4 software
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
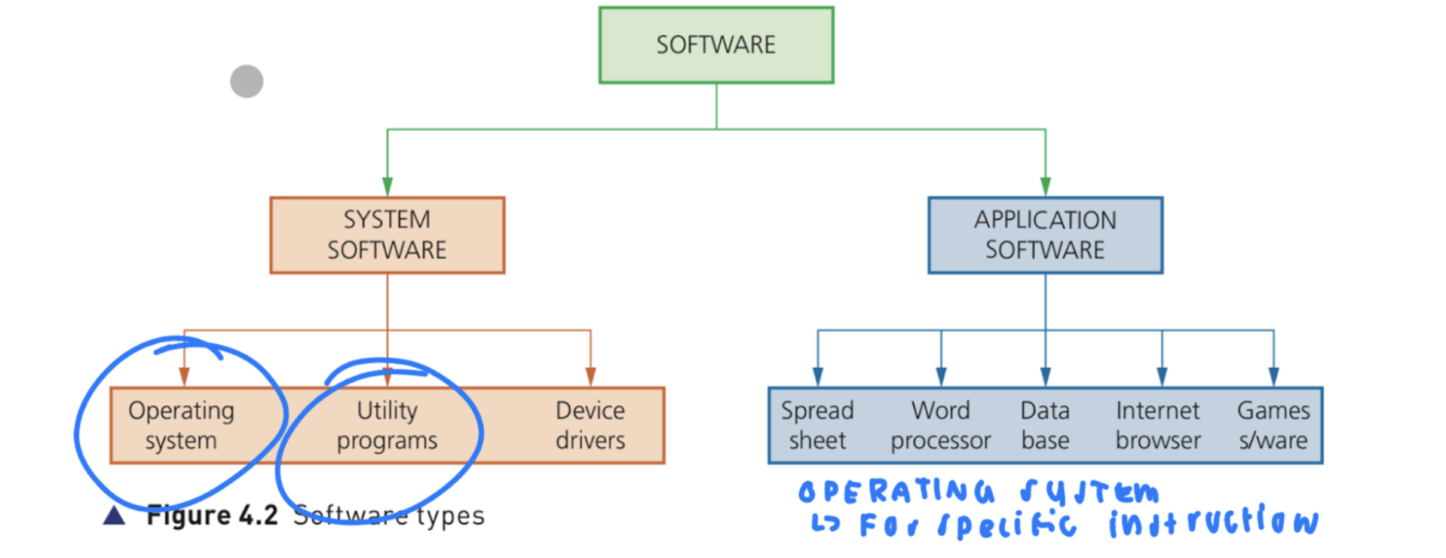
SYSTEM SOFTWARE
is essential for the operation of the computer system
It gives users a platform to run applications and carry out tasks
Software is categorized into system software and application software:
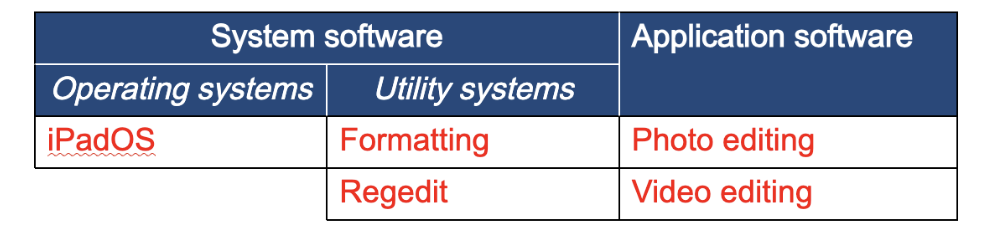
Examples of software:
General features of system software:
A set of programs to control and manage the operation of computer hardware
Provides a platform on which software can be run
Controls allocation and usage of hardware resources
General features of an application software:
Used to perform various applications (apps) on a computer
Allows a user to perform specific tasks using the computer’s resources
May be a single program or a suite of programs
System software consists of?
