Path: Pulmonary Tumors I & II
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
lung adenocarcinoma cytology
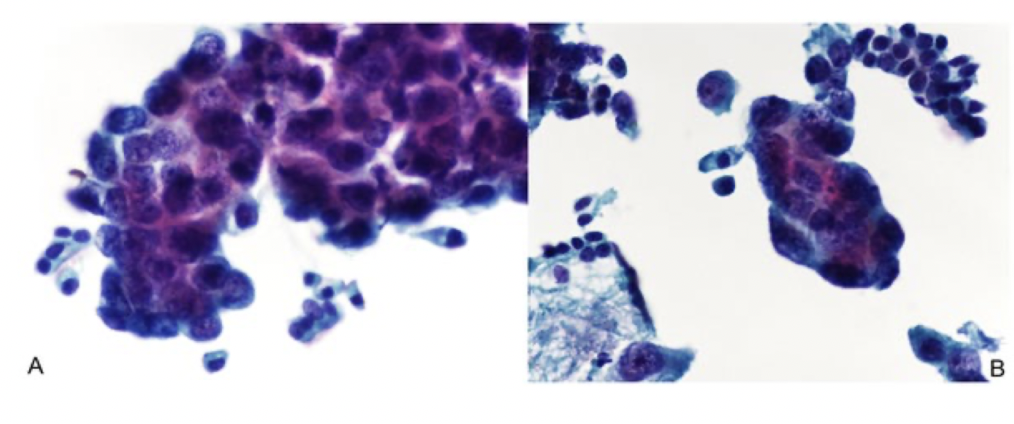
wedge
what type of specimen with a video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
malignant (spiculated)
benign or malignant?
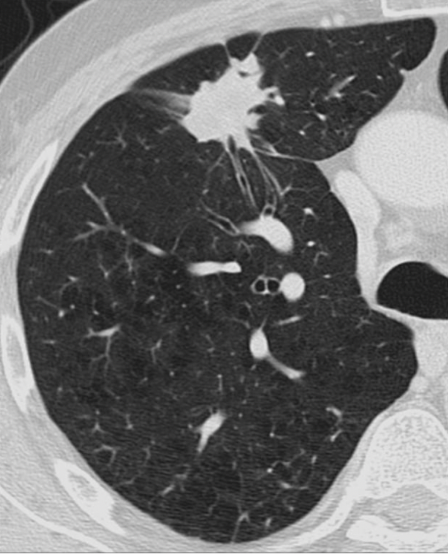
benign
benign or malignant?
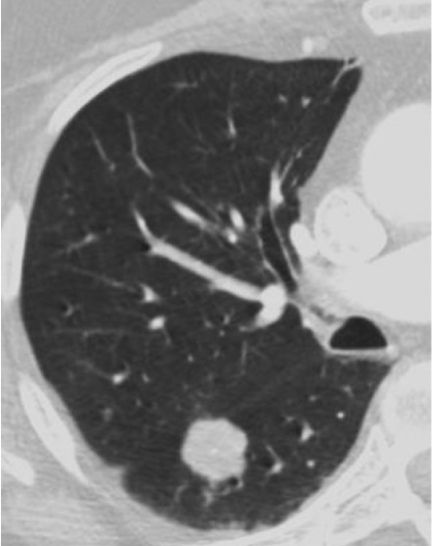
malignant (mets)
benign or malignant?
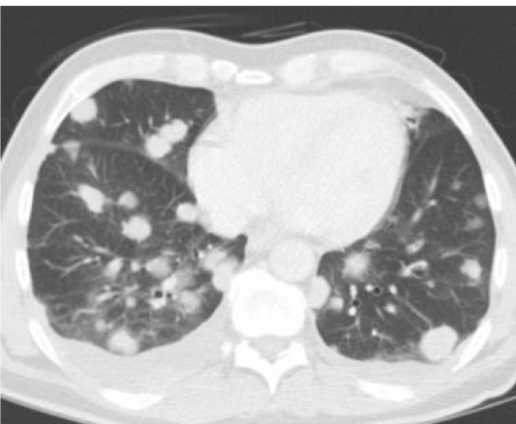
benign (diffuse)
benign or malignant?
malignant
lighting up on pet scan is benign or malignant?
benign (hamartoma)
benign or malignant?
