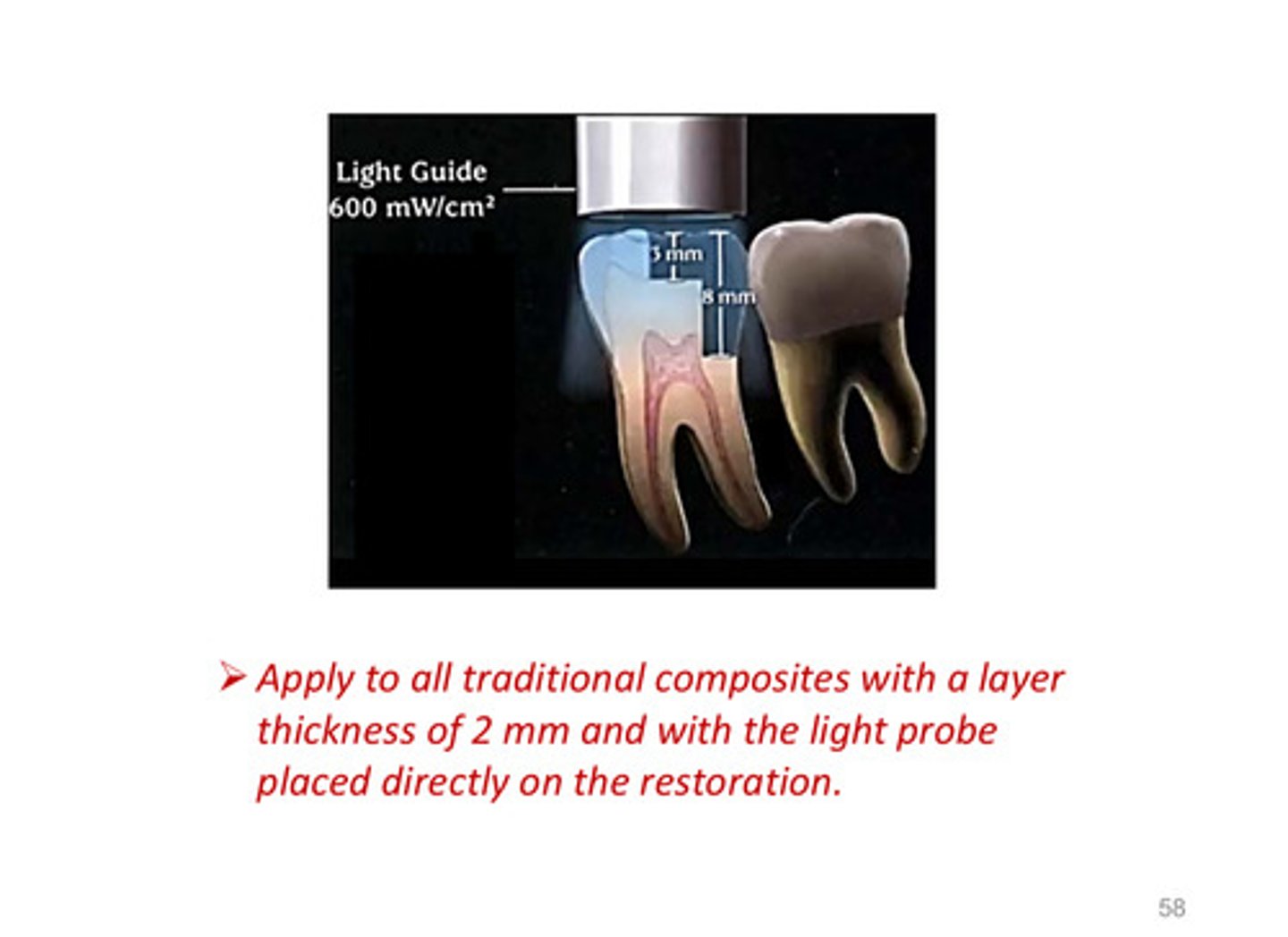
the light curing unit should be applied to all traditional composites with a layer thickness of __ mm and with the light probe placed directly on the restoration
2
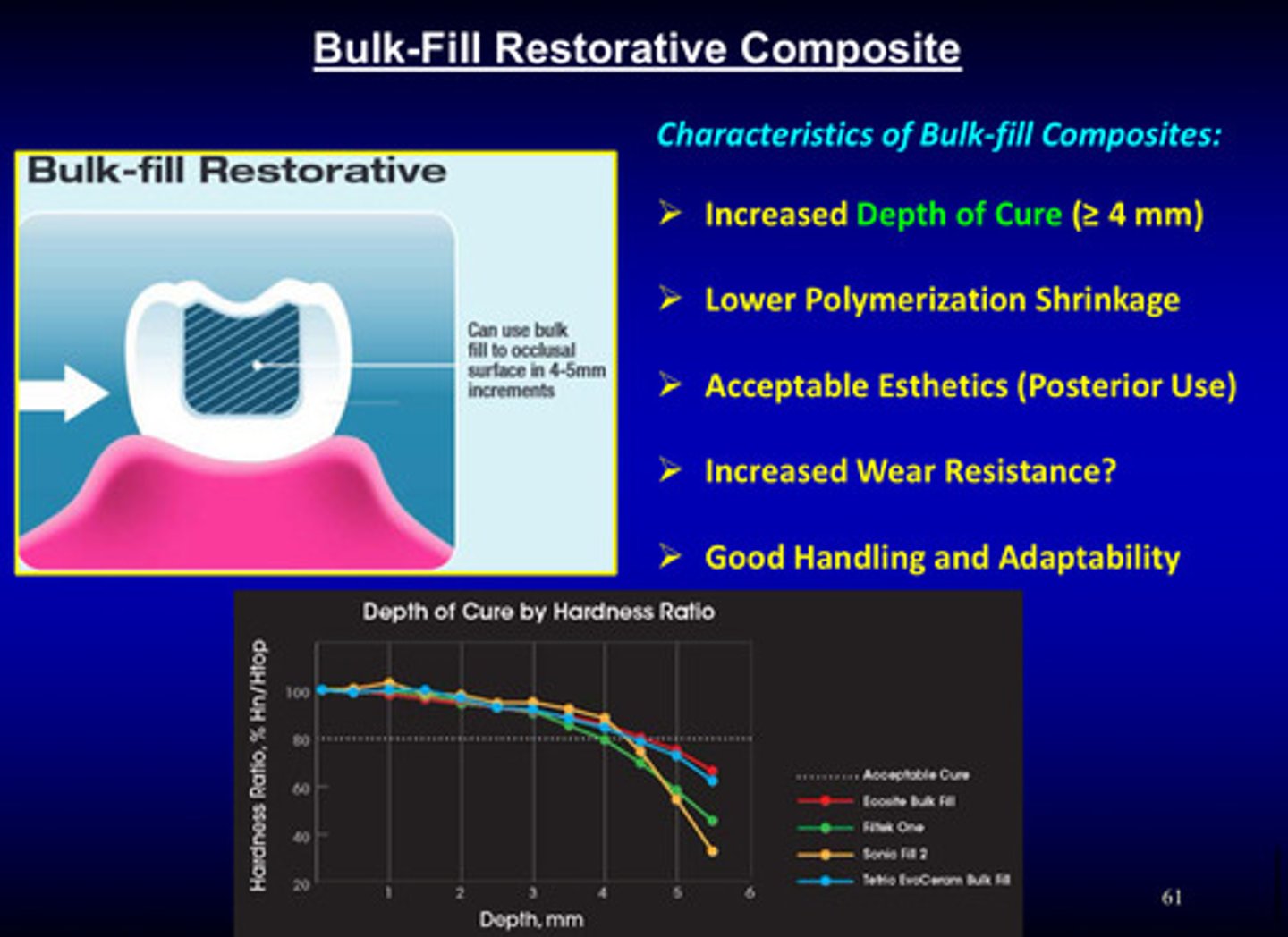
what is a bulk fill restorative composite?
light-cured resin composite material that is placed in a single increment (4-5 mm deep)

what are the 5 characteristics of bulk fill composites
1) increased depth of cure (>/= 4 mm)
2) lower polymerization shrinkage
3) acceptable esthetics (posterior use)
4) increased wear resistance?
5) good handling and adaptability
what are the advantages of bulk fill restorative composites
