Lecture 1 - Fluid Imbalances
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
where is intracellular fluid predominantly found
mostly in muscle cells
H20 and Na+ movement across membranes
H20 moves freely, Na+ doesn’t
what are intracellular osmoles
mostly large proteins that don’t move
what is the dominant extracellular tonically active particle
Na+
(other prevalent ones: K+, glucose, urea, albumin)
ratio of intracellular fluid : extracellular fluid
2/3 : 1/3
ratio of interstitial water : intravascular water of extracellular fluid (1/3 of total fluid)
3/4 : 1/4
hypotonic environment
higher concentration of solute in the cell compared to extracellular environment
water moves INTO cells causing them to swell
isotonic environment
equal concentration of solute inside and outside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
hypertonic environment
higher concentration of solute in the extracellular environment compared to the cell, causing water to move OUT of the cells and shrink them.
what is the function of osmotic pressure
maintain distribution of fluids between compartments of fluid (i.e. intracellular, extracellular)
what is osmotic pressure influenced by
concentration of dissolved electrolytes, proteins, other large molecules (cannot move across membranes so water moves freely to maintain equilibrium)
what is intracellular fluid (ICF) needed for
volume is critical for normal cell function
what is extracellular fluid (ECF) needed for
volume is essential for tissue perfusion
what is interstitial fluid
fluid between or around tissues
What is intravascular water
fluid found inside blood vessels e.g. plasma
s/s of dehydration (adult)
dry mucous membranes
skin tenting (pinch skin and takes long to go back to normal)
decreased urine output
postural changes (lying → standing = decreased SBP, dizziness, increased HR)
decreased capillary refill
cool extremities
decreased cognitive function
s/s of dehydration - infant/young child
dry mouth and tongue
lack of tears when crying
no wet diaper for 3 hours
sunken eyes/cheeks
sunken soft spot on top of skull
irritability
***requires immediate medical attention***
typical fluid maintenance per day
2000-3000mL
6-8 × 250 mL glasses of water
management of mild dehydration
drink - water, WHO-ORS (world health organization oral rehydration solution), water + salt, sports drink and increased fluid intake.
management of severe dehydration
depends on severity, medical attention/IV fluid replacement
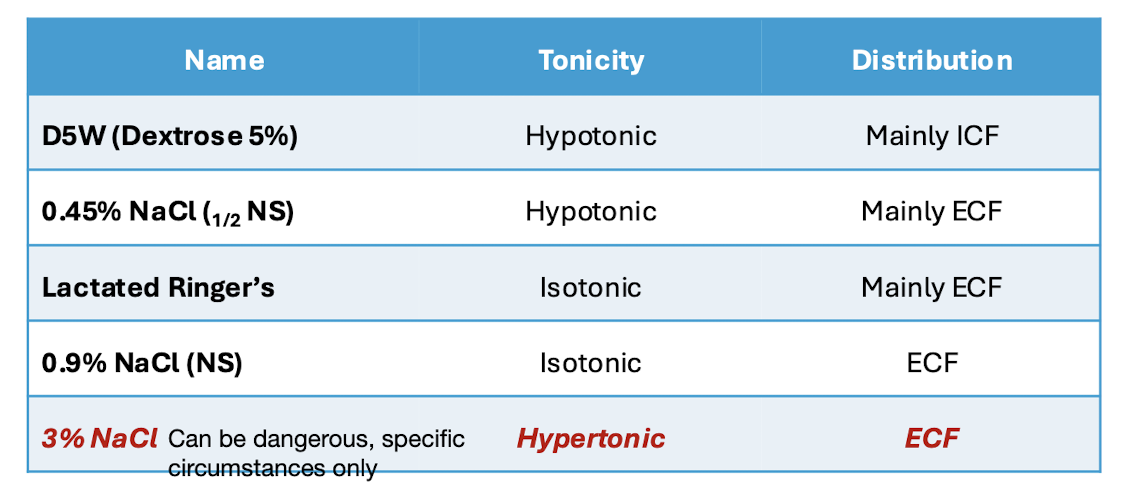
IV replacements for severe dehydration
what is edema
excess fluid volume in extracellular compartment
usually caused by heart/kidney/liver failure
may occur during pregnancy or due to malnutrition
s/s of edema
swelling in feet/ankles/lower legs (gravity), pitting (push on swelled area and it leaves a pit, measure severity of edema by depth and duration of pit)
weight gain
increased jugular venous pressure
Positive hepatojugular reflux (firm pressure over the liver temporarily increases venous return of the heart) (see lecture slides for video)
s/s of pulmonary edema
increased respiratory rate
SOB sensation
crackles present using stethoscope
medications to manage edema
diuretics = increase sodium excretion and water follows
loop diuretics (furosemide, ethacrynic acid) = strong
thiazide diuretics (HCTZ, chlorthalidone, metolazone)
K sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride) (depending on K levels)
loop diuretics
furosemide, ethacrynic acid= strong
thiazide diuretics
HCTZ, chlorthalidone, metolazone
K sparing diuretics
spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride (depending on K levels)