4-1 Mitigating Risk When Connecting to the Internet
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Categories of risk on the internet:
- Hackers
- Malware (viruses, Trojan horses, worms)
- Personal attacks (harassment, fraud, identity theft, data theft)
- Email attacks (phishing, spam, email viruses)
Hackers and predators:
Objective of a hacker is to gain access to a computer system or network to do harm, steal data, or both
Hacker and predators methods include:
-Malware
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in system and application software
- Exploiting poorly configured and insecure networks
- Gaining private credentials and other information through social engineering
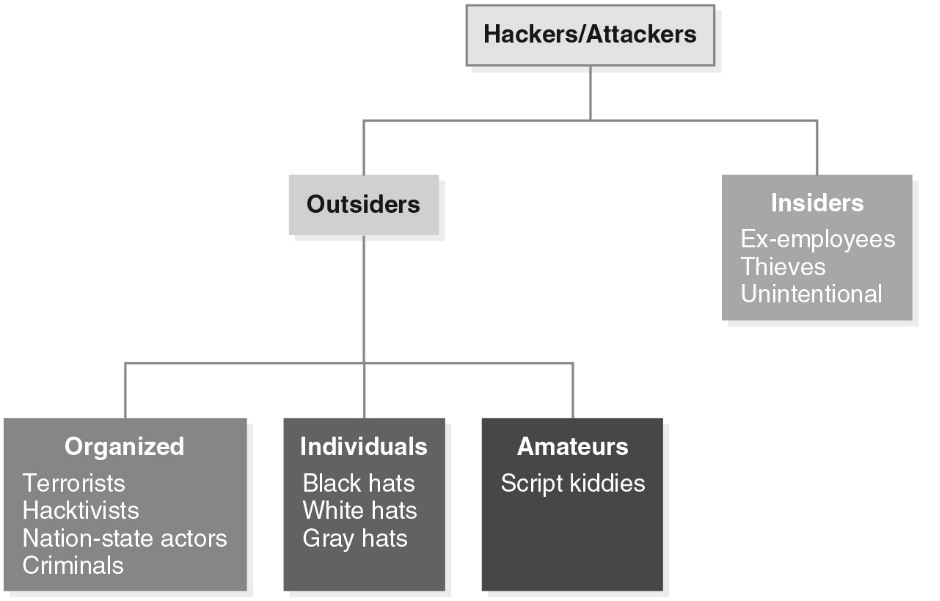
What is this figure showing?
The relationships of hackers to the other elements of risk on the internet
Hackers/Attackers:
- Outsiders
- Insiders
Outsiders:
- Organized
- Individuals
- Amateurs
Organized:
- Terrorists
- Hacktivists
- Nation-state actors
- Criminals
Amateurs:
Script Kiddies
Insiders:
- Ex-employees
- Thieves
- Unintentional
Hackers and motivations:
- White hat hackers
- Black hat hackers
- Grey hat hackers
- Cyberterrorists
- Sponsored hackers
- Hacktivists
- Script kiddies
- Hobbyists
Common motivations for hackers:
- Personal agenda
- Financial
- Sponsored or cyberwarfare
- Corporate espionage
- Organizational agendas
- Resource theft
Hacker attacks:
- Motivation and technology dictates the choice of type of attack
- Attack method fits vulnerabilities of the targeted system
Types of attack methods:
- Password attacks (brute force, dictionary, hash injection)
- Backdoor attack
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack
- Denial of service (DoS) attack (ping flood, Distributed DoS attack)
Malware:
- Umbrella term that covers many kinds and types of software
- Developed for sole purpose of harm
- May be dormant for a long time before becoming active
- Early forms were hoaxes and pranks
MitM:
Man-in-the-middle
DoS:
Denial of service
Denial of service (DoS) attack:
ping flood, Distributed DoS attack
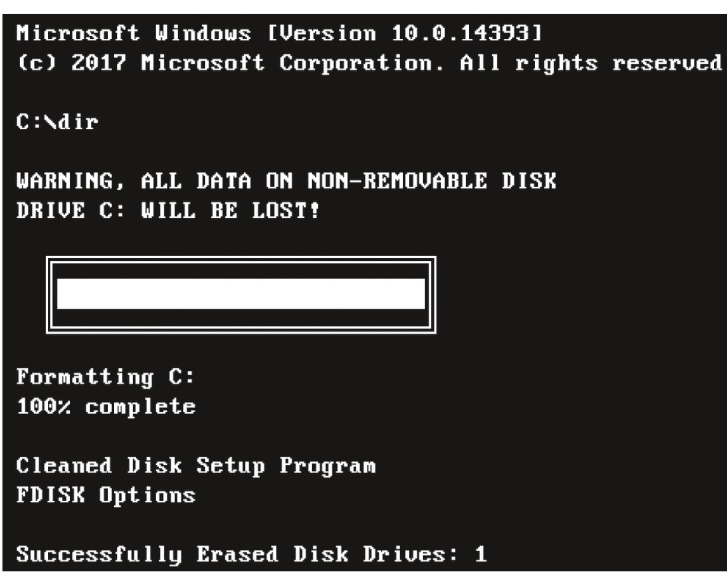
The Following is an example of what?
