Unit 3: Glycolysis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
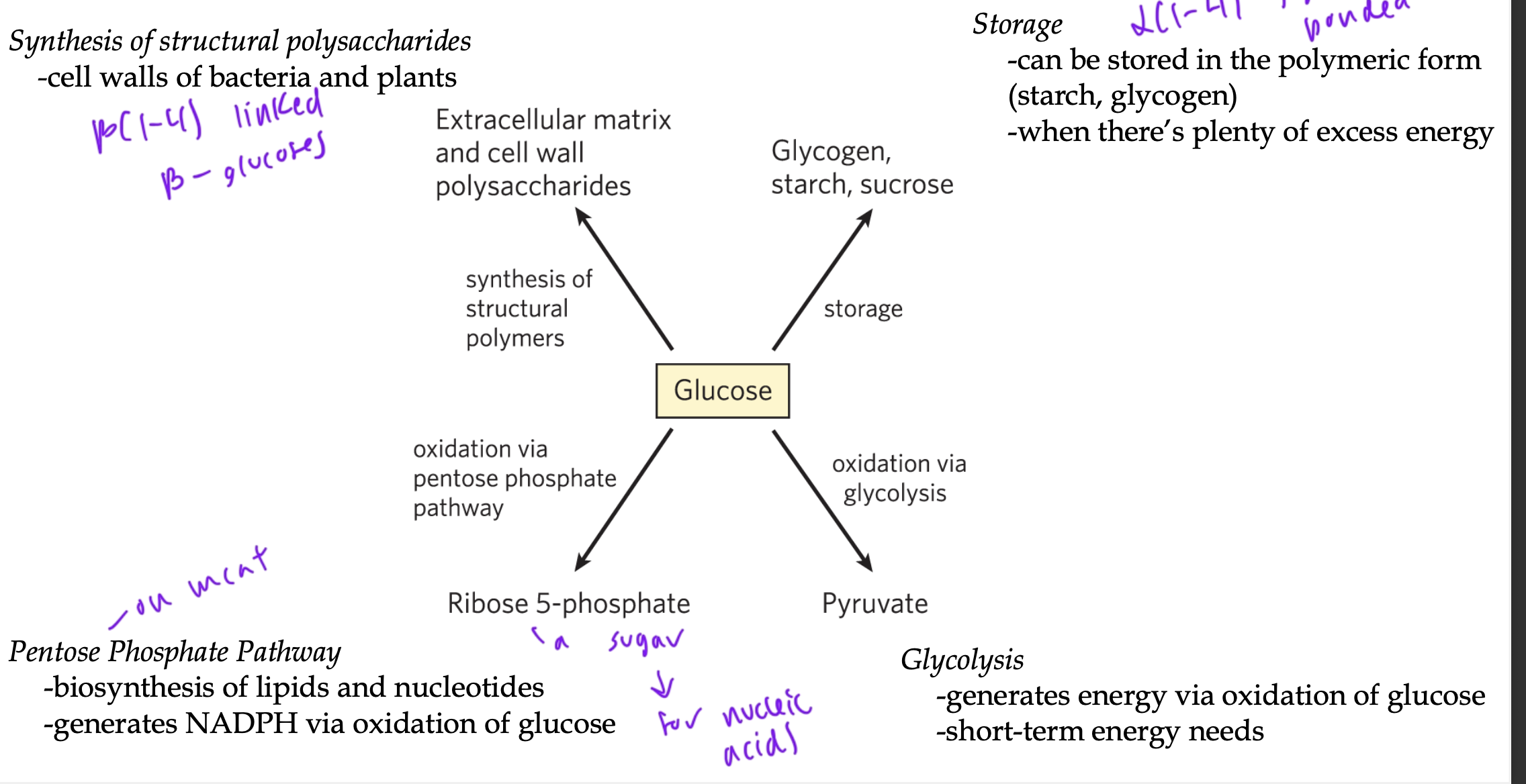
how glucose is used in the body
storage as starch, glycogen
oxidation via glycolysis to pyruvate
oxidation via pentose phosphate pathway to ribose-5-phosphate for nucleic acids
synthesis of structural polysaccharides (cell walls)