Utility Software
Operating System
UTILITY SOFTWARE
A software designed to help maintain, enhance, and troubleshoot/repair a computer system
Designed to perform a limited number of tasks
Interacts with a computer's hardware, for example, secondary storage devices
Some utility software is installed with the operating system
Examples of a utility software
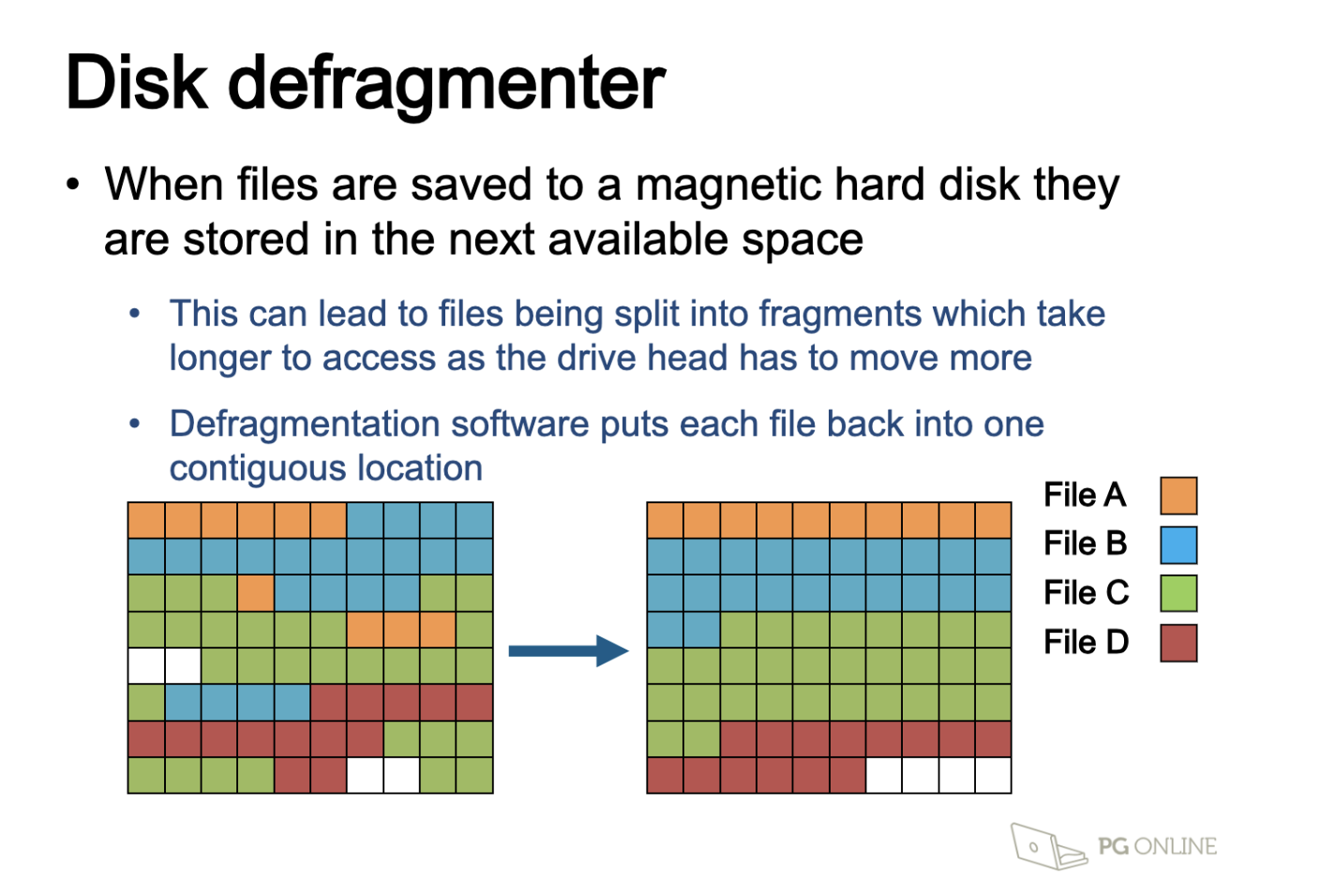
Defragmentation software (maintain)
Compression (enhance)
Encryption (enhance)
Task manager (troubleshoot/repair)
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
A software chosen by a user to help them carry out a specific task, specific to them
Installed on top of system software and is user-chosen to best suit individual preferences
Examples of an application software
Productivity (get things done efficiently using spreadsheets or presentations)
Communication (email, browser, messaging)
Entertainment (movies, games, music)
Utility system - Disk defragmentation
Utility system - Disk cleanup
Disk drives do not need actual cleaning as they are sealed; however, disk clean-up tools help to improve free space and system performance by:
Deleting temporary files
Clearing cached files for a web browser
Removing unnecessary program files
Utility system - Backup and antivirus software
Hard drives sometimes fail and may also be stolen, and therefore need to be regularly backed up to external drives or cloud backup services
Antivirus software scans computers to make sure that they don't contain viruses
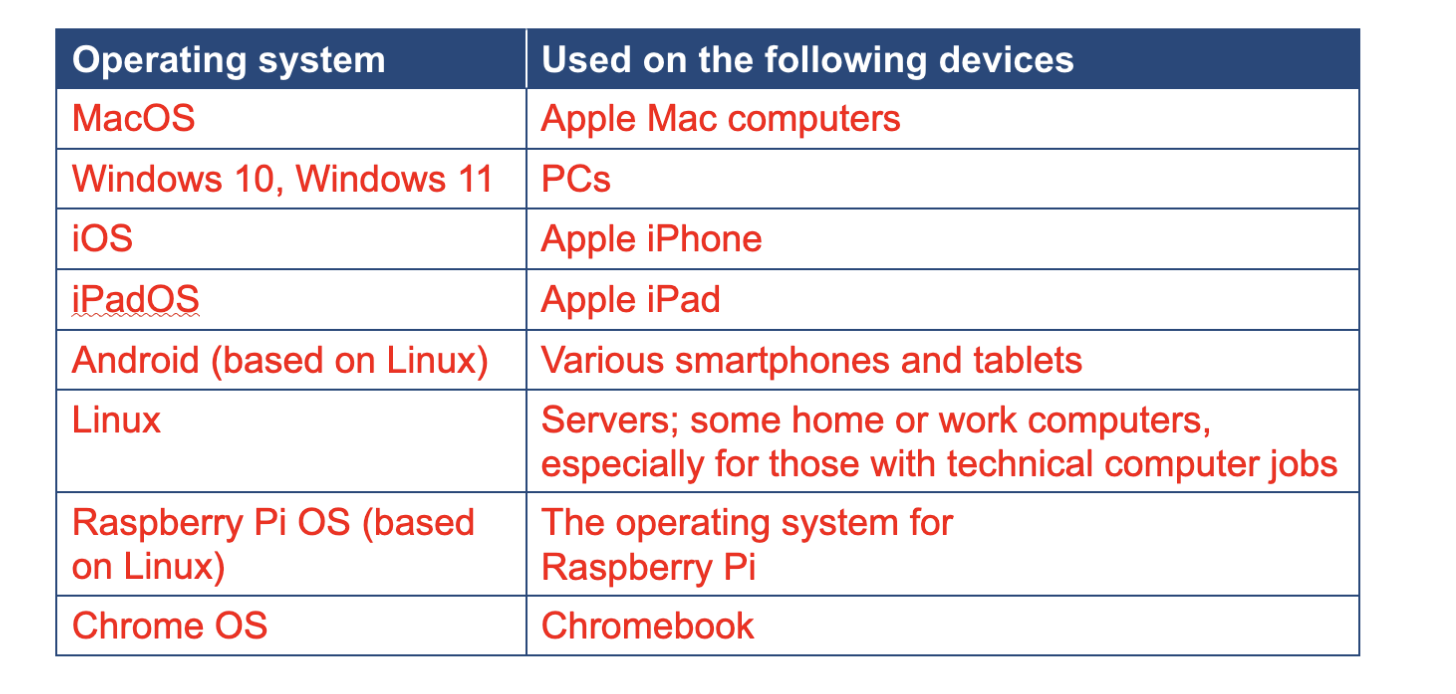
Examples of an operating system
OPERATING SYSTEM
A software that manages computer hardware and provides a platform for running applications
Provides an interface between the user and the hardware in a computer system
Hides the complexities of the hardware from the user
Main functions of an operating system
Managing files, providing an interface, managing peripherals and drivers, managing memory, managing multitasking, providing a platform for running applications, providing system security, and managing user accounts
OS - File Management
A process carried out by the operating system, creating, organizing, manipulating, and accessing files and folders on a computer system
File management gives the user the ability to:
Create files/folders
Name files/folders
Rename files/folders
Copy files/folders
Move files/folders
Delete files/folders
The Operating System allows users to control who can access, modify, and delete files/folders using permissions
The Operating System provides a search facility to find specific files based on criteria
OS - Handling Interrupts
Interrupt events require the immediate attention of the CPU
To maintain the smooth running of the system, interrupts need to be handled and processed promptly
OS - User Interface
How the user interacts with the operating system
Examples of user interfaces include:
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Menu
Natural Language (NL)
OS - User Interface - Command Line Interface
Requires users to interact with the operating system using text-based
commands