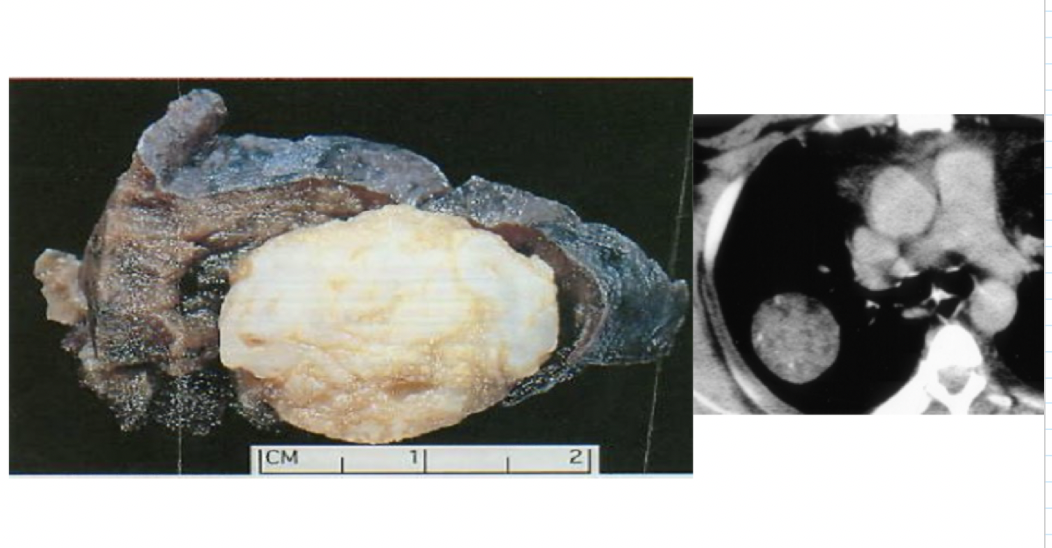
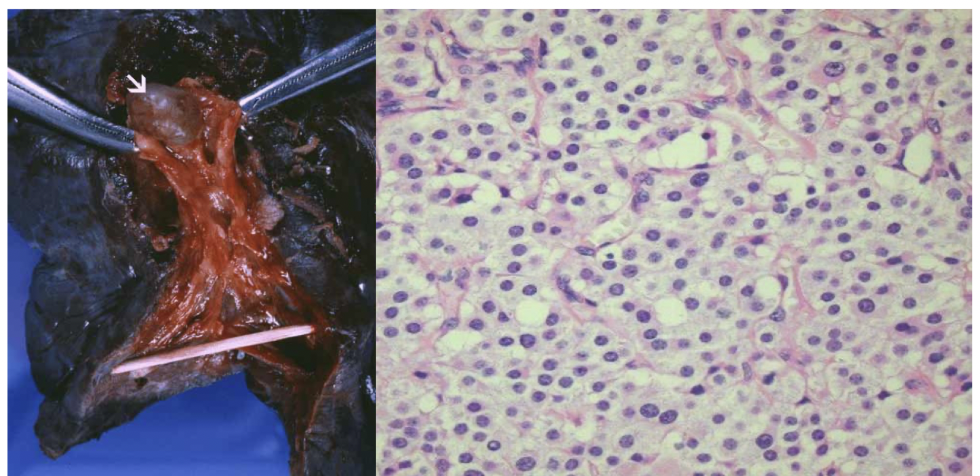
pulmonary hamartoma
mass of disorganized tissue indigenous to a particular site
adults with peak in 6th decade
circumscribed, usually peripheral
pulmonary hamartoma
buzzword: popcorn calcification on x-ray
pulmonary hamartoma
pulmonary hamartoma
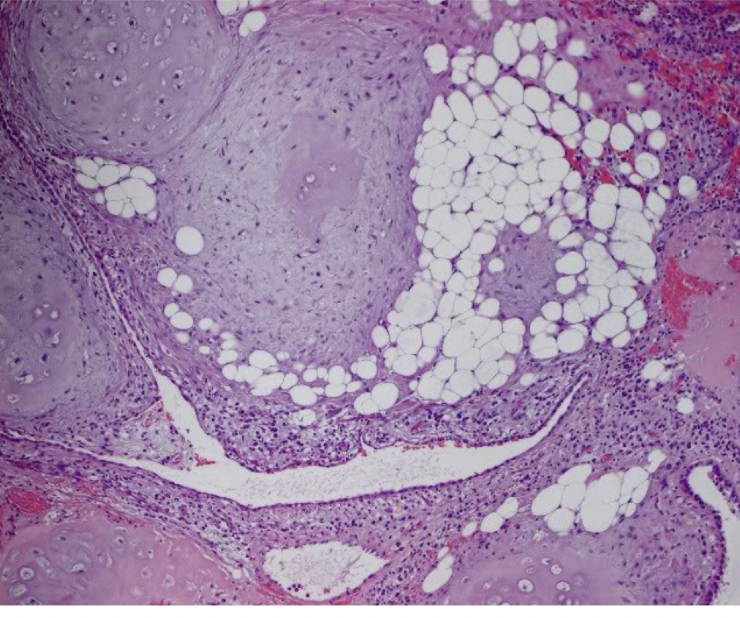
lung
most common cause of cancer death worldwide in men and women
squamous and small cell carcinoma
what type of lung cancers are most associated with smoking?