1) less technique sensitivity
2) reduced chair time
3) fewer voids
what are the disadvantages of bulk fill restorative composites
1) esthetics (sometimes too translucent)
2) limited choice of shades
bulk fill composites are not all the same! it is important to understand how they differ and to use them accordingly. the main difference among bulk fill composites can be seen in what 2 things
the viscosity of the material and its delivery

what are the 4 characteristics of low viscosity bulk fill composites
1) minimum shrinkage effects
2) depth of cure is greater due to less filler content and a higher level of photoinitiators
3) the material is so elastic, it will mitigate polymerization shrinkage effects bc shrinkage effects are compensated by the elasticity of the material
4) recommended to place a high-viscosity composite to achieve better wear resistance when used on high stress areas

what are the 4 characteristics of high viscosity bulk fill composites
1) better wear resistance
2) do not adapt well to the cavity walls due to its high viscosity
3) recommended to place a low-viscosity composite to achieve intimate adaptation to the gingival and pulpal floors
4) this results in two cured layers, although they are bulk fills
describe the biocompatibility issues of the molecular structures of bisphenol A (I) and estrogens (II) and their derivatives
1) bisphenol A is associated with manufacture of some plastics, including composites —> have been safety concerns about BPA
2) lab tests have shown that BPA has same effect as estrogen, such as DNA adduct formation and binding to the estrogen receptor
3) none of these effects have been observed in humans
4) due to action of salivary enzymes on composites, there may be some low level exposure to BPA
5) ADA is not currently expressing any concerns regarding BPA exposure
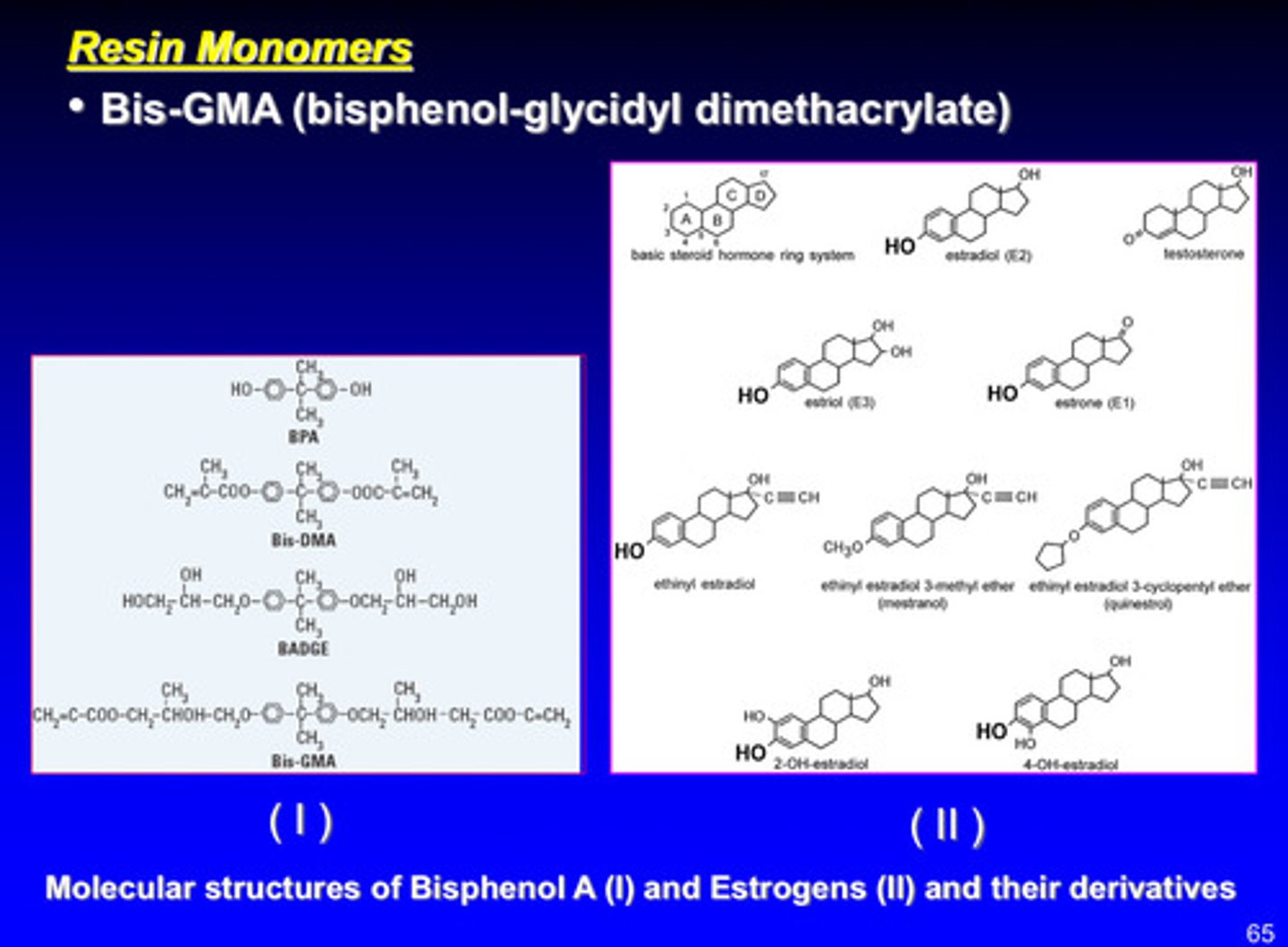
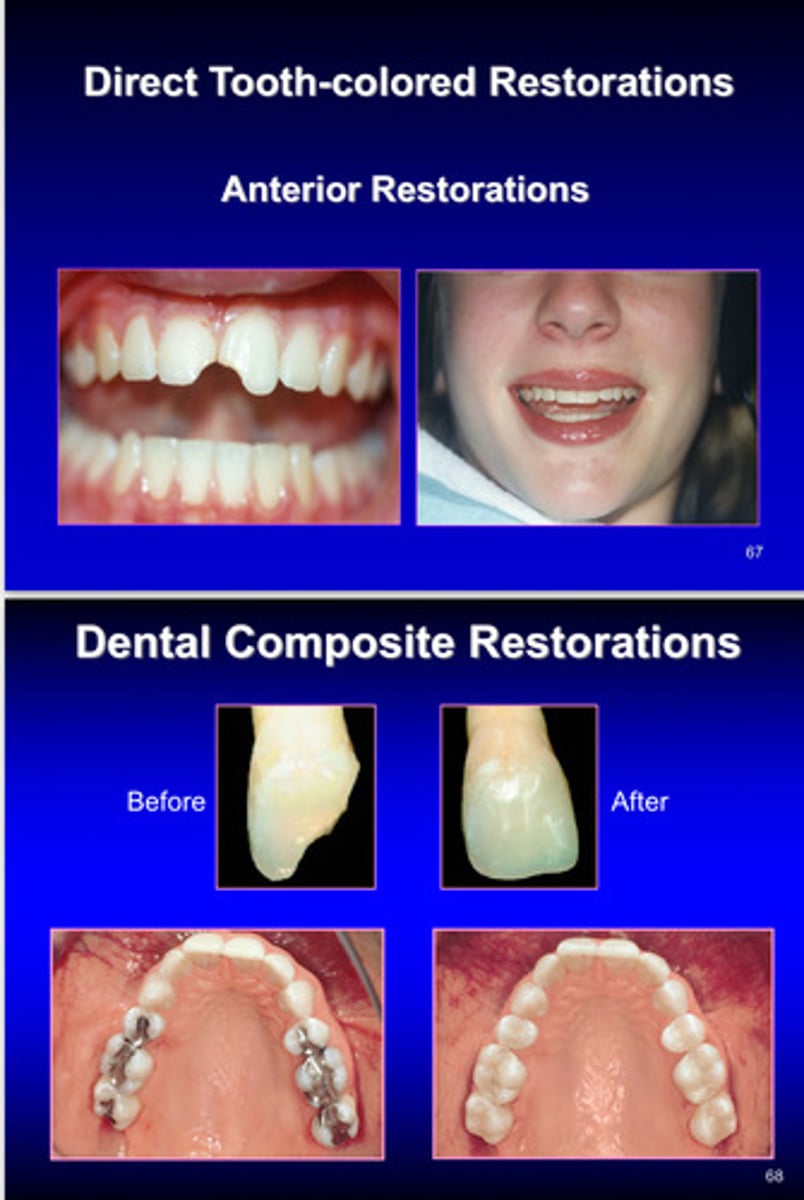
image of dental composite restorations
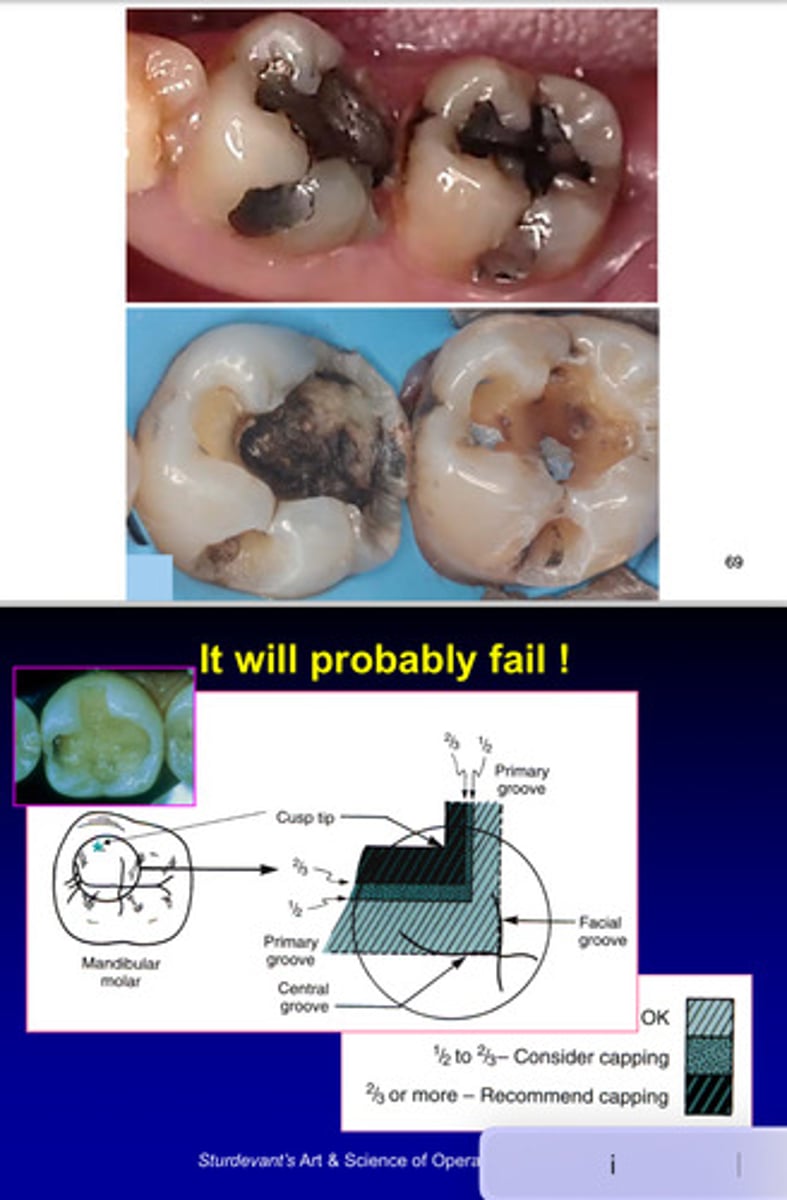
what happens if you try to fill these kinds of teeth?
