physics - magnetism & the motor effect (12.1 - 12.14)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
12.1 what do unlike magnetic poles do?
attract
12.1 what do like magnetic poles do?
repel
12.2 examples of permanent & temporary magnetic materials (not specified)
cobalt
steel
nickel
iron
12.2 uses of permanent & temporary magnetic materials
electric motors
generators
loudspeakers
other electrical devices
door latches
knife holders
12.3 permanent magnets
always magnetic
attract magnetic materials
magnetic field definition
space around magnetic where it attracts magnetic materials
12.3 induced magnets
piece of magnetic material in magnetic field - becomes magnet (induced magnet)
taken out of field - stops being magnetic
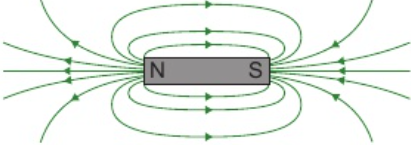
12.4 shape & direction of magnetic field - bar magnets
magnetic field all around bar magnet
field lines go from north → south
field lines closer together = magnetic field stronger
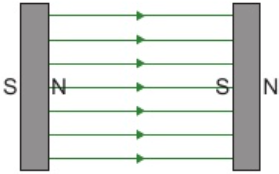
12.4 shape & direction of magnetic field - uniform field
2 flat magnets produce uniform magnetic field between them
field lines go from north → south
field lines closer together = magnetic field stronger
12.5 what does plotting compass show?
shape & direction of field of magnet/Earth’s magnetic field
12.5 how to use plotting compasses?
place magnet on piece of plain paper
place compass near one of magnet’s poles
draw small dot where needle of compass is pointing
move compass so tail of needle is aligned with dot
draw another small dot where needle is pointing
repeat steps 3-5 until reach other pole of magnet/edge of paper
draw lines connecting dots
add arrows to lines from north → south to show direction of magnetic field lines
repeat steps 1-7 starting at diff. points on magnet
12.6 how is behaviour of magnetic compass related to evidence that earth’s core must be magnetic?
needle of compass always points to position near earth’s north pole
shows earth generates own magnetic field - core must be magnetic
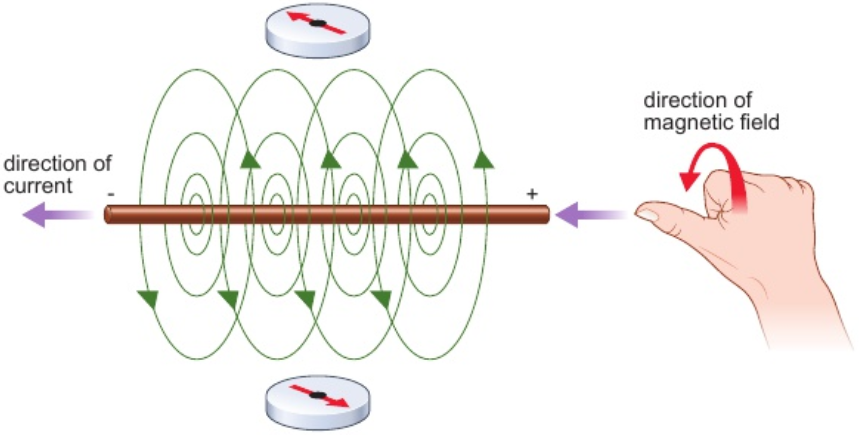
12.7 how to show current can create magnetic effect around long straight conductor?
wire passing through piece of card
current flows through wire - iron filings on card make circular patterns
iron filings line up with direction of magnetic field - shows current causes magnetic field
direction of magnetic field depends on direction of current
12.8 what does strength of field depend on?
size of current
distance from long straight conductor
12.8 how does current affect strength of field?
higher current = stronger field
12.8 how does distance from long straight conductor affect strength of field?
closer to long straight conductor = stronger field
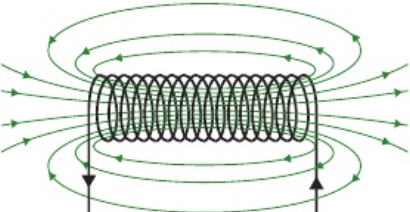
12.9 what is a solenoid an example of?
