Chapter 12: ONE-WAY Analysis of Variance
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
A hypothesis-testing procedure that is used to evaluate mean differences between two or more treatments (or populations).
NULL HYPOTHESIS
NO mean difference between the populations
𝐻0: UN=UR =UU
ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS
There is at least one mean difference between the populations
N=R =/U
N=U R
N=U N
N=/R=/ U (all three means are different)
Why not conduct a bunch of t-test?
Doing multiple t-tests creates multiple chances to make a type 1 error.
ANOVA controls this risk by testing all groups simultaneously using variance (average squared distance from the mean).
Define Between-group Variability
Values used to measure and describe the differences between treatments (mean differences).
Between-group Variability can be due to…(2)
Sampling error
The Effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable
Define Within group Variability
The differences that exist inside each treatment condition.
Within group Variability is also refered to as…
ERROR TERM
Within group Variability are ….
random, individual differences
Within group Variability is used when looking…
looking for an F of 1 if there is little variability (NULL TRUE)
F is always ….
POSITIVE
The distribution of F-ratios should pile up around …
1.00
Shape of F depends on…
Degrees of freedom for between and within group variability
What is the F-ratio numerator?
Variance Between Group
What is the F-ratio denominator?
Variance Within Group
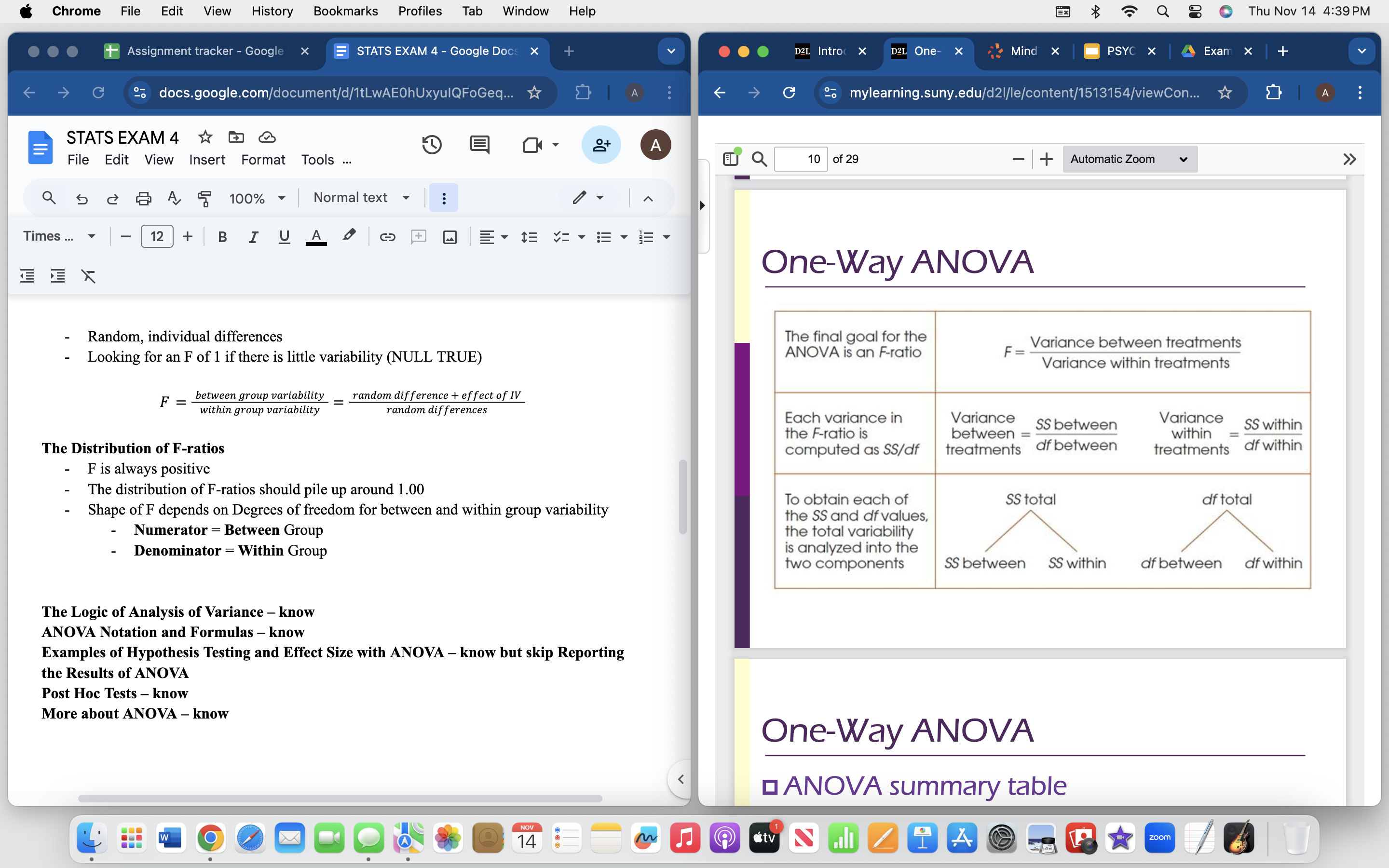
Helpful table
k symbolizes?
Total number of group you have
N symbolizes?
Total number of participants
Variance is called___________ instead of s squared
Mean Square (MS)
F-ratio test
The statistical test to use to compare variance
n2 (greek letter Eta) is the _____________________
percentage of variance explained (effect size)
Small effect, n2 (greek letter Eta)
0.10
Meduim effect, n2 (greek letter Eta)
0.25
Large effect, n2 (greek letter Eta)
0.40
What are Post hoc Tests?
Additional tests that determine which mean differences are significant and which are not.
With Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test you compute …
a single value that determines the smallest difference between the means that meets criteria that is necessary for significance.
For HSD when your df is not exactly in the table, you go with the
smaller number that is closest.
Scheffé test has the
smallest risk of Type 1 error
Anything significant with ______, is significant for ______, but ____________.
Scheffe
Tukey
NOT vice versa
Assumptions
Observations are independent
Normal populations
Homogeneity of variance
Both the F-ratio and the t statistic compare the ____________________________ with the _____________________
actual differences between sample means (numerator)
differences that would be expected if there is no treatment effect (the denominator if H₀ is true).
If the _____ is sufficiently _____ than the _______, you conclude that there is a significant difference between treatments.
numerator
bigger
denominator
What is the principal reason why you should use ANOVA instead of several t tests to evaluate mean differences when an experiment consists of three or more treatment conditions?
Multiple t tests accumulate the risk of a Type I error.