CLIs are more commonly used by advanced users, as specific commands are needed
Examples: MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System) and Raspbian (Raspberry Pi)
OS - User Interface - Graphical User Interface
Requires the users to interact with the operating system using visual
elements such as windows, icons, menus, and pointers
Optimised for mouse and touch gesture input
Examples: Windows, MAC OS, Android
OS - User Interface - Menu-driven Interface
A successive menu presented to a user with a single option at each stage
Often performed with buttons or keypads
OS - User Interface - Natural Language Interface
Uses the spoken word to respond to spoken or textual input from a user
Examples: Virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa), search engines, smart home devices
WIMP interfaces

OS - Peripheral Management and Device Drivers
A peripheral device adds functionality to the hardware, which interacts with the software
The Operating System allocates resources to peripherals to ensure efficient operation
Makes use of plug-and-play (PnP), automatically detecting and configuring new peripherals
OS - Peripheral Management and Device Drivers - Device Driver
A piece of software used to control a piece of hardware
Peripherals require device drivers to be used by the operating system
A separate device driver needs to be downloaded to make use of its maximum capacity
OS - Memory Management
A process carried out by the operating system, allocating main memory (RAM) between different programs that are open at the same time
To run a program, the computer must copy each program from storage into main memory
Data used by the program is also copied into main memory
The operating system keeps a record of where each program and its data are located
The operating system also makes sure that the program does not overwrite existing programs
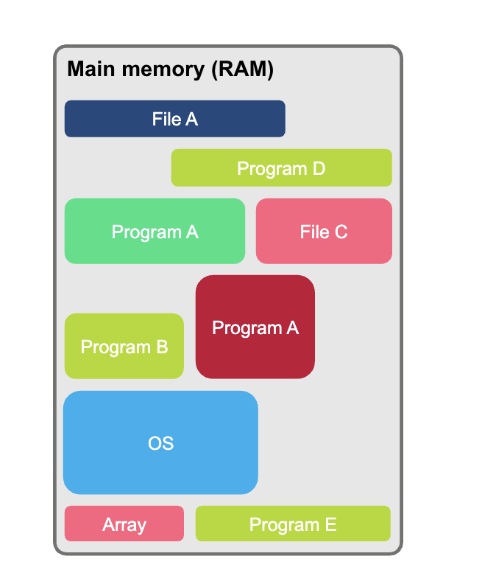
OS - Multi-tasking
The process of using or running several programs at the same time
Each program is given a short time on the CPU before it is paused by the operating system
The operating system then allows the next program to make use of the CPU for a short time
By switching quickly between programs, it appears to the user that all of them are happening at the same
OS - Providing a Platform for Running Applications
This can be done by allowing software access to system resources
OS - Providing System Security
Operating systems provide various security features such as password-protected system accounts, a firewall (montiors incoming and outgoing network traffic), virus scanning and file encryption
System accounts can also be restricted from performing certain actions
OS - User Management
A process carried out by the operating system enabling different users to log onto a computer
The Operating System is able to maintain settings for individual users, such as desktop backgrounds, icons and colour schemes
A system administrator is able to locate different access rights for different users on a network
How Do Application, OS, and Hardware Communicate?
