3 Cell Division
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what is the difference between mitosis & meiosis?
mitosis: division results in 2 identical daughter cells
meiosis: division results in 4 unidentical gametes (sex cells) with half the chromosome no.
define chromosome
threadlike structure of DNA & histones found in the nucleus
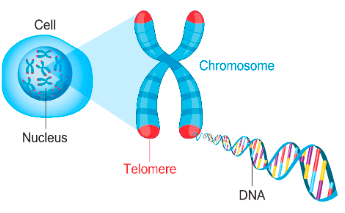
define chromatid
2 threadlike structures (held together by a centromere) that make up the chromosome
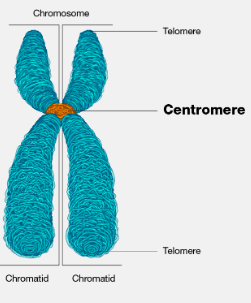
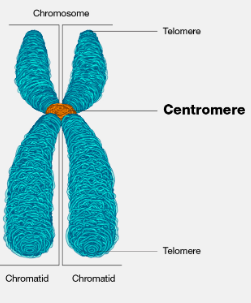
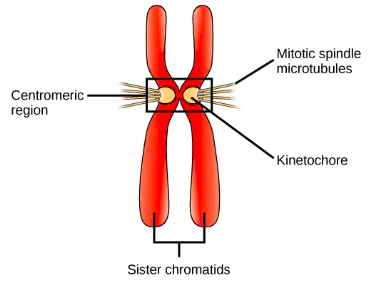
define centromere
a specialised sequence of DNA that links the sister chromatids together
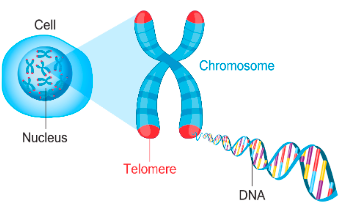
define telomere
a cap at the end of each chromosome arm which maintains stability
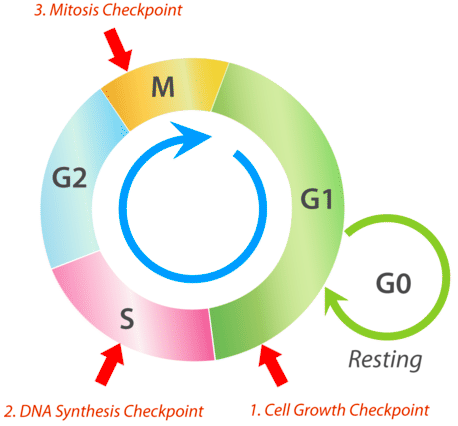
what are the stages of interphase?
G1, S, G2
what occurs in G1 phase?
prepares for DNA replication by synthesising mRNAs & proteins required
cell grows larger & organelles (needed for DNA synthesis) replicate
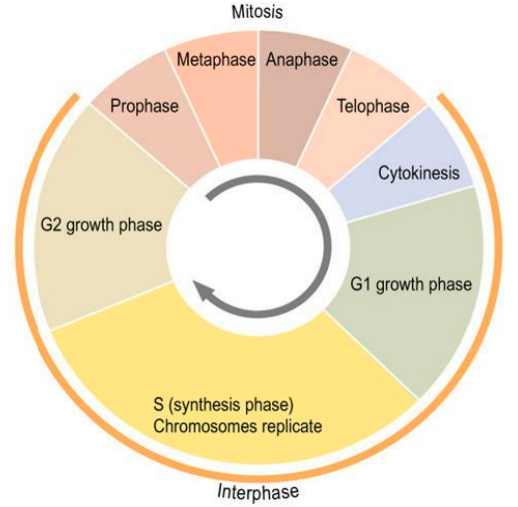
what occurs in S (synthesis) phase?