energy investment phase requires
2 ATP
net products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate
2 H2O
2 ATP
2 NADH
in glycolysis, the oxidation of the carbons in glucose is coupled with
ATP hydrolysis (exergonic)
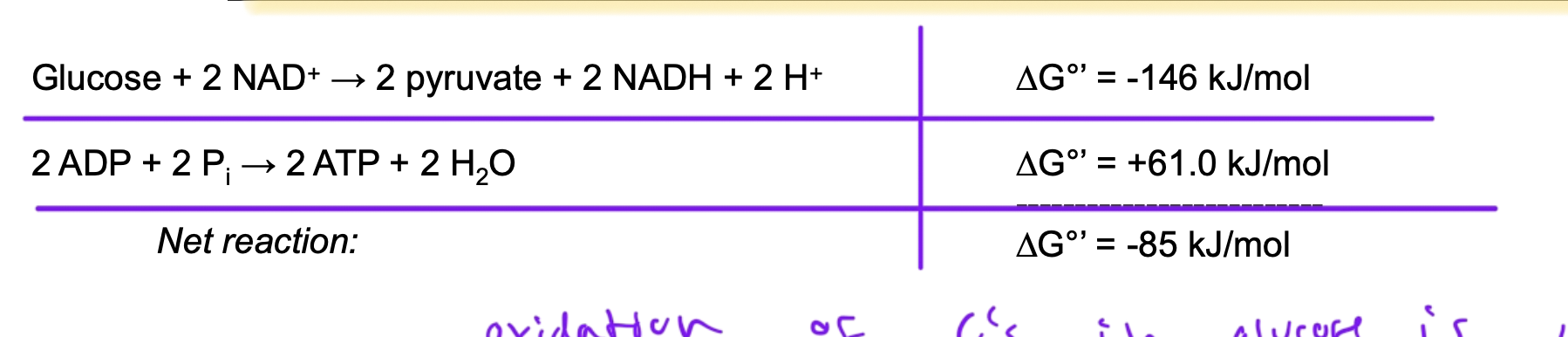
net rxn for glycolysis
glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2 Pi —> 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H+ + 2 H2O
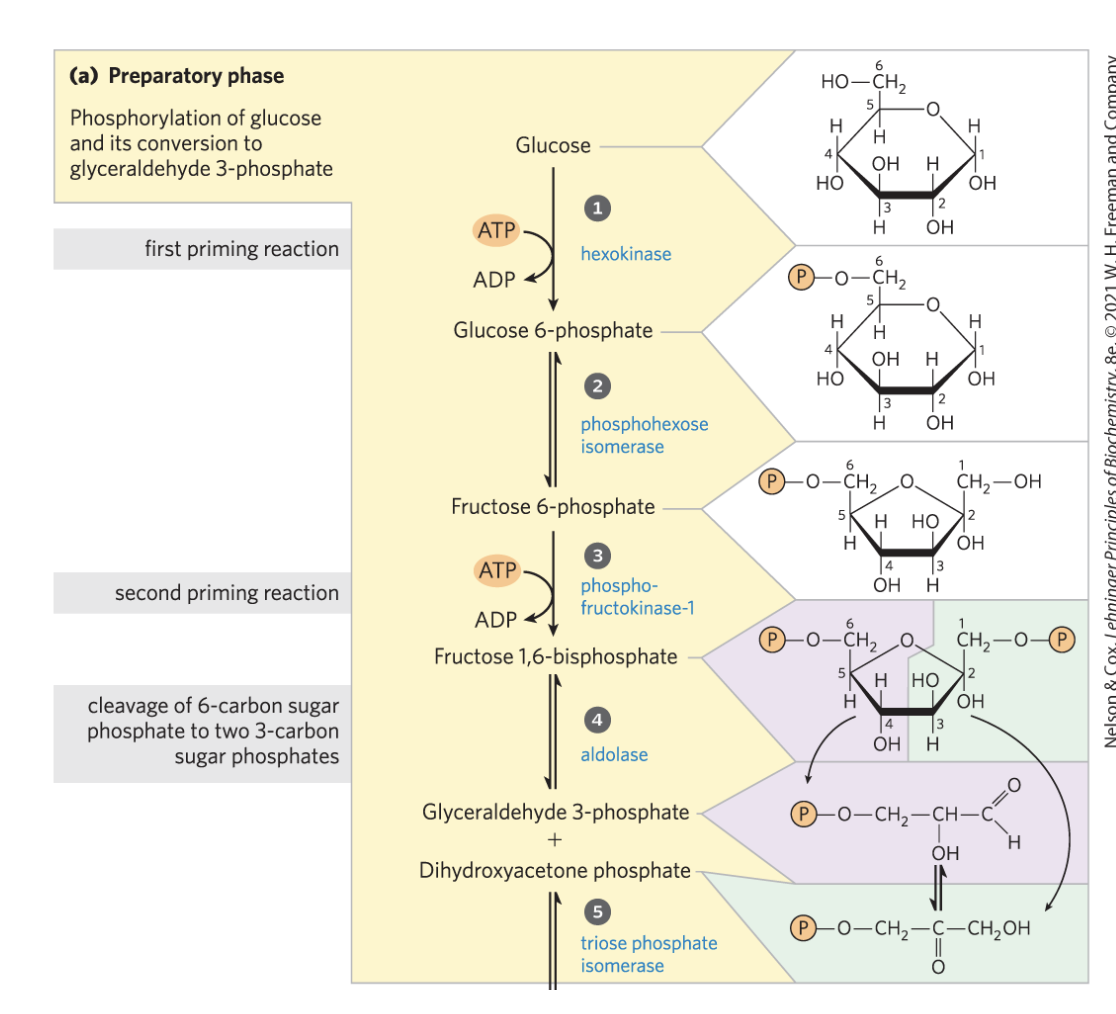
preparatory phase of glycolysis
glucose is made into a symmetrical molecule which is then cleaves to eventually become 2 pyruvate later
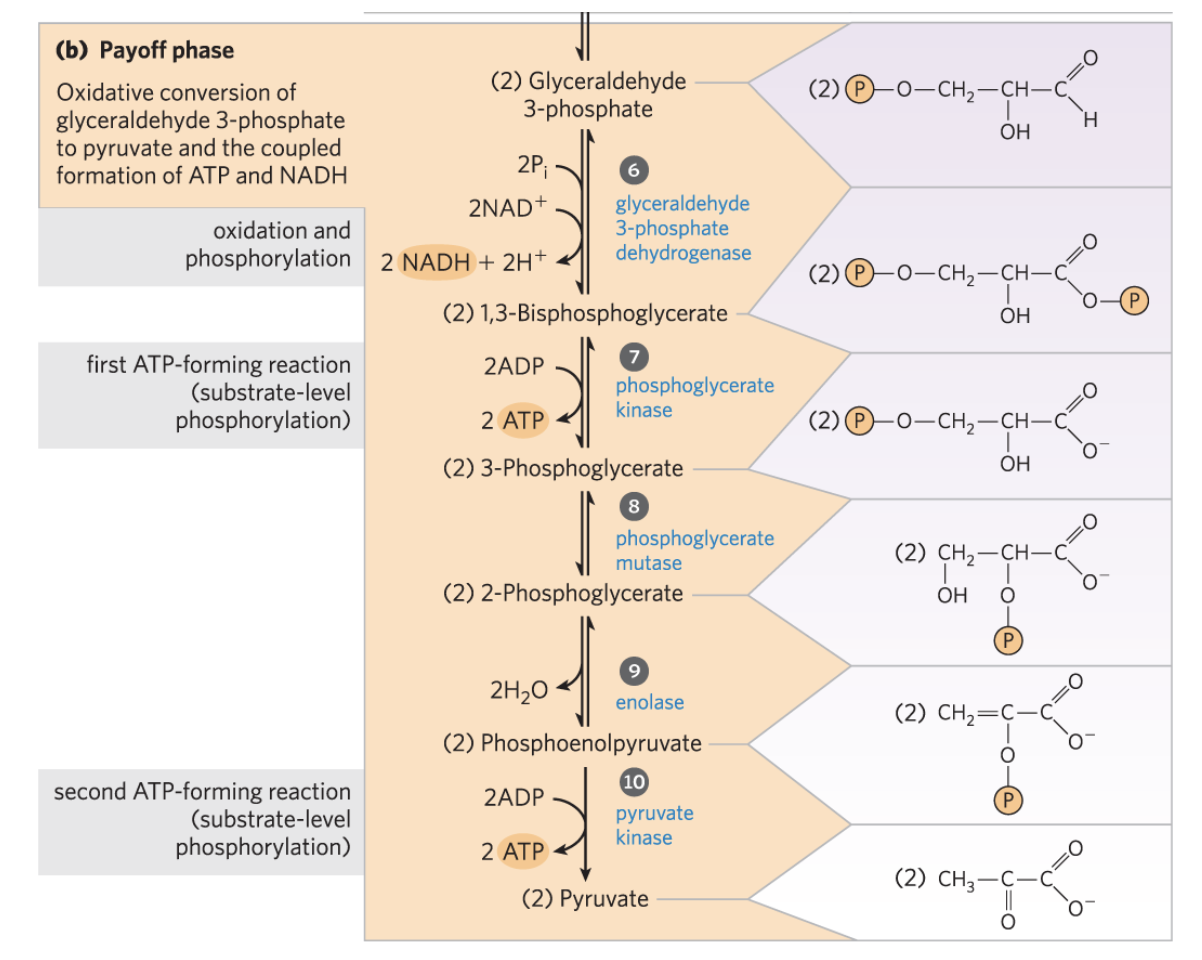
payoff phase of glycolysis