field effect
approximately 10-20 genetic mutations have likely already occured by the time the lung tumor is clinically apparent
peripheral
central or peripheral: adenocarcinoma
central
central or peripheral: SCC
central
central or peripheral: small cell carcinoma
small cell carcinoma
90% smokers
predominantly arise near hilum
rapid growth rate (doubling just over a month)
poor progn
small cell carcinoma
buzzword: paraneoplastic syndromes (ADH, ACTH, antibodies)
small cell carcinoma
buzzword: chromogranin A, synaptophysin, neuron specific enolase (NSE)
small cell carcinoma
extensive necrosis and mitoses
amplification of genes in MYC family
kulchitsky cells (NET)
what type of cells are neoplastic in small cell carcinoma
azzopardi effect
small cell carcinoma
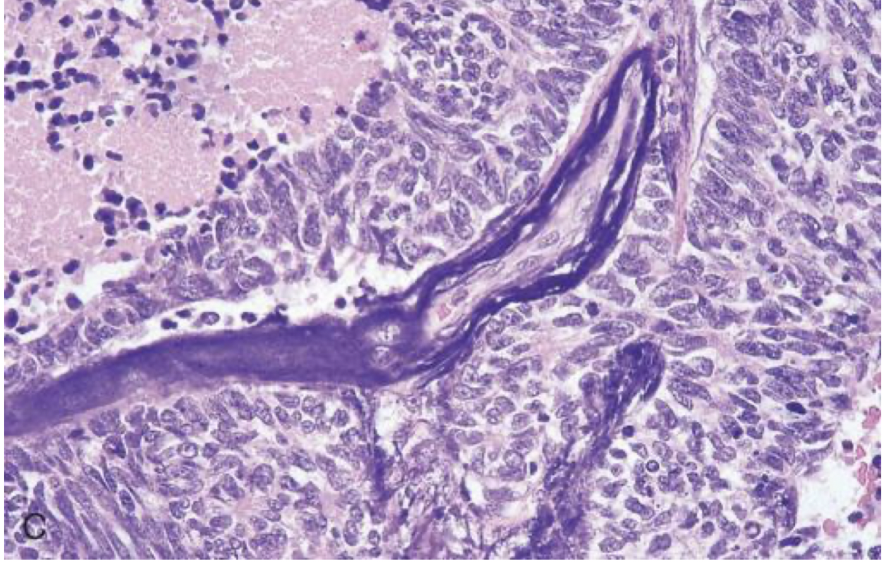
small cell carcinoma
small cell carcinoma
lots of necrosis with azzopardi effect
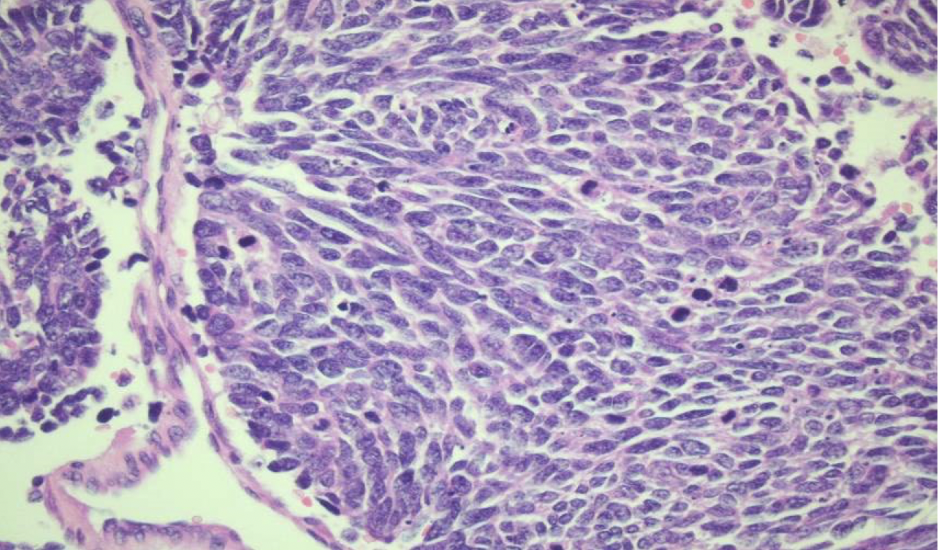
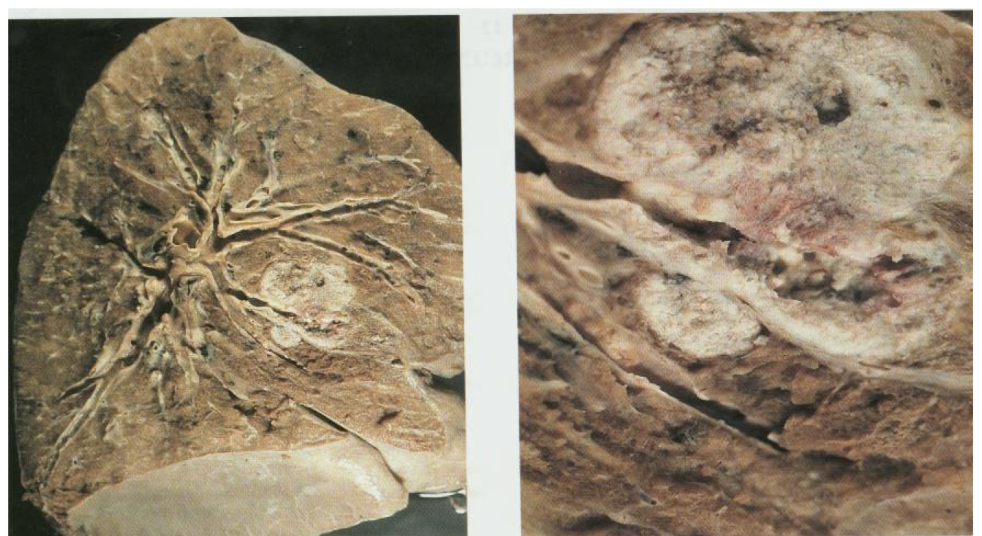
carcinoid tumor
low grade malignant neoplasm
chromogranin A and synaptophysin +
<2 mitoses/10HPF and no necrosis
carcinoid tumor
diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia is a potential precursor lesion for?
carcinoid tumor
ribbon-like architecture, lots of pink cytoplasm

carcinoid tumor
