Arab-Israeli Conflict Test
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
How did the end of the Ottoman Empire change the Middle East?
When the Ottoman Empire was on the verge of political collapse by the end of the 19th century, European powers like Britain, Russia, and France were interested to take over the Middle East. Heading into WWI, Britain expressed interest in positioning themselves to take control of the Middle East. They believed it was important for strategic and economic reasons. In 1870, Brittain gained control over the Suez canal, which is located on the trade route to South and East Asia, and they desired to protect and maintain their control over the canal.
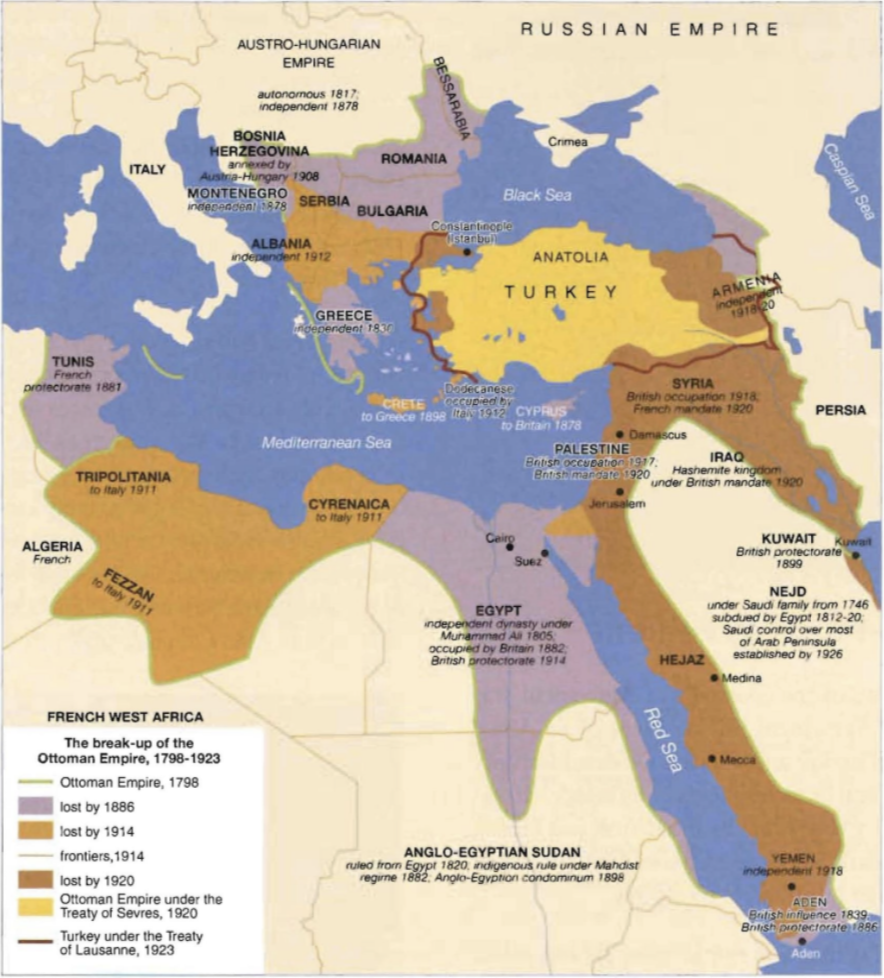
What was the Hussein-McMahon Correspondence?
Before WWI, Hussein informed the British of his opposition to the Ottoman Sultan, and sought British support to establish an independent Arab Kingdom. The Sultan proposed Arab support against the Ottomans if Britain would grant independence of all the Arab provinces of the Ottoman Empire. The British were interested in encouraging an Arab revolt against the Ottomans, and desired their support. McMahon and Hussein exchanged eight letters and Britain ambiguously recognized support of Arab independence in return for Arab support agains the Turks. Hussein argued that ALL the Arab territories should be included, however McMahon instead identified areas to be reserved for British control. The final boundaries were left unresolved, and in June of 1916, Hussein declared independence of the Arabs from the Turks. After the war, a dispute arose regarding whether Palestine was promised to the Arabs as part of the correspondence. Hussein claims that although Palestine was never explicitly mentioned, it was implied, while in the Churchill-White Paper, the British clarified that it was not part of the deal.
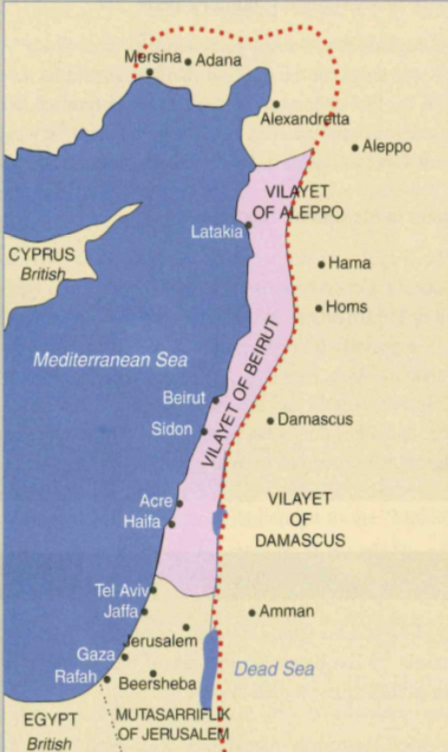
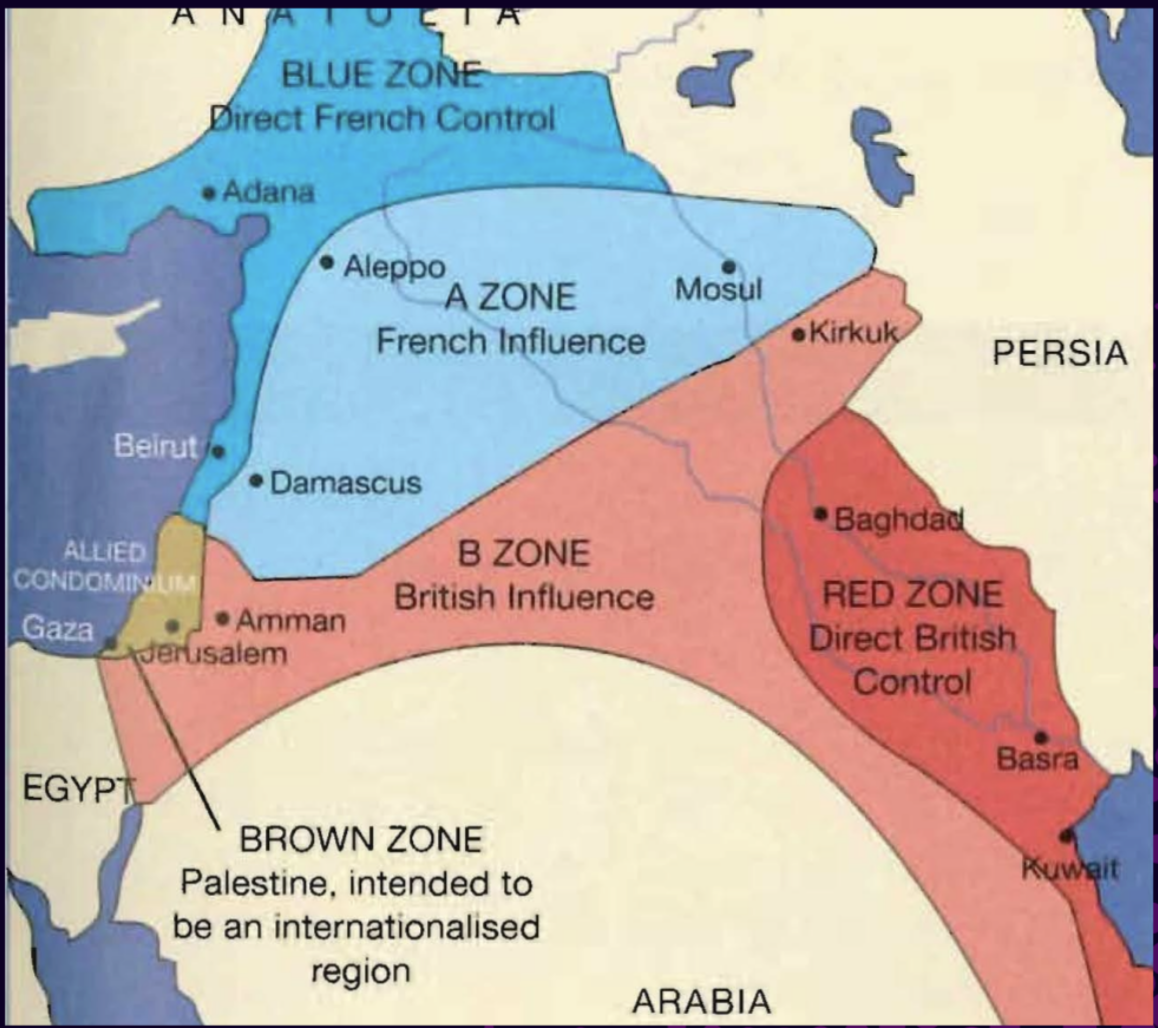
What was the Sykes-Picot Agreement?
In May of 1916, a secret agreement to divide the Ottoman territory was signed between Britain and France. The agreement supports an independent state in areas A & B, while Palestine was intended to become an international region
What is the Balfour Declaration?
On November 2, 1917, Lord Balfour (Britain's foreign minister) wrote a letter on behalf of the British government to Lord Rothschild, where he states, "His Majesty's Government views with favour the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, and will use their best endeavours to facilitate the achievement of this object." The British support for a Jewish homeland in Palestine was the first time in history any major empire favoured the idea of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. The League of Nations accepted the declaration in 1922.