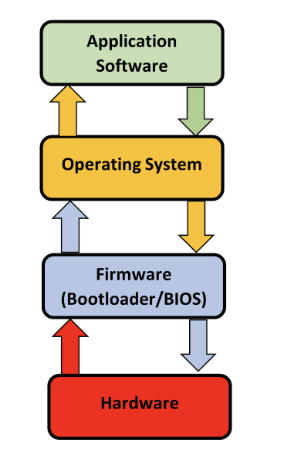
Application software talks to the Operating System, allowing it to interact with the hardware
The hardware then processes and sends information to the Operating System, which talks directly to the application software
The process is repeated while the application software is in use

FIRMWARE
an embedded software within the hardware of a device, to make it function. Contains programs that are stored permanently in hardware.
Provides low-level and control instructions
The BIOS stored on a computer is stored on a flash ROM
It can be updated by flashing the ROM
BOOTLOADER

a small program that runs right after the firmware
loads the operating system
INTERRUPTS
a signal sent from a device by software to the microprocessor. This will cause the microprocessor to STOP what it is currently doing
Example: Printers sending a signal notifying the user that there is no paper, ink, etc

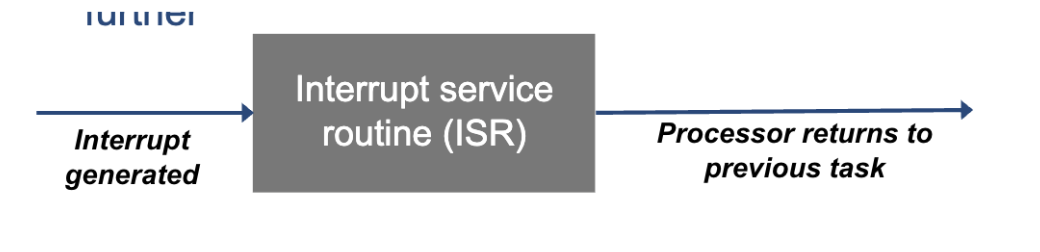
What happens when the CPU is interrupted, and how does it handle the interrupt?
The CPU runs an Interrupt Service Routine (ISR), also called an interrupt handler.
The ISR executes as quickly as possible because it pauses the CPU’s current task.
The ISR contains instructions that must be fetched, decoded, and executed to deal with the interrupt.
To prevent data loss, the contents of CPU registers are copied to a reserved area in RAM called the stack.
Data is pushed onto the top of the stack for safe storage and retrieved once the interrupt is complete, allowing the CPU to resume its previous task.
2 Types of Interrupts - Hardware interrupts
The power button may have been pressed
Moving the mouse
Clicking on an icon to open a new program
Keyboard presses, e.g, ctrl, alt, delete
The interrupts are sent via Interrupt Request Lines (IRQ)
When a mouse is moved, constant interrupts are sent to the computer so that it is able to update the location of the pointer
Same with keyboards, pressing a specific key
2 Types of Interrupts - Software interrupts
A program is not responding
Division by zero
Two processes are trying to access the same memory location
Generated by programs that are running