An example of a hoax that simulated the erasure of data from disk
Common forms of malware:
- Viruses
- Worms
- Trojans
Viruses:
A malicious program that can only spread by attaching or inserting itself into a document or file created by software that supports macros, which the virus needs to execute its programming
Worms:
- A self-sufficient program with the ability to replicate itself from one computer to another unaided
- Attempts to exploit operating system or system software vulnerabilities
Trojans:
- Disguised malware that appears to be something desirable so that you will download it onto your system, bypassing countermeasures that may have stopped it
- Not a virus although commonly referred to as such
Common forms of malware:
- Rootkits
- Spyware
- Ransomware
Rootkits:
Is placed on a target computer and hidden so that it can do its malicious activities, such as stealing and transferring data files, keylogging, or a communications log, undetected
Spyware:
Malware focused on collecting and transmitting information regarding the activities associated with accessing the internet and websites, navigation among sites, and harvesting any personally identifiable information (PII) available, such as passwords, payment information, employments, locations, and the like
Ransomware:
A form of malware that disables any access to a targeted computer’s data until a ransom is paid
A Virus, Trojan Horse, and Worms are types of what?
Types of Malware.
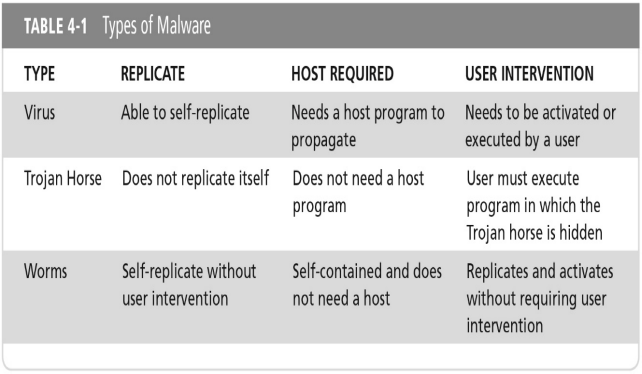
How does a Virus replicate?
Able to self-replicate.
How does a Trojan Horse replicate?
Does not replicate itself.
How do Worms replicate?
Self-replicated without user intervention.
Is a host required for a Virus?
Needs a host program to propagate.
Is a host required for a Worm?
Self-contained and does not need a host.
Does a Virus need user intervention?
Needs to be activated or executed by a user.
Does a Trojan Horse need user intervention?
User must execute program in which the Trojan horse is hidden.
Do worms need user intervention?
Replicates and activates without requiring user intervention.
Common malware delivery types include:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) sharing networks
- Network shares
- Web browsing
To protect a network from hackers and the harm malware can cause:
- Ensure software is current with all patches and service packs
- Install a trusted anti-malware package
To defend systems and networks, administrators and users should be made aware of:
- Software vulnerabilities
- Hardware vulnerabilities
- Malware threats
- Port vulnerabilities
- End-user vulnerabilities
- Physical security vulnerabilities
Personal attacks:
- Protecting against personal attacks and attempts to steal personal data are more about your personal browsing habits than malware.
Fraud:
- Primary trap used on a bad e-commerce site
Ways to spot a fraudulent or malicious site:
- Browser alerts
- Suspicious domain name
- No contact
A safe website displays what and uses what?
A safe website displays the padlock symbol and uses a secure version of HTTP.