it will probably fail; not enough tooth structure left —> you should consider capping because very large fillings will probably fail
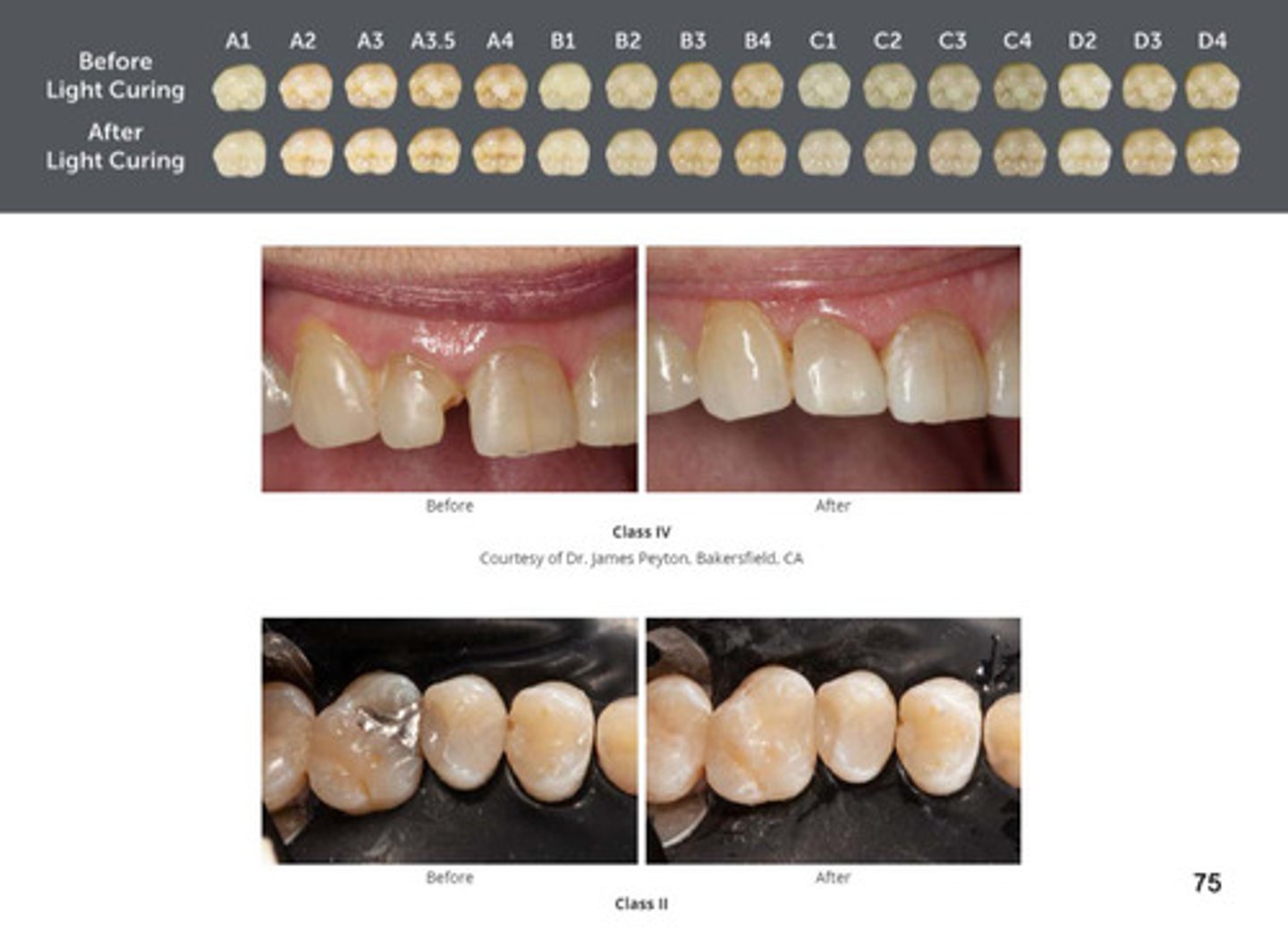
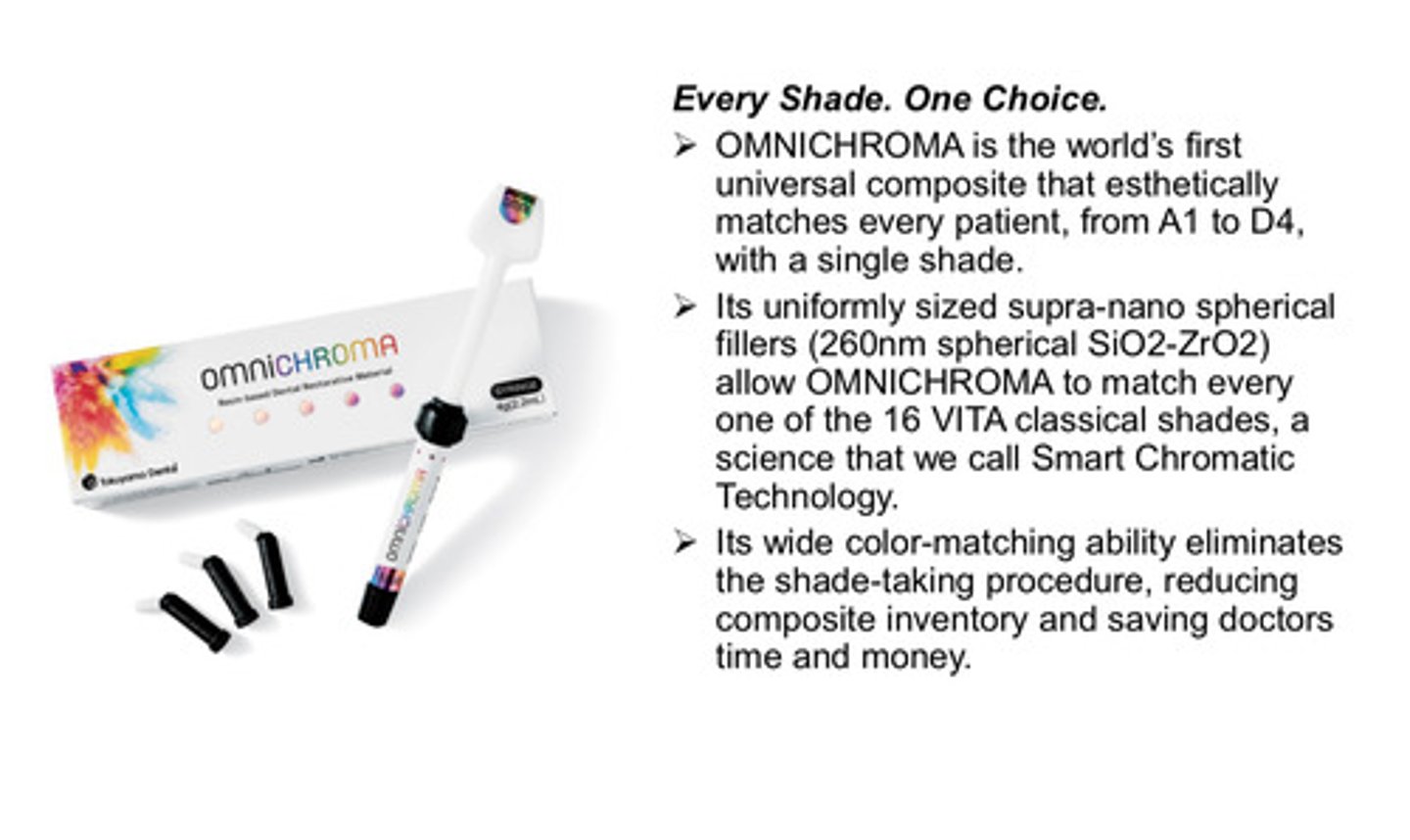
what is omnichroma?
1) world's first universal composite that esthetically matches