What did David Ben Gurion have to say about the Balfour Declaration?
Ben Gurion states the Britain had made a significant gesture to the Jews by recognizing the Jews existent as a nation and a right to country. Ben Gurion states that now the must build the national home with body, soul, strength, and capital.
What did Dawoud El-Alami have to say about the Balfour declaration?
The British were unsure how the war would end, and made promises to different groups to keep them on their side. The Balfour declaration includes a condition that the rights of locals should not be harmed, however he believes that the British promise was unfair.
What occurred at the 1919 Paris Peace conference?
At the end of WWI, the Allies met at Versailles to draw up a peace treaty ending WWI. They redrew the map of Europes, as many pre-war empires no longer existed, and also decided that the Arab lands will be divided by the League of Nations and a mandate system would be established. Britain would assume rule over Iraq, Palestine, and France would assume rule over Syria and Lebanon. Within 10 years these lands would be self-governed, but allied intervention was implemented in order to ensure that they remain stable and reliant on Allied powers.
How did Faisal respond to the Paris Peace conference?
Faisal realized that during the Paris Peace Conference, it was clear that the plan for an independent Arab state would not come to be In July 1919, Faisal, the son of Hussein, called for an independent Greater Syria, incorporating Syria, Lebanon, and Palestine.
What was the Faisal-Weizmann Agreement?
Faisal originally rejected the establishment of a Jewish commonwealth in Palestine. Despite Arab rejection, Chaim Weizmann was convicted that if Fasal educated himself regarding the Zionist movement, he would accept their movement. Chaim tried to reach an understanding to accommodate both Arab and Jewish national aspirations in Palestine. Faisal then stated that the Arabs are sympathetic with the Zionist movement, as both parties are looking for a reformed and revived Middle East. He said that the Arab movement and the Jewish movement complete one another, as they are both nationalists movements not imperial. There is room in Syria for both the Jews and Arabs, and neither can be successful without the other. Faisal looks forward to a future where they both help each other, so they can have a place in the community of civilized peoples. In March of 1920 however, the French rejected Faisal's proclamation as a king, and by July, Fasial fled from Damascus. Once Faisal left Syria, Faisal relinquished from Weizmann, and became a vocal opponent of Zionism.
