Ch. 11 - Reproduction [Dr. Wood Mammalogy]
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Monotremes
Cloaca, only the left ovary is functional
Marsupials
Cloaca, simple placenta• Brief gestation, long nursing period
Altricial
Useless baby for marsupials and Monotremes
Placentals
highly efficient placenta. Respiratory, circulatory, and excretory systems integrated w/mother. Longer gestation, shorter nursing period
Gestation
The process or period of developing inside the uterus between conception and birth. 10-14 days in dasyurids to 650 days in elephants
Lactation
The process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in female mammals, including humans, from 4 days in hooded seals to 900 days in chimps
Intervals
3-4 weeks between litters in rodents to 3-4 years in whales, elephants, rhinos
Testes
produce sperm/testosterone, contained in the scrotum
Position varies
bats/rodents - descend from the abdominal cavity during breeding season, then withdraw
Armadillos: always in the abdominal cavity
Primates, carnivores, and ungulates remain descended
Spermatogenesis
The process by which male germ cells in the testes produce mature sperm cells, or spermatozoa
Seminiferous tubules
sperm production
Sertoli cells
"nurse" cells; provide nutrients
Leydig cells
secretes testosterone
Glands
seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral. secretions to enhance the alkaline level of semen = increased survival in the acidic environment of the urethra/vagina
Coagulating glands
The copulation plug blocks the vagina. Retain sperm, deter other males
Penis
corpora cavernosa fill w/blood
corpora cavernosa
to achieve and maintain an erection by filling with blood
Baculum
"os penis," a bone found in the penis of certain mammals, used for i.d. on species/age
Corkscrew
(hogs), compatible w/female
eutherians, penis position
anterior to scrotum
marsupials, rabbits, penis position
posterior to scrotum
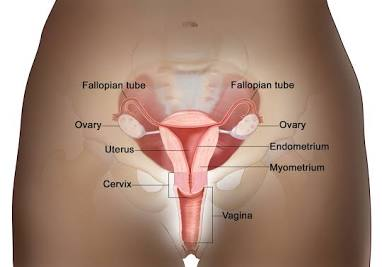
Ovaries
paired, produce ova, hormones
Oviducts
uterus (embryonic development), vagina
Gonadal steroids
androgen, estrogens, and progestin
Androgens
masculinizing
Estrogens
feminizing
Progestins
assist, the hormone that plays a role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Ovulation
follicle bursts with a developed egg then released into oviduct's
Capacitation
The time takes for sperm to penetrate the egg
FSH
follicle-stimulating hormone
LH
Luteinizing hormone, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that regulates the reproductive systems in both men and women.
Corpus luteum: how is it formed
A ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum after it releases an egg during ovulation.
Corpus luteum: What is developed
Releases progesterone after ovulation to prepare the uterus for implantation and stimulates the mammary glands
Corpora lutea: Becomes?
Degenerate to corpora albicans (white bodies)
Corpora lutea
Temporary endocrine glands in the ovary that form after ovulation, Estradiol is produced
Estradiol
The most potent estrogen in the body, primarily used medically to treat symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness, and to prevent osteoporosis
Estrus cycle
"heat", the female ovulates. Ready for sex and reproduction. It can be Spontaneous and induced.
Monoestrous
one heat/yr (carnivores)
Polyestrous
multiple cycles (rodents)
Implantation
The embryo attaches to the uterine wall.
Placenta: What are the functions?
1. anchors fetus
2. nutrients to the embryo
3. excretes metabolites to the mother
4. produces hormones
Placenta
A complex of embryonic/maternal tissues
Allograft
Placenta not rejected as alien due to the placenta's ability to suppress maternal immune responses
Afterbirth: Types?
expelled placenta, Placental scars, no scars
deciduous
expelled placenta
parous
Placental scars
nulliparous
no scars
Gestation: Examples of short and long?
Short in marsupials: opossum = 12.5 days, Long African elephant: 22 mos gestation
Litter reduction
Not a lot survives into weaning.
K vs r selected
Blue whale: long 10-12 mos gestation, but the same as horses. Primates: short = 60 days, long = gorillas, humans 280 d
Precocial
hatched or born in an advanced state and able to feed itself almost immediately.Newborn primates.
Delayed fertilization, for bats
copulate in Sept/Oct prior to hibernation (bats)
Spring: female ovulates, uses sperm, and birth coincides with insect emergence
blastocyst
a ball of cells that develops from a fertilized egg (zygote) about 5-6 days after fertilization
Delayed development/implantation
blastocyst stays in "neutral" for up to 7 months
Unique fertilization in Armadillos
Obligate, where a single fertilized egg splits into four genetically identical quadruplets.
Unique fertilization in Rodents
facultative, where a female can pause embryo development during lactation or stress so implantation occurs only when conditions are favorable for reproduction.
Embryonic diapause
a temporary suspension of embryonic development that occurs in certain mammals
Sliding scale of decisions for a female kangaroo
1. lose joey at foot 1st
2. lose joey in pouch 2nd
3. lose embryo in diapause
4. Stop breeding for the season
Parturition
the first stage involves dilation and effacement of the cervix, the second stage is the expulsion of the fetus through pushing and delivery, and the third stage is the delivery of the placenta then birth
Adrenal gland
secretes cortisols, which induces birth
Cortisols
a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, located on top of the kidneys
Placenta: Releases?
prostaglandins
prostaglandins
causeuterine contractions
Relaxin
loosens the ligaments of the pelvis, allowing spreading for parturition
Lactation: in Bats
milk production,
-Females: functional
-Males: non-functional, except for Dayak fruit bats in Malaysia
Lysozyme
enzyme that kills bacteria/fungi
Components in Bat milk
Nutrition, passive immunity, E. coli bacteria
What type of mammals don't have teats/nipples
Monotremes
How do platypuses consume milk?
Young platypuses suck milk that drains from glands (pores in skin) to tufts of hair on the abdomen