every patient, from A1 to D4, with a single shade
2) its uniformly sized supra-nano spherical fillers allow omnichroma to match every one of the 16 VITA classical shades (we call this smart chromatic technology)
3) its wide color matching ability eliminates shade taking procedure, reducing composite inventory and saving doctors time and money
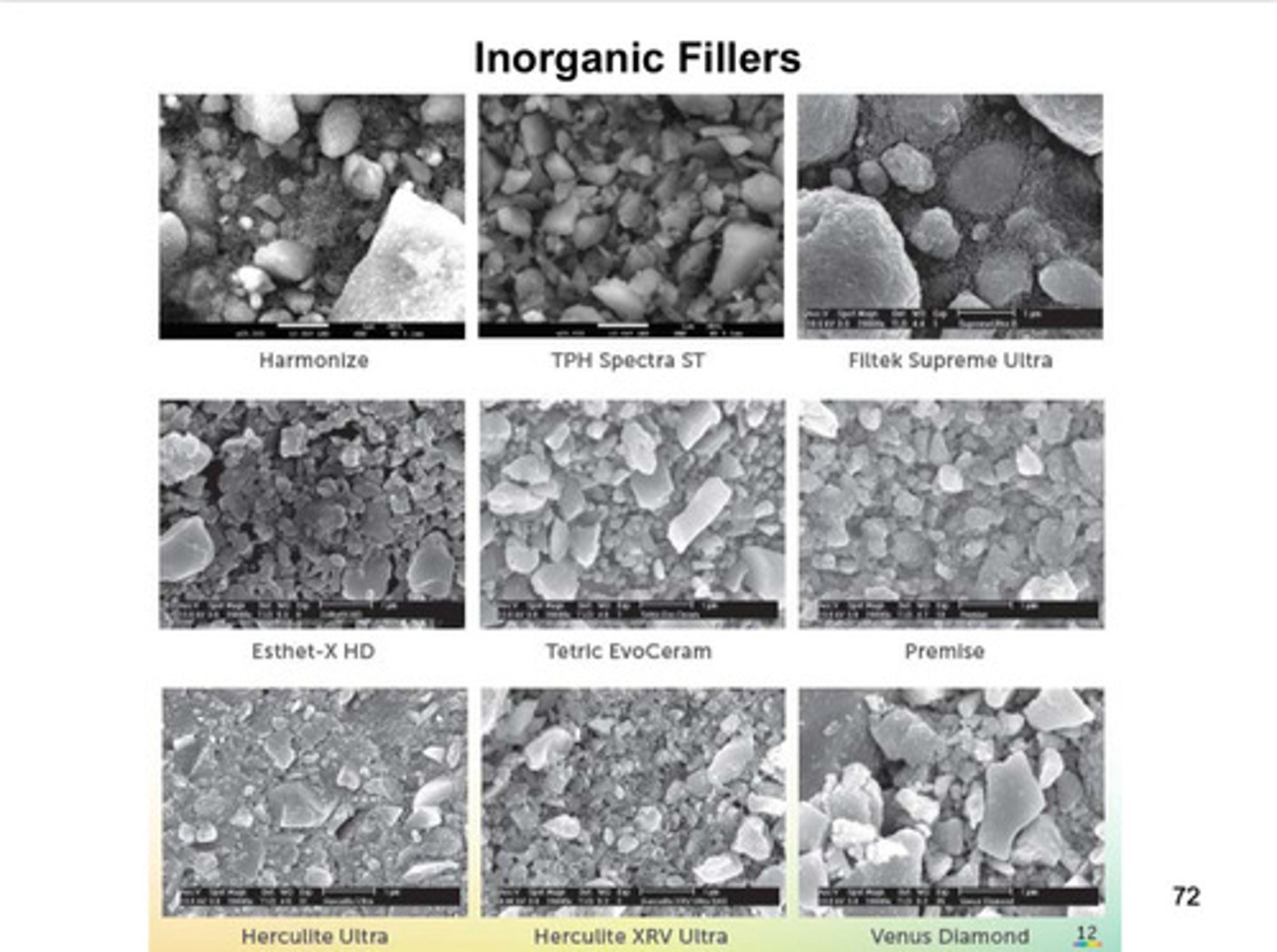
images of various inorganic fillers

more images on omnichroma pt 1
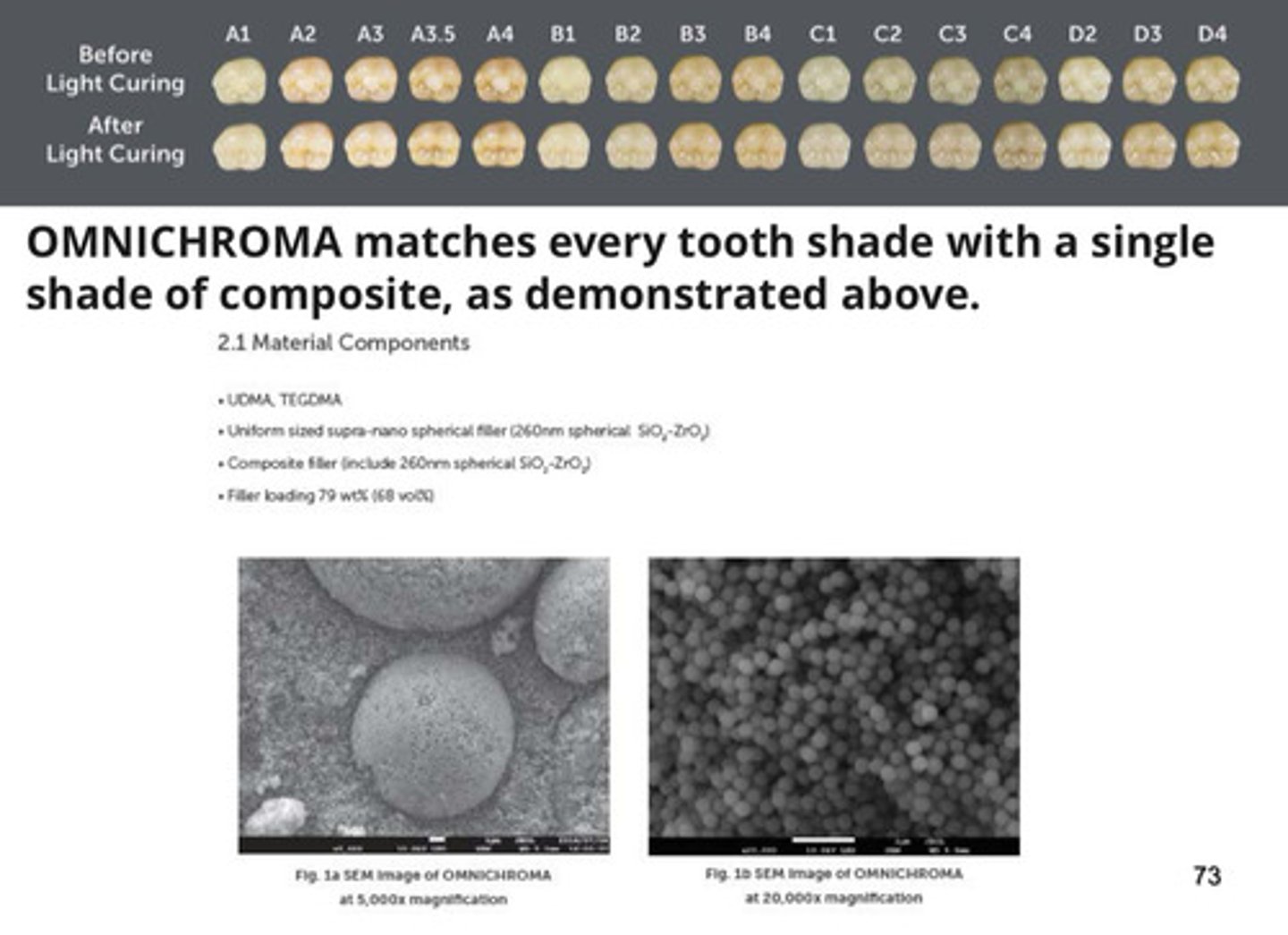
more images on omnichroma pt 2
omnichroma generates red to yellow structural color equivalent to the