2 G3P become 2 pyruvate and 2 ATP are net gained
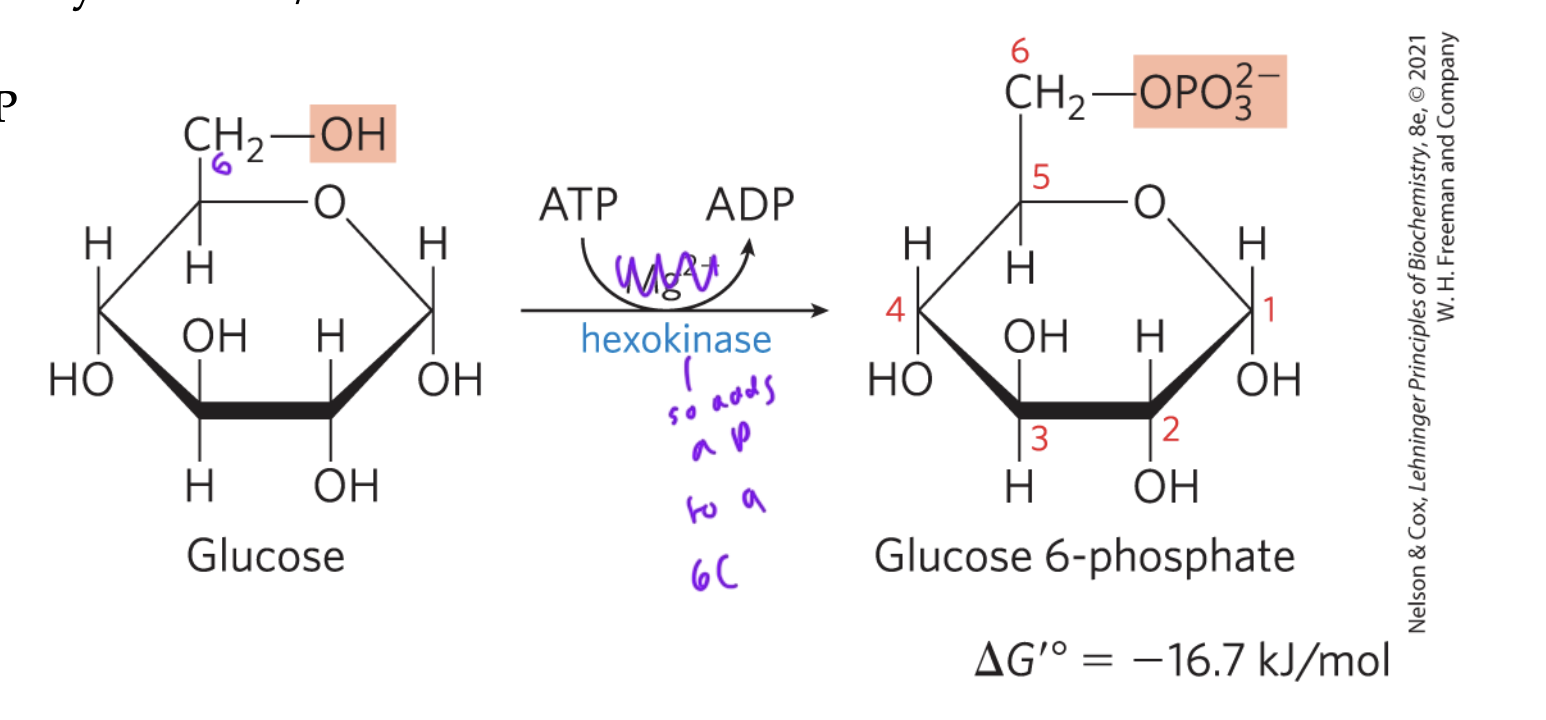
STEP 1 glycolysis
hexokinase phosphorylates the C6 of glucose, turning it into glucose-6-phosphate using ATP
exergonic/favorable rxn
glucose-6-phosphate is an allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase
glucokinase
an unusual hexokinase