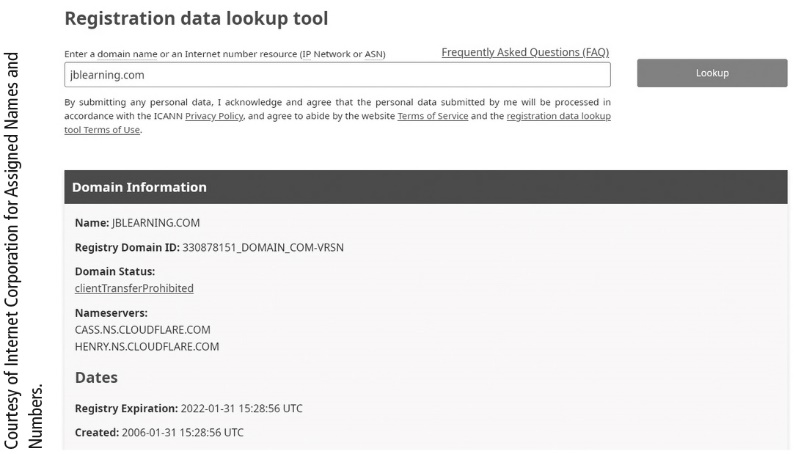
What is the following figure showing?
ICANN Domain and IP Address Lookup Service hat can be used to identify a registered owner
Cyberstalking
A form of harassment; a repeated electronic communication with someone who does not want to communicate
Cyberstalking includes what?
Includes repeated offensive emails, instant messaging spamming, impersonating friends or colleagues, creating hate sites or false online dating ads, stalking target on social media sites
(Physically tracking target and harassing using a smartphone, table, or netbook computer)
To prevent cyberstalking:
- Don’t give out personal information except to a known contact.
- Use filtering features in email and firewalls to block contacts from the harasser.
- Contact the police if it becomes a serious problem.
- Stop all communication with the harasser.
- Block the cyberstalker from social networking sites and only add trusted friends.
Identity theft:
- Goes beyond fraud and occurs when a thief assumes all or some of a victim’s identity
- Uses your personal or financial information without your permission
- Use caution regarding to whom your personal information is given and why it is given
- Keep documents that contain PII locked up
Email attacks:
Email provides a gateway directly into a network through network user accounts
Personal methods to prevent email attacks include not doing the following:
Opening unsolicited emails, unwanted or unknown attachments, sending personal information, giving your email address to a stranger, replying to spam, forwarding chain letters
Technical methods of preventing email attacks include using email checkers or filters to perform the following:
- Email tracking
- Keyword filtering
- Legal disclaimer
- Email blocking
- Message priority
- Message archiving
Online risks and threats:
- Keep applications and operating systems updated.
- Use trusted antivirus/anti-spyware applications. Ensure the applications are up to date.
- Protect portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other portable PCs from theft and password protect and encrypt all data to ensure that should it be stolen, it cannot be read.
- Secure wireless access points and other gateway devices.
- Use properly configured gateway, edge, and perimeter protection, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems and routers.
- Encrypt data at rest and data in transit to ensure integrity and confidentiality.
Types of Website Hosting:
- External web hosting
- Internal web hosting
External web hosting:
Offered by web hosting providers:
- Disk storage space
- Available bandwidth
- Technical support
- Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) email accounts
- Email forwarding
- Email auto-responders
- Email aliases
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP) access
- Password protection
POP3
Post Office Protocol version 3
FTP:
File Transfer Protocol
Internal web hosting:
- Web server with redundant drives and hardware to ensure uptime
- High-speed internet connection to handle bandwidth requirements
- Adequate disk storage to hold the site
- Physical and logical security measures
- IT personnel who can manage the programming, maintenance, and security of the site
- Strong backup procedures including considerations for offsite backup storage
Whois (private or public):
- When signing up for a domain, you use an authorized domain registrar.
- Internet Corporation of Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
Governing body for all domain names
Keeps a record of every domain name, who owns it, and how and where it is being used
Often referred to as Whois data because you can search for a domain owner and
contact information from ICANN registration records
- Registrars offer private settings to provide more protection of personal data.
ICANN:
Internet Corporation of Assigned Names and Numbers
Internet Corporation of Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN):
- Governing body for all domain names
- Keeps a record of every domain name, who owns it, and how and where it is being used
- Often referred to as Whois data because you can search for a domain owner and contact information from ICANN registration records
ICANN is often referred to as . . .
Whois data because you can search for a domain owner and contact information from ICANN registration records
DNS
Domain Name System/Server
Domain Name System (DNS):
- Standard name resolution strategy used on networks today
- Works on all operating system platforms
- Function of DNS is to resolve host names
DNS names:
- Most internal networks and internet use DNS naming.
- You need to plan and design the DNS namespace to be used.
- First, choose the top-level domain name that will be used to host the organization’s name on the internet.
- Second, choose the second-level domain name that identifies the actual organization (google.com, for example). Referred to as parent domain name and is the domain name used on the internet.