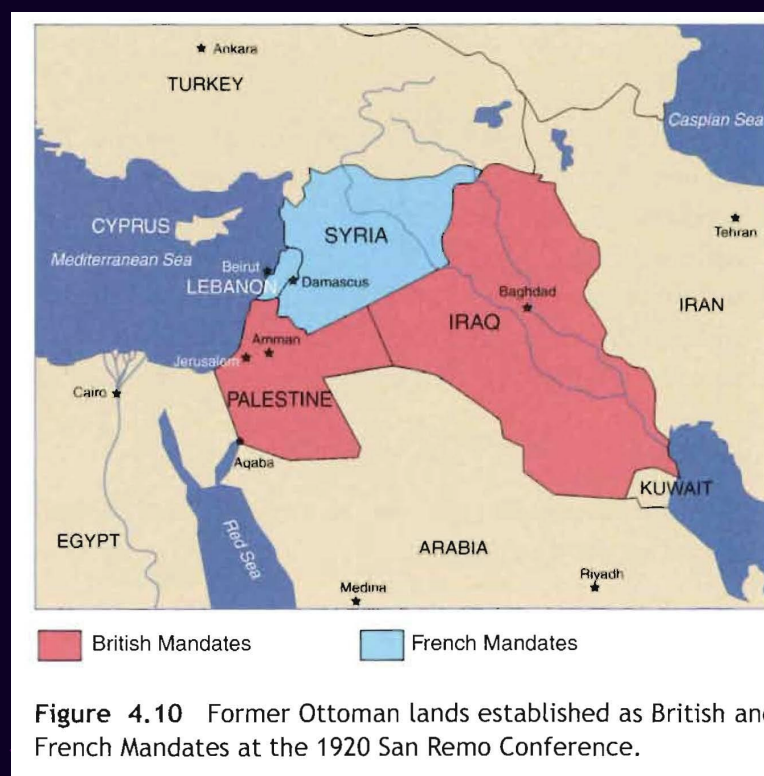
What was the San Remo Conference?
In April 1920, the Allies met in San Remo, Italy, where the territories of the Ottoman Empire were formally turned over to Britain and France. The San Remo conference led to the introduction to the Mandate system, where Britain received two areas of land, being Iraq and Palestine, while France received Syria and Lebanon. It was internationally-backed agreement that recognized Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan and Israel. Also, at San Remo the allied powers recognized the legitimacy of the Jewish people's aspiration to constitute themselves as an organized national community in their ancient homeland. The policy in the Balfour Declaration became a legally binding international treaty between the major powers.
What happened during the 1920 Arab Riots?
The Arabs felt betrayed by the British due to their Mandate system. This system clearly did not reflect the Hussein-McMahon Agreement. The Arabs fully rejected the mandate system and the recognition of the Jewish claims to the land. This led to violence erupting among Arab leaders, where they made false accusations that the Jews were planning to destroy all Muslim Holy sites. Jerusalems mayor called on Muslims to "spill Jewish blood" and a newspaper declared "If we don't use force against the Zionists we will never be rid of them. The crowd chants "we will drink the blood of the Jews" Arabs entered the Jewish quarter in Jerusalem, where they attacked Jews and ransacked their homes. Riots lasted 4 days, where 300 Jews were evacuated and seven were killed. Hundreds were also wounded.
What is the Haganah?
The Haganah was formed out of response to the Arab riots as there were beliefs among the Jews that the British were unable to protect the Jews. The original role of was to defend Jewish neighbourhoods and farms from Arab attacks, and the groups would serve under the direction of the Yishuv (Jewish political leadership committee.)
How did a distinct Palestinian movement arise?
Jews were gaining full support from the British, so the Palestinian committee created its own national movement. It states that the territory of Palestine, is a distinct political entity; Jewish political and moral rights in Palestine are totally rejected; The unity of Palestinian Arabs is more important than loyalty to religion, geography, or clan; The British administration is called to stop sale of land to Jews; Future Jewish immigration should not be permitted; The British administration is called to recognize the Arab as the legitimate representative of the populatio..
What was the 1922 Churchill-White Paper?
In an attempt to calm the rising tension, British colonial secretary Winston Churchill tried to clarify to both the Arabs and Jews that the terms of the Balfour declaration will only apply to the territory west of the Jordan River (reassuring Arabs that it wasn't Britains intent that the whole of Palestine should constitute a Jewish national home.) The British also stated that the promised Jewish national identity of the Balfour declaration has already been achieved, as Jews already have their own school, language, and electric companies, making it necessary to declare a Jewish state; where Jews will be permanent residents. However Jewish immigration should not be permitted to exceed whatever the economic capacity of the country at the time to absorb new arrivals.
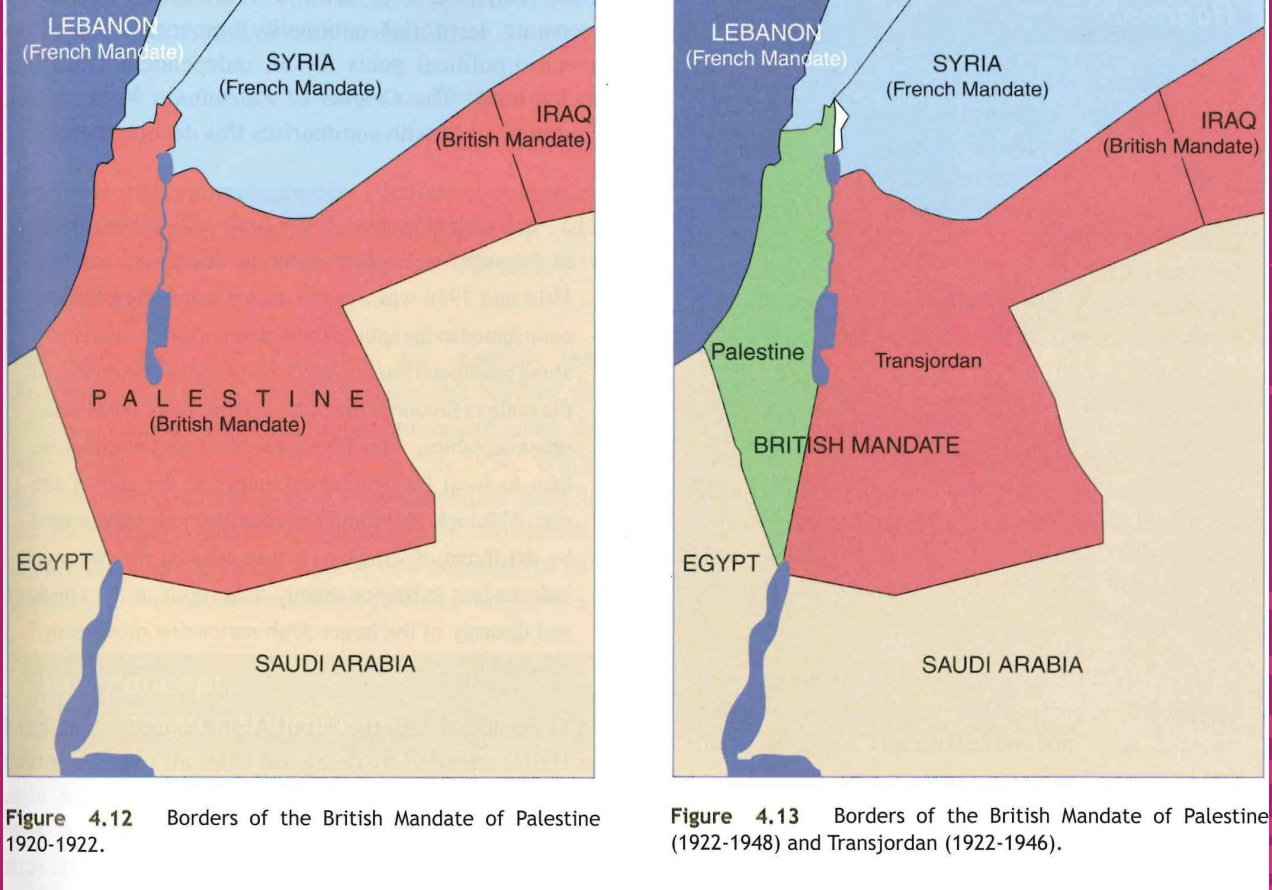
How is the Churchill-White paper seen as a compromise?
