adaptive immunity I
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what are the two types of immunity?
humoral - B cells produce antibodies, for extracellular antigens
cell-mediated - T cells, for intracellular antigens
3 pillars of adaptive immunity
specificity, memory, tolerance
what is specificity?
the ability to recognise specific antigens and generate a response based on immunoglobulin structure, TCRs and clonal selection of B and T cells
what makes TCRs specific?
in their variable regions, each TCR will consist of different CDR loops
what is memory?
the ability to produce an enhanced immune response following reinfection, based on clonal selection of T and B cells and memory cells
why is it important for memory cells to be produced in the primary response?
ensure there is a large population of antigen-specific cells for future reinfection, enabling rapid clonal selection in secondary response
what is tolerance?
the ability to discriminate between self and non-self to avoid autoimmune disease, dependent on the elimination of immature T/B cells that respond to self antigens
name the key components of the adaptive immune system
b lymphocytes - plasma and memory cells, t lymphocytes - cd8+ cytotoxic T cells, cd4+ helper T cells, T regulatory cells, memory cells, APCs, lymphoid organs
what makes plasma cells specialised?
they have a larger ER to support antibody production
what are the 3 subsets of T helper cells?
th1, th2, th17
which T effector cell targets viruses?
CD8+
what are the 3 APCs? (antigen presenting cells)
dendritic, macrophages, B cells
what are some of the secondary lymphoid organs?
lymph nodes, spleen
what is an antigen?
a protein, glycoprotein, polysaccharide on pathogens that marks them as non-self and produces an immune response
what is the epitope?
the part of the antigen that is recognised by the variable region of the antibody and is expressed on MHC molecules
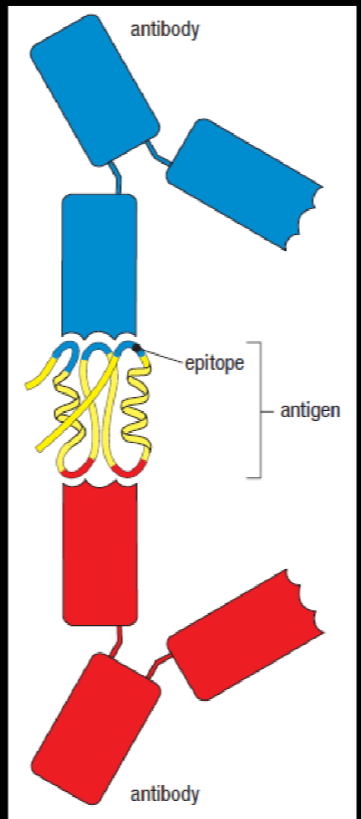
what is able to recognise surface-exposed epitopes?
antibodies
what is able to recognise less accessible epitopes?
TCRs as the antigen can be broken down inside T cells for presentation as MHC later
describe the structure of an IgG antibody
contains 2 heavy and light chains where light are part of the variable region only, disulphide bonds link constant regions together
what are the two antigen receptors?
BCR - membrane bound antibody, TCR
give the structure of the TCR
consists of alpha and beta chains, both with variable and constant regions, held together by disulphide bonds
how are B cells activated to produce antibodies?
resting B cells will express BCRs and when antigen binds, they will produce the antibody without the transmembrane region
what does the Fc region of an antibody bind to?
macrophages/neutrophils
what are the 5 classes of antibody and how do they differ?
IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, IgD, differ by heavy chain
structure of IgM and its importance?
10 heavy mu chains and 10 light chains + J chain. one of the first types of antibodies to be secreted in the primary response, can cluster pathogens for phagocytes due to multiple antigen binding sites
structure of IgA and its importance?
dimer of 4 heavy alpha chains and 4 light chains, secreted in mucosal membranes in gastrointestinal and respiratory systems
IgE structure and importance?
2 heavy epsilon chains and 2 light chains, involved in allergic responses and to parasitic worms
describe clonal selection of B cells
native antigen or dendritic cell expressing pMHC will bind to the B cell with complementary immunoglobulin, stimulating proliferation of that B cell with the selected antigen. some B cells will become plasma cells and some will become memory cells that express BCR on their cell surface membranes
how do antibodies remediate infection?
neutralize bacterial toxins, opsonize bacteria and activate complement system
what are the main MHC glycoproteins?
CD4 and CD8
what is the purpose of MHC glycoproteins?
help with presentation of antigens to TCR, as well as stabilizing their interactions
what is MHC class I?
binds to TCRs on CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, found on all cells except RBCs
what is MHC class II?
binds to TCRs on CD4+ helper T cells on APCs
why are CD4 and CD8 important?
they are co-receptors that facilitate adhesion between T cells and APCs
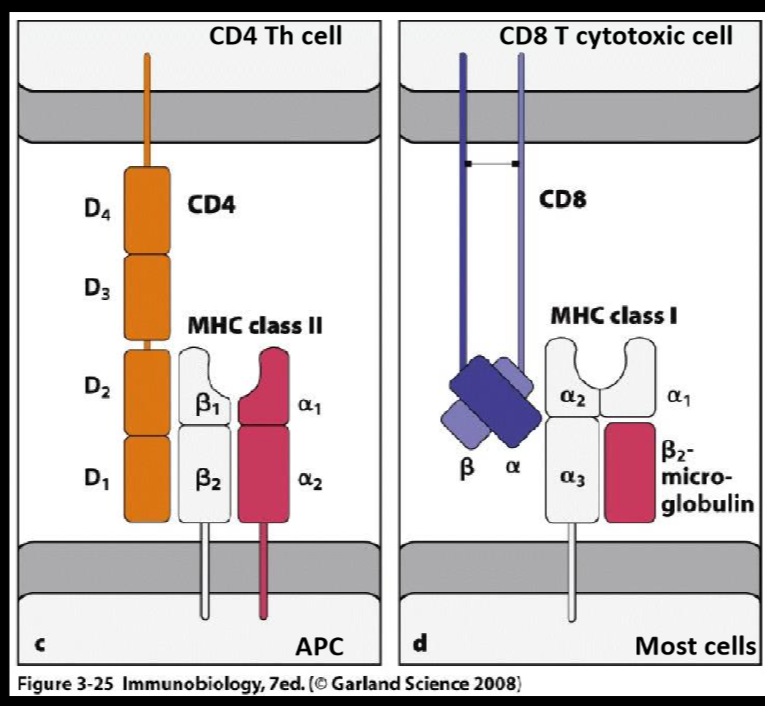
which MHC molecule is expressed for cytosolic antigen presentation and when does it occur?
MHC class I, for viruses and bacteria that can replicate in the cytosol
which MHC molecule is presented in endocytic antigen presentation and for what types of pathogens?
MHC class II, intravesicular and extracellular pathogens and toxins