DNA replication occurs:
sister chromatids replicate
note: these sister chromatids are identical pairs of chromosomes
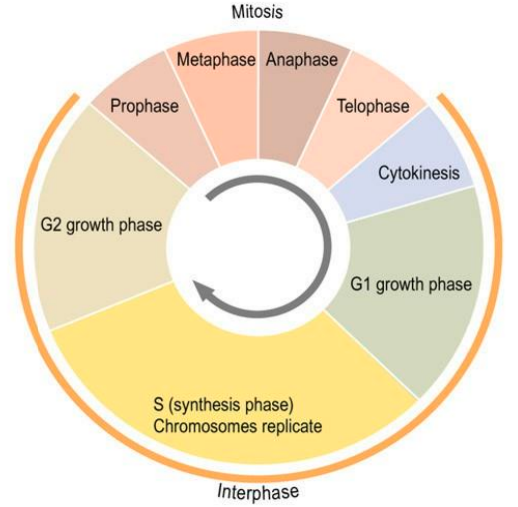
what occurs in G2 phase?
cell continues growing & repleneshies energy stores
cell prepares & reoranises cytoplasmic components for division:
organelles such as mitochondria duplicate
dismantling of the cytoskeleton
outline the 3 checkpoints in the cell cycle.
cell growth checkpoint
DNA synthesis checkpoint
mitosis checkpoint
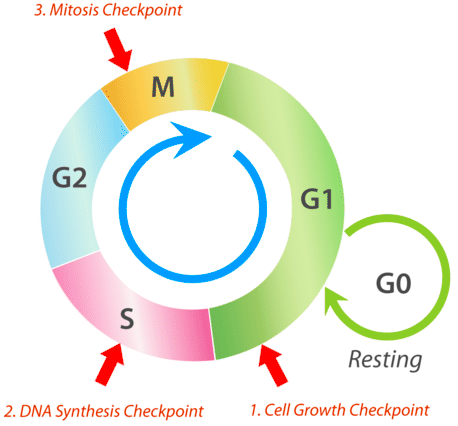
what occurs in the cell growth checkpoint?
at the end of G1 phase, checks whether the cell is big enough & has right proteins for S phase
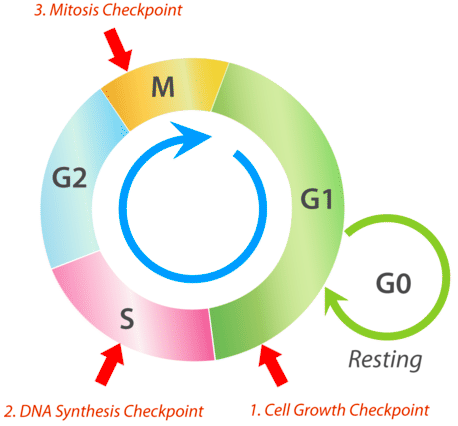
what occurs if the cell isnt big enough or doesnt have the right proteins for S phase?
then it will go through a resting period (G0) until it is ready
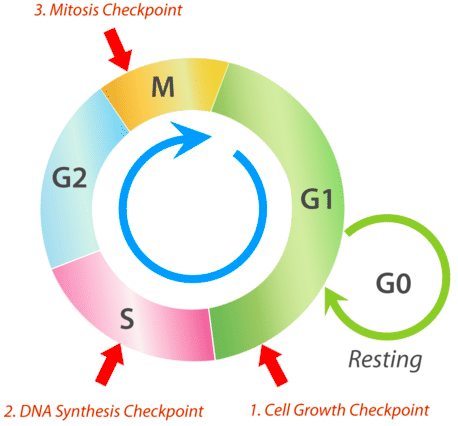
what occurs in the DNA synthesis checkpoint?
during S phase, checks whether DNA has been replicated properly
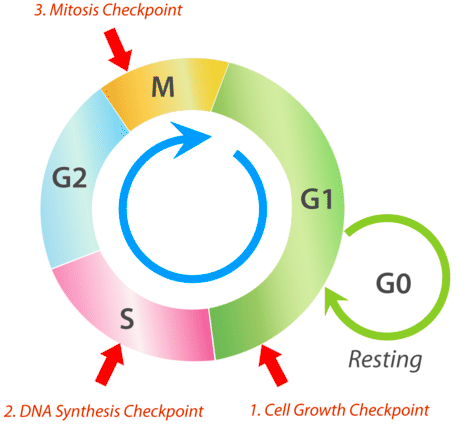
what occurs in the mitosis checkpoint?
during mitosis, checks whether mitosis is complete
define cyclins
a family of proteins that controls the progression of a cell though the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) enzymes needed for synthesis of cell cycle.
which cyclins regulate transition from G1 to S phase?
cyclin D which binds to CDK4
cyclin E which binds to CDK2
which cyclin promotes progression of S phase?
cycin A which binds to CDK2
Cyclins accumulate steadily during __ phase & are abruptly destroyed as cells exit from _____.