bronchial epithelial injury → squamous metaplasia → squamous dysplasia → SCC in situ → invasive SCC
what is the sequence to SCC of the lung
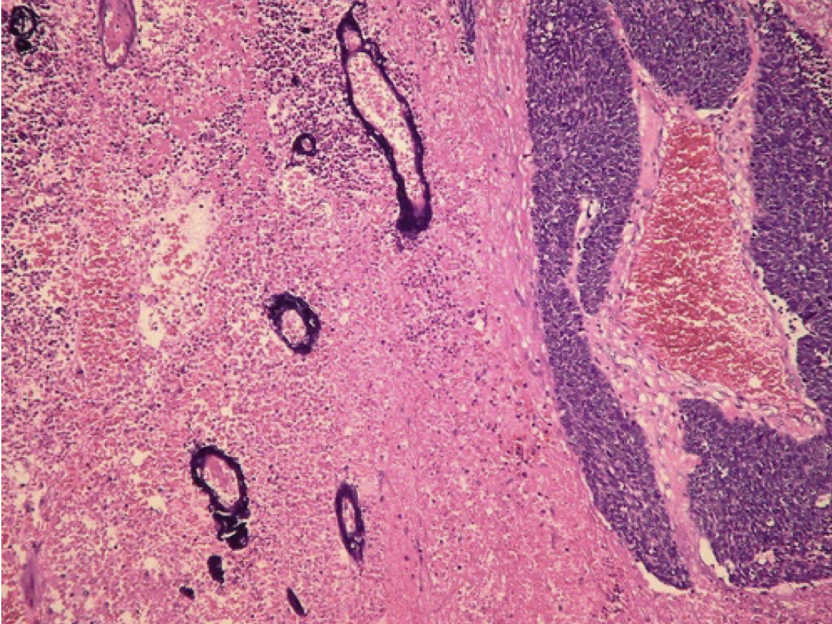
SCC
SCC
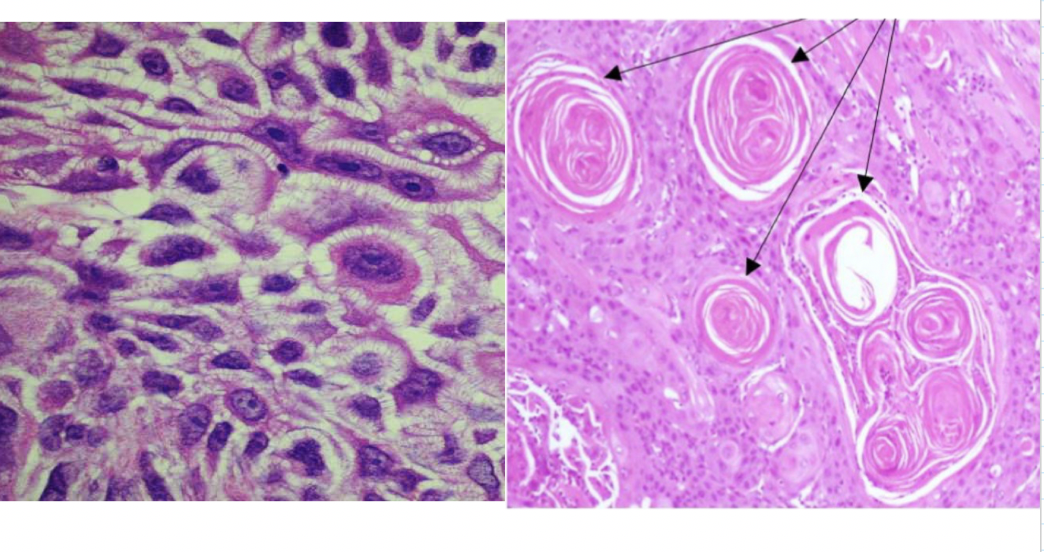
SCC
over 80% smokers
central location
obstructive pneumonitis, frequent cavitation (central necrosis)
majority are resectable
SCC
buzzword: paraneoplastic syndrome of hypercalcemia due to secretion of parathormone related peptide (PTHRP)
adenocarcinoma in situ
lesion that is less than 3 cm and is composed entirely of dysplastic cells growing along preexisting alveolar septae
atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
