Medical Immunology Fever and Inflammation
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What role do Interleukin-1(IL-1) and TNF-α have in fever formation?
They induce prostoglandin synthesis in the hypothalamus
Where does prostaglandin synthesis occur?
In the hypothalamus
Where is IL-1 released from?
Macrophages
Where is TNF-alpha released from?
Macrophages, tissues, and T-cells
What role do prostaglandins play in fever formation?
They produce micro-contractions of muscles that increase body temperature
What happens to the blood when the body has a fever?
It shifts from the surface of the body to the interior
Why does the body induce fever?
To disrupt the function of viral and bacterial proteins
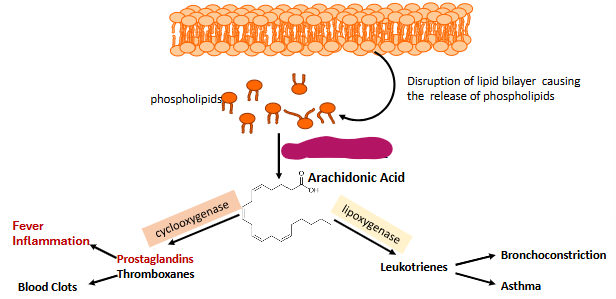
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Phospholipase A2
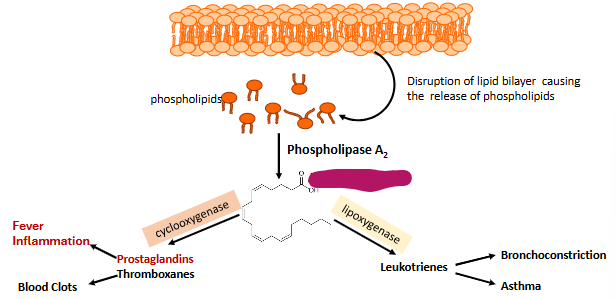
Label this part of prostoglandin synthesis
Arachidonic Acid
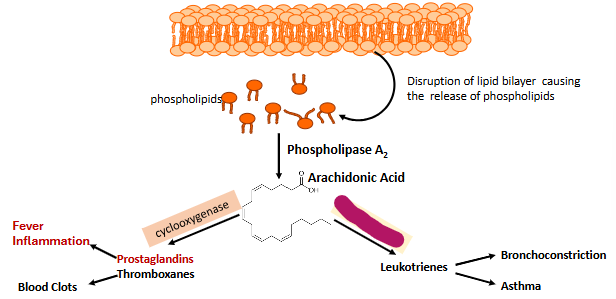
Label this part of prostoglandin synthesis
Lipoxygenase
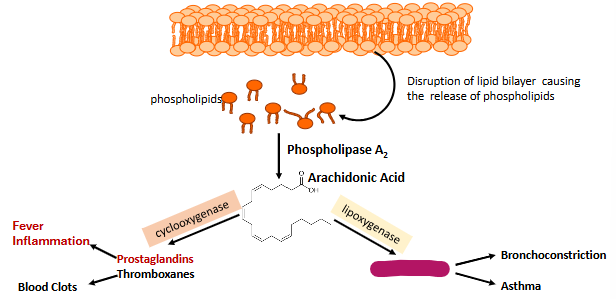
Label this part of prostoglandin synthesis
Leukotrienes
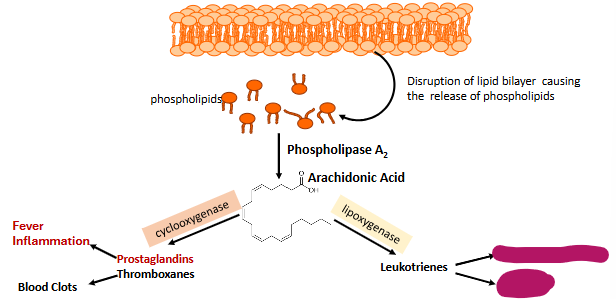
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Bronchoconstriction and asthma
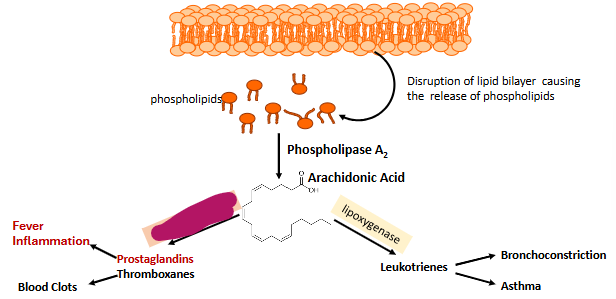
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Cyclooxygenase
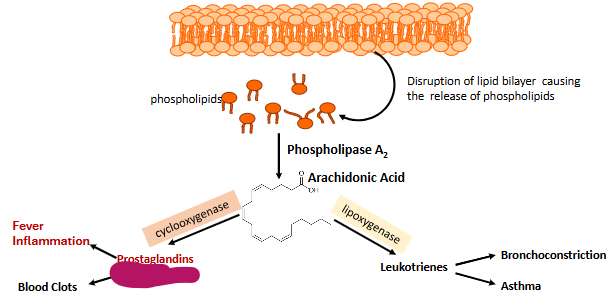
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Prostaglandins
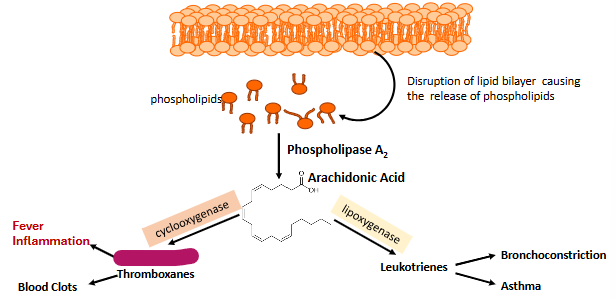
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Thromboxanes
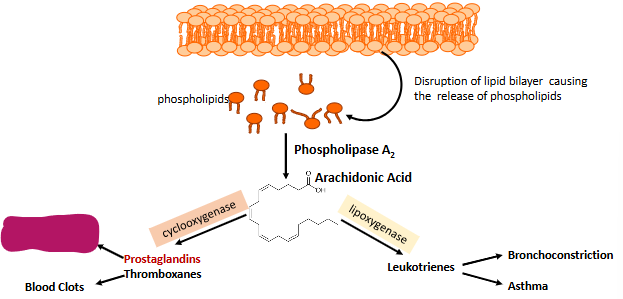
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Fever and inflammation
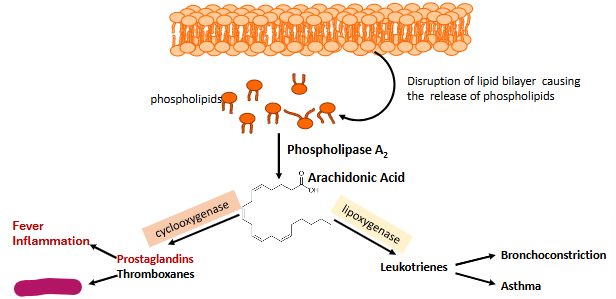
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Blood clots
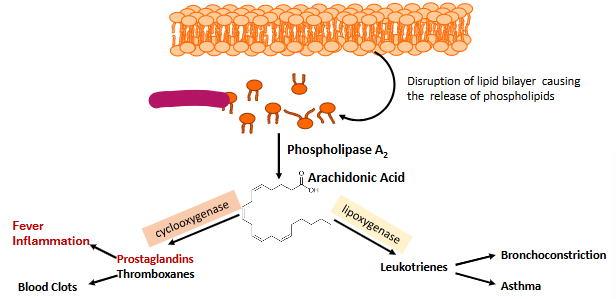
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Phospholipids
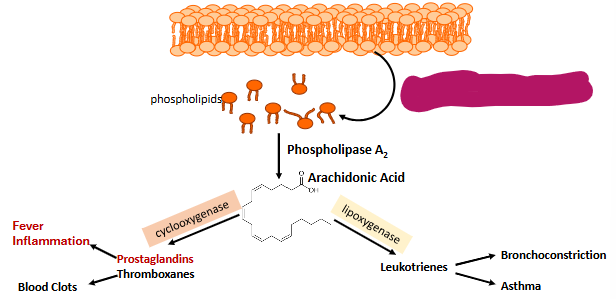
Label this part of prostaglandin synthesis
Disruption of lipid bilayer causing the release of phospholipids
How does acetaminophen help with a fever?
It inhibits cyclooxygenase, the enzyme that produces prostaglandins
What are the functions of inflammation?
To get cells of the immune system to the site of an extravascular injury, prevent spread of toxins, and promote healing