For instance, if a program tries to divide by zero, a ‘division by zero’ interrupt will need to be handled
2 Types of Interrupts - Software interrupts - How do software interrupts deal with faults
Software interrupts deal with faults such as:
Page faults - this is when data is not inside RAM, but in virtual memory, and needs to be loaded back into RAM
Segmentation faults - this is when one program tries to make an illegal memory location, such as the memory used by another program
When a fault occurs, an interrupt service routine is called
Generations of programming languages can be split into two categories…
Low level
First generation
Second generation
High level
Third generation
LOW-LEVEL LANGUAGES
A programming language that directly translates to machine code, which is understood by a processor
Allow direct control over hardware such as memory and registers
Written for specific processors to ensure they embed into the correct machine architecture
Low-level - FIRST GENERATION
Machine code
Instructions are directly executable by the processor
Written in binary code
Low-level - SECOND GENERATION
Assembly code
Written using mnemonics, abbreviated text commands such as LDA (Load), STA (Store)
Using assembly code can write human-readable programs that correspond to the machine code
Needs to be translated into machine code for the computer to be able to execute it
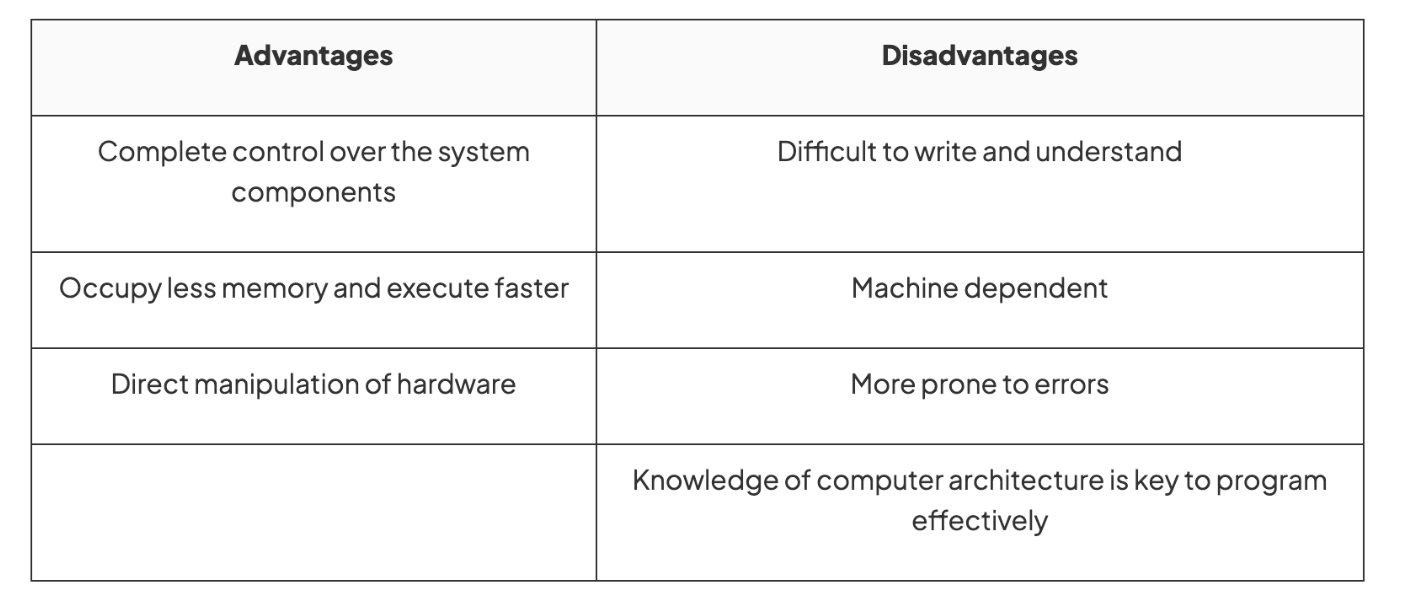
Advantages and disadvantages of second generation
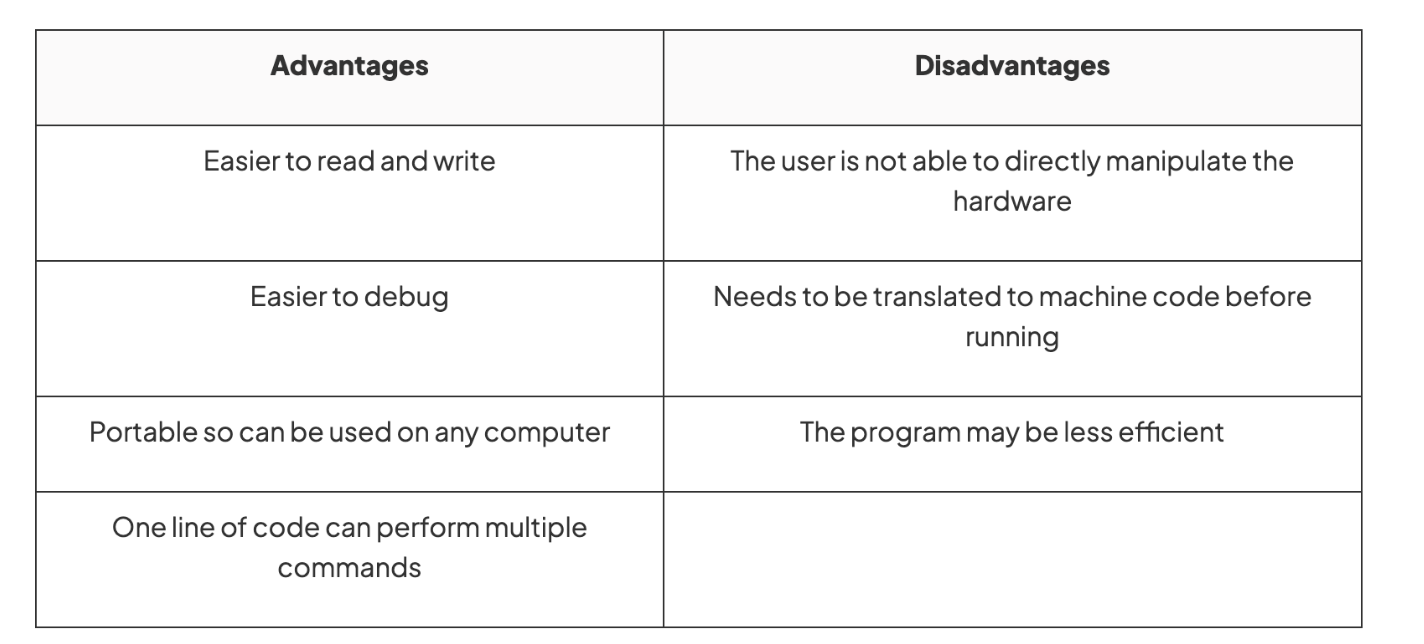
HIGH-LEVEL LANGUAGES
A programming language that uses English-like statements to allow users to program with easy-to-use code
Allow for clear debugging
Easier to maintain programs
Needed due to the development of processor speeds and the increase in memory capacity
One instruction translates into many machine code instructions
Needs to be translated into machine code fo the computer to be able to execute it
EXAMPLES:
Python
Java
Basic
C++
Advantages and disadvantages of high-level languages
Students sometimes confuse machine code and assembly. Remember:
Machine code = binary (1st generation)
Assembly = mnemonics (2nd generation, needs assembler)
What is assembly language, and why do programmers use it?
