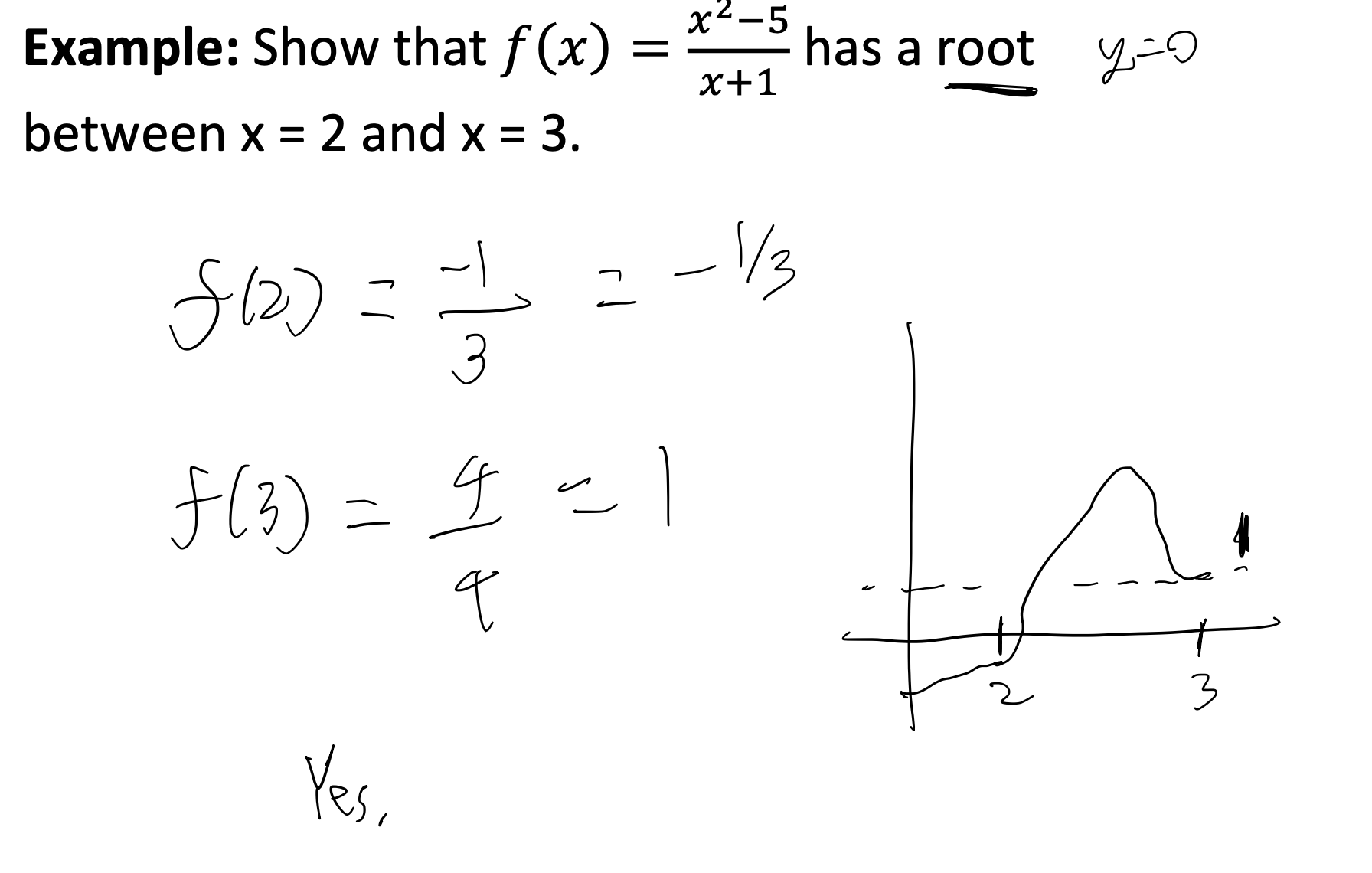Calculus: Limit & Continuity
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
as f(x) x approaches c, it is equal to L
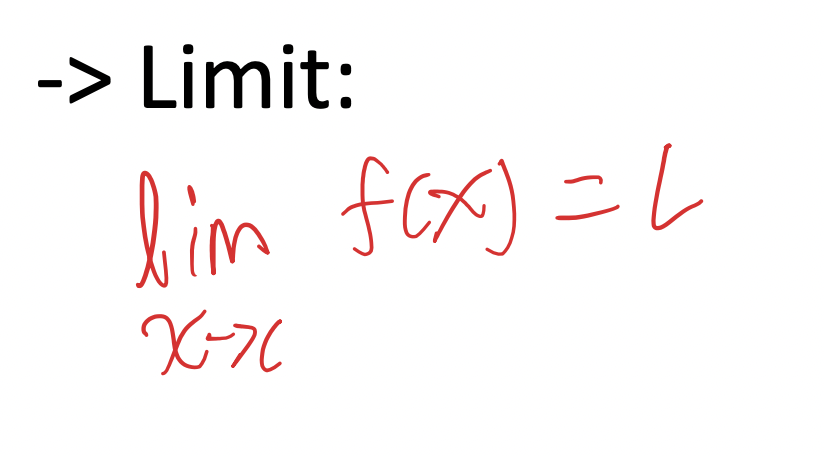
When does limit exist?