precursor to adenocarcinoma in situ that is usually less than 0.5 cm
adenocarcinoma in situ
buzzword: lepidic growth pattern
adenocarcinoma in situ (mucinous)
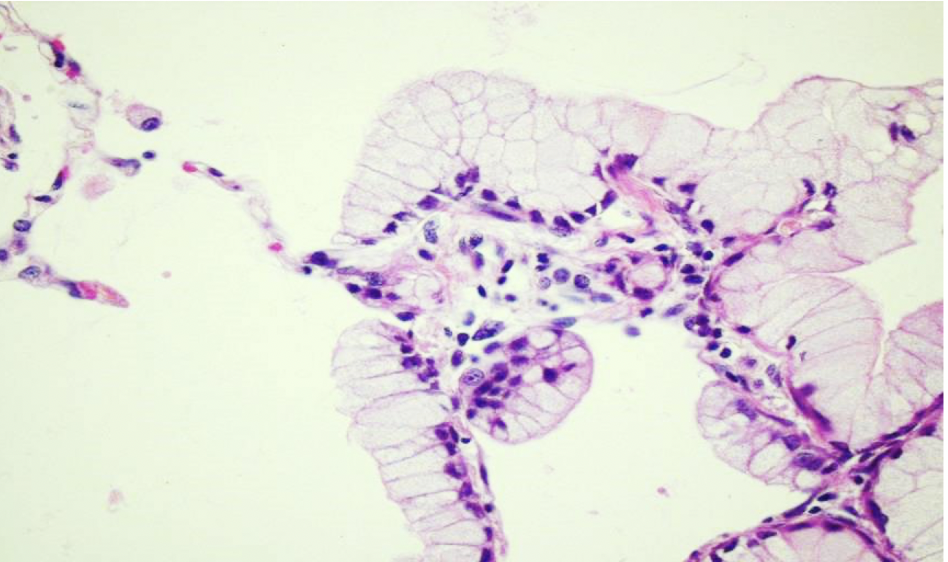
adenocarcinoma in situ
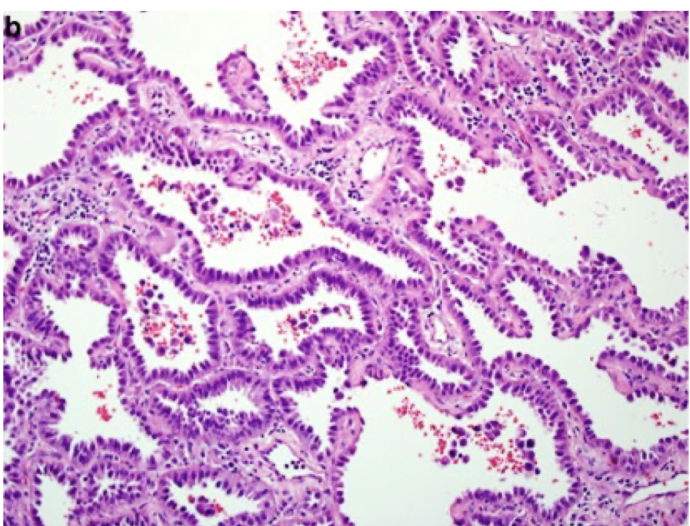
adenocarcinoma
malignant epithelial tumor with glandular differentiation or mucin production
adenocarcinoma
buzzword: TTF1 +
adenocarcinoma
most common in women
less strongly associated with smoking
vascular invasion, brain mets common
often pleural involvement
adenocarcinoma
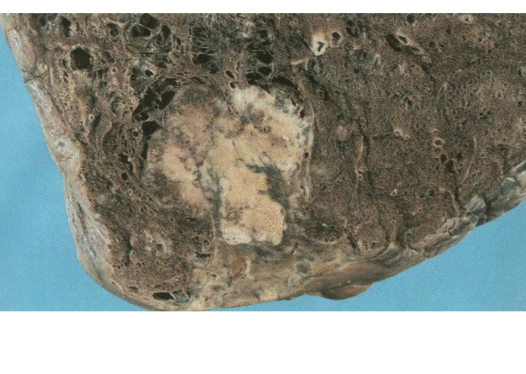
adenocarcinoma
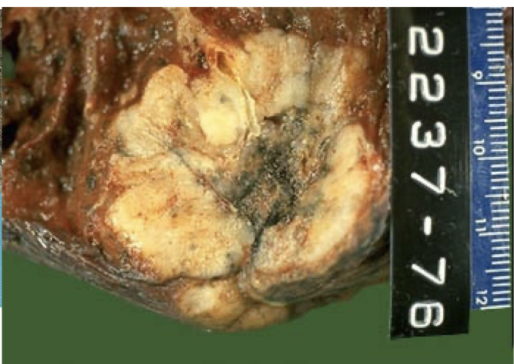
adenocarcinoma
TTF1+ IHC
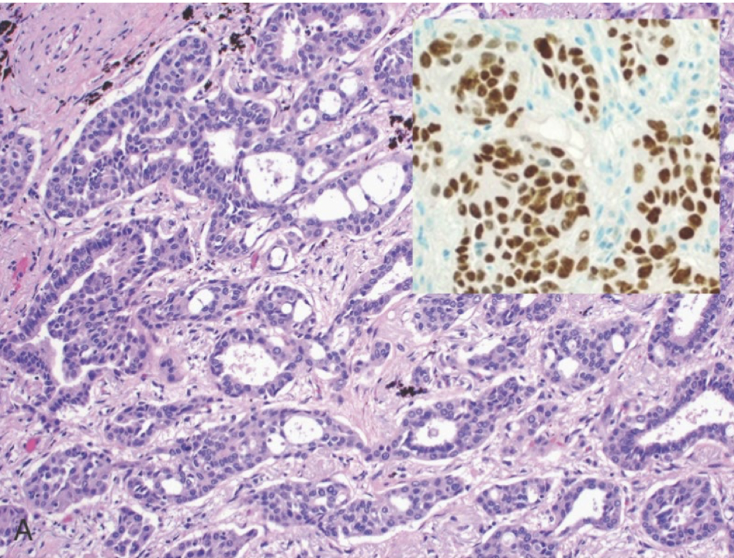