Assembly language is a second-generation, low-level language that simplifies writing machine code instructions.
Programmers use it to:
Access or control specific hardware components.
Execute machine-dependent instructions.
Minimize memory (RAM) usage.
Increase execution speed of programs.
How does assembly language work using mnemonics and an assembler?
Assembly language uses mnemonics (e.g.,
ADD,MOV) to represent machine code instructions.It lets programmers work directly with hardware while reducing complexity.
When a mnemonic is read, it’s looked up in a table.
An assembler converts the mnemonic into its corresponding binary (machine) code.
If a match is found, the mnemonic is replaced with the correct binary sequence.
TRANSLATOR
a program that translates program source code into machine code so that it can be executed directly on a processor
Low-level languages such as assembly code are translated using an assembler
High-level languages such as Python are translated using a compiler or interpreter
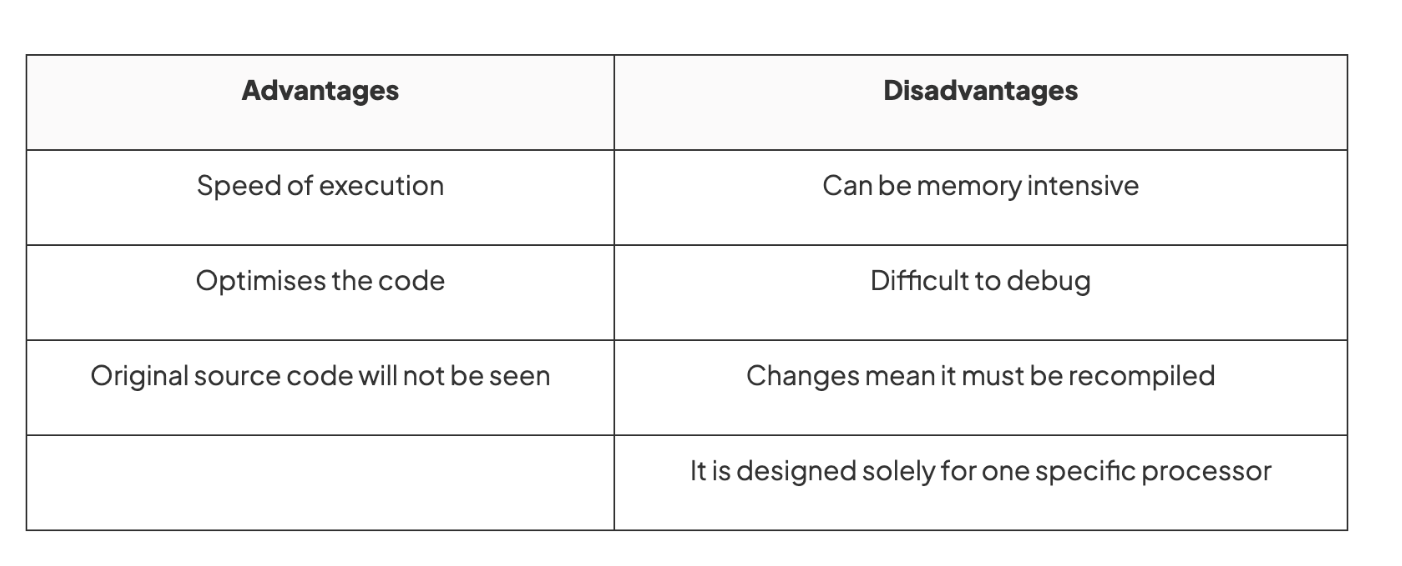
COMPILER
translates high-level language program (the source code) into machine code all in one go
Generally used when a program is finished
Produces an executable file which means the file can be executed
If the compiler encounters a syntax error, it cannot translate the statement so no object code is produced
It provides an error report for all errors that are detected in code
ALTOGETHER
Advantages and disadvantages of using a compiler
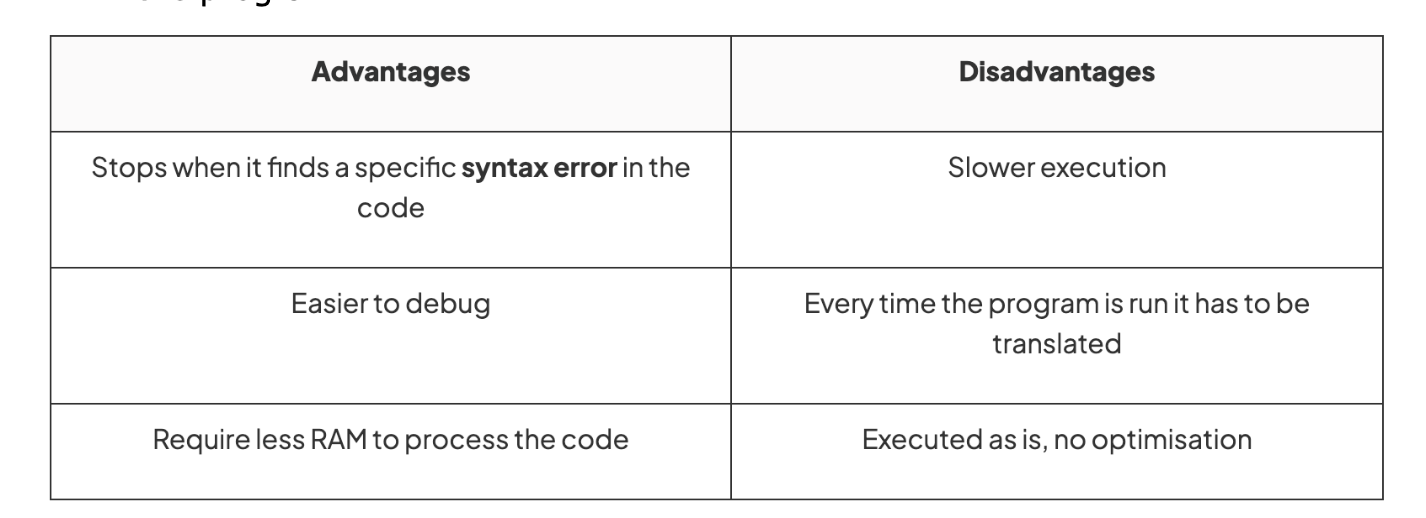
INTERPRETER
translates high-level languages into machine code one line at a time
Continues like this, translating and executing the code line-by-line
If syntax is encounrtered, it displays an error message and stops executing the program
LINE-BY-LINE
Advantages and disadvantages of using an interpreter
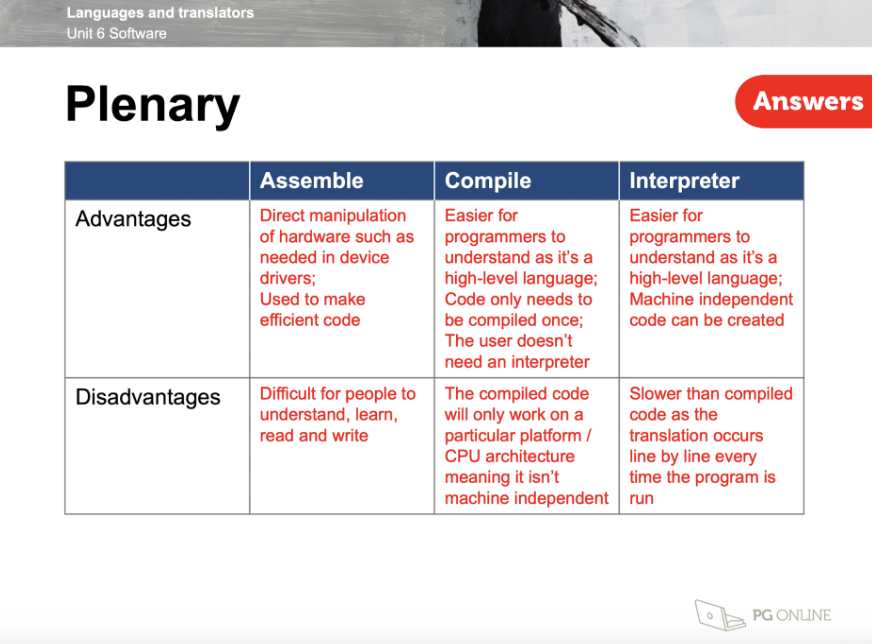
Main advantages and disadvantages of assembly, compiler and interpreter
The advantages and disadvantages of a compiler and interpreter - what should you use?