Both right and left handside limits are equal to each other.
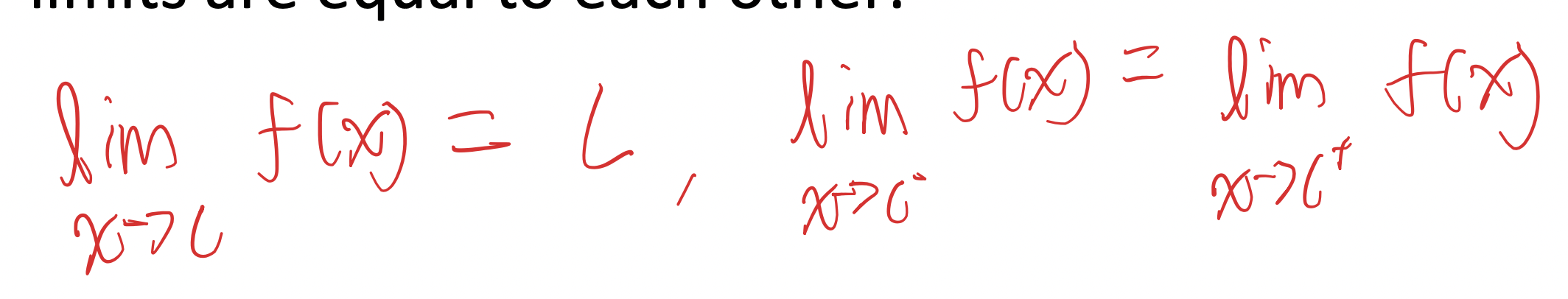
Finding Limits End Behavior
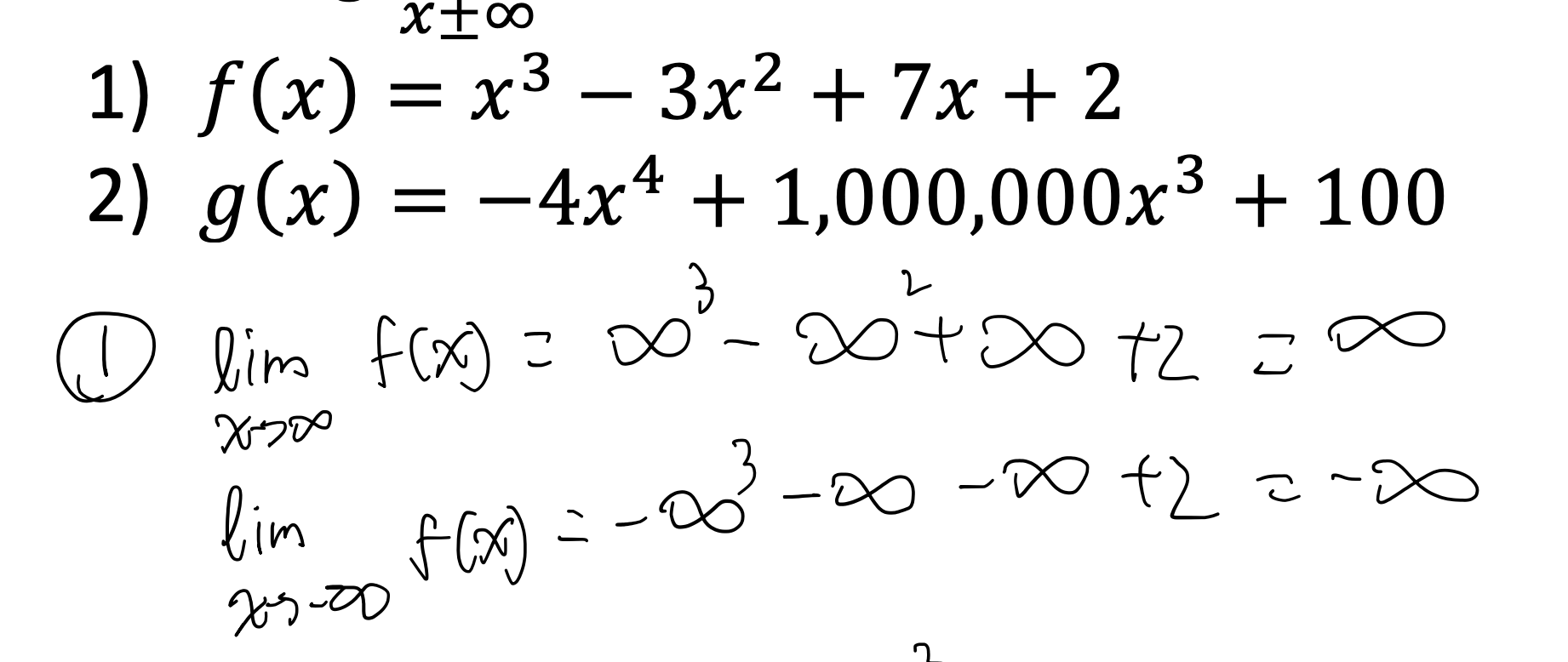
Which value makes vertical asymptotes exist
The value makes denominator (분모) equals to zero.