For the Arabs, Palestine does not become a Jewish state, and they get the territory east of the Jordan river as exclusively theirs. The Jews get to continue moving to Palestine, with permanent resident status and establishing an institutional identity. The Brits benefit because the more that Jews move to Palestine, the more the economy is built up and the more the Brits will make.
What was the British reaction to the Churchill White paper?
The paper ensures that Britain will be successful economically. It sends a clear message to Arabs that the Jews have no national rights on the east side of the Jordan River, that the Arab fears of a Jewish state are unfounded and therefore rioting is not necessary, and that the British allowed continued immigration making both the Jews and Britain happy, while making it clear that there will be no Jewish state.
Why do the Arabs and Jews not like the Churchill White Paper?
The Arabs want all the land, without the Jews, and they dont want more Jewish immigration. The Jews don't like it as although they'd be allowed to move to the part of Palestine that they want to, they don't achieve the goal of Jewish statehood. The Churchill White paper was successfully endorsed by the the British House of Commons. The Jews unhappily accepted the plan, while the Arabs rejected it.
When did the British Mandate Start?
The League of Nations confirmed the British Mandate officially started on July 24th, 1922, however the British government had imposed civil administration in Palestine since June of 1920. The British had to govern two people with antagonistic nationalistic aspirations in the same land.
What was the Third Aliyah?
The Third Aliyah brought 35,000 Jews from Eastern Europe to Palestine from. 1919-1923. Many of these Jews worked on farms or in towns helping build the infrastructure. Most joined the Labour Zionist.
What was the Fourth Aliyah?
From 1924-1931, the fourth Aliyah brought 88,000 Jews from Poland. Many were shopkeepers and artisans; most settled in Tel Aviv. They invested and worked in factories, hotels, restaurants, shops, ad even in citrus orchards.
What was the fifth Aliyah?
The Fifth Aliyah was the largest Aliyah, involving 215,000 Jews between 1932-1939, including 164,000 from Germany. Mant were involved and they lived in cities and towns. Many were highly skilled and educated, and helped raise the standards of universities and hospitals to be more in line with the Europeans.
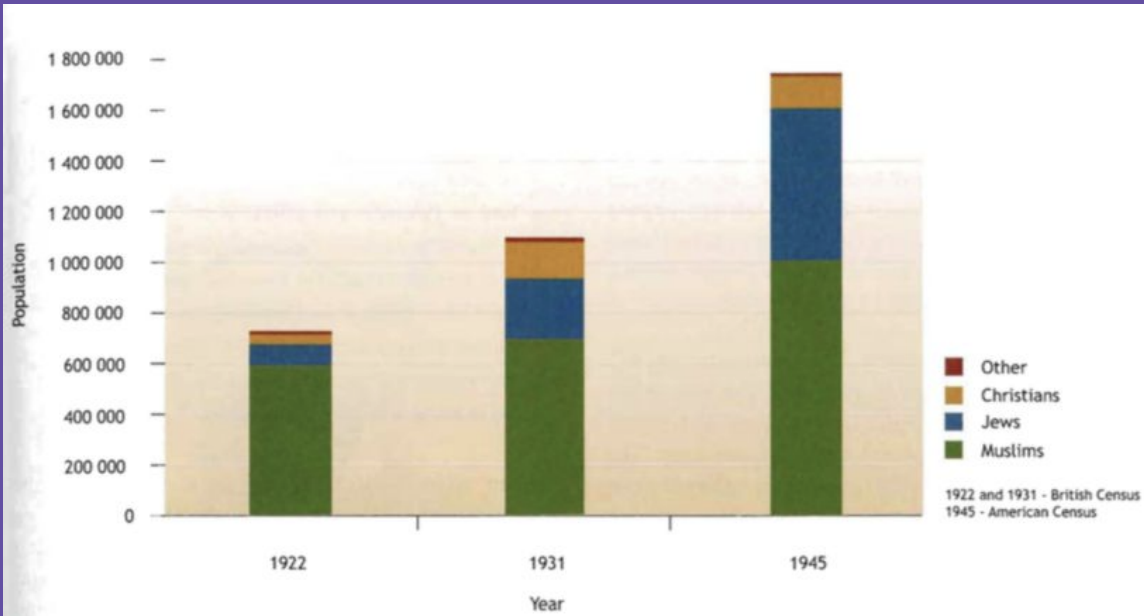
What was the population trend in British Mandate Palestine from 1922-1945
Both the populations of the Arabs and the Jews grew significantly. The Arabs were replenishing their declining population from the 18th and 19th centuries, as new job opportunities attracted Arab immigrants. The most significant increase of Arab population occurred close to Jewish centres. However, the Jewish population grew much more rapidly then the Arab population, with Jews gaining share in the percentage of population in comparison to Arabs.