adenocarcinoma (mucinous)
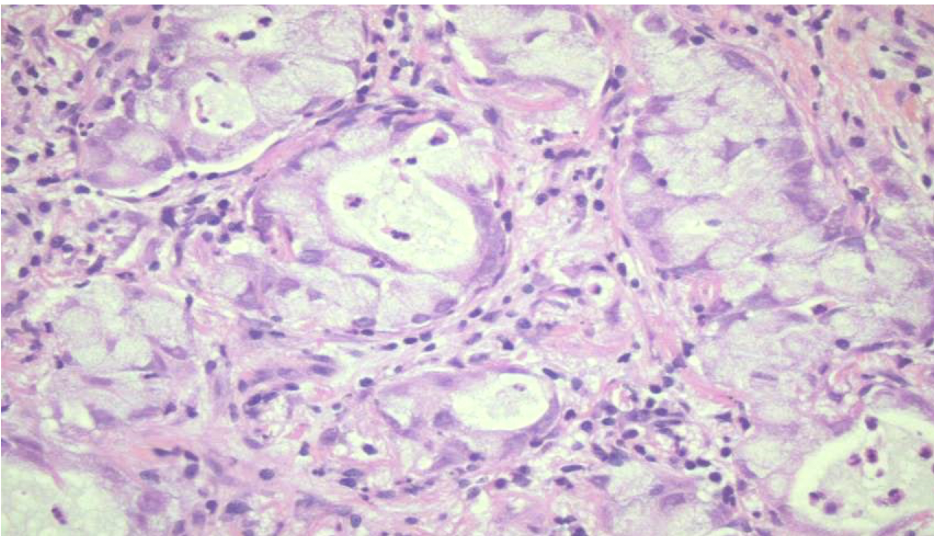
adenocarcinoma
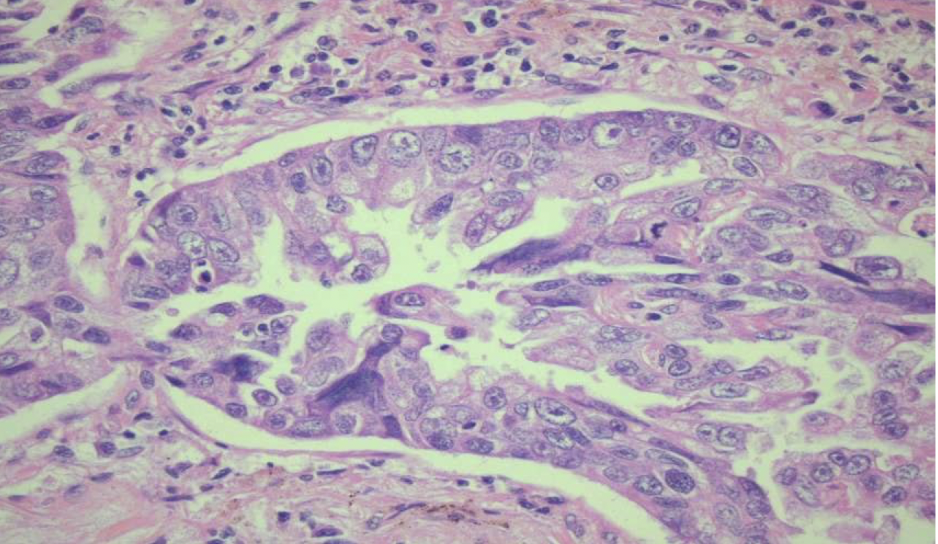
adenocarcinoma
buzzword: cytokeratin 7 +
SCC
buzzword: cytokeratin 5/6 +
SCC
buzzword: p40+
large cell carcinoma
undifferentiated carcinoma with no cytologic, architectural, or IHC features; dx of exclusion and requires thoroughly sampled resection
driver mutations
abnormalities that are essential for tumor-cell survival; inactivation results in cancer cell death
adenocarcinoma
EGFR and ALK mutations
adenocarcinoma (smokers)
KRAS mutations
age
pk year hx of smoking
what are high risk factors for lung tumors?