glucokinase 4 is aka hexokinase 4
is only active in glucose rich environments to convert glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
glucose-6-phosphate is produced from
blood glucose
glucose-6-phosphate is an allosteric inhibitor of
hexokinase
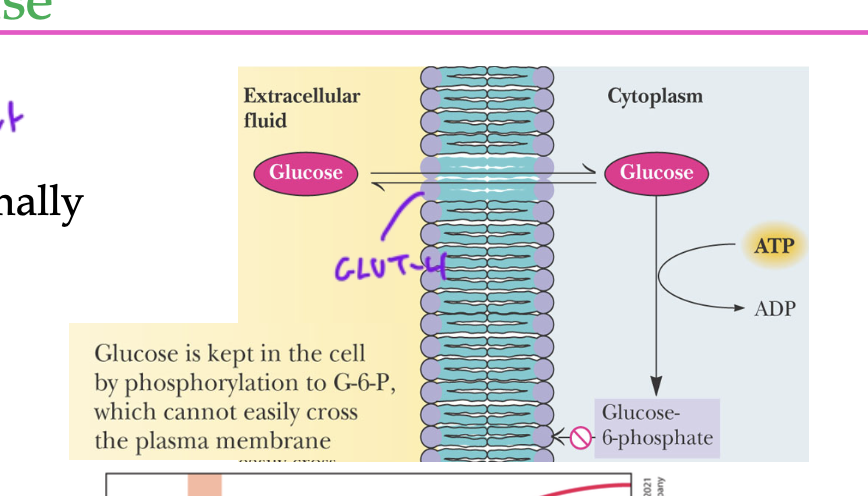
why is step 1 of glycolysis so important?