an electromagnet
12.9 what do fields from individual coils inside solenoid do?
add together to form very strong almost uniform field along centre of solenoid
cancel out to give weaker field outside solenoid
how to make magnetic field of electromagnet stronger?
put piece of iron (iron core) inside coil
12.10 what happens to current carrying conductor when it is placed near magnet?
it experiences a force
12.10 what happens to magnet when current carrying conductor placed near it?
equal & opposite force acts on magnet
12.11 what are magnetic forces due to?
interactions between magnetic fields
12.11 how are magnetic forces due to interactions between magnetic fields?
wire carrying current placed between 2 magnets - experiences force
current in wire creates magnetic field around wire
magnetic field around wire interacts with magnetic field between magnets
when is force greatest? (wire carrying current between 2 magnets)
when wire at right angles to magnetic field produced by magnets
when is force 0? (wire carrying current between 2 magnets)
when wire in same direction as magnetic field produced by magnets
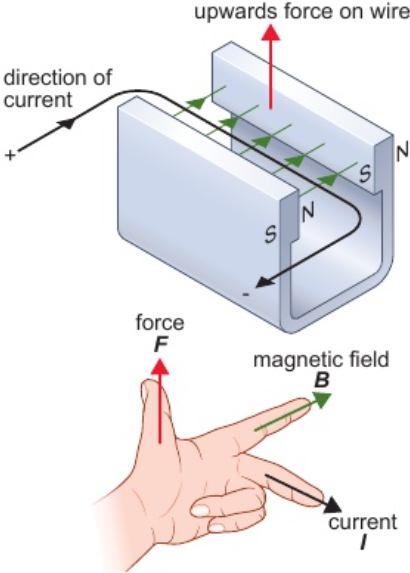
12.12 what does Fleming’s left-hand rule show?
relative directions of:
force
current
magnetic field
12.12 Fleming’s left-hand rule
12.13 force on conductor at right angles to magnetic field carrying current equation
force on conductor at right angles to magnetic field carrying current (N) = magnetic flux density (T) x current (A) x length (m)
F = BIl (BIL)
12.14 how is force on conductor in magnetic field used to cause rotation in electric motors?
force on each part of wire carrying current in magnetic field
split-ring commutator: current changes direction every half turn - ensures force on coil always turns it same direction
carbon brushes: make electrical contacts between circuit & motor
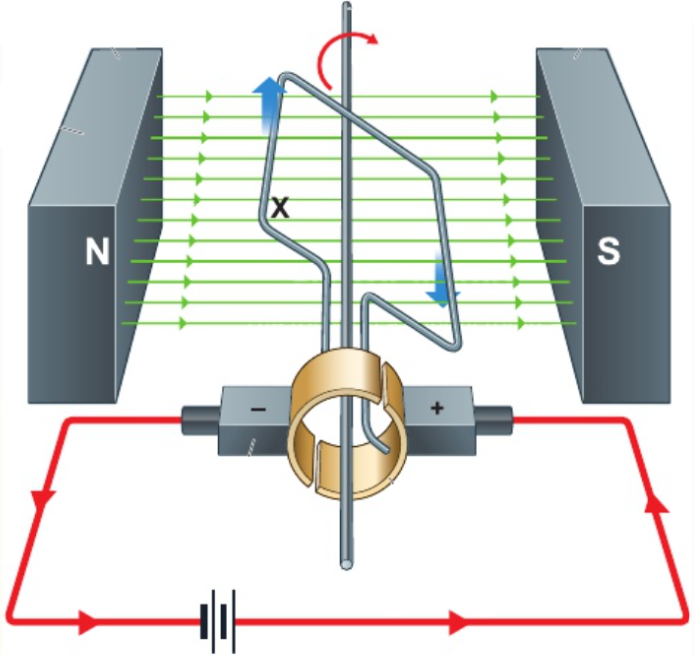
what does using coil with many turns of wire do? (in electric motor)
increases total force turning coil