Cyclins accumulate steadily during G2 phase & are abruptly destroyed as cells exit from mitosis
which cyclin regulates progression from G2 to M (mitosis) phase
cyclin B which binds to CDK1
Define chromatin
DNA coild around histone proteins
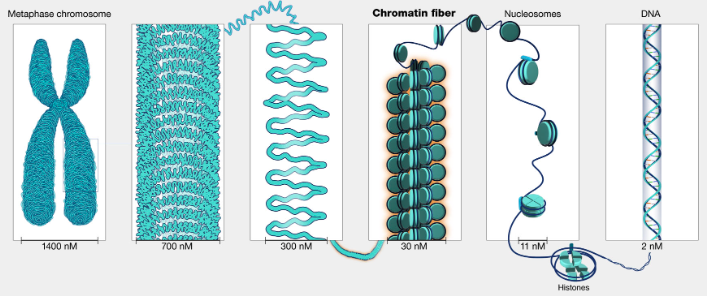
whats the diff between chromosomes & chromatin?
chromatin is lower order of DNA organization whereas chromosomes are higher order of DNA organization
before cell division, chromatin forms itself into chromosomes
what are the 4 stages of mitosis?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
what occurs in prophase?
chromosomes condense & become visible inside the nuclear membrane
they become shorter & thicker & seen as separate structures
nuclear envelope begins to breakdown
centrioles migrate to oppsoite ends of the cell
spindle of microtubules begin to form
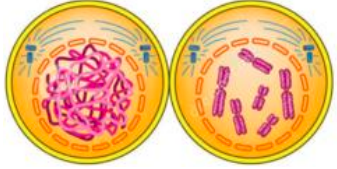
what 2 proteins catalyse the condensation process of chromosomes?
cohesin & condensin
outline the function of cohesin & condensin.
cohesin forms rings that holds sister chromatids together
condensin forms rings that coil the chromsomes compactly
define pro-metaphase
when the nuclear envelope breaks down allowing chromosomes to attach to the spindle microtubules.
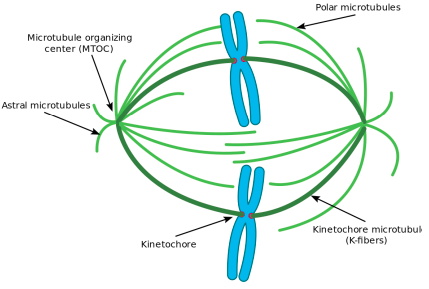
what occurs in pro-metaphase?
phosphphorylation of nuclear lamins by M-CDK causes the nuclear membrane to break down into small vesicles
spindle microtubules connect to each chromosome at its kinetochore
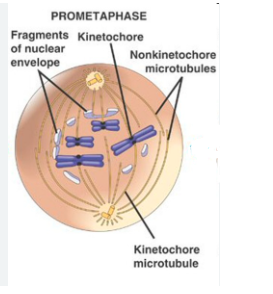
define kinetochore
a complex of proteins positioned at the centromere
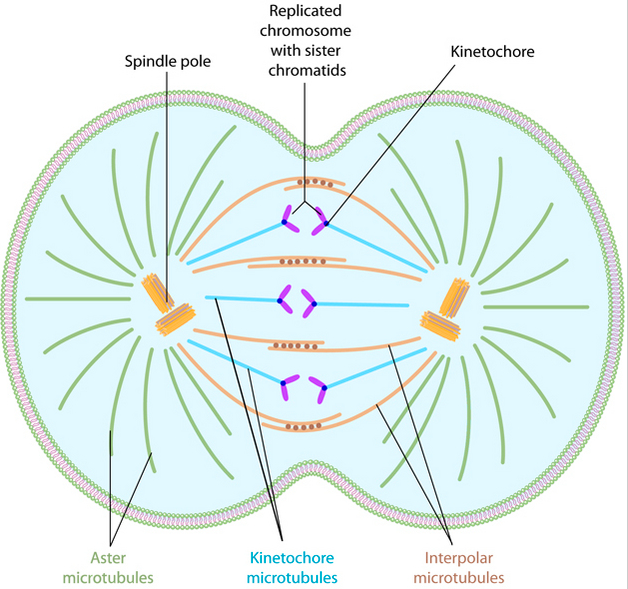
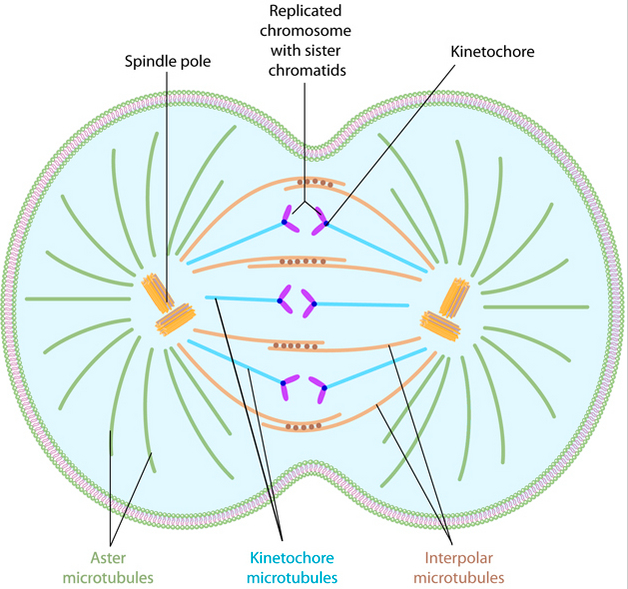
what are polar & astral microtubules?