since it allows glucose to stay inside of the cell, since glucose-6-phosphate cannot easily leave the cell
if it was not phsophorylated and was just normal glucose, it would want to leave the cell due to its EC gradient via GLUT-4
hexokinase is normally
active
maintains the conc of glucose inside the cell
glucokinase 4
aka hexokinase 4
only active in glucose rich environments to convert glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
is the predominant hexokinase in the liver and keeps blood glu low by storing it as glycogen
this is the only hexokinase NOT allosterically regulated via negative feedback by glucose-6-phosphate
so it allows more glu to be brought it and stored as glycogen
hexokinases are generally ______ by glucose-6-P
allosterically inhibited
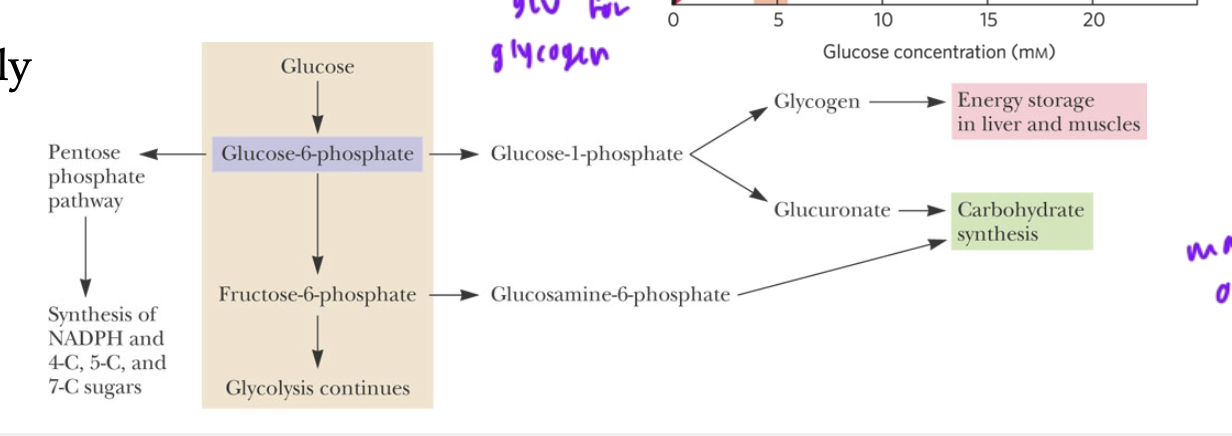
diff fates of glucose-6-P
can become glycogen or glucoronate (for carb synthesis)
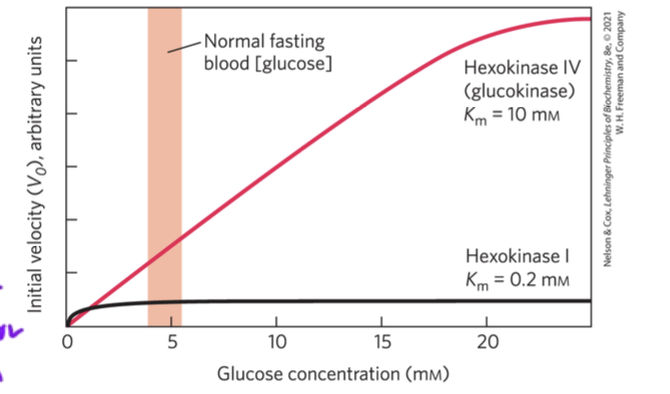
Km of hexokinase vs hexokinase 4
glucokinase 4 has a Km for glucose of 10 mM
hexokinase has Km for glucose of 0.1 mM
so glucokinase works better in glucose rich environments to bind and convert glucose