Diseases that cause _______ often have a suffix of “-itis”
Inflammation
Local manifestations of inflammation
Pain, swelling, warmth, redness
Systemic manifestations of inflammation
Fever, leukocytosis, malaise, loss of function
Who first responds to the inflammatory response?
Mast cells
How do mast cells respond to foreign organisms invading the body?
They release chemicals (histamines, prostaglandins, serotonin, and leukotrienes) to attract phagocytes (neutrophils then macrophages)
What causes heat release?
Vasodilation
What causes pain?
Vasodilation and release of vasoactive and chemotactic factors
What causes redness?
Vasodilation
What causes swelling?
Increased permeability and neutrophil emigration
What is the effect of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and histamines on the body?
They cause blood vessels to widen and the flow of blood to increase
What causes vasodilation?
Release of prostaglandins and histamines
Outcome of vasodilation
Swelling, redness and pain
Histamine, bradykinin, PGE2
Vasodilation and swelling
TNF-α, Interleukin-1, PGE2
Endogenous Pyrogens
What are endogenous pyrogens?
chemical mediators that cause fever
Leukotrienes, C5a (complement)
chemotaxis
What is chemotaxis?
Attraction of white blood cells to infection
What is a complement?
Chemical mediator that actively destroys viruses and bacteria, initiates inflammation
How does a complement become active?
In response to antibodies IgG and IgM bound to surface of bacteria, directly activated when it encounters bacteria
What is the classical pathway to complement activation?
Antibody binds to bacteria, complememnt binds to antibody which is on bacteria
Which immune system uses the classical pathway of complement activation?
Adaptive
What is tehe alternative pathway to complement activation?
Complement proteins bind to LPS (surface molecules) on bacteria
What is the MBL pathway to complement activation?
MBL binds to carbohydrates on bacteria
Whihch immune system uses the alternative pathway?
innate
Which immune system uses the MBL pathway?
Innate
What is the ultimate goal of ALL activation pathways?
to make the membrane attack complex
How does the membrane attack complex kill microbes?
Lysis