.com
Used by commercial organizations
.gov
Government organizations
.net
Network providers
.org
Nonprofit organizations
.edu
Educational organizations
.mil
Military
.ca
Country-specific domains
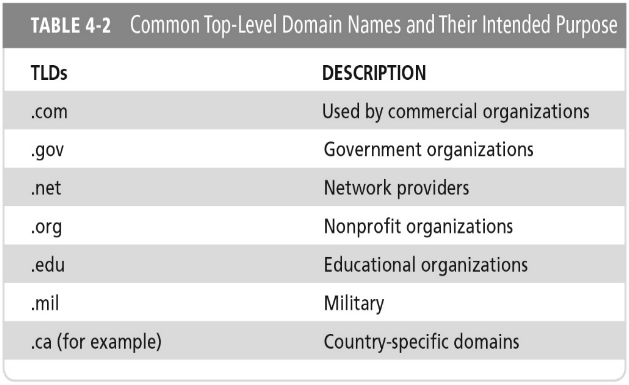
Common Top-Level Domain Names:
.com
.gov
.net
.org
.edu
.mil
.ca
Common DNS attacks:
- DoS attacks
- Footprinting
- Address spoofing
- Redirection
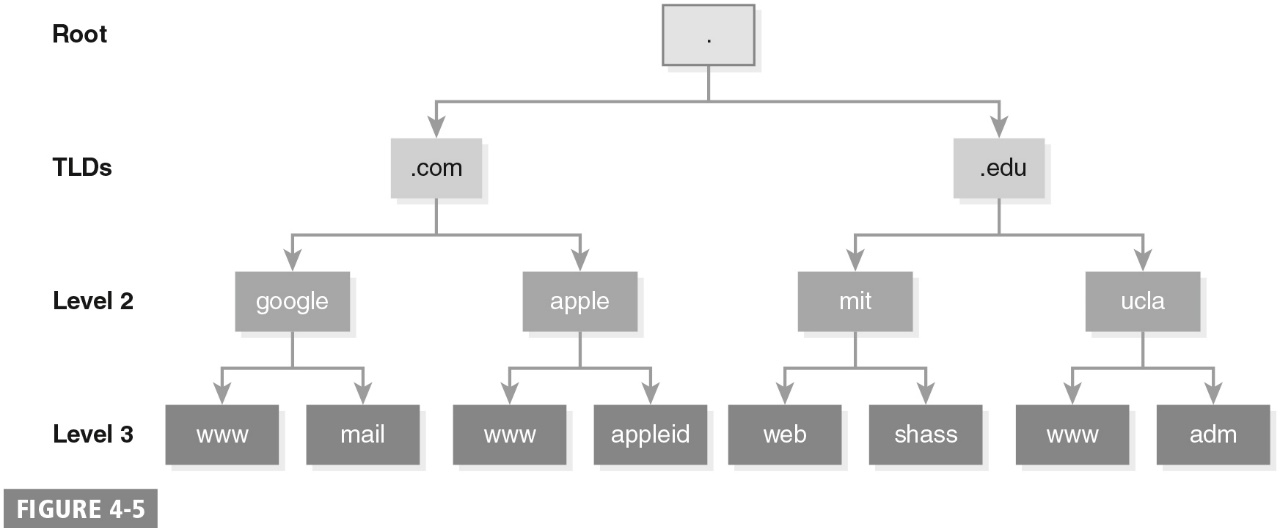
What is the following image a sample of?
- Sample of the DNS Organization of the Internet:
Best Practices for Connecting to the Internet:
- Keep all applications current.
- Use trusted anti-malware software.
- Use perimeter security.
- Secure backups.
- Use secure passwords.
- Report cybercrime.
- Protect personal information.
- Use data encryption.
Keep all applications current:
Look for updates to software including productivity software, virus, and operating systems.
Use trusted anti-malware software:
Antivirus software includes mitigation strategies for known malware. Keep this software installed and current.
Use perimeter security. Home users and corporate networks need to incorporate strong perimeter security strategies:
This includes the firewall, intrusion detection system (IDS), and intrusion prevention system (IPS).
Secure backups:
Backups on removable media such as tape sets and USB needs to be secure in the event of theft.
Use secure passwords:
Choosing hard-to-guess passwords goes a long way to securing many online transactions.
Report cybercrime:
If you suspect that you or someone you know is a victim of cybercrime, such as stalking or bullying, report it to the police.
Protect personal information:
If using social networking sites, use caution when divulging personal information.
Use data encryption:
The ability to encrypt data is built into operating systems. It is a best practice to encrypt data to prevent it from being read if stolen.