polar microtubules extend from the spindle pole across the equator
astral microtubules extend from the spindle pole to the cell membrane
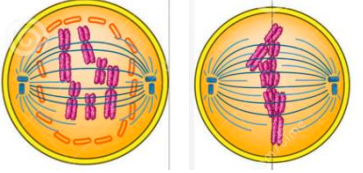
what occurs in metaphase?
chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromere
they are pulled by the microtubules so they line up along the equator of the spindle
what occurs in anaphase?
centromeres split
spindle microtubules attached to centromers shorten & drag chromatids to oppsosite ends of the cell
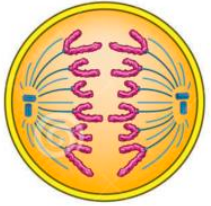
what causes the centromeres to split in anaphase?
enzymatic breakdown of cohesin
cohesin linked sister chromatids together during prophase, so its breakdown causes the centromeres to separate
whats the diff between the 2 parts of anaphase?
Anaphase A - kinetochore microtubules shorten & draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles
Anaphase B - astral microtubules anchored to the cell membrane pull the poles further apart and the interpolar microtubules slide past each other, exerting additional pull on the chromosomes
what occurs in telophase?
chromosomes assemble at opposite poles & uncoil (making them invisible again)
nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
nuecloli reform
what occurs in cytokinesis?
the 2 nuclei separate to form 2 genetically identical daughter cells
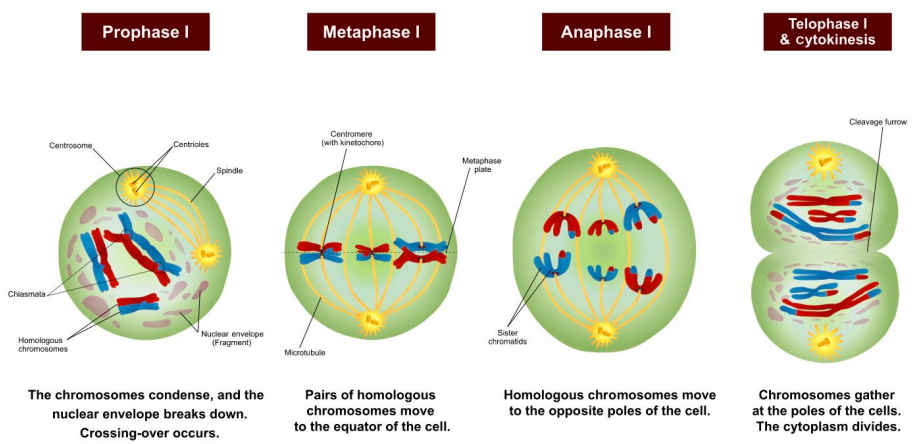
in meiosis what occurs?
PMAT twice
whic stage is different in mitosis & meiosis & why?
prophase 1
crossing over occurs
note: only in prophase 1
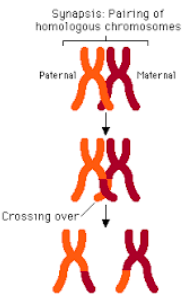
how does crossing over occur?
during synapsis - the pairing of homologus chromosomes
tetrads/bivalents are created when spindle fibres pull homologus chromosomes together
this = crossing over = of genetic material between sister chromatids
what does meiosis produce?
4 genetically non-identical haploid daughter cells