What was the Jewish institution called? What did they accomplish?
The Yishuv. The Yishuv established health services an education system, a defence force, and a trade union. They established the Knesset (an internal governmental body that oversaw religious, educational, and welfare services) and consisted of multiple parties including the Socialist Mapai Party (Ben Gurion's Party), the right wing revolutionist party (led by Zee's Jabotinsky), and the religious Mizrahi party. Milita groups were also formed such as the Irgun which were more right wing than the Haganah, and the Lechi or Stern Gang (in the 1940's) which was even more right wing.
What was the Arab Institution Building?
Led by Hajj-Amin al Husseini, the Palestinians gained some self rule by collecting its own taxes, and controlling its own religious and cultural affairs. Palestinian political parties also formed, allowing Palestinians to form their own local governance.
What was occurring in Jerusalem during the interwar periods?
For 7 years after the 1920 riots, Palestine was relatively calm. On Erev Yom Kippur in 1928, the Jewish community built a mechitza at the Kotel. The Arab community saw it as a sign that the Jews were taking control of Jerusalems holy sites and the city itself. Attacks began in Jerusalem in 1929, and spread to Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Hebron, where 66 Jews were killed.
What was the Passfield White Paper?
The Passfield White Paper called for economic parity between the Jewish and Arab communities (and that the Jewish community can no longer develop unless the Arab community does as well). It limits establishments on Jewish Agricultural settlements, and limits Jewish immigration. Unlike the Arabs who revolt following British policies that upset them, the Jewish leaders travel to Britain and lobby against the Passfield White Paper, which led to their success of having the British overturn their policy.
What was the 1936-1939 Revolt?
In an effort to unite against the British, the Arabs called for a general strike. They stopped paying taxes and boycotted municipal governments until three demands were met: The end of Jewish immigration, the end of land sales to Jews, and the establishment of an Arab national government. From early 1937 until 1939, sporadic outbreaks of violence caused Britain tools controls of large areas of Palestine. Tens of thousands of troops and aircraft squadrons carried out a campaign of repression before finally restoring order. By the end of the revolt, around 5,000 Aras had been killed, 10,000 were wounded, and about 5700 were imprisoned. The Palestinian Arab economy was severely damaged, with business weakened. AS a result of the Arab strikes, many Arab port workers in Jaffa lost their jobs.. while the Jewish port in Tel Aviv flourished. Britain also exiled many of the Arab community's leaders, including Haj-Amin Al-Husseini.
What is the Peel commission?
Britain established another commission of inquiry. Lord Peel reported that the Arab's desire national independence and their fear of a Jewish national home in Palestine were the main causes for disturbances. The report also concluded that the Arab claims of the Jews obtaining too much "good land" cannot be maintained as "Much of the land now carrying orange groves was sand dunes or swamps and uncultivated while purchased". The Peel report figured that Arab and Jewish interests could not be negotiated and suggested that Palestine be partitioned between the two people. The Peel report figured that Arab and Jewish could not be negotiated and suggested that: Palestine was to be partitioned between the two people, Jewish immigration should be limited to 12,000 per year, the sale of land by Arabs to Jews should be restricted, and the Arab agency should be created based on the Jewish model.
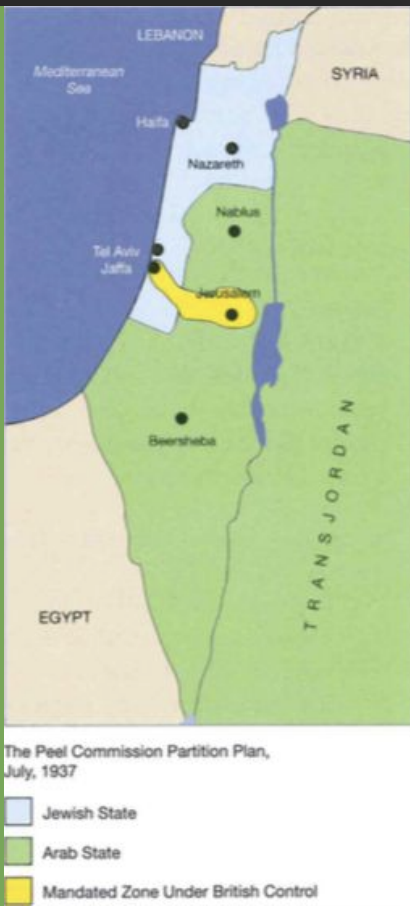
What were the strengths of the Peel Partition Plan?
If it were to be accepted by both groups, conflict would be reduced. Jews would also have port access in the Mediterranean and the most of the Kineret river for drinking water. Additionally, Israel has better and more valuable and more arable land. WWII was imminent and the Nazis already begun making anti-Jewish laws, and Israel could be a clear safe space that the Jews could move to.
What were the weaknesses of the Peel Partition Plan?
The Arabs had significantly more land, and Jerusalem is still under foreign control. If this did occur, there is a potential for violence. Israel is also still split into two countries or regions which makes travel between them difficult and the borders are, at certain spots, and they are not defendable because they are too narrow.
What was the outcome of the Peel Partition plan?
The Peel Partition was rejected by the Arab communities on the ground distributions was not fair, as they felt all the fertile land went to the Jews. They also believed that the Zionists did not have the legitimacy to any of the land. The Jewish community voted in favour despite only receiving roughly a third of the land. Ultimately, the British rejected the plan entirely, and nothing changed again until 1939,
How did Britains strategy change in 1939?
With WWII becoming increasingly likely, Britain had to consider its strategy in the Middle East. The British were concerned that the Arabs would fight against Britain out of frustration, and the momentum grew for adopting a more pro-Arab policy.
What was the 1939 MacDonald White Paper?