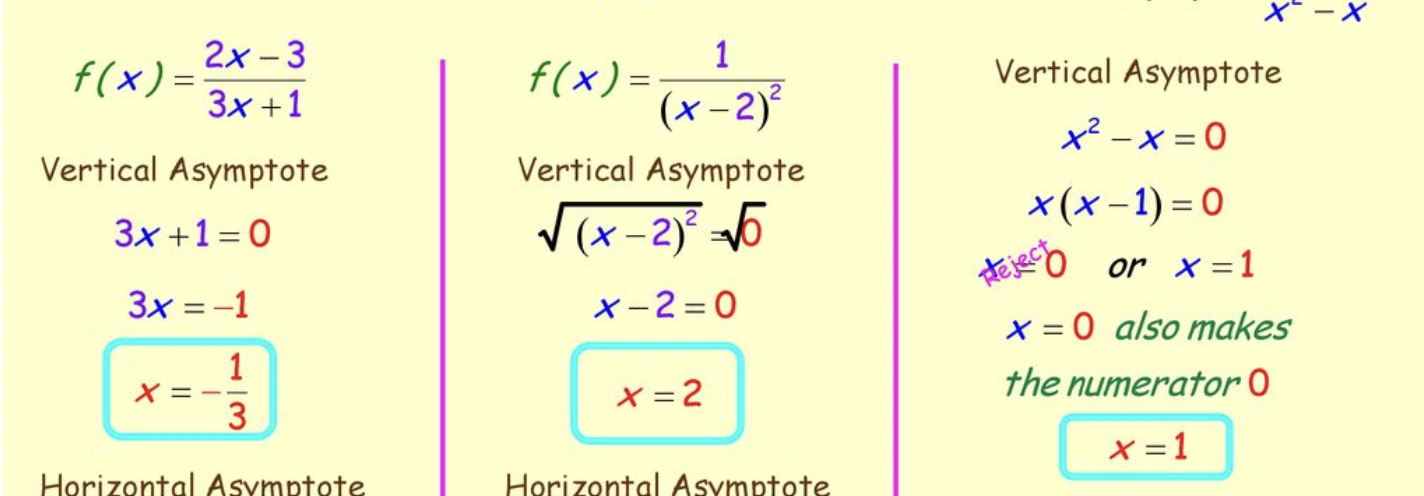
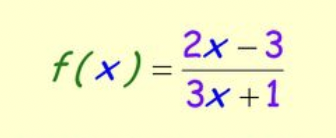
Finding Horizontal Asymptote
y = 2/3
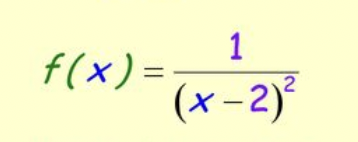
Finding Horizontal Asymptote
y = 0
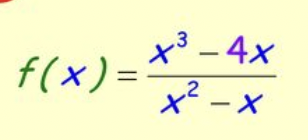
Finding Horizontal Asymptote
No Horizontal Asymptotes
Squeeze Theorem
Squeeze Theorem: If f(x) ≤ g(x) ≤ h(x) for all x in an interval except possibly at x = c, and lim f(x) = lim h(x) = L, then lim g(x) = L.
How to find limits involving infinity?
We need to divide by the biggest power.