color elements of a natural tooth —> this red to yellow structural color combines with reflected light and color of the surrounding tooth in an additive color mixing process, maximizing omnichroma's ability to match natural teeth
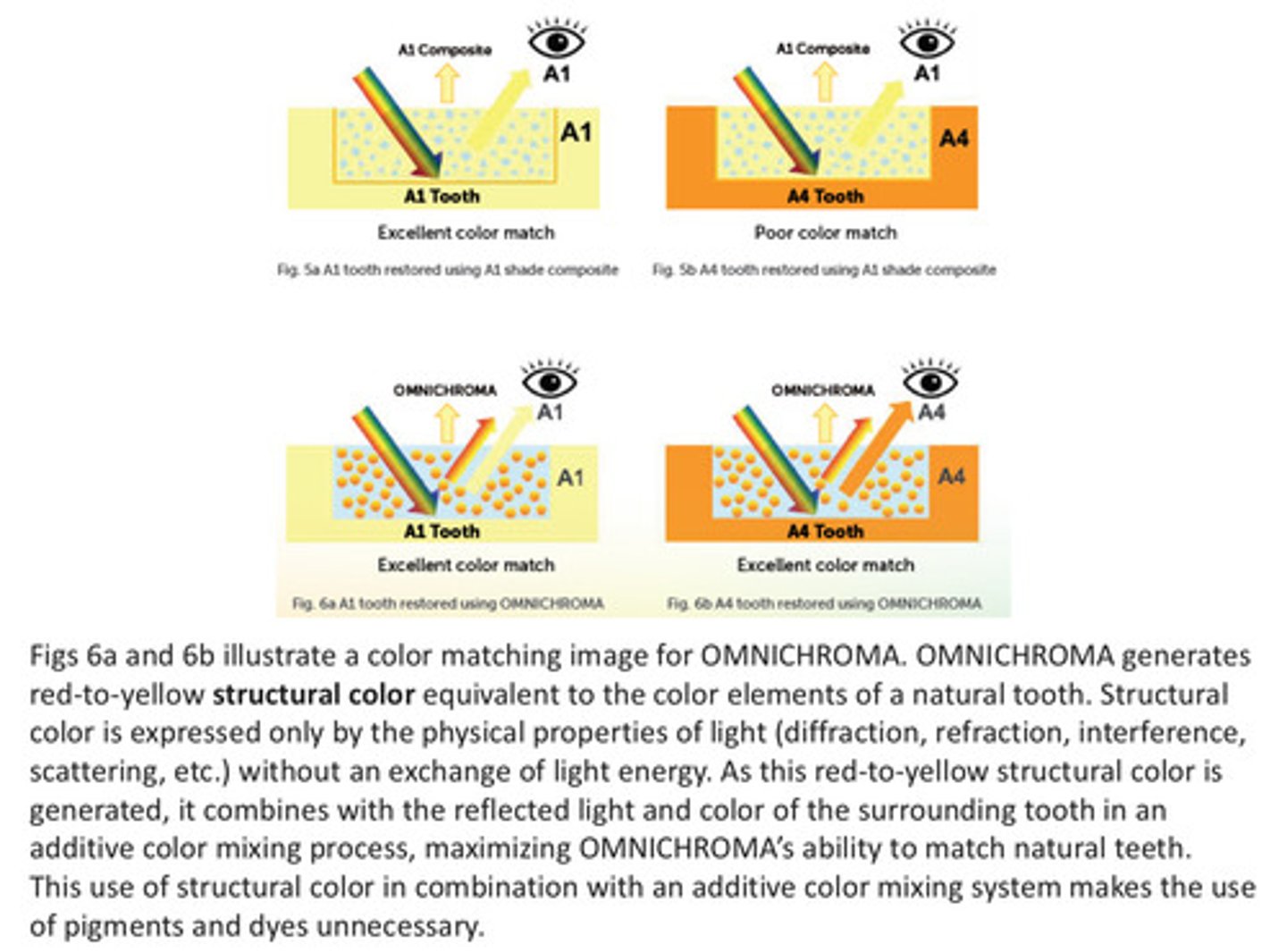
more images on omnichroma pt 3