The MacDonald white paper reversed some of Britain's policies. It is stated that it is not part of Britain's policy that Palestine should become a Jewish state. Palestine west of the Jordan river was excluded from McMahon's plaedge, and cannot agree with the claim that Palestine should be converted into an Arab state. The British reiterate that the mandate is not permanent, and its purpose to prepare all the people in Palestine for Self-Government in one state. The white paper also states that they desire to create a single independent state of Palestine in 10 years, that they want to restrict Jewish immigration to 75,000 over five years and later on, to having it policy that no Jew can immigrate without the agreement of the Arabs, and that Jews cannot exceed over a third of Palestine's population.
How did the Jews respond to the MacDonald White Paper?
Not surprisingly, the Jewish community fully rejected the MacDonald-White paper and (rightly) argued that its intended purpose of creating minority status would result in no autonomy or rights for Jews. Not he question of the Jews supporting the British on the eve of WWII, Ben-Gurion stated that the jews "must assist the British in the war as if there were no White Paper."
How did the Arabs respond to the MacDonald White Paper?
The Arab Higher committee also rejected the MacDonald White Paper and demonstrated that all of Palestine must immediately be declared Arab state, that Jewish immigration must be stopped immediately, and the status of every immigrant from 1918 should be reviewed. Britain ultimately compromised during land purchases.
What was the Alliance between the Arabs and the Nazis?
During the 1930s and war years, Hajj Amin al-Husseini collaborated with the Nazis. The Nazis counted on his loyalty to strong sympathy for their policy, sent arms to the Arabs of Palestine and urged them to reject all proposals for the partition of the land.
Why did violence increase in Israel in 1945?
The end of WWII gave the Jews the opportunity for the Zionist community to actively campaign against British policies they felt were oppressive and undermined the spirt of the Mandate from 1920-1939. Both the Jewish and Arab communities began using violence against the British in an attempt to force them to leave the region. It was becoming clear that Britain had lost control.
What was the King David Hotel Bombing?
The bombing, coordinated by the Irgun was an attempt to disrupt life for the British and force the empire to leave Palestine for good.
How did the United Nations take control of British Palestine?
In October 1946, American President Truman publicly declared that the USA savours partition and a two-state solution. The British government officially still opposed a partition and favoured a single state. The British opposition, led by Winston Churchill, supported turning Palestine over to the United Nations. On February 18th, 1947, Britain announced that it would ask the UN to solve the Palestine Problem, and asked to assemble a special committee to decide on the appropriate course of action.
What was UN Resolution 181?
Members of the United Nations Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) visited Palestine to hear recommendations from the parties. The Arab Higher Committee boycotted UNSCOP, stating that the natural rights of the Palestinian Arabs deserve to recognized without investigation. On August 31st, UNSCOP recommended that the Mandate should end and that Palestine should be partitioned. The driving force behind the partition was the reality that two people with their own distinct nationalisms conflicted over Palestine.
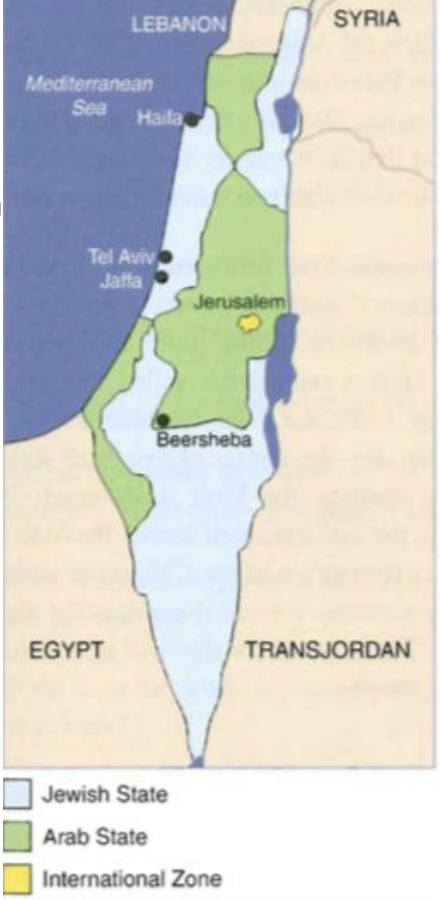
How did the Jews respond to UN resolution 181?
Not all of the Yishuv members agreed to accept the plan, with some arguing that the four separate regions and non-contiguous borders were terrrible. As leader of the Yishuv, Ben-Gurion convinced the opposition to accept the plan on grounds that having a country was necessary in order to have a safe haven for Holocaust survivors and Jewish refugees.
When did the vote take place and what were the results?
The vote took place on November 29th, 1947. In order for resolution 191 to pass, over 2/3rds of the countries needed to support the motion. 56 countries had the opportunity to vote. 13 countries voted against the plan, including all of the Arab countries with votes. India also voted no, as they had a large Muslim population who were against it. 10 countries, including Britain, abstained from voting. 33 countries, including Canada, the United States, and the USSR voted in favour.
What was going on after UN Resolution 181 was passed?
Right after resolution 181 was passed, both the Jews and the Arabs began to prepare for war. The day that the resolution passed, the Arabs ambushed a bus and killed 5 Jewish passengers.
What was the Unofficial war?
Once UN resolution 181 was passed, the unofficial war began. The Palestinian leaders of the Arab states announced their intention to use force to resist the implementation of Resolution 181. They stated that the Arab world would view Israel's Declaration of Independence as a cause for war and an act of aggression against Arab interests. Azzam Pasha, the secretary-general of the Arab league, openly stated that "The partition line shall be nothing but a line of fire and blood." The Arab leader's announcement shaped the political and military climate for the upcoming month when both sides were preparing for wat. Both armies aimed to take control of the main roads and towns on the borders of the UN Resolution 181 map. Keep in mind that resolution 181 had the interest of protecting human rights of minorities in both areas, and never mentioned the words Jewish or Arab state in the resolution.
What is Tochnit Dalet (Plan D)?
The restructuring of the Haganah led to the formation of an organized military called Tochnit Dalet (Plan D). The Jews plan was to defeat the Palestinian militias within the territory allocated by the UN for Jewish statehood before the Mandate expired, and to prepare for invasion by the regular Arab armies. The Haganah's key objectives were to control strategic points vacated by Britain, to regain control of roads, main towns, lines of communications, and to secure borders. Arab villages on main roads, and those used as bases for Arab fighters, would have to be evacuated so they could not be used to attack the Hagannah from the rear once the Arab invasion began. Permission was give to commanders to empty and/or raze any hostile villages.