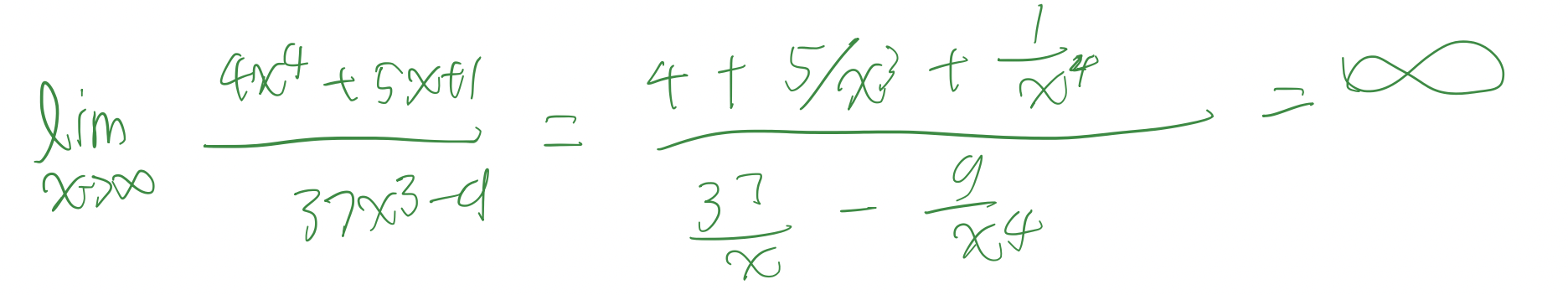
Simplified Version of finding limits involving infinity
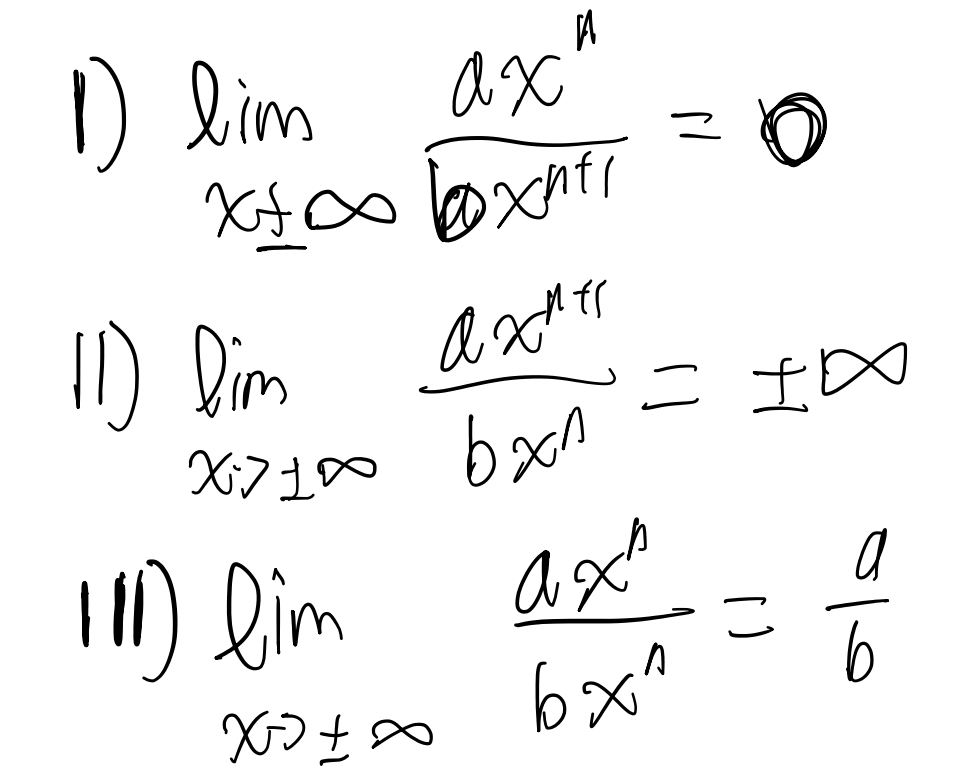
As x approaches 0, limit of sin x/x is
lim (x -> 0) sin(x)/x = 1
As x approaches infinity, limit of sin x/x is
lim (x -> ∞) sin(x)/x = 0
Definition of Continuity
No holes, breaks, or jumps
Three conditions to satisfy that y = f(x) is continuous at x = c.
1) f(c) exists
2) lim (x → c) f(x) exists
3) lim (x → c) f(x) = f(c)
Jump Discontinuity
lim (x→c+) f(x) ≠ lim (x→c-) f(x)
Removable Discontinuity
lim (x→c) f(c) ≠ f(c)
Infinite Discontinuity
When there’s Asymptotes
Theorems on Continuous Functions
1. The Extreme Value Theorem
Extreme Value Theorem: If f is continuous on a closed interval [a, b], then f has both a maximum and minimum value on [a, b].
Theorems on Continuous Functions
1. The Intermediate Value Theorem
If ( f ) is continuous on ([a,b]) and ( k ) is between ( f(a) ) and ( f(b) ), then there exists a ( c ) in ((a,b)) such that ( f(c) = k ).
Example of The Intermediate Value Theorem