superior vena cava syndrome
obstruction of the SVC that impairs blood drainage from the head
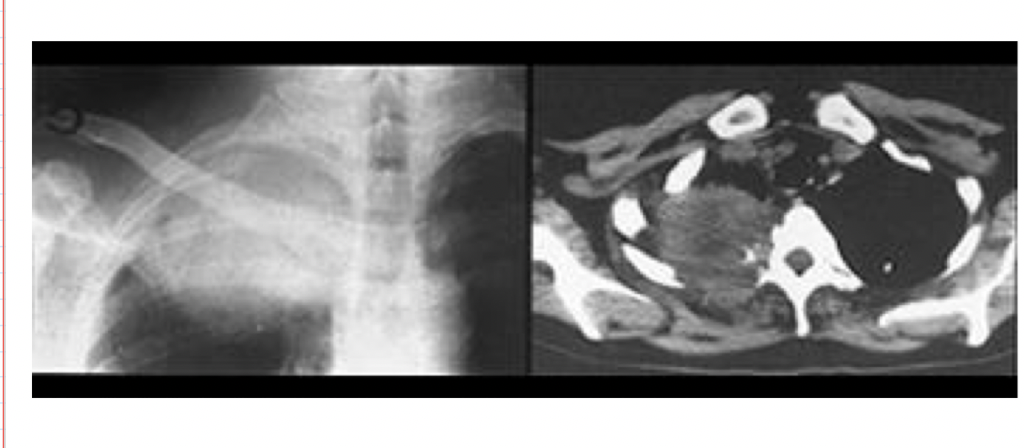
pancoast tumor
apical lung cancers in which the tumor invades neural
pancoast tumor
buzzword: horner syndrome
miosis
anhidrosis
ptosis
endophthalmitis
what is horner syndrome (4)
pancoast tumor
phrenic nerve paralysis
dermatomyositis
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell carcinoma causing inflammatory myopathy with progressive proximal muscle weakness
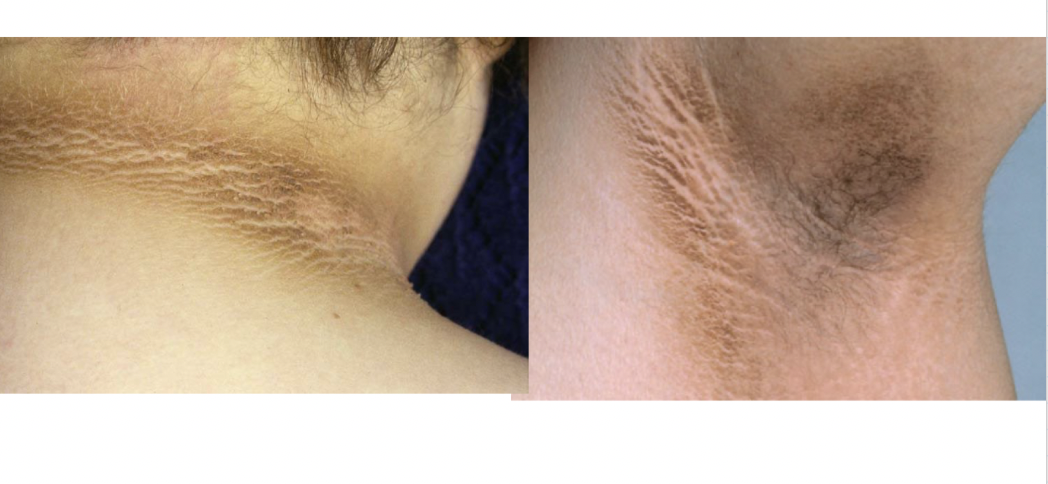
acanthosis nigricans
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell carcinoma that secretes epidermal GF
acanthosis nigricans
hyperkeratosis and pigmentation of axilla, neck, flexures, and anogenital region
lambert-eaton syndrome
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell carcinoma with disease of neuromuscular junction; proximal muscle weakness and does not respond to anti-cholinesterase therapy
cushing syndrome
ectopic production of ACTH causing hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, hypertension, and muscle weakness; associated with pulmonary small cell carcinoma and carcinoid tumors
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell carcinoma with ectopic production of ADH leading to sodium and water retention, altered mental status, seizures, coma, possible death;
hypercalcemia
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with SCC of the lung; production of PTHrP; TGF-alpha activates osteoclasts and active vitamin D
false
T/F: hypercalcemia from bone mets is a paraneoplastic syndrome