How was Tochnit Dalet an offensive and a defence plan?
Tochnit Dalet called for the takeover of Arab villages or the destruction of Arab villages inside the Jewish state that are difficult to control with aggressive Arab populations. The Hagannah also forcefully remove hostile Arabs and were evicted from the borders of the future state of Israel. However, the text states to only temporarily occupy Arab villages along the borders that pose a threat and which can be used as a base for attacking the future Jewish state.
What was the Deir Yassin Massacre?
On April 9th, 1948, members of the Irgun and Stern Gang, which were right wing offshoots of the Haganah, attacked the Arab village of Deir Yassin. After a fierce battle, the Arabs surrendered; eye witnesses reported that 20 villagers were shot in a nearby quarry. Recent research indicates that around 110 Palestinians were killed. Deir Yassin was not the only village that experienced violent acts committed by Jews as a part of an implementation of Tochnit Dalet. It's equally important to acknowledge that there were instances of massacres committed by Palestinians, including the Hadassah Medical Convoy massacre in which Palestinians murdered 79 doctors and nurses bringing medical supplies to a hospital.
What does Benny Morris have to say about Deir Yassin?
Morris says that only a small minority of soldiers committed acts of violence / war crimes against unarmed Arabs, including rape, and that thise soldiers were not punished and should have been. He states that there was clear evidence to transfer Palestinians out of the future Jewish state as a result of violent actions and political opposition to the creation of a Jewish state. It would have been impossible to create a Jewish country with a large minority that rejects the country's right to exist and uses force to disrupt the country's existence. If one were to believe Israel's right to exist, they must reckon with the idea that the only way this could happen is if many Arabs had to leave, and they thought it was better to destroy than to be the ones destroyed. Believing that a population transfer was necessary does not mean that you believe that rape and massacre are acceptable.
How did Israel declare independence?
As the British mandate ended at midnight on May 14th, 1948, Ben-Gurion decided that Israel would declare its independence that day, knowing that the surrounding Arab nations would attack shortly afterwards. Independence was declared at 4pm, and that evening, Egyptian aircraft bombed Tel Aviv, and the next day 5 Arab armies attacked Israel. The war was not a surprise. The Arabs had announced it was coming after resolution 181, as they viewed the resolution illegitimate and illegal. The UN condemned the Arab states invasion as a violation of its charter and an illegal use of force.
Who was involved in the War of Independence?
Israel faced 5 Arab armies, Egypt, Transjordan, Syria, Lebanon, and Iraq (plus assistance from Saudi Arabia and Yemen, Not all Arab states were committed to the Palestinian goal off expelling the Jews and establishing an independent Arab state in all of mandatory Palestine. King Abdullah of Transjordan wanted to expand his territory at the expense of the Palestinians. Sytia and Lebanon sent troops to Palestine more to prevent Abdullah's forced than to help Palestinians. The Arab armies had no coordinated plan or strategy to liberate Palestine.
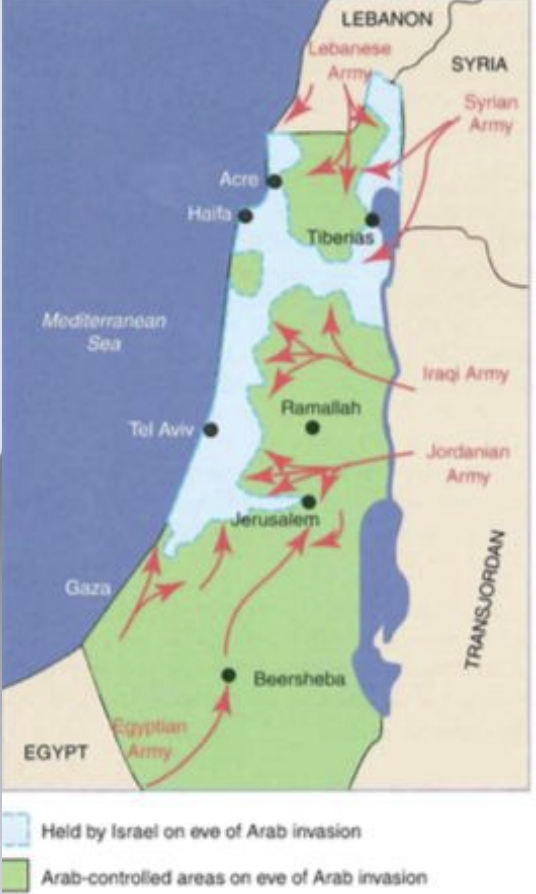
How did the first few weeks of war go for Israel?
The first few weeks of the war went poorly for Israel as they were being attacked on all of its borders. Iraq made it as dar as ten km from the Mediterranean, Egypt reached the outskirts of Tel Aviv and occupied the Negev. Jordan took possession of the Old City of Jerusalem. Syria and Lebanon attacked Israel from the North. On June 11th a ceasefire was implemented, where both sides had the chance to regroup.
What happened after the Ceasefire?