IDE, INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENTS
a software designed to make writing high-level languages more efficient
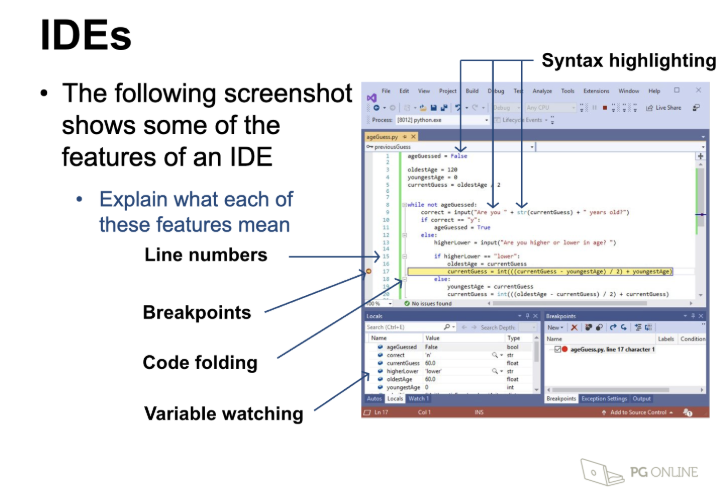
IDE - Line numbers
Allow a programmer to clearly see each new line of code
When errors are found, the line number that they occur on will also be stated
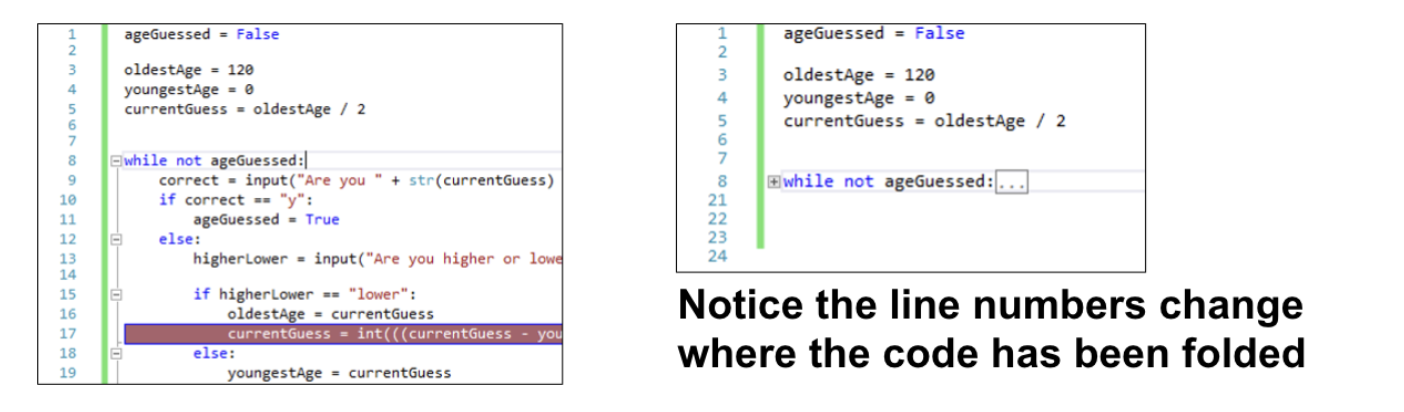
In some IDEs, parts of the program that the programmer doesn’t need to see can be folded
IDE - Syntax highlighting
Where the colour of the text changes to show different parts of a program

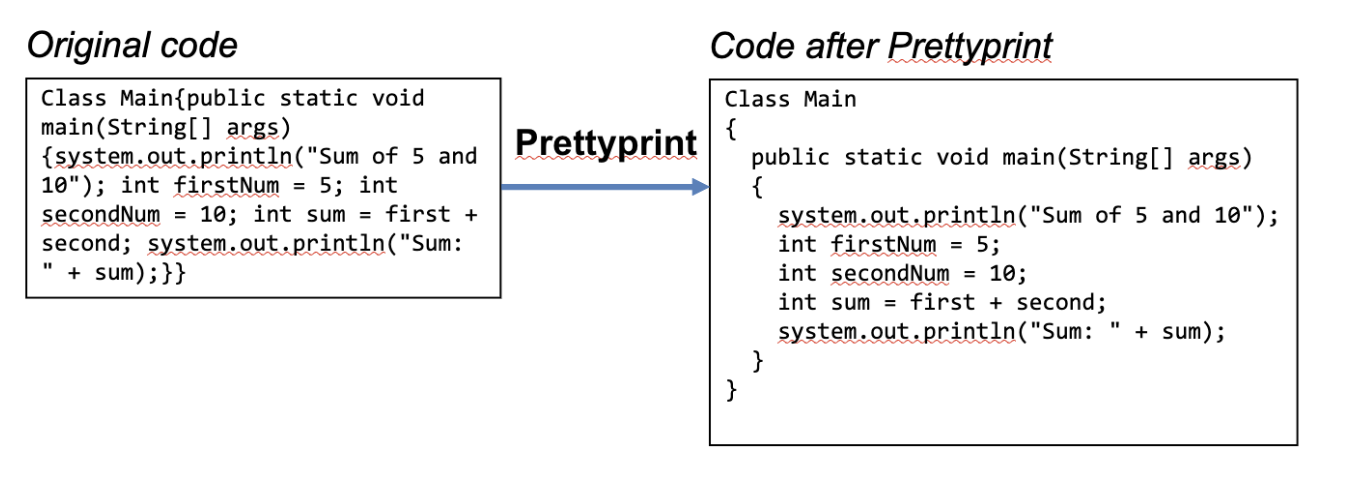
IDE - Prettyprint
Applies indentation and formatting to the code
Makes it easier for other programmers to read
It also makes code consistent across different programs
IDE - Error diagnostics
Help programmer to find where they made a mistake
Errors are identified along with the line number that they occur on
The code may be underlined or highlighted to show the error
IDE - Debugging code
Breakpoints are set by the programmer so that the IDE stops the program mid-way through running
The programmer can step through code line by line
They can watch variables as they change
IDE - Run-time Environment
Allows a programmer to test their program while it is running
If the program crashes the run-time environment can see what happened and give useful information to the programmer
Libraries that come with the programming language will be available to the programmer to use
IDE - Translators
IDEs will contain necessary translators to run and test the code
The IDE may compile the code or interpret it by running it line by line - this is very helpful for debugging the code
IDE - Auto-completion and correction
Gives the programmer suggestions for variable names and keywords as they type
Improves the speed a programmer writes a program
Tabs, brackets and braces may also be added automatically to the code to save the programmer time
Some IDEs have auto-correction which fixes mistakes such as those made in keywords
Summary of all features of IDE