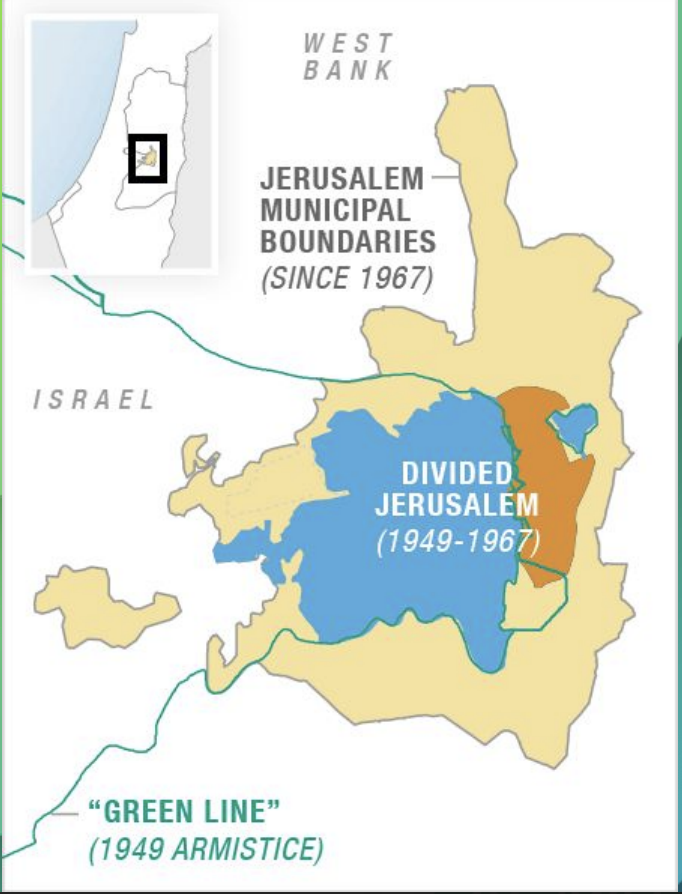
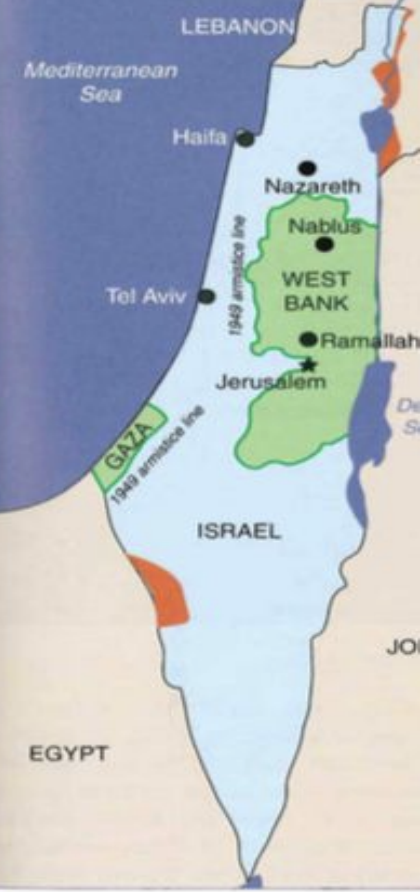
On July 7th, Israel took control of Western Galilee. Some Palestinians fled and others were expelled, and approximately 150,000 remained Israeli citizens. The Arabs conquered no further land, but Jordan remained in control of the Old City of Jerusalem and the West Bank, and they expelled all the Jews from those areas. Another ceasefire occurred on July 17h and lasted untiL October 15th, 1948. On January 7th, 1949, an armistice agreement (not a truce but a temporary end to fighting) was signed with Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, and Transjordan. Formal international bout these agreements were in place to say do not cross or you ill be attacked. Palestinian mandate territory was now 78% Israel, 22% Egyptian and Jordanian, and 0% Palestinian Arab. While the war was officially over, it was clear to all that the war was not actuallyy over.
What was the outcome of the 1948 War of Independence.
A Jewish state with a clear majority was formed. Within 2 years this statehood 1.2 million Jews who lived in Isael including 850,000 who'd been expelled from Arab lands, and about 150,000 Arabs. Israel had expanded its territory and established defendable borders for future conflicts. Jerusalem became a divided city, with parts under Jordanian control and parts under Israeli control. Israel proved its ability to defend itself and gather troops to protect the country and it is no longer dependent only on non-Jewish help. It was impressive how Israel was able to win and get troops to fight for it. No independent Palestinian state emerged from the ashes of the war. The Egyptians held the Gaza Strip and kept it under military occupation while the Jordanians occupied and annexed the West Bank. 700,000 Palestinians became refugees, and the Palestinian Arab's refer to this as the Nakba meaning the catastrophe.
What were some push factors with Palestinian Refugees?
After the war 150,000 of 800,000 Arabs remained in Israel. 700,000 became refugees. There were four major push factors that led to their departure. Palestinians did not want to live in a war zone, the Arab leaders urged them to leave while promising a quick return after the Jews will be defeated, Jews drove Arabs out of towns and villages in the Jewish territory by force, and lastly most Arabs were unwilling to live as Arab citizens.
What was resolution 194?
On December 11, 1948, the UN passed Resolution 194. The primary purpose of the resolution establish the Palestinian Conciliation Commission. The Commission should facilitate the refugees, resettlement and economic anomic social rehabilitation. Article 11 is the basis of the Palestinian claim for the "right of return" The article says that Palestinian refugees should be allowed to return to their homes and receive compensation as long as they promise to live peacefully with Israeli Jews. Both the Israel and the Arab leadership rejected the resolution
What is UNWRA?
Since 1949, the needs of Palestinian refugees have been provided for by the UN Relief and Works for Palestine. In 1949, 800,000 refugees registered to the agency. In 2020, the numbers of Palestinian refugees was 5.6 million. Palestinians refugees is a unique category of refugees differentiated by the UN from any other kind of refugee. Descendants of the 1948 Palestinian refugees differentiated by the UN from any other kind of refugee. Descendants of the 1948 Palestinian refugees are eligible for UNRWA's services and registered as if they are refugees This occurs even if the descendants are natives of other countries and enjoy full citizenship. In 2020 about 1% of the refugees served by UNRWA can be defined as people who lived in Palestine between 1946 and 1948. When the war of independence started, many Jews were forced to leave the Arabs countries they lived in. From 1948 to 1951 856,000 left their homes in Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Syria, and Yemen. Today about 5,000 Jews remind in Arab countries. Israel consistently argues that any resolution to the Palestinian refugee problem must also involve a solution for the Jewish refugees.
What is Israel's position on refugees?
The refugees exist because Arab states declared war. While there were 700k Palestinian Arab refugees, there were also 800k Jewish refugees from Arab lands. Since Israel absorbed Jews from Arab lands, Arab countries should absorb the Palestinian refugees. Only individuals who were expelled or fled in 1948 are actually refugees, the rest are children of refugees, and you can't be. refugee from a country you never lived in. Even sympathetic governments cannot support a Return because of demographic issues.
What is the Arab position of the refugee problem?
Israel was fully responsible for a policy of ethnic cleaning and drove Palestinian Arabs out of their homes. Demand unlimited and unconditional right of return for refugees. Excluding Jordan, no Arab state has permitted Palestinian refugees to settle (instead they remain in camps to keep the refugee issue alive), leaving the 3 million refugees living in refugee camps.